Volcanic rock geochemical characteristics and zircon U-Pb age of the Kulapuhe Formation-complex in the west of East Kunlun Mountains, Xinjiang
-
摘要:
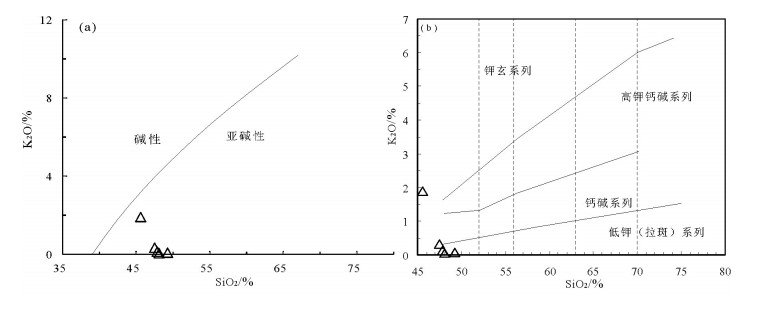
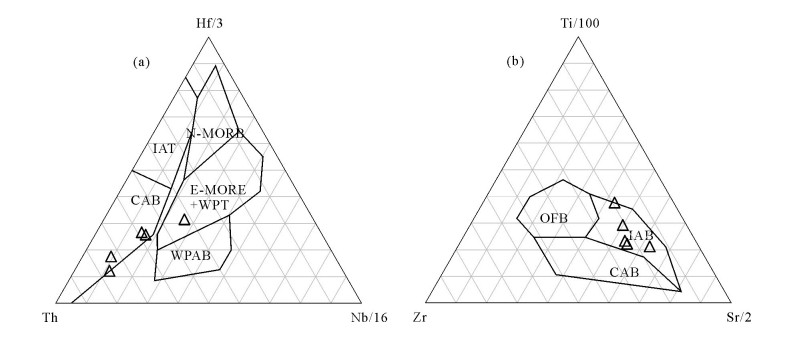
对东昆仑西段库拉甫河岩组火山岩地球化学进行研究,结果显示,主量元素MgO、FeO含量较高,TiO2和K2O含量分别为1.12%、0.63%,与岛弧拉斑玄武岩(0.84%、0.43%)接近;微量元素具有Sr富集,高场强元素Nb、Ta略亏损,P无明显分馏或未分馏的特征,稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线显示良好的同源性(配分曲线变化规律近似一致),且与富集型洋脊玄武岩配分趋势一致。结合构造环境判别,认为其形成于岛弧环境,具有岛弧拉斑玄武岩的特征,来源于与岛弧相关的富集地幔。利用锆石U-Pb测年获得2组年龄,其中一组年龄为688.7±5.1Ma,代表捕获晶年龄,另一组年龄483.4±3.3Ma为结晶年龄,代表玄武岩的形成年龄,属于早奥陶世。结合其构造环境、岩石地球化学特征和年龄数据,认为其是原特提斯洋俯冲消减环境下的产物,且原特提斯洋俯冲至少持续到早奥陶世。
Abstract:In this paper, the authors conducted the study of volcanic rock geochemistry of the Kulapuheyan Formation-complex in the western part of East Kunlun Mountains. The results show that the values of MgO and FeO are1.12% and 0.63%, respectively, the values of TiO2 and K2O are close to the value of island-arc tholeiite (0.84%, 0.43%, respectively), the distribution of trace elements shows enrichment of Sr, slight depletion of HFSE Nb and Ta, and no significant fractionation or no fractionation of P, with rare earth pellet meteorite distribution curve showing good homologous nature (similar distribution curve variations). And it is consistent with the distribution trend of E-MORB. It is concluded that it was in an island arc environment and had the characteristics of islandarc tholeiite. It was derived from island-related enrichment mantle. The 688.7±5.1Ma represents the age of the captured crystal, and 483.4±3.3Ma is the age of the representative age of the basalts, and belongs to the Early Ordovician. In combination with its tectonic setting, geochemical characteristics and chronology, the authors hold that it was produced by the subtraction of the original Tethys Ocean subduction, and the original Tethys ocean subducted continuously at least until the Early Ordovician.
-
Keywords:
- basalt /
- zircon U-Pb dating /
- tectonic evolution /
- East Kunlun
-
-
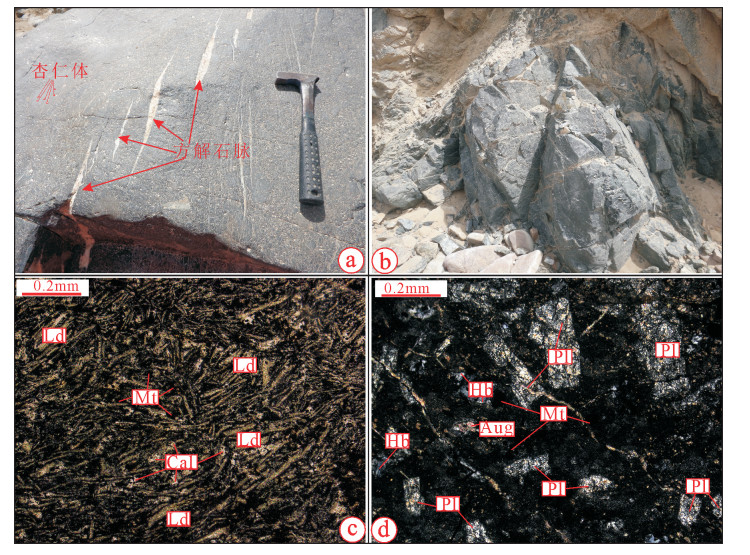
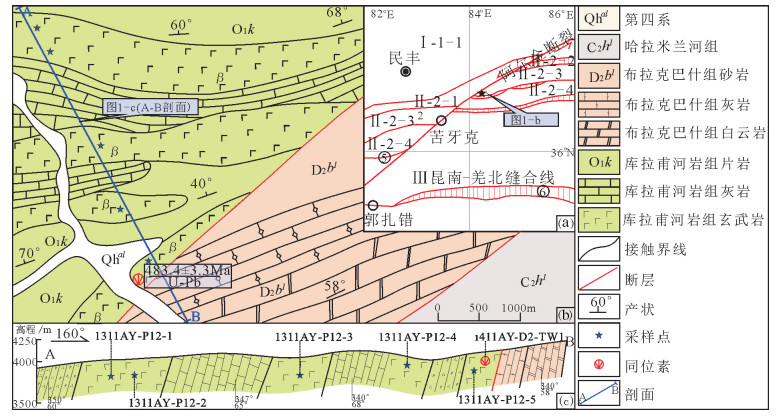
图 1 东昆仑构造简图(a)[24]、区域地质图(b)①和A-B剖面(c)
Ⅰ-1-1—塔里木南缘中新生代盆地;Ⅱ-2-1—北昆仑早古生代岩浆弧;Ⅱ-2-2—库地-其曼于特混杂岩带;Ⅱ-2-3—中昆仑微地块;Ⅱ-2-4—南昆仑古生代增生杂岩楔;Ⅲ—昆南-羌北缝合带
Figure 1. East Kunlun tectonic map(a), regional geological map of the study area(b)and geological section A-B (c)
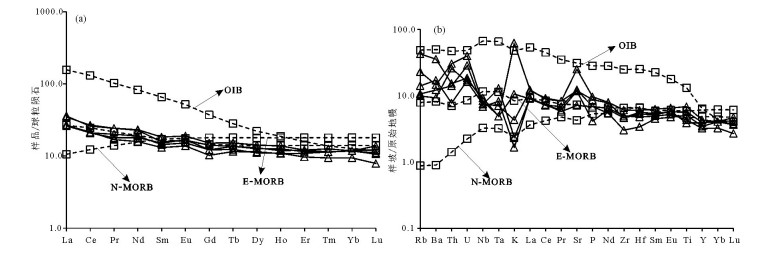
图 7 岩石稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分模式图(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)[36]
OIB—洋岛玄武岩;N-MORB—亏损型洋脊玄武岩;E-MORB—富集型洋脊玄武岩
Figure 7. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns(a)and primitive mantle-normalized spidergrams of trace elements(b)
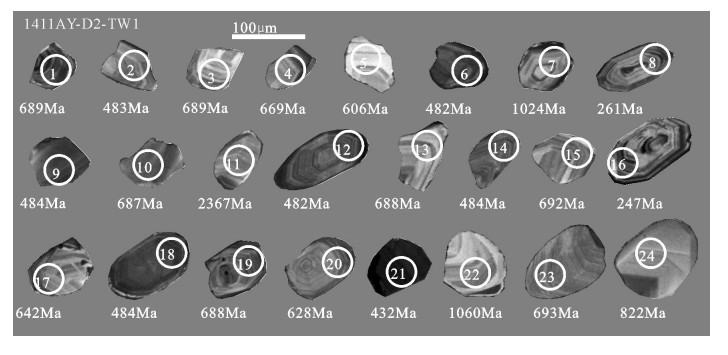
表 1 样品1411AY-D2-TW1锆石U-Th-Pb年龄分析结果
Table 1 Zircon U-Th-Pb dating results of sample 1411AY-D2-TW1
测点 含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 表面年龄/Ma Th U Pb 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 1 890 534 312 1.67 0.0595 0.0024 0.9244 0.0352 0.1128 0.0013 584 63 665 19 689 7 2 81 332 114 0.24 0.0559 0.0022 0.5992 0.0229 0.0777 0.0008 449 67 477 15 483 5 3 289 230 130 1.25 0.0610 0.0052 0.9482 0.0798 0.1127 0.0019 640 154 677 42 689 11 4 114 178 103 0.64 0.1378 0.0039 2.0777 0.0545 0.1094 0.0013 2200 30 1141 18 669 7 5 107 126 60 0.85 0.0721 0.0079 0.9804 0.1044 0.0986 0.0031 989 167 694 54 606 18 6 261 450 160 0.58 0.0567 0.0033 0.6066 0.0343 0.0776 0.0012 481 98 481 22 482 7 7 135 181 147 0.75 0.0743 0.0026 1.7632 0.0594 0.1722 0.0019 1049 51 1032 22 1024 10 8 240 251 50 0.96 0.0538 0.0132 0.3059 0.0743 0.0413 0.0017 361 399 271 58 261 11 9 221 414 146 0.53 0.0547 0.0015 0.5871 0.0145 0.0779 0.0006 399 41 469 9 484 4 10 56 375 183 0.15 0.0625 0.0014 0.9686 0.0204 0.1125 0.0009 691 32 688 11 687 5 11 68 180 386 0.38 0.1512 0.0025 9.2475 0.1375 0.4437 0.0041 2359 13 2363 14 2367 18 12 117 484 165 0.24 0.0558 0.0015 0.5974 0.0145 0.0777 0.0006 444 40 476 9 482 4 13 221 131 77 1.7 0.0588 0.0031 0.9123 0.0462 0.1126 0.0013 558 90 658 25 688 8 14 95 405 138 0.23 0.0548 0.0016 0.5887 0.0164 0.0780 0.0006 403 48 470 10 484 4 15 139 238 124 0.58 0.0634 0.0029 0.9904 0.0443 0.1133 0.0015 723 73 699 23 692 9 16 434 483 90 0.9 0.0494 0.0022 0.2655 0.0114 0.0390 0.0004 164 82 239 9 247 2 17 92 170 82 0.54 0.0659 0.0035 0.9518 0.0490 0.1047 0.0016 804 83 679 25 642 9 18 281 765 265 0.37 0.0569 0.0012 0.6120 0.0118 0.0780 0.0006 489 30 485 7 484 3 19 256 337 180 0.76 0.0657 0.0017 1.0208 0.0239 0.1126 0.0009 798 35 714 12 688 5 20 126 251 118 0.5 0.0651 0.0038 0.9186 0.0520 0.1023 0.0016 779 92 662 28 628 10 21 883 1767 559 0.5 0.0602 0.0012 0.5757 0.0096 0.0694 0.0005 611 25 462 6 432 3 22 56 133 108 0.42 0.0744 0.0025 1.8333 0.0582 0.1787 0.0020 1053 46 1057 21 1060 11 23 77 205 103 0.38 0.0598 0.0029 0.9350 0.0440 0.1135 0.0015 595 79 670 23 693 9 24 70 168 103 0.42 0.0666 0.0018 1.2486 0.0311 0.1360 0.0012 825 38 823 14 822 7 表 2 样品主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 2 Major, trace elements and REE analyses of samples
编号 1311AY-P12-1 1311AY-P12-2 1311AY-P12-4 1311AY-P12-4 1311AY-P12-5 岩石名称 灰绿色块状玄武岩 灰绿色块状玄武岩 紫红色杏仁状玄武岩 玄武岩 玄武岩 SiO2 47.86 47.52 45.61 49.27 48.11 TiO2 1.49 0.94 1.23 1.10 0.84 Al2O3 16.10 15.18 14.71 16.22 16.73 Fe2O3 3.18 1.64 7.79 4.29 3.96 FeO 9.65 7.62 4.24 6.79 7.38 MnO 0.16 0.15 0.19 0.20 0.20 MgO 5.73 7.04 5.00 3.75 5.24 CaO 6.36 7.13 8.33 9.94 9.34 Na2O 2.94 2.95 3.30 2.99 2.80 K2O 0.13 0.32 1.89 0.07 0.05 P2O5 0.21 0.15 0.19 0.15 0.09 烧失量 5.19 8.74 7.89 5.06 5.05 Rb 14.59 9.00 27.18 6.30 6.80 Sr 531.00 260.00 252.00 151.00 249.00 Ba 102.00 120.00 250.00 65.11 85.39 Nb 5.36 6.62 6.00 5.32 4.86 Ta 0.29 0.20 0.20 0.53 0.34 Zr 68.22 56.00 52.72 33.91 52.05 Hf 1.87 1.48 1.74 1.05 1.64 Th 2.60 0.66 1.30 2.20 1.20 K 1078.72 2655.32 15682.98 580.85 414.89 P 916.90 654.93 829.58 654.93 392.96 Ti 8940.00 5640.00 7380.00 6600.00 5040.00 Cr 36.50 170.00 41.90 35.08 26.42 U 0.84 0.36 0.39 0.34 0.60 Y 19.70 14.60 18.10 15.80 17.90 La 8.20 6.20 8.50 6.30 6.40 Ce 16.40 12.80 15.80 13.10 12.70 Pr 2.30 1.90 2.30 1.60 1.70 Nd 10.80 8.80 10.60 7.40 8.40 Sm 2.80 2.20 2.40 2.00 2.30 Eu 1.10 0.88 0.96 0.80 0.98 Gd 3.10 2.50 2.90 2.10 2.50 Tb 0.57 0.46 0.51 0.43 0.51 Dy 3.60 2.80 3.20 2.90 3.30 Ho 0.78 0.62 0.71 0.61 0.67 Er 2.00 1.60 1.90 1.80 2.00 Tm 0.29 0.24 0.29 0.29 0.32 Yb 2.00 1.60 2.00 2.00 2.00 Lu 0.28 0.20 0.27 0.31 0.35 ∑REE 54.22 42.80 52.34 41.64 44.13 LREE/HREE 3.30 3.27 3.44 2.99 2.79 δEu 1.14 1.14 1.11 1.18 1.24 (La/Yb)N 2.94 2.78 3.05 2.26 2.30 (La/Sm)N 1.89 1.82 2.29 2.03 1.80 (Gd/Yb)N 1.28 1.29 1.20 0.87 1.03 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为 10-6 -
莫宣学, 罗照华, 邓晋福, 等.东昆仑造山带花岗岩及地壳生长[J].高校地质学报, 2007, 13(3):403-414. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2007.03.010 许志琴, 杨经绥, 李海兵, 等.中央造山带早古生代地体构架与高压/超高压变质带的形成[J].地质学报, 2006, 80(12):1793-1806. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.12.002 杨经绥, 许志琴, 马昌前, 等.复合造山作用和中国中央造山带的科学问题[J].中国地质, 2010, 37(1):1-11. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201001001 刘彬, 马昌前, 张金阳, 等.东昆仑造山带东段早泥盆世侵入岩的成因及其对早古生代造山作用的指示[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(6):1785-1807. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201206007 刘彬, 马昌前, 蒋红安, 等.东昆仑早古生代洋壳俯冲与碰撞造山作用的转换:来自胡晓钦镁铁质岩石的证据[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(6):2093-2106. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201306017 姜春发.中央造山带开合构造[M].北京:地质出版社, 2000. Xiao W J, Windley B F, Fang A M, et al. Palaeozoic-Early Mesozoic Accretionary Tectonics of the Western Kunlun Range, NW China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2001, 4(4):826-827. doi: 10.1016/S1342-937X(05)70611-0
Xiao W, Windley B, Hao J I E, et al. Arc-ophiolite obduction in the Western Kunlun Range (China):implications for the Palaeozoic evolution of central Asia[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2002, 159(5):517-528. doi: 10.1144/0016-764901-093
Zong Qi W, Jiang C F, Yan Q R, et al. Accretion and collision orogeneses in the West Kunlun Mountains, China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2001, 4(4):843-844.
Matte P, Tapponnier P, Amaud N, et al. Tectonics of Western Tibet, between the Tarim and the Indus[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1996, 142(3):311-330.
Mattern F, Schneider W. Suturing of the Proto-and Paleo-Tethys oceans in the western Kunlun (Xinjiang, China)[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2000, 18(6):637-650. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(00)00011-0
袁超, 孙敏, 肖文交, 等.原特提斯的消减极性:西昆仑128公里岩体的启示[J].岩石学报, 2004, 19(3):399-408. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200303003 张传林, 陆松年, 于海锋, 等.青藏高原北缘西昆仑造山带构造演化:来自锆石SHRIMP及LA-ICP-MS测年的证据[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2007, 37(2):145-154. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd200702001 丁林, Maksatbek S, 蔡福龙, 等.印度与欧亚大陆初始碰撞时限、封闭方式和过程[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2017, 47:293-309. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201703003 王二七.关于印度与欧亚大陆初始碰撞时间的讨论[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2017, 47:284-292. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201703002 马昌前, 熊富浩, 尹烁, 等.造山带岩浆作用的强度和旋回性:以东昆仑古特提斯花岗岩类岩基为例[J].岩石学报, 2015, 31(12):3555-3568. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201512004 孙文军.原特提斯微陆块群的深部结构与拼合方式[D].中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2014. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10423-1014329250.htm 安慧婷.原特提斯南界的厘定及其洋-陆格局[D].中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2014. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=conference&id=8281617 张亚峰, 裴先治, 丁仨平, 等.东昆仑都兰县可可沙地区加里东期石英闪长岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄及其意义[J].地质通报, 2010, 29(1):79-85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.01.010 赵振明, 马华东, 王秉璋, 等.东昆仑早泥盆世碰撞造山的侵入岩证据[J].地质论评, 2008, 54(1):47-56. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2008.01.006 任军虎, 柳益群, 冯乔, 等.东昆仑清水泉辉绿岩脉地球化学及LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年[J].岩石学报, 2009, (5):1135-1145. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200905008 薛友辰.原特提斯北界东-西段交接转换过程: 秦岭-祁连-贺兰构造关系[D].中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2014. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10423-1014368011.htm 王晓霞, 胡能高, 王涛, 等.柴达木盆地南缘晚奥陶世万宝沟花岗岩:锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄, Hf同位素和元素地球化学[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(9):29-50. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7863350 李荣社.昆仑山及邻区地质[M].北京:地质出版社, 2008. 陈邦学, 朱志新, 周能武, 等.新疆博格达东段阿克铁克协山地区辉绿岩岩石地球化学特征及其SHRIMP U-Pb测年意义[J].西北地质, 2015, 48(3):1-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2015.03.001 Anderson T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical geology, 2002, 192(1):59-79.
王岚, 杨理勤, 王亚平, 等.锆石LA-ICP-MS原位微区U-Pb定年及微量元素的同时测定[J].地球学报, 2012, (5):763-772. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb201205011 侯可军, 李延河, 田有荣. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石微区原位UPb定年技术[J].矿床地质, 2009, 28(4):481-492. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2009.04.010 吴元保, 郑永飞.锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J].科学通报, 2004, 49(16):1589-1604. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002 Ludwig K R. Using isoplot/EX, version2, a geolocronolgical toolkit for Microsoft excel[J]. Berkeley Geochronological Center Special Publication, 1999, 47:151-181.
钟玉芳, 马昌前, 佘振兵.锆石地球化学特征及地质应用研究综述[J].地质科技情报, 2006, 25(1):27-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2006.01.005 Cox K G, Bell J D, Pankhurst R J. The Interpretation of Igneous Rocks[C]//Cox K G. The interpretation of igneous rocks. London Allen & Unwin, 1979: 12-41.
Winchester J A, Floyd P A. Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile elements[J]. Chemical Geology, 1977, 20(4):325-343.
Pearce J A. Trace element characteristics of lavas from destructive plate boundaries[C]//Andesites. John wiley & Sons, 1982: 525-548.
Rickwood P C. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J]. Lithos, 1989, 22(4):247-263. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(89)90028-5
Sun S S, Mcdonough W F.Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1):313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
李昌年.火成岩微量元素岩石学[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1992. Wood D A. The application of a Th, Hf, Ta diagram to problems of tectonomagmatic classification and to establishing the nature of crustal contamination of basaltic lavas of the British Tertiary Volcanic Province[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 1980, 50(1):11-30.
Pearce J A, Cann J R. Tectonic setting of basic volcanic rocks determined using trace element analyses[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1973, 19(2):290-300. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(73)90129-5
潘振杰, 张旗, 陈刚, 等.中国东部中生代岩浆活动与板块俯冲的关系——浙闽与日本弧和安第斯弧的对比及其意义[J].岩石学报, 2017, 33(5):1507-1523. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201705010 郑勇, 杨有生, 陈邦学, 等.东昆仑西段巴什康阔勒辉长岩地球化学特征及其构造意义[J].现代地质, 2016, 30(5):1004-1013. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2016.05.006 王冠, 孙丰月, 李碧乐, 等.东昆仑夏日哈木矿区早泥盆世正长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及其动力学意义[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2013, 37(4):685-697. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201304013



 下载:
下载: