A study of the development regularity and formation mechanism of ground subsidence in shallow coal seam mining of Yangchangwan coal mine, Ningxia
-
摘要:
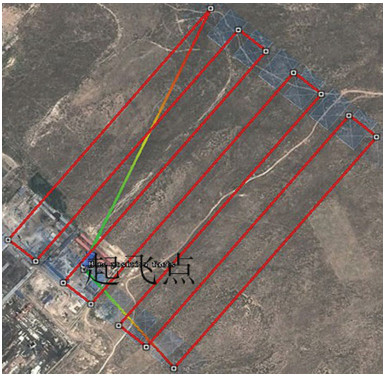
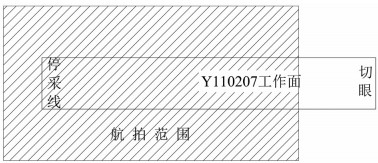
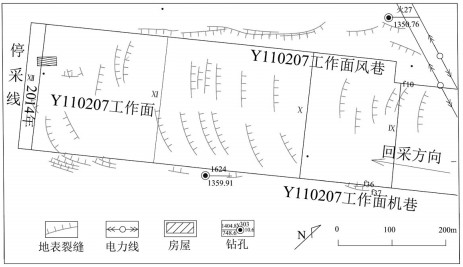
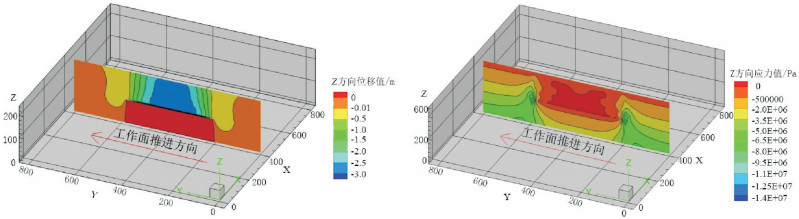
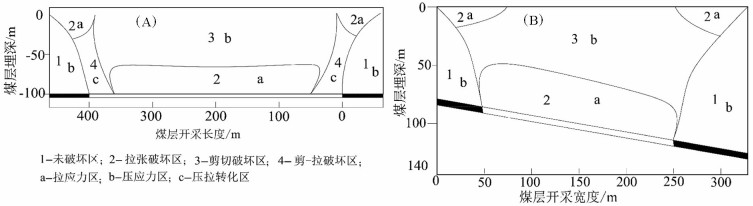
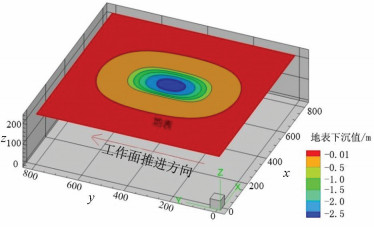
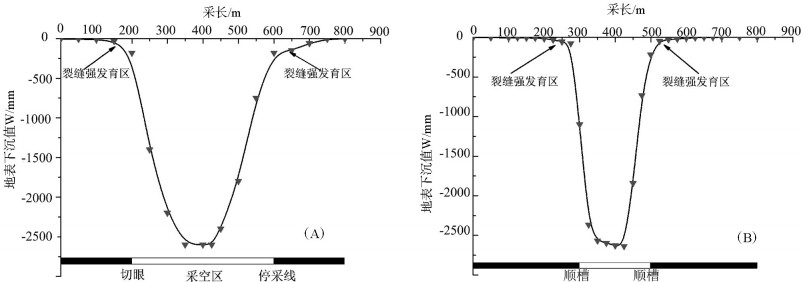
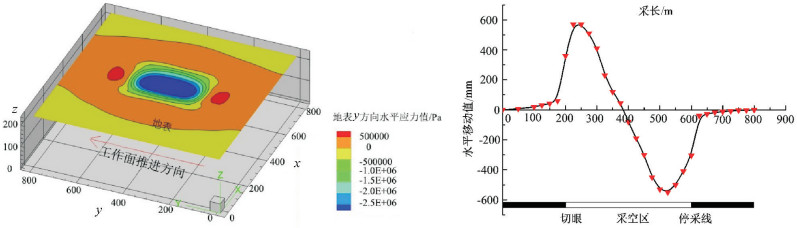
以宁夏羊场湾煤矿Y110207工作面为研究对象,采用无人机遥感技术、野外调查与有限差分软件模拟方法研究浅埋煤层开采的地面塌陷类型、发育规律及其形成机理。①浅埋煤层开采地面塌陷以地表裂缝发育为主,地表破坏严重。②平行切眼裂缝间隔性出现,展布于整个工作面内,间隔距离为10~120m,局部裂缝形成错台高度约为15cm。平行顺槽裂缝为拉张型裂缝,发育在顺槽至外围一定范围。③采煤活动导致地下形成采空区,上覆岩层发生移动破坏,破坏区分为剪切破坏区、拉张破坏区及剪-拉破坏区,分别对压应力区、拉应力区和压-拉转化区。④当应力扰动传递至地表,应力值超过覆盖层抗拉强度时地表产生裂缝。随着工作面推进,覆岩内部裂缝带上行裂缝与地表下行裂缝贯通,形成错台。研究成果丰富了该区浅埋煤层的地面塌陷理论知识,为地面塌陷防治提供了理论依据。
Abstract:The mechanism of ground subsidence induced by coal mining is an important theoretical basis for the prevention and is also one of the hotspots in the study of geological environment. Subsidence type, features and the mechanism were studied by methods of the UAV remote sensing technology, field observation and numerical simulation software on the Y110207 working face in Yangchangwan coal mine, Ningxia. The results show that, during shallow coal seam mining, cracks and surface collapses are developed, which cause ground surface destruction. In the working face, the parallel cutting cracks are distributed with an interval distance between 10~120m. The parallel channel fracture is a tensile fracture, which is developed in a certain range from the trough to the periphery. The coal mining activities lead to the move and destruction of the overlying strata. The damage can be divides into three types, i.e., shear failure zone, tensile failure zone and shear-tensile failure zone, corresponding to compressive stress region, tensile stress zone and compression tensile transition zone. When the stress is more than the tensile strength of the covering layer transferring to the surface, the cracks will occur. With the advancing of the working face, the water flowing fracture zone will develop to the surface. After that cracks will perforate and the staggered platform will emerge. It enriches the theoretical knowledge of ground subsidence in shallow coal seam and provides a theoretical for the prevention.
-
致谢: 地表裂缝的野外调查工作由羊场湾煤矿地测科张仲杰等工作人员协助完成, 在此表示衷心的感谢。
-
表 1 MD4-1000四旋翼低空无人机指数
Table 1 MD4-1000 four indexes of the UAV
性能指标 参数 爬升速率 7.5m/s 最大功率 1000W 飞行时间 <50min/电池 飞行半径 5000m 遥控距离 5000m 巡航速度 15.0m/s 机身自重 2650g 任务载荷 2000g(最大) 飞行高度 1000m 抗风能力 <12m/s 表 2 岩石力学参数
Table 2 Rock mechanical parameter table
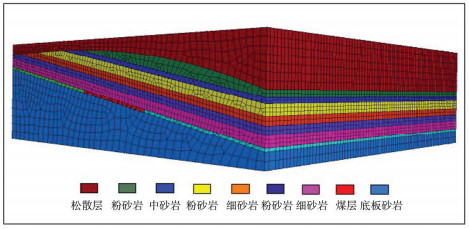
岩性 自重密度/(g·cm3) 体积模量/GPa 切变模量/GPa 粘结力/MPa 内摩檫角/° 抗拉强度/MPa 松散层 1780 2.1 0.4 0.9 28 0.6 粉砂岩 2600 3.0 1.1 1.2 33 0.8 中砂岩 2650 4.6 1.2 1.0 35 1.1 粉砂岩 2600 3.3 1.8 1.3 33 0.8 细砂岩 2750 6.4 2.2 2.0 40 1.0 粉砂岩 2600 3.3 2.5 1.3 33 0.8 砂岩 2900 4.6 1.7 2.0 40 1.3 煤层 2030 2.2 1.0 1.1 31 0.6 底板砂岩 2860 3.9 3.3 3.5 35 1.0 -
何芳, 徐友宁, 袁汉春, 等.煤矿地面塌陷区的防治对策[J].煤炭工程, 2003, 7:10-13. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtgc200307003 初影.采煤诱发地表裂缝数值模拟研究[D].辽宁工程技术大学硕士学位论文, 2009. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10147-1011025019.htm 蔡怀恩, 侯恩科, 张强骅, 等.黄土丘陵区房柱式开采地表塌陷特征及机理分析——以陕北府谷县新民镇小煤矿为例[J].地质灾害与环境保护, 2010, 21(2):101-104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2010.02.023 蔡怀恩.彬长矿区地面塌陷特征及形成机理研究[D].西安科技大学硕士学位论文, 2008. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10704-2008145586.htm 贺卫中, 向茂西, 刘海南, 等.榆神府矿区地面塌陷特征及环境问题[J].煤田地质与勘探, 2016, 44(5):131-135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2016.05.025 赵兵朝, 刘宾, 王建文, 等.柠条塔煤矿叠置开采地表岩移参数分析[J].煤矿安全, 2016, 47(9):213-216. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mkaq201609060 赵兵朝, 刘飞, 凡奋元, 等.黄土沟壑区下斜交叠置开采地表下沉系数研究[J].矿业安全与环保, 2016, 43(5):54-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4495.2016.05.013 杨帆, 余海锋, 郭俊廷.采动地表裂缝形成机理的数值模拟[J].辽宁工程技术大学学报, 2016, 6:566-570. doi: 10.11956/j.issn.1008-0562.2016.06.002 吴侃, 胡振琪, 常江, 等.开采引起的地表裂缝分布规律[J].中国矿业大学学报, 1997, 2:56-59. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10290-2010280128.htm 胡振琪, 王新静, 贺安民.风积沙区采煤沉陷地裂缝分布特征与发生发育规律[J].煤炭学报, 2014, 39(1):11-18. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtxb201401002 胡振琪, 龙精华, 王新静.论煤矿区生态环境的自修复、自然修复和人工修复[J].煤炭学报, 2014, 39(8):1751-1757. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtxb201408048 杜善周.神东矿区大规模开采的地表移动及环境修复技术研究[D].中国矿业大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2010. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11413-2010240648.htm 邓喀中, 王刘宇, 范洪冬.基于InSAR技术的老采空区地表沉降监测与分析[J].采矿与安全工程学报, 2015, 32(6):918-922. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ksylydbgl201506008 王瑞国.基于WorldView-2数据的乌东煤矿地质灾害遥感调查及成因分析[J].国土资源遥感, 2016, 28(2):132-138. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gtzyyg201602022 刘辉, 何春桂, 邓喀中, 等.开采引起地表塌陷型裂缝的形成机理分析[J].采矿与安全工程学报, 2013, 30(3):380-384. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ksylydbgl201303011 余学义, 邱有鑫.沟壑切割浅埋区塌陷灾害形成机理分析[J].西安科技大学学报, 2012, 32(3):269-274. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9315.2012.03.001 刘辉, 刘小阳, 邓喀中, 等.基于UDEC数值模拟的滑动型地裂缝发育规律[J].煤炭学报, 2016, 41(3):625-632. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201603015.htm 黄庆享, 张文忠.浅埋煤层条带充填保水开采岩层控制[M].北京:科学出版社, 2014. 周文生, 吴振宇, 刘海燕.无人机遥感在矿山地质环境调查中的应用[J].地下水, 2014, 2:128-129. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=DXSU201402053&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 张启元.无人机航测技术在青藏高原地质灾害调查中的应用[J].青海大学学报, 2015, 2:67-72. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qhdxxb-zr201502012 侯恩科, 首召贵, 徐友宁, 等.无人机遥感技术在采煤地面塌陷监测中的应用[J].煤田地质与勘探, 2017, 6:102-110. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtdzykt201706017 赵坤阳.煤矿地下开采诱发地表裂缝与导水裂缝分布规律预测[D].中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2015. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1015391331.htm 余学义, 张恩强.开采损害学[M].北京:煤炭工业出版社, 2010.




 下载:
下载: