Zircon U-Pb age and geochemical characteristics of Qinlingliang rapakiwi granite from Western Qinling orogenic belt in Shaanxi
-
摘要:
对秦岭梁岩体进行了地质学、岩石学、地球化学及年代学研究。秦岭梁岩体主要岩石类型有似斑状黑云环斑花岗岩、似斑状角闪黑云环斑花岗岩、中粒黑云二长花岗岩,普遍发育环斑结构,LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年结果为215.1±2.5Ma(MSWD=0.29,n=17),显示秦岭梁环斑花岗岩形成于晚三叠世。秦岭梁环斑花岗岩属于高钾钙碱性系列,具有准铝质-弱过铝质的特点,富集Rb、Th、K、Pb、Nd等,贫Ba、Nb、Ta、La、P、Eu等,明显亏损Nb、Ta、P。稀土元素含量中等偏低,轻、重稀土元素分异程度高,稀土元素标准化配分曲线呈明显的右倾模式。秦岭梁环斑花岗岩岩浆主要来源于地壳熔融,同时具有壳幔混合特点。结合区域地质背景,认为秦岭梁环斑花岗岩形成于造山后伸展环境。
-
关键词:
- 西秦岭 /
- 秦岭梁环斑花岗岩 /
- 地球化学 /
- LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年
Abstract:Based on geological, petrological and geochemical studies, the authors investigated Qinlingliang rapakiwi granite intrusion, porphyritic biotite rapakivi granite, porphyritic hornblende biotite rapakivi granite and medium-grained biotite monzonitic granite. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb analysis suggests that Qinlingliang rapakiwi granite intrusion was formed in late Triassic(215.1±2.5Ma). Qinlingliang rapakiwi granite belongs to high-K calc-alkaline series with aluminous-peraluminous nature, and is characterized by enrichment of Rb, Th, K, Pb and Nd, depletion of Ba, Nb, Ta, La, P and Eu, and significant loss of Nb, Ta and P. In addition, this intrusion has moderate-low REE concentration and right-inclined distribution curve. The magma probably mainly originated from partial melting of the crust, and also had the characteristics of crust-mantle mixing. In combination with regional geological background, the authors hold that Qinlingliang rapakiwi granite intrusion probably originated from a post orogenic extension environment.
-
花岗岩的成因类型和形成时代是探讨地壳生长和地球动力学背景的重要指示标志[1-3]。在秦岭造山带分布有元古宙—中新生代不同类型、不同成因的花岗岩类[4-7]。近年来,在秦岭造山带相继发现中生代环斑结构花岗岩,沿商丹板带两侧出露东江口、柞水、曹坪、沙河湾具环斑结构花岗岩体(200~220Ma)[8-17];北秦岭构造带西段也出露3个奥长环斑花岗岩体,自东而西分别为老君山(215Ma)、秦岭梁(217Ma)、朱厂沟脑岩体,侵位于巨大的宝鸡花岗岩基中[18]。世界上典型环斑花岗岩主要出露于前寒武纪稳定克拉通内部及其边缘,其时代为元古宙,属非造山环斑花岗岩[19-20]。北秦岭造山带中的环斑花岗岩,与世界典型环斑花岗岩存在较大差异,它们的侵位机制对区域构造演化和动力学背景的研究具独特的地质意义。不少学者对秦岭造山带中生代环斑花岗岩进行了研究,并获得了一批研究成果,尤其对沙河湾岩体、老君山岩体、秦岭梁研究成果颇丰[8-11, 16, 18, 21-28]。
本文从秦岭梁环斑花岗岩地质特征、岩石学、岩石地球化学特征、LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄等方面,对其成因构造环境及地质意义予以探讨,以期为解释秦岭造山带中生代花岗岩的成因和反演秦岭造山带演化过程提供新的资料。
1. 区域地质概况与岩石学特征
1.1 区域地质概况
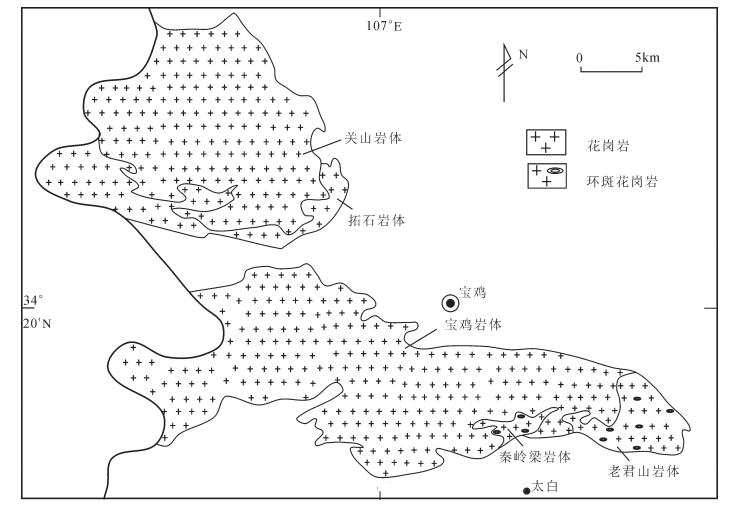
秦岭梁环斑花岗岩体位于北秦岭宝鸡—太白地区,主要分布于宝鸡岩体东南缘的宝鸡—太白公路的秦岭梁一带,呈不规则岩株状产出(图 1),面积约32km2,在岩貌上表现为显著的球状风化。与石炭系草凉驿组及宝鸡岩体呈侵入接触关系。秦岭梁环斑花岗岩体内暗色包体较发育,边部见包体群特征,形态以椭圆状为主,次为圆状、透镜状,大小不等,多数为5~10cm,大者达30~100cm,小者1~ 3cm,岩性以石英闪长岩、闪长岩为主,与寄主岩界线清晰,并在包体内及边部见有钾长石斑晶(捕虏晶),钾长石斑晶晶形与寄主岩中的相同。
1.2 岩石学特征
秦岭梁岩体主要岩石类型有似斑状黑云环斑花岗岩、似斑状角闪黑云环斑花岗岩、中粒黑云二长花岗岩。岩体中暗色包体较发育(图 2),包体为灰黑色-灰绿色,与围岩界线清晰,呈透镜状、椭圆状或不规则状,大小不一,直径多为0.1~1m,部分包体内见钾长石斑晶,少数见斜长石环边现象,暗色包体主要矿物以黑云母和角闪石为主,占30%~ 50%,浅色矿物为斜长石,大于40%,钾长石含量小于5%,石英少量。
环斑结构是秦岭梁岩体普遍发育的特征结构,以发育卵球状、球状碱性长石巨晶和环斑长石为主(图 3)。碱性长石巨晶分布很不均匀,一般为15%~ 30%,局部达50%~60%。大多数碱性长石巨晶呈卵球状和球状,其中,有25%~50%的碱性长石巨晶发育斜长石外壳,且主要呈卵球状。此外,少数长石巨晶为半自形,粒度较小。
(1)似斑状黑云环斑花岗岩
似斑状结构、花岗结构,矿物成分:碱性长石55%,斜长石20%,石英20%,黑云母5%。岩石由长石、石英、黑云母组成。斑晶为碱性长石,呈半自形板状,表面具粘土化,粒径12mm左右。基质为斜长石,呈半自形板状,聚片双晶发育,粒径2.3mm左右。石英呈他形粒状,与长石颗粒构成镶嵌状。黑云母呈片状,部分蚀变绿泥石化(图版Ⅰ-a)。
(2)似斑状角闪黑云环斑花岗岩
似斑状结构、花岗结构,矿物成分:长石52%,石英24%,角闪石8%,黑云母13%,榍石3%。岩石由长石、石英、角闪石、黑云母组成。斑晶为斜长石,呈半自形板状,粒径13mm左右。基质由斜长石、碱性长石、角闪石、黑云母组成。长石呈自形、半自形板状,粒径0.28~0.82mm。石英呈他形粒状,与长石颗粒构成镶嵌状。角闪石呈自形横切面和柱状,角闪石全部具绿泥石化。黑云母呈片状(图版Ⅰ-b)。
(3)中粒黑云二长花岗岩
半自形粒状结构、部分交代残余结构,块状构造,矿物成分:石英22%,斜长石33%,碱性长石40%,黑云母5%。岩石主要由长石、石英组成,矿物粒径大部分在2~4.5mm之间。石英呈他形粒状,长石多呈半自形板状、粒状。岩石条纹长石中的钠长石被钾长石置换(图版Ⅰ-c),构成交代残余结构。斜长石和碱性长石均有不同程度的粘土化、绢云母化(图版Ⅰ-d)。
2. 测试方法
秦岭梁环斑花岗岩样品主量、微量和稀土元素测试分析在陕西省地质矿产实验研究所(自然资源部西安矿产资源监督检测中心)完成。其中,主量元素采用X射线荧光光谱仪(XRF)分析完成,微量和稀土元素采用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICPMS)测定。X射线荧光光谱分析熔片法按国家标准GB/T 14506. 28—1993,相对误差小于2%。微量元素采用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪进行测定,相对误差小于10%。
锆石挑选工作在河北省地调所实验室完成,锆石样品的制靶、锆石阴极发光(CL)图像照相及锆石U-Pb同位素组成分析在西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室完成。使用环氧树脂将挑选好的晶形完整、透明度好的锆石样品固定制靶并抛光,然后进行CL图像照相及定年测试分析。样品锆石的CL图像照相由MonoCL3+型阴极荧光谱仪完成;锆石U-Pb同位素分析由LA-ICP-MS仪器完成,该系统由ELAN 6100DRC四级杆质谱仪、ComPex102激光器及GeoLas200M光学系统组成。激光剥蚀孔径为30μm,激光剥蚀样深度为20~40μm。单个分析点的同位素比值和同位素年龄的误差(标准偏差)为1σ, 采用年龄为206Pb/238U年龄, 其年龄加权平均值具有95%的置信度。锆石年龄计算均采用标准锆石91500为外标,元素含量采用美国国家标准物质局人工合成的硅酸盐玻璃NIST SRM610作为外标,29Si为内标元素进行校正,样品的同位素比值和元素含量数据处理采用GLITTER(4.0版,Macquarie University)软件,并采用Anderson(2002)软件对测试数据进行普通铅校正[29],年龄计算及谐和图采用Isoplot(3.00版) [30]软件完成。
3. 锆石U-Pb测年
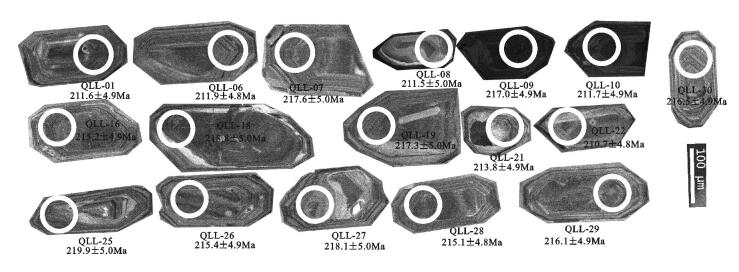
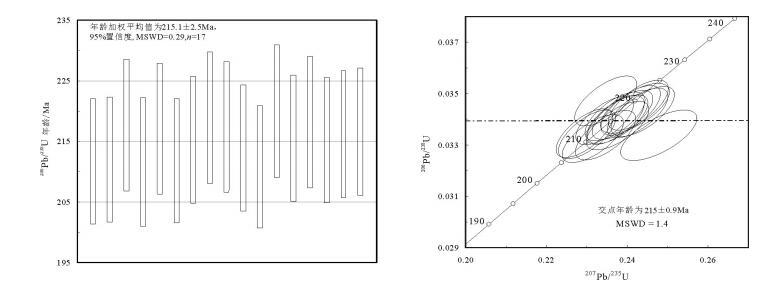
本文所采秦岭梁岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄样品QLL-1RZ的采样点地理坐标为北纬34° 09.613′、东经107°18.694′。用于测年的样品为似斑状黑云环斑花岗岩。锆石晶体为浅黄色-无色,大部分颗粒较大;呈自形长柱状-短柱状,个别颗粒较小,呈浑圆状。锆石CL图像显示,晶体有少量溶蚀,个别破裂明显,生长环带清晰(图 4)。样品QLL-1RZ选取17颗锆石进行LA-ICP-MS分析,分析结果见表 1。17个测点谐和度较好,数据点在谐和图上整体落在谐和曲线上,其Th/U值为0.54~ 0.71,Th、U含量较高,分别为9×10-6~34×10-6、13× 10-6~70×10-6。锆石生长环带清晰,为岩浆成因锆石[31-32],该岩浆岩锆石的U-Pb同位素体系保持完全封闭,未受后期变质作用扰动。17个测定数据点拟合的直线与谐和曲线的交点年龄为215.0±0.9Ma。17个锆石最终测定的206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值为215.1±2.5Ma(95%置信度;MSWD=0.29)(图 5)。卢欣祥等[21]获得的秦岭梁环斑花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄为217±3Ma[21],与本次获得的锆石U-Pb年龄基本吻合,由此判断秦岭梁环斑花岗岩岩体侵位于晚三叠世。
表 1 秦岭梁岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果Table 1. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb dating results of Qinlingliang rapakiwi granite samples样品编号 同位素比值 同位素年龄/Ma 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 208Pb/232Th 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 208Pb/232Th 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ QLL-1 0.05101 0.00122 0.2344 0.0061 0.03336 0.00079 0.00991 0.00034 241 54 214 5 212 5 199 7 QLL-2 0.04980 0.00112 0.2291 0.0057 0.03343 0.00078 0.00979 0.00030 186 52 210 5 212 5 197 6 QLL-3 0.05092 0.00117 0.2406 0.0061 0.03433 0.00080 0.01018 0.00032 237 52 219 5 218 5 205 6 QLL-4 0.05395 0.00163 0.2476 0.0078 0.03335 0.00081 0.01032 0.00050 369 66 225 6 212 5 208 10 QLL-5 0.05146 0.00119 0.2424 0.0062 0.03423 0.0008 0.0105 0.00034 261 52 220 5 217 5 211 7 QLL-6 0.05002 0.00116 0.2298 0.0058 0.03339 0.00078 0.01005 0.00030 196 53 210 5 212 5 202 6 QLL-7 0.05076 0.00115 0.2369 0.0059 0.03395 0.00078 0.01047 0.00031 230 52 216 5 215 5 211 6 QLL-8 0.05111 0.00115 0.2425 0.0061 0.03453 0.0008 0.01057 0.00033 246 52 221 5 219 5 213 7 QLL-9 0.05173 0.00126 0.2437 0.0064 0.03428 0.0008 0.01081 0.00040 273 55 221 5 217 5 217 8 QLL-10 0.05124 0.00129 0.2374 0.0064 0.03373 0.00078 0.01007 0.00038 252 57 216 5 214 5 202 8 QLL-11 0.05068 0.00129 0.2314 0.0062 0.03322 0.00077 0.01087 0.00044 226 58 211 5 211 5 219 9 QLL-12 0.04922 0.00125 0.2344 0.0063 0.03469 0.0008 0.01015 0.00039 158 58 214 5 220 5 204 8 QLL-13 0.05090 0.00123 0.2373 0.0061 0.03398 0.00078 0.0104 0.00036 236 55 216 5 215 5 209 7 QLL-14 0.05120 0.00143 0.2417 0.0070 0.03441 0.0008 0.01065 0.00050 250 63 220 6 218 5 214 10 QLL-15 0.05031 0.00117 0.2342 0.0059 0.03393 0.00077 0.01126 0.00036 209 53 214 5 215 5 226 7 QLL-16 0.05062 0.00122 0.2367 0.0061 0.03409 0.00078 0.01093 0.00039 223 55 216 5 216 5 220 8 QLL-17 0.05094 0.00124 0.2386 0.0062 0.03415 0.00078 0.01093 0.00039 238 55 217 5 217 5 220 8 4. 岩石地球化学特征
4.1 主量元素
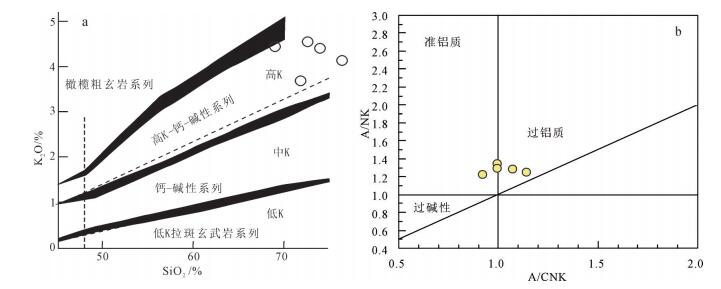
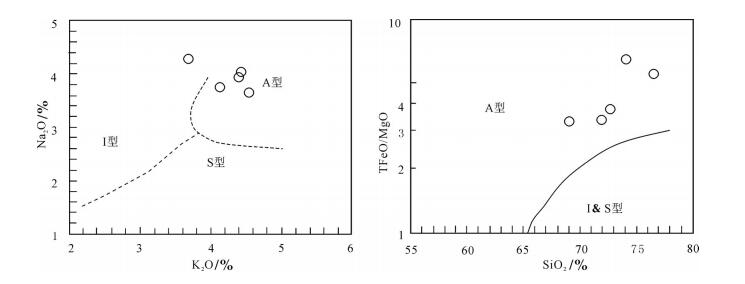
秦岭梁环斑花岗岩5个样品主量元素分析结果及特征参数见表 2。秦岭梁环斑花岗岩具有较高的SiO2(68.58%~75.76%)和Al2O3(13.15%~15.0823%)含量,具有较高的K2O(3.7%~4.55%)含量和全碱含量,里特曼指数(σ=1.85~2.76)较低,具有高钾钙碱性特征,在K2O- SiO2图解中落入高钾钙碱性区域(图 6)。A/NK(Al2O3 /(Na2O + K2O)mol。)=1.22~1.34和A/CNK(Al2O3 /(CaO + Na2O + K2O)mol。)=0.92~ 1.14,显示岩石具有准铝质-过铝质的特点(图 6)。Mg#值为21.52 ~34.79。
表 2 秦岭梁环斑花岗岩主量元素分析结果Table 2. The main elements analytical results of samples from Qinlingliang rapakiwi granite% 样品号 SiO2 TiO2 Al2O3 TFe2O3 MnO MgO CaO Na2O K2O P2O5 烧失量 总计 A/CNK Mg# QLL-5 75.76 0.11 13.15 1.34 0.05 0.22 0.55 3.71 4.09 0.04 0.40 99.42 1.14 24.29 QLL-6 72.25 0.50 13.50 3.09 0.09 0.82 2.00 4.30 3.70 0.19 0.21 100.65 0.92 34.43 QLL-11 68.58 0.56 15.23 3.29 0.07 0.89 2.20 4.01 4.41 0.14 0.23 99.61 0.99 34.79 QLL-14 73.55 0.15 14.27 1.51 0.07 0.21 1.21 3.91 4.37 0.05 0.03 99.32 1.07 21.52 QLL-18 72.67 0.24 14.13 2.25 0.06 0.53 1.82 3.65 4.55 0.11 0.42 100.44 0.99 31.94 注:A/CNK=Al2O3/(CaO+Na2O+K2O);Mg#=Mg2+/(Mg2++Fe2+(全铁))×100 4.2 稀土和微量元素
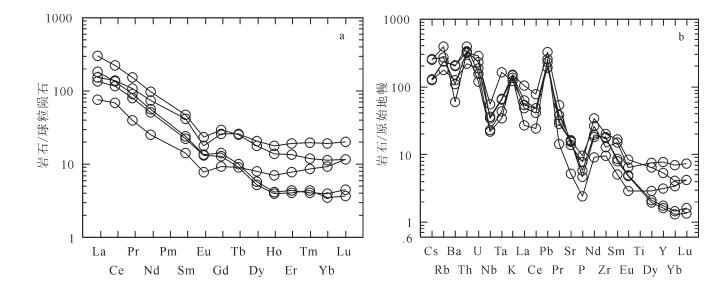
秦岭梁环斑花岗岩5个样品的微量、稀土元素分析结果见表 3。秦岭梁岩体稀土元素总量(∑REE)中等偏低,∑REE平均182×10-6,∑LREE/ ∑HREE值为3.1~9.5。轻、重稀土元素分异程度高,(La/Yb)N为7.9~44.1,稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线呈明显的右倾分配模式(图 7), 反映岩浆作用过程中轻、重稀土元素之间发生了分异作用。δEu值为0.53~0.76,平均为0.67,整体表现出明显的负Eu异常,暗示斜长石分离结晶的发生。基本未表现出Ce异常。微量元素蛛网图主体右倾(图 7),富集Rb、Th、K、Pb、Nd等,贫Ba、Nb、Ta、La、P、Eu等,明显亏损Nb、Ta、P。
表 3 秦岭梁环斑花岗岩稀土和微量元素分析结果Table 3. The rare earth elements analytical results of samples from Qinlingliang rapakiwi granite10-6 样品号 La Ba Ce Rb Pr Sr Nd Y Sm Zr Eu Nb Gd Th Tb Ga Dy Ni Ho Cr Er Hf Tm Sc Yb Ta Lu Co U Pb Cs QLL-5 18.30 417.00 43.20 249.00 3.92 108.00 12.40 14.40 2.26 108.00 0.48 24.50 2.03 26.72 0.36 17.00 2.12 2.16 0.42 13.40 1.36 6.96 0.23 2.88 1.66 2.67 0.31 1.30 6.07 48.00 8.08 QLL-6 37.30 778.00 85.60 172.00 10.50 340.00 35.60 35.50 6.64 145.00 1.07 39.30 5.48 28.33 1.00 20.00 5.54 6.81 1.06 12.80 3.31 6.64 0.52 6.11 3.38 6.66 0.54 5.82 4.92 35.70 8.17 QLL-11 43.70 1450.00 85.30 151.00 8.72 322.00 26.80 7.84 3.80 197.00 0.82 15.60 3.07 27.92 0.39 18.40 1.54 3.32 0.25 7.46 0.78 6.04 0.11 2.05 0.71 1.41 0.12 2.41 2.49 42.30 3.97 QLL-14 33.00 1435.00 73.50 150.00 7.84 336.00 24.40 7.32 3.54 205.00 0.81 16.30 2.77 33.47 0.36 18.20 1.42 4.25 0.24 3.95 0.72 7.28 0.12 4.23 0.64 1.77 0.10 2.74 3.22 43.20 4.15 QLL-18 71.50 875.00 139.00 112.00 14.80 295.00 46.20 24.40 7.38 228.00 1.41 26.00 6.30 18.63 0.98 18.70 4.75 9.40 0.83 19.50 2.32 3.76 0.32 5.65 2.01 2.73 0.31 6.38 3.88 61.20 3.97 ![]() 图 7 秦岭梁环斑花岗岩体球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式图(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)(标准化数据据参考文献[33])Figure 7. Chondrite-normalized of REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle- normalized spidergrams of trace elements (b) of Qinlingliang rapakiwi granite
图 7 秦岭梁环斑花岗岩体球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式图(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)(标准化数据据参考文献[33])Figure 7. Chondrite-normalized of REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle- normalized spidergrams of trace elements (b) of Qinlingliang rapakiwi granite5. 讨论
5.1 岩石成因
秦岭梁环斑花岗岩SiO2(68.58%~75.76%)含量低于典型的环斑花岗岩[18-19]。秦岭梁环斑花岗岩具有较高的K2O、Na2O含量,以及高的TFeO/MgO值,在I-A型图中主要投在A型花岗岩区(图 8),反映秦岭梁环斑花岗岩可能形成于板内环境。Mg#值可以很好地指示岩浆的性质,典型MORB的Mg#值在60左右,玄武质地壳部分熔融可产生Mg# < 45的熔体[34-35]。秦岭梁环斑花岗岩的Mg#=21.52 ~34.79,平均29.39(小于45)。此外,主量元素特征反映秦岭梁环斑花岗岩属于高钾钙碱性系列,具有准铝质-过铝质的特点,说明研究区岩浆岩主要来源于地壳熔融。岩体中暗色包体发育,主要类型为细粒闪长质和二长质的岩浆包体,有的岩浆包体具有细粒边,有的与寄主岩石呈过渡关系。包体的矿物组合明显不平衡, 出现石英+角闪石眼斑;暗色矿物中有石英包裹体;磷灰石呈针状。在包体、寄主岩石及其边界广泛出现卵球状的碱性长石斑晶。这些特征表明,秦岭梁环斑结构花岗岩、环斑结构与岩浆混合关系紧密[25]。以上说明,秦岭梁岩体主要来源于地壳熔融,同时具有岩浆混合特征,即基性岩浆和酸性岩浆的混合。
5.2 构造环境
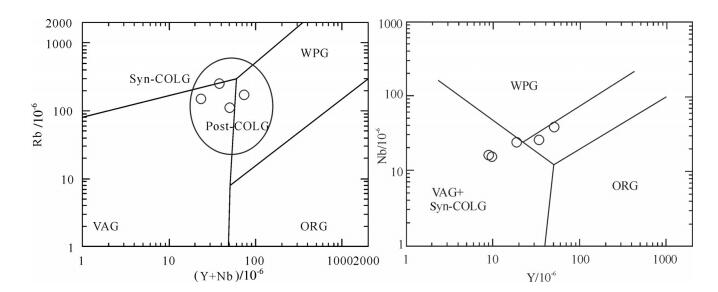
秦岭梁环斑花岗岩产于造山带中,在(Y+Nb)- Rb和Y-Nb图解中主要投入后碰撞花岗岩范围(图 9),反映由造山挤压向相对稳定、伸展环境的转折过渡。前人研究也提出秦岭梁环斑结构花岗岩属于造山带型环斑花岗岩[21-22, 25-28],即与造山作用有关的一种环斑花岗岩或环斑结构花岗岩,不同于世界上主要产在地台区克拉通及其边缘深断裂带中的环斑花岗岩,都是非造山运动的产物,与地壳的伸展时期断裂发育有关。
印支期末—燕山期初,陕西秦岭造山带由后碰撞造山挤压体制末向陆内伸展体制转换,后碰撞增生造山期尾声,整体成山(陆),在特提斯构造域商丹结合带汇聚-碰撞末期陆-陆碰撞,以及太平洋构造域向西俯冲的双重联合影响,使得地壳垂向增生加厚,导致中上地壳部分熔融,产生大量晚三叠世中-酸性花岗岩体,商丹带主体两侧为老君山(214 Ma)、秦岭梁、东江口、沙河湾(209~213Ma)等环斑花岗岩焊接商丹带构造。该阶段既受秦岭板块后碰撞的主造山末期作用控制,又受太平洋板块远程效应影响。
6. 结论
(1)秦岭梁环斑花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石UPb测年结果为215.1±2.5Ma(MSWD=0.29,n=17),显示秦岭梁环斑花岗岩形成于晚三叠世。
(2)秦岭梁环斑花岗岩属于高钾钙碱性系列,具有准铝质-弱过铝质特点,富集Rb、Th、K、Pb、Nd等,贫Ba、Nb、Ta、La、P、Eu等,明显亏损Nb、Ta、P。稀土元素含量中等偏低,轻、重稀土元素分异程度高,稀土元素标准化配分曲线呈明显的右倾配分模式,岩浆主要来源于地壳熔融,同时也具有壳幔混合特点,结合区域地质背景,认为秦岭梁环斑花岗岩形成于造山后伸展环境。
(3)印支期末—燕山期初,陕西秦岭造山带由后碰撞造山挤压体制向陆内伸展体制转换,商丹带主体环斑花岗岩焊接商丹带构造,该阶段既受秦岭板块后碰撞的主造山末期作用控制,又受太平洋板块远程效应影响。
-
图 7 秦岭梁环斑花岗岩体球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式图(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)
(标准化数据据参考文献[33])
Figure 7. Chondrite-normalized of REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle- normalized spidergrams of trace elements (b) of Qinlingliang rapakiwi granite
表 1 秦岭梁岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb dating results of Qinlingliang rapakiwi granite samples
样品编号 同位素比值 同位素年龄/Ma 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 208Pb/232Th 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 208Pb/232Th 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ QLL-1 0.05101 0.00122 0.2344 0.0061 0.03336 0.00079 0.00991 0.00034 241 54 214 5 212 5 199 7 QLL-2 0.04980 0.00112 0.2291 0.0057 0.03343 0.00078 0.00979 0.00030 186 52 210 5 212 5 197 6 QLL-3 0.05092 0.00117 0.2406 0.0061 0.03433 0.00080 0.01018 0.00032 237 52 219 5 218 5 205 6 QLL-4 0.05395 0.00163 0.2476 0.0078 0.03335 0.00081 0.01032 0.00050 369 66 225 6 212 5 208 10 QLL-5 0.05146 0.00119 0.2424 0.0062 0.03423 0.0008 0.0105 0.00034 261 52 220 5 217 5 211 7 QLL-6 0.05002 0.00116 0.2298 0.0058 0.03339 0.00078 0.01005 0.00030 196 53 210 5 212 5 202 6 QLL-7 0.05076 0.00115 0.2369 0.0059 0.03395 0.00078 0.01047 0.00031 230 52 216 5 215 5 211 6 QLL-8 0.05111 0.00115 0.2425 0.0061 0.03453 0.0008 0.01057 0.00033 246 52 221 5 219 5 213 7 QLL-9 0.05173 0.00126 0.2437 0.0064 0.03428 0.0008 0.01081 0.00040 273 55 221 5 217 5 217 8 QLL-10 0.05124 0.00129 0.2374 0.0064 0.03373 0.00078 0.01007 0.00038 252 57 216 5 214 5 202 8 QLL-11 0.05068 0.00129 0.2314 0.0062 0.03322 0.00077 0.01087 0.00044 226 58 211 5 211 5 219 9 QLL-12 0.04922 0.00125 0.2344 0.0063 0.03469 0.0008 0.01015 0.00039 158 58 214 5 220 5 204 8 QLL-13 0.05090 0.00123 0.2373 0.0061 0.03398 0.00078 0.0104 0.00036 236 55 216 5 215 5 209 7 QLL-14 0.05120 0.00143 0.2417 0.0070 0.03441 0.0008 0.01065 0.00050 250 63 220 6 218 5 214 10 QLL-15 0.05031 0.00117 0.2342 0.0059 0.03393 0.00077 0.01126 0.00036 209 53 214 5 215 5 226 7 QLL-16 0.05062 0.00122 0.2367 0.0061 0.03409 0.00078 0.01093 0.00039 223 55 216 5 216 5 220 8 QLL-17 0.05094 0.00124 0.2386 0.0062 0.03415 0.00078 0.01093 0.00039 238 55 217 5 217 5 220 8 表 2 秦岭梁环斑花岗岩主量元素分析结果
Table 2 The main elements analytical results of samples from Qinlingliang rapakiwi granite
% 样品号 SiO2 TiO2 Al2O3 TFe2O3 MnO MgO CaO Na2O K2O P2O5 烧失量 总计 A/CNK Mg# QLL-5 75.76 0.11 13.15 1.34 0.05 0.22 0.55 3.71 4.09 0.04 0.40 99.42 1.14 24.29 QLL-6 72.25 0.50 13.50 3.09 0.09 0.82 2.00 4.30 3.70 0.19 0.21 100.65 0.92 34.43 QLL-11 68.58 0.56 15.23 3.29 0.07 0.89 2.20 4.01 4.41 0.14 0.23 99.61 0.99 34.79 QLL-14 73.55 0.15 14.27 1.51 0.07 0.21 1.21 3.91 4.37 0.05 0.03 99.32 1.07 21.52 QLL-18 72.67 0.24 14.13 2.25 0.06 0.53 1.82 3.65 4.55 0.11 0.42 100.44 0.99 31.94 注:A/CNK=Al2O3/(CaO+Na2O+K2O);Mg#=Mg2+/(Mg2++Fe2+(全铁))×100 表 3 秦岭梁环斑花岗岩稀土和微量元素分析结果
Table 3 The rare earth elements analytical results of samples from Qinlingliang rapakiwi granite
10-6 样品号 La Ba Ce Rb Pr Sr Nd Y Sm Zr Eu Nb Gd Th Tb Ga Dy Ni Ho Cr Er Hf Tm Sc Yb Ta Lu Co U Pb Cs QLL-5 18.30 417.00 43.20 249.00 3.92 108.00 12.40 14.40 2.26 108.00 0.48 24.50 2.03 26.72 0.36 17.00 2.12 2.16 0.42 13.40 1.36 6.96 0.23 2.88 1.66 2.67 0.31 1.30 6.07 48.00 8.08 QLL-6 37.30 778.00 85.60 172.00 10.50 340.00 35.60 35.50 6.64 145.00 1.07 39.30 5.48 28.33 1.00 20.00 5.54 6.81 1.06 12.80 3.31 6.64 0.52 6.11 3.38 6.66 0.54 5.82 4.92 35.70 8.17 QLL-11 43.70 1450.00 85.30 151.00 8.72 322.00 26.80 7.84 3.80 197.00 0.82 15.60 3.07 27.92 0.39 18.40 1.54 3.32 0.25 7.46 0.78 6.04 0.11 2.05 0.71 1.41 0.12 2.41 2.49 42.30 3.97 QLL-14 33.00 1435.00 73.50 150.00 7.84 336.00 24.40 7.32 3.54 205.00 0.81 16.30 2.77 33.47 0.36 18.20 1.42 4.25 0.24 3.95 0.72 7.28 0.12 4.23 0.64 1.77 0.10 2.74 3.22 43.20 4.15 QLL-18 71.50 875.00 139.00 112.00 14.80 295.00 46.20 24.40 7.38 228.00 1.41 26.00 6.30 18.63 0.98 18.70 4.75 9.40 0.83 19.50 2.32 3.76 0.32 5.65 2.01 2.73 0.31 6.38 3.88 61.20 3.97 -
李先梓, 严阵, 卢欣祥.秦岭-大别山花岗岩[M].北京:地质出版社, 1993:1-214. 王涛.花岗岩混合成因研究及大陆动力学意义[J].岩石学报, 2000, 16(2):161-168. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200002003 肖庆辉, 邢作云, 张星, 等.当代花岗岩研究的几个重要前沿[J].地学前缘, 2003, 10(3):222-229. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy200303021 张国伟, 袁学诚, 张本仁, 等.秦岭造山带与大陆动力学[M].北京:科学出版社, 2001:1-806. 张本仁, 骆庭川, 高山.秦巴岩石圈构造及成矿规律地球化学研究[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1994:1-446. 张成立, 王涛, 王晓霞.秦岭造山带早中生代花岗岩成因及其构造环境[J].高校地质学报, 2008, 14(3):304-316. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2008.03.003 张宏飞, 靳兰兰, 张利, 等.西秦岭花岗岩类地球化学和Pb-SrNd同位素组成对基底性质及其构造属性的限制[J].中国科学(D辑), 2005, 35(10):914-926. 卢欣祥, 董有, 常秋玲, 等.秦岭印支期沙河湾奥长环斑花岗岩及动力学意义[J].中国科学(D辑), 1996, 26(3):244-248. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9267.1996.03.005 张宗清, 张国伟, 唐索寒, 等.秦岭沙河湾奥长环斑花岗岩的年龄及其对秦岭造山带主造山期时间的限制[J].科学通报, 1999, 44(9):981-984. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1999.09.020 王晓霞, 王涛, 卢欣祥.北秦岭沙河湾岩体环斑结构特征及有关问题的讨论[J].地球学报, 2002, 23(1):30-36. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2002.01.006 张成立, 王晓霞, 王涛, 等.东秦岭沙河湾岩体成因——来自锆石U-Pb定年及其Hf同位素的证据[J].西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 39(3):453-465. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdxxb200903013 胡建民, 崔建堂, 孟庆任, 等.秦岭柞水岩体锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].地质论评, 2004, 50(3):323-329. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2004.03.016 杨恺, 刘树文, 李秋根, 等.秦岭柞水岩体和东江口岩体的锆石U-Pb年代学及其意义[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 45(5):841-847. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0479-8023.2009.05.017 弓虎军, 朱赖民, 孙博亚, 等.南秦岭地体东江口花岗岩及其基性包体的锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素组成[J].岩石学报, 2009, 25(11):337-350. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200911031 Jiang Y H, Jin G D, Liao S Y, et al. Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints on the origin of Late Triassic granitoids from the Qinling orogen, central China:Implications for a continental arc to continent-continent collision[J]. Lithos, 2010, 117(s1/4):183-197. doi: 10.1016-j.lithos.2010.02.014/
刘春花, 吴才来, 郜源红, 等.南秦岭麻池河乡和沙河湾花岗岩体锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年代学及Lu-Hf同位素组成[J].地学前缘, 2013, 20(5):36-56. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201305004 刘春花, 吴才来, 郜源红, 等.南秦岭东江口、柞水和梨园堂花岗岩类锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年代学与锆石Lu-Hf同位素组成[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(8):2402-2420. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201408021 卢欣祥, 尉向东, 肖庆辉, 等.西秦岭发现奥长环斑花岗岩带[J].地质论评, 1998, 14(5):535. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1998.05.019 Rämö O T, Haapala I. One hundred years of rapakivi granite[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 1995, 52(3):129-185. doi: 10.1007-BF01163243/
Haapala I, Rämö O T. Rapakivi granites and related rocks:an introduction[J]. Precambrian Research, 1999, 95(1/2):1-7. doi: 10.1016-S0301-9268(98)00124-7/
卢欣祥, 尉向东, 肖庆辉, 等.秦岭环斑花岗岩的年代学研究及意义[J].高校地质学报, 1999, 5(4):373-377. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10697-2010115961.htm 王晓霞, 王涛, 卢欣祥.环斑花岗岩研究及存在的问题[J].地质科技情报, 2001, 20(4):19-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2001.04.004 赵太平.对秦岭奥长环斑花岗岩的质疑[J].地质论评, 2001, 17(5):487-491. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2001.05.006 张静, 陈衍景, 舒桂明, 等.陕西西南部秦岭梁花岗岩体的矿物成分研究和相关问题讨论[J].中国科学(D辑), 2002, 2:113-120. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd200202003 王晓霞, 王涛, 卢欣祥, 等.北秦岭老君山、秦岭梁环斑结构花岗岩岩浆混合的岩相学证据及其意义[J].地质通报, 2002, 21(8):523-529. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.08.011 雷泓晏, 张占武, 赵选社, 等.北秦岭老君山环斑花岗岩的成因及大地构造意义[J].陕西地质, 2003, 21(2):49-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6996.2003.02.007 王晓霞, 王涛, 卢欣祥, 等.北秦岭老君山和秦岭梁环斑结构花岗岩及构造环境——一种可能的造山带型环斑花岗岩[J].岩石学报, 2003, 19(4):650-660. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200304006 卢欣祥, 王晓霞, 肖庆辉, 等.答"对秦岭奥长环斑花岗岩质疑"[J].地质论评, 2003, 49(2):146-154. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2003.02.005 Anderson T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192(1):59-79.
Ludwig, K R. User's Manual for Isoplot 3.00. A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J]. Berkeley Geochronology Center, 2003:1-70. doi: 10.1016-j.immuni.2011.10.010/
Wu Y B, Zheng Y F. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(15):1554-1569. doi: 10.1007/BF03184122
Siebel W, Blaha U, Chen F K, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of a dyke-host rock association and implications for the formation of the Bavarian Pfahl shear zone, Bohemian Massif[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2005, 94(1):8-23. doi: 10.1007/s00531-004-0445-0
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processed. Magmatism in Ocean Basins, Geological Society of London Special Publication, 1989, 42:313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Rapp R P, Watson E B. Dehydration melting of metabasalts at 8~32 kbar:Implications for continental growth and crust-mantle recycling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36:891-931. doi: 10.1093/petrology/36.4.891
Rapp R P. Heterogeneous source regions for Archean granitoids.[C]//Wit M J, Ashwal L D. Greenstone Belts. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1997: 35-37.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 严镜,刘景显,蒲万峰,魏学平,李智斌. 西秦岭中—晚三叠世构造属性:来自将其那梁侵入杂岩体的年代学及地球化学证据. 现代地质. 2021(06): 1677-1690 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 柳永刚,杨玉平,李建军,刘文龙,薛金牛,苏秋红,吴建福,胡晓隆. 西秦岭造山带天子坪金矿床成矿时代及成因. 地质通报. 2020(08): 1212-1220 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 武鹏飞,毛深秋,赵旭阳,张学东,陈书文,陈柳. 西秦岭尖藏花岗闪长岩地球化学特征、岩石成因及构造背景. 世界地质. 2020(04): 784-795 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: