Geochemistry, chronology and zircon Lu-Hf isotopic characteristics of the Miren rocks in Riduo area of east part of Southern Gangdise belt and their geological significance
-
摘要:
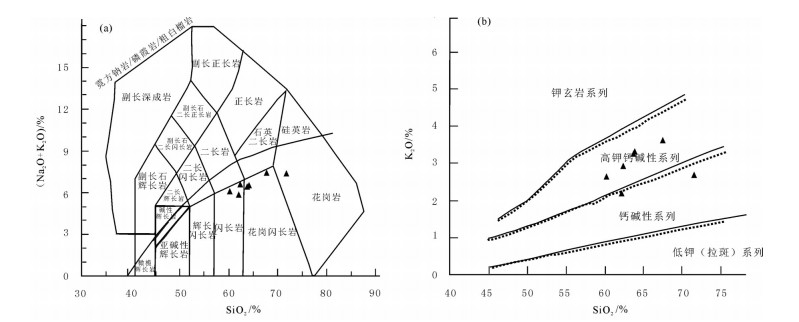
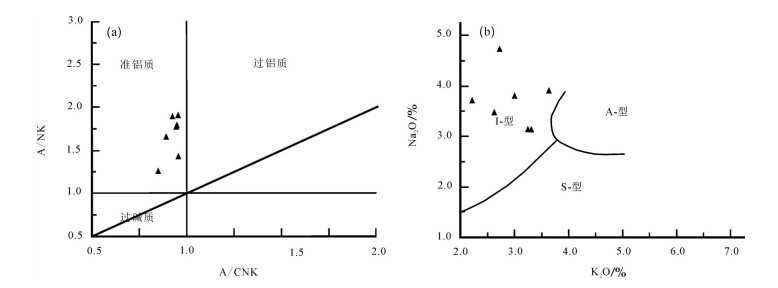
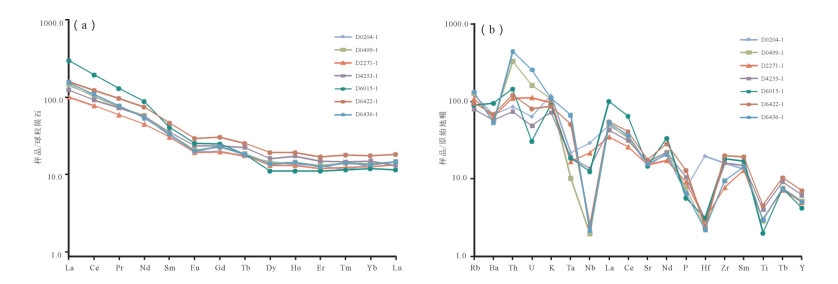
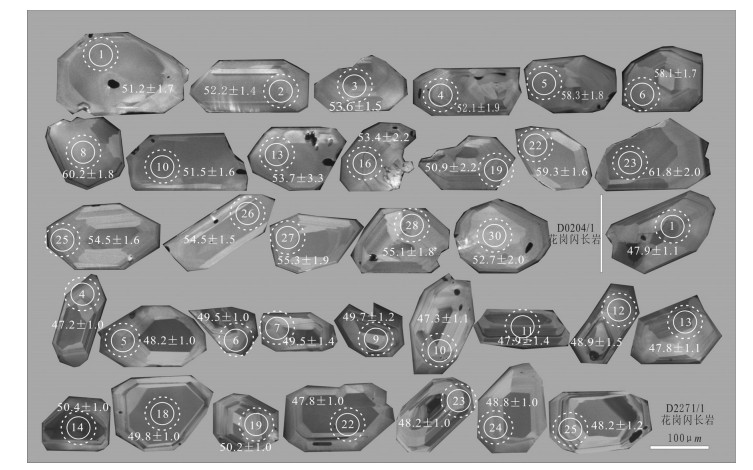
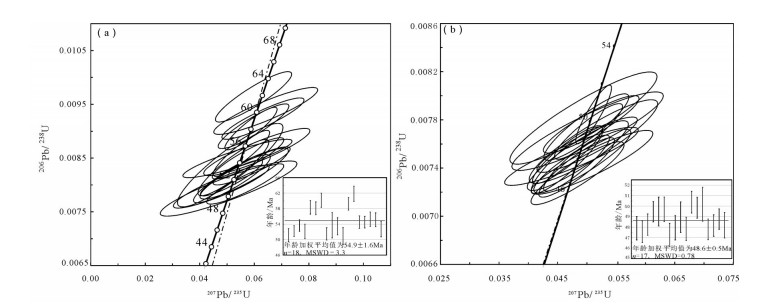
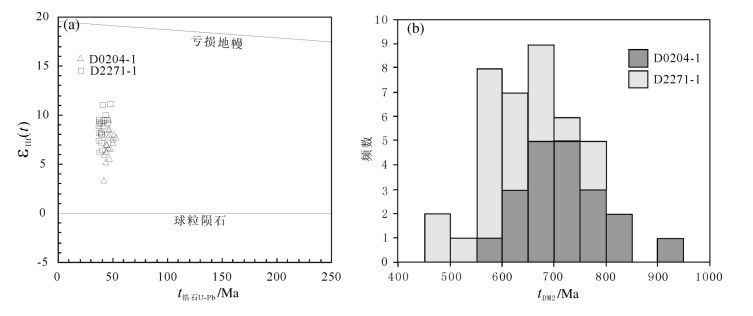
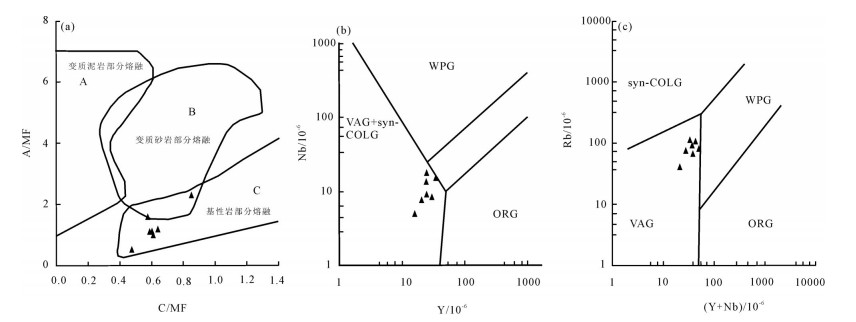
日多地区米忍岩体位于冈底斯南带东段,2件锆石U-Pb测年样品显示其形成年龄为54.9±1.6Ma和48.6±0.5Ma,岩石SiO2含量为60.18%~71.53%,全碱含量为5.85%~7.49%,K2O/Na2O值为0.58~1.05,里特曼指数在1.79~2.30之间,属钙碱性岩石,A/CNK值为0.85~0.95,投图显示为准铝质岩石,具有I型花岗岩的特征。岩石轻稀土元素及大离子亲石元素(Rb、K、Ba、Th、U)相对富集,重稀土及高场强元素(Nb、P、Hf、Ti)相对亏损,弱负Eu异常,具火山弧岩浆岩地球化学特征。176Hf/177Hf平均值为0.282945,Hf同位素二阶段模式年龄较年轻(613~719Ma),εHf(t)值为2.74~10.47,表明其岩浆源区以新生地壳的部分熔融为主或有地幔物质参与了成岩过程,据C/MF-A/MF投图分析,可能为基性或铁镁质岩浆底侵,导致中下地壳的物质发生熔融,这些特征均表明,日多地区始新世花岗闪长岩的形成可能与新特提斯洋板片的回转、断离有关。
Abstract:The Miren rock in the Riduo Area is located in the eastern part of southern Gangdise belt. Zircon U-Pb dating of two samples reveals that the formation ages are 54.9±1.6Ma and 48.6±0.5Ma, and SiO2 content of the rock is 60.18%~71.53%, total alkali content is 5.85%~7.49%, K2O/Na2O ratio is 0.58~1.05, and Liteman index (σ) is 1.79~2.30, suggesting calc-alkaline rocks, with A/CNK value being 0.85~0.95. The diagram shows a quasi-aluminous rock with characteristics of type I granite. The light rare earth and large lithosphere ionic elements (Rb, K, Ba, Th, and U) are relatively enriched, and the characteristics of heavy rare earth and high-field strength elements (Nb, P, Hf, Ti) are relatively depleted with weak negative Eu anomalies, showing features of volcanic arc magma. The ratio of 176Hf/177Hf is 0.282819~0.283036, 0.282945 on average. The Hf isotope two-stage model is younger (613~719Ma) and the εHf(t) value is between 2.74 and 10.47, indicating that the magma source area was part of the new genetic crust. Melting or mantle material was involved in the rock-forming process. According to C/MF-A/MF mapping analysis, it may be basic or iron-magnesian magmatic intrusion, resulting in melting of material in the middle and lower crust. The formation of the Riduo granodiorite may have been related to the rotation and separation of the Neo-Tethys plate.
-
Keywords:
- Gangdise /
- Riduo area /
- granite /
- zircon U-Pb dating /
- Hf isotope
-
致谢: 感谢陕西省矿产地质调查中心边小卫、李新林等教授级高工和陕西省区研院韩芳林教授级高工对本项目野外工作的热情指导,陕西省地质规划研究中心周斌、陕西省矿产地质调查中心韩奎两位工程师在撰写过程给予很大帮助,审稿专家提出很多宝贵意见,在此一并表示感谢。
-
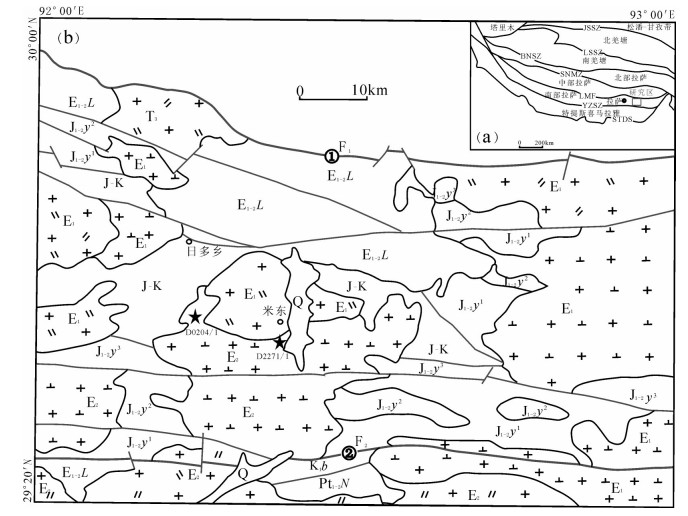
图 1 日多地区大地构造位置(a)及区域地质简图(b)(据参考文献①修改)
JSSZ—金沙江缝合带;LSSZ—龙木错-双湖缝合带;BNSZ—班公湖-怒江缝合带;SNMZ—狮泉河-纳木错蛇绿混杂岩带;LMF—洛巴堆-米拉山断裂带;YZSZ—印度-雅鲁藏布江缝合带;STDS—藏南拆离系;Pt1-2N—念青唐古拉岩群;J1-2y—叶巴组;J-K—包括多底沟组、林布宗组、楚木龙组、塔克那组和设兴组;K1b—比马组;E1-2L—林子宗群;Q—第四系;★—测年样位置及年龄;F1—米拉山口逆冲推覆带;F2—沃卡脆韧性剪切带
Figure 1. Tectonic position (a) and geological map (b) of Riduo area
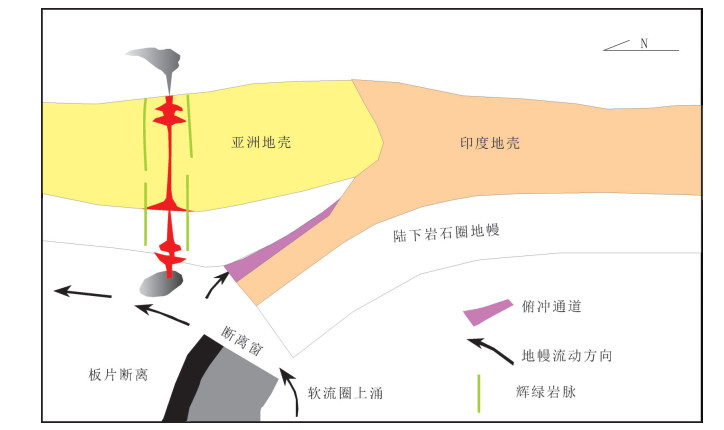
图 10 冈底斯东段始新世构造-岩浆演化模式图(据参考文献[44]修改)
Figure 10. Eocene tectonic-magmatic evolution pattern of the eastern Gangdise belt
表 1 日多地区米忍岩体主量、微量和稀土元素分析数据
Table 1 Major, trace and rare earth element compositions of Miren rocks in Riduo area
样品编号 D4253/1 D0204/1 D6015/1 D2271/1 D0499/1 D6422/1 D6436/1 SiO2 62.15 67.46 71.53 62.41 63.69 60.18 63.88 Al2O3 15.93 14.83 13.40 15.27 15.34 16.17 15.25 TFe2O3 6.47 4.46 3.22 6.13 5.89 7.04 6.04 MgO 2.35 1.47 0.77 2.60 2.44 2.88 2.46 CaO 4.96 2.95 2.73 4.70 4.47 5.33 4.45 Na2O 3.66 3.88 4.71 3.75 3.14 3.48 3.15 K2O 2.19 3.61 2.71 2.93 3.26 2.63 3.31 P2O5 0.19 0.16 0.08 0.15 0.14 0.24 0.14 MnO 0.13 0.08 0.09 0.12 0.11 0.12 0.11 TiO2 0.81 0.61 0.40 0.59 0.57 0.91 0.59 烧失量 0.79 1.03 0.27 0.63 0.81 0.64 0.71 总计 99.63 100.54 99.91 99.28 99.86 99.62 100.09 K2O/ Na2O 0.60 0.93 0.58 0.78 1.04 0.76 1.05 Σ 1.79 2.29 1.93 2.30 1.98 2.17 2.00 DI 76.88 65.88 65.85 62.48 83.79 59.38 66.3 SI 11.19 16.99 17.29 16.50 6.86 18.53 16.84 A/CNK 0.95 0.91 0.85 0.92 0.86 0.89 0.90 La 30.3 33.9 71.6 24.6 36.2 39.0 37.6 Ce 58.9 67.3 122 49.5 63.9 77.5 69.2 Pr 7.25 7.44 12.8 5.84 7.44 9.51 7.73 Nd 28.0 27.8 43.3 22.2 28.2 36.7 26.3 Sm 5.78 5.12 6.58 4.99 5.4 7.46 5.46 Eu 1.46 1.23 1.58 1.19 1.3 1.83 1.25 Gd 5.2 4.43 5.44 4.34 4.96 6.68 5.06 Tb 0.9 0.69 0.74 0.71 0.75 1.02 0.73 Dy 4.43 4 3.05 3.62 3.9 5.3 3.76 Ho 1.06 0.84 0.68 0.8 0.88 1.18 0.88 Er 2.68 2.33 1.98 2.14 2.34 3.03 2.25 Tm 0.4 0.32 0.32 0.34 0.39 0.49 0.39 Yb 2.75 2.48 2.21 2.33 2.54 3.22 2.47 Lu 0.36 0.4 0.32 0.37 0.4 0.5 0.4 Y 30 24.7 20.6 24.1 25.3 34.5 24.6 P 953 677 515 820 690 1172 587 Sr 386 330 339 347 368 405 355 Ba 428 507 714 483 440 515 400 Zr 177 177 199 84.9 104 221 104 Rb 67.9 106 76.8 93.6 110 81.4 113 Th 7.07 8.2 13.8 10.5 31.9 11.6 42.2 U 1.31 1.7 0.82 3 4.38 2.17 6.87 Nb 8.42 17.8 7.68 13.4 9.12 15.3 9.21 Hf 1.06 6.91 1.1 1.04 1.21 1.53 1.33 Ta 0.82 0.92 0.8 0.72 0.82 0.83 0.77 ΣREE 179.47 182.98 293.2 147.07 183.9 227.92 188.08 LREE/HREE 2.76 3.55 7.30 2.80 3.44 3.08 3.64 (La/Yb)N 9.81 10.22 7.57 7.90 23.24 8.69 10.92 (La/Sm)N 4.27 4.33 3.18 3.38 7.02 3.37 4.45 (Gd/Yb)N 1.48 1.62 1.54 1.56 2.04 1.72 1.69 δEu 0.79 0.77 0.78 0.81 0.81 0.79 0.73 Th/Yb 5.86 22.24 7.98 4.55 11.06 6.38 30.25 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 表 2 日多地区米忍岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果
Table 2 LA-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb isotopic data of zircons from Miren rocks in Riduo area
分析点 含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Pb Th U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ D0204-1-01 2.30 130.01 60.88 2.14 0.04383 0.01053 0.04788 0.01161 0.00797 0.00026 47 11 51 2 D0204-1-02 2.13 84.80 62.02 1.37 0.04506 0.00638 0.05166 0.00753 0.00813 0.00022 51 7 52 1 D0204-1-03 1.60 59.30 42.04 1.41 0.05112 0.00780 0.05903 0.00934 0.00835 0.00023 256 309 58 9 54 1 D0204-1-04 1.99 74.73 61.37 1.22 0.04792 0.00889 0.05180 0.00931 0.00811 0.00030 95 389 51 9 52 2 D0204-1-05 1.55 53.09 53.42 0.99 0.04988 0.00743 0.05973 0.00857 0.00909 0.00027 191 311 59 8 58 2 D0204-1-06 2.08 71.87 64.75 1.11 0.04563 0.00429 0.05879 0.00632 0.00905 0.00026 58 6 58 2 D0204-1-07 1.45 61.92 75.31 0.82 0.11571 0.01014 0.07259 0.00611 0.00469 0.00020 1891 159 71 6 30 1 D0204-1-08 1.47 55.36 46.34 1.19 0.04885 0.00915 0.06421 0.01260 0.00938 0.00029 139 393 63 12 60 2 D0204-1-09 10.74 360.72 168.73 2.14 0.12331 0.01948 0.19709 0.03913 0.01025 0.00042 2006 283 183 33 66 3 D0204-1-10 2.80 128.42 81.77 1.57 0.05172 0.00898 0.05667 0.00933 0.00802 0.00025 272 356 56 9 51 2 D0204-1-11 1.42 55.71 46.69 1.19 0.05735 0.01238 0.06456 0.01420 0.00876 0.00027 506 415 64 14 56 2 D0204-1-12 2.36 87.76 66.41 1.32 0.05594 0.00782 0.06469 0.00841 0.00843 0.00028 450 319 64 8 54 2 D0204-1-13 1.83 65.40 58.94 1.11 0.05205 0.01037 0.05118 0.01279 0.00837 0.00051 287 400 51 12 54 3 D0204-1-14 3.04 97.51 94.71 1.03 0.02920 0.00560 0.03688 0.00740 0.01010 0.00028 37 7 65 2 D0204-1-15 2.75 67.75 58.33 1.16 0.13019 0.00961 0.20104 0.01756 0.01154 0.00048 2102 130 186 15 74 3 D0204-1-16 2.71 96.78 92.07 1.05 0.00000 0.00000 0.05232 0.00859 0.00832 0.00034 52 8 53 2 D0204-1-17 2.89 83.24 62.58 1.33 0.08117 0.04934 0.08451 0.04577 0.00846 0.00027 1226 880 82 43 54 2 D0204-1-18 4.17 165.06 146.94 1.12 0.05976 0.00885 0.06593 0.00744 0.00839 0.00022 594 326 65 7 54 1 D0204-1-19 1.87 69.10 68.68 1.01 0.04307 0.01402 0.05060 0.01656 0.00793 0.00034 50 16 51 2 D0204-1-20 1.64 46.71 41.46 1.13 0.06426 0.01556 0.08741 0.02308 0.00985 0.00047 750 497 85 22 63 3 D0204-1-21 1.43 51.46 44.76 1.15 0.05601 0.01257 0.06549 0.01417 0.00891 0.00031 454 433 64 14 57 2 D0204-1-22 1.62 63.43 53.29 1.19 0.05102 0.00777 0.06318 0.00996 0.00923 0.00025 243 318 62 10 59 2 D0204-1-23 2.83 120.98 73.61 1.64 0.04670 0.00707 0.05972 0.00925 0.00964 0.00031 35 326 59 9 62 2 D0204-1-24 2.81 101.48 66.37 1.53 0.05630 0.00678 0.07465 0.00898 0.00985 0.00031 465 269 73 8 63 2 D0204-1-25 1.99 73.25 65.81 1.11 0.05043 0.00757 0.05771 0.00867 0.00849 0.00025 213 315 57 8 55 2 D0204-1-26 2.89 113.01 70.90 1.59 0.04505 0.01110 0.05384 0.01323 0.00849 0.00024 53 13 55 2 D0204-1-27 1.63 50.32 44.07 1.14 0.05382 0.01148 0.06092 0.01287 0.00861 0.00029 365 418 60 12 55 2 D0204-1-28 3.10 111.91 96.60 1.16 0.04884 0.00674 0.05526 0.00685 0.00859 0.00028 139 296 55 7 55 2 D0204-1-29 1.77 62.05 56.57 1.10 0.06036 0.00950 0.07073 0.01088 0.00860 0.00029 617 344 69 10 55 2 D0204-1-30 1.47 53.51 47.48 1.13 0.05141 0.01039 0.05628 0.01072 0.00821 0.00031 261 472 56 10 53 2 D2271-1-01 12.93 454.74 458.20 0.99 0.04883 0.00566 0.04922 0.00547 0.00746 0.00017 139 252 49 5 48 1 D2271-1-02 7.23 318.13 311.42 1.02 0.04454 0.01133 0.04555 0.01133 0.00739 0.00031 45 11 47 2 D2271-1-03 6.28 352.21 316.30 1.11 0.07228 0.03483 0.03771 0.03663 0.00773 0.00069 994 756 38 36 50 4 D2271-1-04 12.81 487.61 555.00 0.88 0.04759 0.00427 0.04827 0.00427 0.00741 0.00016 80 200 48 4 48 1 D2271-1-05 14.52 487.01 576.02 0.85 0.04601 0.00420 0.04668 0.00394 0.00751 0.00016 46 4 48 1 D2271-1-06 21.46 782.84 796.98 0.98 0.04715 0.00355 0.05028 0.00384 0.00770 0.00015 58 170 50 4 49 1 D2271-1-07 14.86 531.33 547.43 0.97 0.08643 0.04655 0.05013 0.00853 0.00771 0.00021 1348 791 50 8 49 1 D2271-1-08 6.59 302.13 299.78 1.01 0.05649 0.01536 0.05044 0.01374 0.00743 0.00024 472 511 50 13 48 2 D2271-1-09 18.59 650.14 571.68 1.14 0.04744 0.00471 0.04991 0.00479 0.00774 0.00018 78 222 49 5 50 1 D2271-1-10 17.62 625.43 652.63 0.96 0.04782 0.00497 0.04841 0.00525 0.00736 0.00017 100 220 48 5 47 1 D2271-1-11 28.91 1250.91 916.96 1.36 0.04631 0.00430 0.04663 0.00403 0.00747 0.00018 13 220 46 4 48 1 D2271-1-12 10.02 355.94 376.33 0.95 0.04806 0.00698 0.05113 0.00724 0.00762 0.00023 102 311 51 7 49 1 D2271-1-13 13.49 581.85 419.23 1.39 0.05066 0.00736 0.05088 0.00686 0.00745 0.00017 233 298 50 7 48 1 D2271-1-14 99.43 4785.10 1917.08 2.50 0.04752 0.00187 0.05115 0.00201 0.00784 0.00016 76 89 51 2 50 1 D2271-1-15 13.99 451.56 485.18 0.93 0.04791 0.00722 0.05333 0.00808 0.00832 0.00030 95 322 53 8 53 2 D2271-1-16 8.34 310.14 312.87 0.99 0.03803 0.01050 0.04417 0.01413 0.00774 0.00022 44 14 50 1 D2271-1-17 27.12 1148.15 679.00 1.69 0.04938 0.00404 0.05728 0.00520 0.00866 0.00048 165 181 57 5 56 3 D2271-1-18 13.71 546.36 433.97 1.26 0.04897 0.00539 0.05073 0.00539 0.00776 0.00016 146 241 50 5 50 1 D2271-1-19 22.72 694.60 647.13 1.07 0.04584 0.00805 0.04942 0.00829 0.00781 0.00025 49 8 50 2 D2271-1-20 25.23 755.58 817.03 0.92 0.07766 0.00653 0.08193 0.00712 0.00767 0.00018 1139 169 80 7 49 1 D2271-1-21 11.05 447.91 370.70 1.21 0.04849 0.00949 0.05336 0.01056 0.00812 0.00020 124 404 53 10 52 1 D2271-1-22 19.61 881.08 624.44 1.41 0.04731 0.00372 0.04823 0.00371 0.00744 0.00015 65 178 48 4 48 1 D2271-1-23 9.72 362.06 351.35 1.03 0.04713 0.00756 0.04736 0.00753 0.00750 0.00016 58 341 47 7 48 1 D2271-1-24 11.40 465.90 530.57 0.88 0.04720 0.00537 0.05005 0.00565 0.00759 0.00015 61 248 50 5 49 1 D2271-1-25 13.46 514.88 490.81 1.05 0.04724 0.00556 0.04846 0.00570 0.00750 0.00019 61 259 48 6 48 1 表 3 日多地区米忍岩体锆石Hf同位素组成分析结果
Table 3 Hf isotopic data of zircons from Miren rocks in Riduo area
样品号 t/Ma 176Yb/177Hf 2σ 176Lu/177Hf 2σ 176Hf/177Hf 2σ εHf(0) εHf(t) (176Hf/177Hf)i tDM1/Ma tDM2/Ma fLu/Hf D0204-1-01 51.2 0.04228206 0.00092 0.001194067 0.0000261 0.282819 0.0000199 1.7 2.7 0.282817859 616.6 949.9 -0.964045 D0204-1-02 52.2 0.04038035 0.000381 0.001167999 0.00000986 0.2828985 0.0000202 4.5 5.6 0.282897361 503.0 769.3 -0.96483 D0204-1-03 53.6 0.02271428 0.0000674 0.000651701 0.00000134 0.2829529 0.0000182 6.4 7.6 0.282952247 419.7 644.0 -0.980376 D0204-1-04 52.1 0.02556968 0.000232 0.000752814 0.00000547 0.2828695 0.0000171 3.4 4.6 0.282868767 538.3 834.1 -0.977332 D0204-1-06 58.1 0.05982562 0.000278 0.001749438 0.00000851 0.282933 0.0000199 5.7 6.9 0.282931102 461.0 689.0 -0.947322 D0204-1-08 60.2 0.02376553 0.000101 0.000685301 0.00000281 0.2829455 0.0000187 6.1 7.4 0.28294473 430.5 656.8 -0.979365 D0204-1-10 51.5 0.06452603 0.00127 0.001795006 0.0000363 0.2828958 0.0000205 4.4 5.4 0.282894074 515.5 777.1 -0.94595 D0204-1-11 56.2 0.02167035 0.0000771 0.000626035 0.00000136 0.2829046 0.0000182 4.7 5.9 0.282903942 487.3 751.8 -0.981149 D0204-1-12 54.1 0.04413258 0.000333 0.001245586 0.0000103 0.2829119 0.0000192 4.9 6.1 0.282910641 484.9 738.0 -0.962494 D0204-1-13 53.7 0.02336732 0.000227 0.000669959 0.00000515 0.2829074 0.0000199 4.8 5.9 0.282906728 483.9 747.1 -0.979827 D0204-1-16 53.4 0.03600378 0.000142 0.001062279 0.00000422 0.2829181 0.0000175 5.2 6.3 0.28291704 473.8 723.9 -0.968013 D0204-1-18 53.9 0.04790006 0.000286 0.001387101 0.00000709 0.2829377 0.0000175 5.9 7.0 0.282936304 449.8 679.9 -0.958232 D0204-1-19 50.9 0.05050586 0.000554 0.001417883 0.0000163 0.2829526 0.0000198 6.4 7.5 0.282951251 428.8 647.9 -0.957306 D0204-1-22 59.3 0.03527519 0.000674 0.000982377 0.0000167 0.2829224 0.0000169 5.3 6.6 0.282921313 466.7 710.5 -0.970419 D0204-1-23 61.8 0.03530693 0.000187 0.000993284 0.0000046 0.2829396 0.0000209 5.9 7.2 0.282938453 442.4 670.0 -0.970091 D0204-1-25 54.5 0.03495778 0.000115 0.001038461 0.00000411 0.2829622 0.0000196 6.7 7.9 0.282961142 410.8 623.2 -0.96873 D0204-1-26 54.5 0.04224788 0.000776 0.001160659 0.0000219 0.2828813 0.0000199 3.9 5.0 0.282880118 527.4 806.9 -0.965051 D0204-1-27 55.3 0.0400008 0.00016 0.001136954 0.0000037 0.282946 0.0000208 6.2 7.3 0.282944826 435.0 659.7 -0.965765 D0204-1-28 55.1 0.03602579 0.000241 0.001225747 0.00000798 0.2829891 0.000018 7.7 8.8 0.282987838 374.4 562.2 -0.963091 D0204-1-30 52.7 0.0286314 0.000116 0.000810488 0.00000437 0.2829194 0.00002 5.2 6.3 0.282918602 468.8 720.8 -0.975595 D2271-1-01 47.9 0.02714477 0.0000158 0.00078377 0.00000164 0.2829532 0.0000127 6.4 7.4 0.282952499 420.7 647.1 -0.976399 D2271-1-02 47.5 0.02702843 0.0002020 0.00079536 0.00000509 0.2829790 0.0000124 7.3 8.3 0.282978294 384.4 588.8 -0.976051 D2271-1-03 49.6 0.04025495 0.0001490 0.00119915 0.00000641 0.2829463 0.0000153 6.2 7.2 0.282945188 435.3 662.5 -0.963892 D2271-1-04 47.6 0.02768171 0.0000842 0.00081525 0.00000151 0.2829662 0.0000131 6.9 7.9 0.282965476 402.7 617.8 -0.975452 D2271-1-05 48.2 0.03151712 0.0000443 0.00093078 0.00000224 0.2829869 0.0000145 7.6 8.6 0.282986061 374.6 570.6 -0.971973 D2271-1-06 49.5 0.03453471 0.0002490 0.00100078 0.00000553 0.2829792 0.0000137 7.3 8.4 0.282978275 386.2 587.5 -0.969865 D2271-1-07 49.5 0.03121221 0.0000248 0.00090820 0.00000047 0.2829588 0.0000136 6.6 7.7 0.282957961 414.2 633.6 -0.972653 D2271-1-09 49.7 0.02593469 0.0000548 0.00077669 0.00000173 0.2829064 0.0000133 4.8 5.8 0.282905679 486.7 752.1 -0.976613 D2271-1-10 47.3 0.03278806 0.0000662 0.00095816 0.00000219 0.2829030 0.0000141 4.6 5.6 0.282902154 493.8 761.6 -0.971148 D2271-1-11 47.9 0.05085269 0.0006780 0.00143998 0.00002100 0.2829726 0.0000148 7.1 8.1 0.28297131 400.3 604.3 -0.95664 D2271-1-12 48.9 0.02664593 0.0000907 0.00079030 0.00000183 0.2829288 0.0000131 5.5 6.6 0.282928078 455.3 701.8 -0.976203 D2271-1-13 47.8 0.03217512 0.0004540 0.00091555 0.00001080 0.2829376 0.0000149 5.9 6.9 0.282936782 444.3 682.7 -0.972431 D2271-1-14 50.4 0.08687010 0.0002610 0.00243093 0.00001040 0.2830360 0.0000164 9.3 10.4 0.283033713 317.5 460.9 -0.926801 D2271-1-15 53.4 0.03728973 0.0001040 0.00111316 0.00000264 0.2829868 0.0000128 7.6 8.7 0.28298569 376.6 568.2 -0.966481 D2271-1-17 55.6 0.08208087 0.0021700 0.00232414 0.00005900 0.2830360 0.0000241 9.3 10.5 0.283033587 316.6 457.9 -0.930017 D2271-1-18 49.8 0.05583740 0.0007450 0.00160083 0.00002340 0.2829888 0.0000158 7.7 8.7 0.282987309 378.6 566.7 -0.951797 D2271-1-19 50.2 0.02709782 0.0001690 0.00079420 0.00000380 0.2829462 0.0000144 6.2 7.2 0.282945456 430.7 661.6 -0.976086 D2271-1-20 49.3 0.03317768 0.0003490 0.00098266 0.00000973 0.2829399 0.0000134 5.9 7.0 0.282938996 441.8 676.8 -0.970411 D2271-1-21 52.1 0.03766566 0.0005250 0.00109122 0.00001600 0.2830032 0.0000142 8.2 9.3 0.283002137 353.0 531.6 -0.967142 D2271-1-22 47.8 0.03258577 0.0001410 0.00096239 0.00000283 0.2829886 0.0000144 7.7 8.7 0.282987741 372.5 567.1 -0.971021 D2271-1-23 48.2 0.04579663 0.0011800 0.00128907 0.00003010 0.2829803 0.0000152 7.4 8.4 0.282979141 387.6 586.4 -0.961184 -
莫宣学.岩浆作用与青藏高原演化[J].高校地质学报, 2011, 17(3):352-354. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxdzxb201103001 刘峰, 张泽明, 董昕, 等.青藏高原冈底斯带东南部新生代多期岩浆作用及其构造意义[J].岩石学报, 2011, 27(11):3296-3305. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201111011 管琪, 朱弟成, 赵志丹, 等.西藏南部冈底斯带东段晚白垩世埃达克岩:新特提斯洋脊俯冲的产物[J].岩石学报, 2010, 6(7):2166. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201007018 Mo X X, Dong G C, Zhao Z D, et al. Timing of magma mixing in Gangdise magmatic belt during the India-Asia collision:Zircon SHIRMP U-Pb dating[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2005, 79:66-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2005.tb00868.x
Mo X X, Hou Z Q, Niu Y L, et al. Mantle contributions to crustal thickening during continentalcollision:Evidence from Cenozoic igneous rocks in southern Tibet[J]. Lithos, 2007, 96:225-242. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2006.10.005
Chung S L, Liu D Y, Ji J Q, et al. Adakites from continental collisionzones:Melting of thickened lower crust beneath southern Tibet[J]. Geology, 2003, 31:1021-1024. doi: 10.1130/G19796.1
Hou Z Q, Gao Y F, Qu X M, et al. Origin of adakitic intrusives generated during Mid-Miocene east-west extension in southern Tibet[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 220:139-155. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(04)00007-X
Chu M F, Chung S L, Song B, et al. Zircon U-Pb and Hf isotope constraints on theMesozoic tectonics and crustal evolution of Southern Tibet[J]. Geology, 2007, 34:745-748. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/259323913_Zircon_U-Pb_and_Hf_isotope_constraints_on_the_Mesozoic_tectonics_and_crustal_evolution_of_southern_Tibet?ev=auth_pub
张宏飞, 徐旺春, 郭建秋, 等.冈底斯南缘变形花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素组成:新特提斯洋早侏罗世俯冲作用的证据[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(6):1347-1353. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.06.011 纪伟强, 吴福元, 锺孙霖, 等.西藏南部冈底斯岩基花岗岩时代与岩石成因[J].中国科学(D辑), 2009, 39(7):849-871. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd200907002 孟元库, 许志琴, 陈希节, 等.冈底斯中段碱长花岗岩锆石UPb-Hf同位素特征及地质意义[J].中国地质, 2015, 42(5):1203-1213. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90050X/201505/666523454.html 孟元库, 许志琴, 陈希节, 等.藏南冈底斯中段谢通门始新世复式岩体锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素特征及其地质意义[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2015, 39(5):933-945. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201505015 董瀚, 齐玥, 马涛, 等.拉萨地块南部冈底斯~50Ma负εNd(t)花岗质侵入岩的发现及其地质意义[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2017, 41(3):604-616. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201703015 王立全, 潘桂堂, 丁俊, 等.青藏高原及邻区地质图及说明书(1:1500000)[M].北京:地质出版社, 2013:9-48. 夏代祥, 刘世坤.西藏自治区岩石地层[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1997:72-83. 路远发. GeoKit:一个用VBA构建的地球化学工具软件包[J].地球化学, 2004, 33(5):459-464. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2004.05.004 Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematic of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publicatin, 1989, 42(1): 313-345.
Anderson T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chem. Geol., 2002, 192:59-79. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00195-X
Ludwig K R. Users manual for Isoplot 3.00:A geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J]. Berkeley Geochron. Cent. Spec. Pub., 2003, 4:25-32.
Yuan H L, Gao S, Dai M N, et al. Simultaneous determinations of U-Pb age, Hf isotopes and trace element compositions of zircon by excimer laser ablation quadrupole and multiple collector ICPMS[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 247:100-117. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.10.003
Irvine T N, Baragar W R A. A guide to the chemical classification of ht common volcanic rocks[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994, 37:215-224. doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(94)90029-9
Peccerillo A, Talor A R. Geochemistry of Eocene calcalkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, northern Turkey[J]. Contribution to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58:63-81. doi: 10.1007/BF00384745
Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5):635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
Collins W J, Beams S D, White A J R. et al. Nature and origin of A type granites with paticular reference to Southeastern Australia[J]. Contrib. Miner. Petro., 1982, 80:189-200. doi: 10.1007/BF00374895
Wood D A, Joron J L, Treuil M. A re-appraisal of the use of trace elements to classify and discriminate between magma series erupted in different tectonic setting[J]. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1979, 45:326-336. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(79)90133-X
吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 等. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(2):185-220. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200702001 Vervoort J D, Patchett P J, Gehrels G E, et al. Constraints on early earth differentiation from hafnium and neodymium isotopes[J]. Nature, 1996, 379:624-627. doi: 10.1038/379624a0
孟元库.藏南冈底斯中段南缘构造演化[D].中国地质科学院博士学位论文, 2016. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-82501-1016056636.htm Elburg M A, Van Bergen M, Hoogewerff J, et al. Geochemica ltrendsacrossan arc-continentcollision zone:Magma sources and slab-wedge transferprocesses below the Pantar Strait volcanoes[J]. Indonesia Geochimicaet Cosmochimica Acta, 2002, 66:2771-2789. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(02)00868-2
Guo Z, Hertogen J, Liu J, et al. Potassic magmatism in western Sichunand Yunnan provinces, SE Tibet, China Petrological and geochemical constraints on petrogenesis[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2005, 46:33-78. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egh061
韩奎, 周斌, 乔新星, 等.拉萨地块南缘日多地区叶巴组火山岩地球化学、年代学、锆石Lu-Hf同位素特征及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2018, 37(8):100-103. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180819&flag=1 白涛, 樊炳良, 肖霞, 等.西藏玉龙斑岩铜矿带夏日多矿区始新世岩浆活动与成矿作用——来自锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学的证据[J].地质通报, 2019, 38(2/3):324-326. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2019020313&flag=1 Altherr R, Holl A, Hegner E, et al. High-potassium, calc-alkaline I-type plutonism in the European Variscides:Northern Vosges (France) and northern Schwarzwald (Germany)[J].Lithos, 2000, 50:51-73. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(99)00052-3
莫宣学, 赵志丹, 喻学惠, 等.青藏高原新生代碰撞-后碰撞火成岩[M].北京:地质出版社, 2009:1-5. Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25:956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
Yang T S, Ma Y M, Bian W W, et al. Paleomagnetic results from the Early Cretaceous Lakang Formation lavas:Constraints on the paleolatitude of the Tethyan Himalaya and the India-Asia collision[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 428:2:1-133. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X15004756
H X M, Garzanti E, Moore T, et al. Direct stratigraphic dating of India-Asia collision at the Selandian (middle Paleocene, 59±1Ma)[J]. Geology, 2015, 43(10):859-862. doi: 10.1130/G36872.1
Zhu D C, Wang Q, Zhao Z D, et al. Magmatic record of ndiaAsia collision[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5:14289, doi: 10.1038/srep14289.
李皓扬, 钟孙霖, 王彦斌, 等.藏南林周盆地林子宗火山岩的时代、成因及其地质意义:锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素证据[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(2):494-499. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200702025 李忠海.大陆俯冲-碰撞-折返的动力学数值模拟研究综述[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2014, 44(5):817-841. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201405001 Duretz T, Schmalholz S M, Gerya T V. Dynamics of slab detachment[J]. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst., 2012, 13:Q03020, doi: 10.1029/2011GC004024.
莫学宣, 赵志丹, 邓晋福, 等.印度-亚洲大陆主碰撞过程的火山作用相应[J].地学前缘, 2003, 10(3):135-148. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.03.013 周肃, 莫学宣, 董国臣, 等.西藏林周盆地林子宗火山岩40Ar-39Ar年代格架[J].科学通报, 2001, 49(20):2095-2103. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kxtb200420014 朱弟成, 王青, 赵志丹.岩浆岩定量限定陆-陆碰撞时间和过程的方法和实例[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2017, 47(6):657-673. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201706002 周斌, 韩奎, 乔新星, 等.西藏日多地区古近纪双峰式脉岩年代学、地球化学及其揭示的伸展背景[J].矿产勘查, 2018, 9(9):1753-1754. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytgcj201809014 张显廷, 周光弟, 杨延兴. 1: 20万下巴淌(沃卡)幅区域地质调查报告.青海地矿局区调队, 1994.



 下载:
下载: