The influence of ground fissure on Vegetation ecological environment in Ningdong coal mine
-
摘要:
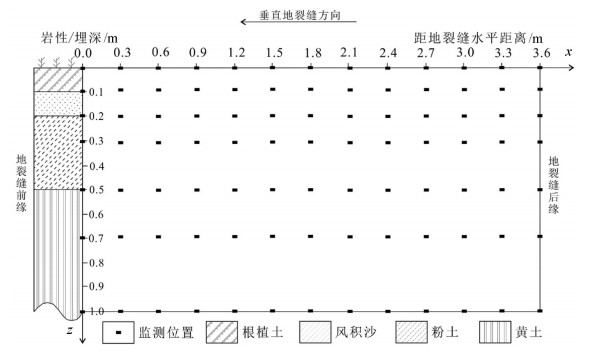
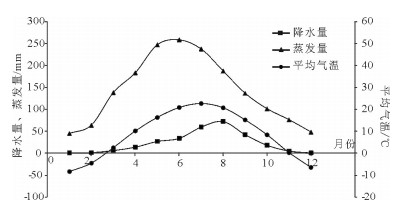
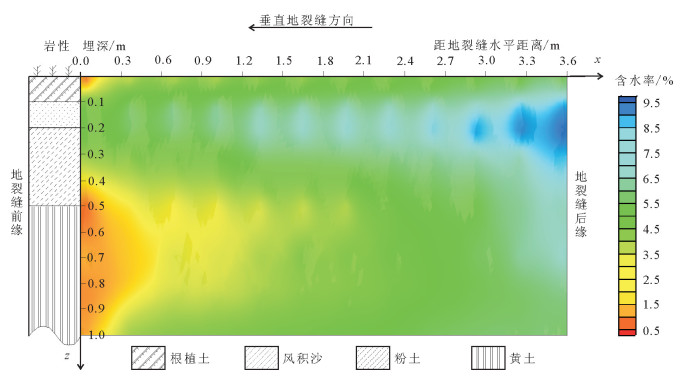
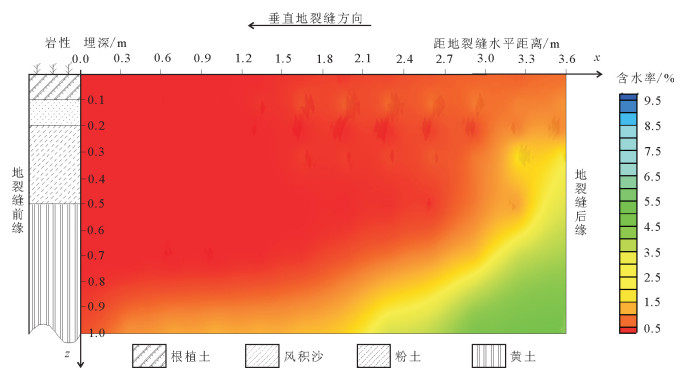
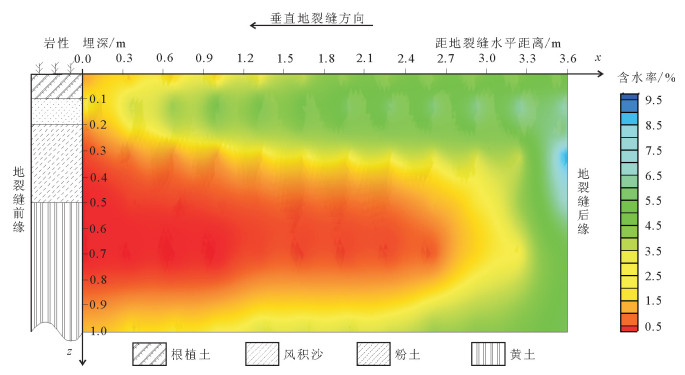
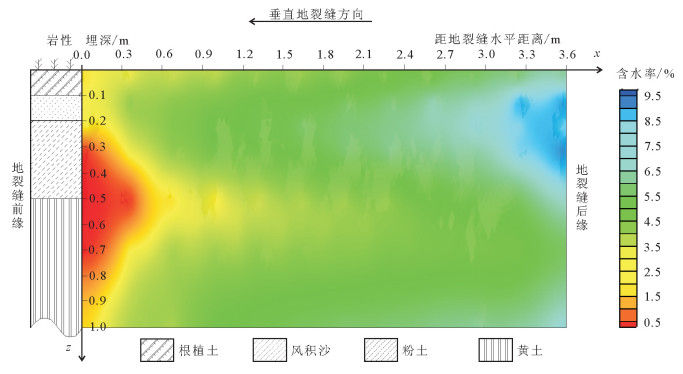
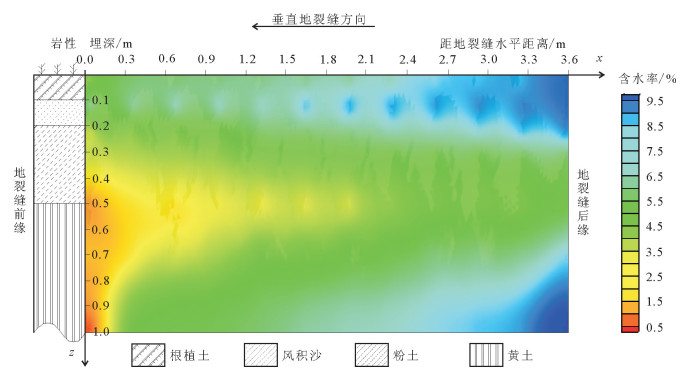
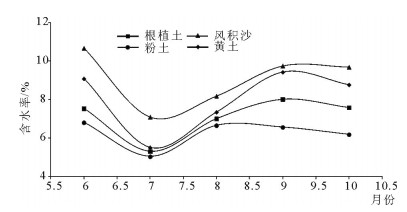
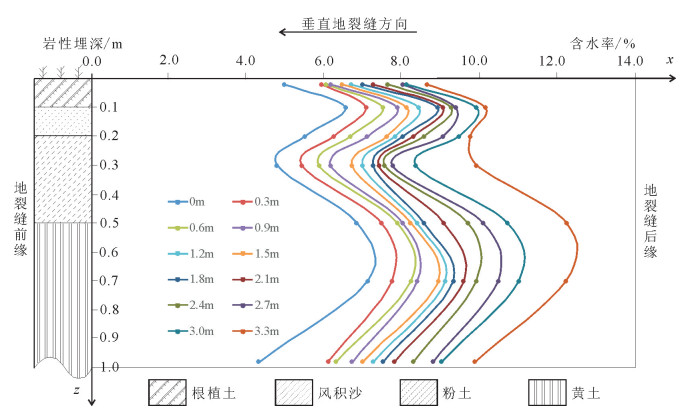
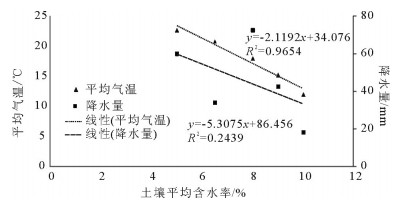
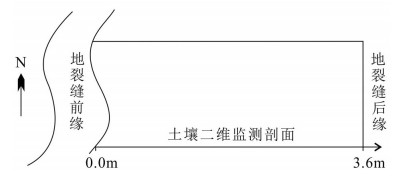
地裂缝地质灾害是植被生态地质环境破坏的一种重要的方式,查明地裂缝对植被生态环境影响的方式、程度、范围等对于宁东煤矿区植被生态环境保护具有重要意义。土壤水分是评价地裂缝是否影响植被生态的重要指标,地裂缝的存在加剧了植被赖以生存的土壤水分的散失,因此,选取典型植被区、土壤岩性结构区的煤矿采空区开展原位试验,分别动态监测裂缝边缘、远离裂缝区包气带剖面不同埋深的土壤水分,结合气象要素分析,以达到研究地裂缝对植被生态环境影响的目的。结果表明:①土壤水分散失空间上水分优先自裂缝裸露面散失,其次才会自地表散失;②土壤水分散失时间呈动态变化,同气温呈正相关关系,其中,7月最大,呈现2个蒸发面,8月次之,呈现1个蒸发面;③受土壤岩性的影响,随着土壤埋深增加,土壤含水率呈"S"形变化特征,不同岩性持水性大小顺序是:风积沙>黄土>根植土>粉土;该结论对于宁东煤矿区植被生态地质环境保护具有重要指导意义。
Abstract:The geological disaster of ground fissures is a kind of important vegetation ecological geological environmental damage, and hence the detection of the influence of ground fissures on the vegetation ecological environment in such aspects as the way, degree and extent for vegetation ecological environment protection of east Ningxia coal mining area is of great significance. Soil moisture is an important index to evaluate whether cracks affect the vegetation ecology; the existence of the ground fissures exacerbates soil water loss of the vegetation; therefore, the selection of typical vegetation area and soil lithology structure area for in situ experiment in the coal mine goaf, the dynamic monitoring of crack edge, and the soil moisture of different buried depths away from the fracture zone vadose section should be done in combination with meteorological elements analysis so as to achieve the purpose of the study of vegetation ecological environment effect of the ground fissures. Some conclusions have been reached:(1) Water loss of soil water is that the water is lost first and the surface is then lost. (2) The time of soil moisture dissipation is dynamic and positively correlated with temperature, with the largest occurring in July, which exhibits two evaporation surfaces, and the second occurring in August, which exhibits one evaporation surface. (3) Affected by soil lithology, soil moisture content shows "S" characteristics with the increase of soil depth, with the order of water-holding property of different lithologic characters being aeolian sand > loess soil > root soil > silt. This conclusion has important guiding significance for the protection of vegetation ecology and geological environment in Ningdong coal mine area.
-
Keywords:
- geofracture /
- vegetation /
- ecological environment /
- moisture content /
- Ningdong
-
致谢: 成文过程中得到中国科学院西北高原生物研究所曹广民教授的指导,在此表示衷心的感谢。
-
-
李海欣, 雷少刚, 申艳琴.煤矿开采沉陷地裂缝对植被覆盖的影响[J].生态与农村环境学报, 2016, 32(2):195-199. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ncsthj201602004 张舞燕.高强度煤炭开采区遥感植被指数响应规律研究——以鄂尔多斯神东矿区为例[D].河南理工大学硕士学位论文, 2014. 申艳琴.半干旱区煤炭开采对植被扰动规律的研究——以神东矿区为例[D].中国矿业大学硕士学位论文, 2014. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10290-1014074772.htm 胡伟, 邵明安, 王全九.黄土高原退耕坡地土壤水分空间变异性研究[J].水科学进展, 2006, 17(1):74-81. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/skxjz200601012 易亮.黄土高原沟壑区生态经济型防护林土壤水分养分特征与空间配置研究[D].西北农林科技大学硕士学位论文, 2009. http://www.lunwentianxia.com/product.sf.4018686.1/ 李小英, 段争虎.黄土高原土壤水分与植被相互作用研究进展[J].土壤通报, 2012, 43(6):1508-1514. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRTB201206042.htm 乔冈, 王文科.西北干旱内陆盆地区裸土蒸发强度[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2014, 44(4):1327-1332. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb201404027 李剑, 赵忠, 袁志发, 等.黄土高原刺槐林地土壤水分垂直分布特征及其动态模型的建立[J].西北植物学报, 2014, 34(8):1666-1675. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbzwxb201408023 赵红梅, 张发旺, 宋亚新, 等.大柳塔采煤塌陷区土壤含水量的空间变异特征分析[J].地球信息科学学报, 2010, 12(6):753-760. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxxkx201006002 张发旺, 赵红梅, 宋亚新, 等.神府东胜矿区采煤塌陷对水环境影响效应研究[J].地球学报, 2007, 28(06):521-527. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb200706002 王云强, 邵明安, 刘志鹏.黄土高原区域尺度土壤水分空间变异性[J].水科学进展, 2012, 23(3):310-316. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/skxjz201203003 Wang W K, Yang Z Y, Kong J L, et al. Ecological impacts induced by groundwater and their thresholds in the arid areas in northwest China[J]. Environmental, Engineering and Management Journal, 2013, 12(7):1497-1507. doi: 10.30638/eemj.2013.184
杨泽元, 范立民, 许登科, 等.陕北风沙滩地区采煤塌陷裂缝对包气带水分运移的影响:模型建立[J].煤炭学报, 2017, 42(1):155-161. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtxb201701021 张延旭, 毕银丽, 陈书琳, 等.半干旱风沙区采煤后裂缝发育对土壤水分的影响[J].环境科学与技术, 2015, 38(3):11-14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS201503005.htm 曹军胜, 朱清, 薛智德.黄土高原地区土地植被承载力与植被生态恢复建设[J].西北林学院学报, 2008, 23(1):39-43. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xblxyxb200801009 程东会, 王文科, 侯光才, 等.毛乌素沙地植被与地下水关系[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 42(1):184-189. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb201201022 范立民, 冀瑞君.论榆神府矿区煤炭资源的适度开发问题[J].中国煤炭, 2015, 41(2):40-44. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgmt201502009 马雄德, 范立民, 张晓团, 等.基于遥感的矿区土地荒漠化动态及驱动机制[J].煤炭学报. 2016, 41(8):2063-2070. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtxb201608025 马雄德, 范立民, 张晓团, 等.榆神府矿区水体湿地演化驱动力分析[J].煤炭学报, 2015, 40(5):1126-1133. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtxb201505023 马雄德, 范立民, 严戈, 等.植被对矿区地下水位变化响应研究[J].煤炭学报, 2017, 42(1):44-49. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtxb201701006 武强, 李学渊.基于计算几何和信息图谱的矿山地质环境遥感动态监测[J].煤炭学报, 2015, 40(1):160-166. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtxb201501024



 下载:
下载: