Zircon U-Pb dating, geochemistry and tectonic implications of Akechukesai gabbro in East Kunlun orogenic belt
-
摘要:
东昆仑地区基性-超基性岩石的研究较薄弱,缺乏对东昆仑幔源岩浆活动及岩浆演化的整体认识。对阿克楚克塞辉长岩进行了地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素研究,结果显示,该岩石形成于晚三叠世早期(219.3±1.1Ma,MSWD=0.80);岩石SiO2含量为49.03%~57.26%,Mg#值为49~57,属于钙碱性系列岩石;稀土元素配分曲线为轻稀土元素富集的右倾型,富集大离子亲石元素Rb、Ba、K,相对亏损高场强元素Nb、Ta、Ti;εHf(t)=-1.81~3.25,锆石Hf模式年龄大于锆石结晶年龄。地球化学特征显示,阿克楚克塞辉长岩岩浆源区应为受俯冲板片流体交代的岩石圈地幔。结合区域构造背景分析,阿克楚克塞辉长岩形成于印支期造山后伸展的构造环境,继承了早期板片俯冲改造的地幔源区特征。
Abstract:The study of basite and ultrabasite in East Kunlun is relatively limited, which results in a lack of an overall understanding of mantle-source magmatic activities and magmatic evolution in East Kunlun. This paper presents geochemical, U-Pb chronological and Hf isotopic studies of gabbro in Akechukesai. The results indicate that the rock was formed in early Late Triassic(219.3±1.1Ma, MSWD=0.80). The rock belongs to calc-alkaline series. The content of SiO2 is 49.03%~57.26% and the values of Mg# are 49~57. The REE distribution curve shows right-dipping feature of LREE. The rock is enriched in LILE(Rb, Ba, K)and depleted in HFSE (Nb, Ta, Ti). The εHf(t)values vary from -1.81 to 3.25 and the Hf model age of zircon is older than the crystallizational age of zircon. Geochemical features of the rock indicate that the Akechukesai gabbro originated from partial melting of the metasomatized lithospheric mantle caused by the dehydration of the subducting slab. Combined with the analysis of regional tectonic setting, the authors hold that the Akechukesai gabbro was formed in an extensional regime of the Late Indosinian, inheriting the characteristics of mantle source altered by early subduction of slab.
-
Keywords:
- gabbro /
- zircon U-Pb age /
- geochemical characteristics /
- tectonic setting /
- Akechukesai /
- East Kunlun
-
川-滇-黔铅锌银多金属成矿区是中国主要的铅锌银矿产基地之一,共发现400多个铅-锌矿床和矿化点。前人主要针对震旦系—二叠系沉积岩中的典型铅锌矿床进行了较系统的矿床地质、矿床地球化学及成矿年代学研究,取得了诸多重要进展[1-4]:① 矿床分布明显受构造控制,属于后生热液矿床;② 成矿物质具有多来源特征,其中基底岩石是重要的物源岩;③ 尽管成矿年龄差别较大,但主要集中于192~226Ma,暗示矿床形成与印支运动有关。而滇中铅锌矿集区赋矿层位多,从昆阳群到第四系各时代地层中均有铅锌矿床赋存,几乎涵盖了所有川-滇-黔成矿区赋矿地层。云南禄劝噜鲁铅锌矿床滇中矿集区赋存于下寒武统梅树村组顶部白云岩地层中。前人仅对滇中矿集区做过报道[5-10],对云南禄劝噜鲁铅锌矿床研究较薄弱,地球化学资料未见报道,制约了该矿床成矿过程和成矿预测研究。
本次在详实的矿床地质研究基础上,开展系统的同位素地球化学和年代学研究,以期查明噜鲁铅锌矿床的成矿特征、物质来源和形成时代,分析矿床形成机制及成矿动力学背景。
1. 区域及矿床地质概况
滇中铅锌矿集区位于扬子地块西南缘,上扬子铅锌成矿带上,其大地构造位置大致北起东川东西向的宝台厂-洪门厂断裂,南到红河断裂西至绿汁江断裂,东达小江断裂。滇中铅锌矿集区地壳结构复杂,具有多层结构的特征。滇中铅锌矿集区地层从古元古界大红山群(苴林群)到新生界第四系均有分布。沉积岩岩性以碳酸盐岩为主。滇中铅锌矿集区经历了多期的构造运动,断裂构造主要有元谋-绿汁江断裂、普渡河-滇池断裂、西昌-易门断裂、小江断裂、红河断裂、弥勒-师宗断裂(图 1)。
![]() 图 1 噜鲁铅锌矿床矿区地质图P2β—上二叠统峨眉山玄武岩组;P1q+m—下二叠统茅口组+栖霞组;∈1d+s—中寒武统双龙潭+陡坡寺组;∈1l—下寒武统龙王庙组;∈1c—下寒武统仓浪铺组;∈1q—下寒武统筇竹寺组;∈1m2—下寒武统梅树村组上段;∈1m1—下寒武统梅树村组下段;Zbdn—上震旦统灯影组;1—城市名;2—断裂(①—元谋-绿汁江断裂;②—西昌-易门断裂;③—普渡河-滇池断裂;④—小江断裂;⑤—红河断裂;⑥—弥勒-师宗断裂);3—湖泊; 4—铅锌矿体;5—断层;6—地层产状;7—地理点;8—地质界线;9-勘探线Figure 1. Geological map of the Lulu Pb-Zn ore district
图 1 噜鲁铅锌矿床矿区地质图P2β—上二叠统峨眉山玄武岩组;P1q+m—下二叠统茅口组+栖霞组;∈1d+s—中寒武统双龙潭+陡坡寺组;∈1l—下寒武统龙王庙组;∈1c—下寒武统仓浪铺组;∈1q—下寒武统筇竹寺组;∈1m2—下寒武统梅树村组上段;∈1m1—下寒武统梅树村组下段;Zbdn—上震旦统灯影组;1—城市名;2—断裂(①—元谋-绿汁江断裂;②—西昌-易门断裂;③—普渡河-滇池断裂;④—小江断裂;⑤—红河断裂;⑥—弥勒-师宗断裂);3—湖泊; 4—铅锌矿体;5—断层;6—地层产状;7—地理点;8—地质界线;9-勘探线Figure 1. Geological map of the Lulu Pb-Zn ore district滇中矿集区受扬子板块与印度板块碰撞及板内攀西裂谷作用的影响,岩浆活动频繁,从古—中生代均有岩浆活动,最重要的是二叠纪基性火山活动,其次为燕山期中酸性岩浆侵入活动。
噜鲁铅锌矿床位于昆明市禄劝县,大地构造位置地处扬子地块西南边缘,小江深大断裂与普渡河-滇池深大断裂之间,目前该矿床仍处于勘查阶段,资源量已达小型矿床规模。
矿区出露地层有新元古界震旦系灯影组(Zbdn)、下寒武统梅树组(∈1m)、筇竹寺组(∈1q)、沧浪铺组(∈1c)、龙王庙组(∈1l)、陡坡寺+双龙潭组(∈1d+s)、下二叠统茅口+栖霞组(P1q+m)、上二叠统峨眉山玄武岩组(P2β)。铅锌矿体赋存于下寒武统梅树组下段(∈1m1)(图 1)。
矿区内构造简单,为宏宽背斜东翼的单斜岩层构造,走向北北西,倾向约70°,倾角多为12°~20°,局部出现小的次级褶曲。在矿区范围内断层不发育,仅南部有1条,且离铅锌矿体较远,对矿体没有明显的破坏作用。
矿区内岩浆活动较强,主要为中上二叠统(P2β),形成上部、下部2个旋回。第一旋回岩性主要以灰绿色斜斑玄武岩为主夹致密玄武岩或斜斑玄武岩。第二旋回岩性主要为底部火山角砾岩、火山角砾玄武质凝灰岩、凝灰岩夹灰岩;向上为熔岩,上部为杏仁状玄武岩;中部致密状玄武岩为主夹杏仁状玄武岩;下部以斜长玄武岩为主。
矿区目前圈定铅锌矿体1个(图 2),矿体赋存于下寒武统梅树村组下段(∈1m1)顶部白云岩中,矿体产状与地层基本一致,呈似层状、局部地段有脉状矿体。矿体地表出露长约150m,倾向南,倾角15°~ 20°,矿体厚度一般为1.70~10.71m,平均厚约3.26m,随深度增大,矿体厚度有逐步变厚的趋势。矿体倾向延伸控制约350m。随着矿体的延深见少量的白云岩夹石呈透镜状分布。矿体Pb品位为0.44%~ 20.00%,平均品位为1.78%;Zn品位为0.56%~9.06%,平均品位为2.01%。
矿石中金属矿物主要为方铅矿、闪锌矿、黄铁矿、白铁矿、毒砂等;非金属矿物主要为重晶石、石英、方解石。矿石中常见菊花状、放射状重晶石(图 3),也可见少量乳滴状沥青。矿石结构主要为自形-他形中细晶状结构、压碎结构、纤维状结构、交代溶蚀结构等。矿石构造主要为块状构造、网脉状构造、浸染状构造、脉状构造、条带状-条纹状构造。围岩蚀变主要有黄铁矿化、硅化、重晶石化、碳酸盐化等。其中黄铁矿化常见黄铁矿呈团块状、星散状、脉状等分布,脉宽最大可达1m,在坑道及老硐见矿位置均普遍分布。重晶石化常见重晶石呈团块状、放射状及细脉状分布于铅锌矿体及黄铁矿周围,较富集。碳酸盐化以白云石化为主,广泛发育于含矿层及顶板、底板,并贯穿于成矿过程的始终。
矿区经历了多期成矿作用,根据矿脉穿插关系、矿物组合及矿石结构,结合区域构造演化过程,将噜鲁铅锌的成矿作用划分为沉积成岩期、热液成矿期和表生氧化期3期,其中热液成矿期可进一步划分为3个成矿阶段,即重结晶白云岩-石英-黄铁矿阶段、黄铁矿-方铅矿-闪锌矿阶段(主成矿阶段)和黄铁矿阶段。
2. 样品及分析方法
样品采自噜鲁铅锌矿床矿区坑道内,新鲜。用于Rb-Sr同位素定年的黄铁矿与方铅矿为矿物共生组合。
Rb-Sr化学分离与质谱测试在中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所固体同位素地球化学实验室完成。同位素比值测试在高精度固体热电离质谱计(IsoProbe-T)上完成。采用单W和单Ta灯丝载入Sr和Rb样品,以纯化的TaF5作为发射剂,以Faraday接收器静态测量锶同位素组成,以Daly接收器监测Rb对Sr的同质异素干扰。测定方法和仪器参数见参考文献[9-10],锶同位素比值采用保守外精度误差0.05‰。
硫同位素组成分析在中国科学院贵阳地球化学研究所环境地球化学国家重点实验室,采用EAIRMS法在连续流质谱仪上完成。用国标GBW04415和04414,Ag2S做内标,以CDT为标准,分析精度约为0.2‰(2σ)。
铅同位素样品测试在核工业北京地质研究院分析测试研究中心进行,先称取适量样品放入聚四氟乙烯坩埚中,加入氢氟酸中、高氯酸溶样。样品分解后,将其蒸干,再加入盐酸溶解蒸干,加入0.5N氢溴酸(HBr)溶液溶解样品进行铅的分离;将样品溶解倒入预先处理好的强碱性阴离子交换树脂中进行铅的分离,用0.5N氢溴酸(HBr)溶液淋洗树脂,再用2N盐酸(HCl)溶液淋洗树脂,最后用6N盐酸(HCl)溶液解脱,将解脱溶液蒸干备质谱测定;用热表面电离质谱法进行铅同位素测量,仪器型号为JY/T004-1996,对1μg的铅,208Pb/206Pb测量精度优于0.005%,NBS981标准值(2δ):208Pb/206Pb= 2.1681 ± 0.0008,207Pb/206Pb=0.91464 ± 0.00033,204Pb/ 206Pb=0.059042±0.000037。
3. 测试结果
3.1 Rb-Sr同位素组成
本次对噜鲁铅锌矿床中的5件硫化物样品进行测试。根据测试结果可知,噜鲁铅锌矿床方铅矿单矿物Rb、Sr含量存在变化。由表 1可见,全部硫化物样品的Rb含量较低(0.1476×10-6~2.013×10-6),Sr含量不高(0.2279 × 10-6~2.957 × 10-6),Rb/Sr值为0.1142~4.0158;87Rb/86Sr值为0.3205~12.17,87Sr/86Sr值为0.712331~0.746457。
表 1 噜鲁铅锌矿床硫化物Rb-Sr同位素组成Table 1. Rb-Sr isotopic composition of sulfides from the Lulu Pb-Zn deposit编号 矿物 Rb/10-6 Sr/10-6 87Rb/86Sr 87Sr/86Sr LL-0-02 黄铁矿 0.1476 1.293 0.3205 0.712331±10 LL-0-04 黄铁矿 2.013 2.957 2.036 0.717113±8 LL-13 方铅矿 0.3405 0.9726 1.037 0.714388±9 LL-34 方铅矿 1.594 1.231 3.814 0.722339±11 LL-36 方铅矿 0.9152 0.2279 12.17 0.746457±8 3.2 硫同位素组成
本次共测试噜鲁铅锌矿床硫化物和硫酸盐矿物样品40件,硫同位素组成见表 2。其中13件方铅矿的δ34S值介于10.32‰~12.82‰之间,平均值为11.32‰;6件闪锌矿的δ34S值介于9.72‰~18.76‰之间,平均值为12.87‰;12件黄铁矿的δ34S值介于12.52‰~22.44‰之间,平均值为17.29‰;9件重晶石的δ34S值介于26.08‰ ~29.34‰之间,平均值为27.29‰;矿石中硫化物δ34S的变化规律为:方铅矿δ34S<闪锌矿δ34S<黄铁矿δ34S<重晶石δ34S,说明热液成矿作用过程中硫同位素分馏达到平衡。硫同位素直方图浓度中心为9‰~15‰(图 4)。
表 2 噜鲁铅锌矿床硫同位素组成Table 2. Sulfur isotopic composition of the Lulu Pb-Zn deposit编号 测试矿物 δ34S/‰ 编号 测试矿物 δ34S/‰ LL-0-01 方铅矿 11.09 LL-27 黄铁矿 16.80 LL-0-02 方铅矿 10.86 LL-29 黄铁矿 13.78 LL-0-04 方铅矿 10.77 LL-32 黄铁矿 16.86 LL-12 方铅矿 11.63 LL-42 黄铁矿 22.44 LL-13 方铅矿 11.66 LL-45 黄铁矿 13.30 LL-16 方铅矿 12.10 LL-0-07 闪锌矿 14.22 LL-28 方铅矿 12.82 LL-32 闪锌矿 10.97 LL-32 方铅矿 11.08 LL-38 闪锌矿 18.76 LL-34 方铅矿 12.27 LL-0-10 闪锌矿 10.38 LL-36 方铅矿 11.01 LL-33 闪锌矿 13.18 LL-41 方铅矿 10.87 LL-0-08 闪锌矿 9.72 LL-42 方铅矿 10.32 LL-0-07 重晶石 27.02 LL-45 方铅矿 10.67 LL-34 重晶石 27.12 LL-01 黄铁矿 22.30 LL-0-08 重晶石 26.36 LL-12 黄铁矿 11.63 LL-0-04 重晶石 27.21 LL-13 黄铁矿 21.57 LL-12 重晶石 26.08 LL-14 黄铁矿 14.35 LL-0-10 重晶石 29.34 LL-14-1 黄铁矿 17.33 LL-13 重晶石 27.92 LL-16 黄铁矿 14.53 LL-16 重晶石 28.47 LL-17 黄铁矿 21.67 LL-14 重晶石 26.09 3.3 铅同位素组成
本次共测试噜鲁铅锌矿床硫化物矿物样品12件,铅同位素组成见表 3。样品206Pb/204Pb值为18.259~18.342,平均值为18.307;207Pb/204Pb值为15.608~15.639,平均值为15.623;208Pb/204Pb值为38.46~38.821,平均值为38.540;铅同位素组成相对均一。样品ω值为36.070~40.860,平均值为37.740;Th/U值为3.690~4.160,平均值为3.838;μ值在9.470~9.560之间,平均值为9.516。样品μ值均小于9.81(现代海洋沉积物的μ值)。
表 3 噜鲁铅锌矿床铅同位素组成Table 3. The lead isotope composition of the Lulu Pb-Zn ore deposits样号 矿物 206Pb/204Pb 207Pb/204Pb 208Pb/204Pb 206Pb/207Pb μ ω Th/U LL-42 黄铁矿 18.342 15.629 38.543 1.174 9.530 37.600 3.820 LL-45 黄铁矿 18.339 15.626 38.532 1.174 9.520 37.540 3.820 LL-0-01 方铅矿 18.283 15.608 38.564 1.171 9.490 37.820 3.860 LL-0-02 方铅矿 18.298 15.615 38.557 1.172 9.510 37.770 3.840 LL-0-04 方铅矿 18.315 15.624 38.561 1.172 9.520 37.780 3.840 LL-13 方铅矿 18.329 15.617 38.545 1.174 9.510 37.570 3.820 LL-32 方铅矿 18.316 15.612 38.46 1.173 9.500 37.240 3.790 LL-34 方铅矿 18.291 15.627 38.558 1.171 9.530 37.930 3.850 LL-36 方铅矿 18.331 15.618 38.537 1.174 9.510 37.530 3.820 LL-41 方铅矿 18.326 15.632 38.535 1.172 9.540 37.690 3.820 LL-42 方铅矿 18.259 15.639 38.539 1.168 9.560 38.150 3.860 LL-45 方铅矿 18.262 15.636 38.548 1.168 9.550 38.140 3.870 4. 讨论
4.1 成矿年代学及成矿构造背景
热液矿物中Rb-Sr主要赋存在矿物晶格中,或赋存在固态微包体、流体包裹体中。随着测试技术的发展,以及Rb-Sr等时线法成功地运用于MVT铅锌矿床定年,众多学者对Rb-Sr定年法进行了研究,证明了Rb-Sr等时线法对铅锌矿床定年的有效性[11-12]。同理,许多学者也运用Rb-Sr法对研究区周边铅锌矿床进行了大量的定年研究[13-15]。前人对铅锌矿床闪锌矿的Rb-Sr同位素定年研究较多,这是因为闪锌矿较其他热液矿物Rb、Sr含量较高,且Rb/Sr值较高、变化范围较大[16]。随着测试技术的发展,方铅矿和黄铁矿的Rb-Sr同位素定年也成为可能[17-19]。田世洪等[18]对玉树地区东莫扎抓铅锌矿床方铅矿与黄铁矿矿物共生组合Rb-Sr等时线年龄进行了研究,并与闪锌矿单矿物Rb-Sr等时线年龄进行比较,两者的等时线年龄在误差范围内一致。黄华等[19]对云南保山金厂河铁铜铅锌多金属矿床方铅矿与闪锌矿矿物共生组合Rb-Sr等时线年龄进行了研究,并与闪锌矿单矿物Rb-Sr等时线年龄进行比较,两者的等时线年龄在误差范围内一致。刘建明等[20]认为,由于不同矿物相具有不同的化学势,化学性质不同的Rb和Sr将发生化学分异,从而使同一成矿母液中沉淀出的一组共生矿物具有不同的Rb/Sr值,用热液矿物组合Rb-Sr等时线测定热液矿床的成矿时代比较理想。因此,笔者运用噜鲁铅锌矿床方铅矿和黄铁矿矿物组合进行Rb-Sr等时线定年。经过Isoplot软件计算,5件硫化Rb-Sr同位素初始值(87Sr/86Sr)i为0.71135± 0.00012,得到202.8±1.4Ma等时线年龄(MSWD= 0.58)(图 5),表明该矿床形成于印支晚期—燕山早期。
前人对区域上其他铅锌矿床做了大量的定年工作,黄智龙[13]等利用闪锌矿单矿物颗粒Rb-Sr法测定的会泽铅锌矿床成矿年龄为226±1Ma、225±1Ma、226±7Ma;蔺志永等[14]利用闪锌矿单矿物颗粒Rb-Sr法测定跑马铅锌矿床成矿年龄为200.1±4.0Ma;包广萍等[15]利用方解石Sm-Nd法测定的茂租铅锌矿成矿年龄为196±13Ma,前人获得年代学数据与本次取得的年代学数据在误差范围内一致。
前人在研究87Sr/86Sr值的二元混合体系时提出,一组参加等时线拟合的样品,通过对其87Sr/86Sr-Sr-1、87Rb/86Sr-Rb-1作图,可以判断是否为混合线。当二者为正相关时,为混合线;二者非正相关时,获得的等时线年龄代表成矿阶段的成矿年龄[18-19]。本次将噜鲁铅锌矿床硫化物Rb-Sr同位素的87Sr/86Sr-Sr-1、87Rb/86Sr-Rb-1作图(图 6)。由图 6可知,典型铅锌矿床各要素之间不存在相关性。因此认为,硫化物Rb-Sr样品拟合的直线具有等时线意义。
川滇黔成矿域C-O-S-Pb-Sr同位素研究表明,峨眉山玄武岩与铅锌矿床成矿存在联系[13]。此外,在川滇黔成矿域,幔源的碱性岩浆岩体形成时代为204~225Ma[21]。晚二叠世—三叠纪,扬子地块和与特提斯洋闭合有关的邻近板块发生碰撞,即印支运动,前人研究认为,印支晚期古特提斯洋向北不断俯冲消减,使华南板块与印支板块在早中三叠世沿松马缝合带碰撞拼合,区内随后向陆内构造体制转化[22]。年代学数据表明,川滇黔成矿域的大规模成矿主要发生在印支晚期—燕山早期,成矿作用和华南板块与印支板块拼合造山作用的时限相吻合。印支运动可能与以上岩浆活动存在联系。韩润生等[23]认为,印支期造山作用对川-滇-黔成矿区铅锌多金属成矿作用产生重要影响。刘肇昌等[24]认为,该区毗邻的龙门山于三叠纪早期开始隆升;高振敏等[25]认为,南盘江-右江在三叠纪几乎同时封闭造山。因此,龙门山造山带、南盘江-右江增生弧型冲褶带在印支期演化过程中必然对该区铅锌成矿作用产生重要影响。前人也认为,川滇黔成矿区天桥铅锌矿床逆冲断层与印支运动存在联系[26]。而噜鲁铅锌矿床成矿时代为印支运动晚期—燕山早期,因此,印支运动可能与噜鲁铅锌矿床成矿存在联系。
4.2 成矿物质来源
4.2.1 硫来源及形成机制
噜鲁铅锌矿床存在硫化物和硫酸盐共同沉淀析出现象。根据矿物组合规律推测,噜鲁铅锌矿床具有较高的氧逸度fO2,成矿流体的总硫同位素组成需综合考虑硫化物中的硫同位素及重晶石的硫同位素[27],即δ34SΣS>δ34S硫化物,δ34SΣS﹤δ34S重晶石。因此,下文将详细讨论该矿床的硫化物和重晶石的硫同位素组成,从而得出成矿流体中硫的来源。噜鲁铅锌矿床矿石矿物黄铁矿、闪锌矿和方铅矿相对富集重硫,其δ34S值浓度中心为9‰~15‰。明显不同于δ34S值在0附近的幔源硫。柳贺昌等[28]认为,区域上震旦系灯影组、寒武系龙王庙组及石炭系大塘组、摆佐组、马平组、黄龙组等中均有石膏、重品石等硫酸盐矿物,其δ34S值约为15%。与噜鲁铅锌矿床硫同位素组成相近,因而噜鲁铅锌矿床硫化物中的硫可能主要来自多个时代地层,为海相硫酸盐的还原产物。
噜鲁铅锌矿床重晶石的δ34S值介于26.08‰~ 29.34‰之间,平均值为27.29‰。滇中矿集区缺少下寒武统硫酸盐硫同位素数据,但Claypool等[29]报道世界其他地区寒武纪海相硫酸盐的δ34S值为30‰左右;于津生等[30]在总结前人研究成果的基础上,认为晚前寒武纪海相硫酸盐岩的δ34S值约为18‰,进入显生宙后,海相硫酸盐岩δ34S值急剧增加到30‰左右,尔后逐渐减小。笔者认为,该矿床中重晶石的硫主要来源于下寒武统海相硫酸盐。因此,硫化物与重晶石中的硫具有同源性。
海相硫酸盐的还原过程主要存在3种观点:热化学还原、细菌还原和有机质热降解。热化学还原较细菌还原发生在相对高温条件且能产生许多还原态硫,形成还原态硫的δ34S值变化范围较小,细菌还原作用发生条件与热化学还原相反[31]。热水塘铅锌矿床δ34S值集中在8‰~13‰之间。笔者测得噜鲁铅锌矿床方解石流体包裹体的均一温度主要分布在12~180℃之间(未发表数据)。前文已述,矿石沉淀时成矿流体中硫已达平衡,可利用矿物对δ34S差值计算成矿温度,利用统一手标本黄铁矿和方铅矿的δ34S差值(表 1)计算的成矿温度为122~ 227℃[32]。综合上述观点,成矿温度超过了细菌可以存活的温度[33]。因此,细菌还原作用对噜鲁锌矿床可能影响较小。有机质热降解通常发生在100~ 150℃, 虽然矿石中常发育有沥青,证明有机质在一定程度上参与成矿,但噜鲁铅锌矿床还没有由碳酸盐岩中有机质热降解作用产生硫的报道,有机质热降解作用贡献大小不能确定。这些特征均表明, 噜鲁铅锌矿床成矿流体中的硫可能为各时代碳酸盐岩地层的海相硫酸盐热化学还原的产物,有机质可能参与了成矿作用。
4.2.2 铅来源
川滇黔铅-锌-银多金属成矿域绝大部分铅锌矿床赋存于不同时代的碳酸盐岩地层的粗晶白云岩、白云质灰岩中,区域分布大面积峨眉山玄武岩。柳贺昌等[28]认为,川滇黔成矿域成矿物质由碳酸盐岩地层和玄武岩提供;李连举等[34]认为,上震旦统、下寒武统、中上泥盆统和石炭系是区域重要的矿源层;胡耀国[35]则认为,成矿物质主要来源于区域基底岩石。
前已述及,206Pb/204Pb、207Pb/204Pb、208Pb/204Pb组成相对均一。据Zartman等[36]的铅同位素构造模式图解,可将数据投在206Pb/204Pb-207Pb/204Pb图(图 7)上,数据点落入上地壳和造山带演化曲线之间,表明在成矿作用过程中,铅是多源混合的产物。该区域在基底岩石的铅同位素组成范围内(图 7),靠近不同时代碳酸盐地层和峨眉山玄武岩,与震旦系灯影组白云岩分布范围相差较远(表 4),与会泽及天桥铅锌矿床也存在差异。这些铅同位素组成特征表明,本区成矿物质主要由基底岩石提供,区域上不同时代碳酸盐岩地层和峨眉山玄武岩可能提供了部分成矿物质。
表 4 噜鲁铅锌矿床铅同位素组成统计对比Table 4. Statistics of Pb isotopic compositions of various rock units in the area统计对象 样品个数 206Pb/204Pb 207Pb/204Pb 208Pb/204Pb 会泽铅锌矿 95 18.251~18.530 15.439~15.855 38.487~39.433 天桥铅锌矿 33 18.378~18.601 15.519~15.811 38.666~39.571 栖霞~茅口组 2 18.189~18.759 15.609~16.522 38.493~38.542 黄龙组 2 15.656~16.675 18.136~18.167 38.204~38.236 摆佐组 8 18.120~18.673 15.500~16.091 38.235~39.685 大埔组 5 18.397~18.828 15.537~16.499 38.463~39.245 灯影组 10 18.198~18.517 15.699~15.987 38.547~39.271 昆阳群 27 17.781~20.993 15.582~15.985 37.178~40.483 会理群 6 18.094~18.615 15.630~15.827 38.274~38.932 峨眉山玄武岩 16 18.175~19.019 15.528~15.662 38.380~39.928 噜鲁铅锌矿床铅同位素组成相对稳定,可能是由于成矿物质来源铅同位素组成相对稳定的地质体或成矿物质来源于铅同位素组成相对不稳定的地质体,成矿流体在沉淀成矿之前存在均一化过程[13]。从表 2可见,区域上基底岩石、玄武岩及碳酸盐岩地层铅同位素组成均有较宽的变化范围,即本区不存在铅同位素组成相对稳定的地质体。因此,笔者认为,本矿床成矿流体在成矿之前可能存在均一化过程。
4.2.3 (87Sr/86Sr)i组成及成矿物质来源
87Sr/86Sr值是判断成岩成矿物质来源的重要指标,在矿床地质研究中,常利用其示踪成矿物质来源。但应用锶同位素组成示踪成矿物质来源时,需要对潜在源区的锶同位素组成进行成矿年龄校正。噜鲁铅锌矿床成矿年龄为202.8±1.4Ma,且近年来,川滇黔成矿域成矿年代学研究取得了重要进展,成矿作用时间集中于约200Ma[28]。经年龄(200Ma)校正后,印支运动产生的基性玄武岩在成矿时的87Sr/86Sr值为0.7039~0.7078[38];扬子地块西南缘各时代沉积的碳酸盐岩在成矿时的87Sr/86Sr值为0.7073~0.7111[23, 41-42];昆阳群基底地层在成矿时的87Sr/86Sr值为0.7243~0.7288 [23]。地幔的87Sr/86Sr值为0.704±0.002[26]。而噜鲁铅锌矿床硫化物在成矿时的87Sr/86Sr值为0.7112~0.7115。通过分析,矿床中硫化物较地幔和峨眉山玄武岩有更多放射性成因锶,成矿物质可能来自于基底地层,或成矿流体流经这些富放射性成因岩体。
4.3 成矿机制
噜鲁铅锌矿床成矿时代主要发生在印支晚期,成矿作用和华南板块与印支板块拼合造山作用的时限相吻合。硫化物和硫酸盐矿物的硫同位素分析结果说明,硫主要为海相硫酸盐热化学还原的产物;硫化物铅同位素组成和Rb-Sr同位素组成证实,成矿物质主要来自基底岩石或成矿流体流经这些富放射性成因岩石。因此,噜鲁铅锌矿床成矿流体中组分来源不同,主要来自于基底岩石,或成矿流体流经这些富放射性成因岩体。基底岩石为噜鲁铅锌矿床提供了成矿流体及重要的成矿物质。噜鲁铅锌矿床围岩和黄铁矿稀土元素揭示,噜鲁铅锌矿床赋矿地层可能为成矿提供了成矿流体,成矿流体可能为富Cl流体,暗示成矿温度应该为中低温,成矿流体可能遭受了外来热液的混入(另文探讨)。
综合上述认识,基底岩石是矿床的成矿流体与成矿物质的重要来源。将该矿床成矿过程描述为,印支期构造旋回过程中,伴随着西面地区大面积玄武岩喷发与沉积建造,产生的热、气与地下热水,驱动来自基底岩石以氯化物络合物形式携带大量成矿金属的含矿热卤水溶液,含矿热卤水溶液沿途不断萃取、溶解高背景地层中的铅-锌-银等矿质,并还原不同时代地层沉积岩中海相硫酸盐的大气降水或层间水发生流体混合,伴随着物理、化学等成矿条件的改变,在有利的空间部分聚集成矿,金属硫化物沉淀形成具有工业价值的矿体。
5. 结论
噜鲁铅锌矿床成矿流体中不同组分来源不同。原生矿石硫化物硫同位素组成δ34S在9.72‰~ 22.44‰之间,多数为9‰~15‰。重晶石δ34S值介于26.08‰~29.34‰之间,平均为27.29‰。矿床中的硫同位素组成变化较大,δ34S值在6.33‰~9.75‰之间。噜鲁铅锌矿床主要是碳酸盐地层的海相硫酸盐热化学还原的产物。铅同位素组成特征表明,本区成矿物质可能由基底地层提供,区域上不同时代碳酸盐岩地层可能提供了部分成矿物质。由锶同位素可知,噜鲁铅锌矿床成矿物质可能来自基底地层,或成矿流体流经这些富放射性成因岩体。Rb-Sr同位素测年表明,噜鲁铅锌矿床成矿年龄为印支中晚期,印支运动对噜鲁铅锌成矿作用产生了重要影响。
硫、铅、铷-锶同位素数据研究成果表明,噜鲁铅锌矿床成矿流体中不同组分来源不同,但主要来自于基底地层,在印支运动强大的驱动力作用下,促使成矿元素活化-混合-迁移-聚集成矿。
致谢: 资料收集过程中得到青海康华矿业公司的大力帮助,实验过程中得到北京燕都中实测试技术有限公司和吉林大学测试实验中心的帮助和指导,在此一并致谢。 -
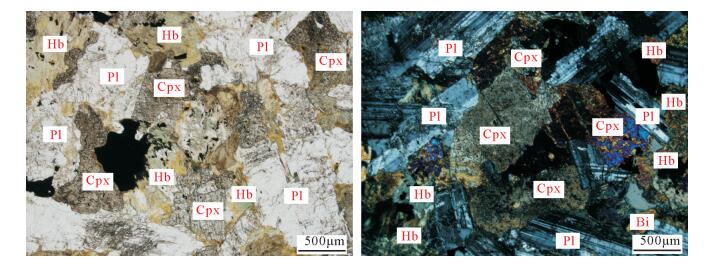
图 1 阿克楚克塞区域大地构造简图[3](a)和研究区地质图(b)
Ⅰ—塔里木地块;Ⅱ—阿北-敦煌地块;Ⅲ—阿尔金造山带;Ⅲ-1—阿红柳沟-拉配泉蛇绿构造混杂岩带;Ⅲ-2—阿中地块;Ⅲ-3—阿帕-茫崖早古生代蛇绿构造混杂岩带;Ⅳ—东昆仑造山带;Ⅳ-1—昆北(祁漫塔格)岩浆岩带;Ⅳ-2—昆中微地块;Ⅳ-3—昆南增生楔杂岩带;Ⅴ—巴颜喀拉褶皱带;Ⅵ—柴达木陆块;Ⅶ—祁连造山带。①—阿尔金北缘断裂带;②—阿尔金南缘断裂带;③—昆北断裂带;④—黑山-那陵格勒断裂;⑤—白干湖断裂;⑥—昆中断裂带;⑦—昆南断裂带;⑧—柴北缘断裂。1—第四系冲洪积物;2—第四系残坡积物;3—滩间山群大理岩段;4—金水口群大理岩段;5—金水口群片麻岩段;6—晚三叠世辉长岩;7—早泥盆世石英闪长岩;8—地质界线;9—实测逆断层;10—推测逆断层;11—韧性剪切带;12—取样位置
Figure 1. Regional tectonic sketch map of Akechukesai(a)and geological map of the study area(b)
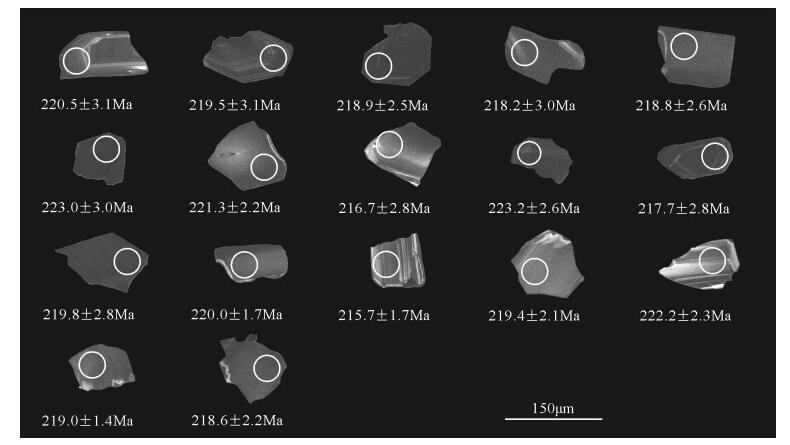
表 1 阿克楚克塞辉长岩(16AKCKS-1-N1)LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素定年分析结果
Table 1 LA-MC-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb dating results of sample 16AKCKS-1-N1 from Akechukesai gabbro
点位 元素含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Th U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 1 420 401 1.05 0.0505 0.0009 0.2427 0.0051 0.0348 0.0005 219 42 221 4 220 3 4 940 1617 0.58 0.0515 0.0007 0.2459 0.0037 0.0346 0.0005 262 31 223 3 220 3 5 1708 3800 0.45 0.0515 0.0009 0.2458 0.0050 0.0346 0.0004 264 38 223 4 219 2 6 957 800 1.20 0.0509 0.0007 0.2418 0.0040 0.0344 0.0005 238 30 220 3 218 3 9 1163 900 1.29 0.0503 0.0007 0.2399 0.0043 0.0345 0.0004 209 34 218 4 219 3 11 2000 6087 0.33 0.0511 0.0005 0.2483 0.0031 0.0352 0.0005 244 24 225 3 223 3 12 797 768 1.04 0.0506 0.0010 0.2441 0.0054 0.0349 0.0004 224 44 222 4 221 2 13 635 575 1.10 0.0514 0.0010 0.2425 0.0043 0.0342 0.0004 257 43 220 3 217 3 14 0 1558 0 0.0510 0.0010 0.2477 0.0049 0.0352 0.0004 239 43 225 4 223 3 15 1527 3080 0.50 0.0510 0.0007 0.2421 0.0034 0.0344 0.0005 243 31 220 3 218 3 16 2220 1324 1.68 0.0511 0.0009 0.2443 0.0030 0.0347 0.0005 247 39 222 2 220 3 18 918 733 1.25 0.0510 0.0006 0.2443 0.0033 0.0347 0.0003 239 27 222 3 220 2 19 1462 993 1.47 0.0512 0.0009 0.2404 0.0043 0.0340 0.0003 251 38 219 3 216 2 21 283 301 0.94 0.0508 0.0012 0.24177 0.0059 0.0346 0.0003 230 56 220 5 219 2 22 251 271 0.93 0.0496 0.0013 0.24021 0.0065 0.0351 0.0004 176 62 219 5 222 2 23 485 498 0.97 0.0511 0.0009 0.24331 0.0046 0.0346 0.0002 244 41 221 4 219 1 24 448 423 1.06 0.0504 0.0013 0.23943 0.0062 0.0345 0.0004 212 62 218 5 219 2 表 2 阿克楚克塞辉长岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 2 Major elements, trace elements and REE concentrations of the Akechukesai gabbro
样品编号 16AKCKS-1-Y1-1 16AKCKS-1-Y1-2 16AKCKS-1-Y1-3 16AKCKS-1-Y1-4 16AKCKS-1-Y1-5 SiO2 47.64 50.82 51.40 55.97 48.12 TiO2 1.59 1.04 0.91 0.65 1.05 Al2O3 16.94 20.03 20.12 16.57 17.54 MnO 0.18 0.13 0.12 0.13 0.17 MgO 5.80 3.63 3.27 3.84 6.11 CaO 10.35 9.05 8.90 8.60 10.13 Na2O 2.86 3.44 3.52 2.97 3.33 K2O 1.93 1.88 2.30 2.81 1.09 P2O5 0.25 0.32 0.20 0.24 0.12 TFe2O3 9.61 7.23 6.65 5.96 9.11 烧失量 2.62 1.84 2.09 1.50 2.59 总计 97.15 97.57 97.40 97.74 96.76 La 22.54 25.98 17.11 31.16 16.64 Ce 45.80 47.75 30.73 56.30 28.67 Pr 5.41 5.64 3.66 6.57 3.35 Nd 22.77 23.89 15.67 27.41 13.27 Sm 4.68 4.84 3.29 5.81 2.89 Eu 1.61 1.73 1.48 1.48 0.99 Gd 5.06 5.09 3.56 6.14 2.82 Tb 0.67 0.67 0.48 0.86 0.46 Dy 3.87 3.76 2.79 4.86 2.66 Ho 0.73 0.71 0.52 0.92 0.55 Er 2.10 2.01 1.53 2.69 1.46 Tm 0.28 0.27 0.21 0.37 0.19 Yb 1.83 1.68 1.34 2.40 1.31 Lu 0.26 0.24 0.19 0.33 0.19 Y 19.20 18.34 15.36 27.70 12.50 ΣREE 117.60 124.25 82.56 147.30 75.45 LREE 102.81 109.83 71.95 128.73 65.81 HREE 14.79 14.41 10.61 18.57 9.64 LREE/HREE 6.95 7.62 6.78 6.93 6.82 (La/Yb)N 8.32 10.40 8.60 8.75 8.56 δEu 1.00 1.06 1.31 0.75 1.05 δCe 0.97 0.91 0.89 0.90 0.87 Cs 5.36 8.41 6.74 3.57 7.05 Rb 128.76 91.08 102.18 111.82 64.76 Ba 380.71 472.74 396.46 663.72 210.74 Th 1.93 3.48 2.87 8.27 3.42 U 0.84 0.68 0.56 1.15 1.06 Nb 7.97 8.11 5.71 7.57 4.15 Ta 0.34 0.34 0.26 0.41 0.23 K 16084.57 15666.18 19149.38 23523.26 9091.933 Pb 6.50 15.52 10.01 9.83 9.46 Sr 577.54 670.00 601.23 483.69 460.97 P 1111.02 1409.11 894.77 1055.37 535.92 Zr 53.00 58.20 39.16 86.80 67.23 Hf 1.47 1.53 1.09 2.26 1.67 Ti 9576.13 6276.32 5475.95 3895.52 6310.78 Sc 23.20 15.25 13.28 18.75 23.54 V 303.20 178.90 144.70 130.00 157.35 Cr 110.54 41.99 49.04 63.57 135.61 Mn 1403.39 1024.20 930.51 990.73 1377.07 Co 31.86 25.02 19.08 20.30 26.02 Ni 50.90 29.60 23.12 28.14 35.58 Cu 12.23 14.67 14.49 16.62 10.21 Zn 100.31 60.84 46.93 41.98 94.77 注:主量元素含量单位为%,稀土和微量元素含量为10-6 表 3 阿克楚克赛辉长岩Hf同位素分析结果
Table 3 Zircon Hf isotopic compositions of the Akechusai gabbro
点号 t /Ma 176Yb/177Hf 2σ 176Lu/177Hf 2σ 176Hf/177Hf 2σ εHf (0) εHf(t) 2σ tDM1/Ma tDM2/Ma fLu/Hf 1 220 0.080605 0.000559 0.001609 0.000013 0.282676 0.000019 -3.4 1.2 0.7 830 1177 -0.95 4 220 0.027226 0.000078 0.000620 0.000001 0.282623 0.000019 -5.3 -0.5 0.7 881 1286 -0.98 5 219 0.126196 0.001662 0.002596 0.000028 0.282645 0.000030 -4.5 0.0 1.1 897 1255 -0.92 9 219 0.099150 0.002275 0.001982 0.000048 0.282641 0.000024 -4.6 -0.1 0.8 889 1260 -0.94 11 223 0.160456 0.003339 0.003265 0.000058 0.282596 0.000023 -6.2 -1.8 0.8 988 1370 -0.90 12 221 0.075851 0.000254 0.001547 0.000003 0.282706 0.000021 -2.3 2.3 0.8 785 1109 -0.95 16 220 0.156747 0.002172 0.003063 0.000036 0.282740 0.000025 -1.1 3.2 0.9 768 1046 -0.91 18 220 0.103134 0.000766 0.002052 0.000015 0.282717 0.000023 -2.0 2.6 0.8 780 1089 -0.94 19 216 0.116287 0.002945 0.002305 0.000060 0.282702 0.000022 -2.5 1.9 0.8 807 1126 -0.93 20 211 0.056081 0.000533 0.001161 0.000012 0.282598 0.000023 -6.2 -1.7 0.8 930 1353 -0.97 21 219 0.055959 0.000086 0.001130 0.000001 0.282623 0.000021 -5.3 -0.6 0.7 894 1292 -0.97 22 222 0.076007 0.000632 0.001552 0.000012 0.282701 0.000022 -2.5 2.1 0.8 792 1118 -0.95 23 219 0.072205 0.001062 0.001528 0.000014 0.282625 0.000022 -5.2 -0.6 0.8 901 1292 -0.95 24 219 0.075165 0.000576 0.001527 0.000011 0.282661 0.000024 -3.9 0.7 0.9 849 1210 -0.95 -
黄汲清, 任纪舜, 姜春发, 等.中国大地构造基本轮廓[J].地质学报, 1977, 51(2):117-135. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000000377523 姜春发, 杨经绥, 冯秉贵.昆仑开合构造[M].北京:地质出版社, 1992:59-78. 李荣社, 计文化, 杨永成, 等.昆仑山及邻区地质[M].北京:地质出版社, 2008:1-400. 谌宏伟, 罗照华, 莫宣学, 等.东昆仑造山带三叠纪岩浆混合成因花岗岩的岩浆底侵作用机制[J].中国地质, 2005, 32(3):386-395. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2005.03.006 莫宣学, 罗照华, 邓晋福, 等.东昆仑造山带花岗岩及地壳生长[J].高校地质学报, 2007, 13(3):403-414. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2007.03.010 李碧乐, 孙丰月, 于晓飞, 等.东昆中隆起带东段闪长岩U-Pb年代学和岩石地球化学研究[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(4):1163-1172. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7667375 丰成友, 王松, 李国臣, 等.青海祁漫塔格中晚三叠世花岗岩年代学、地球化学及成矿意义[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(2):665-678. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201202024 罗照华, 柯珊, 曹永清, 等.东昆仑印支晚期幔源岩浆活动[J].地质通报, 2002, 21(6):292-297. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.06.003 闫佳铭.青海东昆仑阿克楚克塞铜镍矿床地质特征及成因探讨[D].吉林大学硕士学位论文, 2017. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10183-1017156284.htm 袁洪林, 吴福元, 高山, 等.东北地区新生代侵入体的锆石激光探针U-Pb年龄测定与稀土元素成分分析[J].科学通报, 2003, 48(14):1511-1520. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.14.008 Yuan H L, Gao S, Liu X M, et al. Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinations of zircon by Laser Ablation Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2004, 28(3):353-370. doi: 10.1111/ggr.2004.28.issue-3
Anderseon T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2003, 192(1/2):59-79. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S000925410200195X
Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Gao S, et al. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 257(1/2):34-43. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=babd721ac13e2675d9485b52683be64c
Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen:U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51(1/2):537-571. doi: 10.1093-petrology-egp082/
Ludwing K R. User's Manual for Isoplot 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, 2003: 1-70.
侯可军, 李延河, 邹天人, 等. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石Hf同位素的分析方法及地质应用[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(10):2595-2604. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.10.025 Middlemost E A K. Naming Materials in the Magma/Igneous Rock System[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 1994, 37(3/4):215-224. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0012825294900299
Peccerillo R, Taylor S R. Geochemistry of Eocene Calc-alkaline Volcanic Rocks from the Kastamonu Area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrolpgy, 1976, 58(1):63-81. doi: 10.1007/BF00384745
Boynton W V. Cosmochemistry of thr Rare Earth Elements:Meteorite Studies[J]. Developments in Geochemistry, 1984, 2(2):63-114. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780444421487500083
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts:Implication for Mantle Composition and Processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1):313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Yang J H, Wu F Y, Shao J A, et al. Constraints on the Timing of Uplift of the Yanshan Fold and Thrust Belt, North China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 246(3/4):336-352. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=445d837b993421105b8443c8f17b51ba
吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 等. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(2):185-220. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200702001 赵忠华, 孙德有, 苟军, 等.满洲里南部塔木兰沟组火山岩年代学与地球化学研究[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2011, 41(6):1865-1880. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=CCDZ201106017&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 邓晋福, 罗照华, 苏尚国, 等.岩石成因、构造环境与成矿作用[M].北京:地质出版社, 2004:1-381. 李承东, 张福勤, 苗来成, 等.吉林色洛河晚二叠世高镁安山岩SHRIMP锆石年代学及其地球化学特征[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(4):767-776. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200704008 Sklyarov E V, Gladkochub D P, Mazukabzov A M. Neoproterozoic mafic dike swarms of the Sharyzhalgai metamorphic massif, southern Siberian craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 2003, 122(1):359-376. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S030192680200219X
Zhao J H, Zhou M F. Geochemistry of Neoproterozoic mafic intrusions in the Panzhihua district (Sichuan Province, SW China):implications for subduction-related metasomatism in the upper mantle[J]. Precambrican Research, 2007, 152(1):22-47. doi: 10.1016-j.precamres.2006.09.002/
Taylor S R, McLennan S M. The Continental Crust:Its Composition and Evoluton[M]. London:Blackwell, 1985:57-72.
Sajona F G, Maury R C, Pubellier M, et al. Magmatic source enrichment by slab-derived melts in a young post-collision setting, central Mindanao, Philippines[J]. Lithos, 2000, 54:173-206. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(00)00019-0
Tian L Y, Castillo P R, Hilton D R, et al. Major and trace element and Sr-Nd isotope signatures of the northern Lau Basin lavas:Implications for the composition and dynamics of the back-arc mantle[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2011, 116:75-92. doi: 10.1029/2011JB008791/full
Wang Q, Zhao Z, Bai Z, et al. Carboniferous adakites and Nb-enriched arc basaltic rocks association in tha Alataw Mountains, north Xinjiang:interactions between slab melt and mantle peridodite and implications for crustal growth[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2003, 48(19):2108-2115. doi: 10.1007/BF03037015
Woodhead J D, Hergt J M, Davidson J P, et al. Hafnium isotope evidence for 'conservative' element mobility during subducting zone processes[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2001, 192(3):331-346. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00453-8
Hanyu T, Tatsumi Y, Nakai S I, et al. Contribution of slab melting and slab dehydration to magmatism in the NE Japan arc for the last 25Myr:Constrains from geochemistry[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2006, 7(8):12-40. doi: 10.1029/2005GC001220/citedby
Pearce J A. Basalt geochemistry used to investigate past tectonic environments on Cyprus[J]. Tectonophysics, 1975, 25(1):41-67. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0040195175900104
Shervais J W. Ti-V plots and the petrogenesis of modern and ophiolitic lavas[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1982, 59(1):101-118. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(82)90120-0
EI Aouli E H, Gasquet D, Cheilletz A. Lower Cryogenian calc-alkaline mafic rocks of the Western Anti-Atlas(Morocco):An example of orogenic-like magmatism in an extensional setting[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2010, 58(1):81-88. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2010.01.010
Wang Y J, Zhang A M, Fan W M, et al. Origin of paleosubduciton modified mantle for Silurian gabbro in the Cathaysis Block:Geochronoligical and Geochemical evidence[J]. Lithos, 2013, 160/161:37-54. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.11.004
王秉璋.祁漫塔格地质走廊域古生代-中生代火成岩岩石构造组合研究[D].中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2011. Zhang J Y, Ma C Q, Xiong F H, et al. Petrogenesis and tectonic significance of the Late Permian-Middle Triassic calc-alkaline granites in the Balong region, easrern Kunlun Orogen, China[J]. Geological Magazine, 2012, 149(05):892-908. doi: 10.1017/S0016756811001142
赵财胜.青海东昆仑造山带金、银成矿作用[D].吉林大学博士学位论文, 2004. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10183-2004100082.htm 郭正府, 邓晋福, 许志琴, 等.青藏东昆仑晚古生代末中生代中酸性火成岩与陆内造山过程[J].现代地质, 1998, 12(3):345-352. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800618575 孙丰月, 陈国华, 迟效国, 等.新疆-青海东昆仑成矿带成矿规律和找矿方向综合研究成果报告, 2003. 孙丰月, 李碧乐, 丁清峰, 等.东昆仑成矿带重大找矿疑难问题研究成果报告. 2009. -
期刊类型引用(9)
1. 刘玲,张创,孙明. 志丹油田纸坊北油区三叠系延长组长6—长9储层致密史与油藏成藏史研究. 地质与资源. 2023(03): 327-334 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 韩晓洁,范昌育,高潮,张丽霞,尹锦涛,王成达,王宁. 构造抬升区欠压实超压恢复方法——以鄂尔多斯盆地下寺湾地区延长组为例. 天然气地球科学. 2023(07): 1163-1172 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 徐泽阳,刘震,赵靖舟,党佳城,李军,唐子怡. 基于测井响应特征的烃源岩古超压成因分析——以鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组7段烃源岩为例. 天然气地球科学. 2023(11): 1950-1960 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王苗,吴柏林,李艳青,刘池阳,郝欣,刘明义,张婉莹,李琪,姚璐航,张效瑞. 鄂尔多斯盆地深部富铀烃源岩提供铀源可能性的实验研究. 地球科学. 2022(01): 224-239 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 邹敏,云金表,王濡岳,于岚,伍岳,吉圆圆,成立,何维领,赵刚. 镇泾地区中侏罗统延安组低幅度圈闭成因类型与评价. 断块油气田. 2022(03): 313-318+330 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 胡艳飞,孔庆莹. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南部长8油层储层主控因素及分布规律. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版). 2022(04): 1078-1090 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 马立元,邱桂强,胡才志,徐士林,陈纯芳,李松. 鄂尔多斯盆地红河油田延长组致密砂岩成藏机制分析. 沉积学报. 2022(06): 1762-1773 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 郑登艳,王震亮,王联国,黄昊. 低幅度构造特征及其对油气成藏的控制作用:以鄂尔多斯盆地彭阳地区延安组为例. 现代地质. 2021(04): 1114-1123 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 庞宏,吴松,胡英杰,王海朋,丁旭光,刘兴周,惠沙沙,陈昌,郭军敏. 辽河拗陷牛心坨沙四段致密砂岩油形成主控因素及有利区预测. 石油科学通报. 2020(04): 467-482 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: