Observation and consideration of the vestiges of Quaternary glacier on Lushan Mountain
-
摘要:
在前人研究和笔者长期地质观察的基础上,针对庐山跨世纪的第四纪冰川之争,介绍了庐山白垩纪以来由S形复背斜-地垒式断块山-变质核杂岩的成山过程、地层岩石分布状况及第四纪冰期时的山体地质结构与地貌;就庐山地区冰蚀地貌与冰期、间冰期沉积物争议问题介绍了观察结果与认识。通过更新世冰期与全新世亚热带湿润多雨气候形成的地貌与沉积物对比,揭示了二者的显著差异及泥石流与冰碛的不同;阐明了冰期后流水作用对冰蚀地形的强烈改造作用,以及庐山典型的冰蚀与水蚀复合地貌景观。最后指出,庐山第四纪山岳冰川的形成与其独特的地垒式断块山构造地貌、特凉的小气候等条件密切相关,特厚特硬的莲沱组砂岩是冰川遗迹保存的重要条件。因此,庐山成为中国第四纪冰川地质学的奠基之地和世界上中低纬度、中低山第四纪山岳冰川遗迹保存完美的唯一的地方。
Abstract:On the basis of research results, geological survey in Jiangxi Province and the authors' long-term geological observation and in view of the trans-century controversy of the Lushan Quaternary glacier, this paper deals with the mountain-building processes from S-type anticlinorium through horst block mountain to metamorphic core complexes, the outcrop condition of stratigraphic rock, and the mountain outline during the Quaternary glacier since the Cretaceous period. In addition, it gives the observation results and ideas concerning the disputed problems on the glaciated landform, glacier period and interglacier sedimentation. In comparison with the landform and sedimentation formed as a result of Pleistocene glaciation and Helocene subtropical moist and rainy climate, it reveals the significant differences between them and the differences between debris flow and glacier drift, and clarifies the flowing water influence on the glaciated landform and the typical glaciated and composite equeolandform. Finally, it indicates that the formation and remains of Lushan Quaternary alpine glacier are closely associated with the unique horst block mountain tectonic landform, the coolest microclimate and the thickest and hardest sandstone in Liantuo Formation, thus laying a foundation of the Quaternary glacial geology in China, and holding the unique well-preserved Quaternary alpine glacier vestiges in the mid-low latitude and mid-low mountains in the world.
-
当前,资源保障已上升到国家经济高质量持续发展的战略高度,提高关键矿产资源储备是矿业企业的最紧迫需求之一。在现今世界矿产调查转向“绿地”、深部和覆盖区的大背景下,基于以往国内外一系列大型—超大型矿床的不断发现,覆盖区地质矿产调查日益得到重视,越来越多的地质工作者关注和研究如何更有效地开展覆盖区矿产资源调查[1]。回顾覆盖区地质矿产调查过程,目前主要有2种思路和调查方案:①强调在矿床成矿理论模型或概念(经验)模型指导下直接或借助地球物理异常,以隐伏矿体为目标开展矿产调查,在发现有经济价值的矿体后逐步开展系统的地质、地球物理和地球化学勘探与研究;②强调在获取盖层下伏基岩地质信息的基础上,研究成矿规律和完善成矿模型,进而明确找矿方向和找矿勘探模型,通过系统开展地质-地球物理勘探和研究,借助“穿透性”探测技术“剥离”盖层, 以隐伏矿体或关键控矿因素为目标开展地质矿产调查。从以往国内外实践看,受经济及探测技术发展制约,覆盖区矿产调查早期主要以第一种思路和调查为主,如澳大利亚的奥林匹克坝(Olympic dem)铜-金-铀-稀土矿、美国的卡拉马祖斑岩铜钼矿床和中国20世纪60~70年代的铁矿会战发现的一系列铁矿等。但随着找矿难度越来越大,覆盖区找矿勘探周期加长,成功率降低,第二种思路和方案可持续性的优势逐步体现,在世界许多重要成矿带,大多采用反循环钻和地球物理技术获得盖层之下的基础地质和矿化信息,助力找矿突破,如智利的斯潘塞、加比苏尔、科亚瓦西斑岩铜矿床等[2-3]。
中国地质工作者很早就意识到制约找矿突破的关键首先在于能否有效“剥离”覆盖层,获得下伏基岩的基础地质信息(地层、构造、侵入岩、变质岩、矿化蚀变等)。通过持续安排一些浅覆盖区区域地质填图项目[4-5],中国地质调查局于2017年发布了“1:5万覆盖区区域地质调查规范(试行)”,按照服务对象不同,调查主体分别为:①以覆盖层为调查主体,兼顾基岩基底概略或局部详细地质属性调查,主要服务后续水文、工程、环境、灾害和城市调查;②以盖层下伏基岩为调查主体,兼顾上覆盖层概略调查,主要服务后续成矿带地质找矿调查。重点调查覆盖层下伏基岩中与成矿有关的地层、岩浆岩、变质岩、构造及其与矿化蚀变的关系,查明或推断其空间分布、规模等特征,进而研究区域成矿地质背景和成矿地质条件,并进行成矿预测。对部署在重要成矿区带,服务于浅覆盖区地质找矿的图幅,主要任务是开展覆盖区基岩地质填图和成矿预测,属于浅覆盖区专项地质矿产调查。
浅覆盖区基岩地质填图是一项探索性很强的综合性调查研究工作,不同于传统基岩区地质填图,尚未形成系统的技术规范。因受到探测方法技术经济合理性和有效性的制约,大多数浅覆盖区基岩地质填图可以理解为在局部约束条件下的综合推断解译填图,其填图内容与不同覆盖层属性及下伏基岩地质情况的不确定性均有密切关系。近年来,国内一些地质研究人员运用遥感、放射性、磁法和地球化学元素分析技术[6-7],在原地风化薄层覆盖区(0~3 m)取得较好的填图效果。但对于具有异地风化性质的浅覆盖区(3~200 m)及深覆盖区(大于200 m),多属于专项地质调查(如断裂构造、隐伏岩体或特定地质体)、专项矿产调查(如某类隐伏矿)和基于物性和岩性相关联的岩性填图[8-9]。目前,对如何系统开展1:5万尺度覆盖区基岩地质填图尚处于探索研究阶段[10-11]。
研究区属于典型的异地风化浅覆盖区,其覆盖层较厚,针对此类覆盖区的基岩地质填图工作,目前缺少1:5万尺度的系统研究。前期的地质填图工作①主要根据传统的基岩区1:5万区域地质调查技术规范执行,该项浅覆盖区调查以覆盖层(第四系、古近系—新近系及白垩系)为主体,侧重地表基岩出露区矿产和地表地质环境调查,未能有效填制盖层下伏基岩基础地质图。本文基于近年来在东准噶尔成矿带浅覆盖区的基岩地质填图实践[12],从区域控制局部、深部控制浅部出发,按照由已知到未知,相似类比的基本原则,在分析对比区域地质-地球物理-地球化学信息的基础上,采用地球物理(重力-磁法-激电及电磁法)探测技术先行,结合浅钻验证信息约束,利用多方法、多尺度、多参数互约束解译技术,从填图的基本原则、技术思路、填图内容等方面,尝试探索和总结1:5万尺度的西部戈壁荒漠覆盖区基岩地质填图技术,补齐这方面研究的短板。
1. 填图背景
1.1 地质背景
在大地构造单元划分中,填图区(图 1)位于哈萨克斯坦-准噶尔板块(Ⅰ级)、准噶尔微板块(Ⅱ级),属于阿尔泰南缘-准噶尔北缘增生造山带, 处于北部额尔齐斯-玛因鄂博缝合带以南、乌伦古前陆凹陷盆地北侧。
![]() 图 1 区域地质简图(据参考文献②修改)Figure 1. Simplified regional geological map
图 1 区域地质简图(据参考文献②修改)Figure 1. Simplified regional geological map据全国资源潜力评价研究成果,填图区位于准噶尔北缘成矿带(Ⅲ级),跨越了北部萨吾尔—二台(铜-镍-钼-金-铁)和南部谢米斯台-库兰喀孜干(金-铜-铁)2个Ⅲ级成矿带, 矿带向东西两侧延伸出国(西至哈萨克斯坦、东至蒙古境内),矿带内均已发现中—大型、甚至大型—超大型多金属矿床[13-17],在境内主要分布有索尔库都克铜钼矿、沙尔布拉克金矿、喀拉通克铜镍矿、哈腊苏铜矿等众多中大型矿床, 其中索尔库都克铜钼矿位于填图区西北侧,近年来,新疆地矿局第四地质大队在填图区东南侧和西北侧分别新发现蕴都卡拉铜金钴矿和玉依塔斯铜金矿。
填图区北侧及东侧邻区均以基岩出露为主体,北侧分布早—中泥盆世托让格库都克组、北塔山组和蕴都卡拉组火山岩及火山碎屑岩建造, 为萨吾尔-二台古生代复合岛弧带的一部分; 东侧分布有阿尔曼太-扎河坝蛇绿混杂岩带、泥盆纪—二叠纪火山岩及火山碎屑岩和正常沉积岩。区域上侵入岩主体为华力西中晚期中酸性侵入岩,有少量同期中基性(闪长岩-辉石闪长岩-辉长岩类)侵入体。填图区内主体为第四纪和古近纪—新近纪松散盖层,约占填图面积的90%,仅出露东部和东北角2处基岩。东北角出露早泥盆世托让格库都克组,为一套滨岸相火山熔岩-火山碎屑岩建造,总体产状南倾,以喷溢相为主,岩石组合为玄武岩、安山岩、安山质凝灰熔岩,其中安山岩类较发育。东部基岩区主要出露正(钾)长花岗岩和钠铁闪石碱性花岗岩体(涌动接触),岩体南侧有少量中泥盆世北塔山组,侵入岩与地层呈断层接触,北塔山组火山岩主要为一套海相火山碎屑岩-碎屑岩和少量碳酸盐岩沉积。
1.2 区域重磁场
区域重磁异常显示(图 2),填图区主体位于准噶尔北缘重力高异常带的东南缘,处于乌伦古(索索泉)凹陷重力低异常区北部、扎河坝-二台重力-磁力同低异常带西南部的杜热重力-磁力同高异常区附近。区域重、磁异常走向总体呈北西向,与区域地质构造走向基本一致,西南部乌伦古前陆断陷盆地北侧断裂构造系在重、磁异常场中均有明显显示。填图区围绕喀巴克重力高以断续的似环状重力低异常为特征(图 2-a),北侧索尔库都克南正长花岗岩和区内花岗岩均呈现出局部重力低异常。布格异常最大值出现在喀巴克附近,幅值约-104.1×10-5 m/s2,最低值位于东南部,幅值约-120.1×10-5 m/s2。在区域航磁图中(图 2-b),填图区主体位于北西向低负磁异常区,仅西南部处于北西向高磁异常带的北西段,区内东部局部出露的正长花岗岩和钠铁闪石碱性花岗岩体表现为低负磁异常, 东北部早泥盆世托让格库都克组中基性—中酸性火山岩及其碎屑岩建造呈现主体低负磁异常,伴有零星局部正磁异常,在西南部喀巴克重磁同高异常区局部出露少量正常花岗岩小岩株,东南部和西南部低负磁异常区为第四系覆盖区,对应明显的重力低异常,初步判断存在隐伏中酸性侵入岩体。
1.3 基础地质矿产问题梳理
(1)Ⅲ级构造单元归属问题
在Ⅲ级大地构造单元划分中,前人多以阿尔曼太-扎河坝蛇绿混杂岩带为界,北部属于萨吾尔-二台古生代复合岛弧带,南部为谢米斯台-库兰喀孜干古生代复合岛弧带[18-20]。但扎河坝蛇绿岩带向西是否延伸进入本次填图区,存在较大疑问,按其延伸趋势,呈北北西向在填图区东侧尖灭,在本次填图区邻侧尚无蛇绿混杂岩带再现的地质实证,相应的邻侧仅出露有华力西中晚期花岗岩、中泥盆世北塔山组碎屑沉积岩和第四纪覆盖层(图 1)。1:5万区域地质调查将本次填图区主要归属为中新生代凹陷盆地,但从区域重磁场特征看,蛇绿混杂岩带很可能延伸进入填图区。
(2) 火山穹隆构造问题
火山穹隆构造是否存在直接关系到进一步的找矿方向。新疆地调院李咸阳等①认为,本次填图区西南部喀巴克重磁同高异常现象由火山穹隆引起(图 2)。该区主体为第四纪—古近纪+新近纪松散盖层区,仅于西南部出露一正常花岗岩小岩株,填图区南部外侧出露有华力西晚期碱长花岗岩和早泥盆世托让格库都克中酸性-中基性火山岩、火山碎屑岩建造,火山穹隆构造解译具有较大的不确定性。如此大规模(大于100 km2)的火山穹隆构造有无明显的环状或放射状断裂构造的重磁异常痕迹等证据,均需进一步查证。
(3) 成矿规律与找矿方向问题
与成矿相关的火山活动及岩浆侵入岩活动的时空分布特点是什么?与周边或邻区的矿床成矿作用能否对比?
晚古生代为新疆北部阿尔泰南缘和准噶尔北缘成矿带重要的成矿高峰期,发育有火山岩型铁铜矿(乔夏哈拉-老山口铁铜矿)、斑岩型铜矿(索尔库都克、哈腊苏、希勒库都克)和韧性剪切带中的石英脉-蚀变岩性金矿。从本次填图区邻区已有矿床、矿点分布看,北侧相邻基岩区分布有索尔库都克铜钼矿(中泥盆世北塔山组),东南侧相邻基岩区分布有新发现的蕴都卡拉铜金钴矿(蛇绿混杂岩带),西北侧相邻基岩区分布有斑岩型玉依塔斯铜金矿(中泥盆世北塔山组),南侧相邻基岩区分布有喀巴克南铜金矿点(早泥盆世托让格库都克组)。近年来的研究显示,索尔库都克铜矿成矿时代及矿床类型具有一定争议,但成矿与中酸性侵入岩活动有关和具有多期成矿叠加的特征逐步得到多数学者的认可[17, 21-24]。其西部的玉依塔斯铜金矿也有相似特征,分布在蛇绿混杂岩带中的蕴都卡拉铜金钴矿也具有明显的多期热液叠加成矿特征。因而,对代表不同期次热活动过程的侵入岩体及其地质属性的调查,是指示找矿方向的关键,如区内是否存在钙碱性或高钾钙碱性中酸性侵入岩体活动,是进一步探寻斑岩型铜矿的基础地质因素。
综上所述,无论哪种内生矿床均与特定的中酸性侵入岩体或火山活动、构造单元和地层单元分布等基础地质要素有关。因而,有效“剥离”浅覆盖层,查明下伏地质基本信息(地层、构造、侵入岩、矿化蚀变等),是进一步明确找矿方向和总结成矿规律的基础。
2. 填图方法与技术路线
2.1 基本原则与方法选择
有别于传统基岩区地质填图,浅覆盖区下伏基岩地质图实质上是受局部钻孔地质信息约束的推断解译图,具有较强的探索性,填图结果具有一定的不确定性。类比基岩区地质填图,初步认为,服务于后续矿产专项调查的浅覆盖区基岩地质填图应遵循因地制宜、由已知到未知和相似类比的基本原则。
用于浅覆盖区具有“穿透性”的方法技术很多,包括地质工程(钻探)、地球物理(重力、磁法、电法、电磁法、地震、放射性和遥感)和深穿透地球化学(地气、地电等)。对主体属于异地风化的东准噶尔浅覆盖区,填图基本方法技术选择主要考虑:①具有较好的“穿透性”,可有效获取盖层下伏基岩的有关信息;②方法技术理论成熟,便于野外实施;③具有较好的适用性,宜于推广使用。
考虑到成矿带浅覆盖区的主要服务对象为后续专项矿产资源调查,东准噶尔成矿带浅覆盖区填图采用以地球物理探测方法技术为先导,结合地表已知基岩区和浅钻获取的盖层之下的地质、地球化学综合信息,开展浅覆盖区基岩地质填图。
本次浅覆盖区基岩地质填图主要采用:①1:5万重、磁面积性探测技术,主要用于构造、隐伏岩体和特殊地质体推断解译;②1:5万激电(IP)中梯面积性探测技术,主要用于提取深部隐伏金属硫化物等矿化蚀变信息,辅助判断重磁有关断裂、岩体和特殊地质体的推断解译;③大比例尺综合地球物理(重力-磁法-激电及电磁法)剖面探测技术,主要用于重要地质体定位和定性-半定量调查和找矿远景区或靶区预测;④浅钻化探取样探测和分析技术,主要用于获取盖层下伏基岩地质和地球化学信息,验证和约束地球物理推断解译;⑤岩石地球化学、同位素地球化学取样与分析技术,主要用于成矿地质背景调查。
2.2 填图技术方法
服务于后续专项矿产资源调查的浅覆盖区基岩地质填图,一方面需要尽可能多地提取下伏基岩的基础地质信息,另一方面还需要尽可能提高下伏基岩地质信息推断解译质量,因此,需要结合成矿地质背景调查-地球物理探测-钻孔验证和约束综合推断解译的总体思路。实践中,遵循由已知到未知、相似类比的原则, 按照区域控制局部的基本思路,在区域成矿地质背景、地球物理背景调查和对比分析的基础上, 对区域地质背景关键要素(构造单元、深大断裂构造、地层、侵入岩等)进行预研究分析、梳理出需要关注和解决的关键地质及矿产问题,以地球物理“穿透性”探测技术(重力-磁法-激电及电磁法)为先导开展浅覆盖区探测,利用建立的物性-岩性-地质体初始关联模型,通过对比填图区及邻区基岩区地球物理异常场特征,初步推断解译浅覆盖区的各类基岩地质信息(断裂构造-隐伏岩体-特殊地质体-地质构造单元-地层单元-矿化蚀变带等),通过钻探验证推断解译结果,约束和修正地球物理推断解译结果,完成浅覆盖区基岩地质填图。
3. 填图实践与效果
3.1 物性特征
填图区基岩出露较少,物性样品主要采自北部和东部邻区基岩区。物性(密度及磁性)主要按火山熔岩、火山碎屑岩、沉积岩、侵入岩和含矿岩石进行分类统计(图 3)。
(1) 密度特征:填图区附近松散覆盖层密度较低(1.0~1.76 g/cm3),含矿岩石密度最高(均值大于3.1 g/cm3);火山熔岩类以中基性岩(玄武岩、玄武安山岩)为主,密度值较高(均值2.80 g/cm3),火山碎屑岩(多为安山质或玄武质凝灰岩类)次之(均值2.75 g/cm3);沉积岩类密度一般较低(2.2~2.70 g/cm3)。按照岩石基性程度降低或酸性程度增高,侵入岩类密度幅值呈降低趋势(辉长岩/辉绿岩:2.80 g/cm3,闪长岩:2.72 g/cm3,花岗岩类:2.60 g/cm3)。
(2) 磁性特征:填图区附近沉积岩类呈弱—无磁特征(多小于0.3×10-3SI),含矿岩石表现为弱—无磁性(均值0.8×10-3SI);火山熔岩类和火山碎屑岩类磁性略强(均值6.0×10-3SI),但同类岩石变化范围较大;侵入岩类中,花岗岩类基本呈弱—无磁特征。
依据邻区开展岩(矿)石电性调查,结合以往实践经验,松散覆盖层、火山碎屑岩及正常沉积岩类电阻率和极化率一般均较低,但含有炭质、泥质沉积物时,极化率明显较高;火山熔岩、侵入岩类电阻率一般较高,与其(节理与片理)破碎发育程度负相关,发生热液蚀变时,通常电阻率降低,极化率与其所含金属硫化物数量正相关。含矿岩石基本呈现低阻、高极化特征。
从物性(密度和磁性)统计结果看,尽管同类岩石有时呈现较宽的幅值变化范围,但整体基本符合随岩石基性(或酸性)程度增高(降低)幅值发生规律性变化的一般规律。利用正常物性变化与岩石类型建立的物性-岩石关系,通过重磁位场三维反演技术,可获得填图区内具有不同物性(密度和磁性)特征的地质体(或地质混杂体)的空间分布特征(图 4),作为辅助判断或约束判断填图区覆盖层下伏隐伏岩体、断裂构造和特殊地质体的基础参考。
3.2 地球物理(重磁)场特征
1:5万重磁异常图(图 5)的中部及南部均以成规模的面状异常为主, 北部以条带状异常为主。显示其受到北西向和北东向2组构造控制, 且异常分布以北西向为主。
1:5万重磁异常更好地展示了区域重磁异常未能表达的细节, 为图幅内隐伏构造、隐伏岩体及特殊地质体信息的识别提供了数据保障。图幅北部重力异常表现为多个条带状、似椭圆形异常交错出现,磁异常表现为多个条带状或串珠状异常形态,异常走向多为北西向,夹东北向条带状负异常及异常边界, 判断在图幅中至少存在北西向及北东向2组不同方向的构造。根据2组异常的空间形态可初步判断, 图幅内北西向构造被北东向构造截断, 进一步判断图幅内被截断的北西向构造运动早于北东向构造运动。图幅中部及南部存在一处重磁同高的复合异常, 仔细核对其中重、磁异常的对应关系后发现,重力高异常主体方向为北西向,与低缓磁异常大体一致, 而浅部线状高频磁异常呈现北东向和北西向2组方向, 与基性脉体关系密切,故初步判断该重磁同高异常主体应为基性火成岩的反映;经后期浅钻验证,证实重磁同高异常与后期侵入的闪长岩、辉石闪长岩、辉长岩基性侵入岩杂岩体有密切关系,由此得到了与前人“重磁同高异常由火山穹隆构造引起”①不同的认识,该重磁同高异常应由沿断裂构造分布的中基性侵入杂岩体引起。
3.3 隐伏断裂与构造分区
隐伏断裂构造识别与划分是覆盖区基岩地质填图研究的重点内容之一。区域地质及地球物理场对比显示,在填图区北部和南部分别为额尔齐斯深大断裂和乌伦古深大断裂,均以规模很大的重力梯级带、带状磁异常和两侧有明显差异的重力场区为明显标志。本次填图区断裂构造按大断裂、主要断裂和次级断裂逐级划分。基于断裂破碎带低密度和高导电性基本属性,以重力梯级带和线状重力低异常带作为大断裂的主要划分依据,同时结合磁法线状和局部电法异常成果印证作为辅助判断依据;大断裂的划分与邻区相应的断裂应有较好的对比性,可作为三级构造单元或成矿带的分界断裂;主要断裂和次级断裂主要按照异常规模大小进行逐级划分。填图区共识别出北西向和北东向2组断裂,其中北西向大断裂2条,主要断裂和次级断裂20条(图 6)。
F1大断裂位于填图区北部, 走向北西,区内长约12 km, 两侧延出填图区。该断裂被后期北东向左行断裂F3错断成东西两段,该断裂在地球物理场上呈现明显条带状重力低-低阻异常和负磁异常,重磁边缘检测和局部电磁测深成果显示断裂向北东陡倾。该断裂与东部扎河坝蛇绿混杂岩带北部大断裂可对比相连。
F2大断裂呈北西—南东向(走向约295°)贯穿填图区,区内长约37 km, 两端延出,被后期北东向左行断裂F3错断,重磁边缘检测和局部电磁测深成果显示,该断裂南东段呈现向深部延伸较深,断裂略向南陡倾。
F5断裂为区内北东向主断裂,走向约232°,区内长约28 km,向北东延伸出填图区,南西止于北西向主断裂F13,为后期压扭性左行走滑断裂,呈明显线状重力低异常,两侧串珠状磁异常明显左行偏移。
F13断裂位于填图区西南部,走向北西,区内长约33 km,为后期断裂,两端延出填图区,在地球物理场中表现为明显串珠状、线状重力低异常分割两侧重力高异常,沿断裂有因后期较强磁性的基性岩脉侵入(浅钻验证为辉石闪长岩或辉长岩脉)而呈现的线状高磁异常。
通过与东部扎河坝基岩区地质对比,结合后期浅钻验证,基本可判定F1、F2为填图区2条重要的构造分区断裂带,F1和F2为阿尔曼太-扎河坝蛇绿混杂岩带南北分界断裂,F1以北为萨吾尔-二台古生代复合岛弧带, F2以南为谢米斯台-库兰喀孜干古生代复合岛弧带。华力西晚期为新疆北部增生造山期,区域构造-岩浆作用活跃,地层单元间多为断层接触,对比东部邻区,判断F4为早泥盆世托让格库都克组与中泥盆世北塔山组分界断裂。
3.4 隐伏岩体与成矿专属性
隐伏岩体识别与划分是覆盖区基岩地质填图的主要研究内容之一,因其在物性上与同类溢流喷出火山岩(熔岩)物质成分十分相似,识别与划分隐伏侵入岩体也是基岩地质填图的难点之一。区域侵入岩调查显示,填图区及邻区的各类侵入岩均有分布,以华力西中晚期泥盆纪—石炭纪规模较大的中—酸性侵入岩为主,其中正长花岗岩和碱性花岗岩规模较大,且在填图区已局部出露;次为中—基性侵入岩体(闪长岩及辉石闪长岩),一般规模较小。另在东部扎河坝邻区蛇绿混杂岩带中分布有加里东期代表洋壳残片的基性—超基性侵入岩,超基性岩多蚀变为蛇纹岩。
对已有局部中酸性侵入岩出露的临近覆盖区,主要依据出露区的地质-物性-重磁异常场关联性和异常特征解译,划分该岩体在覆盖区延伸的范围;对填图区内大范围覆盖区,首先依据邻区或外围出露的各类侵入岩体的地球物理场响应特征,建立基岩区不同类型侵入岩体的地球物理场异常标志,结合填图区内已知岩体的地球物理场特征,通过区域地质-地球物理异常场对比,对区内主要岩体的分布及类型进行初步分析和预判;其次,根据不同类型侵入岩的物性变化规律和实测地球物理重磁异常场成果,结合断裂构造及构造分区认识,开展不同类型侵入岩体的识别与分布范围的初步划分,最后,通过电法探测成果和浅钻验证成果,进一步修正和补充各类隐伏岩体的划分范围、种类和属性。
内生金属矿产与侵入岩浆活动有密切关系,在成矿作用研究中,侵入岩体常作为重要的热源体及可能物源体。不同类型的侵入岩活动有不同的成矿专属性,对岩体地质属性的调查有助于成矿规律和找矿方向的认识。岩体地质属性的识别主要依据钻探验证,获取岩石样品局部识别,通常情况下,利用地球物理异常难以准确判别。
区内中酸性岩体主要有正长花岗岩、碱性花岗岩、二长花岗岩、花岗闪长岩和花岗岩,区域上,偏碱性的中酸性侵入岩与稀有金属矿产在空间分布上关联性较好,该类侵入岩规模较大,但在相邻地质单元中尚无成型矿床发现;钙碱性或高钾钙碱性侵入岩体在空间分布上与斑岩型矿床关联性较强,北部萨吾尔-二台古生代复合带中已有索尔库都克和希勒库都克铜钼矿床分布,由此,区内分布的二长花岗岩、花岗闪长岩、花岗岩分布区应注意进一步判断是否有斑岩铜钼矿的其他地质、地球物理和地球化学依据。中—基性岩主要包括(石英)闪长岩、辉石闪长岩和辉长辉绿岩,其中,近年在西北部邻区玉依塔斯已发现与(石英)闪长岩空间分布密切相关的铜金矿床。基性—超基性岩主要包括辉长岩和蛇纹石化超基性岩,为阿尔曼太-扎河坝蛇绿混杂岩带向西的延伸,在邻区该类侵入岩为晚寒武世—早奥陶世的残余洋壳残片[25],近年,扎河坝一带已发现在空间分布上与该类侵入岩有密切关系的蕴都卡拉铜金钴矿床和一些零星分布的铬铁矿点。
隐伏岩体的识别划分主要按照侵入岩体的规模和识别标志复杂或难易程度,依次开展中酸性岩体、中基性岩体和基性—超基性岩体的识别和划分。区内共识别隐伏岩体43处,包括中酸性岩体18处,中基性岩体21处, 基性—超基性岩体4处(图 6)。
(1) 中酸性岩体
依据物性统计和已知中酸性岩体与地球物理异常场关联性分析,通常情况下,中酸性岩体具有明显的较低密度、较高电阻率和弱—无磁性,相应的地球物理异常场判别标志为低重、低磁、高阻异常组合特征,如本次填图区东部出露的正长花岗岩和碱性花岗岩复合岩体。
区内中酸性岩体规模较大、分布较广。对呈等轴状(或似等轴状)负重力-低负磁异常组合判别为中酸性侵入岩体时,应注意与局部断陷盆地的区分关键在于电阻率变化,一般情况下,高阻异常为侵入岩体存在的主要标志;对呈带(墙)状、具一定规模的隐伏岩体与断裂破碎带的区分须借助其高电阻率特征识别;对处于断裂破碎带中、经历后期变形变质、热液蚀变后的该类岩体, 在没有先验地质信息时, 通常不能有效识别,须借助其他信息综合判别;当覆盖层之下的隐伏中酸性岩体呈层状“岩盖”局部上覆于规模较大的中基性侵入岩(或火山熔岩)时,若无先验地质信息佐证,利用地球物理异常标志判别岩体往往会出现较大偏差,如填图区西南部喀巴克一带中酸性侵入岩(局部有正长花岗岩小岩株出露)区表现为明显的重磁同高。
对热侵入岩体,尚需注意其外接触带出现的角岩化或矽卡岩化或后期中基性岩墙或岩脉引起的条带状磁异常、重力场梯度速变带、岩浆期后热液活动可能引起的极化率异常分布特征等,可作为进一步识别中酸性侵入岩体的标志,也是区分同类中酸性火山熔岩(英安岩、流纹岩类)的重要辅助标识。
(2) 中基性岩体
相对于中酸性侵入岩体,填图区及邻区中基性的分布规模明显较小,多呈小的岩株、透镜状或脉状岩墙,在1:5万尺度有明显反映时,通常情况下,具有较明显的高磁、高重和高阻异常组合特征,较易与中酸性岩体区分,但在多数情况下难以与同期的中基性火山熔岩(安山岩、玄武岩类)区分,须结合具体地质背景条件分析。
同期、不同阶段的中基性侵入岩体,通常按基性程度的不同,在磁场中表现为岩体基性程度越高其对应的磁异常幅值越高,但因形态、规模和埋深不同或未知,仍须借助钻探验证成果辨识具体岩性;对于不同期次的中基性侵入岩体,通常晚期侵入的同类中基性岩体的磁异常幅值较强;对于与中基性侵入岩在物质成分或物性相近的同期中基性火山熔岩,依据火山岩区杂乱磁异常特征,条件有利时,可依据孤立的面状磁异常特征,辨识出具有一定规模的的中基性侵入岩体。
区内早—中泥盆世地层经历了较强的区域热变质作用,相应的中基性火山岩(玄武、安山类熔岩)大多发生较强的退磁作用,依据区内物性调查和浅钻验证结果(同类火山岩磁性变化很大),后期侵入的中基性侵入岩多呈现较明显的正磁异常;但在蛇绿混杂岩带,情况有所不同,在后期与成矿相关的较强热液流体作用下,处于热液活动中心附近的中基性侵入岩也会发生较强的蚀变和退磁,虽不能依据地球物理异常辨识出中基性侵入岩体,但对预测和提取成矿信息和圈定找矿远景区或靶区有利。
(3) 基性—超基性岩体
通常,基性—超基性岩体与中基性岩体(或中基性火山熔岩)在地球物理异常场中均表现为“三高”(高磁、高重、高阻)异常组合,一方面,二者均有物质成分(物性)相同的基性岩单元(辉长/辉绿岩);另一方面,由于岩体在形态、规模大小、埋深、经历后期变质作用程度等方面的差异,基性—超基性岩体与中基性岩体难以区分,须结合具体产出的地质背景条件和钻孔验证信息才可能区分。
基性—超基性岩体作为空间上密切相关的杂岩体,通常产出于深大断裂构造附近或蛇绿混杂岩带中。与东部邻区扎河坝蛇绿混杂岩带中蚀变超基性岩体地球物理异常场对比发现,强烈变质变形和热液蚀变作用使基性岩体发生强退磁而呈现无磁特征,超基性岩体强蛇纹石化后形成明显的低重-强磁-低阻异常组合。利用浅钻验证填图区内该类组合异常,证实均为超基性蚀变岩体。
对于区内基性岩体,如辉长岩,在不同的构造区有不同的异常组合特征,在蛇绿混杂岩带,表现为高重-无磁特征,在火山岩区则多为高重-高磁特征。
3.5 特殊地质体
在完成断裂构造和隐伏岩体识别和划分的同时,可进一步研究和确定地质构造单元和地层单元。特殊地质体指对地质构造单元、地层单元具有明确指示意义的地质体,该地质体具有区别于其他地质体的特殊地球物理异常组合,特殊地质体的识别对提高地层单元和构造单元划分可信度具有重要作用。
对特殊地质体的确认,首先从区域地质背景对比中获取填图区内可能存在的地质构造单元及地层单元的基本信息,需要从地层岩石建造的角度分析是否存在能明确指示其存在的特定岩性,且该岩性能在地球物理场上有明显区别于其他岩性的特定地球物理异常或异常组合。对比蛇绿岩套和蕴都喀拉组岩石建造发现,填图区附近,蛇纹石化超基性岩和含炭泥沙岩或含炭沉凝灰岩可明确指示蛇绿混杂岩带和中泥盆世蕴都喀拉组地层单元的存在,同时二者具有明显区别于其他岩性建造的特定的地球物理异常组合。北塔山组火山岩在区域上主要为一套以中基性熔岩为主体的浅海-深海相火山岩,岩石建造类型与早泥盆世托让格组部分段的火山岩组合较相似,单元划分须对比邻区地层展布趋势和地球物理异常场响应特征进行综合判别,判别结果可能有一定主观性。
(1) 蛇纹石化超基性岩
蛇纹石化超基性岩(含铬铁矿)是蛇绿混杂岩带的标志性指示岩性。高重-高磁-高阻的超基性岩蛇纹石化后,由于体积膨胀(35%~40%)和磁铁矿析出,与相伴的基性侵入杂岩体(辉长岩)和基性火山岩(玄武岩)均发生较强退磁,在宏观地球物理场中蛇纹石化超基性岩呈现为高重背景中显著的强磁-低重-低阻异常组合,易于辨识。
(2) 含炭泥砂岩(沉火山凝灰岩)
含炭泥砂岩(沉火山凝灰岩)是指示含炭地层单元存在的重要指示岩性,具有显著区别于其他地质体(或岩性)的地球物理异常:高极化-低阻-低磁-低重异常组合,较容易识别和划分。在区域上分布的含炭质地层单元中,除中泥盆世蕴都喀拉组外,尚有石炭纪姜巴斯陶组(或南明水组),区域对比显示,与北塔山组呈断层接触的含炭地层单元为同期蕴都喀拉组,且在北部邻区与北塔山组呈断层接触。因而,判别区内该类异常组合可直接指示蕴都喀拉组地层单元的存在。
3.6 矿化信息提取与找矿预测
调查下伏基岩矿化蚀变分布信息,进而开展成矿远景区及找矿靶区预测是成矿带浅覆盖区专项地质填图的主要研究目标之一。
矿化信息提取和成矿(找矿)预测基本思路是:在区域成矿地质背景调查和成矿规律对比研究的基础上,初步确定找矿方向和宏观地质地球物理异常场特征,以隐伏断裂构造、岩体和特殊地质体解译为先导,进一步判别可能与成矿用作用有关的隐伏构造、岩体或特殊地质体,继而通过激电(IP)探测获取可能指示金属硫化物分布的极化率异常,利用钻探(浅钻化探)验证提取盖层下基岩的岩性、矿化蚀变信息和主要成矿元素的富集特征,最后,在区域典型矿床调查和与已知矿床综合对比分析的基础上预测找矿靶区。
据前人研究成果③,填图区分属北部萨吾尔—二台铜-镍-钼-金-铁多金属成矿带和南部谢米斯台-库兰喀孜干(金-铜-铁)2个Ⅲ级成矿带,周边泥盆纪火山作用和华力西中晚期岩浆侵入活动发育,与中基性火山作用有关的火山-次火山热液型铜矿和与中酸性侵入岩浆活动有关的斑岩型铜钼(金)矿床是重要的找矿方向。
本次区域成矿地质背景调查发现,阿尔曼太-扎河坝蛇绿混杂岩带受南北2条断裂控制,其内各类岩石强烈片理化、糜棱岩化,为一构造变形强烈的韧性剪切带,东部基岩区发育众多铬铁矿点、金矿点、铜矿点,近年蕴都喀拉铜-金-钴矿床的发现表明,该韧性剪切带是重要的铜-金-钴、铬铁矿成矿远景区,且具有多期复合叠加成矿的特点。填图区隐伏断裂构造、岩体和特殊地质体解译揭示,阿尔曼太-扎河坝蛇绿混杂岩带(韧性剪切带)向西延伸至填图区第四系盖层之下(奥依达格-吉勒库木蛇绿混杂岩带),已有信息表明,在本次填图区内,与蛇绿混杂岩带(韧性剪切带)有关的铜、金、钴矿和铬铁矿是填图区重要的找矿方向。
与西北部玉依塔斯铜金矿和东南部蕴都喀拉铜金钴矿床地质-地球物理特征对比分析发现,矿化蚀变与闪长岩类在时空分布上有密切的关联性,由于在区域热变质作用下中基性火山岩类退磁明显,依据高磁、高重异常组合特征可较好地识别该类岩体的分布范围。在矽卡岩-斑岩型铜金矿区,矿化多与蚀变闪长岩在空间分布上相邻,部分矿化体甚至产于蚀变闪长岩中,在扎河坝蛇绿混杂岩带中,与蛇纹石化超基性岩相伴的蚀变闪长岩中发育铜金钴矿化。
在区域成矿地质背景、成矿规律、找矿方向和邻区已知矿床调查和地球物理场对比的基础上,通过激电测量和钻探验证分析,在填图区提出奥依达格-吉勒库木铜金钴、铬铁矿找矿远景区1处,圈定找矿靶区4处。其中查证程度较高的玉塔斯铜金钴找矿靶区特征如下。
靶区以第四系为主,仅在东北角出露一套基性熔岩-火山碎屑岩夹少量正常沉积碎屑岩建造,未见顶底。该区Au、As、Sb等元素分布形态基本一致(图 7-e),主要沿北西西向断裂构造展布。地球物理异常则是以呈“C”型的极化率异常(图 7-a、b)最明显。该异常规模较大, 北翼长约8 km, 向东未封闭, 南翼长约6 km, 异常强度高, 峰值近8.8%;对应的电阻率异常总体呈带状低阻。经浅钻验证, 高极化率异常主要由含金属硫化物的地质体引起。“C”型高极化率异常与其两翼的低负磁异常和重力低异常带有较好的对应关系。其中,在蛇纹石化超基性岩体和蚀变闪长岩上表现为明显的高极化率-低阻异常特征。
剩余重力异常显示(图 7-c), 在北部重力高异常区中部的较明显带状重力低异常,为F1大断裂的反映, 该异常北侧的高重力异常主体由萨吾尔-二台岛弧带中的中基性火山岩引起, 其南侧高重力异常则由蛇绿混杂岩带中的中基性侵入岩体(闪长岩及辉长岩)引起。南部重力低异常由隐伏中酸性侵入岩体引起, 该隐伏岩体主体为以正长花岗岩和碱性花岗岩(钠铁闪石花岗岩)为主体的复式岩体, 浅钻显示局部有花岗闪长岩、二长花岗岩分布。正磁异常(图 7-d)具明显的条带状特征, 经浅钻验证,其南部线状强正磁异常为蛇纹石化超基性岩的反映, 中部中弱正磁异常为蛇绿混杂岩带中侵入岩体(闪长岩)引起,而沿中部中等磁异常带两侧的低负磁异常带内既有中基性火山岩(玄武安山岩及其碎屑岩), 也有中基性的侵入岩(辉长岩、闪长岩)和酸性岩脉(正长岩脉、霏细岩脉、二长花岗岩脉等), 显示各类岩石均发生较强烈的热蚀变退磁作用。
通过对靶区内“C”形极化率异常、局部磁异常的检查及浅钻验证, 发现玉塔斯靶区与邻区蕴都卡拉铜金钴矿床的地质背景及物化探特征具有较好的可对比性。同时, 浅钻取样分析进一步显示, 在玉塔斯靶区金铜铬镍钴砷等与成矿相关的元素异常相关性明显:靶区内Cu、Au元素具有很好的相关性,为蚀变的中基性火山岩及蚀变闪长岩的反映;Cu、Au元素异常局部与Co元素及Co、Ni元素异常相关性很好,综合分析认为, 该靶区具有寻找隐伏铜金钴矿的较好前景。
4. 结论与建议
(1) 成矿带覆盖区矿产资源潜力巨大,是实现矿产资源战略保障的重要前沿阵地之一,但找矿勘探难度很大;开展覆盖区地质填图是破解找矿勘探难题(风险)的专项基础地质工作;受经济技术条件制约,获取盖层下伏基岩地质信息在较大范围内具有一定的不确定性,尽管国内外已经开展过一些实践探索,就实际效果而言,成矿带基岩地质填图目前尚属于探索性阶段。
(2) 当前经济技术条件下,受经济合理性和方法有效性双重制约,在成矿地质背景调查的基础上,采用成熟的地球物理探测和钻探(获取验证地质、地球化学信息)验证约束解译,是现今开展成矿带覆盖区地质填图的主流趋势。
(3) 本次调查从区域控制局部出发,按照由已知到未知、相似类比的基本原则,在分析对比已知区域地质-地球物理-地球化学信息的基础上,采用地球物理(重力-磁法-激电及电磁法)探测技术先行,结合浅钻验证信息约束,利用多方法、多尺度、多参数互约束综合解译和填图技术,获得了杜热一带浅覆盖区基岩地质图,通过推断解译和钻孔验证,成功预测并发现了覆盖层下伏蛇绿混杂岩带,为区域大地构造环境、成矿地质背景和找矿靶区预测提供重要的基础地质和矿化蚀变信息。
(4) 破解地球物理异常多解性难题是提高覆盖区基岩地质填图质量的关键,实践中尚存在不少问题,如不同地层单元界线划分、岩性识别与界线划分、地质体产状等,其核心问题是通常所建立的地质体-物性-地球物理异常场的关联性模型受多种地质因素影响往往具有较大的不确定性,尤其在成矿带中,区域变质作用、与成矿有关的复杂构造-岩浆活动、变质变形和多期次的热液活动(矿化蚀变)通常会使各类岩性的物性发生明显的变化,使岩性识别与界线划分很难实现。
(5) 钻探验证是有效提高覆盖区填图质量的重要环节,一方面可以通过有效获取盖层下伏基岩的地质和地球化学信息提供成矿地质背景和找矿方向,另一方面通过了解下伏基岩的物性变化情况来减少异常解释多解性和约束区域地球物理场推断解译,但在实践中,因为难以事先了解下伏基岩地质情况的复杂程度,钻探工作量的投入往往具有较大的不确定性。
(6) 在“以钻代槽、以探代钻”等“绿色勘查”发展背景下,基于多视角(方法)探测和观察、相互印证和综合对比分析的大数据融合技术、人工智能技术,因地制宜,加强采用“穿透性”探测技术和高技术含量的新方法技术,开展立体探测和三维地质填图,将成为覆盖区地质填图发展的主要趋势。
致谢: 中国地质科学院陈安泽先生、地质力学所何培元先生对文稿提出了宝贵的修改意见,英文承江西省地质学会龙梅梅女士翻译,谨致感谢。 -
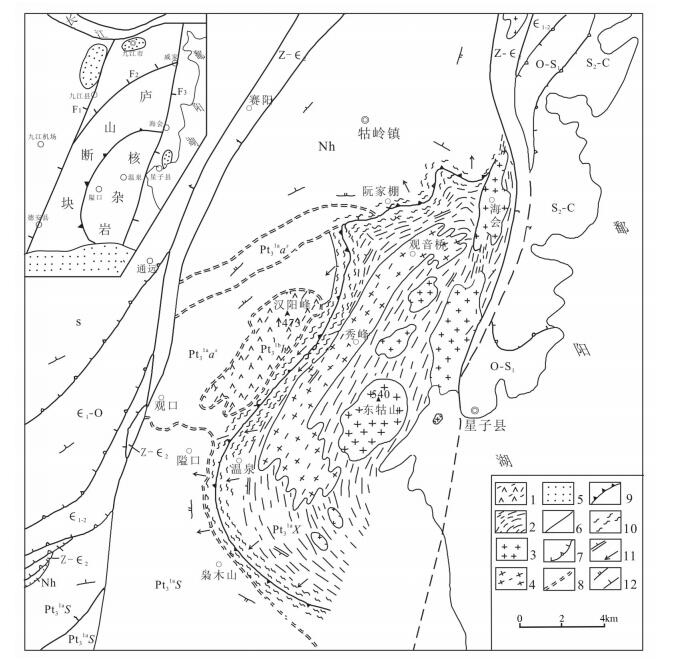
图 2 江西庐山星子变质核杂岩构造地质略图(据参考文献[36]修改)
S2-C—中志留统-石炭系;S—志留系;O-S1—奥陶系-下志留统;∈2-O—中寒武统-奥陶系;∈1-2—中下寒武统;Z-∈2—震旦系-寒武系下统;Nh—南华系;Pt31bh—青白口纪晚期汉阳峰组;Pt31aas—青白口纪晚期筲箕洼段;Pt31aS—新元古代早期双桥山群;Pt31aX—青白口纪早期星子岩群(中深变质);1—陆相火山岩;2—片麻岩;3—燕山期花岗岩;4—晋宁期片麻状花岗岩;5—古近纪红色砂砾岩;6—断层;7—浅层次剥离断层;8—韧性剪切带;9—基底拆离构造带;10—热动力变质带;11—片理和线理;12—劈理和层理;F1—九江-德安断裂带;F2—威家-观口断裂带;F3—湖口(西)-星子(赣江)断裂带
Figure 2. Schematic showing Xingzi metamorphic core complex in Lushan Mountain, Jiangxi
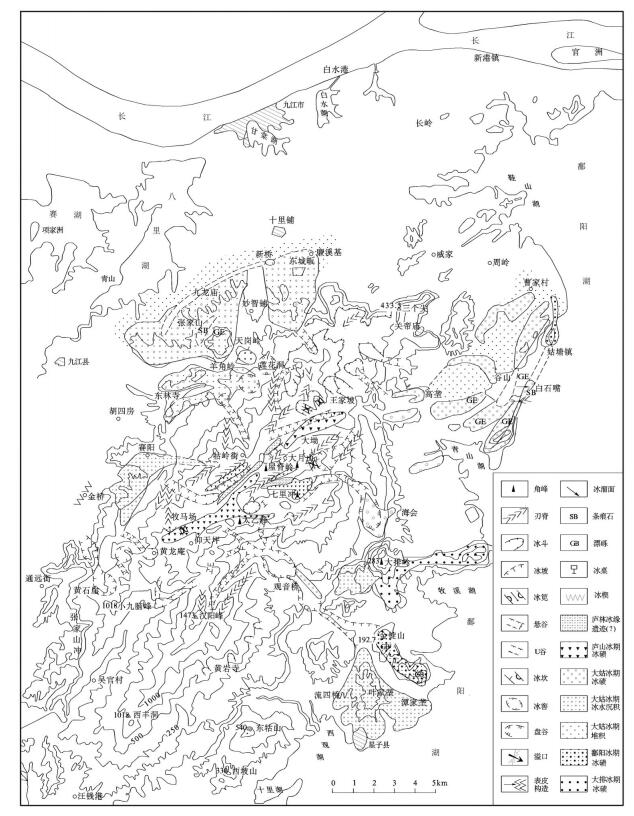
图 3 庐山第四纪冰川遗迹分布图(据参考文献[16]和李四光绘制的原图修改)
Figure 3. Distribution of Quaternary glacier vestiges in Lushan Mountain
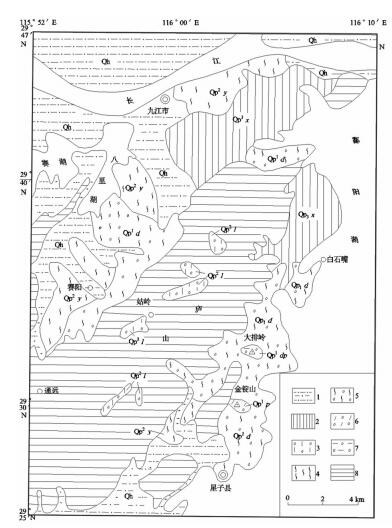
表 1 江西省第四纪地层划分
Table 1 Division of Quaternary strata in Jiangxi Province

-
李四光.扬子流域之第四纪冰期[J].中国地质学会志, 1933, 13(1):15-62. 李四光.关于研究长江下游冰川问题的材料[J].中国地质学会志, 1934, 15(3):359-432. 李四光.冰期之庐山.中国第四纪冰川[M].北京: 科学出版社, 1973: 56-110, 1947: 1-60. 李四光地质工作者在科学战线上做了些什么?[J].新华月报, 3月号, 1952: 167-172. 孙殿卿, 杨怀仁.大冰期时期中国的冰川遗迹[J].地质学报, 1961, 41(3/4):233-239. 方鸿琪.长江中下游地区的第四纪沉积[J].地质学报, 1961, 41(3/4):410-411. 景才瑞.关于庐山冰蚀地形的讨论[J].地质论评, 1958, 18(3):214-223. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1958.03.008 景才瑞, 刘昌茂, 罗志刚, 等.庐山西北麓第四纪冰川作用表皮构造的新发现[J].科学通报, 1980, 25(9):410-411 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB198009007.htm 景才瑞.庐山没有第四纪冰川吗?[J].自然辩证法通讯, 1981, 3(4):42-46. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDZK198302002.htm 景才瑞, 刘昌茂.再论庐山冰川遗迹[J].地理学报, 1987, 42(1):82-85. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1987.01.008 周慕林.庐山真的有第四纪泥石流吗?[J].自然辩证法通讯, 1982, 4(2):40-42. 杨达源.关于更新世冰川作用新认识[J].天津地质矿产研究所所刊.1985, 9:149-151. 杨达源.中国东部山地更新世冰川研究[C]//中国第四纪冰川冰缘学术论文集.北京: 科学出版社, 1985: 31-33. 吴锡浩, 钱方, 浦庆余.东昆仑第四纪冰川地质[C]//青藏高原地质文集.北京: 地质出版社, 1982: 6-23. 何培元.从庐山第四纪地层中高价铁与低价铁的比值关系探讨古温度的变化[J].地质力学研究所刊, 1989:13:61-70 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX198902006.htm 何培元, 段万倜, 邢历生, 等.庐山第四纪冰期与环境[M].北京:地震出版社, 1992:1-167 何培元.中国第四纪古气候环境的重建[J].中国地质科学院院报, 1992, 25:121-130. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ199200003011.htm 何培元.长江干流第四纪沉积相与环境演变[M].北京:地震出版社, 1994:48-55. 蒋复初, 吴锡浩, 肖华国, 等.九江地区网纹红土的时代[J].地质力学学报, 1997, 3(4):27-32. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX704.003.htm 江西省地质矿产局.江西省区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社, 1984:331-357. 江西省地质矿产勘查开发局.江西省环境地质志[M].北京:地质出版社, 2017:44-74. 江西省地质矿产勘查开发局.中国区域地质志·江西志[M].北京:地质出版社, 2017:259-289. 马振兴, 余志庆.江西九江长虹大道第四纪地层剖面特征[J].中国区域地质, 2001, 20(3):352-358. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz200104004 胡东生, 庞西磊, 张华京, 等.庐山冰川活动遗迹新证据[J].华中师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 42(3):467-470. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1190.2008.03.031 陈安东, 田明中, 赵志中.江西庐山牧马场剖面泥砾堆积物的成因分析及年代测定[J].地球学报, 2014, 35(1):111-118. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb201401018 Barbour G B.Analysis of Lushan Glaciion Problem[J]. Bull.Geol. Soe. China., 1934, XⅢ:647-656.
Teilhard, Yong. The Cenozoic Squence in Yangtz Valley[J]. Bull. Geol. Soc. China., 1935, XIN(2):161.
黄培华.中国第四纪时期气候演变的初步探讨[J].科学通报, 1963, (10):29-33 施雅风.庐山真的有第四纪冰川吗?[J].自然辩证法通讯, 1981, 3(2):41-45 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT198201007.htm 施雅风, 崔之久, 李吉均.中国东部第四纪冰川与环境问题[M].北京:科学出版社, 1989:1-462. 施雅风.论李四光教授的庐山第四纪冰川是对泥石流的误读[J].地质论评, 2010, 56(2):683-692. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlp201005009 邓养鑫.庐山羊角岭附近"泥砾"成因的泥石流解释[J].冰川冻土, 1982, 5(1):33-35. 张林源, 牟昀智.庐山羊角岭"表皮构造"成因探讨[J].科学通报, 1981, 26(16):1006-1008. 姚庆元, 庐山地区第四纪沉积物及冰期问题[C]//第四纪冰川与第四纪地质论文集(第一集).北京: 地质出版社, 1984: 98-103. 张兰庭.庐山第四纪地层研究[C]//第四纪冰川与第四纪地质论文集(第一集).北京: 地质出版社, 1984: 86-97. 尹国胜, 谢国刚.江西庐山地区伸展构造与星子变质核杂岩[J].江西地质, 1995, (1):3-15. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXDZ501.000.htm 李武显, 徐夕生, 周新民, 等.庐山星子杂岩中绿帘石花岗岩的定年和成因[J].地质论评, 1998, (2):143-148. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1998.02.005 董树文, 薛怀民, 项新蔡, 等.赣北庐山地区新元古代细碧-角斑岩系枕状熔岩的发现及其地质意义[J].中国地质, 2010, 37(4):1021-1033. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.04.017 史志刚, 高林志, 李廷栋, 等.庐山汉阳峰组变流纹岩锆石U-Pb同位素定年及其地质意义[J].中国地质, 2014, 41(2):326-334. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.02.002 李中兰, 崔学军, 王冉, 等.庐山星子地区中生代构造-岩浆事件与赣江断裂多期活动的关系[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(4):839-848 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200704015 邢厉生.庐山地区第四纪冰期的古地磁年代[J].地质力学研究所刊, 1989, 13:70-78. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ198900021010.htm 李吉均, 舒强, 周尚哲, 等.中国第四纪冰川研究的回顾与展望[J].冰川冻土, 2004, l26(3):235-243. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0240.2004.03.001 马长信, 孙树槐.试论彭山第四纪泥砾的成因[J].江西地质, 1987, 1(2):141-146. 余成就.德安彭山第四纪红色泥砾层的基本特征及成因分析[J].江西地质, 1993, (3):204-222. 赵良政.庐山东南麓冰川作用表皮构造特征及意义[J].地球科学, 1985, 10(4):71-75 赵良政.庐山更新世冰川作用构造特征与辩析[J].地球科学, 1988, 13(6):635-643 潘建英.庐山更新世冰碛与相关沉积的新发现及微结构的研究[J].中国地质科学院地质力学研究所所刊, 1989, 13:45-55. 叶正伟, 吴威.庐山旅游区气候变化特征及其影响因素分析[J].地理科学, 2011, 31(10):1221-1227. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX201110011.htm 傅逸贤.中国东部山地第四纪冰期气候的初步分析[J].中国科学(B辑), 1982, (11):1050-1056. 杨怀仁, 赵英时, 谢志仁.中国东部晚更新世以来的海面升降运动与气候变化[J].第四纪冰川与第四纪地质论文集(第二集).北京: 地质出版社, 1985: 19-30. 竹淑贞, 陈业裕, 孙永福, 等.上海地区第四纪地层与古气候[J].科学通报, 1985, (5):220-223. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10269-2004087116.htm 陈安泽, 浦庆余, 张招崇, 等.黄山花岗岩地貌景观研究[M].北京:科学出版社, 2013:1-156. 江西省区域地质调查大队冰川专题组 .庐山第四纪冰川、 庐山第四纪地层研究,1978. 江西省水文地质工程地质大队 . 鄱阳湖第四纪地质研究报告,1986. 余志庆,何培元,马振兴,等 .庐山第四纪冰川和鄱阳湖第四纪地质研究,1996. -
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 刘诚,唐卫东,杨凯,李含,贺景龙,姚川,李新斌. 荒漠浅覆盖区萤石矿定位预测技术研究. 西北地质. 2024(04): 144-156 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 康磊,刘生荣,张海迪,王国灿,郭伟立,罗彦军,任广利,吕鹏瑞,曹凯. 戈壁荒漠浅覆盖区1:5万区域地质填图技术方法探索——以东天山哈密地区为例. 地质通报. 2023(04): 616-630 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 王幻,王书来,黄波,王泉,冉皞,张培烈. 新疆希勒库都克铜钼矿床成矿地质特征与找矿勘查模型. 地质通报. 2023(09): 1467-1479 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 程先钰,张天福,程银行,刘行,胡鹏,吴志伟,武志宇. 准噶尔盆地东缘中—晚侏罗世细碎屑岩地球化学特征:物源与古沉积环境恢复. 地质通报. 2022(11): 1950-1966 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 韩庆彬. 新疆西南天山地区水系沉积物测量地球化学特征及找矿方向. 山东国土资源. 2022(12): 10-17 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: