The mechanisms for the formation of the alteration halos in tungsten deposits of Nanling Mountains, South China
-
摘要:
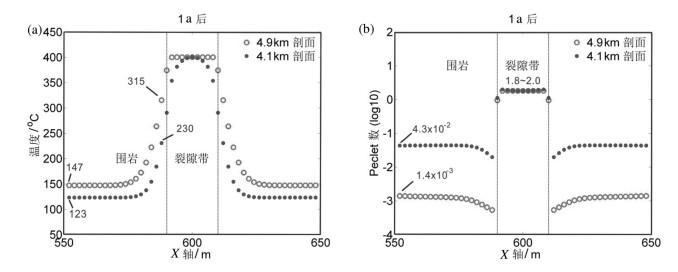
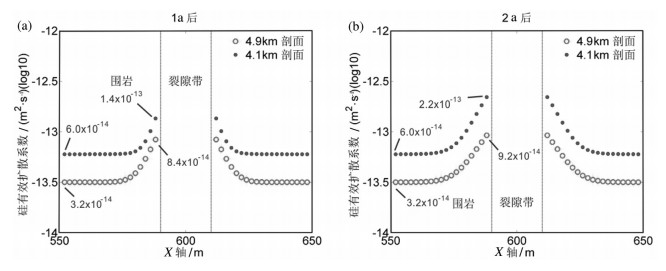
中国地质工作者在20世纪80年代已发现南岭地区许多石英脉型钨矿床的蚀变晕宽度随深度递减,然而这一蚀变特征的形成机制至今仍未得到较好的解释。通过模拟热液运移和硅从裂隙带向邻近围岩的扩散过程,发现流体温度和围岩孔隙度是影响石英脉型钨矿床蚀变特征的重要变量。高温和高孔隙度会加速硅从裂隙向邻近围岩扩散,从而形成较宽的蚀变。在围岩孔隙度均一分布的情况下,由于深部温度高于浅部,深部围岩蚀变宽于浅部蚀变。围岩孔隙度随深度递减会抵消温度对硅扩散速率的影响,使深部围岩形成较窄的蚀变。围岩孔隙度随深度递减可能是形成石英脉型钨矿床蚀变宽度随深度减小的有效机制。前人将钨矿蚀变特征归因于岩浆热液过渡性流体不均一的物理性质,该研究为这一科学问题提供新的解释。
Abstract:Geologists discovered in the 1980s that alteration halos decrease with increasing depth in many tungsten deposits of the Nanling Mountains. However, the mechanism for the formation of the alteration characteristics remains poorly understood. In this paper, the authors investigated hydrothermal flow and silica diffusion from fractures to adjacent wallrock at these tungsten deposits by using finite element based numerical experiments. The authors have found that fluid temperature and wallrock porosity exert a strong influence on silica diffusion from fractures to adjacent wallrock. Both high temperature and high porosity favor silica diffusion from fractures to adjacent wallrock and form wide alteration halos. Constant-porosity wallrock forms wider alteration halos at deeper levels, which is inconsistent with alteration characteristics of the tungsten deposits in the Nanling Mountains. Wallrock porosity that decreases with increasing depth forms alteration halos like those in those the tungsten deposits. The wall rock lithology and fracture distribution those tungsten deposits favor the formation of depth-dependent porosity and permeability. Evaluation of these two factors may help the exploration. Aqueous NaCl solutions were used in the numerical experiments. It is therefore concluded that inhomogeneous magmatic hydrothermal fluids are unnecessary in explaining the alteration characteristics at these tungsten deposits.
-
Keywords:
- tungsten deposits /
- alteration halos /
- fluid flow /
- porosity /
- diffusion coefficient /
- Nanling
-
致谢: 本文数值实验在澳大利亚昆士兰大学超级计算机Savanna上完成,审稿专家提出了详细的修改意见,在此一并致谢。
-
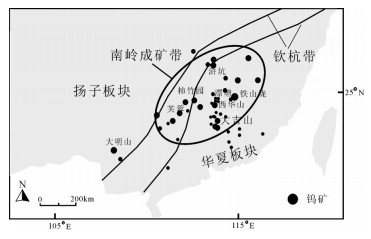
图 1 南岭成矿带钨矿分布示意图[29]
Figure 1. Distribution of tungsten deposits in the Nanling Mountains, South China
-
陈毓川, 裴荣富, 张宏良, 等.南岭地区与中生代花岗岩类有关的有色及稀有金属矿床地质[M].北京:地质出版社, 1989:507. 朱焱龄, 李崇佑, 林运淮.赣南钨矿地质[M].南昌:江西人民出版社, 1981:440. 祝新友, 王京彬, 王艳丽, 等.南岭锡钨多金属矿区碱长花岗岩的厘定及其意义[J].中国地质, 2012, 39(2):359-381. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.02.009 阙梅登, 夏卫华.江西大吉山脉钨矿床矿化富集特征及其机理初探[J].地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 1988, 13(2):177-185. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQKX198802011.htm 林新多, 张德会, 章传玲.湖南宜章瑶岗仙黑钨矿石英脉成矿流体性质的探讨[J].地球科学, 1986, 11(2):153-160. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD1986-DQKX198602006.htm 张德会.石英脉型黑钨矿床成矿流体性质的进一步探讨[J].地球科学, 1987, 12(2):185-192. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQKX198702012.htm 祝新友, 王京彬, 王艳丽, 等.论石英脉型钨矿成矿系统的相对封闭性——以湖南瑶岗仙脉型钨矿床为例[J].地质学报, 2014, 88(5):825-835. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201405002 Audétat A, Keppler H. Viscosity of fluids in subduction zones[J]. Science, 2004, 303(56/57):513-516. http://petrology.oxfordjournals.org/external-ref?access_num=10.1126/science.1092282&link_type=DOI
常海亮, 黄惠兰.西华山黑钨矿石英脉绿柱石中熔融包裹体的发现及其意义[J].华南地质与矿产, 2001, 2:21-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3701.2001.02.004 Ni P, Wang X D, Wang G G, et al. An infrared microthermometric study of fluid inclusions in coexisting quartz and wolframite from Late Mesozoic tungsten deposits in the Gannan metallogenic belt, South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 65(4):1062-1077. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a2bb56209e6f77391eecd3ab68bbe24c
Wei W F, Hu R I, Bi X W. Infrared microthermometric and stable isotopic study of fluid inclusions in wolframite at the Xihuashan tungsten deposit, Jiangxi province, China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2012, 47(6):589-605. doi: 10.1007/s00126-011-0377-0
曹晓峰, 吕新彪, 何谋春, 等.共生黑钨矿与石英中流体包裹体红外显微对比研究——以瑶岗仙石英脉型钨矿床为例[J].矿床地质, 2009, 28(5):611-620. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2009.05.007 董少花, 毕献武, 胡瑞忠, 等.湖南瑶岗仙石英脉型黑钨矿床成矿流体特征[J].矿物岩石, 2011, 31(2):54-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2011.02.008 宋生琼, 胡瑞忠, 毕献武, 等.赣南淘锡坑钨矿床流体包裹体地球化学研究[J].地球化学, 2011, 40(3):237-248. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhx201103003 宋生琼, 胡瑞忠, 毕献武, 等.赣南崇义淘锡坑钨矿床氢、氧、硫同位素地球化学研究[J].矿床地质, 2011, 30(1):1-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2011.01.001 王巧云, 胡瑞忠, 彭建堂, 等.湖南瑶岗仙钨矿床流体包裹体特征及其意义[J].岩石学报, 2007, 9:2263-2273. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.09.024 王旭东, 倪培, 蒋少涌, 等.赣南漂塘钨矿流体包裹体研究[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(9):2163-2170. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200809025 王旭东, 倪培, 张伯声, 等.江西盘古山石英脉型钨矿床流体包裹体研究[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2012, 29(5):539-550. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yskwxzz201005009 王旭东, 倪培, 袁顺达, 等.江西黄沙石英脉型钨矿床流体包裹体研究[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(1):122-132. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201201010 王旭东, 倪培, 袁顺达, 等.赣南漂塘钨矿锡石及共生石英中流体包裹体研究[J].地质学报, 2013, 87(6):850-859. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2013.06.009 席斌斌, 张德会, 周利敏, 等.江西省全南县大吉山钨矿成矿流体演化特征[J].地质学报, 2008, 82(7):956-966. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.07.014 赵波.江西漂塘石英脉型黑钨矿床成矿深度估算[D].中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文: 2013. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1013265943.htm Hayba D O, Ingebritsen S E. Multiphase groundwater flow near cooling plutons[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1997, 102(B6):12235-12252. doi: 10.1029/97JB00552
Zhao C B, Reid L B, Regenauer-Lieb K. Some fundamental issues in computational hydrodynamics of mineralization:A review[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 112:21-34. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2011.10.005
Ingebritsen S E, Appold M S. The physical hydrogeology of ore deposits[J]. Economic Geology, 2012, 107:559-584. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.107.4.559
池国祥, 薛春纪.成矿流体动力学的原理、研究方法及应用[J].地学前缘, 2011, 18(5):1-18. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201105002 邓军, 王庆飞, 黄定华.成矿流体输运物理机制研究的关键难题与方法体系[J].地球科学进展, 2004, 19(3):393-398. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2004.03.008 周利敏, 张德会, 席斌斌.岩石中的渗透率、流体流动及热液成矿作用[J].地学前缘, 2008, 15(3):299-310. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2008.03.027 毛景文, 谢桂青, 郭春丽, 等.南岭地区大规模钨锡多金属成矿作用-成矿时限及地球动力学背景[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(10):2329-2338. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.10.002 王碟, 卢焕章, 毕献武.与花岗质岩浆系统有关的石英脉型钨矿和斑岩型铜矿成矿流体特征比较[J].地学前缘, 2011, 18(5):121-131. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201105012 黄惠兰, 常海亮, 付建明, 等.西华山脉钨矿床的形成压力及有关花岗岩的侵位深度[J].矿床地质, 2006, 25(5):562-571. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2006.05.003 穆治国, 黄福生, 陈成业, 等.漂塘-西华山石英脉型钨矿床碳、氢和氧稳定同位素研究[C]//余鸿彰.钨矿地质讨论会论文集.北京: 地质出版社, 1984: 153-169. 张国新, 谢越宁, 虞福基, 等.江西大吉山钨矿床不同成矿阶段稳定同位素地球化学[J].地球学报, 1997, 18(增刊):197-199. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/310114 张理刚, 庄龙池, 钱雅倩.江西西华山-漂塘地区花岗岩及其钨锡矿床的稳定同位素地球化学[C]//余鸿彰.钨矿地质讨论会论文集.北京: 地质出版社, 1984: 325-338. 庄龙池, 林伟圣, 谢廷焕.大吉山钨矿的稳定同位素地球化学[C]//中国地质科学院宜昌地质矿产研究所文集, 1991: 16. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ199101001010.htm 古菊云.华南隐伏-半隐伏脉钨矿床的地表标志带[J].矿床地质, 1984, 3(1):67-76. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KCDZ198401010.htm Cathles, L M, Shannon R. How potassium silicate alteration suggests the formation of porphyry ore deposits begins with the nearly explosive but barren expulsion of large volumes of magmatic water[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 262(1/2):92-108. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c19020c9c4c93abdc98e8fada5fe2bdf
Geiger S, Haggerty R, Dilles J H, et al. New insights from reactive transport modelling:the formation of the sericitic vein envelopes during early hydrothermal alteration at Butte, Montana[J]. Geofluids, 2002, 2(3):185-201. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-8123.2002.00037.x
Steefel C I, Lichtner P C. Multicomponent reactive transport in discrete fractures: Ⅰ. Controls on reaction front geometry[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1998, 209(1/4):186-199. doi: 10.1016-S0022-1694(98)00146-2/
Li Q, Xing H. Numerical analysis of the material parameter effects on the initiation of hydraulic fracture in a near wellbore region[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2015, 2(3):1597-1608. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=23d81587cbaab41491fca034a40fe00c
Liu X, Xing H, Zhang D. Fluid focusing and its link to vertical morphological zonation at the Dajishan vein-type tungsten deposit, South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014, 62(1):245-258. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=9c06fb749eab45a9db8a0dbe909d8e75
Liu X, Xing H, Zhang D, The mechanisms of the infill textures and its implications for the five-floor zonation at the Dajishan vein-type tungsten deposit, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 65, Part 1(0): 365-374. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169136814002625
Liu X, Xing H, Zhang D. Influences of fluid properties on the hydrothermal fluid flow and alteration halos at the Dajishan tungsten deposit, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 163:53-69. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.01.014
Xing H. Finite element simulation of transient geothermal flow in extremely heterogeneous fractured porous media[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 144:168-178. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.03.002
Xing H, Yu W, Zhang J. 3D Mesh Generation in Geocomputing, Advances in Geocomputing[M]. Lecture Notes in Earth Sciences. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2009: 27-64.
Xing H L, Ding R W, Yuen D A. Tsunami Hazards along the Eastern Australian Coast from Potential Earthquakes:Results from Numerical Simulations[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 2014:1-29. doi: 10.1007/s00024-014-0904-x
Xing H L, Makinouchi A. Three dimensional finite element modeling of thermomechanical frictional contact between finite deformation bodies using R-minimum strategy[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2002, 191(37/38):4193-4214. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a959131123b33e7256b622c20c2b2fc6
Xing H L, Makinouchi A, Mora P. Finite element modeling of interacting fault systems[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 2007, 163(1/4):106-121. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f880511e3c2ec01187b1ed11d87fb5f0
Xing H L, Zhang J, Gao J F, et al. PANDAS and its New Applications in Geothermal Modelling[C]//Australian Geothermal Energy Conference, Melbourne. 2011. https://espace.library.uq.edu.au/view/UQ: 301264
Batzle M L, Wang Z. Seismic properties of pore fluids[J]. Geophysics, 1992, 57(11):1396-1408. doi: 10.1190/1.1443207
Van Loon L R, Mibus J. A modified version of Archie's law to estimate effective diffusion coefficients of radionuclides in argillaceous rocks and its application in safety analysis studies[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2015, 59:85-94. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2015.04.002
Li Y, Gregory S. Diffusion of ions in sea water and in deep-sea sediments[J]. Geochimica et cosmochimica acta, 1974, 38(5):703-714. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(74)90145-8
Rimstidt D. Geochemical Rate Models[M]. Cambridge University Press, New York, 2014:232.
Huysmans M, Dassargues A. Review of the use of Péclet numbers to determine the relative importance of advection and diffusion in low permeability environments[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2005, 13(5):895-904. doi: 10.1007/s10040-004-0387-4
Lester D R, Ord A, Hobbs B E. The mechanics of hydrothermal systems:Ⅱ. Fluid mixing and chemical reactions[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2012, 49(0):45-71. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169136812001734
陈尊达, 胡立檖.黄沙脉钨矿床地质特征及原生分带[C]//余鸿彰.钨矿地质讨论会论文集.北京: 地质出版社, 1984: 25-34. 刘向冲.江西大吉山石英脉型黑钨矿床"五层楼"垂直形态分带动力学机制[D].中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2015: 114. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-11415-1015518056.htm 周利敏.江西省全南县大吉山钨矿构造应力场数值模拟与成矿预测[D].中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2009: 67. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-2009075726.htm Genter A, Evans K, Cuenot N, et al. Contribution of the exploration of deep crystalline fractured reservoir of Soultz to the knowledge of enhanced geothermal systems (EGS)[J]. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 2010, 342(7/8):502-516. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1631071310000179
Rebreanu L, Vanderborght J P, Chou L. The diffusion coefficient of dissolved silica revisited[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2008, 112(3):230-233. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304420308001400
Ingebritsen S E, Manning C E. Permeability of the continental crust:dynamic variations inferred from seismicity and metamorphism[J]. Geofluids, 2010, 10:193-205. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-8123.2010.00278.x/full
Stein H J, Cathles L M. A special issue on the timing and duration of hydrothermal events-preface[J]. Economic Geology, 1997, 92(7/8):763-765.
Cathles L M, Erendi A H J, Barrie T. How long can a hydrothermal system be sustained by a single intrusive event[J]?Economic Geology, 1997, 92(7/8):766-771.
Cox S F. Coupling between deformation, fluid pressures, and fluid flow in ore-producing hydrothermal systems at depth in the crust[C]//Hedenquist J W, Thompson J F H, Goldfarb R J, et al. Economic Geology One Hundredth Anniversary Volume. Society of Economic Geologists, Litteton, Colorado, 2005: 39-76.
Henley R W, Berger B R. Self-ordering and complexity in epizonal mineral deposits[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2000, 28:669-719. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.669
Ingebritsen S E, Appold M S. The physical hydrogeology of ore deposits[J]. Economic Geology, 2012, 107:559-584. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.107.4.559
Ingebritsen S E, Manning C. E. Permeability of the continental crust:dynamic variations inferred from seismicity and metamorphism[J]. Geofluids, 2010, 10:193-205. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-8123.2010.00278.x/full
David C, Wong T F, Zhu W, et al. Laboratory measurement of compaction-induced permeability change in porous rocks:implications for the generation and maintenance of pore pressure excess in the crust[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 1994, 143(1/3):425-456. doi: 10.1007/BF00874337
Heiland J. Laboratory testing of coupled hydro-mechanical processes during rock deformation[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2003, 11(1):122-141. doi: 10.1007/s10040-002-0236-2



 下载:
下载: