Big data and future development of geological science
-
摘要:
地质学定量化是地质学自身发展臻于成熟的重要标志。地质学家们经过长期艰难的探索和尝试,扫清了许多障碍并取得了令人瞩目的进展,但并未越过定性描述和不确定性门槛。在人类进入信息化和大数据时代的今天,地质学家们发现并找到了越过定量化之门的捷径。在以大数据和数据密集型计算为基础的第四范式支配下,地质学家有可能突破各种主客观因素的限制,使地质学进入更全面的定量化发展阶段,并取得地质科学原理和规律方面的新发现。换言之,在地质信息学的引领和支撑下,地质学将在新世纪得到快速发展。地质学家需要逐步建立与第四范式相适应的新地质科学观,即以查找和揭示隐藏于大数据中的多种地质要素关联关系为主要目标,然后在此基础上追究成因关系。
Abstract:Quantification of geology is an important indicator of the development of geology itself. After long and hard explorations and attempts, geologists have overcome many obstacles and made remarkable progress, but they have not crossed the threshold of qualitative description and uncertainty. Today, when human beings enter into the era of informatization and big data, geologists have discovered the shortcut to quantification. Under the domination of the Fourth Paradigm which is based on big data and dataintensive computing, all kinds of limitations from both subjective and objective factors may be overcome by geologists. Geological science will be brought into a more comprehensive stage of quantitative development, and new discoveries in principles and laws will be acquired. In other words, guided and supported by geoinformatics, geology will develop rapidly in the 21st Century. Geologists need to gradually establish a new concept of geological science that is compatible with the Fourth Paradigm, that is, to find and reveal the relationship between various geological factors concealed in big data as the primary goal, and then to identify the genetic relationships on such a basis.
-
Keywords:
- quantification /
- informatization /
- big data /
- geological science /
- geological information science /
- geoinformatics
-
-
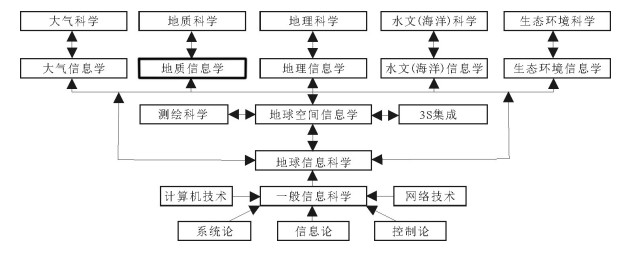
图 1 地质信息科学(地质信息学)的学科地位图解[7]
Figure 1. Illustration of the academic status of geological information science(geoinformatics)
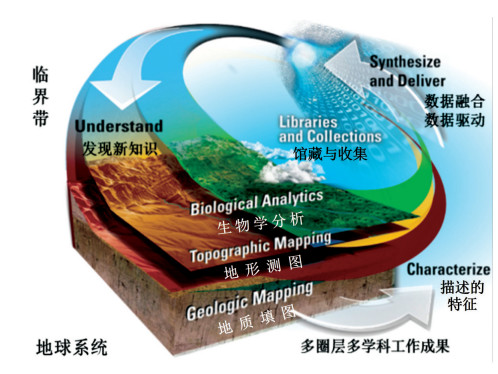
图 2 美国地质调查局基于大数据的核心科学体系[19]
Figure 2. Big data-based core scientific system of the US Geological Survey
表 1 科学研究的4个范式及其特征比较
Table 1 Four paradigms of scientific research and the comparison of their characteristics
序号 范式 属性 方式 方法 参照 目标 认知 结果 第一 经验 描述 定性+定量 综合 概念模型 协调 模糊 功效 第二 理论 演绎 定量 分析 理论模型 因果 清晰 规律 第三 计算 仿真 定量 模拟 数值模型 过程 系统 模式 第四 数据 本体 定量+定性 挖掘 无模型 关联 透明 智能 -
Merriam D F. Roots of quantitative geology[C]//Merriam D F. Down-to-earth statistics: solutions looking for geological problems New York: Syracuse Univ.. Geology Contribution, 1981, (8): 1-15.
赵鹏大, 孟宪国.地质学的定量化问题[J].地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 1992, 17(增刊):51-56. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX1992S1008.htm 吴冲龙, 张洪年, 周江羽.盆地模拟的系统观与方法论[J].地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 1993, 18(6):741-747. Gray J, Szalay A. eScience-A Transformed Scientific Method[C]//Presentation to the Computer Science and Technology Board of the National Research Council, Mountain View, CA, 2007.
Hey T, Tansley S, Tolle K.The fourth paradigm:Data-Intensive Scientific Discovery[M]. Redmond:Microsoft Research, 2009.
吴冲龙, 刘刚, 田宜平.地矿勘查工作信息化的理论与方法问题[J].地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 2005, 30(3):359-365. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2005.03.013 吴冲龙, 刘刚, 田宜平, 等.论地质信息科学[J].地质科技情报, 2005, 24(3):1-8. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkjqb200503001 赵鹏大.数字地质与矿产资源评价[J].地质学刊, 2012, 3:225-228. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2012.03.225 吴冲龙, 刘刚, 田宜平, 等.地质信息科学与技术概论[M].北京:科学出版社, 2014. Mayer-Schonberger V, CuKier K. Big Data:A Revolution That Will Transform How We Live, Work and Think[M]. New York:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company, 2013.
Hey T, Tansley S, Tolle K. Jim Grey on eScience: A transformed scientific method[C]//Hey T, Tansley S, Tolle K. The Fourth Paradigm: Data-Intensive Scientific Discovery. Redmond: Microsoft Research, 2009: xvii-xxxi.
邓仲华李志芳.科学研究范式的演化——大数据时代的科学研究第四范式[J].情报资料工作, 2013, (4):19-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0314.2013.04.004 Anderson C. The End of Theory: The Data Deluge Makes the Scientific Method Obsolete[EB/OL] (2019-03-20)http://www.wired.com/2008/06/pb-theory/.2016.
Norvig P. All we want are the facts, ma'am[EB/OL](2019-03-20) http://norvig.com/fact-check.html). 2009.
李国杰, 程学旗.大数据研究:未来科技及经济社会发展的重大战略领域——大数据的研究现状与科学思考[J].中国科学院院刊, 2012, 27(6):647-657. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3045.2012.06.001 李德仁, 王树良, 李德毅.空间数据挖掘理论与应用(第二版)[M].北京:科学出版社, 2013. Goodchild M, Guo H D, Annoni A, et al. Next-generation Digital Earth[M]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2012: 1-7.
Linda G, Belnap J, Goldhaber M, et al. Geology for a changing world 2010-2020 Implementing the U.S Geological Survey science strategy: U.S. Geological Survey Circular 1369[M]. U.S. Geological Survey, 2011.
Bristol R S, Euliss N H, Booth N L, et al. Science strategy for core science systems in the U.S. Geological Survey, 2013-2023[M]. U.S. Geological Survey, 2012.
吴冲龙, 刘刚, 张夏林, 等.地质科学大数据及其利用的若干问题探讨[J].科学通报, 2016, 61(16):1797-1807. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201616010 Fabbri A G. Quantification and geology:methods of pattern defection and of integrating multi-disciplinary knowledge[J]. Netherlands:Enschede, l990:1.
Watts D J. A twenty-first century science[J]. Nature, 2007, 445(7127):489. doi: 10.1038/445489a



 下载:
下载: