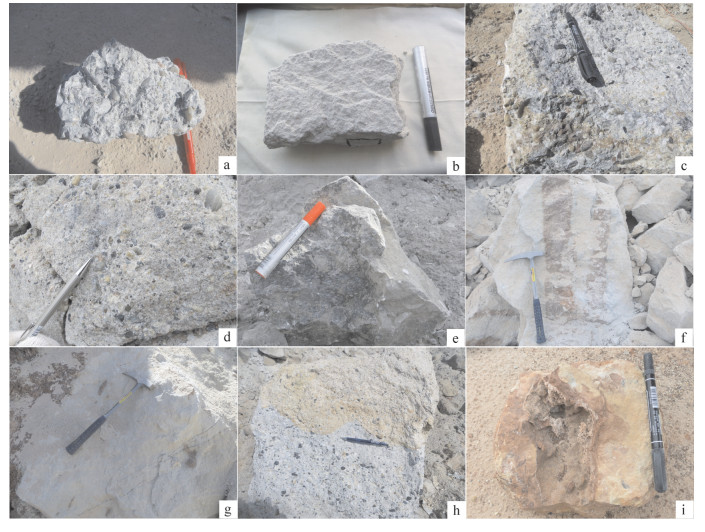
An analysis of ore-controlling conditions and geological features of the Wulagen sandstone-type Pb-Zn ore deposit in Xinjiang
-
摘要:
新疆乌拉根铅锌矿是与含油气盆地有关的砂岩型矿床,发育于塔里木盆地西北缘的喀什凹陷。在区域地层、构造、沉积岩和最新勘探资料综合分析的基础上,对该矿床的地质特征和控矿地质条件进行了研究。结果表明,其矿化层为一套海退砂、砾-泥-碳酸盐岩沉积建造,下白垩统克孜勒苏群(K1kz)和古新统阿尔塔什组(E1a)是成矿的物质基础,矿化蚀变发育于下白垩统克孜勒苏群第五岩性段+古近系阿尔塔什组第一岩性段,铅锌矿体呈层状、似层状产出,总体产状与地层产状一致。碎屑岩与矿化关系显示,从砾岩-砂砾岩-含砾砂岩-砂岩-泥岩,矿化强度依次减弱,除白云质(角砾)灰岩由于后期热液叠加多形成块状、细脉状矿石,矿化最强外,其余岩性按岩石颗粒粒度从小到大,矿化强度依次增强。该矿床的形成明显受乌拉根向斜和后期张性裂隙构造的制约,主矿体主要分布在砂砾岩层和白云质(角砾)灰岩中,矿体和上盘白云质(角砾)灰岩接触带局部张裂隙中发育黄铁矿型铅锌矿。塔西南喀什凹陷北缘中新生代碎屑岩盆地,是寻找砂岩型铜铅锌等多金属矿床最有利的远景区带。
Abstract:The Wulagen lead-zinc ore deposit, located in Kashi Sag on the northwestern margin of the Tarim basin of Xinjiang, is a sandstone-type ore deposit related to the petroliferous basin. On the basis of analysis of regional strata, tectonics, sedimentary rocks and recent prospecting data, the authors studied geological features and ore-controlling conditions of the Wulagen ore deposit. It is suggested that the Paleocene Wulagen Group seems to be significant ore-bearing strata, the ore-bearing horizon is composed of a set of regressive sand, gravel, mud-carbonate sedimentary formations. The mineralization zone is developed in the contact between the second bed of first lithologic member of Wulagen Group and the dolomitic limestone (breccia). These regular tabular orebodies are consistent with the attitude of the strata. The degree of mineralization is related to the type of clastic rocks and decreases from conglomerate glutenite, pebbly-sandstone, sandstone, to mudstone.The peak of this mineralization happened in the dolomitic limestone, some of which was brecciated. It was formed by deuteric hydrothermal process. The orebody is mainly massive or small veined form. With increasing grain size, mineralization becomes stronger in other types of clastic rocks. The authors have reached the conclusion that the Wulagen ore deposit was obviously controlled by the syncline of Wulagen and the late extensional fracture structure. The major ore is mainly distributed in gravel strata and dolomitic limestone (breccia). Pyrite type lead-zinc ore was found in some part of the extensional fractures, which was developed in the contact zone between the orebody and overlying dolomitic limestone (breccia). It is also pointed out that the clastic Mesozoic-Cenozoic basin in Kashi sag on the northwestern margin of the Tarim basin is a valuable metallization prospective area for sandstone type copper-lead-zinc ore deposits.
-
Keywords:
- lead-zinc deposit /
- ore-controlling conditions /
- Mesozoic-Cenozoic /
- Wulagen /
- sandstone-type
-
致谢: 论文撰写过程中,得到中国地质大学(北京)地球科学与资源学院狄永军教授的指导和帮助,审稿专家对论文提出了宝贵意见和建议,在此一并致以衷心的感谢。
-
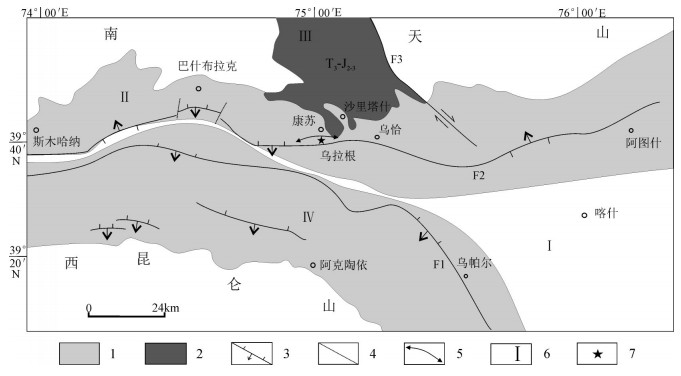
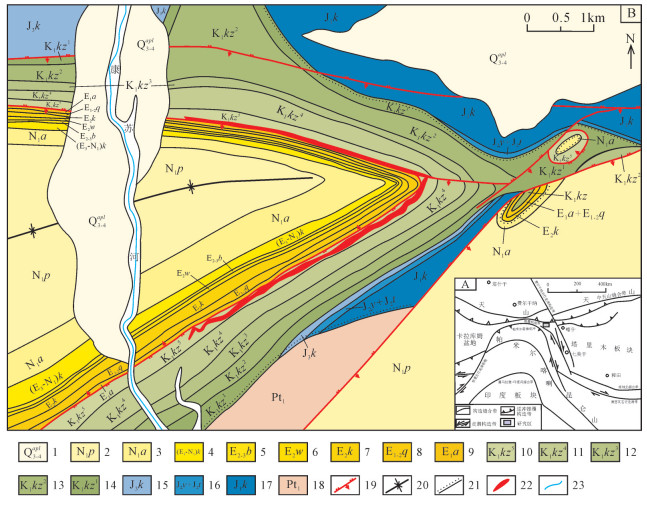
图 1 乌拉根铅锌矿区构造位置(A,据参考文献[9, 19]修改)和地质图(B,据参考文献献[7, 9, 15]修改)
1—上更新统-全新统冲洪积层;2—中新统帕卡布拉克组;3—中新统安居安组;4—上渐新统-中新统克孜洛依组;5—上始新统-渐新统巴什布拉克组;6—中始新统乌拉根组;7—中始新统卡拉塔尔组;8—中-上古新统-下始新统齐姆根组;9-下古新统阿尔塔什组;10—下白垩统克孜勒苏群第五段;11—下白垩统克孜勒苏群第四段;12—下白垩统克孜勒苏群第三段;13—下白垩统克孜勒苏群第二段;14—下白垩统克孜勒苏群第一段;15—上侏罗统库孜贡苏组;16—中侏罗统塔尔尕组和杨叶组;17—下侏罗统康苏组;18—古元古界阿克苏群;19—逆断层;20—向斜轴;21—不整合面;22—铅锌矿体;23—河流
Figure 1. Tectonic location (A) and geological map of the Wulagen lead-zinc deposit (B)
图 2 喀什凹陷地质构造简图[13]
1—造山带前缘褶皱-冲断带;2—库孜贡苏晚三叠世-中侏罗世断陷;3—逆断层;4—推测断层;5—背斜转折端;6—次级构造单元代号;7—研究区;Ⅰ—喀什深洼陷;Ⅱ—南天山山前褶皱-冲断带;Ⅲ—库孜贡苏晚三叠世-中侏罗世断陷;Ⅳ—昆仑山前褶皱-冲断带;F1—乌赤别里山口断裂;F2—乌恰断裂;F3—塔拉斯-费尔干纳巨型走滑断裂带
Figure 2. Sketch geological map of Kashi sag
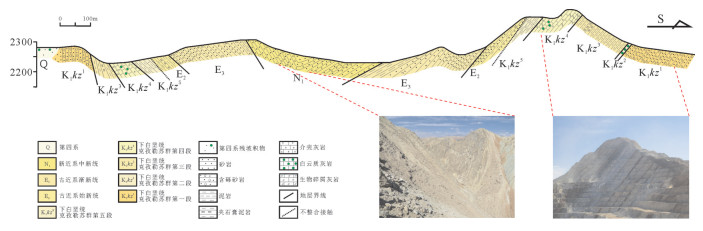
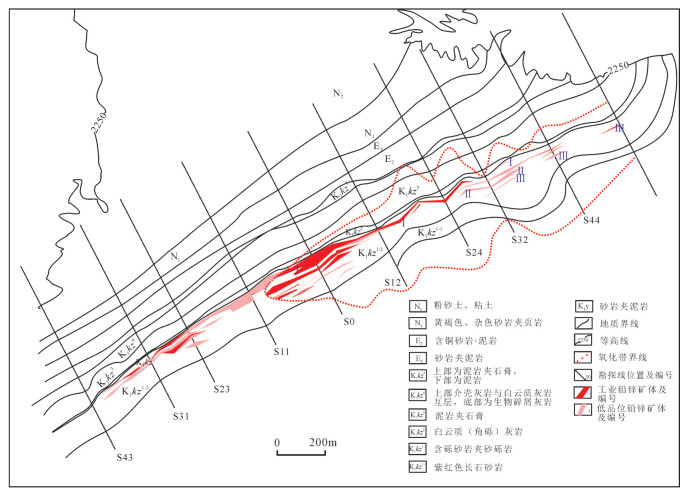
图 4 乌拉根铅锌矿2250平台切面简图①
Figure 4. Geological section of 2250 platform of the Wulagen lead-zinc ore deposit
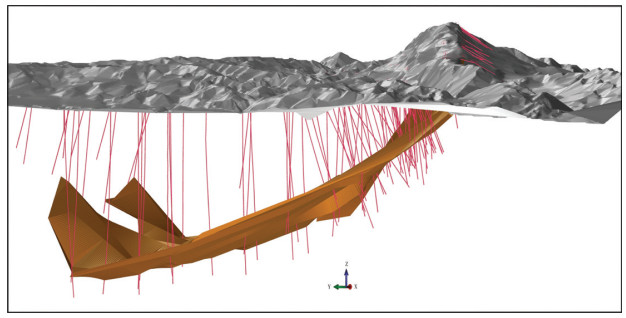
图 5 乌拉根铅锌矿床Ⅰ号矿体三维立体图①
Figure 5. The three-dimensional diagram of No. I orebody in the Wulagen deposit
表 1 各岩性与铅锌品位分析结果
Table 1 Analytical results of lithology and lead-zinc grades
序号 岩石名称 样品个数/件 占样品数的百分比/% Pb/% Zn/% (Zn+Pb)/% 1 白云质角砾岩 22 0.64 1.58 3.46 5.04 2 砾岩 146 4.25 0.95 3.2 4.15 3 砾砂岩 635 18.47 0.72 2.81 3.53 4 含砾砂岩 994 28.91 0.57 2.46 3.03 5 砂岩(含细砂岩、粗砂岩) 1625 47.27 0.42 2.35 2.77 6 泥岩 16 0.47 0.72 2.09 2.81 表 2 乌拉根铅锌矿矿体特征①
Table 2 Features of the orebody from the Wulagen lead-zinc ore deposit
矿体编号
矿体形态Ⅰ
似层状、层状Ⅱ
似层状、层状Ⅲ
似层状、层状Ⅳ
似层状、层状矿体规模/m 长度 2870 2400 2200 700 平均真厚度 15.06 11.26 10.98 5.31 最大延深 2480 2000 2040 560 赋矿标高 1290~2469 1260~2395 1320~2374 1500~2368 平均品位/% 矿体 Zn 2.47 2.14 2.07 1.80 Pb 0.43 0.32 0.47 0.21 厚度变化系数/% 85.64 62.86 90.26 / Zn品位变化系数/% 68.17 63.03 61.74 / Pb品位变化系数/% 151.61 145.22 124.1 / 含矿岩石 砂砾岩、含砾砂岩,次为砂岩 砂岩、含砾砂岩,次为砂砾岩 砂砾岩、含砾砂岩,次为砂岩 砂岩,次为含砾砂岩、砂砾岩 注:/表示无分析 表 3 乌拉根铅锌矿床硫同位素组成
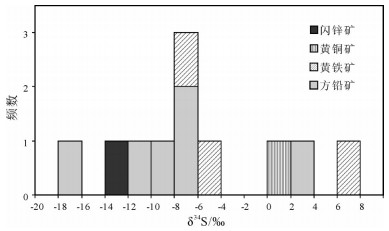
Table 3 Sulfur isotope compositions of the Wulagen leadzinc ore deposit
样品名称 测试矿物 δ34SV-CDT/‰ 砾岩型矿石 方铅矿 -8.2 细砂岩型矿石 方铅矿 -7.7 砾岩型矿石 方铅矿 2.4 砾岩型矿石 黄铁矿 -5.8 砂砾岩型矿石 方铅矿 -6.2 砂砾岩型矿石 黄铜矿 1.1 砂砾岩型矿石 黄铁矿 6.7 角砾岩型矿石 方铅矿 -10.3 角砾岩型矿石 闪锌矿 -12.9 角砾岩型矿石 黄铁矿 -6.5 角砾岩型矿石 方铅矿 -17.9 -
叶庆同, 吴一平, 傅旭杰, 等.南天山金和有色金属矿床成矿条件和成矿预测[M].北京:地质出版社, 1999:1-170. 张志斌, 叶霖, 李文铅, 等.新疆霍什布拉克铅锌矿床地质、地球化学特征研究[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2007, 31(2):205-217. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2007.02.010 张舒.南天山典型铅锌矿床地质-地球化学特征及成因研究[D].中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2010. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-2010085579.htm 李志丹, 薛春纪, 辛江, 等.新疆乌恰县萨热克铜矿床地质特征及硫、铅同位素地球化学[J].现代地质, 2011, 25(4):720-729. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2011.04.013 蔡宏渊, 邓贵安, 郑跃鹏.新疆乌拉根铅锌矿床成因探讨[J].矿产与地质, 2002, 16(1):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2002.01.001 谢世业, 莫江平, 杨建功, 等.新疆乌恰县乌拉根新生代热卤水喷流沉积铅锌矿成因研究[J].矿产与地质, 2003, 17(1):11-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2003.01.003 祝新友, 王京彬, 刘增仁, 等.新疆乌拉根铅锌矿床地质特征与成因[J].地质学报, 2010, 84(5):694-702. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201005008 韩凤彬, 陈正乐, 刘增仁, 等.塔里木盆地西北缘乌恰地区乌拉根铅锌矿床S-Pb同位素特征及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2012, 31(5):783-793. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.05.015 韩凤彬, 陈正乐, 刘增仁, 等.西南天山乌拉根铅锌矿床有机地球化学特征及其地质意义[J].矿床地质, 2013, 32(3):591-602. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2013.03.010 李志丹, 薛春纪, 董新丰, 等.新疆乌恰县乌拉根铅锌矿床地质特征S-Pb同位素组成[J].地学前缘, 2013, 20(1):40-54. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy201301004 董连慧, 徐兴旺, 范廷宾, 等.喀喇昆仑火烧云超大型喷流-沉积成因碳酸盐型Pb-Zn矿的发现及区域成矿学意义[J].新疆地质, 2015, (1):41-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2015.01.008 孔祥兴.塔里木盆地西部乌拉根多金属矿床[J].新疆地质, 1984, 2(2):75-80. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-XJDI198402005.htm 高珍权, 刘继顺, 舒广龙, 等.新疆乌恰铅锌矿床成矿的地质条件及成因[J].中南工业大学学报, 2002, 33(2):116-120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3104.2002.02.003 高珍权, 刘继顺, 舒广龙, 等.新疆乌恰地区中新生代盆地寻找热卤水成因的超大型铅锌矿床的地球化学证据[J].地质地球化学, 2002, 30(1):13-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9250.2002.01.003 李丰收, 王伟, 杨金明.新疆乌恰县乌拉根铅锌矿床地质地球化学特征及其成因探讨[J].矿产与地质, 2005, 19(4):335-340. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2005.04.002 李博泉, 王京彬.中国新疆铅锌矿床[M].北京:地质出版社, 2006:22-91. 刘增仁, 陈正乐, 韩凤彬, 等.新疆喀什乌拉根铅锌矿油气还原迹象与成矿作用关系初析[J].矿床地质, 2010, S1:1049-1050. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7413008 董新丰, 薛春纪, 李志丹, 等.新疆喀什凹陷乌拉根铅锌矿床有机质特征及其地质意义[J].地学前缘, 2013, 20(1):129-145. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201301012 李向东, 王克卓.塔里木盆地西南及邻区特提斯格局和构造意义[J].新疆地质, 2000, 18(2):113-120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2000.02.003 Yin A, Nie S, Craig P, et al. Late Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the southern Chinese Tian Shan[J]. Tectonics, 1998, 17:1-27 doi: 10.1029/97TC03140
李锦轶, 肖序常.对新疆地壳结构与构造演化几个问题的简要评述[J].地质科学, 1999, 34(4):405-419. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.1999.04.001 马华东, 杨子江.塔里木盆地西南新生代盆地演化特征[J].新疆地质, 2003, 21(2):92~95. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xjdz200301015 周新源, 罗金海, 买光荣.塔里木盆地喀什凹陷及其周边地区构造特征与油气地质[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2005:1-233. 罗金海, 周新源, 邱斌, 等.塔里术盆地西部中、新生代5次构造事件及其石油地质学意义[J].石油勘探与开发, 2005, 32(1):18-22. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.01.005 李盛富, 曾耀明.喀什凹陷构造演化与砂岩型铀成矿关系[J].新疆地质, 2007, 25(3):302-306. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2007.03.016 张振亮, 冯选洁, 董福辰, 等.西南天山砂砾岩容矿矿床类型及找矿方向[J].西北地质, 2014, 47(3):70-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2014.03.011 胡剑辉, 吉蕴生, 曾志钢.新疆乌拉根铅锌矿床地球化学异常模式研究[J].矿产勘查, 2010, 1(3):260-268. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2010.03.013 张立新, 王磊, 刘增仁, 等.新疆乌拉根铅锌矿开发技术经济评价[J].矿产勘查, 2019, (4):705-713 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2019.04.001 康亚龙, 欧阳玉飞, 樊俊昌, 等.新疆乌恰地区乌拉根铅锌矿床热卤水成因探讨[J].四川地质学报, 2009, 29(4):400-405. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2009.04.006 刘增仁, 田培仁, 祝新友, 等.新疆乌拉根铅锌矿成矿地质特征及成矿模式[J].矿产勘查, 2011, 2(6):669-680. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2011.06.005 王勃, 莫新华, 杨泽军.新疆乌恰县乌鲁干塔什铅锌矿勘探报告.紫金矿业集团股份有限公司, 2013.



 下载:
下载: