Zircon U-Pb dating of Bolongke A-type granite on the margin of northern North China Plate and its geological significance
-
摘要:
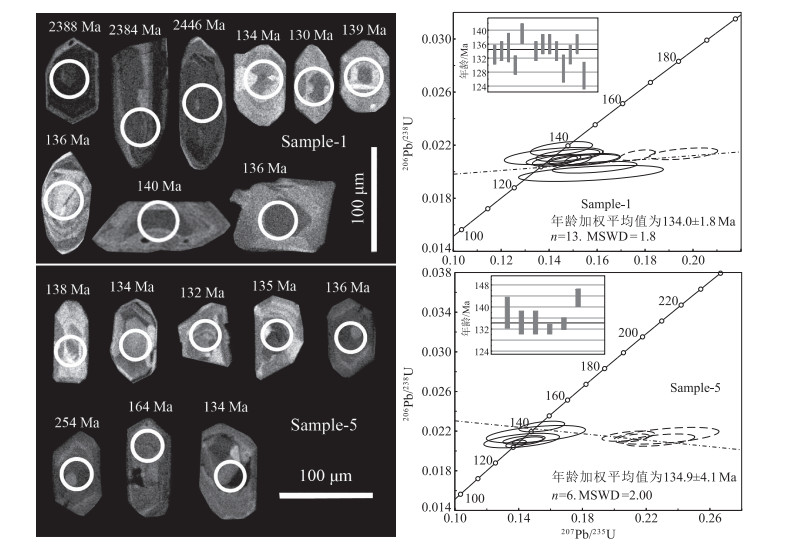
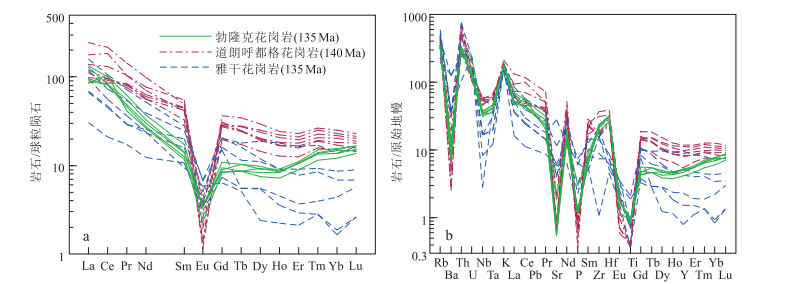
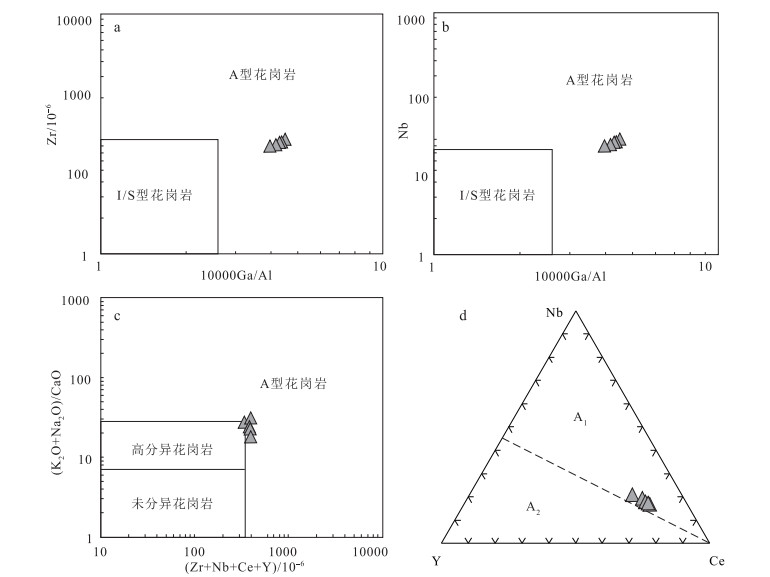
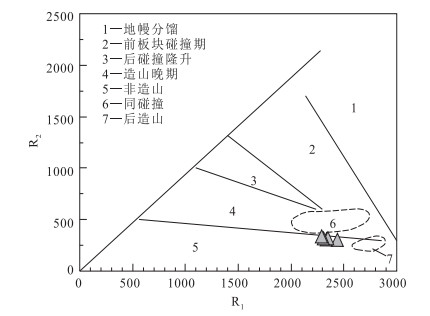
内蒙古翁牛特旗勃隆克岩体位于华北板块北缘,侵位于上侏罗系火山岩地层中。详细的岩相学研究显示,勃隆克花岗岩具有粒状结构、蠕虫结构和文像结构,块状构造,部分斜长石已绢云母化、泥化。对勃隆克花岗岩进行了LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年,获得134.0±1.8Ma和134.9±4.1Ma的侵位年龄,表明其形成于早白垩世。地球化学特征显示,花岗岩属于高钾钙碱性系列,有较高的SO2(74.1%~75.6%)、Na2O+K2O(8.98%~9.2%)、Rb(210×10-6~225×10-6)含量和10000×Ga/Al(2.69~2.80)、Rb/Sr(5.8~18.9)值,具有较低的CaO、MgO、Ba和Sr含量。铝饱和指数A/CNK=0.99~1.03,属于偏铝质或过铝质A型花岗岩。稀土元素球粒陨石标准化图解显示,轻稀土元素相对富集,负Eu异常明显;在原始地幔标准化图解上,Ba、Sr、Nb、Ta、P、T强烈亏损,富集Rb、Th、K、Hf等元素,与华北板块北缘早白垩世A型花岗岩类似。结合区域构造演化,认为勃隆克花岗岩形成于伸展构造背景。晚中生代,华北板块北缘构造体制经历了重大的转变,地壳从挤压体制转为岩石圈减薄和地壳伸展体制,软流圈物质上涌导致上覆地壳长英质物质的部分熔融形成勃隆克A型花岗岩。
-
关键词:
- A型花岗岩 /
- 早白垩世 /
- LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄 /
- 华北板块北缘
Abstract:Bolongke granite, emplaced in the Upper Jurassic volcanic strata, is located on the north margin of the North China Craton (NCC).Detailed petrographical observation reveals that the granite occurs in the forms of euhedral and subeuhedral crystals and exhibits mymekitic and pegmatitic texture and massive structure.Sencitization and argillation exist in part of plagioclases caused by weathering. The LA-ICP-MS analysis of zircons yielded empkcement ages of 134.0±1.8Ma(MSWD=1.8) and 134.9±4.1Ma(MSWD=2.0), indicating that the Bolongke granite was fomied in the Early Cretaceous.A geochemical study of the intrusion suggests that it belongs to high-K calc-alkaline series and is characterized by depletion of Ba, Sr and enrichment of such elements as Rb, Th, Pb and Hf, with obviously negative Eu anomalies. To sum up, the intrusion shows the charactejstics of A-type granite. Tectonic discrimination diagrams indicate that Bolongke granite was fomed in an anorogenic extension environment. Combined with the achievements obtained by previous researchers, the authors tentatively hold that the emplacement of Bolongke granite belonged to the Mesozoic magmatic events in the North China Craton and was produced by lithospheric thinning.
-
致谢: 感谢审稿专家给出的建设性修改意见。
-
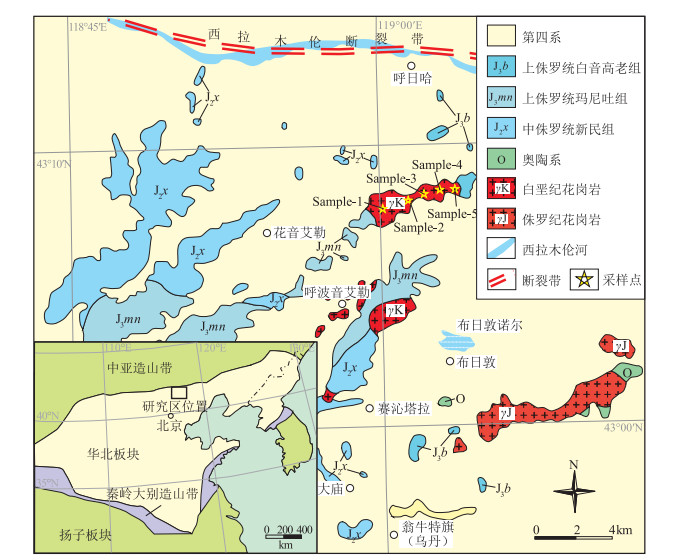
图 1 内蒙古翁牛特旗勃隆克地区区域地质简图(据参考文献①修改)
Figure 1. Simplified geological map of Bolongke area in Onguid Banner, Inner Mongolia
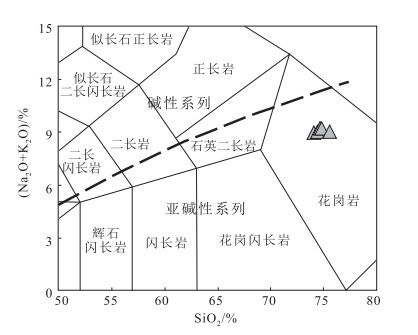
图 4 花岗岩类TAS图解[39]
Figure 4. Total alkali versus silica diagram of granite
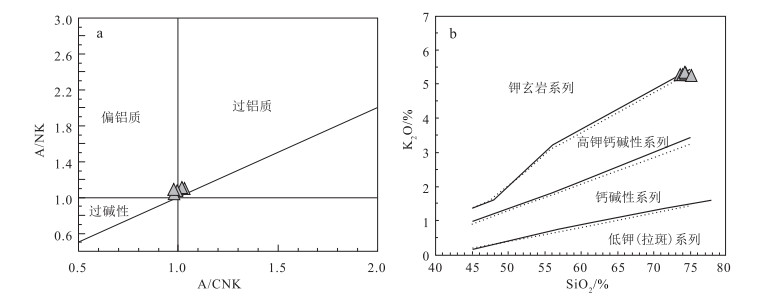
图 5 勃隆克花岗岩A/CNK-A/NK图解(a)和SiO2-K2O图解(b)[40]
Figure 5. Diagrams of A/CNK-A/NK(a)and SiO2-K2O(b)for granite
图 8 R1-R2构造环境判别图解[70]
Figure 8. Plot of R1-R2 discrimination diagram
表 1 翁牛特勃隆克花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb年龄测定结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb data for Bolongke granite
点号 Th/10-6 U/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ Sample-1(119°02′40.5″E、43°07′31.2″N) 1 113 242 0.5 0.1158 0.0016 0.5394 0.1042 0.3465 0.0040 1918 19 2 130 114 1.1 0.0491 0.0020 0.1425 0.0062 0.0209 0.0003 133 2 3 218 141 1.6 0.0491 0.0025 0.1419 0.0075 0.0209 0.0003 134 2 4 156 127 1.2 0.0488 0.0045 0.1420 0.0136 0.0212 0.0004 135 3 5 170 169 1 0.0567 0.0042 0.1591 0.0116 0.0204 0.0003 130 2 6 263 118 2.2 0.0483 0.0027 0.1453 0.0085 0.0218 0.0004 139 2 7 42 96 0.4 0.1627 0.0024 0.1015 0.2172 0.4466 0.0052 2380 23 8 277 465 0.6 0.1660 0.0024 0.9904 0.1916 0.4483 0.0052 2388 23 9 269 227 1.2 0.0808 0.0025 0.2430 0.0083 0.0214 0.0003 136 2 10 77 203 0.4 0.1693 0.0025 0.1051 0.2178 0.4475 0.0052 2384 23 11 1251 1155 1.1 0.0552 0.0011 0.1522 0.0037 0.0210 0.0003 134 2 12 552 375 1.5 0.0615 0.0015 0.1769 0.0048 0.0213 0.0003 136 2 13 102 97 1.1 0.0489 0.0028 0.1479 0.0088 0.0213 0.0003 136 2 14 193 182 1.1 0.0534 0.0035 0.1545 0.0099 0.0210 0.0003 134 2 15 356 256 1.4 0.0839 0.0092 0.2346 0.0252 0.0203 0.0005 129 3 16 76 168 0.5 0.1818 0.0047 0.1157 0.2681 0.4615 0.0055 2446 24 17 269 222 1.2 0.0537 0.0035 0.1548 0.0098 0.0209 0.0003 133 2 18 230 141 1.6 0.0660 0.0030 0.1961 0.0095 0.0214 0.0003 136 2 19 178 143 1.3 0.0574 0.0074 0.1575 0.0200 0.0199 0.0004 127 3 20 1017 385 2.6 0.1639 0.0034 0.4727 0.0119 0.0219 0.0003 140 2 Sample-5(119°01′49.01″E、43°07′30.2″N) 1 67 47 1.4 0.0486 0.0064 0.1504 0.0206 0.0217 0.0006 138 5 2 119 143 0.8 0.0492 0.0031 0.1429 0.0088 0.0211 0.0003 134 4 3 244 457 0.5 0.0741 0.0036 0.2086 0.0109 0.0214 0.0004 137 2 4 260 197 1.3 0.0667 0.0212 0.2371 0.0752 0.0258 0.0006 164 4 5 129 145 0.9 0.0491 0.0053 0.1414 0.0157 0.0210 0.0005 134 4 6 537 285 1.9 0.0495 0.0014 0.1380 0.0043 0.0207 0.0003 132 2 7 477 259 1.8 0.1676 0.0051 0.4671 0.0163 0.0211 0.0003 135 2 8 220 146 1.5 0.0709 0.0092 0.1802 0.0231 0.0184 0.0004 118 2 9 246 194 1.3 0.0711 0.0021 0.2116 0.0068 0.0213 0.0003 136 2 10 331 412 0.8 0.0614 0.0011 0.3313 0.0076 0.0402 0.0005 254 3 11 350 219 1.6 0.1072 0.0076 0.2806 0.0193 0.0190 0.0003 121 2 12 227 165 1.4 0.0813 0.0072 0.2326 0.0219 0.0215 0.0006 137 4 13 188 167 1.1 0.0486 0.0020 0.1453 0.0064 0.0210 0.0003 134 2 14 436 254 1.7 0.1283 0.0071 0.3530 0.0187 0.0199 0.0003 127 2 15 527 341 1.5 0.1237 0.0086 0.3108 0.0211 0.0182 0.0003 116 2 16 371 241 1.5 0.0492 0.0029 0.1541 0.0095 0.0224 0.0004 143 3 17 616 294 2.1 0.0794 0.0047 0.2285 0.0145 0.0211 0.0004 134 3 18 361 213 1.7 0.1280 0.0034 0.4084 0.0128 0.0228 0.0003 145 2 表 2 勃隆克花岗岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 2 Whole-rock major, trace and rare earth elements compositions of the Bolongke, InnerMongolia
Samples Sample-1 Sample-2 Sample-3 Sample-4 Sample-5 SiO2 75.6 74.1 74.4 74.8 74.7 Al2O3 12.3 12.7 12.9 12.8 12.9 Fe2O3 1.06 1.1 1.08 1 1.03 FeO 0.15 0.15 0.2 0.15 0.15 MgO 0.34 0.34 0.37 0.4 0.52 CaO 0.33 0.3 0.41 0.39 0.52 Na2O 3.73 3.69 3.75 3.88 3.84 K2O 5.27 5.29 5.28 5.32 5.36 MnO 0.02 0.08 0.08 0.03 0.03 TiO2 0.18 0.2 0.21 0.2 0.2 P2O5 0.07 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.03 烧失量 1.02 2.04 1.35 0.99 0.72 总计 99.87 99.86 99.84 99.86 99.86 TFeO 1.10 1.14 1.17 1.05 1.08 A/CNK 0.99 1.03 1.02 1.00 0.99 K2O/Na2O 1.41 1.43 1.41 1.37 1.4 Ga 18 18.1 18.7 18.3 19.2 Rb 222 210 220 217 225 Sr 38.6 17.1 12.4 11.5 12 Y 19.1 21.2 23 23.6 24.1 Nb 22.3 23.2 24.4 25.6 26.8 Mo 1.33 1.31 2.05 1.09 1.15 Cs 4.35 5.13 6.93 4.97 5.08 Ba 78.2 95 68 46.9 48.2 La 47.6 31.7 49.1 33.4 35.1 Ce 78.9 101 96.9 77.3 79.1 Pr 7.69 5.62 8.59 6.27 6.65 Nd 23.4 18.7 26.5 19.4 21.5 Sm 3.3 2.7 4 2.9 3.2 Eu 0.3 0.3 0.3 0.2 0.3 Gd 2.89 2.61 3.35 2.57 2.76 Tb 0.5 0.5 0.6 0.5 0.6 Dy 2.85 3.17 3.71 3.54 3.46 Ho 0.62 0.71 0.74 0.72 0.78 Er 2.22 2.64 2.61 2.64 2.78 Tm 0.41 0.49 0.48 0.5 0.53 Yb 2.99 3.66 3.39 3.79 3.87 Lu 0.52 0.56 0.58 0.64 0.64 Ta 1.51 1.68 1.74 1.89 1.88 Pb 32 30.4 44.6 32.4 33.3 Th 27.1 26.2 27.1 27.9 28.5 U 2.99 2.46 4.9 2.55 2.68 Zr 209 251 239 266 267 Hf 8.31 9.64 9.51 9.84 9.74 ∑REE 173.77 174.6 201.42 154.01 161.76 δEu 0.3 0.3 0.3 0.3 0.3 (La/Yb)N 10.7 5.84 9.76 5.94 6.11 TZr/℃ 809 829 823 830 829 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 -
Loiselle M C, Wones D R.Characteristics and origin of anorogenic granites[J]. Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs, 1979, 11:468. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=9108a701005035f04fb9accc13dc243b
Eby G N.Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids:Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 1992, 20:641-644. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0641:CSOTAT>2.3.CO;2
Pitcher W S.The nature and origin of granite[M]. Blackie:Academic and Professional, 1993:1-316.
King P L, White A J R, Chappell B W, et al.Characterization and origin of aluminous A-type granites form the Lachlan Fold Belt, Southeastern Australia[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1997, 38(3):371-391. doi: 10.1093/petroj/38.3.371
King P L, Chappell B W, Allen C M, et al.Are A-type granites the high-temperature felsic granites?Evidence from fractionated granites of the Wangrah Suite[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2001, 48(4):501-514. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-0952.2001.00881.x
Feio G R L, Dall'Agnol R, Dantas E L, et al.Geochemistry, geochronology, and origin of the Neoarchean Planalto Granite suite, Carajás, Amazonian craton:A-type or hydrated charnockitic granites?[J]. Lithos, 2012, 151(151):57-73. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0228765229/
Breiter K, Lamarão C N, Borges R M K, et al.Chemical characteristics of zircon from A-type granites and comparison to zircon of S-type granites[J]. Lithos, 2014, 192-195:208-225. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.02.004
Moreno J A, Molina J F, Montero P, et al.Unraveling sources of A-type magmas in juvenile continental crust:Constraints from compositionally diverse Ediacaran post-collisional granitoids in the Katerina Ring Complex, southern Sinai, Egypt[J]. Lithos, 2014, 192/195:56-85. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.01.010
Bonin B.A-type granites and related rocks:Evolution of a concept, problems and prospects[J]. Lithos, 2007, 97:1-29. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2006.12.007
吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等.花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(6):1217-1238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.06.001 Chappell B W, White A J R.I-and S-type granites in the Lachlan Fold Belt[J]. Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh Earth Sciences, 1992, 83(1/2):1-26.
Whalen J B, Currie K L, Chappell B W.A-type granites:geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95:407-419. doi: 10.1007/BF00402202
Clemens J D.Granites and granitic magmas:strange phenomena and new perspectives on some old problems[J]. Proceedings of the Geologists' Association, 2005, 116:9-16.
Douce P, Alberto E.Generation of metaluminous A-type granites by low-pressure melting of calc-alkaline granitoids[J]. Geology, 1997, 25(8):743-746. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0743:GOMATG>2.3.CO;2
邓晋福.中国大陆根-柱构造:大陆动力学的钥匙[M].北京:地质出版社, 1996. 翟明国, 樊祺诚.华北克拉通中生代下地壳置换:非造山过程的壳幔交换[J].岩石学报, 2002, 18(1):1-18. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200201001 刘俊来, 关会梅, 纪沫, 等.华北晚中生代变质核杂岩构造及其对岩石圈减薄机制的约束[J].自然科学进展, 2006, 16(1):21-26. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2006.01.004 翟明国, 朱日祥, 刘建明, 等.华北东部中生代构造体制转折的关键时限[J].中国科学(D辑), 2003, 33(10):913-920. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd200310001 翟明国.华北克拉通构造演化[J].地质力学学报, 2019, 25(5):722-745. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd199901001 嵇少丞, 王茜, 许志琴.华北克拉通破坏与岩石圈减薄[J].地质学报, 2008, 82(2):174-193. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.02.005 刘红涛, 翟明国, 刘建明, 等.华北克拉通北缘中生代花岗岩:从碰撞后到非造山[J].岩石学报, 2002, 18(4):433-448. 刘伟, 潘小菲, 谢烈文, 等.大兴安岭南段林西地区花岗岩类的源岩:地壳生长的时代和方式[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(2):441-460. 韩振哲, 王洪杰, 李中会, 等.内蒙古东北部阿龙山地区早白垩世A型花岗岩特征及其意义[J].华南地质与矿产, 2009, (4):1-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3701.2009.04.001 孙金凤, 杨进辉.华北东部早白垩世A型花岗岩与克拉通破坏[J].地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2009, 34(1):137-147. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx200901013 周振华, 吕林素, 杨永军, 等.内蒙古黄岗锡铁矿区早白垩世A型花岗岩成因:锆石U-Pb年代学和岩石地球化学制约[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(12):3521-3537. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201012006 解洪晶, 武广, 朱明田, 等.内蒙古道郎呼都格地区A型花岗岩年代学、地球化学及地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(2):483-494. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201202011 Wu F, Sun D, Li H, et al.A-type granites in northeastern China:age and geochemical constraints on their petrogenesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 187(1/2):143-173.
Khain E V, Bibikova E V, Kröner A, et al.The most ancient ophiolite of the Central Asian fold belt:U-Pb and Pb-Pb zircon ages for the Dunzhugur Complex, Eastern Sayan, Siberia, and geodynamic implications[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 199(3/4):311-325.
Xiao W, Zhang L, Qin K, et al.Paleozoic accretionary and collisional tectonics of the eastern Tianshan(China):implications for the continental growth of Central Asia[J]. American Journal of Science, 2004, 304:370-395. doi: 10.2475/ajs.304.4.370
Windley B F, Alexeiev D, Xiao W, et al.Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2007(164):31-47. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=407c8a0b623113b1dd6b69ee8fde6a21
Xiao W J, Windley B F, Hao J, et al.Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture, Inner Mongolia, China:Termination of the central Asian orogenic belt[J]. Tectonics, 2003, 22(6):1069.
李锦轶, 高立明, 孙桂华, 等.内蒙古东部双井子中三叠世同碰撞壳源花岗岩的确定及其对西伯利亚与中朝古板块碰撞时限的约束[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(3):565-582. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200703004 李益龙, 周汉文, 钟增球, 等.华北与西伯利亚板块的对接过程:来自西拉木伦缝合带变形花岗岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄证据[J].地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2009, 32(6):931-938. 张琪琪, 张拴宏.华北地块北缘泥盆纪岩浆活动及其构造背景[J].地质力学学报, 2019, 25(1):125-138. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlxxb201901013 高立明.西拉木伦河断裂带基本特征及其动力学意义[D].中国地质科学院硕士学位论文, 2004. 崔盛芹, 马寅生, 吴珍汉, 等.燕山地区中新生代陆内造山作用[M].北京:地质出版社, 2006. 邵济安, 张履桥, 贾文, 等.内蒙古喀喇沁变质核杂岩及其隆升机制探讨[J].岩石学报, 2001, 17(2):283-290. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200102013 徐备, 刘树文, 王长秋, 等.内蒙古西北部宝音图群Sm-Nd和Rb-Sr地质年代学研究[J].地质论评, 2000, 46(1):86-90. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2000.01.012 Maitre R W L.A Classification of igneous rocks and glossary of terms: recommendations of the International Union of Geological Sciences Subcommission on the Systematics of Igneous Rocks[M]. Blackwell, 1989.
Peccerillo A, Taylor S R.Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 1976, 58(1):63-81.
Sun S S, McDonough W F.Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1):313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Boynton W V.Geochemistry of the rare earth elements:Meteorite studies[M]. Amsterdam:Elservier, 1989:63-144.
Miller C F, McDowell S M, Mapes R W.Hot and cold granites?Implications of zircon saturation temperatures and preservation of inheritance[J]. Geology, 2003, 31(6):529-532. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2003)031<0529:HACGIO>2.0.CO;2
王强, 赵振华, 熊小林.桐柏-大别造山带燕山晚期A型花岗岩的厘定[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2000, 19(4):297-315. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2000.04.002 Turner S P, Foden J D, Morrison R S.Derivation of some A-type magmas by fractionation of basaltic magma:An example from the Padthaway Ridge, South Australia[J]. Lithos, 1992, 28(2):151-179.
Mushkin A, Navon O, Halicz L, et al.The Petrogenesis of A-type Magmas from the Amram Massif, Southern Israel[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2003, 44(5):815-832. doi: 10.1093/petrology/44.5.815
Harris C, Marsh J S, Milner S C.Petrology of the Alkaline Core of the Messum Igneous Complex, Namibia:Evidence for the Progressively Decreasing Effect of Crustal Contamination[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1999, 40(9):1377-1397. doi: 10.1093/petroj/40.9.1377
Mingram B, Trumbull R B, Littman S, et al.A petrogenetic study of anorogenic felsic magmatism in the Cretaceous Paresis ring complex, Namibia:evidence for mixing of crust and mantle-derived components[J]. Lithos, 2000, 54(1/2):1-22. doi: 10.1016-S0024-4937(00)00033-5/
Clemens J D, Holloway J R, White A J R.Origin of an A-type granite; experimental constraints[J]. American Mineralogist, 1986, 71(3):317-324.
Skjerlie K P, Johnston A D.Vapor-absent melting at 10 kbar of a biotite-and amphibole-bearing tonalitic gneiss:Implications for the generation of A-type granites[J]. Geology, 1992, 20(3):263-266. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0263:VAMAKO>2.3.CO;2
Creaser R A, Price R C, Wormald R J.A-type granites revisited:Assessment of a residual-source model[J]. Geology, 1991, 19(2):163-166.
Rapp R P, Watson E B.Dehydration Melting of Metabasalt at 8~32 kbar:Implications for Continental Growth and Crust-Mantle Recycling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36(4):891-931. doi: 10.1093/petrology/36.4.891
Sylvester P J.Post-Collisional Alkaline Granites[J]. Journal of Geology, 1989, 97(3):261-280. doi: 10.1086/629302
Bonin B.From orogenic to anorogenic settings:Evolution of granitoid suites after a major orogenesis[J]. Geological Journal, 1990, 25(3/4):261-270. doi: 10.1002-gj.3350250309/
Hong D, Wang S, Han B, et al.Post-orogenic alkaline granites from China and comparisons with anorogenic alkaline granites elsewhere[J]. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 1996, 13(1):13-27. doi: 10.1016/0743-9547(96)00002-5
Batchelor R A, Bowden P.Petrogenetic interpretation of granitoid rock series using multicationic parameters[J]. Chemical Geology, 1985, 48(1):43-55.
Davis G A, Darby B J, Zheng Y, et al.Geometric and temporal evolution of an extensional detachment fault, Hohhot metamorphic core complex, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Geology, 2002, 30(11):1003-1006. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<1003:GATEOA>2.0.CO;2
王新社, 郑亚东, 张进江, 等.呼和浩特变质核杂岩伸展运动学特征及剪切作用类型[J].地质通报, 2002, 21(4/5):238-245. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20020466&flag=1 王新社, 郑亚东.楼子店变质核杂岩韧性变形作用的40Ar/39Ar年代学约束[J].地质论评, 2005, 51(5):576-582. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlp200505012 李益龙, 周汉文, 钟增球, 等.华北-西伯利亚板块对接带早白垩纪的裂解:来自西拉木伦断裂带中性岩墙群的锆石U-Pb年龄及地球化学证据[J].地球科学, 2010, 35(6):921-932. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201006004 刘燊, 胡瑞忠, 冯光英, 等.华北克拉通中生代以来基性岩墙群的分布及研究意义[J].地质通报, 2010, 29(2/3):259-267. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2010020310&flag=1 Xue F, Santosh M, Tsunogae T, et al.Geochemical and isotopic imprints of early cretaceous mafic and felsic dyke suites track lithosphere-asthenosphere interaction and craton destruction in the North China Craton[J]. Lithos, 2019, 326/327:174-199. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=541a8925aa93f67060eecf4ca20d59d7
Guo P, Niu Y, Sun P, et al.The Early Cretaceous bimodal volcanic suite from the Yinshan Block, western North China Craton:Origin, process and geological significance[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 160:348-364. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.10.023
Li S, Zhao G, Dai L, et al.Mesozoic basins in eastern China and their bearing on the deconstruction of the North China Craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 47:64-79. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.06.008
Wang T, Zheng Y, Li T, et al.Mesozoic granitic magmatism in extensional tectonics near the Mongolian border in China and its implications for crustal growth[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2004, 23(5):715-729. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(03)00133-0
李毅, 吴泰然, 罗红玲, 等.内蒙古四子王旗早白垩世钾玄岩的地球化学特征及其形成构造环境[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(11):2791-2800. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200611017 Xu Y, Huang X, Ma J, et al.Crust-mantle interaction during the tectono-thermal reactivation of the North China Craton:constraints from SHRIMP zircon U-Pb chronology and geochemistry of Mesozoic plutons from western Shandong[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 2004, 147(6):750-767.
Zheng J, Griffin W L, O Reilly S Y, et al.Mechanism and timing of lithospheric modification and replacement beneath the eastern North China Craton:Peridotitic xenoliths from the 100 Ma Fuxin basalts and a regional synthesis[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(21):5203-5225. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.07.028
Zhang H.Transformation of lithospheric mantle through peridotite-melt reaction:A case of Sino-Korean craton[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 237(3):768-780.
Zhang H, Nakamura E, Sun M, et al.Transformation of Subcontinental Lithospheric Mantle through Peridotite-Melt Reaction:Evidence from a Highly Fertile Mantle Xenolith from the North China Craton[J]. International Geology Review, 2007, 49(7):658-679. doi: 10.2747/0020-6814.49.7.658
Wu F, Lin J, Wilde S A, et al.Nature and significance of the Early Cretaceous giant igneous event in eastern China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, (233):103-119. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=d6b3600a84a03c13d0b9d2e363e47ff6
邓晋福, 苏尚国, 刘翠, 等.关于华北克拉通燕山期岩石圈减薄的机制与过程的讨论:是拆沉, 还是热侵蚀和化学交代?[J].地学前缘, 2006, 13(2):105-119. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.02.009 Liu J, Cai R, Pearson D G, et al.Thinning and destruction of the lithospheric mantle root beneath the North China Craton:A review[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2019, 196:102873. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.05.017
邓晋福, 苏尚国, 赵海玲, 等.华北地区燕山期岩石圈减薄的深部过程[J].地学前缘, 2003, 3:42-51. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy200303003 内蒙古自治区有色地质勘查局.赤峰地区1: 50000区域矿产资源图.2009.



 下载:
下载: