Geochemical characteristics and zircon U-Pb ages of porphyroclastic lava in the Bayaerhushuo area, the south-central segment of Great Xing'an Range, and its geological significance
-
摘要:
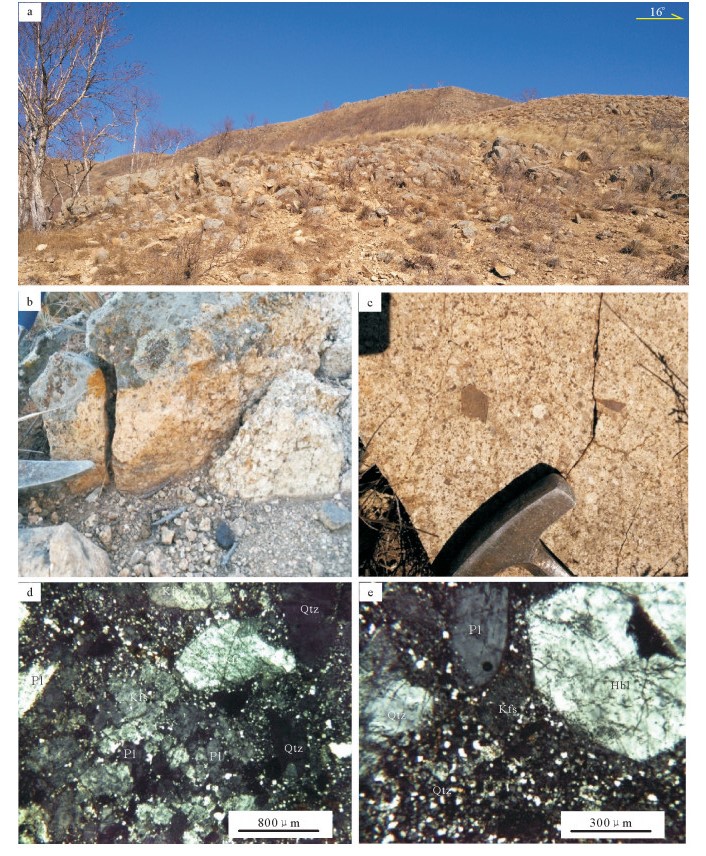
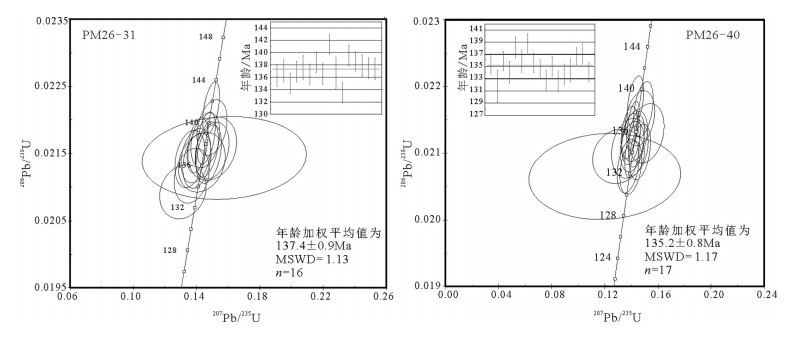
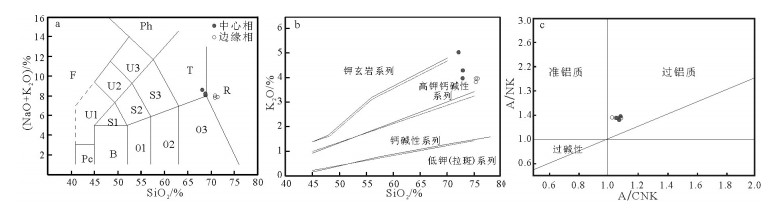
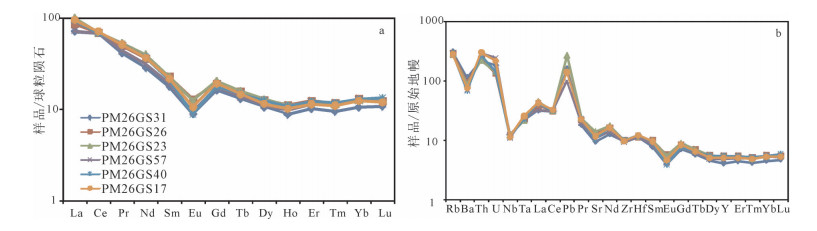
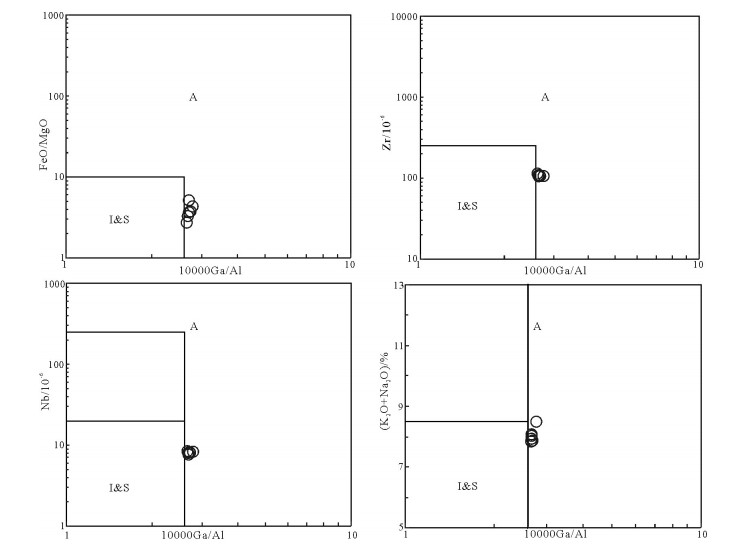
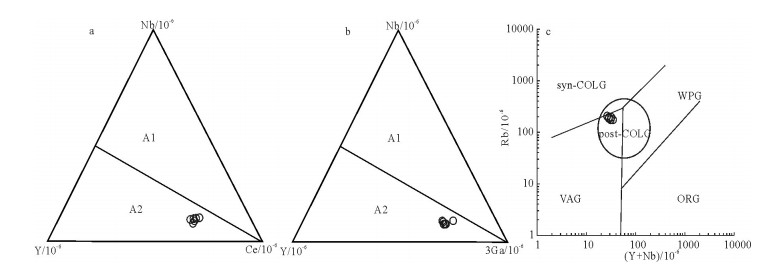
在大兴安岭中南段巴雅尔吐胡硕地区发现一套碎斑熔岩。根据野外调查,可分为中心相的细微粒斑状石英二长岩(-石英二长斑岩)和边缘相的英安流纹质碎斑熔岩。通过SHRIMP锆石U-Pb测年,获得细微粒斑状石英二长岩的年龄加权平均值为137.4±0.9Ma(MSWD=1.13),英安流纹质碎斑熔岩的年龄加权平均值为135.2±0.8Ma(MSWD=1.17),二者的形成时代均属于早白垩世早期。由元素地球化学分析可知,6件样品均属于过铝质的高钾钙碱性A型花岗岩,且具有完全一致的微量元素蛛网图和稀土元素配分曲线,均具有明显的负Eu异常,均富集大离子亲石元素Rb、Pb和轻稀土元素,亏损高场强元素Nb,Th较富集,Ba、Sr、Eu具有一定亏损,Pb强烈富集,表明岩石来源于地壳部分熔融。在构造环境判别分析的基础上,提出研究区碎斑熔岩属于碰撞后或造山期后的张性构造环境花岗岩(A2型花岗岩),形成于拉张环境,代表了伸展的大地构造背景。结合大兴安岭地区的大地构造演化特征,其形成与蒙古-鄂霍茨克闭合造山后的岩石圈伸展作用有关。
Abstract:The porphyroclastic lava is located in the Bayaerhushuo area, the south-central segment of Great Xing'an Range, which can be divided into two parts, the central facies of fine-grained quartz monzonites (-quartz monzonitic porphyry) and the margin facies of dacitic rhyolitic porphyroclastic lava. Based on the SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating, the porphyry monzonitic granite and dacitic ryholititic porphyroclastic lava samples yielded U-Pb ages of 137.4±0.9Ma (MSWD=1.13) and 135.2±0.8Ma (MSWD=1.17) respectively, indicating that the porphyroclastic lava samples in the study area were formed during the Early Cretaceous. The results of geochemical analyses show that the six samples are all high-K calc-alkaline A-typed granites and have the same characteristics in the trace element spidergrams and REE patterns. The features of evident negative Eu anomaly, enrichment in the LILEs Rb and Pb, LREE and Th, depletion in HFSE Nb, Ba, Sr and Eu, reveal that these samples may originate from the partial melting of crust. By tectonic environment discriminations, the porphyroclastic lava are plotted into the A2-typed granite, revealling the post-collisional extension environment. Combined with the Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the Great Xing'an Range, the formation of the Early Cretaceous porphyroclastic lava should be related to the lithospheric extensional envrinment caused by the closure of MongoliaOkhotsk ocean.
-
致谢: 成文过程中得到中国地质调查局沈阳地质调查中心宋维民高级工程师和辽宁省地质矿产研究院有限责任公司关文彬工程师的帮助,审稿专家提出了详细的修改意见,在此一并致谢。
-
图 1 研究区大地构造位置(a,据参考文献[9]修改)和地质简图(b)
Qheol—第四系风积物;Qhapl—第四系冲洪积物;Qhspl—第四系坡洪积物;J3m—上侏罗统满克头鄂博组;K1b—下白垩统白音高老组;K1ml—下白垩统梅勒图组;ηοπK1b—白音高老期细微粒斑状石英二长岩(-石英二长斑岩);λπK1b—白音高老期英安流纹质碎斑熔岩;λK1b—白音高老期潜流纹岩;ηγK1—早白垩世细微粒斑状二长花岗岩;γπK1—早白垩世花岗斑岩;δμ—闪长玢岩脉;测年样品位置如图所示。F1—蒙古-鄂霍茨克缝合带;F2—得尔布干断裂带;F3—贺根山缝合带;F4—佳木斯-伊通断裂;F5—敦化-密山断裂
Figure 1. The tectonic location (a) and geological sketch map (b) of the study area
图 5 碎斑熔岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分模式(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)
(球粒陨石和原始地幔标准化数据据参考文献[16])
Figure 5. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns(a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element patterns(b) of the porphyroclastic lava
表 1 碎斑熔岩SHRIMP锆石U-Th-Pb测年数据分析结果
Table 1 SHRIMIP zircon U-Th-Pb data for the porphyroclastic lava
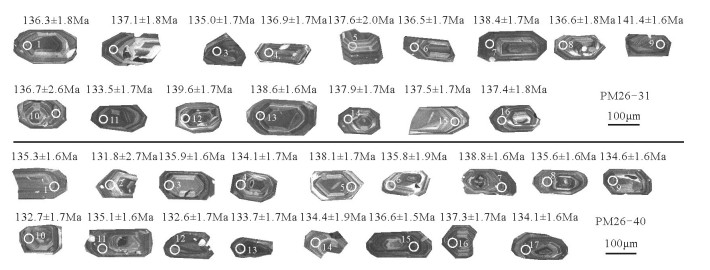
点号 元素含量 232Th/238U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma 206Pbc/% U/10-6 Th/10-6 206Pb*/10-6 207Pb*/206Pb* 1σ 207Pb*/235U 1σ 206Pb*/238U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 细微粒斑状石英二长岩PM26-31 1 0.47 493 134 9.09 0.28 0.0487 6.7 0.1433 6.8 0.0214 1.4 136.3 1.8 2 0 467 149 8.61 0.33 0.0498 3.3 0.1477 3.6 0.0215 1.3 137.1 1.8 3 0.42 746 303 13.6 0.42 0.0469 5.2 0.1369 5.4 0.0212 1.3 135 1.7 4 0.36 711 274 13.2 0.4 0.0471 4.3 0.1395 4.4 0.0215 1.2 136.9 1.7 5 0.3 326 118 6.06 0.37 0.0504 6.7 0.15 6.8 0.0216 1.4 137.6 2.0 6 0.49 612 184 11.3 0.31 0.0475 4 0.1402 4.2 0.0214 1.3 136.5 1.7 7 0.1 710 226 13.3 0.33 0.0487 4 0.1456 4.2 0.0217 1.2 138.4 1.7 8 0.36 457 186 8.44 0.42 0.046 4.4 0.1357 4.6 0.0214 1.3 136.6 1.8 9 0.09 1204 390 23 0.33 0.04881 2 0.1492 2.4 0.0221 1.2 141.4 1.6 10 10.42 518 160 10.7 0.32 0.053 22 0.157 22 0.0214 1.9 136.7 2.6 11 0.73 608 305 11 0.52 0.0455 7.3 0.1313 7.4 0.0209 1.3 133.5 1.7 12 0.23 626 354 11.8 0.58 0.0496 4 0.1497 4.2 0.0219 1.2 139.6 1.7 13 -- 835 325 15.6 0.4 0.0487 2.3 0.1459 2.6 0.0217 1.2 138.6 1.6 14 0 636 170 11.8 0.28 0.0472 2.8 0.1406 3.1 0.0216 1.3 137.9 1.7 15 0 530 194 9.81 0.38 0.0493 3 0.1466 3.3 0.0216 1.3 137.5 1.7 16 0.26 512 201 9.5 0.41 0.0504 4.5 0.1497 4.7 0.0215 1.3 137.4 1.8 英安流纹质碎斑熔岩PM26-40 1 0.15 935 260 17.1 0.29 0.0478 3.1 0.1398 3.3 0.0212 1.2 135.3 1.6 2 10.15 405 134 8 0.34 0.042 31 0.12 31 0.0207 2.1 131.8 2.7 3 0 672 295 12.3 0.45 0.0471 2.6 0.1384 2.9 0.0213 1.2 135.9 1.6 4 0 399 144 7.2 0.37 0.0505 3.3 0.1463 3.6 0.0210 1.3 134.1 1.7 5 0 478 179 8.89 0.39 0.0499 3 0.149 3.3 0.0217 1.3 138.1 1.7 6 0.11 381 149 6.98 0.4 0.0515 5.7 0.1513 5.8 0.0213 1.4 135.8 1.9 7 0.23 1108 342 20.8 0.32 0.0477 2.6 0.1431 2.8 0.0218 1.2 138.8 1.6 8 0.06 990 454 18.1 0.47 0.0486 4.3 0.1425 4.5 0.0213 1.2 135.6 1.6 9 0.06 1061 359 19.2 0.35 0.0484 4 0.1406 4.2 0.0211 1.2 134.6 1.6 10 0.58 577 189 10.4 0.34 0.048 3.8 0.1376 4 0.0208 1.3 132.7 1.7 11 -- 730 279 13.3 0.4 0.0492 2.5 0.1436 2.8 0.0212 1.2 135.1 1.6 12 0.28 504 109 9.02 0.22 0.0487 3.7 0.1395 3.9 0.0208 1.3 132.6 1.7 13 1.41 853 425 15.6 0.52 0.0451 9.8 0.13 9.9 0.021 1.3 133.7 1.7 14 0.13 360 113 6.53 0.32 0.0478 6.4 0.1388 6.5 0.0211 1.4 134.4 1.9 15 0.15 1631 552 30 0.35 0.04782 1.9 0.1411 2.2 0.0214 1.1 136.6 1.5 16 0.08 732 392 13.5 0.55 0.0494 4.8 0.1465 4.9 0.0215 1.3 137.3 1.7 17 0.13 1107 405 20 0.38 0.0485 2.3 0.1407 2.6 0.0210 1.2 134.1 1.6 注:Pbc和Pb*分别代表普通铅和放射性成因铅 表 2 碎斑熔岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 2 Major, trace and REEs data for volcanic rocks of the porphyroclastic lava in the Bayaerhushuo area, the south-central segment of Great Xing' an Range
元素 细微粒斑状石英二长岩(-石英二长斑岩) 英安流纹质碎斑熔岩 PM26-31 PM26-26 PM26-23 PM26-57 PM26-40 PM26-17 SiO2 68.26 68.91 69.04 71.07 71.02 71.38 TiO2 0.42 0.61 0.48 0.59 0.34 0.43 Al2O3 15.17 15.13 15.27 14.86 14.93 14.76 Fe2O3 1.79 2.4 0.78 1.08 0.92 1.43 FeO 3.26 2.32 3.48 2.36 2 1.76 MnO 0.1 0.04 0.03 0.05 0.05 0.05 MgO 0.74 0.65 1.07 0.48 0.77 0.48 CaO 1.58 1.79 1.72 1.55 2.08 1.82 Na2O 3.52 3.94 4.05 4 4.02 3.92 K2O 5.04 4.21 3.96 3.94 3.81 3.94 P2O5 0.11 0.01 0.12 0.02 0.07 0.02 Li 22.21 26.25 21.53 22.77 16.23 15.26 Be 2.98 3.43 3.51 3.78 4.04 3.85 Sc 4.88 4.89 4.9 3.44 3.44 3.41 Ti 2573.69 2562.46 2564.4 1625.08 1808.61 1675.53 V 19.55 18.24 18.98 12.96 13.33 12.71 Cr 2.66 6.08 2.71 3.78 2.83 3.11 Mn 636.53 206.99 249.42 220.3 265.92 274.95 Co 2.55 2.74 2.97 2.88 3 2.45 Ni 2.31 5.02 6.12 5.68 3.43 3.73 Cu 199.63 41.48 8.36 13.56 8.34 6.97 Zn 110.4 70.29 98.29 49.84 86.93 80.25 Ga 22.16 21.14 20.85 20.84 20.86 20.77 Ge 1.68 1.51 1.55 1.51 1.5 1.56 As 12.57 26.24 7.32 14.81 16.76 6.69 Rb 196.1 188.85 175.62 180.36 187.58 178.01 Sr 200.21 275.98 293.04 226.24 220.23 246.85 Y 18.55 24.64 24.46 22.11 24.85 22.98 Zr 107.84 111.6 112.57 103.66 111.91 108.37 Nb 8.8 8.71 8.75 7.78 8.03 8.08 Mo 1.43 1.43 0.57 1.31 0.34 0.56 Cd 0.16 0.58 0.58 0.2 0.65 0.09 In 0.59 0.13 0.15 0.05 0.05 0.06 Sn 14.31 15.14 17.35 8.83 7.77 7.75 Sb 0.72 0.52 0.44 0.64 1.06 0.53 Cs 3.95 5.22 3.67 3.89 4.13 3.53 Ba 794.05 659.02 615.76 500.36 477.23 532.78 La 22.01 26.33 30.78 22.33 28.66 29.35 Ce 55.23 55.28 55.6 54.87 54.75 57.48 Pr 5.01 6.08 6.46 5.37 6.29 6.23 Nd 17.18 21.72 23.75 18.9 22.29 22.13 P 480.11 43.65 523.75 87.29 305.52 87.29 Sm 3.46 4.46 4.43 3.77 4.13 4.26 Eu 0.66 0.95 0.91 0.69 0.65 0.78 Gd 4.19 5 5.3 4.46 4.57 4.98 Tb 0.62 0.75 0.75 0.65 0.7 0.7 Dy 3.41 4.1 4.13 3.58 4.02 3.73 Ho 0.64 0.81 0.79 0.71 0.78 0.74 Er 2.15 2.62 2.53 2.4 2.55 2.43 Tm 0.31 0.38 0.37 0.37 0.38 0.36 Yb 2.22 2.73 2.66 2.66 2.7 2.61 Lu 0.35 0.4 0.42 0.39 0.43 0.39 Hf 3.46 3.48 3.56 3.46 3.75 3.76 Ta 0.9 0.93 0.89 0.98 0.94 1.05 K 41838.55 34948.47 32873.15 32707.12 31627.95 32707.12 W 3.62 0.91 0.93 1.31 1.34 0.82 Tl 1.68 1.37 1.35 0.98 1.00 0.83 Pb 29.53 28.25 49.92 18.50 28.12 26.01 Bi 0.17 0.58 0.26 0.57 0.84 0.30 Th 18.67 20.28 18.87 24.88 23.08 25.70 U 3.85 2.87 3.04 5.12 3.07 4.59 A/CNK 1.07 1.06 1.09 1.09 1.03 1.05 A/NK 1.35 1.37 1.39 1.37 1.39 1.38 ∑REE 140.87 161.14 168.24 146.70 161.19 162.56 ∑LREE 126.98 144.35 151.29 131.48 145.06 146.62 ∑HREE 13.89 16.79 16.95 15.22 16.13 15.94 ∑LREE/∑HREE 9.14 8.60 8.93 8.64 8.99 9.20 δEu 0.53 0.61 0.57 0.51 0.46 0.52 (La/Yb)N 6.68 6.50 7.80 5.66 7.16 7.58 (Ce/Yb)N 6.44 5.24 5.41 5.34 5.25 5.70 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 -
陶奎元, 黄光昭, 王美星, 等.中国东南部碎斑熔岩基本特征及成因基理的探讨[J].中国地质科学院南京地质矿产研究所所刊, 1985, 6(1):1-19. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=HY000002490483 赖绍聪, 徐海江.内蒙古镶白旗碎斑熔岩长石特征及其岩石学意义[J].矿物学报, 1990, 12(1):26-35. 赵焕利, 韩彦东, 李仰春, 等.大兴安岭北段斯木科流纹质碎斑熔岩特征及成因[J].地质与资源, 2004, 13(4):207-210. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2004.04.003 崔天日, 杨芳林, 司秋亮, 等.大兴安岭中段柴河地区碎斑熔岩的发现及其意义[J].地质与资源, 2012, 21(1):35-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2012.01.006 司秋亮, 崔天日, 王恩德, 等.大兴安岭柴河流纹质碎斑熔岩锆石U-Pb定年及成因探讨[J].东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 35(3):443-446. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3026.2014.03.031 曹光跃, 刘哲, 薛怀民.内蒙古西太仆寺破火山碎斑熔岩与流纹岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄和地球化学特征[J].地质通报, 2018, 37(2/3):397-410. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2018020318&flag=1 周万蓬, 郭福生, 刘林清, 等.中国东南部碎斑熔岩问题再探讨[J].资源调查与环境, 2015, 36(6):98-103. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hsdzykc201502003 谢家莹, 陶奎元, 谢芳贵, 等.熔离熔结凝灰岩及其成因[J].中国地质科学院南京地质矿产研究所所刊, 1986, 7(4):76-87. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=HY000001799999 徐久磊, 郑常青, 施璐, 等.大兴安岭北段雅尔根楚Ⅰ型花岗岩年代学、岩石地球化学及其地球动力学意义[J].地质学报, 2013, 87(9):1311-1321. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201309009 宋彪, 张玉海, 万渝生, 等.锆石SHRIMP样品靶制作、年龄测定及有关现象讨论[J].地质评论, 2002, 48(S1):26-30. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/OA000005931 Ludwig K R. User's Manual for Isoplot 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronolog-ical Center Special Publication, 2003.
Le Maitre R W. A classification of igneous rocks and glossary of terms[M]. Blackwell, Oxford, 1989: 193.
Peccerillo R, Taylor S R. Geochemistry of eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey[J]. Con-trib. Mineral Petrol., 1976, 58:63-81. doi: 10.1007/BF00384745
Middlemost E A K. Magmas and Magmatic Rocks[M]. London:Longman, 1985:1-266.
Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5):635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
Sun S S, McDongough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oce-anic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in Ocean Basins. Geological Society of Special Publication, London, 1989, 42: 313-345.
Whalen J B, Currie K L, Chappell B W. A-type granites:geo-chemical characteristics, discriminatuon and petrogenesis[J]. Contri-butions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95:407-419. doi: 10.1007/BF00402202
Turner S, Sandiford M, Foden J. Some geodynamic and composi-tional constraints on "postorogenic" magmatism[J]. Geology, 1992, 20(10):931-934. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0931:SGACCO>2.3.CO;2
Yang J H, Wu F Y, Chung S L, et al. A hybrid origin for the Qian-shan A-type granite, northeast China:geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic evidence[J]. Lithos, 2006, 89(1):89-106.
Hofmann A W.Chemical differentiation of the Earth:the relation-ship between mantle, continental crust, and oceanic crust[J]. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1988, 90:297-314. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(88)90132-X
Taylor S R, McLennan S M. The continental crust:Its composi-tion and evolution[M]. Oxford:Blackwell, 1985.
Wedepohl K H. The composition of the continental crust[J]. Geo-chimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(7):1217-1232. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00038-2
高山, 骆庭川, 张本仁, 等.中国东部地壳的结构和组成[J].中国科学(D辑), 1999, 29(3):204-213. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd199903002 Creaser R A, Price R C, Wormald R J. A-type granites revisited:assessment of a residual-source model[J]. Geology, 1991, 19(2):163-166. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1991)019<0163:ATGRAO>2.3.CO;2
Litvinovsky B A, Steele I M, Wickham S M. Silicic magma forma-tion in Overthickened Crust:melting of Charnockite and Leuco-granite at 15, 20 and 25 kbar[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2000, 41(5):717-737. doi: 10.1093/petrology/41.5.717
Skjerlie K P, Johnston A D. Fluid-absent melting behavior of an F-rich tonalitic gneiss at mid-crustal pressures:implications for the generation of anorogenic granites[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1993, 34(4):785-815. doi: 10.1093/petrology/34.4.785
Douce A E P. Generation of metaluminous A-type granites by low-pressure melting of calc-alkaline granitoids[J]. Geology, 1997, 25(8):743-746. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0743:GOMATG>2.3.CO;2
King P L, White A J R, Chappell B W, et al. Characterization and origin of aluminous A-type granites from the Lachlan Fold Belt, southeastern Australia[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1997, 38(3):371-391. doi: 10.1093/petroj/38.3.371
隋振民, 陈跃民.大兴安岭东部花岗岩类锆石饱和温度及其地质意义[J].世界地质, 2011, 30(2):162-172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2011.02.003 Shao J A, Zang S X, Mou B L, et al.Extensional tectonics and asthe-nospheric upwelling in the orogenic belt:a case study from Hing-gan-Mongolia Orogenic belt[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1994, 39:533-537. doi: 10.1360/csb1994-39-6-533
邵济安, 张履桥, 牟保磊.大兴安岭中南段中生代的构造热演化[J].中国科学(D辑), 1998, 28(3):193-200. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9267.1998.03.003 邵济安, 张履桥, 牟保磊.大兴安岭中生代伸展造山过程中的岩浆作用[J].地学前缘, 1999, 6(4):339-346. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1999.04.017 邵济安, 张履桥, 贾文, 等.内蒙古喀喇沁变质核杂岩及其隆升机制探讨[J].岩石学报, 2001, 17(2):283-290. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200102013 林强, 葛文春, 孙德有, 等.中国东北地区中生代火山岩的大地构造意义[J].地质科学, 1998, 33(2):129-139. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800069875 林强, 葛文春, 曹林, 等.大兴安岭中生代双峰式火山岩的地球化学特征[J].地球化学, 2003, 32(3):208-222. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2003.03.002 Fan W M, Guo F, Wang Y J, et al. Late Mesozoic Calc-alkaline Volcanism of Post-orogenic Extension in the Northern Da Hing-ganMountains, Northeastern China[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2003, 121(1):115-135.
Zhang J H, Ge W C, Wu F Y, et al. Large-scale Early Cretaceous volcanic events in the northern Great Xing'an Range, northeastern China[J]. Lithos, 2008, 102(1):138-157.]38[Zhang J H, Gao S, Ge W C, et al. Geochronology of the Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the Great Xing'an Range, northeastern China:Implications for subduction-induced delamination[J]. Chemical Geology, 2010, 276(3):144-165. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=d14ba8be8a38a9512101ffec46cee93d
Liu J L, Davis G A, Lin Z Y, et al. The Liaonan metamorphic core complex, Southeastern Liaoning Province, North China:a likely contribution to Cretaceous rotation of Eastern Liaoning, Korea and contiguous areas[J]. Tectonophysics, 2005, 407:65-80. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2005.07.001
Liu J L, Guan H M, Ji M, et al. Late Mesozoic metamorphic core complexes:new constraints on lithosphere thinning in North China[J]. Prog. Nat. Sci., 2006, 16(6):633-638. doi: 10.1080/10020070612330045
刘俊来, Davis G A, 纪沫, 等.地壳的拆离作用与华北克拉通破坏:晚中生代伸展构造约束[J].地学前缘, 2008, 15(3):72-81. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2008.03.005 刘俊来, 纪沫, 申亮, 等.辽东半岛早白垩世伸展构造组合、形成时代及区域构造内涵[J].中国科学(D辑), 2011, 41(5):618-637. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201105003 关会梅, 刘俊来, 纪沫, 等.辽宁南部万福变质核杂岩的发现及其区域构造意义[J].地学前缘, 2008, 15(3):199-208. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2008.03.016 纪沫, 刘俊来, 胡玲, 等.辽南变质核杂岩饮马湾山和赵房岩体锆石SHRIMPU-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].地质学报, 2009, 25(1):173-181. 林伟, 王清晨, 王军, 等.辽东半岛晚中生代伸展构造——华北克拉通破坏的地壳响应[J].中国科学(D辑), 2011, 41(5):638-653. Darby B J, Davis G A, Zhang X H, et al. The newly discovered Waziyu metamorphic core complex, Yiwulü Shan, western Liaon-ing Province, Northwest China[J]. Earth Sci. Front., 2004, 11(3):143-155.
申亮, 刘俊来, 纪沫, 等.辽东半岛大营子拆离断层系及其区域构造意义[J].中国科学(D辑), 2011, 41(4):437-451. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7241306 张旗.中国东部中生代岩浆活动与太平洋板块向西俯冲有关吗?[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2013, 32(1):113-128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2013.01.010 张乐彤, 李世超, 赵庆英, 等.大兴安岭中段白音高老组火山岩的形成时代及地球化学特征[J].世界地质, 2015, 34(1):44-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2015.01.006 许文良, 王枫, 裴福萍, 等.中国东北中生代构造体制与区域成矿背景:来自中生代火山岩组合时空变化的制约[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(2):339-353. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201302001 Maruyama S, Send T. Orogeny and relative plate motions:Example of the Japanese Islands[J]. Tectonophysics, 1986, 127(3/4):305-329.
Kimura G, Takahashi M, Kono M. Mesozoic collision-extrusion tectonics in eastern Asia[J]. Tectonophysics, 1990, 181(1/4):15-23.
孙德有, 苟军, 任云生, 等.满洲里南部玛尼吐组火山岩锆石UPb年龄与地球化学研究[J].岩石学报, 2011, 27(10):3083-3094. Tang J, Xu W L, Wang F, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of Early-Middle Triassic magmatism in the Erguna Massif, NE Chi-na:constraints on the tectonic evolution of the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean[J]. Lithos, 2014, 184/187(1):1-16.
Metelkin D V, Vernikovsky V A, Kazansky A Y, et al. Late Meso-zoic tectonics of central Asia based on paleomagnetic evidence[J]. Gondwana Research, 2010, 18(2):400-419.
Eby G N. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids:Petroge-netic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 1992, 20:641-644. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0641:CSOTAT>2.3.CO;2
Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. Trace element discrimina-tion diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25:956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
Foster H J, Tischendorf G, Trumbull R B. An evaluation of the Rb-(Y+Nb) discrimination diagram to infer tectonic setting of si-licic igneous rocks[J]. Lithos, 1997, 40:261-293. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(97)00032-7
-
期刊类型引用(15)
1. 唐永香,林建旺,李嫄嫄,阮传侠,张雪梅,赵娜,刘志龙,张芬娜,李哲,栾鹏宇,王世豪,刘文杰. 天津滨海地热田北部深部地热资源赋存规律. 华北地质. 2024(01): 77-84 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 汪新伟,郭世炎,高楠安,刘慧盈,王婷灏,魏广仁,雷海飞. 雄安新区牛东断裂带碳酸盐岩热储探测及其对地热勘探的启示. 地质通报. 2023(01): 14-26 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 雷晓东,赵玉,唐显春,王立发,何付兵,关伟,李娟. 基于重磁异常的北京副中心地质构造特征和地热控制作用研究. 地球学报. 2023(01): 79-92 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王卓卓,尉小永,孟杉,杨茜婷,江剑,马静晨,王维逸,郭帅,刘哲,施立志. 北京平谷地区万庄子-镇罗营背斜地热地质条件研究. 城市地质. 2023(02): 169-177 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 肖礼军,杨飞,付宜兴. 武汉西部蔡甸地区中深层地热资源主控因素分析. 岩石矿物学杂志. 2023(05): 757-765 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 于丹丹,徐成华,骆祖江,顾问,周玲玲. 南京汤泉地下热水补给来源与成因模式. 地质通报. 2023(11): 2006-2013 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 李方震,方同明,赵勇,何静,霍雨佳. 北京市浅山区地质资源环境现状及保护对策刍议. 城市地质. 2022(01): 13-20 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 刘庆,林天懿,杨淼,柯柏林,项悦鑫,杨茜婷. 北京地区雾迷山组地热储层微观孔隙结构及孔渗特征. 地质通报. 2022(04): 657-668 .  本站查看
本站查看
9. 雷晓东,李晨,王立发,赵玉,尤志鑫,唐显春,关伟,李娟. 延庆盆地大地热流异常及其构造背景. 地球物理学报. 2022(09): 3405-3418 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 李状,周训,方斌,沈晔,徐艳秋,陈柄桦,王蒙蒙,隋丽嫒. 安徽大别山区温泉的水化学与同位素特征及成因. 地质通报. 2022(09): 1687-1697 .  本站查看
本站查看
11. 卢丽,王喆,邹胜章,樊连杰,林永生,周长松. 四川昭觉县地热温度解析及成因模式. 地质通报. 2021(Z1): 434-441 .  本站查看
本站查看
12. 李文. 北京通州地温场特征及其影响因素. 地质通报. 2021(07): 1189-1194 .  本站查看
本站查看
13. 饶家健,张文涛,刘启蒙. 应力对背斜构造中地热的控制作用研究. 安徽理工大学学报(自然科学版). 2020(03): 46-52 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 刘元晴,周乐,吕琳,李伟,王新峰,邓启军,宋绵,郑一迪,马雪梅. 山东鲁中山区地热地质特征及热水成因. 地质通报. 2020(12): 1908-1918 .  本站查看
本站查看
15. 刘峰,王贵玲,张薇,岳晨,甘浩男,肖则佑,欧小科. 江西宁都县北部大地热流特征及地热资源成因机制. 地质通报. 2020(12): 1883-1890 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(4)




 下载:
下载: