Heavy metal distribution in the wetland sediments of the Liaohe delta: Implications for filter function of wetlands
-
摘要:
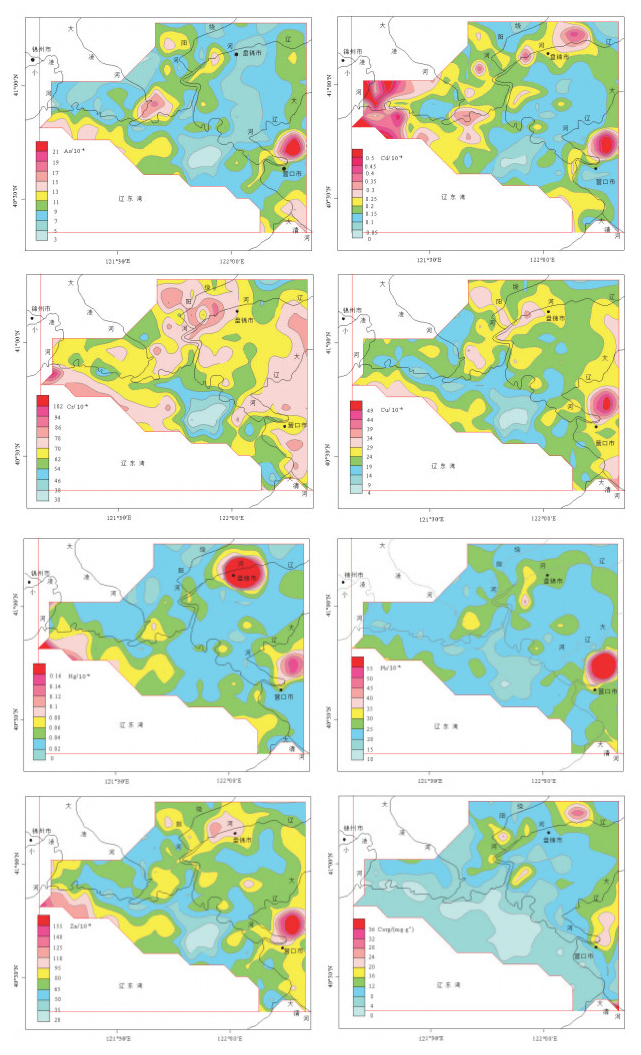
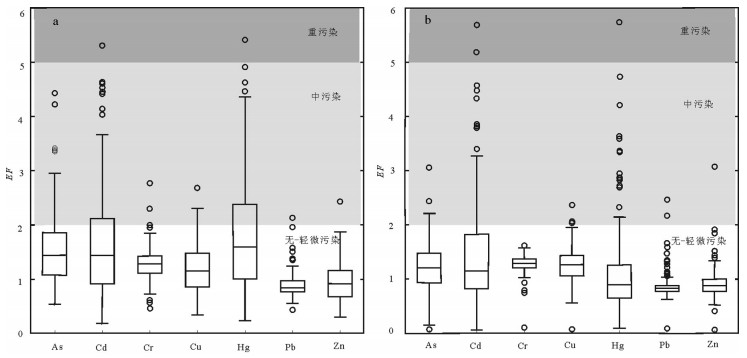
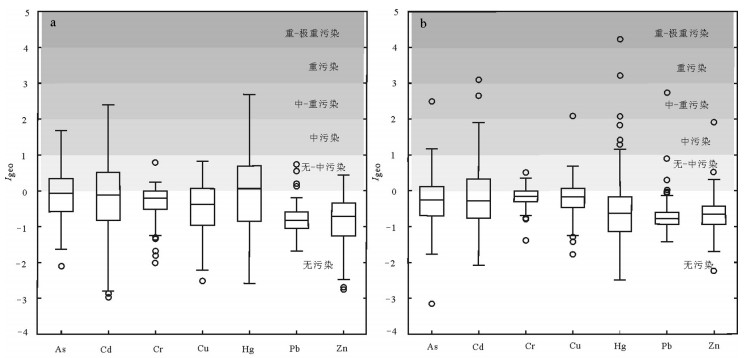
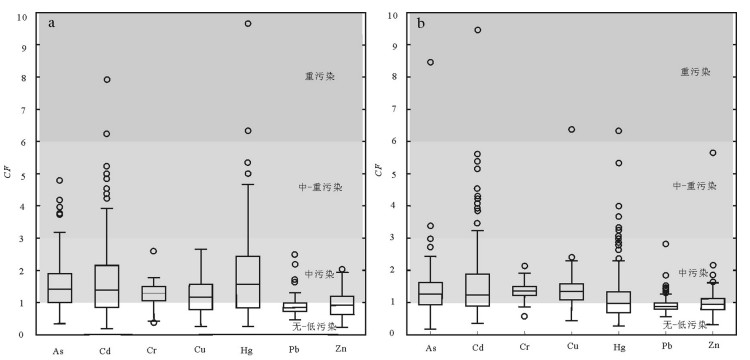
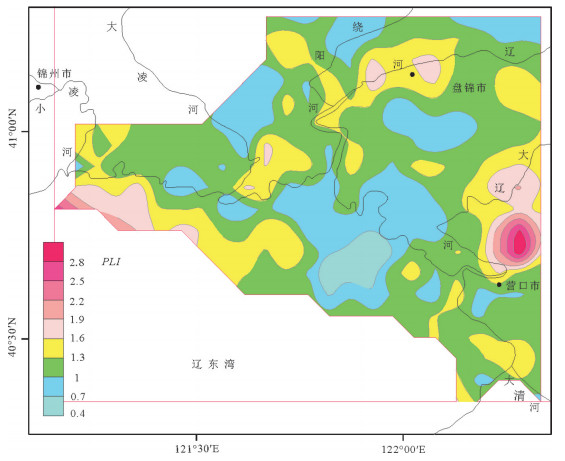
为了研究辽河三角洲湿地表层沉积物中重金属元素含量及其与有机碳的相关性,探讨湿地对重金属元素的移除作用,对233个辽河三角洲上三角洲平原湿地(典型湿地)表层沉积物样品和150个相邻浅海湿地(浅水湿地)表层沉积物样品,进行了化学分析测试及数理统计分析,并运用多种评价方法进行重金属污染风险评价。结果显示:①重金属元素浓度量级大小均遵循Cr(Zn) > Pb > Cu > As > Cd > Hg的分布规律;②除As和Hg外,其他金属元素浓度均表现为浅水湿地显著低于典型湿地,暗示湿地生态系统对污染物的移除作用;③除Pb和Zn外,其他重金属元素对环境均造成了中度污染;④重金属元素分布受有机碳和粒径大小的显著影响,浓度存在显著的相关性,浅水湿地表层沉积物重金属元素浓度及其与有机碳之间的相关性更显著,揭示有机碳对重金属的螯合作用;⑤在有湿地分布的浅海湿地区,重金属元素浓度均表现为浅水湿地显著低于典型湿地,暗示湿地生态系统对污染物的移除作用,相反,在大规模湿地被改造成农田的锦州海岸带地区,造成了近海浅水湿地的严重污染。该研究揭示了滨海湿地对重金属元素的过滤作用及在缓解环境污染过程中的重要意义。
Abstract:Heavy metals (As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Pb, Zn), organic carbon (Corg) and grain size of 223 surface sediment samples in the Liaohe upper delta plain wetland (UDPW) and 150 surface sediment samples in neighboring shallow sea wetland (SSW) were analyzed to evaluate the spatial distribution and assess the risk of metal pollution. Concentrations of heavy metals in sediments from both UDPW and SSW are in the decreasing order of Cr (Zn) > Pb > Cu > As > Cd > Hg. The results of two-sample-t-tests indicate significant higher heavy metal concentrations in UDPW compared with SSW except As and Hg, implying the accumulation or biouptake of particulate metal within the wetland ecosystem and reducing metal input to marine coastal systems. Multiple assessment approaches, namely, the metal enrichment factor (EF), geoaccumulation index (Igeo), contamination factor (CF) and pollution load index (PLI) were jointly used to explore the risks of the anthropogenic contaminations. The results indicate unpolluted nature for Pb and Zn, moderate degree of contamination for the remaining metals both in UDPW and SSW. Furthermore, the distribution of heavy metals is substantially influenced by grain size and the concentration of Corg, and there is significant correlation between the concentrations of heavy metal, especially for the concentration of Corg and heavy mentals in surface sediment samples of shallow sea wetland (r=0.439, p < 0.01), revealing the metal chelation acted by organic matter.
-
Keywords:
- heavy mental /
- surface sediment /
- pollution assessment /
- wetlands /
- filtration function of wetlands
-
-
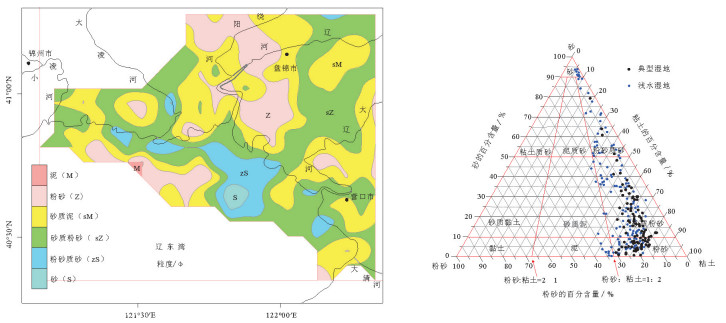
图 2 粒径分布图(a)和粒径分类图(b)(FOLK) [22]
Figure 2. Particle size distribution (a) and particle size classification (b)
表 1 典型湿地和浅水湿地的表层沉积物重金属元素含量分布
Table 1 Heavy metal distributions in the sediments of the UDPW and SSW
元素 典型湿地 浅水湿地 背景值 平均值 值域范围 变异系数 平均值 值域范围 变异系数 As/10-6 8.970±0.3300a 1.130~56.50 51.79% 10.34±0.4100b 2.320~32.00 48.41% 6.880 Cd/10-6 0.2000±0.01000a 0.04600~1.680 85.82% 0.2200±0.01300a 0.02500~1.030 72.54% 0.1300 Cr/10-6 68.52±0.7900a 29.00~108.0 16.42% 63.30±1.300b 18.90~131.0 26.11% 50.50 Cu/10-6 24.03±0.6200a 7.700~112.0 37.09% 20.80±0.7000b 4.600~46.60 41.92% 17.60 Hg/10-6 0.04000±0.00a 0.008000~0.8500 165.73% 0.05560±0.003300b 0.007500~0.2900 73.09% 0.03000 Pb/10-6 26.10±1.280a 15.30~272.0 70.23% 23.90±0.6000a 12.80~68.20 30.78% 27.30 Zn/10-6 77.04±2.310a 24.90~441.0 42.83% 72.40±2.400a 17.40~159.0 41.00% 78.00 Corg/(mg·g-1) 10.96±0.5400 1.700~72.00 70.77% 4.920±0.2000 0.9000~13.20 49.37% Na 粒度/Φ 5.850±0.04000a 3.440~7.340 10.20% 5.190±0.1000b 2.330~7.370 24.67% Na 注:Na代表无数据;a、b表示两组数据存在显著差异 表 2 研究区域与其他区域表层沉积物重金属元素含量平均值对比[13-21]
Table 2 Variations of heavy metals among various coastal areas in the world
10-6 地理位置 As Cd Cr Cu Hg Pb Zn 典型湿地 8.970 0.2000 68.52 24.03 0.04000 26.09 77.04 浅水湿地 10.34 0.2200 63.32 20.79 0.05560 23.94 72.41 中国大亚湾 Na Na 75.60 12.70 Na 32.70 94.40 中国泉州湾 21.70 0.5900 82.00 71.40 0.4000 67.70 179.6 土耳其伊兹密尔湾 21.80 4.900 74.30 67.60 Na 102.0 930.0 土耳其Aliaǧa湾 Na 1.470 111.0 321.0 1.590 284.0 86.40 中国渤海湾南部 Na 0.1400 33.50 22.70 Na 21.70 71.70 中国珠江河口 Na Na 106.0 45.70 Na 57.90 176.8 中国长江河口 Na 0.2600 78.90 30.70 Na 31.80 94.30 中国山东半岛近岸1区北部 8.900 0.09000 59.00 18.70 Na 18.20 61.00 辽东湾湿地 Na 0.654 Na 18.175 Na 18.521 96.696 中国国家标准
(海洋沉积物质量)20.00 0.5000 80.00 35.00 0.2000 60.00 150.0 注:Na代表无数据 表 3 典型湿地和浅水湿地相关分析
Table 3 The correlation analysis of heavy metal content in the UDPW and SSW
元素 As Cd Cr Cu Hg Pb Zn 有机碳 粘土 典型湿地 As 1 0.532** 0.456** 0.889** 0.354** 0.804** 0.838** 0.368** 0.347** Cd 1 0.111 0.559** 0.355** 0.620** 0.687** 0.327** -0.050 Cr 1 0.561** 0.112 0.093 0.375** 0.163* 0.654** Cu 1 0.440** 0.801** 0.916** 0.473** 0.369** Hg 1 0.444** 0.482** 0.233** 0.050 Pb 1 0.866** 0.444** 0.009 Zn 1 0.503** 0.243** 有机碳 1 0.036 粘土 1 元素 As Cd Cr Cu Hg Pb Zn 有机碳 粘土 浅水湿地 As 1 0.503** 0.581** 0.783** 0.481** 0.841** 0.728** 0.768** 0.433** Cd 1 0.475** 0.528** 0.770** 0.578** 0.754** 0.436** 0.371** Cr 1 0.786** 0.451** 0.586** 0.831** 0.707** 0.582** Cu 1 0.533** 0.793** 0.899** 0.903** 0.722** Hg 1 0.564** 0.698** 0.423** 0.345** Pb 1 0.781** 0.784** 0.405** Zn 1 0.799** 0.665** 有机碳 1 0.606** 粘土 1 注:*代表p < 0.05; **代表p < 0.01 -
蔡奎, 段亚敏, 栾文楼, 等.河北平原农田土壤重金属元素Pb、Hg地球化学行为的影响因素[J].中国地质, 2016, (4):1420-1428. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201604025 Suthar S, Nema A K, Chabukdhara M, et al. Assessment of Metals in Water and Sediments of Hindon River, India:Impact of Industrial and Urban Discharges[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 171(1/3):1088-1095. http://europepmc.org/abstract/med/19616893
Yang Z F, Wang Y, Shen Z Y, et al. Distribution and speciation of heavy metals in sediments from the mainstream, tributaries, and lakes of the Yangtze River catchment of Wuhan, China[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 166(2/3):1186-1194. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=4dc30ecc754e03a44fca1f5bb45def14
Förstner U, Wittmann G T W. Metal Pollution in the Aquatic Environment[J]. Springer, 1979. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_7a2282931e291928d4bb2b81ca25f4b0
Wang S, Jia Y, Wang S, et al. Fractionation of heavy metals in shallow marine sediments from Jinzhou Bay, China[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2010, 22(1):23-31. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(09)60070-X
Liu H, Liqing L I, Yin C, et al. Fraction distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Moshui Lake[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2008, 20(4):390-397. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62069-0
Bastami K D, Bagheri H, Kheirabadi V, et al. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments along southeast coast of the Caspian Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2014, 81(1):262-267. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.01.029
Dou Y, Li J, Zhao J, et al. Distribution, enrichment and source of heavy metals in surface sediments of the eastern Beibu Bay, South China Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2013, 67(1/2):137-145. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=d1885e2c5249119cf033ca7dcc5c1a15
Brix H, Ye S, Laws E A, et al. Large-scale management of common reed, Phragmites australis, for paper production:A case study from the Liaohe Delta, China[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2014, 73:760-769. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.09.099
Ye S, Krauss K W, Hans B, et al. Inter-Annual Variability of AreaScaled Gaseous Carbon Emissions from Wetland Soils in the Liaohe Delta, China[J]. Plos One, 2016, 11(8):e0160612. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160612
Li X, Liang C, Shi J. Developing Wetland Restoration Scenarios and Modeling Its Ecological Consequences in the Liaohe River Delta Wetlands, China[J]. CLEAN-Soil, Air, Water, 2012, 40(10):1185-1196. doi: 10.1002/clen.201200025
Yang F, Zhao D Z, Suo A N. The Study of Shuangtaizihekou Wetland Landscape Temporal and Spatial Changes[J]. Remote Sensing Technology & Application, 2008, 23(1):51-56. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ygjsyyy200801010
周秀艳, 李宇斌, 王恩德, 等.辽东湾湿地重金属污染及潜在生态风险评价[J].环境科学与技术, 2004, 27(5):60-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2004.05.025 Ruilian Y, Xing Y, Yuanhui Z, et al. Heavy metal pollution in intertidal sediments from Quanzhou Bay, China[J]. Journal of Environmental Science, 2008, 20(6):664-669. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62110-5
Yamada M, Senna S, Fujiwara H. The distribution and speciation of trace metals in surface sediments from the Pearl River Estuary and the Daya Bay, Southern China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2010, 60(8):1364-1371. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.05.012
Hu B, Li G, Li J, et al. Spatial distribution and ecotoxicological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the southern Bohai Bay, China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2013, 20(6):4099-4110. doi: 10.1007/s11356-012-1332-z
Pekey H. Heavy metal pollution assessment in sediments of the Izmit Bay, Turkey[J]. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 2006, 123(1/3):219-231. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=63174ac61007cb4faa9102b35900be66
Neşer G, Kontas A, Ünsalan D, et al. Heavy metals contamination levels at the Coast of Aliaga (Turkey) ship recycling zone[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2012, 64(4):882-887. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.02.006
Zhang W, Feng H, Chang J, et al. Heavy metal contamination in surface sediments of Yangtze River intertidal zone:an assessment from different indexes[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2009, 157(5):1533-1543. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2009.01.007
Xu G, Pei S, Liu J, et al. Surface sediment properties and heavy metal pollution assessment in the near-shore area, north Shandong Peninsula[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2015, 95(1):395-401. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.03.040
中国国家质量技术监督局.中华人民共和国国家标准GB 18668-2002-海洋沉积物质量[S]. 2002. Robert L. Folk. A Review of grain size parameters[J]. Sedimentology, 1996, 6(2):73-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.1966.tb01572.x/full
张敏.长江中下游浅水湖泊富营养化机制与重金属污染研究[D].中国科学院研究生院(水生生物研究所)博士学位论文, 2005. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-80119-2005152035.htm Sutherland R A. Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii[J]. Environmental Geology, 2000, 39(6):611-627. doi: 10.1007/s002540050473
Srinivasa G S, Ramakrishna R M, Govil P K. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soils at Jajmau (Kanpur) and Unnao industrial areas of the Ganga Plain, Uttar Pradesh, India[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 174(1/3):113-121. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e73830f4696f092d8ed25c8f128d608e
Lu X, Wang L, Kai L, et al. Contamination assessment of copper, lead, zinc, manganese and nickel in street dust of Baoji, NW China[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 161(2/3):1058-1062. doi: 10.1016-j.jhazmat.2008.04.052/
管后春, 李运怀, 彭苗枝, 等.黄山城市土壤重金属污染及其潜在生态风险评价[J].中国地质, 2013, 40(6):1949-1958. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201306024 Fritioff Å, Kautsky L, Greger M. Influence of temperature and salinity on heavy metal uptake by submersed plants[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2005, 133(2):265-274. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2004.05.036
Du Laing G, De Vos R, Vandecasteele B, et al. Effect of salinity on heavy metal mobility and availability in intertidal sediments of the Scheldt estuary[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2008, 77(4):589-602. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2007.10.017
Hakanson L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. a sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8):975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
Tomlinson D L, Wilson J G, Harris C R, et al. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index[J]. Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen, 1980, 33(1/4):566-575. doi: 10.1007/BF02414780



 下载:
下载: