Zircon U-Pb ages, geochemical characteristics and petrogenesis of ringed pluton in the Hancaohu area, eastern Tianshan Mountains of Xinjiang
-
摘要:
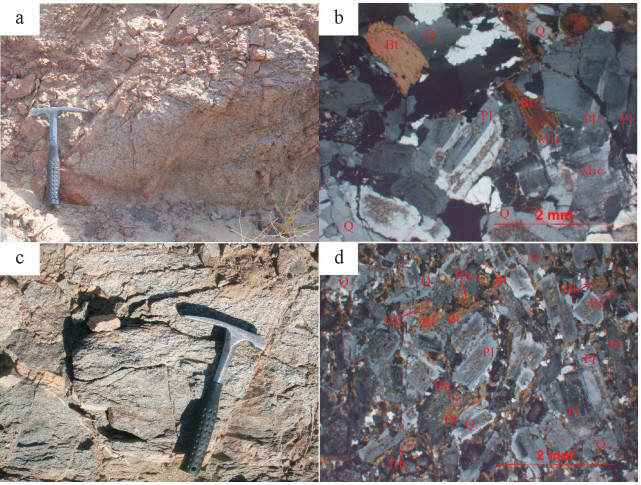
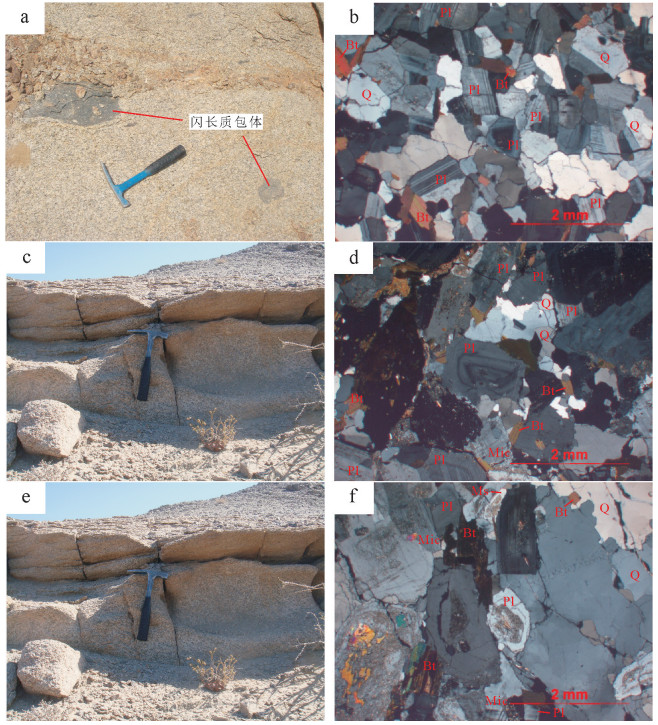
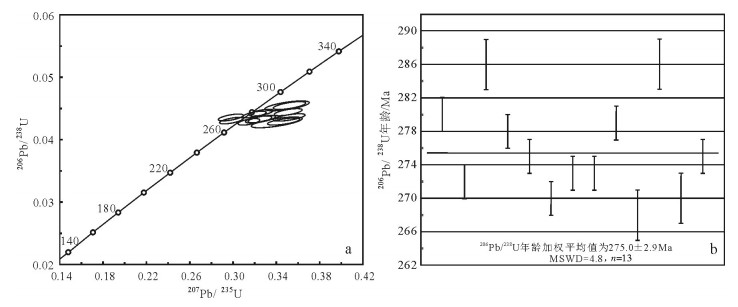
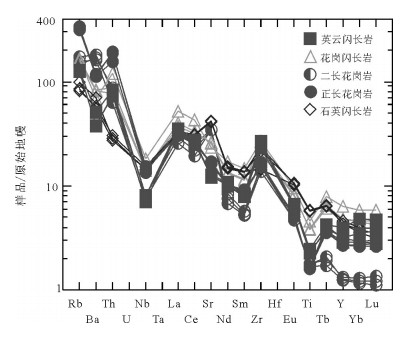
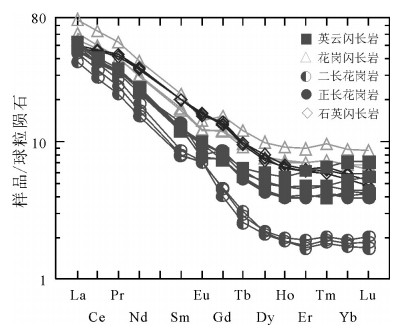
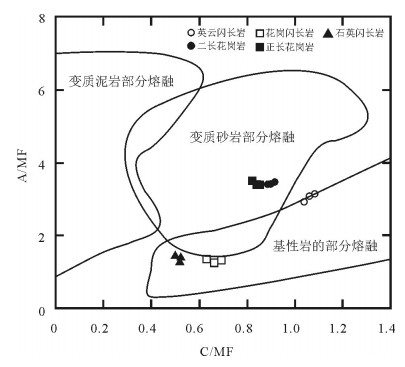
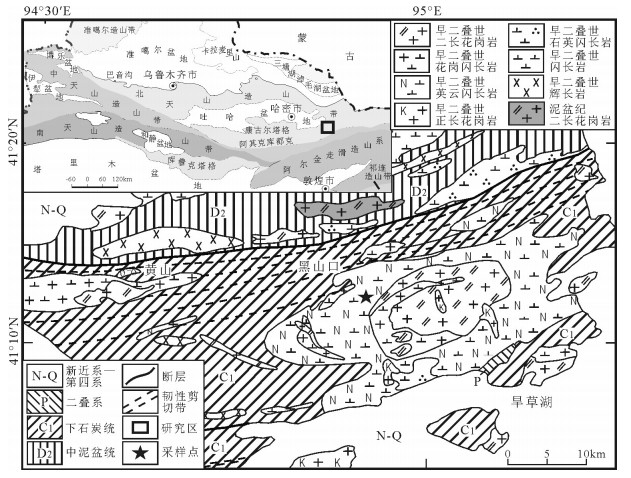
以新疆东天山旱草湖地区中酸性环状岩体为研究对象,进行LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩地球化学研究,探讨其成因和地质意义。结果表明,侵入英云闪长岩的最老年龄为275.0±2.9Ma(MSWD=4.8),侵位时代为二叠纪。岩体Al2O3含量为14.46%~17.05%,A/CNK为0.93~1.09,属准铝质和弱过铝质系列,较富集K2O,MgO含量较低,为0.71%~2.84%,Mg#值为33.3~48.6。微量元素高Sr、低Y,Sr含量为217×10-6~740×10-6,Y含量为4.26×10-6~21.4×10-6,Sr/Y值为16.87~145.07,富集大离子亲石元素Rb、Sr、Ba,亏损高场强元素Nb、Ta、Ti。稀土元素配分模式图呈现平坦右倾的轻稀土元素富集、重稀土元素亏损,表明岩体来源于石榴子石和金红石较稳定而斜长石不稳定的区域,属于角闪岩相向榴辉岩相过渡阶段,可能是同时期底侵的产物。地球化学特征表明岩体不是一期岩浆事件结晶分离演化的结果,不同岩性的岩体之间没有发生结晶分离。部分熔融程度和新生幔源组分的不同导致了旱草湖环状花岗质岩体的形成,二叠纪旱草湖地区存在较强烈的中酸性岩浆活动,是东天山二叠纪构造-岩浆演化的响应。
Abstract:Choosing the Hancaohu intermediate-acid annular pluton distributed in East Tianshan Mountains of Xinjiang as the study object, the authors used LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb isotope chronology and geochemical characteristics to study the petrogenesis and geological significance of the pluton. The results indicate that the age of the earliest intrusive tonalite pluton is 275.0 ±2.9Ma (MSWD=4.8), suggesting that its emplacement epoch is Permian. The Al2O3 of the ringed pluton is 14.46%~17.05%, and A/CNK is 0.93~1.09, suggesting metaluminous and weak peraluminous series. The rocks are enriched in K2O, and their MgO content is 0.71%~2.84% and Mg# value is 33.3~48.6. Their trace elements are high in Sr and low in Y, the content of Sr is 217×10-6~740×10-6, that of Y is 4.26×10-6~21.4×10-6, and Sr/Y ratio is 16.87~145.07. They are enriched in LILEs(Rb, Sr, Ba) and depleted in HFSEs(Nb, Ta, Ti). They are characterized by LREE enrichment and HREE depletion, implying that they were formed in an area with stable garnet, rutile and unstable plagioclase, belonging to the transitional stage from amphibolite facies to eclogite facies; they were probably formed by underplating in the same period. The variation of main elements and race elements content and discontinuous LREE/HREE show that the pluton was not formed by crystallization evolution of one magmatic event, and the plutons of different lithologies are not separately crystallized from each other. Comprehensive analyses show that the lithospheric extension after Permian collision in Huangshan-Jingerquan area caused asthenosphere mantle upwelling and lithosphere delamination. The lithosphere vertical accretion at the boundary of the underplating crust and mantle induced the partial melting and produced high K calc-alkaline magma. With the instant intrusion of the magma, the difference of partial melting and newly formed mantle source components led to the formation of Hancaohu granitic pluton. It is shown that there was violent intermediate-acid magmatism in the Hancaohu area in Permian, and it was the response to tectonic-magmatism evolution in Permian in East Tianshan Mountains.
-
Keywords:
- Xinjiang /
- East Tianshan Mountains /
- Hancaohu /
- intermediate-acid annular pluton /
- zircon U-Pb ages /
- geochemistry
-
致谢: 样品测试工作得到自然资源部岩浆作用成矿与找矿重点实验室郑民奇教授级高工和韩延兵、程秀花、李艳广高级工程师的大力支持;研究过程中得到中国地质调查局西安地质调查中心陈隽璐、贾群子研究员的有益指导;审稿专家提出宝贵的意见,在此一并致谢。
-
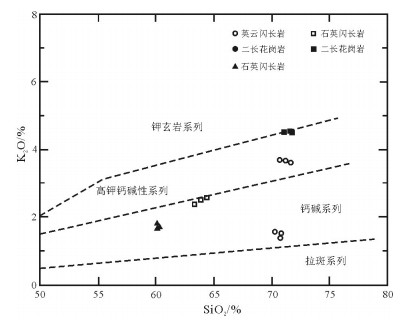
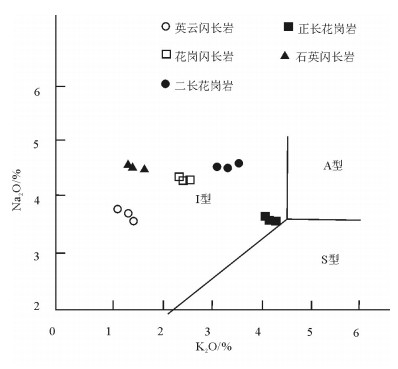
图 4 旱草湖环状岩体SiO2-K2O图解[22]
Figure 4. SiO2-K2O diagram of Hancaohu ringed pluton
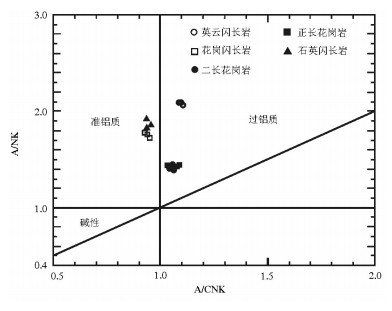
图 5 旱草湖环状岩体A/CNK-A/NK图解[23]
Figure 5. A/CNK-A/NK diagram of Hancaohu ringed pluton
图 6 旱草湖环状岩体K2O-Na2O成因图解[25]
Figure 6. K2O-Na2O origin diagram of Hancaohu ringed pluton
图 8 旱草湖环状岩体球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式图
(标准化值据参考文献[26])
Figure 8. Normalized REE patterns of Hancaohu ringed pluton
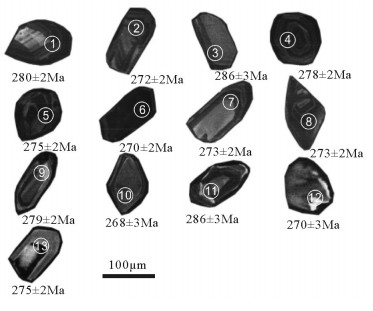
表 1 旱草湖环状岩体英云闪长岩锆石U-Th-Pb定年分析数据
Table 1 Zircon U-Th-Pb analytic results of tonalite in Hancaohu ringed pluton
测定点号 含量/10-6 同位素比值 同位素年龄/Ma 232Th/238U Pb Th 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 208Pb/232Th 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 208Pb/232Th 1σ 1 28.19 7.51 0.05337 0.00132 0.3260 0.0075 0.04432 0.00035 0.01451 0.00025 345 38 287 6 280 2 291 5 0.31 2 25.62 335.37 0.05027 0.00129 0.2983 0.0072 0.04306 0.00034 0.01447 0.00024 207 41 265 6 272 2 290 5 0.37 3 54.73 242.8 0.05589 0.00228 0.3497 0.0137 0.04542 0.00052 0.0162 0.00043 448 67 305 10 286 3 325 9 0.36 4 21.01 149.6 0.05273 0.00127 0.3199 0.0071 0.04405 0.00034 0.01428 0.00027 317 36 282 5 278 2 287 5 0.16 5 24.64 215.82 0.0497 0.00135 0.2980 0.0076 0.04355 0.00036 0.01399 0.00024 181 44 265 6 275 2 281 5 0.33 6 21.98 107.43 0.05332 0.00123 0.3146 0.0067 0.04285 0.00032 0.01342 0.00016 342 34 278 5 270 2 269 3 0.29 7 21.12 141.68 0.05457 0.00163 0.3253 0.0091 0.0433 0.00039 0.01403 0.00028 395 47 286 7 273 2 282 6 0.41 8 14.38 90.15 0.05455 0.00131 0.3248 0.0072 0.04324 0.00034 0.01233 0.00019 394 36 286 6 273 2 248 4 0.38 9 409.11 451.27 0.05504 0.00174 0.3361 0.0102 0.04428 0.00037 0.01382 0.00009 414 72 294 8 279 2 277 2 0.35 10 15.33 25.29 0.05326 0.00282 0.3118 0.0161 0.04246 0.00052 0.0133 0.00012 340 123 276 12 268 3 267 2 0.24 11 28.29 7.76 0.05339 0.00198 0.3335 0.0120 0.04531 0.00041 0.01419 0.0001 345 86 292 9 286 3 285 2 0.39 12 14.75 103.07 0.05595 0.00217 0.3303 0.0124 0.04281 0.00041 0.01333 0.0001 451 88 290 9 270 3 268 2 0.35 13 20.19 149.86 0.05866 0.00174 0.3520 0.0098 0.04357 0.00039 0.00795 0.00024 555 45 306 7 275 2 160 5 0.20 表 2 旱草湖环状岩体主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 2 Major, trace elements and REE analytic data of Hancaohu ringed pluton
样号 YY-01 YY-02 YY-03 HG-01 HG-02 HG-03 EC-01 EC-02 EC-03 ZC-01 ZC-02 ZC-03 SY-01 SY-02 SY-03 岩性 英云闪长岩 花岗闪长岩 二长花岗岩 正长花岗岩 石英闪长岩 SiO2 70.58 71.36 71.59 63.07 64.32 64.06 71.54 70.95 71.80 71.19 71.92 71.54 60.03 60.24 60.17 Al2O3 15.59 15.36 15.28 16.45 16.57 16.48 14.98 15.33 14.87 14.79 14.53 14.46 16.88 16.97 17.05 Fe2O3 0.31 0.38 0.33 1.62 1.46 1.47 0.78 0.81 0.74 0.82 0.85 0.86 2.30 2.17 2.26 FeO 2.60 2.30 2.34 3.00 2.52 2.54 1.00 0.98 0.92 1.00 0.92 1.02 3.34 3.43 3.37 CaO 3.68 3.78 3.66 4.53 4.33 4.36 2.09 2.14 2.17 1.95 2.01 2.09 4.61 4.73 4.72 MgO 0.88 0.75 0.76 2.47 2.10 2.14 0.72 0.71 0.71 0.73 0.72 0.77 2.77 2.80 2.84 K2O 1.38 1.07 1.13 2.26 2.40 2.47 3.30 3.21 3.07 4.28 4.12 4.04 1.76 1.39 1.30 Na2O 3.71 3.79 3.74 4.21 4.16 4.13 4.28 4.51 4.34 3.52 3.54 3.62 4.56 4.60 4.59 TiO2 0.40 0.37 0.36 0.73 0.61 0.62 0.29 0.28 0.27 0.26 0.26 0.27 0.91 0.92 0.93 P2O5 0.11 0.10 0.11 0.24 0.20 0.21 0.096 0.098 0.095 0.08 0.084 0.088 0.38 0.37 0.37 MnO 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.077 0.066 0.067 0.037 0.037 0.037 0.042 0.042 0.045 0.082 0.084 0.084 烧失量 0.70 0.69 0.65 1.22 1.12 1.33 0.84 0.86 0.90 0.96 0.90 1.11 2.24 2.20 2.20 总计 100.00 100.01 100.01 99.877 99.856 99.877 99.953 99.915 99.922 99.622 99.896 99.913 99.862 99.904 99.884 σ 0.93 0.83 0.82 2.08 2.01 2.06 2.01 2.13 1.90 2.15 2.02 2.05 2.34 2.08 2.02 K2O/Na2O 0.37 0.28 0.30 0.54 0.58 0.59 0.77 0.71 0.71 1.21 1.16 1.12 0.39 0.31 0.28 TFeO/MgO 3.27 3.52 3.46 1.80 1.82 1.80 2.36 2.40 2.23 2.38 2.34 2.32 1.95 1.92 1.90 A/CNK 1.09 1.07 1.08 0.93 0.95 0.94 1.03 1.03 1.03 1.05 1.04 1.02 0.94 0.96 0.97 A/NK 2.05 2.07 2.07 1.75 1.75 1.74 1.41 1.40 1.42 1.41 1.410 1.40 1.79 1.87 1.90 Cu 3.57 3.42 5.34 25.10 21.8 21.70 7.87 7.62 7.51 8.72 9.59 8.88 39.70 37.70 33.80 Pb 8.59 6.96 6.41 16.40 17.80 19.50 44.10 28.30 25.20 117.00 36.00 93.40 16.70 9.29 13.10 Zn 52.10 47.30 46.70 73.40 69.60 63.60 50.40 49.20 47.80 40.50 48.10 42.60 99.20 98.70 98.00 Cr 1.65 2.58 1.63 47.90 38.80 40.80 8.53 9.48 7.49 23.50 12.80 10.70 58.80 56.40 60.60 Ni 0.76 1.19 0.89 28.70 24.20 25.70 3.38 3.82 3.34 6.90 6.09 4.40 26.30 26.10 28.20 Co 4.73 4.01 4.15 14.20 14.00 13.70 3.48 3.41 3.96 3.60 4.18 3.41 16.90 21.40 16.40 Li 45.40 37.20 39.90 32.20 26.20 25.90 48.60 45.90 43.60 45.70 45.80 44.20 34.00 36.60 38.90 Rb 70.70 69.50 69.30 90.60 87.20 90.70 95.40 79.40 84.80 184.00 175.00 174.00 55.00 47.20 44.60 Cs 2.96 2.15 2.17 4.31 3.67 3.44 3.79 3.57 3.36 3.86 3.91 4.02 3.19 2.70 2.59 Sr 226.00 223.00 217.00 422.00 468.00 453.00 619.00 615.00 618.00 305.00 290.00 289.00 737.00 724.00 740.00 Ba 260.00 191.00 194.00 348.00 414.00 425.00 912.00 865.00 823.00 597.00 575.00 573.00 356.00 282.00 294.00 V 31.20 27.40 26.30 81.00 66.60 68.20 28.10 28.50 25.30 27.50 27.00 26.30 96.60 97.60 104.00 Sc 7.56 7.53 5.76 10.00 8.48 9.16 3.80 3.17 3.07 3.64 3.36 3.42 11.00 9.70 10.60 Nb 4.49 3.96 3.96 10.10 7.84 7.86 4.48 4.47 4.22 8.49 7.61 7.82 8.07 8.01 8.66 Ta 0.60 0.40 0.42 1.14 0.86 0.87 0.46 0.48 0.43 1.16 0.98 1.04 0.61 0.55 0.59 Zr 220.00 193.00 208.00 220.00 192.00 173.00 128.00 126.00 115.00 126.00 131.00 139.00 118.00 195.00 181.00 Hf 4.72 4.06 4.46 5.41 4.73 4.28 3.56 3.56 3.13 3.92 3.82 4.34 3.35 4.72 4.46 Be 1.51 1.30 1.25 2.20 2.06 2.10 1.51 1.68 1.61 2.63 2.52 2.59 1.48 1.52 1.48 Ga 16.40 15.60 15.70 19.50 19.30 18.70 17.90 18.40 17.60 17.40 16.50 16.60 20.60 20.10 20.80 U 0.98 1.26 1.21 1.86 1.40 1.48 1.41 1.49 1.49 2.56 2.49 2.55 0.70 0.72 0.77 Th 5.30 4.65 4.79 7.68 4.91 5.53 5.06 5.60 4.00 12.00 9.87 12.20 1.83 1.74 1.93 Rb/Sr 0.31 0.31 0.32 0.21 0.19 0.20 0.15 0.13 0.14 0.60 0.60 0.60 0.07 0.07 0.06 Nb/Ta 7.48 9.90 9.43 8.86 9.12 9.03 9.74 9.31 9.81 7.32 7.77 7.52 13.23 14.56 14.68 Sr/Y 16.87 22.97 19.91 19.72 28.54 27.62 138.48 142.36 145.07 28.77 31.45 31.24 49.80 49.25 47.44 La 19.60 18.60 19.00 28.60 20.20 22.30 18.20 16.20 14.00 16.60 19.00 17.20 18.30 17.50 18.30 Ce 39.00 37.50 38.00 61.40 45.80 48.10 36.20 31.90 27.70 35.90 39.20 36.90 44.60 43.60 44.90 Pr 4.60 4.34 4.47 7.30 5.46 5.56 3.90 3.48 3.03 4.36 4.60 4.32 5.89 5.69 5.90 Nd 17.60 16.10 17.10 27.60 21.80 21.30 13.40 12.10 11.00 16.20 16.80 16.10 24.70 23.70 24.20 Sm 2.92 2.72 2.88 5.06 4.04 3.93 1.98 1.84 1.80 3.17 2.90 2.86 4.73 4.67 4.67 Eu 0.87 0.84 0.83 1.24 1.08 1.06 0.62 0.61 0.62 0.70 0.66 0.67 1.34.00 1.37.00 1.40 Gd 2.53 2.20 2.53 4.68 3.62 3.73 1.39 1.41 1.22 2.65 2.29 2.29 4.30 4.02 4.17 Tb 0.37 0.32 0.34 0.69 0.53 0.56 0.17 0.18 0.15 0.36 0.31 0.32 0.57 0.55 0.57 Dy 2.26 1.70 1.94 3.75 2.96 2.91 0.85 0.84 0.8 1.89 1.62 1.61 2.91 2.77 3.06 Ho 0.47 0.34 0.40 0.78 0.62 0.6 0.17 0.16 0.16 0.40 0.34 0.33 0.54 0.55 0.58 Er 1.52 1.03 1.18 2.21 1.74 1.74 0.48 0.44 0.42 1.12 0.96 0.97 1.52 1.51 1.57 Tm 0.23 0.14 0.17 0.34 0.26 0.26 0.072 0.068 0.065 0.17 0.15 0.15 0.21 0.22 0.23 Yb 1.78 1.07 1.30 2.18 1.70 1.68 0.48 0.45 0.43 1.10 0.98 1.00 1.33 1.41 1.47 Lu 0.27 0.16 0.21 0.33 0.26 0.24 0.078 0.07 0.064 0.17 0.15 0.16 0.18 0.20 0.22 Y 13.40 9.71 10.90 21.40 16.40 16.40 4.47 4.32 4.26 10.60 9.22 9.25 14.80 14.70 15.60 ∑REE 94.02 87.06 90.35 146.16 110.07 113.97 77.99 69.748 61.459 84.79 89.96 84.88 111.12 107.76 111.24 LREE/HREE 8.97 11.51 10.20 8.76 8.42 8.73 20.13 18.26 17.58 9.78 12.24 11.43 8.62 8.59 8.37 δEu 0.98 1.05 0.94 0.78 0.86 0.85 1.14 1.16 1.28 0.74 0.78 0.80 0.91 0.97 0.97 Eu/Eu* 0.96 1.02 0.92 0.77 0.85 0.83 1.09 1.12 1.21 0.72 0.76 0.78 0.89 0.94 0.95 (La/Yb)N 7.42 11.72 9.85 8.84 8.01 8.95 25.56 24.27 21.95 10.17 13.07 11.60 9.28 8.37 8.39 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 表 3 旱草湖环状岩体CIPW标准矿物计算结果
Table 3 CIPW normative mineral calculation data of Hancaohu ringed pluton
% 岩性 样品号 Q Or Ab An C Di wo Di en Di fs Hy en Hy fs Mt Il Ap 英云闪长岩 YY-01 33.26 8.22 31.58 17.75 1.53 2.22 3.99 0.45 0.77 0.24 YY-02 34.97 6.37 32.25 18.3 1.3 1.89 3.43 0.55 0.71 0.22 YY-03 35.46 6.73 31.81 17.64 1.48 1.91 3.56 0.48 0.69 0.24 花岗闪长岩 HG-01 16.37 13.55 36.07 19.54 0.76 0.48 0.24 5.78 2.9 2.38 1.41 0.53 HG-02 18.33 14.38 35.61 19.66 0.38 0.24 0.12 5.07 2.45 2.14 1.17 0.44 HG-03 17.99 14.83 35.42 19.37 0.56 0.35 0.17 5.08 2.41 2.16 1.2 0.47 二长花岗岩 EC-01 28.63 19.69 36.5 9.9 0.76 1.82 0.79 1.14 0.56 0.21 EC-02 26.99 19.17 38.48 10.14 0.75 1.79 0.74 1.19 0.54 0.22 EC-03 29.34 18.34 37.04 10.32 0.66 1.79 0.71 1.08 0.52 0.21 正长花岗岩 ZC-01 29.31 25.66 30.15 9.34 0.99 1.85 0.82 1.21 0.5 0.18 ZC-02 30.43 24.62 30.22 9.58 0.76 1.82 0.64 1.24 0.5 0.19 ZC-03 29.63 24.19 30.97 9.98 0.51 1.95 0.81 1.26 0.52 0.19 石英闪长岩 SY-01 12.8 10.66 39.48 20.85 0.13 0.08 0.03 7.01 2.91 3.42 1.77 0.85 SY-02 13.7 8.41 39.79 21.81 0.08 7.16 3.21 3.22 1.79 0.83 SY-03 14.1 7.87 39.71 21.76 0.3 7.27 3.01 3.35 1.81 0.83 注:Q—石英;Or—正长石;Ab—钠长石;An—钙长石;C—刚玉;Di Wo—透辉石中的硅辉石;Di En—透辉石中的顽火辉石;Di Fs—透辉石中的正铁辉石,Hy En—紫苏辉石中的顽火辉石;Hy Fs—紫苏辉石中的正铁辉石;Mt—磁铁矿;Il—钛铁矿;Ap—磷灰石 -
Chen Y J, Chen H Y, Zaw K, et al. Geodynamic settings and tectonic model of skarn gold deposits in China:An overview[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2007, 31(1/4):139-169. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ca5271a66f4f9ac2d6437b6ef9c97bec&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Chen Y J, Pirajno F, Wu G, et al. Epithermal deposits in North Xinjiang, NW China[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2012, 101(4):889-917. doi: 10.1007/s00531-011-0689-4
Huang X W, Qi L, Gao J F, et al. First reliable Re-Os ages of pyrite and stable isotope compositions of Fe(-Cu) deposits in the Hami region, Eastern Tianshan Orogenic Belt, NW China[J]. Resource Geology, 2013, 63(2):166-187. doi: 10.1111/rge.12003
Pirajno F. The Geology and Tectonic Settings of China's Mineral Deposits[M]. Berlin:Springer, 2013:1-671.
Mao J W, Goldfarb R T, Wang Y T, et al. Late Paleozoic base and precious metal deposits, East Tianshan, Xinjiang, China:Characteristics and geodynamic setting[J]. Episodes, 2005, 28(1):23-36. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ027203778/
顾连兴, 张遵忠, 吴昌志, 等.关于东天山花岗岩与陆壳垂向增生的若干认识[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(5):1103-1122. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200605005 Zhang L C, Qin K Z, Xiao W J. Multiple mineralization events in the eastern Tianshan district, NW China:Isotopic geochronology and geological significance[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2008, 32(2/4):236-246.
周涛发, 袁峰, 张达玉, 等.新疆东天山觉罗塔格地区花岗岩类年代学、构造背景及其成矿作用研究[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(2):478-502. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201002012 王银宏, 薛春纪, 刘家军, 等.新疆东天山土屋斑岩铜矿床地球化学、年代学、Lu-Hf同位素及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(11):3383-3399. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201411022 Wang Y H, Zhao C B, Zhang F F, et al. SIMS zircon U-Pb and molybdenite Re-Os geochronology, Hf isotope, and whole-rock geochemistry of the Wunugetushan porphyry Cu-Mo deposit and granitoids in NE China and their geological significance[J]. Gondwana Research, 2015, 28:1228-1245. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2014.10.001
吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等.花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(6):1217-1238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.06.001 张连昌, 秦克章, 英基丰, 等.东天山土屋-延东斑岩铜矿带埃达克岩及其与成矿作用的关系[J].岩石学报, 2004, 20(2):259-268. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200402008 Wang Y H, Xue C J, Wang J P, et al. Early Carboniferous adakiticrocks in the area of the Tuwu deposit, eastern Tianshan, NW China:Slab melting and implications for porphyry copper mineralization[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 103:332-349. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.09.032
Wang Y H, Xue C J, Wang J P, et al. Petrogenesis of magmatism in the Yandongregion of Eastern Tianshan, Xinjiang:Geochemical, geochronological and Hf isotope Constraints[J]. International Geology Review, 2015, 57(9/10):1130-1151.
黄汲清, 任纪舜, 姜春发, 等.中国大地构造及其演化[M].北京:科学出版社, 1980:1-124. 王洪亮, 徐学义, 何世平, 等.中国天山及邻区地质图及说明书(1:100万)[M].北京:地质出版社, 2008:22-23. Anderson T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192(1/2):59-79.
Rubatto D. Zircon trace element geochemistry:Partitioning with garnet and link between U-Pb ages and metamorphism[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 184:123-138. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(01)00355-2
Kosler J, Fonneland H, Sylvester P. U-Pb dating of detrital zircons for sediment provenance studies)A comparison of laser ablation LAICPMS and SIMS techniques[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 182:605-618. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(01)00341-2
吴元保, 郑永飞.锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J].科学通报, 2004, 16:1589-1604. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002 王海然, 赵红格, 乔建新, 等.锆石U-Pb同位素测年原理及应用[J].地质与资源, 2013, 3:229-242. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2013.03.012 Le Maitre. Igneous Rocks:A classification and Glossary of Terms (2nd edition)[M]. Cambridge University Press, 2002:23-86.
Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitiods[J]. Geological Society of American Bulletin, 1989, 101:635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
邱家骧.岩浆岩岩石学[M].北京:地质出版社, 1985:282-287. Collins W J. Nature and origin of A type granites with particular referen-ce to Southeast Austrilia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1982, 80:189-200. doi: 10.1007/BF00374895
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/231575101_Chemical_and_isotopic_systematics_of_oceanic_basalts_Implications_for_mantle_composition_and_processes
熊小林, 蔡志勇, 牛贺才, 等.东天山晚古生代埃达克岩成因及铜金成矿意义[J].岩石学报, 2005, 3:967-976. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200503034 赵振华, 王强, 熊小林, 等.新疆北部的两类埃达克岩[J].岩石学报, 2006, 5:1249-1265. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200605016 张旗, 王焰, 李承东, 等.花岗岩的Sr-Yb分类及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2006, 9:2249-2269. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200609001 罗照华, 黄忠敏, 柯珊.中酸性岩石的基本问题[J].地质评论, 2007, 53(增刊):180-226. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1017126687.htm 张旗, 潘国强, 李承东, 等.花岗岩混合问题:与玄武岩对比的启示——关于花岗岩研究的思考之一[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(5):1141-1152. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200705026 Boztu D, Arehart G B, Platevoet B, et al. High-K, calc-alkaline I-type granitoids from the composite Yozgat batholith generated in a post-collisional setting following continent-oceanic island arc collision in central Anatolia, Turkey[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2007, 91(3):191-223. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=102c6d0220333665da3f27b4d633a738
Pitcher W S. Granite type and tectonic environment[C]//Hsu K J. Mountain Building Process, London, 1983: 19-40.
张旗, 王焰, 李承东, 等.花岗岩按照压力的分类[J].地质通报, 2006, 25(11):1274-1278. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.11.004 Petford N, Atherton M. Na-rich partial melts from newly underplated basaltic crust:the Cordillera Blanca bathloith, Peru[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1996, 37:1491-1521. doi: 10.1093/petrology/37.6.1491
金振民, 高山.底侵作用(underplating)及其壳-幔演化动力学意义[J].地质科技情报, 1996, (2):1-7. doi: 10.1016-j.bmcl.2010.06.083/ 韩宝福, 何国琦, 吴泰然.天山早古生代花岗岩锆石U-Pb定年、岩石地球化学特征及其大地构造意义[J].新疆地质, 2004, 22(1):4-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2004.01.002 王京彬, 王玉往, 周涛发.新疆北部后碰撞与幔源岩浆有关的成矿谱系[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(4):743-752. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200804013 王涛, 李伍平, 李金宝, 等.东天山东段同造山到后造山花岗岩幔源组分的递增及陆壳垂向生长意义-Sr、Nd同位素证据[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(4):762-772. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200804015 肖序常, 汤耀庆, 冯益民, 等.新疆北部及邻区大地构造[M].北京:地质出版社, 1992:1-169. 夏林圻, 李向民, 夏祖春, 等.天山石炭-二叠纪大火成岩省裂谷火山作用与地幔柱[J].西北地质, 2006, 39(1):1-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2006.01.001 王京彬, 王玉往, 何志军.东天山大地构造演化的成矿示踪[J].中国地质, 2006, 33(3):461-469. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.03.002 秦克章, 方同辉, 王书来, 等.东天山板块构造分区、演化与成矿地质背景研究[J].新疆地质, 2002, 20(4):302-308. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2002.04.002 马瑞士, 王赐银, 叶尚夫.东天山构造格架及地壳演化[M].南京:南京大学出版社, 1993:16-78. 周济元, 崔炳芳, 肖惠良, 等.新疆康古尔-黄山对接碰撞带的存在、成矿模式及成矿预测[J].火山地质与矿产, 2001, 22(4):252-262. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4814.2001.04.004 李锦轶, 王克卓, 孙桂华, 等.东天山吐哈盆地南缘古生代活动陆缘残片:中亚地区古亚洲洋板块俯冲的地质记录[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(5):1087-1102. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200605004 顾连兴, 胡受奚, 于春水, 等.论博格达俯冲撕裂型裂谷的形成与演化[J].岩石学报, 2001, 17(4):585-597. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200104009 唐俊华, 顾连兴, 张遵忠, 等.东天山黄山-镜儿泉过铝花岗岩矿物学、地球化学及年代学研究[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(5):921-946. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200805001 韩宝福, 季建清, 宋彪, 等.新疆喀拉通克和黄山东含铜镍矿镁铁-超镁铁杂岩体的SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].科学通报, 2004, 49(22):2324-2328. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.22.012 顾连兴, 张遵忠, 吴昌志, 等.东天山黄山-镜儿泉地区二叠纪地质-成矿-热事件:幔源岩浆内侵及其地壳效应[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(11):2869-2880. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.11.017



 下载:
下载: