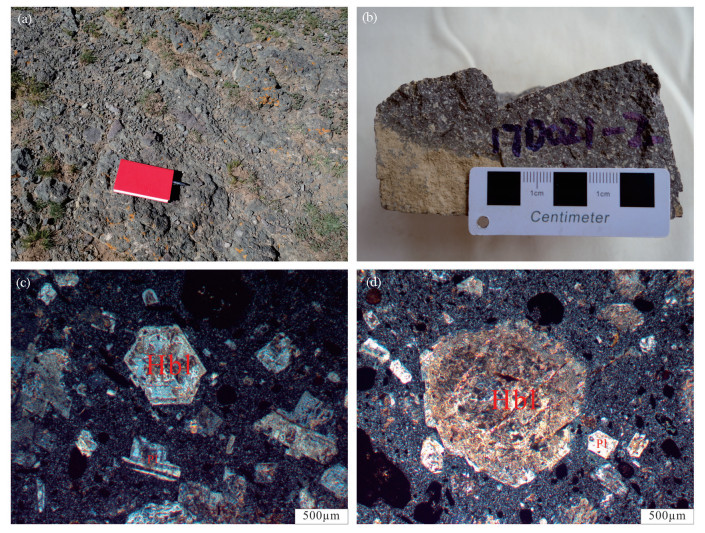
Zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotopic characteristics of Qushenla Formation volcanic rocks in the middle part of the Bangong Co-Nujiang suture, Tibet
-
摘要:
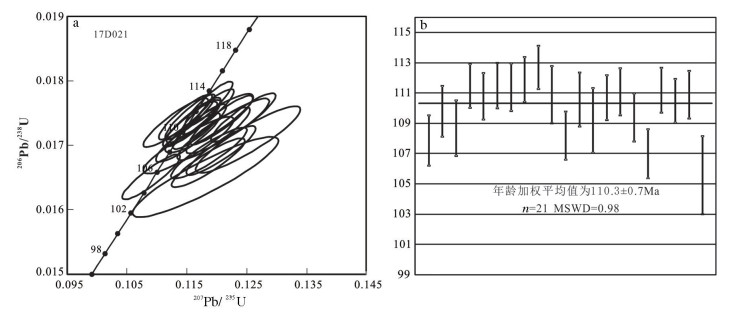
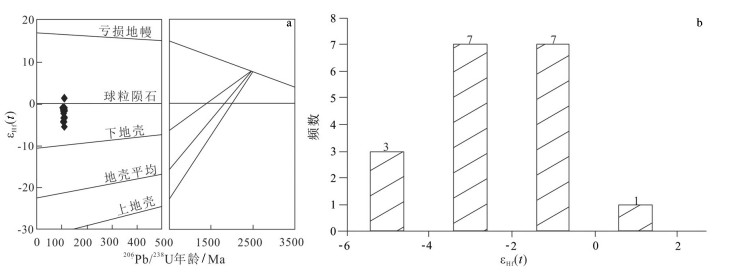
西藏班公湖-怒江缝合带广泛分布中生代岩浆活动,对于认识特提斯洋的演化有重要的启示。班公湖-怒江缝合带中段东卡错微陆块去申拉组安山岩的锆石U-Pb测年和Hf同位素测试结果显示,其中21个测点给出的锆石206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值为110.3±0.7Ma;εHf(t)值为-5.66~1.05,二阶段Hf模式年龄为1020~1448Ma,表现出壳幔混源的特征。综合区域构造沉积演化及前人研究成果,认为东卡错微陆块内发育的去申拉组火山岩很可能与早白垩世班公湖-怒江洋壳南向俯冲消减引起的板片断离有关,并形成于板内伸展环境,其岩浆来源于聂荣微陆块成熟地壳物质发生深熔或重熔作用形成的酸性熔体与古老岩石圈地幔部分熔融产生的基性熔体的混合。
-
关键词:
- LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年 /
- Hf同位素 /
- 岩浆混合 /
- 东卡错微陆块 /
- 班公湖-怒江缝合带
Abstract:Mesozoic magmatic activities are widely distributed in the Bangong Co-Nujiang suture zone in Tibet, and it is important to study them for understanding the evolution of the Tethys Ocean. This paper reports the zircon U-Pb dating and zircon Hf isotope data of the andesites of the Qushenla Formation in the Dongkaco microcontinental block of the middle Bangong Co-Nujiang suture zone. The zircon 206Pb/238U weighted age of the andesites obtained from 21 sites is 110.3±0.7Ma. Zircon Hf isotope analysis shows that the zircon εHf(t) varies in the range of -5.66~1.05, and second stage Hf model ages are 1020~1448Ma, showing the characteristics of crust-mantle mixing. Considering regional tectonic sedimentary evolution and previous research results, the authors hold that the volcanic rocks of the Qushenla Formation were probably related to the slab break-offduring southward subduction of the Bangong Co-Nujiang oceanic crust in the Early Cretaceous, and were produced in an intraplate extensional environment. The magma was derived from the mixing of acidic melt formed by deep melting or remelting of mature crustal material in Nyainrong microcontinent with basic melt formed by partial melting of ancient lithospheric mantle.
-
致谢: 野外工作中得到西藏自治区地质矿产勘查开发局第六地质大队的大力支持,广州市拓岩检测技术有限公司在本文锆石挑选、制靶、拍照工作中给予支持,锆石U-Pb和Lu-Hf同位素分析得到了国家地质实验测试中心李超副研究员的大力支持和耐心指导,审稿专家对本文提出了诸多宝贵意见和建议,在此一并深表衷心的感谢。
-
图 1 研究区大地构造位置(a)及地质简图(b)
a—拉萨地体构造格架及早白世火山岩分布图[2];b—班戈地区地质简图[3]。BNSZ—班公湖-怒江缝合带;SNMZ—狮泉河-纳木错混杂岩带;LMF—洛巴堆-米拉山断层;IYZSZ—印度河-雅鲁藏布江缝合带;1—全新统冲洪积层;2—全新统冲积层;3—第四系全新统;4—上更新统冲洪积层;5—蛇绿岩;6—白垩纪花岗闪长岩;7—白垩纪花岗岩类;8—上白垩统竟柱山组;9—下白垩统去申拉组;10—下白垩统多尼组;11—中-上侏罗统接奴群;12—下-中侏罗统希湖群;13—侏罗系粉砂岩;14—上三叠统曲龙共巴组;15—上三叠统确哈拉群;16—下二叠统下拉组;17—中-上泥盆统查果罗玛组;18—下泥盆统达尔东组;19—下志留统东卡组;20—湖;21—河流;22—采样位置
Figure 1. Geotectonic location map(a) and simplified geological map(b) of the study area
图 7 去申拉组玄武岩Zr-Zr/Y和Ta/Hf-Th/Hf图解(盐湖地区去申拉玄武岩数据据Sui等[35],物玛地区数据据康志强等[37];查格隆地区数据据麦源君等[36],改则地区数据据李伟等[38],达查沟地区数据据吴亮等[34])
WPB—板内玄武岩;MORB—洋中脊玄武岩;IAB—岛弧玄武岩;3种玄武岩分布范围数据见参考文献[40];Ⅱ2—大陆边缘岛弧+大陆边缘火山弧;Ⅳ1—陆内裂谷+大陆边缘裂谷拉斑玄武岩;Ⅳ2—陆内裂谷碱性玄武岩;Ⅳ3—大陆伸展带/初始裂谷玄武岩
Figure 7. Zr-Zr/Y and Ta/Hf-Th/Hf diagrams of basalts in the Qushenla Formation
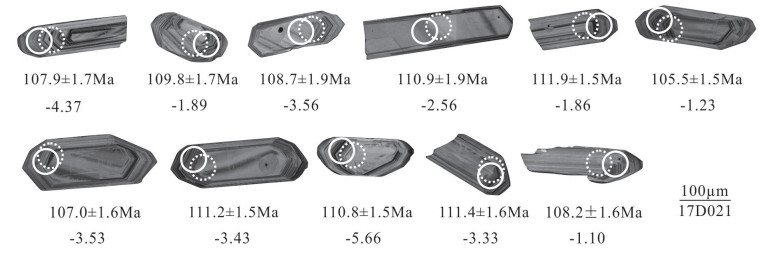
表 1 去申拉组安山岩样品(17D021)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素组成
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircons U-Th-Pb isotope composition from andesites(17D021) in the Qushenla Formation
测点
编号Pb Th U Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma /10-6 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 1 1.78 85.2 230 0.37 0.0488 0.0017 0.1187 0.0041 0.0168 0.0002 142 81 113.9 3.8 107.9 1.7 2 3.10 124 386 0.32 0.0497 0.0016 0.1195 0.0040 0.0171 0.0002 184 77 114.7 3.6 109.8 1.7 4 1.85 112 241 0.47 0.0480 0.0020 0.1153 0.0049 0.017 0.0002 104 99 110.8 4.5 108.7 1.9 5 3.45 153 445 0.34 0.0474 0.0011 0.1155 0.0027 0.0174 0.0002 72 55 111.0 2.5 111.5 1.5 6 3.17 180 408 0.44 0.0477 0.0013 0.1158 0.0032 0.0173 0.0002 87 65 111.3 3.0 110.8 1.5 7 2.79 168 356 0.47 0.0480 0.0012 0.1148 0.0029 0.0174 0.0002 99 60 110.3 2.7 111.5 1.5 8 2.65 127 318 0.40 0.0512 0.0014 0.1244 0.0035 0.0174 0.0002 252 64 119.1 3.2 111.4 1.6 9 3.39 166 417 0.40 0.0496 0.0012 0.1184 0.0029 0.0175 0.0002 178 55 113.7 2.6 111.9 1.5 10 5.26 199 656 0.30 0.0486 0.0010 0.1187 0.0026 0.0176 0.0002 129 50 113.9 2.4 112.7 1.4 11 1.31 62.3 164 0.38 0.0495 0.0020 0.1188 0.0048 0.0173 0.0003 176 93 114.0 4.4 110.9 1.9 12 2.82 142 344 0.41 0.0518 0.0016 0.1207 0.0038 0.0169 0.0002 279 70 115.8 3.5 108.2 1.6 13 1.78 78.7 218 0.36 0.0505 0.0018 0.1218 0.0045 0.0173 0.0002 219 84 116.8 4.1 110.6 1.8 14 0.95 33.6 109 0.31 0.0542 0.0025 0.1252 0.0057 0.0170 0.0003 383 102 119.8 5.2 109.2 2.1 15 2.87 152 366 0.41 0.0484 0.0012 0.1156 0.0029 0.0173 0.0002 122 59 111.1 2.7 110.7 1.5 16 2.42 101 304 0.33 0.0492 0.0014 0.1208 0.0034 0.0173 0.0002 157 65 115.8 3.2 111.1 1.6 17 1.97 106 256 0.41 0.0481 0.0014 0.1152 0.0035 0.0171 0.0002 108 71 110.7 3.2 109.4 1.6 19 2.60 128 333 0.39 0.0501 0.0016 0.1186 0.0040 0.0167 0.0002 203 77 113.8 3.7 107.0 1.6 20 2.95 167 377 0.44 0.0483 0.0012 0.1161 0.0030 0.0173 0.0002 114 59 111.6 2.7 111.2 1.5 21 3.45 178 437 0.41 0.0490 0.0012 0.1171 0.0029 0.0172 0.0002 149 57 112.5 2.7 110.5 1.5 22 3.02 209 400 0.52 0.0467 0.0014 0.1131 0.0035 0.0173 0.0002 34 73 108.9 3.3 110.9 1.6 24 1.66 63.5 203 0.31 0.0531 0.0036 0.1181 0.0080 0.0165 0.0004 333 147 113.4 7.3 105.6 2.6 表 2 去申拉组安山岩样品(17D021)锆石Hf同位素组成
Table 2 Hf isotopic composition of zircons from andesites (17D021) in the Qushenla Formation
测点编号 176Hf/177HfCorr 2σ 176Lu/177Hf 2σ 176Yb/177Hf 2σ εHf(0) εHf(t) tDM1/Ma tDM2/Ma f(Lu/Hf) 1 0.282648 0.000021 0.001459 0.000019 0.036403 0.000556 -4.37 -4.37 865 1366 -0.96 2 0.282719 0.000019 0.000676 0.000014 0.015172 0.000324 -1.89 -1.89 749 1208 -0.98 4 0.282671 0.000018 0.001128 0.000013 0.025349 0.000304 -3.56 -3.56 825 1314 -0.97 5 0.282730 0.000018 0.001134 0.000012 0.026297 0.000291 -1.47 -1.47 742 1181 -0.97 6 0.282612 0.000019 0.001052 0.000011 0.028600 0.000264 -5.66 -5.66 907 1448 -0.97 7 0.282675 0.000017 0.001050 0.000009 0.024113 0.000240 -3.43 -3.43 818 1306 -0.97 8 0.282678 0.000020 0.001322 0.000008 0.031477 0.000223 -3.33 -3.33 820 1299 -0.96 10 0.282719 0.000018 0.001098 0.000006 0.024985 0.000146 -1.86 -1.86 757 1206 -0.97 11 0.282802 0.000018 0.000701 0.000012 0.015777 0.000312 1.05 1.05 633 1020 -0.98 12 0.282700 0.000017 0.001348 0.000034 0.032514 0.000958 -2.56 -2.56 790 1250 -0.96 13 0.282741 0.000018 0.001106 0.000009 0.025384 0.000208 -1.10 -1.10 726 1157 -0.97 14 0.282643 0.000021 0.000891 0.000032 0.022070 0.000808 -4.58 -4.58 860 1379 -0.97 15 0.282669 0.000020 0.001449 0.000027 0.035175 0.000638 -3.66 -3.66 836 1320 -0.96 16 0.282740 0.000018 0.000846 0.000019 0.019199 0.000453 -1.13 -1.13 722 1159 -0.97 17 0.282729 0.000018 0.001000 0.000003 0.022321 0.000095 -1.54 -1.54 742 1185 -0.97 19 0.282737 0.000016 0.001078 0.000003 0.025248 0.000119 -1.23 -1.23 731 1166 -0.97 20 0.282672 0.000019 0.001237 0.000004 0.029806 0.000138 -3.53 -3.53 826 1312 -0.96 21 0.282675 0.000024 0.001004 0.000014 0.023222 0.000334 -3.43 -3.43 817 1306 -0.97 注:同位素校正公式:εHf(t)=104×{[(176Hf/177Hf)S-(176Lu/177Hf)S×(eλt-1)]/[(176Hf/177Hf)CHUR(0)-(176Lu/177Hf)CHUR(t)×(eλt-1)]1},tDM=1/λ×ln{1+ [(176Hf/177Hf)S- (176Hf/177Hf)DM]/[(176Lu/177Hf)S- (176Lu/177Hf)DM]},tDMC=tDM- (tDM- t) × [(fCC- fS)/(fCC- fDM)], fLu/Hf =(176Lu/177Hf)S/ (176Lu/177Hf)CHUR-1, 其中λ=1.867×10-11a-1[23]; (176Lu/177Hf)S和(176Hf/177Hf)S为样品测量值; (176Lu/177Hf)CHUR(t)=0.0332, (176Hf/177Hf)CHUR(0) =0.282772[24]; (176Lu/177Hf)DM=0.0384, (176Hf/177Hf)DM=0.28325, (176Hf/177Hf) 平 均 地 壳 =0.015[25]; fCC=(176Hf/177Hf) 平 均 地 壳/ (176Lu/177Hf)CHUR-1; fS=fLu/Hf ;fDM=(176Lu/177Hf)DM/(176Lu/177Hf)CHUR-1; t为锆石结晶年龄 -
Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, Niu Y L, et al. Cambrian bimodal volcanism in the Lhasa Terrane, southern Tibet:Record of an Early Paleozoic Andean-type magmatic arc in the Australian proto-Tethyan margin[J]. Chemical Geology, 2012, 328:290-308. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.12.024
Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, Niu Y, et al. The Lhasa Terrane:Record of a microcontinent and its histories of drift and growth[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2011, 301:241-255. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2010.11.005
陈国荣, 陈玉禄, 张宽忠, 等.班戈县幅地质调查新成果及主要进展[J].地质通报, 2004, 23(5):520-524. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.05.020 Matte P, Taponnie P, Arnaud N, et al. Tectonics of western Tibet, between the Tarims and the Indus[J]. Earth Planet Sci Lett., 1996, 142(3/4):311-320.
史仁灯.班公湖SSZ型蛇绿岩年龄对班-怒洋时限的制约[J].科学通报, 2007, 52(2):223-227. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2007.02.016 高顺宝, 郑有业, 王进寿, 等.西藏班戈地区侵入岩年代学和地球化学:对班公湖-怒江洋盆演化时限的制约[J].岩石学报, 2011, 27(7):1973-1982. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201107006 Sui Q L, Wang Q, Zhu D C, et al. Compositional diversity of ca. 110 Ma magmatism in the northern Lhasa Terrane, Tibet:Implications for the magmatic origin and crustal growth in a continent-continent collision zone[J]. Lithos, 2013, 168(3):144-159.
朱弟成, 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 等.冈底斯中北部晚侏罗世-早白垩世地球动力学环境:火山岩约束[J].岩石学报, 2006, (3):534-546. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB200603002.htm 朱弟成, 潘桂棠, 王立全, 等.西藏冈底斯带侏罗纪岩浆作用的时空分布及构造环境[J].地质通报, 2008, (4):458-468. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.04.003 Zhu D C, Pan G T, Zhao Z D, et al. Early Cretaceous subductionrelated adakite-like rocks in the Gangdese, South Tibet:Products ofslab melting and subsequent melt-peridotite interaction?[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 34(3):298-309. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.05.003
Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, Niu Y, et al. The origin and pre-Cenozoic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 23(4):1429-1454. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.02.002
Wang Q, Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, et al. Origin of the ca. 90 Ma magnesia-rich volcanic rocks in SE Nyima, central Tibet:Products of lithospheric delamination beneath the Lhasa-Qiangtang collision zone[J]. Lithos, 2014, 198/199(3):24-37. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493714001029
陈玉禄, 何建社, 张宽忠, 等.班公错-怒江结合带中段的构造格局探讨[C]//青藏高原及邻区地质与资源环境学术讨论会论文摘要汇编. 2003. 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 侯增谦, 等.冈底斯造山带的时空结构及演化[J].岩石学报, 2006, (3):521-533. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200603001 中国科学院成都地质矿产研究所.青藏高原及邻区地质图, 1:1500000[M].北京:地质出版社, 1988. 王岚, 杨理勤, 王亚平, 等.锆石LA-ICP-MS原位微区U-Pb定年及微量元素的同时测定[J].地球学报, 2012, 33(5):763-772. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb201205011 Nasdala L, Kronz A, Wirth R, et al. The phenomenon of deficient electron microprobe totals in radiation-damaged and altered zircon[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 2008, 73(6):1637-1650. https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/19719161.pdf
Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Zong K Q, et al. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS[J]. Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(15):1535-1546. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4
Ludwig K R. User's Manual for Isoplot 3.0: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, 2003, 4: 1-71.
侯可军, 李延河, 田有荣. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石微区原位UPb定年技术[J].矿床地质, 2009, 28(4):481-492. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2009.04.010 侯可军, 李延河, 邹天人, 等. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石Hf同位素的分析方法及地质应用[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(10):2595-2604. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.10.025 Hoskin P W O, Black L P. Metamorphic zircon formation by solid-state recrystallization of protolith igneous zircon[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 2010, 18(4):423-439. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=20f7cb4f6d72be021ecb081c5fa74229
Söderlund U, Patchett P J, Vervoort J D, et al. The 176Lu decay constant determined by Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotope systematics of precambrian mafic intrusions[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 219(3/4), 311-324. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c0792ad455eb65fadd619aef64d4bef9
Blichert T J, Albarède F. The Lu-Hf isotope geochemistry of chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1998, 148:24-258. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=3b98f85ed58d4e89bfc4a296554bb9fd&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Griffin W L, Wang X, Jackson S E, et al. Zircon chemistry and magma mixing, SE China:In-situ analysis of Hf isotopes, Tonglu and Pingtan igneous complexes[J]. Lithos, 2002, 61(3):237-269. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=c097aa188f06ce2fa75dc423db446c4e&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
李学森, 程立人.藏北申扎、班戈地区奥陶纪和志留纪的一些头足类化石[J].吉林大学学报(地), 1988, (3):241-248. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD1988-CCDZ198803000.htm 姚建新, 纪占胜, 武桂春, 等.西藏申扎地区德日昂玛-下拉剖面:冈瓦纳和特提斯晚石炭世-早二叠世地层和古生物对比的桥梁[J].地质通报, 2007, 26(1):31-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.01.005 杨桂芝, 王军, 王铁成.西藏班戈西南地区中二叠统下拉组岩性特征及时代讨论[J].吉林地质, 2016, 35(4):11-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2427.2016.04.003 张勇强, 钟康惠, 刘珂辛.西藏确哈拉群、嘎加组中火山岩特征及其构造意义探讨[C]//全国岩石学与地球动力学研讨会. 2013: 545-547. 西藏自治区地质矿产局.西藏自治区区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社, 1993. 李小波, 王保弟, 刘函, 等.西藏达如错地区晚侏罗世高镁安山岩——班公湖-怒江洋壳俯冲消减的证据[J].地质通报, 2015, (2/3):251-261. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2015020302&flag=1 李华亮, 高成, 李正汉, 等.西藏班公湖地区竟柱山组时代及其构造意义[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2016, 40(4):663-673. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201604004 吴浩, 李才, 胡培远, 等.西藏尼玛县塔色普勒地区去申拉组火山岩的发现及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2013, 32(7):1014-1026. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2013.07.007 吴浩, 李才, 胡培远, 等.藏北班公湖-怒江缝合带早白垩世双峰式火山岩的确定及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2014, 33(11):1804-1814. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.11.016 Sui Q L, Wang Q, Zhu D C, et al. Compositional diversity of ca. 110 Ma magmatism in the northern Lhasa Terrane, Tibet:implications for the magmatic origin and crustal growth in a continent-continent collision zone[J]. Lithos, 2013, 168(3):144-159. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493713000273
麦源君, 杨文光, 朱利东, 等.西藏羌塘南缘查格隆去申拉组火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征——对班公湖-怒江洋盆演化时限的制约[J].矿物岩石, 2018, 38(2):70-79. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwys201802009 康志强, 许继峰, 王保弟.拉萨地块北部去申拉组火山岩:班公湖-怒江特提斯洋南向俯冲的产物?[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(10):3106-3116. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201010022 李伟.西藏改则地区去申拉组火山岩地球化学特征及锆石年代学制约[D].中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2012. 朱弟成, 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 等.西藏南部二叠纪和早白垩世构造岩浆作用与特提斯演化:新观点[J].地学前缘, 2009, (2):1-20. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.02.001 陈莉, 徐军, 苏犁.场发射环境扫描电子显微镜上阴极荧光谱仪特点及其在锆石研究中的应用[J].自然科学进展, 2005, 15(11):1403-1408 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2005.11.019 吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 等. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(2):185-220. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200702001 Wu F Y, Yang Y H, Xie L W, et al. Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons and baddeleyites used in U-Pb geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 234(1):105-126. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=24086f166a5d00f31562408bac3ae1f4&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Bolhar R, Weaver S D, Whitehouse M J, et al. Sources and evolution of arc magmas inferred from coupled O and Hf isotope systematics of plutonic zircons from the Cretaceous Separation Point Suite (New Zealand)[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 268(3/4):312-324. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X08000411
Kapp P, Murphy M A, Yin A, et al. Mesozoic and Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Shiquanhe area of western Tibet[J]. Tectonics, 2003, 22(4):1029. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8d3146d937154efa73fb230d976358e6




 下载:
下载: