Carbon and oxygen isotope fractionation of carbonate rocks in the fault zone of Wenchuan earthquake:Implications for the mechanism of fault healing
-
摘要:
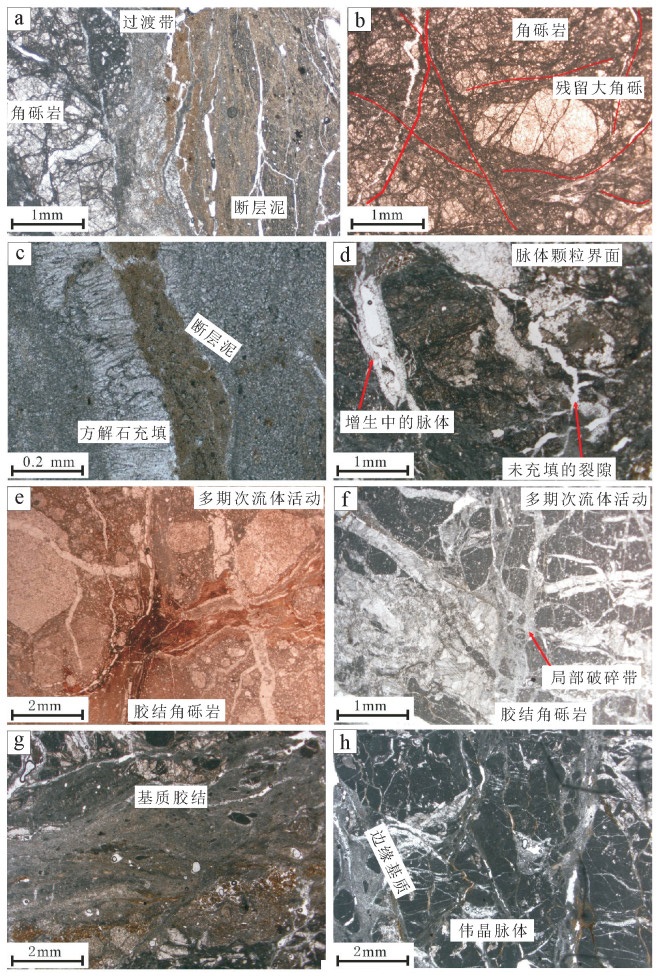
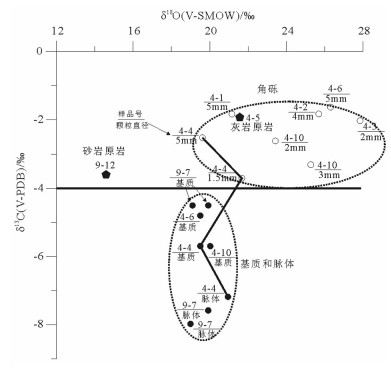
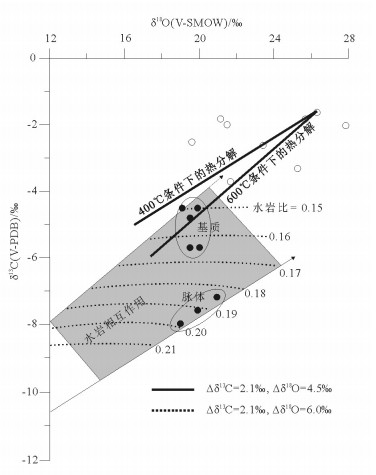
汶川地震断层带北川擂鼓镇赵家沟剖面的露头及显微结构均发现多期次脉体纵横交错,角砾岩被胶结。通过对断层岩相关的碳酸盐矿物同位素分析得知,断层岩角砾和脉体中大量的白云石来源应是断层带内富Mg离子的流体,且碳氧同位素显著分异,角砾的δ18O值和δ13C值与灰岩围岩更接近,脉体和基质显示重同位素亏损。通过“同震热分解”和“水-岩相互作用”2种可能模型的研究分析,同震热分解模型δ13C值明显高于实际,而水-岩相互作用则可形成这种分异结果。故震后深部流体上涌所导致的表层大气水再循环可能是导致震后断层快速愈合的重要原因,同震破裂和间震期愈合则形成完整的断层系统。
Abstract:The outcrop and microscopic structure analysis of Zhaojiagou section at Leigu Town in Beichuan area of Wenchuan earthquake fault zone revealed that multi-phase veins crisscross and the breccia has been cemented.The isotope analysis of carbonate minerals related to fault rocks shows that the source of a large amount of dolomite in the fault breccia and veins should be the Mgrich fluid in the fault zone, and the carbon and oxygen isotopes exhibit significant differentiation.The δ18O and δ13C values of breccia are more close to values of surrounding rocks of limestone, and the veins and matrix exhibit heavy isotope losses. It is found that the δ13C values of the coseismic thermal decomposition model is obviously higher than the real values and the water-rock interaction model can form this differentiation result, as shown by comparison of these two possible models.Therefore, the surface water recirculation caused by the upwelling of deep fluids may be the significant cause of the fault rapid healing after earthquake. The coseismic rupture and inter-seismic healing form a complete fault system.
-
Keywords:
- Wenchuan earthquake /
- fault zone /
- carbonate rock /
- isotope /
- fault healing
-
致谢: 中国地震局地质研究所陈建业博士在研究课题上给予了指导,山西省地质环境监测中心刘瑾高级工程师在论文修改过程中提出了宝贵意见和建议,审稿专家提出宝贵的修改意见,在此一并表示衷心的感谢。
-
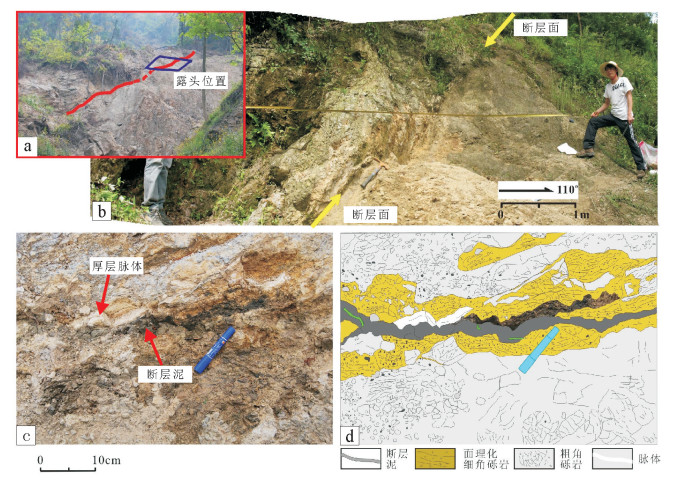
图 1 龙门山断裂带地质简图及工作区位置[12]
Figure 1. Geological sketch map and working area location of the Longmen Mountain fault zone
表 1 北川擂鼓镇赵家沟剖面断层岩成分分析结果
Table 1 Fault rock composition analytical results of Zhaojiagou section at Leigu Town, Beichuan area
岩性 全岩成分 粘土组成(相对含量) 石英 长石 白云石 方解石 粘土 蒙脱 伊利 伊/蒙 绿泥 混层比 上盘灰岩原岩 0.5% 0.5% 98% 1% 96% 4% 上盘粗角砾岩 1% 1% 29% 68% 1% 95% 5% 5 上盘细角砾岩 24% 7% 11% 40% 18% 39% 55% 6% 10 灰色断层泥 29% 2% 27% 7% 35% 3% 83% 14% 36 白色伟晶脉体 6% 1% 37% 51% 5% 3% 30% 55% 12% 10 下盘细角砾岩 6% 62% 24% 8% 19% 73% 8% 33 下盘粗角砾岩 42% 33% 8% 17% 51% 49% 5 下盘砂岩原岩 43% 39% 9% 9% 47% 53% 注:混层比为伊蒙混层中蒙脱石的含量 -
Li Y G, Vidale J E, Day S M, et al. Postseismic fault healing on the rupture zone of the 1999 M 7.1 Hector Mine, California, earthquake[J]. Bulletin seismological Society of America, 2003, 93(2):854-869. doi: 10.1785/0120020131
Kitagawa Y, Fujirmori K, Koizumi N. Temporal change in permeability of the Nojima fault zone by repeated water injection experiments[J]. Tectonophysics, 2007, 443:183-192. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2007.01.012
Xue L, Li H B, Brodsky E E, et al. Continuous permeability measurements record healing inside the Wenchuan Earthquake Fault Zone[J]. Science, 2013, 340(6140):1555-1559. doi: 10.1126/science.1237237
Marone C. Laboratory-derived friction laws and their application to seismic faulting[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1998, 26(1):643-696. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.26.1.643
Wang P L, Wu J J, Yeh E C, et al. Isotopic constraints of vein carbonates on fluid sources and processes associated with the ongoing brittle deformation within the accretionary wedge of Taiwan[J].Terra Nova, 2010, 22(4):251-256. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=854f7997668c4f5ae9b42dc97f3f9dbf
Gratier J P, Richard J, Renard F, et al. Aseismic sliding of active faults by pressure solution creep:Evidence from the San Andreas Fault Observatory at Depth[J]. Geology, 2011, 39(12):1131-1134. doi: 10.1130/G32073.1
Hickman S, Sibson R, Bruhn R. Introduction to special section:Mechanical involvement of fluids in faulting[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 1995, 100(B7):12831-12840. doi: 10.1029/95JB01121
Kanagawa K, Cox S F, Zhang S. Effects of dissolution precipitation processes on the strength and mechanical behavior of quartz gouge at high-temperature hydrothermal conditions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 2000, 105(B5):11115-11126. doi: 10.1029/2000JB900038
Yasuhara H, Marone C, Elsworth D. Fault zone restrengthening and frictional healing:The role of pressure solution[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 2005, 110(6):10-1029. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=d269ce7c8d000ef1de5c0a981eca216d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Chen J Y, Yang X S, Duan Q B, et al. Importance of thermochemical pressurization in the dynamic weakening of the Longmenshan Fault during the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake:Inferences from experiments and modeling[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 2013, 118(8):4145-4169. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=5b9efd121a7b6cf67187d6f75cf274e6&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Yang T, Chen J, Wang H, et al. Rock magnetic properties of fault rocks from the rupture of the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake, China and their implications:Preliminary results from the Zhaojiagou outcrop, Beichuan County (Sichuan)[J]. Tectonophysics, 2012, s530-531(2):331-341. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=995530802a44cb9766d403560db20d23&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
陈建业, 杨晓松, 党嘉祥, 等.汶川地震断层带结构及渗透率[J].地球物理学报, 2011, 54(7):1805-1816. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.07.014 Zhang L, He C. Frictional properties of natural gouges from Longmenshan fault zone ruptured during the Wenchuan Mw7.9 earthquake[J].Tectonophysics, 2013, 594(3):149-164. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c30f4b9099fe9a7eb6055bb2e891ca83
Shieh Y N, Taylor H P. Carbon and hydrogen isotope studies at contact metamorphism in the Santa Rosa Range, Nevada and other areas[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1969, 20(4):306-356. doi: 10.1007/BF00373303
Hirose T, Shimamoto T. Growth of molten zone as a mechanism of slip weakening of simulated faults in gabbro during frictional melting[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Solid Earth, 2005, 110(B5):147-155. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=335e40801f6bdbf507f4443fd3d939c5
Hirono T, Fujimoto K, Yokoyama T, et al. Clay mineral reactions caused by frictional heating during an earthquake:An example from the Taiwan Chelungpu fault[J].Geophysical Research Letters, 2008, 35:L16303. doi: 10.1029/2008GL034476
Han R, Shimamoto T, Hirose T, et al. Ultralow friction of carbonate faults caused by thermal decomposition[J]. Science, 2007, 316(5826):878-881. doi: 10.1126/science.1139763
Hirono T, Ikehara M, Otsuki K, et al. Evidence of frictional melting from disk-shaped black material, discovered within the Taiwan Chelungpu fault system[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2006, 33(19):677-688. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=5f04feed082fcf3282bb46c01e3f46a5
Di Toro G, Han R, Hirose T, et al. Fault lubrication during earthquakes[J]. Nature, 2011, 471(7339):494-498. doi: 10.1038/nature09838
De Paola N, Chiodini G, Hirose T, et al. The geochemical signature caused by earthquake propagation in carbonate-hosted faults[J]. Earth and Planet Science Letters, 2011, 310(3):225-232. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=5eee432a72e8b03251eca6c514621053
Sheppard S M, Schwarcz H P. Fractionation of carbon and oxygen isotopes and magnesium between coexisting metamorphic calcite and dolomite[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1970, 26(3):161-198. doi: 10.1007/BF00373200
Hausegger S, Kurz W, Rabitsch R, et al. Analysis of the internal structure of a carbonate damage zone:Implications for the mechanisms of fault breccia formation and fluid flow[J].Journal of Structural Geology, 2010, 32(9):1349-1362. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2009.04.014
Molli G, Cortecci G, Vaselli L, et al. Fault zone structure and fluidrock interaction of a high angle normal fault in Carrara marble (NW Tuscany, Italy)[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2010, 32(9):1334-1348. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2009.04.021
Kirschner D L, Kennedy L A. Limited syntectonic fluid flow in carbonate-hosted thrust faults of the Front Ranges, Canadian Rockies, inferred from stable isotope data and structures[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 2001, 106(B5):8827-8840. doi: 10.1029/2000JB900414
Pili E, Poitrasson F, Gratier J P. Carbon-oxygen isotope and trace element constraints on how fluids percolate faulted limestones from the San Andreas Fault system:partitioning of fluid sources and pathways[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 190(1/4):231-250. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=f69bad13dc8c266f1b17b1b3c610212c&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Pili E, Kennedy B M, Conrad M. E, et al. Isotopic evidence for the infiltration of mantle and metamorphic CO2-H2O fluids from below in faulted rocks from the San Andreas Fault System[J]. Chemical Geology, 2011, 281(3/4):242-252. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=955ce23cf989db9931f64d5173ecb015
Hellings L, Dehairs F, Tackx M, et al. Origin and fate of organic carbon in the freshwater part of the Scheldt Estuary as traced by stable carbon isotope composition[J]. Biogeochemistry, 1999, 47(2):167-186. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e90391aa418628cb86729b876ba431d6
Ballentine C, O'Nions R K. The use of natural He, Ne and Ar isotopes to study hydrocarbon-related fluid provenance, migration and mass balance in sedimentary basins[J]. Geological Society Special Publication, 1994, 78(1):347-361.
Zheng Y F, Hoefs J. Carbon and oxygen isotopic covariations in hydrothermal calcites[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 1993, 28(2):79-89. doi: 10.1007-BF00196332/
Ohomoto H, Rye R O. Isotopes of sulfur and Carbon, in Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits, edited by H. L. Barnes[M]. New York: Wiley, 1979: 509-567.
O'Neil J R, Clayton R N, Mayeda T K. Oxygen Isotope Fractionation in Divalent Metal Carbonates[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1969, 51(12):5547-5558. doi: 10.1063/1.1671982
Chen J Y, Yang X S, Ma, S L, et al. Mass removal and clay mineral dehy-dration/rehydration in carbonate-rich surface exposures of the 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake fault:geochemical evidence and implications for fault zone evolution and coseismic slip[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 2013, 118(2):474-496. doi: 10.1002/jgrb.50089




 下载:
下载: