The discovery of Late Silurian quartz diorite in Langshan area of Inner Mongolia and its geological implications
-
摘要:
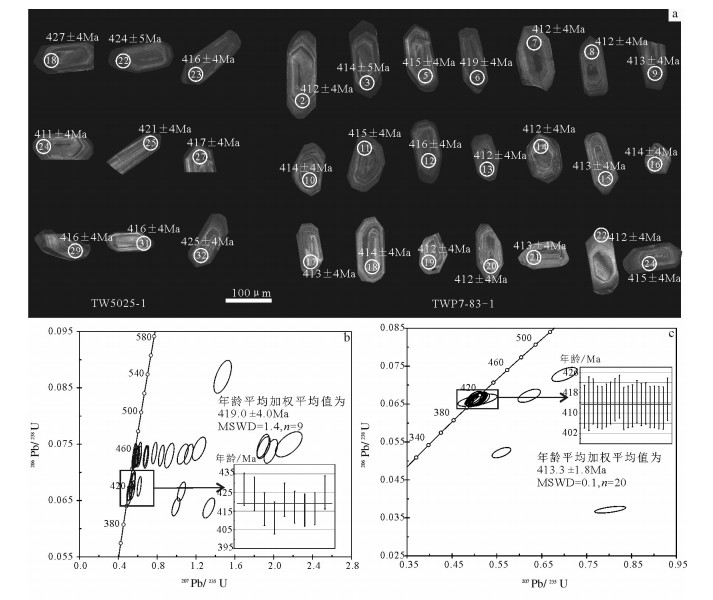
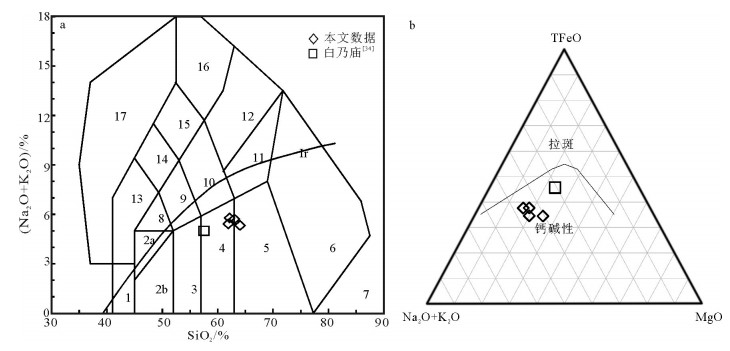
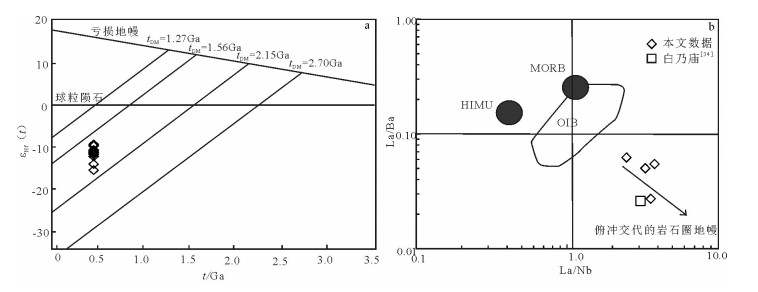
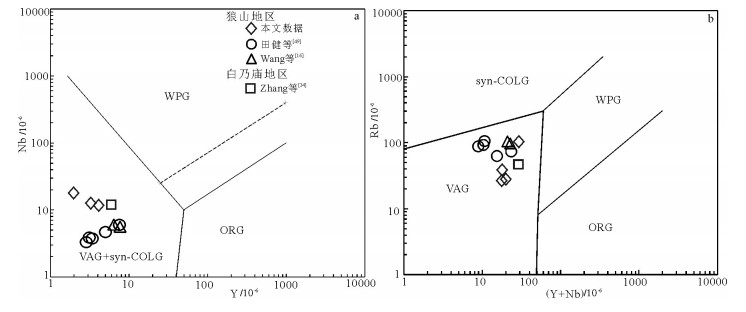
内蒙古狼山山脉西侧分布零星的早古生代岩浆岩,晚志留世石英闪长岩主要出露于哈日音熬瑞一带。该岩体岩性为石英闪长岩,块状构造,LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄显示,其206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值为419.0±4.0~413.3±1.8Ma。岩石暗色矿物为黑云母,富铁(4.27%~4.65%)、富钠(4.17%~4.45%),富集大离子亲石元素Sr、K、Pb,不同程度亏损高场强元素P、Ti、Nb,轻稀土元素富集,重稀土元素亏损,弱负Eu异常,这些特征与弧岩浆岩的地球化学特征相似;La/Ba-La/Nb图解显示俯冲交代地幔的源区特点;岩石负的εHf(t)值(-12.1~-8.8)及较大的TDM2值(1981~2362Ma)反映了古元古代古老地壳熔融的特点。花岗岩类构造判别图解及区域地质资料显示岩体形成于弧陆拼贴的构造背景。对比白乃庙地区新发现的晚志留世弧陆拼贴的石英闪长岩,两者的岩石地球化学特征及同位素特征基本一致,因此,华北地块北缘晚志留世弧陆拼贴作用向西延伸至狼山地区。
Abstract:The Early Paleozoic magmatites are sporadically distributed in the west of Langshan Mountain of Inner Mongolia, whereas the Late Silurian quartz diorite is mainly exposed in the zone of Hariyinaorui. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating shows that the weighted average 206Pb/238U age of quartz diorite is 419.0±4.0~413.3±1.8Ma. The characteristics of quartz diorite mainly exhibit that the biotite is the main dark mineral, which is characterized by enrichment of TFeO (4.27%~4.65%) and Na2O (4.17%~4.45%), enrichment of LILE (Sr, K, Pb), depletion of P, Ti and Nb, enrichment of LREE, and depletion of HREE with weak negative Eu anomaly, similar to the characteristics of arc magmatite. La/Ba-La/Nb determinant diagram shows the characteristics of metasomatic mantle, and isotopic characteristics reflect the characteristics of melting of ancient continental crust which has an obvious negative εHf(t) value (-12.1~-8.8) and older TDM2 value (1981~2362Ma). Tectonic discrimination diagrams and regional geological data show the pluton probably formed the tectonic setting of arc-continent collision. A comparative study of recently published relevant data of Late Silurian quartz diorite in the Bainaimiao area shows that the geochemical characteristics are basically the same, and, therefore, arc-continent collision of Late Silurian extended westward to Langshan area on the northern margin of North China Craton.
-
Keywords:
- Inner Mongolia /
- Langshan area /
- Late Silurian /
- quartz diorite /
- arc-continent collision
-
致谢: 写作过程中,与中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心赵风清研究员、辛后田教授级高级工程师的讨论使笔者受益匪浅,审稿专家提出了宝贵意见及建议,在此一并致谢。
-
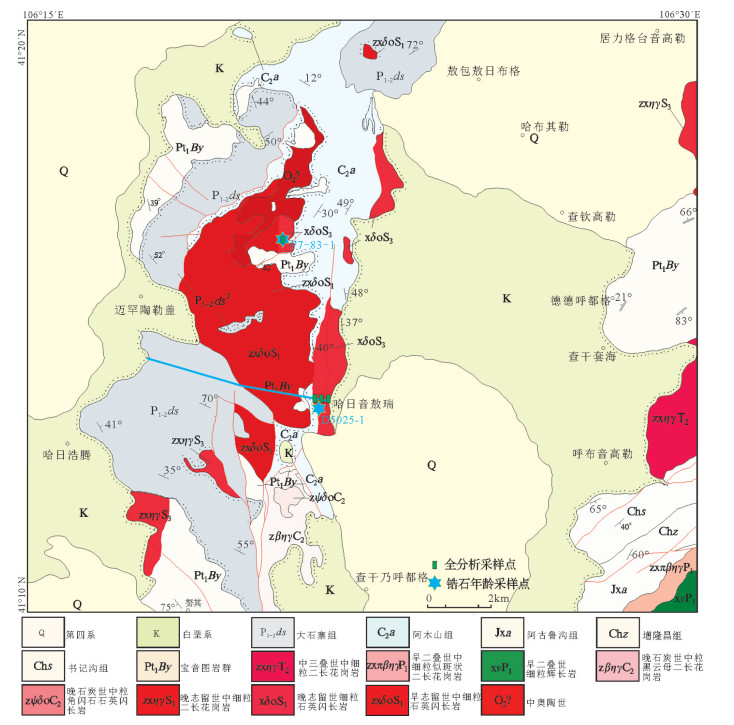
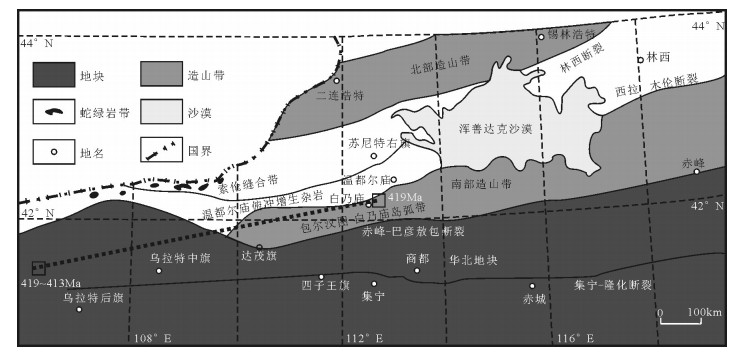
图 1 研究区大地构造位置(a)和地质简图(b)(据参考文献[16]修改)
Figure 1. The tectonic location(a)and simplified geological map(b)of the study area
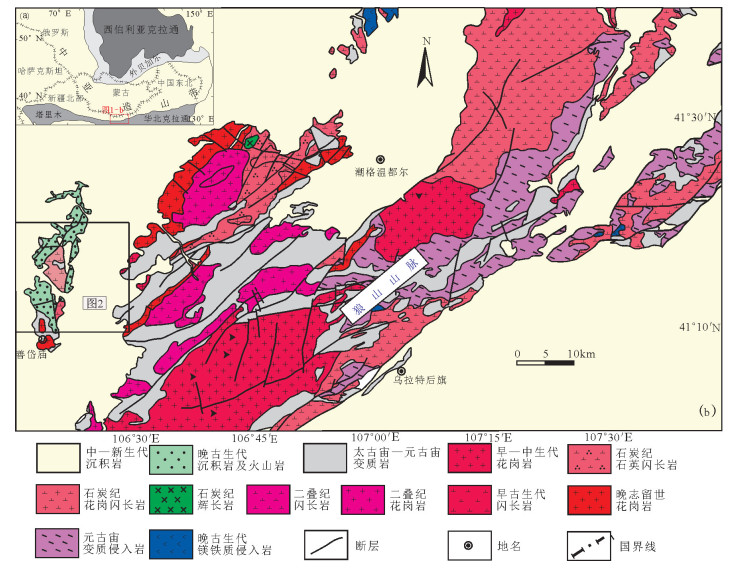
图 2 那仁宝力格幅1:5万地质图①
Figure 2. Geological map of the study area
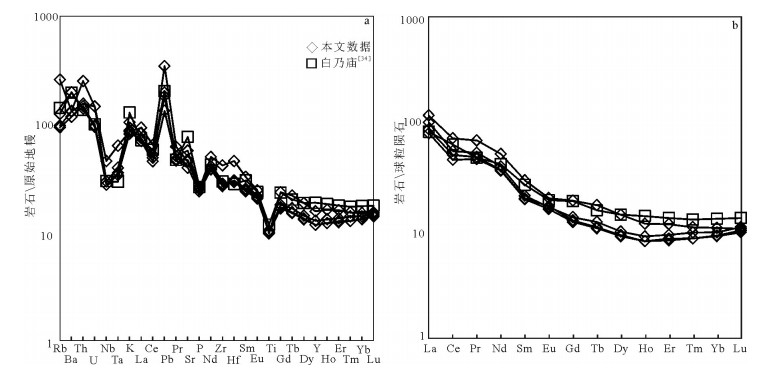
图 6 微量元素蛛网图(a)和稀土元素配分曲线(b)[43]
Figure 6. Primitive mantle-normalized trace element spidergrams(a)and chondrite-normalized REE patterns(b)
图 9 内蒙古地区地质简图(据参考文献[29]修改)
Figure 9. Sketch map of the geology of Inner Mongolia
表 1 石英闪长岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析数据
Table 1 Whole-rock major, trace and rare earth elements of quartz diorite
样品号 P7-83-1 P10-142-1 P10-144-1 P10-146-1 SiO2 64.06 62.13 61.94 62.96 TiO2 0.45 0.47 0.49 0.46 Al2O3 16.26 16.56 16 16.24 Fe2O3 0.07 2.16 2.46 0.28 FeO 4.49 2.71 2.38 4.02 MnO 0.13 0.09 0.11 0.078 MgO 2.21 2 3.32 2.46 CaO 4.38 4.05 3.24 2.91 Na2O 4.17 4.23 4.33 4.45 K2O 1.13 1.47 1.06 1.17 P2O5 0.16 0.16 0.17 0.15 H2O+ 1.98 3.67 4.23 4.39 CO2 2.19 1.88 1.61 2.37 烧失量 0.66 17.17 23.77 19.48 总和 99.49 99.70 99.73 99.57 TFeO 4.55 4.65 4.59 4.27 TFe2O3 4.11 4.60 4.60 3.90 Cs 4.5 0.96 0.87 0.58 Rb 104 28.3 39.3 26.8 Sr 336 461 354 284 Ba 471 462 800 398 Ga 19.6 14.7 15.3 14.4 Nb 11.6 6.5 5.92 5.92 Ta 1.03 0.55 0.45 0.48 Zr 161 95.6 91.3 89.3 Hf 5.03 2.89 2.77 2.81 Th 13.4 7.05 6.13 6.57 V 88.7 98.3 106 123 Cr 16.6 8.6 9.69 9.12 Co 10.1 10.1 9.47 10.3 N1 5.23 4.31 4.73 4.64 Li 18.4 6.25 7.27 7.72 Sc 14.6 12.4 12.9 13.8 U 1.6 1.61 0.9 0.94 Pb 17.1 7.24 8.03 4.81 Zn 88.6 68.7 54.4 57.6 Cu 6.12 16.80 5.06 13.60 La 28.8 24.8 21.3 19.6 Ce 45.5 34.5 31.8 28.6 Pr 6.74 5.17 4.72 4.53 Nd 24.8 18.9 17.6 17.3 Sm 4.6 3.3 3.12 3.06 Eu 1.19 0.98 1 0.94 Gd 4 2.8 2.61 2.52 Tb 0.66 0.46 0.41 0.4 Dy 3.64 2.54 2.35 2.29 Ho 0.67 0.51 0.46 0.46 Er 1.94 1.54 1.42 1.37 Tm 0.28 0.25 0.22 0.22 Yb 1.84 1.67 1.56 1.54 Lu 0.27 0.28 0.26 0.25 Y 17.8 13.6 12.1 12.1 ΣREE 142.73 111.30 100.93 95.18 LREE 111.63 87.65 79.54 74.03 HREE 31.10 23.65 21.39 21.15 LREE/HREE 3.59 3.71 3.72 3.50 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 表 2 石英闪长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb定年数据
Table 2 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb data for quartz diorites
样品号 含量/10-6 232Th/238U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Pb U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ TW5025-1 1 89 1201 0.277 0.001 0.0730 0.0008 0.844 0.0121 454 5 621 9 2 65 919 0.141 0.001 0.0729 0.0008 0.680 0.0095 454 5 527 7 3 145 1955 0.217 0.003 0.0734 0.0008 0.772 0.0111 457 5 581 8 4 92 1112 0.305 0.002 0.0742 0.0008 1.23 0.0283 461 5 815 19 5 100 1293 0.474 0.005 0.0727 0.0008 0.689 0.0102 453 5 532 8 6 73 867 0.408 0.006 0.0732 0.0007 1.065 0.0232 456 5 736 16 7 66 933 0.192 0.001 0.0732 0.0008 0.569 0.0083 456 5 458 7 8 40 536 0.343 0.006 0.0728 0.0008 0.597 0.0088 453 5 476 7 9 44 538 0.307 0.001 0.0730 0.0009 0.926 0.0199 454 6 666 14 10 24 306 0.490 0.002 0.0728 0.0008 0.587 0.0125 453 5 469 10 11 45 440 0.244 0.003 0.0870 0.0012 1.47 0.0368 538 7 920 23 12 57 847 0.063 0.001 0.0723 0.0007 0.560 0.0082 450 5 451 7 13 129 1271 0.338 0.001 0.0737 0.0009 1.97 0.0284 459 5 1106 16 14 198 1976 0.392 0.004 0.0747 0.0008 1.89 0.0259 464 5 1078 15 15 198 1965 0.331 0.002 0.0744 0.0008 1.90 0.0278 462 5 1080 16 16 28 371 0.384 0.001 0.0728 0.0007 0.615 0.0104 453 5 486 8 17 43 533 0.561 0.002 0.0637 0.0007 1.33 0.0248 398 5 860 16 18 37 528 0.378 0.007 0.0684 0.0007 0.556 0.0085 427 4 449 7 19 221 3211 0.085 0.000 0.0727 0.0007 0.586 0.0079 453 5 468 6 20 101 1433 0.116 0.002 0.0734 0.0008 0.618 0.0086 457 5 488 7 21 42 576 0.357 0.003 0.0723 0.0007 0.562 0.0085 450 4 453 7 22 19 275 0.448 0.002 0.0680 0.0007 0.544 0.0109 424 5 441 9 23 16 233 0.298 0.004 0.0667 0.0007 0.518 0.0124 416 4 424 10 24 16 237 0.402 0.001 0.0659 0.0007 0.514 0.0112 411 4 421 9 25 71 1046 0.259 0.001 0.0675 0.0007 0.616 0.0088 421 4 487 7 26 140 1393 0.328 0.005 0.0750 0.0009 2.16 0.0563 466 6 1167 30 27 18 255 0.489 0.015 0.0668 0.0007 0.544 0.0111 417 4 441 9 28 127 1688 0.218 0.001 0.0666 0.0007 1.05 0.0171 416 4 729 12 29 21 272 0.664 0.009 0.0639 0.0007 0.994 0.0171 399 4 701 12 30 38 443 0.511 0.004 0.0732 0.0007 1.13 0.0186 456 5 766 13 31 15 228 0.383 0.000 0.0667 0.0007 0.523 0.0115 416 4 427 9 32 16 218 0.593 0.001 0.0682 0.0007 0.541 0.0130 425 4 439 11 TWP7—83—1 1 22 295 0.2304 0.0009 0.0728 0.0008 0.701 0.0115 453 5 539 9 2 22 330 0.3291 0.0021 0.0661 0.0007 0.508 0.0081 412 4 417 7 3 27 407 0.3479 0.0029 0.0663 0.0008 0.500 0.0067 414 5 412 6 4 60 1105 0.2189 0.0004 0.0522 0.0006 0.560 0.0085 328 3 452 7 5 31 457 0.3598 0.0027 0.0664 0.0007 0.508 0.0089 415 4 417 7 6 23 317 0.4917 0.0007 0.0672 0.0007 0.622 0.0103 419 4 491 8 7 22 332 0.2979 0.0036 0.0661 0.0007 0.502 0.0093 412 4 413 8 8 21 322 0.3762 0.0018 0.0660 0.0007 0.504 0.0072 412 4 414 6 9 27 405 0.2973 0.0010 0.0662 0.0007 0.514 0.0080 413 4 421 7 10 22 330 0.4002 0.0043 0.0663 0.0007 0.508 0.0073 414 4 417 6 11 29 430 0.3305 0.0008 0.0665 0.0007 0.507 0.0079 415 4 416 6 12 26 387 0.2942 0.0016 0.0667 0.0007 0.501 0.0072 416 4 412 6 13 26 375 0.3984 0.0044 0.0660 0.0007 0.503 0.0081 412 4 414 7 14 26 390 0.3682 0.0030 0.0661 0.0007 0.510 0.0073 412 4 418 6 15 29 440 0.3739 0.0015 0.0661 0.0007 0.505 0.0073 413 4 415 6 16 28 413 0.4278 0.0036 0.0664 0.0007 0.503 0.0070 414 4 414 6 17 17 242 0.5087 0.0016 0.0662 0.0007 0.501 0.0086 413 4 412 7 18 18 258 0.4637 0.0020 0.0663 0.0007 0.504 0.0073 414 4 414 6 19 28 450 0.0628 0.0002 0.0661 0.0006 0.501 0.0079 412 4 412 6 20 23 346 0.4553 0.0022 0.0661 0.0007 0.501 0.0083 413 4 412 7 21 21 311 0.4855 0.0048 0.0660 0.0007 0.507 0.0179 412 4 416 15 22 16 220 0.6473 0.0014 0.0660 0.0007 0.505 0.0065 412 4 415 5 23 164 3480 0.4333 0.0010 0.0371 0.0004 0.803 0.0141 235 2 598 11 24 28 404 0.5038 0.0013 0.0666 0.0007 0.506 0.0072 415 4 416 6 表 3 石英闪长岩锆石Hf同位素数据
Table 3 Zircon Hf isotopic composition of U-Pb data for quartz diorite of Late Silurian
样品号 年龄/Ma 176Lu/177Hf(corr) 2σ l76Hf/l77Hf(corr) 2σ εHf(0) εHf(t) 2σ TDM1/Ma 2σ fLu/Hf TDM2/Ma 1 413 0.0006 0.000003 0.3 0.00001 19.5 - 10.5 0.5 1438 36 -0.98 2063 2 413 0.0006 0.000005 0.3 0.00001 20.0 - 11.1 0.4 1460 34 -0.98 2098 3 413 0.0006 0.000002 0.3 0.00001 19.5 - 10.6 0.5 1442 35 -0.98 2068 4 413 0.0006 0.000006 0.3 0.00001 20.5 - 11.6 0.5 1482 37 -0.98 2131 5 413 0.0006 0.000004 0.3 0.00001 21.0 - 12.1 0.5 1498 41 -0.98 2158 6 413 0.0006 0.000006 0.3 0.00001 18.2 -9.2 0.4 1389 34 -0.98 1982 7 413 0.0006 0.000006 0.3 0.00001 19.6 - 10.7 0.5 1443 39 -0.98 2072 8 413 0.0006 0.000011 0.3 0.00001 20.2 - 11.3 0.5 1469 38 -0.98 2111 9 413 0.0008 0.000005 0.3 0.00001 19.8 - 11.0 0.5 1462 40 -0.98 2091 10 413 0.0006 0.000006 0.3 0.00001 20.4 - 11.5 0.5 1478 38 -0.98 2125 11 413 0.0006 0.000004 0.3 0.00002 22.8 - 13.9 0.5 1569 42 -0.98 2273 12 413 0.0005 0.000004 0.3 0.00002 20.1 - 11.2 0.6 1462 43 -0.98 2103 13 413 0.0004 0.000005 0.3 0.00002 24.3 - 15.3 0.6 1619 43 -0.99 2363 14 413 0.0008 0.000002 0.3 0.00002 18.5 -9.6 0.6 1407 44 -0.98 2004 -
Windley B F, Alexeiev D, Xiao W J, et al. Tectonics models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. J. Geol. Soc., Lond., 2007, 164:31-47. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492006-022
Han B F, He G Q, Wang X C, et al. Late Carboniferous collision between the Tarim and Kazakhstan-Yili terranes in the western segment of the South Tian Shan Orogen, Central Asia, and implications for the Northern Xinjiang, western China[J]. Earth-Sci. Rev., 2011, 109:74-93. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2011.09.001
Xu Z, Han B F, Ren R, et al. Ultramafic-mafic mélange, island arc and post-collisional intrusions in the Mayile Mountain, West Junggar China:implications for Paleozoic intraoceanic subduction-accretion process[J]. Lithos., 2012, 132/133:141-161. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2011.11.016
Xu B, Charvet J, Chen Y, et al. Middle Paleozoic convergent orogenic belts in western Inner Mongolia (China):framework, kinematics, geochronology and implications for tectonic evolution of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Gondwana Res., 2013, 23:1342-1364. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.05.015
Zhang X H, Gao Y L, Wang Z J, et al. Carboniferous appinitic intrusions from the northern North China craton:geochemistry, petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. J. Geol. Soc., Lond., 2012, 169:337-351. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492011-062
Coleman R G. Continental growth of Northwest China[J]. Tectonics, 1989, 8(3):621-635. doi: 10.1029/TC008i003p00621
Windley B F, Allen M B, Zhang C, et al. Paleozoic accretion and Cenozoic redeformation of the Chinese Tien Shan range, Central Asia[J]. Geology, 1990, 18(2):128-131. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1990)018<0128:PAACRO>2.3.CO;2
Allen M B, Windley B F, Zhang C. Palaeozoic collisional tectonics and magmatism of the Chinese Tien Shan, Central Asia[J]. Tectonophysics, 1992, 220(1/4):89-115. doi: 10.1016-0040-1951(93)90225-9/
Allen M B, Engor A M C, Natalin B A. Junggar, Turfan and Alakol basins as Late Permian to Early Triassic extensional structures in a sinistral shear zone in the Altaid orogenic collage, Central Asia[J]. J. Geol. Soc., Lond., 1995, 152(2):32-338. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=d93ec7e7a85de5d3e1296212feefd909
Sengor A M C, Natalin B A, Burtman V S. Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Palaeozoic crustal growth in the Eurasia[J]. Nature, 1993, 364:299-304. doi: 10.1038/364299a0
Gao J, Li M S, Xiao X C, et al. Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the Tianshan orogen, northwestern China[J]. Tectonophysics, 1998, 287(1/4):213-231. doi: 10.1016-S0040-1951(98)80070-X/
Jahn B M, Griffin W L, Windley B F. Continental growth in the Phanerozoic:Evidence from Central Asia[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000, 328(1):vii-x. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/9222271
Xiao W J, Zhang L C, Qin K Z, et al. Paleozoic accretionary and collisional tectonics of the eastern Tianshan (CHINA):Implications for the continental growth of Central Asia[J]. American Journal of Science, 2004, 304(4):370-395. doi: 10.2475/ajs.304.4.370
Xiao W J, Han C, Yuan C, et al. Middle Cambrian to Permian subduction-related accretionary orogenesis of northern Xinjiang, NW China:Implications for the tectonic evolution of Central Asia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2008, 32(2/4):102-117. https://core.ac.uk/display/37905021
Xiao W J, Windley B F, Huang B C, et al. End-Permian to mid-Triassic termination of the accretionary processes of the southern Altaids:implications for the geodynamic evolution, Phanerozoic continental growth, and metallogeny of Central Asia[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2009, 98(6):1189-1217. doi: 10.1007/s00531-008-0407-z
Wang Z Z, Han B F, Feng L X, et al. Geochronology, geochemistry and origins of the Paleozoic-Triassic plutons in the Langshan area, western Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 97:337-351. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.08.005
Zhang S H, Zhao Y, Song B, et al. Carboniferous granitic plutons from the northern margin of the North China block:implications for a late Paleozoic active continental margin[J]. J. Geol. Soc., Lond., 2007, 164:451-463. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492005-190
Zhang S H, ZhaoY, Song B, et al. Contrasting Late Carboniferous and Late Permian-Middle Triassic intrusive suites from the northern margin of the North China craton:geochronology, petrogenesis, and tectonic implications[J]. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull., 2009, 121:181-200.
Zhang S H, Zhao Y, Kröner A, et al. Early Permain plutons from the northern North China Block:constraints on continental arc evolution and convergent margin magmatism related to the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Int. J. Earth Sci., 2009, 98:1441-1467. doi: 10.1007/s00531-008-0368-2
Zhang X H, Wilde S, Zhang H F, et al. Early Permian high-K calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from NW Inner Mongolia, North China:geochemistry, origin and tectonic implications[J]. J. Geol. Soc., Lond., 2011, 168:525-543. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492010-094
Zhang X H, Mao Q, Zhang H F, et al. Mafic and felsic magma interaction during the construction of high-K calc-alkaline plutons within a metacratonic passive margin:the Early Permian Guyang batholith from the northern Northern China Craton[J]. Lithos, 2011, 125:569-591. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2011.03.008
周志广, 张华锋, 刘还林, 等, 内蒙中部四子王旗地区基性侵入岩锆石定年及其意义[J].岩石学报, 2009, 25(6):1519-1528. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200906023 罗红玲, 吴泰然, 赵磊, 华北板块北缘乌梁斯太A型花岗岩体锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及构造意义[J].岩石学报, 2009, (3):515-526. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200903004 吴亚飞, 曾键年, 曹建劲, 等.内蒙古东升庙海西期岩体锆石U-Pb年龄[J].地质科技情报, 2013, 32(6):23-30. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201306004 Feng J Y, Xiao W J, Windley B, et al. Field geology, geochronology and geochemistry of mafic-ultramafic rocks from Alxa, China:implications for Late Permian accretionary tectonics in the southern Altaids[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 78:114-142. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.01.020
刘敦一, 简平, 张旗, 等.内蒙古图林凯蛇绿岩中埃达克岩SHRIMP测年:早古生代洋壳消减的证据[J].地质学报, 2003, 77(3):317-327. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2003.03.004 许立权, 邓晋福, 陈志勇, 等.内蒙古达茂旗北部奥陶纪埃达克岩类的识别及其意义[J].现代地质, 2003, 17(4):428-434. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2003.04.011 许立权, 陶继雄.内蒙古达茂旗北部奥陶纪花岗岩类特征及其构造意义[J].华南地质与矿产, 2003, (1):17-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3701.2003.01.004 Jian P, Liu D, Kröner A, et al. Time scale of an early to mid-Paleozoic orogenic cycle of the long-lived Central Asian Orogenic Belt, Inner Mongolia of China:implications for continental growth[J]. Lithos, 2008, 101:233-259. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2007.07.005
张维, 简平.内蒙古达茂旗北部早古生代花岗岩类SHRIMP U-Pb年代学[J].地质学报, 2008, 82(6):778-787. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.06.007 范宏瑞, 胡芳芳, 杨奎锋.内蒙古白云鄂博地区晚古生代闪长质-花岗质岩石年代学框架及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2009, 25(11):2933-2938. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200911022 李建锋, 张志诚, 韩宝福.内蒙古达茂旗北部闪长岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb、角闪石40Ar/39Ar年代学及其地质意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2010, 29(6):732-740. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2010.06.010 冯丽霞, 张志诚, 韩宝福, 等.内蒙古达茂旗花岗岩类LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2013, 32(11):1737-1748. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2013.11.006 Zhang W, Jian P, Kröner A, et al. Magmatic and metamorphic development of an early to mid-Paleozoic continental margin arc in the southernmost Central Asian Orogenic Belt, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 72:63-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.05.025
Wu T R, He G Q, Zhang C. On Paleozoic tectonics in the Alxa region, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Acta Geol, Sin., 1998, 72:256-263.
李怀坤, 耿建珍, 郝爽, 等.用激光烧灼多接收器等离子体质谱仪(LA-MC-ICPMS)测定锆石U-Pb同位素年龄的研究[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2009, 28(增刊):77. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KWXB2009S1311.htm Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North of mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51:537-571. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egp082
Ludwig K R. Users manual for Isoplot 3.0:A geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Exccel[J]. Berkeley:Berkeley Geochronology Center, California, 2003:1-39.
Griffin W L, Wang X, Jackson S E, et al. Zircon chemistry and magma mixing, SE China:In situ analysis of Hf isotopes, Tonglu and Pingtan igneous complexes[J]. Lithos, 2002, 61:237-269. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(02)00082-8
Wu F Y, Yang Y H, Xie L W, et al. Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons and baddeleyites used in U-Pb geochronology[J]. Chem. Geol., 2006, 234:105-126. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.05.003
Middlemost E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews. 1994, 37(3/4):215-224.
Kuno H. "Differentiation of basaltic magmas"[C]//Hess H, Poldervaart A. Basalts: The Poldervaart treatise on rocks of basaltic composition. New York: Interscience, 1968: 623-688.
Sun S S, Mcdonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1):313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Yang J H, Wu F Y, Shao J A, et al. Constrains on the timing of the Yanshan fold and thrust belt, North China[J]. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2006, 246:336-352. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2006.04.029
Wilson M. Igneous Petrogenesis[M]. London:Unwin Hyman, 1989:1-466.
Saunders A D, Storey M, Kent R W, et al. Consequences of plume-lithosphere interactions[C]//Storey B C, Alabaster T, Pankhurst R J. Magmatism and the Cause of Continental Breakup. Geological Society, Special Publications, London, 1992: 41-60.
Woodhead J D, Hergt J M, Davidson J P, et al. Hafnium isotope evidence for"conservative"element mobility during subduction zone processes[J]. Earth and Planet Science Letters, 2001, 192:331-346. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00453-8
田健, 张永, 滕学建, 等.内蒙古狼山地区晚志留世二云母二长花岗岩体的厘定及其地质意义[J].地质学报, 2019, 93(3):661-673. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201903012 Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rock[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4):956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
邓晋福, 肖庆辉, 苏尚国, 等.火成岩组合与构造环境:讨论[J].高校地质学报, 2007, 11:392-404. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2007.03.009 邓晋福, 刘翠, 冯艳芳, 等.关于火成岩常用图解的正确使用:讨论与建议[J].地质论评, 2015, 61(4):718-734. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlp201504002 李文国, 李庆富, 姜万德, 等.内蒙古自治区岩石地层[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1996. 天津地质调查中心.区域地质矿产调查报告(查干呼舒庙等六幅). 2016.



 下载:
下载: