Zircon U-Pb geochronology and petrogenesis of rhyolites in Manketouebo Formation from the Kundu area in Jarud Basin, Inner Mongo-lia
-
摘要:
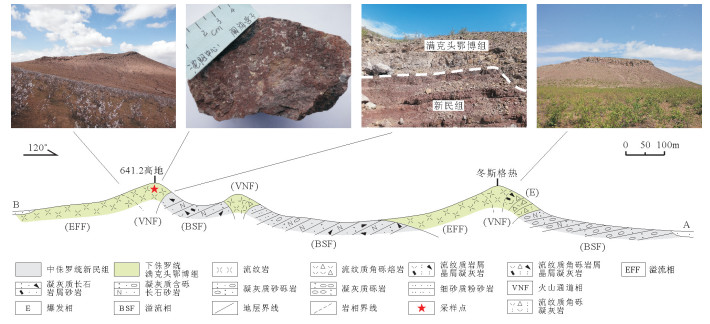
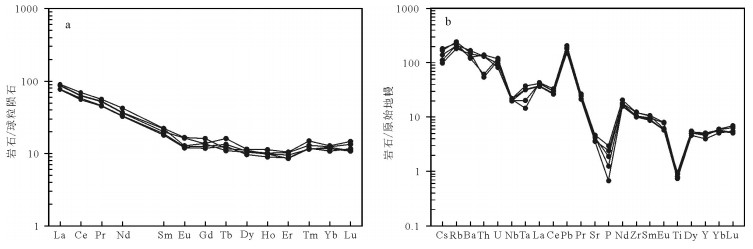
为研究内蒙古扎鲁特盆地坤都地区晚侏罗世火山岩的构造属性,对研究区内流纹岩开展了锆石U-Pb定年和原位Lu-Hf同位素研究。锆石U-Pb定年结果显示,流纹岩形成于151.2±1.2Ma,属于晚侏罗世。岩石地球化学研究表明,火山岩具高硅富碱、贫镁钙的特征,稀土元素总量为110.38×10-6~138.88×10-6,轻、重稀土元素分馏中等,弱负Eu异常(δEu=0.72~0.98),微量元素特征为富集Cs、Rb、Ba和轻稀土元素,强烈亏损Sr、P、Ti,相对亏损Nb、Ta,εHf(t)值为-10.1~4.9,对应的地壳模式年龄(TDMC)为1192~3639Ma,反映其岩浆来源于元古宙、太古宙地壳物质的部分熔融,之后经历矿物分离结晶作用。通过对比大兴安岭地区同时代岩浆-构造活动,研究区满克头鄂博组流纹岩形成于后造山伸展背景,与蒙古-鄂霍茨克造山后伸展作用有关。
Abstract:Age and tectonic implications of the Late Jurassic rhyolites in Kundu area of Jarud Basin were studied by using zircon U-Pb dating, in situ Lu-Hf isotopic analysis, petrographic analysis and other geochemical methods. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating results show that the rhyolites were formed in Late Jurassic, with their formation age being 151.2±1.2Ma. The geochemical study suggests that rhyolites are rich in silicon and alkali, but poor in calcium and magnesia. The REE values of them are between 110.38×10-6 and 138.88×10-6, displaying medium LREE-enriched and HREE-depleted REE patterns[(La/Yb)N=6.24~7.43], with weak negative Eu anomaly (δEu=0.72~0.98). The trace element geochemistry is characterized evidently by enrichment of Cs, Rb, Ba and LREE, strong depletion of Sr, P, Ti, and mediate depletion of Nb, Ta, with the εHf(t) values varying from -10.1~4.9, corresponding to TDMC model ages of 1192~3639Ma, which shows that the rhyolitc magma originated mainly from the partial melting of Proterozoic and Archean crustal rocks, and suffered fractional crystallization. Based on the above result, in combination with previous studies of the contemporaneous magma-tectonic activities in Da Hinggan Mountains, the authors hold that the rhyolites in Manketouebo Formation were formed in an extensional setting related to Mongolia Okhotsk orogenesis
-
Keywords:
- Jarud Basin /
- Late Jurassic /
- rhyolites /
- Manketouebo Formation /
- zircon U-Pb dating /
- Hf isotope
-
祁连造山带是中央造山带的重要组成部分,自北向南可划分为北祁连、中祁连和南祁连3个构造单元。前人对显生宙以来的大地构造格局及演化开展了较多的工作,并取得了大量的研究成果[1-8],但对前寒武纪基底的研究较少,少量的变质基底的研究仅局限于中祁连东段一带[9-11]。作为中祁连山西段变质结晶基底的托赖岩群,目前对其系统的岩石学、岩石化学、地球化学特征、构造演化等方面的研究资料较少,且在其时代归属上尚存在争议[12-13]。托赖岩群的深入研究,对确定祁连造山带发育的地质背景具有重要意义,尤其对恢复重建中国大陆前寒武纪构造格局及拼贴过程意义重大。本文对中祁连西段托赖岩群主要岩石组成进行了详细的地质和地球化学特征分析,初步恢复其原岩的物质组成,探讨其形成环境。
1. 地质背景及岩石学特征
祁连造山带是华北板块、塔里木板块和柴达木板块所夹持的一个呈北西走向的加里东期的造山带。中祁连陆块是夹持于北祁连和南祁连的中间隆起带,其北缘和南缘均发育蛇绿岩。中祁连前寒武纪变质地层有古元古界湟源群、托赖岩群,中元古界托来南山群,新元古界化隆岩群、龚岔群。
托赖岩群是中祁连西段古元古代的结晶基底,在青海祁连县托勒牧场、疏勒南山一带有较大规模出露(图 1)。
![]() 图 1 祁连造山带及邻区前寒武纪结晶基底的空间分布(据参考文献[14]修改)Ⅰ—华北板块;Ⅱ—祁连造山带;Ⅲ—柴达木板块;1—深变质结晶基底;2—浅变质基底;3—研究区位置;4—地质界线;5—断层Figure 1. Sketch map of the Qilian orogenic belt and its adjacent areas, showing the distribution of Precambrian masses
图 1 祁连造山带及邻区前寒武纪结晶基底的空间分布(据参考文献[14]修改)Ⅰ—华北板块;Ⅱ—祁连造山带;Ⅲ—柴达木板块;1—深变质结晶基底;2—浅变质基底;3—研究区位置;4—地质界线;5—断层Figure 1. Sketch map of the Qilian orogenic belt and its adjacent areas, showing the distribution of Precambrian masses托赖岩群由片岩、片麻岩、石英岩、大理岩、斜长角闪岩等变质岩石类型组成,变质作用类型为区域动力热流变质,变质程度达低角闪岩相,特征变质矿物有铁铝榴石、钾长石、黑云母、普通角闪石、斜长石、透辉石等。
2. 样品及矿物组合特征
样品主要采自疏勒南山北缘的大白石头沟一带,其中片麻岩样品2件、片岩3件、石英岩2件、大理岩3件、斜长角闪岩3件。岩石类型及特征变质矿物组合见表 1。
表 1 托赖岩群岩石类型及特征矿物组合Table 1. Metamorphic rocks and characteristic mineral assemblage of the Tuolai Group类型 岩性 岩石组合特征 含石榴子石黑云二长片麻岩 Alm+Kf+Pl+Bi+Q 含石榴子石白云母二长片麻岩 Alm+Kf+Pl+Ms+Bi+Q 长英质 绿帘黑云母石英片岩 Pl+Ep+Bi+Ms+Q 变质岩 含石榴子石阳起石长石二云母石英片岩 Alm+Act+Pl+Ms+Bi+Q 含石榴子石长石白云母石英片岩 Alm+Ms+Ep+Pl+Kf+Q 含石榴子石细粒石英岩 Alm+Ms+Bi+Kf+Q 钙质变 方解石大理岩 Di+Cc+Ms+Q 质岩 白云石大理岩 Dol 镁铁质 含黑云母斜长角闪岩 Hb+Pl+Kf+Bi+Q 变质岩 细粒斜长角闪岩 Hb+Pl+Q 注:Alm—铁铝榴石;Kf—钾长石;Pl—斜长石;Ms—白云母;Bi—黑云母;Q—石英;Ep—绿帘石;Di—透辉石;Cc—方解石;Dol—白云石;Hb—普通角闪石;Act—阳起石 片岩:主要岩石类型以石英片岩为主。岩石呈灰色-深灰色,鳞片粒状变晶结构,片状构造。主要矿物有石英(40%~45%)、黑云母(5%~25%),次要矿物有白云母(5%~10%)、斜长石少量、铁铝榴石个别,副矿物有磁铁矿、磷灰石、锆石。矿物粒径为0.1~1mm。
片麻岩:岩石类型为含石榴子石白云二长片麻岩和含石榴子石黑云二长片麻岩。岩石呈浅灰色-深灰色,鳞片粒状变晶结构,片麻状构造。主要矿物为斜长石(20%~25%)、钾长石(10%~30%)、石英(25%~40%),次要矿物为白云母(3%~5%)、黑云母(5%~10%)、铁铝榴石个别,副矿物为锆石、磁铁矿。矿物粒径多为0.5~1mm。
石英岩:呈透镜状产出,灰白色,鳞片粒状变晶结构,块状构造。主要矿物为石英(85%~90%),次要矿物为黑云母、白云母、钾长石、石榴子石,副矿物为磷灰石、锆石。矿物粒径多为0.1~1mm。
大理岩:主要岩石类型为白云石大理岩和方解石大理岩。白云石大理岩呈白色、灰色,块状构造,主要矿物白云石占99%,副矿物为黄铁矿;方解石大理岩呈灰白色,粒状变晶结构,块状构造,主要矿物为方解石(85%~90%),次要矿物为透辉石、白云母,副矿物为黄铁矿、锆石。矿物粒径多为0.1~0.5mm。
斜长角闪岩:呈透镜状、夹层状产于片麻岩、片岩中。深灰色,粒状变晶结构,块状构造。主要矿物有角闪石(50%~55%)、斜长石(25%~40%)、石英(10%~15%),次要矿物有黑云母和钾长石,副矿物为磁铁矿、磷灰石、榍石。矿物粒径多为0.1~0.5mm。
3. 原岩恢复及分类
在A-C-FM判别图解(图 2)、Log(SiO2/Al2O3)-Log(Na2O/K2O)判别图解(图 3)、Si-(al+fm)-(c+alk)判别图解(图 4)和∑REE-La/Yb判别图解[15](图 5)上,片岩、片麻岩落入了砂质岩、杂砂岩区域,石英岩落入了石英砂屑岩区域,指示其原岩为碎屑岩;大理岩则落入了钙质碳酸盐岩范围,指示其原岩为灰岩、白云质灰岩;斜长角闪岩样品落入了基性火山岩区域,显示其原岩为火成岩。综上可见,托赖岩群为长英质变质岩、钙质变质岩、镁铁质变质岩组成的变质岩石组合,其原岩组合为碎屑岩+碳酸盐岩+基性火山岩。
4. 地球化学特征
4.1 主量元素特征
4.1.1 长英质变质岩
泥质、长英质变质岩以片岩、片麻岩、石英岩为主要类型,岩石化学分析结果见表 2。片岩、片麻岩的SiO2含量为56.3%~72.3%;Al2O3含量为10.34%~14.87%,TiO2含量普遍小于1%,Na2O<K2O。石英岩的SiO2含量为95.92%~97.3%;Al2O3含量为0.88%~1.61%。尼格里参数:片岩、片麻岩Si值介于154.9~405.7之间,fm值介于23~38之间;石英岩Si值介于3717.8~5068.8之间,fm值介于42~47之间,可见泥质、长英质变质岩整体以富硅、高镁铁含量为特征,因此岩石中有较多的石英含量及较多的云母矿物和石榴子石。
表 2 托赖岩群变质岩主量元素分析结果Table 2. Major element content of metamorphic rocks of the Tuolai Group样号 L1731/4 D3030/2 D3030/5 D50/4 D3030/6 D50/5 D51/1 L2100/1 D51/3 D3030/8 D8534/1 D50/1 D3030/4 岩性 片岩 片麻岩 石英岩 大理岩 斜长角闪岩 黑云石英片岩 白云母石英片岩 二云石英片岩 黑云斜长片麻岩 黑云二长片麻岩 纯石英岩 纯石英岩 白云质 大理岩 大理岩 含黑云母斜长角闪岩 含榴斜长角闪岩 细粒黑云斜长角闪岩 SiO2 56.33 71.23 66.74 67.74 72.30 97.32 95.92 14.43 3.56 3.73 54.75 56.74 52.14 Al2O3 12.96 13.07 14.87 10.34 12.85 0.88 1.61 2.65 1.19 1.72 13.31 13.17 13.67 FeO 4.03 4.51 5.50 2.88 3.31 0.82 0.78 1.45 0.27 0.30 10.57 9.95 10.31 Fe2O3 1.59 0.82 1.01 1.98 1.41 0.09 0.35 0.22 0.13 0.36 2.61 1.44 1.83 MgO 6.13 1.00 1.26 0.92 1.06 0.13 0.13 17.25 3.72 3.66 4.54 4.67 6.18 MnO 0.11 0.08 0.09 0.05 0.06 0.03 0.03 0.04 0.04 0.01 0.22 0.20 0.23 CaO 10.12 0.61 0.64 8.64 0.99 0.11 0.09 24.60 49.14 48.29 7.10 7.93 9.13 Na2O 1.65 1.14 1.15 0.82 1.68 0.15 0.14 0.02 0.25 0.29 2.48 1.51 2.17 K2O 3.85 3.92 5.32 2.72 3.28 0.24 0.38 0.22 0.22 0.25 0.59 1.29 0.92 P2O5 0.15 0.06 0.06 0.08 0.05 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.03 0.14 0.13 0.11 TiO2 0.84 0.85 1.00 0.71 0.61 0.03 0.12 0.14 0.05 0.06 1.50 1.09 1.17 CO2 0.44 0.46 0.47 1.94 0.39 0.10 0.10 35.14 41.03 40.05 0.48 0.52 0.54 Total 98.20 97.75 98.11 98.82 97.99 99.92 99.67 96.19 99.62 98.75 98.29 98.64 98.40 尼格里特征参数 al 21 43 41 26 42 28 37 3 1 2 22 22 20 fm 38 33 34 23 31 47 42 49 10 10 50 47 49 alk 11 20 21 11 21 16 14 0 1 1 8 6 7 c 30 4 3 40 6 6 5 48 88 87 21 24 24 si 154.9 398.4 314.2 292.5 405.7 5068.8 3717.8 26.1 6 6.3 152.1 161.7 130.5 k 0.60 0.70 0.75 0.69 0.56 0.60 0.67 1.00 0.33 0.38 0.13 0.37 0.22 mg 0.66 0.25 0.26 0.26 0.29 0.20 0.17 0.95 0.93 0.92 0.38 0.42 0.48 o 0.09 0.10 0.11 0.28 0.20 0.07 0.22 0.01 0.02 0.04 0.11 0.07 0.07 c/fm 0.78 0.11 0.09 1.73 0.20 0.13 0.11 0.96 8.78 8.62 0.43 0.51 0.50 注:主量元素单位为10-2 4.1.2 钙质变质岩
钙质变质岩主要岩石类型为大理岩,岩石化学分析结果见表 2。SiO2含量为3.56%~14.43%;Al2O3含量为1.19%~2.65%之间;Mg含量介于3.66%~17.25%之间;CaO含量介于24.6%~49.14%之间,整体显示贫硅、铝,富钙的特征,白云质大理岩具富镁的特征。尼格里系数:c值介于48~88,指示来自钙质组分的贡献,mg值介于0.92~0.95之间,显示来自镁质组分的贡献。整体上,钙质变质岩以富钙、镁为特征,指示其原岩为灰岩、白云质灰岩。
4.1.3 镁铁质变质岩
镁铁质变质岩以斜长角闪岩为主要岩石类型,岩石化学分析结果见表 2。SiO2含量为52.14%~56.74%;Al2O3含量为13.17%~13.67%;MgO含量为4.54%~6.18%;Na2O>K2O。尼格里参数fm值为47~50,其主要来自铁质、镁质组分的贡献。在MgO-CaO-TFeO和TiO2-MnO图解(图 6)上,样品点均落入正斜长角闪岩区域,指示其原岩为基性火山岩。
4.2 微量元素特征
稀土元素分析结果见表 3。片岩、片麻岩稀土元素总量(∑REE)为100.6×10-6~752.4×10-6,轻、重稀土元素比值LREE/HREE为4.12~21.16;石英岩稀土元素总量为50.8×10-6~117.5×10-6,轻、重稀土比值LREE/HREE为5.75~14.64;大理岩稀土元素总量为22.7×10-6~51.3×10-6,轻、重稀土元素比值LREE/HREE为6.46~8.49;斜长角闪岩稀土元素总量为117.4×10-6~213.3×10-6,轻、重稀土元素比值LREE/HREE为3.70~6.52。片岩和片麻岩整体具较高的稀土元素含量,石英岩次之,大理岩最少。
表 3 托赖岩群变质岩微量和稀土元素分析结果Table 3. Trace and rare earth element concentrations of metamorphic rocks of the Tuolai Group样号 L1731/4 D3030/2 D3030/5 D50/4 D3030/6 D50/5 D51/1 L2100/1 D51/3 D3030/8 D8534/1 D50/1 D3030/4 岩性 片岩 片麻岩 石英岩 大理岩 斜长角闪岩 黑云石英片岩 白云母石英片岩 二云石英片岩 黑云斜长片麻岩 黑云二长片麻岩 纯石英岩 纯石英岩 白云质 大理岩 大理岩 含黑云母斜长角闪岩 含榴斜长角闪岩 细粒黑云斜长角闪岩 Y 39.9 27.3 27.8 21.6 25.9 3.97 7.54 8.49 4.76 3.96 43.8 34.4 29.2 La 37.1 43.2 42.0 30.6 31.5 11.0 9.72 9.06 5.90 4.7 24.7 40.0 14.4 Ce 78.8 99.7 96.5 58.3 67.6 23.2 17.3 15.3 8.82 6.56 49.6 70.6 29.0 Pr 10.2 11.0 11.1 6.84 8.07 1.81 1.99 1.99 1.05 0.81 6.30 7.76 3.81 Nd 39.6 42.7 42.2 25.1 32.4 6.55 7.72 8.53 4.67 3.81 27.3 28.6 16.8 Sm 8.58 8.32 8.12 4.79 6.36 1.42 1.62 1.90 1.06 0.8 6.68 6.35 4.23 Eu 1.44 1.50 1.59 1.12 1.15 0.17 0.23 0.30 0.21 0.088 1.54 1.80 1.18 Gd 8.06 7.76 7.64 4.79 5.79 1.14 1.43 1.87 0.87 0.65 7.08 6.72 4.41 Tb 1.05 0.88 0.89 0.55 0.70 0.12 0.17 0.20 0.096 0.075 1.11 0.82 0.64 Dy 7.35 5.88 5.88 3.98 5.38 0.95 1.34 1.44 0.84 0.67 7.77 6.55 5.66 Ho 1.36 1.05 1.03 0.70 0.92 0.080 0.19 0.26 0.097 0.077 1.50 1.16 0.98 Er 4.47 3.16 3.34 2.24 2.84 0.39 0.72 0.80 0.39 0.28 4.76 3.92 3.22 Tm 0.60 0.44 0.51 0.36 0.40 0.075 0.13 0.11 0.062 0.065 0.69 0.54 0.44 Yb 4.24 3.07 3.12 2.25 2.83 0.24 0.60 0.97 0.28 0.13 4.64 3.59 3.00 Lu 0.51 0.42 0.44 0.29 0.44 0.021 0.085 0.086 0.051 0.028 0.61 0.50 0.42 I REE 243.3 256.4 252.2 163.5 192.3 51.1 50.8 51.3 29.2 22.7 188.1 213.3 117.4 LREE/HREE 6.36 9.11 8.82 8.36 7.62 14.64 8.27 6.46 8.08 8.49 4.12 6.52 3.70 La/Yb 8.75 14.07 13.46 13.60 11.13 45.83 16.20 9.34 21.07 36.15 5.32 11.14 4.80 Sc 12.3 10.7 13.90 9.9 9.70 2.1 2.2 6.4 0.5 0.80 33.0 27.2 33.7 Ti 4033 4111.4 4590.5 2491 3078.8 175 496 1325 340 361.2 7878 5070 5305.1 V 82.2 107 128.20 84.1 68.90 8.3 11.4 44.2 16.0 15.30 295 286 336.2 Cr 57.9 47.2 50.90 50.9 36.80 9.1 8.2 23.8 4.6 12.50 46.1 103 61.3 Mn 740 569 605.40 356 434.30 157 171 319 315 119.90 1468 1397 1645.8 Zn 96.0 66.3 64.90 79.3 75.70 7.6 22.2 44.8 71.2 323.80 137 115 132.1 Ga 18.4 17.1 17.40 14.1 16.40 5.6 6.0 8.3 5.4 6.00 21.6 17.6 17.7 Sr 296 93.0 131.50 123 93.70 13.1 14.5 298 160 161.50 123 125 140.0 Zr 206 408 364.10 265 315.50 34.7 226 38.3 24.6 22.80 166 151 104.0 Ba 728 683.5 1045.0 463 493.8 28.9 27.0 560 196 21.2 124 244 184.5 Pb 19.4 26.3 42.20 63.8 35.50 7.0 19.8 11.4 18.2 17.00 19.5 15.6 22.0 Rb 104 136 174.70 103 109.30 36.9 38.1 22.3 7.3 9.90 11.1 27.6 26.7 Cs 3.99 9.60 10.80 5.52 5.50 0.46 1.09 2.65 1.00 1.02 4.35 4.92 3.7 Th 16.4 15.6 15.40 10.9 12.60 2.50 2.66 4.24 2.18 2.02 10.1 11.2 4.9 Co 16.1 15.3 19.00 18.9 7.87 1.94 2.35 4.79 9.26 2.35 43.3 37.8 39.4 Ni 28.5 18.2 25.90 23.4 11.50 3.08 3.75 12.5 10.4 9.62 15.0 44.1 11.6 Nb 16.8 15.6 17.60 10.5 14.20 2.85 8.04 10.8 3.01 2.00 11.6 11.4 6.0 Hf 2.89 2.00 4.40 1.29 4.58 0.38 1.53 0.80 0.48 0.47 3.41 1.36 1.1 Ta 2.77 0.88 0.82 0.47 2.16 0.39 0.73 12.8 0.54 0.37 2.17 3.04 1.1 T1 0.78 0.59 0.75 0.38 0.39 0.064 0.070 0.14 0.096 0.11 0.20 0.22 0.3 Zr/Ti〇2 245.1 479.6 364.1 373.5 517.2 1156.7 1879.2 273.6 492.0 380.0 110.4 138.2 88.9 Sr/Ba 0.4 0.1 0.1 0.3 0.2 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.8 7.6 1.0 0.5 0.8 Cr/Ni 2.0 2.6 2.0 2.2 3.2 3.0 2.2 1.9 0.4 1.3 3.1 2.3 5.3 Ba/Rb 7.00 5.01 5.98 4.50 4.52 0.78 0.71 25.10 26.84 2.14 11.16 8.86 6.91 Ni/Co 1.77 1.19 1.36 1.24 1.46 1.59 1.60 2.61 1.12 4.09 0.35 1.17 0.29 Rb/Sr 0.35 1.47 1.33 0.84 1.17 2.82 2.63 0.07 0.05 0.06 0.09 0.22 0.19 沉积岩(片岩、片麻岩、石英岩、大理岩)经北美页岩标准化的稀土元素配分模式图见图 7。由图 7明显可以看出,经北美页岩标准化的稀土元素配分模式十分相似,均呈平坦型,与王仁民等[15]所给出的无花果树杂砂岩、布拉瓦约石灰岩所显示的特征一致,指示其为前寒武纪沉积岩系。
变质火山岩(斜长角闪岩)稀土元素总量为117.4×10-6~213.3×10-6,轻、重稀土元素比值LREE/HREE为3.70~6.52。在球粒陨石标准化配分模式图(图 8)上显示轻稀土元素弱分馏,重稀土元素不分馏的特征,整体显示右倾,无负Eu异常。在原始地幔标准化不相容元素蛛网图(图 9)上,显示出Nb、Sr、Hf负异常,与埃塞俄比亚裂谷玄武岩微量元素配分模式相似[16],指示其形成于裂谷环境。在Zr-Zr/Y构造判别图(图 10)和TFeO -MgOAl2O3构造判别图(图 11)上,样品均落入板内玄武岩区,进一步印证了托赖岩群斜长角闪岩形成于板内环境。
5. 构造环境判别
5.1 托赖岩群形成时代讨论
王忠良[13]在祁连县央隆乡大央隆沟上游一带所采集的托赖岩群二云石英片岩中获得了80个点的锆石U-Pb同位素数据,在同位素年龄频谱图(图 12)上明显出现了1700~1800Ma和1350~1500Ma两个峰期年龄,认为托赖岩群应属于中元古界。而从其所给出的锆石特征照片及主体为变质锆石的结论看,所测的锆石年龄值代表了锆石的变质年龄,说明二云石英片岩形成及形成期后曾经历2期变质事件。
![]() 图 12 二云石英片岩U-Pb同位素年龄频谱图(据参考文献[12]修改)Figure 12. Histogram of two-mica-quartz schist U-Pb isotope age
图 12 二云石英片岩U-Pb同位素年龄频谱图(据参考文献[12]修改)Figure 12. Histogram of two-mica-quartz schist U-Pb isotope age从本文变质岩原岩恢复的结果看,二云石英片岩的原岩为碎屑岩(长石砂岩),其原岩的沉积时代应早于变质时代。从变质的下限年龄(1800Ma)看,托赖岩群变质岩系原岩的沉积时代应为古元古代。
5.2 构造环境判别
张雪亭[5]指出,青海及邻区的板块构造体制始于寒武纪,而托赖岩群变质岩原岩的沉积时代为古元古代,其应为古元古代古陆核增生的产物。因其经历了后期多期变质事件的改造,原始层理已被Sn+1片理、片麻理置换,上下岩层之间的接触关系已不清晰,原岩形成的构造环境已很难恢复。
斜长角闪岩作为托赖岩群中的特殊夹层,其形成环境为托赖岩群原岩的形成环境提供了重要指示。在A-C-FM图解(图 2)和Si-(al+fm)-(c+alk)判别图解(图 4)上,样品点均落入火山岩区;在MgO-CaO-TFeO和TiO2-MnO图解(图 6)上,样品点均落入正斜长角闪岩区域,指示原岩为火山岩。在原始地幔标准化不相容元素蛛网图上,显示出Nb、Sr、Hf负异常,指示其形成于裂谷环境;在ZrZr/Y构造判别图(图 10)和TFeO -MgO-Al2O3构造判别图(图 11)上,样品点均落入板内玄武岩区,指示斜长角闪岩原岩的形成环境为板内裂谷环境。
作为斜长角闪岩的赋存层位,托赖岩群原岩的形成环境应与斜长角闪岩原岩的产出环境一致,仍为板内环境。
6. 结论
(1)托赖岩群片岩、片麻岩、石英岩、大理岩原岩为沉积岩,其中片岩、片麻岩原岩为砂质岩、杂砂岩,石英岩原岩为石英砂屑岩,大理岩原岩为灰岩、白云岩。斜长角闪岩原岩为火山岩,岩性为玄武安山岩。托赖岩群原岩的岩石组合为碎屑岩+大理岩+中基性火山岩。
(2)托赖岩群原岩的沉积时代为古元古代,变质时代为中元古代。
(3)托赖岩群变质火山岩微量元素特征、构造环境判别结果显示,变质中基性火山岩形成于板内裂谷环境。
致谢: 沈阳地质调查中心基础地质室全体成员、中国科学院海洋研究所郭鹏远研究员对本文提供帮助,审稿专家提出了宝贵的修改意见及建议,在此一并致以衷心的感谢。 -
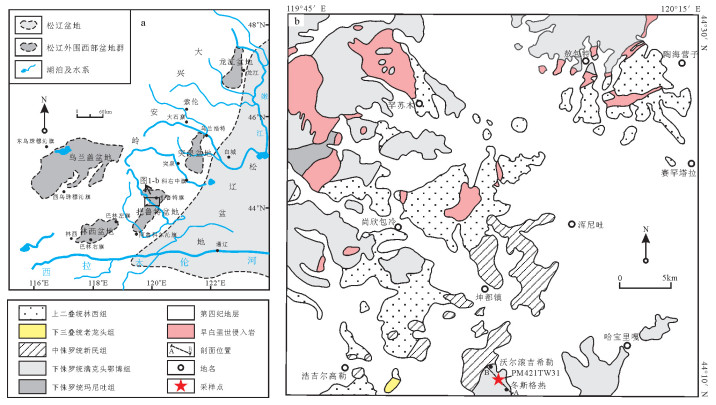
图 1 松辽外围西部盆地群分布图(a)[1]和扎鲁特盆地地质简图(b)
Figure 1. Distribution of basin groups of Songliao peripheral basins (a) and simplified geological map of Jarud Basin (b)
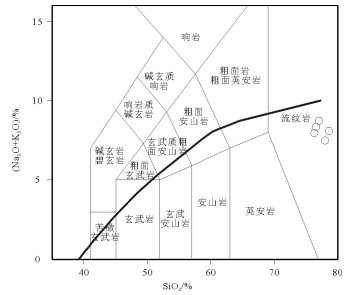
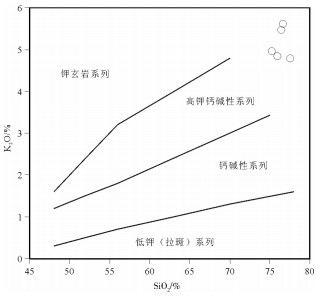
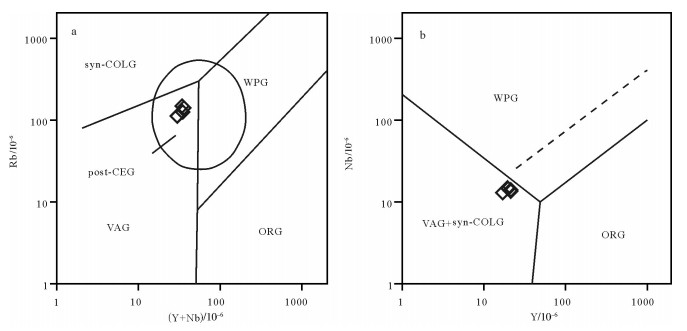
图 7 满克头鄂博组流纹岩样品SiO2-K2O图解[19]
Figure 7. SiO2-K2O diagram of rhyolites in Manketouebo Formation
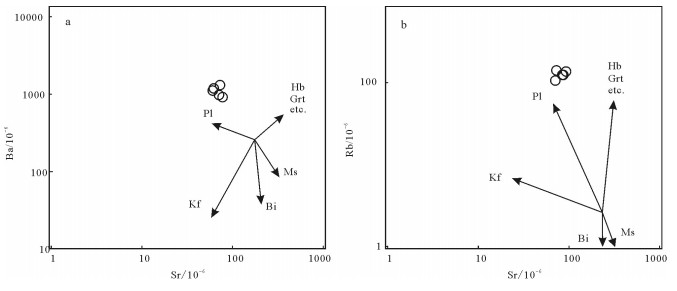
图 9 满克头鄂博组流纹岩Sr-Ba(a)与Sr-Rb(b)关系图[31]
Pl—斜长石;Kf—钾长石;Bi—黑云母;Ms—白云母;Hb—角闪石;Grt—石榴子石
Figure 9. Sr-Ba (a) and Sr-Rb (b) diagrams of rhyolites in Manketouebo Formation
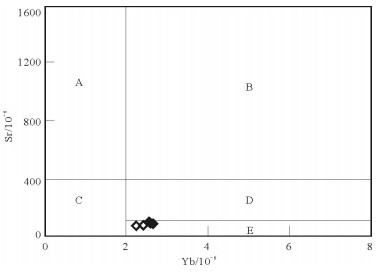
图 12 满克头鄂博组流纹岩Yb-Sr分类图解[5]
A—高Sr、低Yb花岗岩;B—高Sr、高Yb花岗岩;C—低Sr、低Yb花岗岩;D—低Sr、高Yb花岗岩;E—非常低Sr、高Yb花岗岩
Figure 12. Yb-Sr diagram of rhyolites in Manketouebo Formation
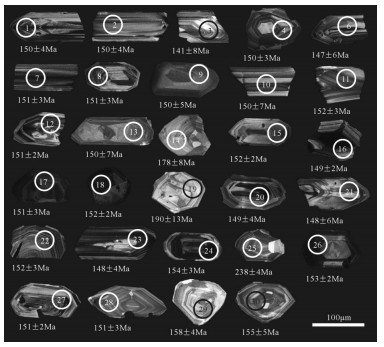
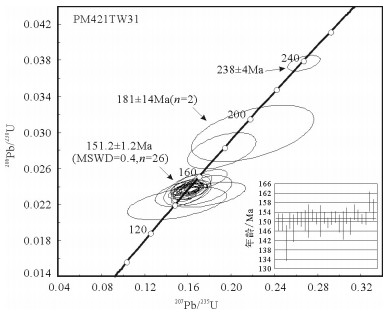
表 1 满克头鄂博组流纹岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb分析结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb analytical results of rhyolites in Manketouebo Formation
分析点 含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Pb 232Th 238U 207Pb/
206Pb±1σ 207Pb/
235U±1σ 206Pb/
238U±1σ 208Pb/
232Th±1σ 207Pb/
206Pb±1σ 207Pb/
235U±1σ 206Pb/
238U±1σ 208Pb/
232Th±1σ 01 7 93 106 0.88 0.0527 0.0042 0.1619 0.0110 0.0235 0.0006 0.0074 0.0003 322 183 152 10 150 4 148 6 02 11 152 114 1.34 0.0507 0.0040 0.1601 0.0119 0.0235 0.0006 0.0080 0.0003 228 181 151 10 150 4 161 5 03 11 149 107 1.40 0.0478 0.0085 0.1498 0.0303 0.0221 0.0012 0.0068 0.0006 100 378 142 27 141 8 137 12 04 14 201 183 1.09 0.0486 0.0029 0.1598 0.0102 0.0236 0.0005 0.0070 0.0003 128 137 151 9 150 3 141 5 05 26 153 115 1.33 0.1441 0.0096 0.5493 0.0491 0.0261 0.0009 0.0130 0.0008 2277 115 445 32 166 6 261 16 06 8 90 102 0.89 0.0539 0.0056 0.1793 0.0225 0.0231 0.0009 0.0094 0.0009 369 235 167 19 147 6 190 18 07 18 238 225 1.06 0.0497 0.0025 0.1617 0.0080 0.0237 0.0004 0.0079 0.0002 189 119 152 7 151 3 158 4 08 17 244 162 1.51 0.0495 0.0028 0.1593 0.0084 0.0237 0.0005 0.0076 0.0002 169 130 150 7 151 3 153 4 09 4 42 92 0.46 0.0467 0.0037 0.1622 0.0103 0.0236 0.0007 0.0074 0.0005 32 178 153 9 150 5 149 10 10 17 304 205 1.48 0.0505 0.0050 0.1595 0.0142 0.0236 0.0011 0.0061 0.0003 220 215 150 12 150 7 123 5 11 20 303 190 1.59 0.0484 0.0020 0.1613 0.0076 0.0239 0.0004 0.0075 0.0002 117 100 152 7 152 3 152 4 12 18 200 186 1.08 0.0488 0.0023 0.1641 0.0068 0.0237 0.0004 0.0079 0.0002 139 111 154 6 151 2 159 4 13 9 47 71 0.66 0.0524 0.0060 0.1727 0.0184 0.0236 0.0011 0.0078 0.0007 306 263 162 16 150 7 158 13 14 9 77 90 0.86 0.0504 0.0062 0.1914 0.0209 0.0280 0.0013 0.0093 0.0005 213 263 178 18 178 8 187 10 15 16 136 202 0.67 0.0496 0.0020 0.1614 0.0061 0.0238 0.0004 0.0076 0.0002 189 125 152 5 152 2 152 4 16 17 239 227 1.05 0.0499 0.0021 0.1601 0.0067 0.0235 0.0004 0.0072 0.0002 191 100 151 6 149 2 144 4 17 11 109 228 0.48 0.0472 0.0020 0.1528 0.0058 0.0238 0.0004 0.0072 0.0002 58 109 144 5 151 3 146 5 18 24 293 371 0.79 0.0498 0.0018 0.1630 0.0061 0.0239 0.0004 0.0075 0.0002 183 118 153 5 152 2 151 4 19 7 56 59 0.95 0.0536 0.0089 0.2200 0.0374 0.0299 0.0021 0.0143 0.0014 354 341 202 31 190 13 286 28 20 30 425 263 1.62 0.0496 0.0024 0.1585 0.0080 0.0234 0.0006 0.0074 0.0002 176 113 149 7 149 4 150 4 21 10 88 102 0.87 0.0496 0.0053 0.1559 0.0170 0.0233 0.0010 0.0074 0.0004 176 230 147 15 148 6 149 8 22 9 94 137 0.69 0.0489 0.0029 0.1585 0.0088 0.0239 0.0005 0.0086 0.0003 143 137 149 8 152 3 173 7 23 14 182 169 1.08 0.0507 0.0025 0.1593 0.0072 0.0232 0.0006 0.0076 0.0003 228 115 150 6 148 4 154 5 24 31 349 573 0.61 0.0497 0.0016 0.1654 0.0056 0.0242 0.0005 0.0077 0.0002 189 76 155 5 154 3 154 4 25 11 76 139 0.55 0.0512 0.0020 0.2672 0.0100 0.0377 0.0006 0.0132 0.0004 256 89 240 8 238 4 265 8 26 40 572 436 1.31 0.0499 0.0016 0.1654 0.0057 0.0240 0.0004 0.0080 0.0002 191 71 155 5 153 2 160 3 27 16 167 200 0.83 0.0502 0.0022 0.1620 0.0066 0.0237 0.0003 0.0076 0.0002 211 102 152 6 151 2 154 4 28 13 188 159 1.19 0.0494 0.0020 0.1621 0.0063 0.0237 0.0004 0.0075 0.0002 165 96 153 6 151 3 151 4 29 8 59 59 1.01 0.0467 0.0034 0.1797 0.0108 0.0249 0.0007 0.0081 0.0003 35 176 168 9 158 4 163 7 30 9 101 108 0.93 0.0512 0.0040 0.1648 0.0115 0.0243 0.0007 0.0083 0.0003 250 180 155 10 155 5 168 6 表 2 满克头鄂博组流纹岩主量、微量及稀土元素分析结果
Table 2 Major, trace and REE compositions of rhyolites in Manketouebo Formation
样品号 PM421YQ31 PM421YQ34 KD-2 KD-3 KD-4 SiO2 76.61 75.22 75.91 77.53 76.39 TiO2 0.15 0.18 0.19 0.15 0.16 Al2O3 12.24 13.1 12.71 11.7 12.27 Fe2O3 0.93 1.14 1.3 0.85 0.79 FeO 0.22 0.29 0.27 0.27 0.54 MnO 0.03 0.02 0.04 0.07 0.07 MgO 0.35 0.37 0.26 0.002 0.04 CaO 0.32 0.41 0.19 0.08 0.23 Na2O 1.76 2.89 3.43 3.23 3.22 K2O 5.63 4.97 4.86 4.79 5.48 P2O5 0.05 0.06 0.04 0.01 0.03 烧失量 1.29 1.05 0.98 0.95 0.91 总量 99.59 99.72 100.18 99.63 100.13 A/CNK 1.28 1.2 1.13 1.1 1.05 AR 3.86 2.50 3.27 3.43 3.13 Na2O+K2O 7.39 7.86 8.29 8.02 8.7 La 26.77 28.29 27.07 23.77 24.2 Ce 50.35 56.11 51.53 44.8 46.63 Pr 6.32 6.83 6.43 5.53 5.58 Nd 21.98 25.75 22.4 19.61 20.02 Sm 3.89 4.37 4.3 3.52 3.69 Eu 1.21 1.23 0.95 0.88 0.92 Gd 3.55 4.16 3.6 3.07 3.26 Tb 0.52 0.56 0.76 0.6 0.63 Dy 3.36 3.59 3.73 3.13 3.48 Ho 0.71 0.71 0.81 0.64 0.74 Er 1.8 1.99 2.19 1.83 2.17 Tm 0.38 0.37 0.49 0.38 0.42 Yb 2.43 2.57 2.67 2.25 2.61 Lu 0.35 0.35 0.47 0.38 0.43 ∑REE 123.6 136.88 127.4 110.38 114.78 (La/Yb)N 7.42 7.43 6.83 7.13 6.24 (La/Sm)N 4.33 4.07 3.96 4.25 4.13 (Gd/Lu)N 1.27 1.46 0.95 1.01 0.94 δEu 0.98 0.87 0.72 0.8 0.79 Y 21.49 21.79 19.92 17.11 19.9 Rb 144.7 137.58 124.45 109.29 125.56 Ba 1000 795.03 824.49 952.51 1100 Th 4.33 4.87 11.13 10.55 10.52 U 2.19 2.41 2.38 1.65 1.93 Nb 13.3 13.99 14.4 13.03 14.14 Ta 0.75 0.54 1.38 1.19 1.2 Hf 3.07 3.27 4.87 4.44 4.46 Sc 4.85 3.41 4.45 3.63 3.68 Ga 16.61 17.03 15.12 14.24 15.43 Pb 22.97 31.06 30.72 23.72 27.76 Sr 73.36 93.63 84.48 71.57 87.1 Cr 16.75 11.8 13.72 10.85 13.88 Zr 111.2 127.06 128.07 105.25 109.53 Co 2.04 1.76 2.83 2.76 2.53 Ni 2.7 0.87 2.59 6.56 11.2 V 11.67 10.76 13.79 10.59 13.67 Sb 0.23 0.3 0.38 0.21 0.22 Rb/Sr 1.97 1.47 1.47 1.53 1.44 Ti/Y 42.68 49.39 58.39 52.56 48.40 Ti/Zr 8.25 8.47 9.08 8.54 8.87 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素为10-6 表 3 满克头鄂博组流纹岩锆石Hf同位素分析结果
Table 3 Zircon Hf isotopic compositions of rhyolites in Manketouebo Formation
测点 年龄/Ma 176Yb/177Hf 2σ 176Lu/177Hf 2σ 176Lu/177Hf 2σ (176Lu/177Hf)i εHf(0) εHf(t) TDM/Ma TDMc/Ma fLu/Hf 4 150 0.049168 0.000388 0.002152 0.000015 0.282399 0.000045 0.282393 -13.2 -10.1 1244 2546 -0.94 6 147 0.027371 0.000573 0.001190 0.000025 0.282645 0.000038 0.282642 -4.5 -1.4 865 1761 -0.96 8 151 0.039872 0.001256 0.001744 0.000055 0.282438 0.000039 0.282434 -11.8 -8.7 1174 2417 -0.95 9 150 0.018361 0.000418 0.000814 0.000017 0.282821 0.000034 0.282818 1.7 4.9 609 1192 -0.98 13 150 0.018636 0.000201 0.000796 0.000008 0.282808 0.000030 0.282806 1.3 4.5 627 1233 -0.98 17 151 0.026776 0.000433 0.001162 0.000018 0.282782 0.000023 0.282779 0.3 3.5 670 1319 -0.96 19 190 0.032803 0.000714 0.001378 0.000028 0.282904 0.000047 0.282899 4.7 8.7 499 880 -0.96 22 152 0.024753 0.000163 0.001047 0.000008 0.282518 0.000031 0.282515 -9.0 -5.8 1040 2157 -0.97 24 154 0.032726 0.000341 0.001349 0.000012 0.282720 0.000040 0.282716 -1.8 1.4 762 1515 -0.96 25 238 0.051298 0.000561 0.002218 0.000025 0.282450 0.000034 0.282440 -11.4 -6.5 1173 2282 -0.93 26 153 0.062658 0.000703 0.002614 0.000029 0.282780 0.000042 0.282772 0.3 3.4 700 1336 -0.92 29 158 0.040499 0.000318 0.001729 0.000014 0.282710 0.000039 0.282705 -2.2 1.1 784 1544 -0.95 30 155 0.041874 0.000374 0.001793 0.000018 0.282598 0.000044 0.282593 -6.1 -2.9 946 1905 -0.95 -
陈树旺, 丁秋红, 郑月娟, 等.松辽盆地外围新区、新层系——油气基础地质调查进展与认识[J].地质通报, 2013, 32(8):1147-1158. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2013.08.002 林强.东北亚中生代火山岩研究若干问题的思考[J].世界地质, 1999, 18(2):14-22. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SJDZ902.002.htm 吴福元, 曹林.东北地区的若干重要基础地质问题[J].世界地质, 1999, 18(2):1-13. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gjsdz201304016 葛文春, 林强, 孙德有, 等.大兴安岭中生代两类流纹岩成因的地球化学研究[J].地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2000, 25(2):172-178. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx200002012 张渝金, 张超, 郭威, 等.内蒙古阿鲁科尔沁旗林西组植物化石新材料[J].地质与资源, 2017, 26(4):333-338. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2017.04.001 王成文, 金巍, 张兴洲, 等.东北及领区晚古生代大地构造属性新认识[J].地层学杂志, 2008, 32(2):119-136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4959.2008.02.001 杨兵, 张雄华, 葛孟春, 等.内蒙古林西地区晚二叠世-早三叠世孢粉组合及三叠系的发现[J].地球科学, 2014, 39(7):784-794. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201407002 程银行, 滕学建, 杨俊泉, 等.内蒙古东乌旗敖包查干地区中生代陆相火山构造特征[J].地质调查与研究, 2011, 34(1):16-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2011.01.003 宋彪, 张玉海, 万渝生, 等.锆石SHRIMP样品靶制作、年龄测定及有关现象讨论[J].地质评论, 2002, 48(S1):26-30. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/OA000005931 Wu F Y, Yang Y H, Xie L W, et al. Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons and baddeleyites used in U-Pb geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 234:105-126. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.05.003
Xie L W, Zhang Y B, Zhang H H, et al. In situ simultaneous determination of trace elements, U-Pb and Lu-Hf isotopes in zircon and baddeleyite[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53:1565-1573. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=cd47cc68037bb1beb96d37816ba0f6cc&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Scherer E, Munker C, Mezger K. Calibration of the lutetium-hafnium clock[J]. Science, 2001, 293:683-687. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=b37331af347519a1f8cb28936795f4dd&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Blichert-Toft J, Albarede F. The Lu-Hf isotope geochemistry of chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system[J]. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1997, 148:243-258. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(97)00040-X
Vervoort J D, Blichert-Toft J. Evolution of the depleted mantle:Hf isotope evidence from juvenile rocks through time[J]. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1999, 63:533-556. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00274-9
Griffin W L, Wang X, Jackson S E, et al. Zircon geochemistry and magma mixing, SE China:In-situ analysis of Hf isotopes, Tonglu and Pingtan igneous conplexes[J]. Lithos, 2002, 61:237-269. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=c097aa188f06ce2fa75dc423db446c4e&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Koschek G. Origin and significance of the SEM cathodoluminescence from zircon[J]. Journal of Microscopy, 1993, 171:223-232. doi: 10.1111/jmi.1993.171.issue-3
Middlemost E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth Science Review, 1994, 37:215-224. doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(94)90029-9
Irvine T N, Baragar W R. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Science, 1971, 8:523-548. doi: 10.1139-e71-055/
Peccerillo A, Taylor S R. Geochemistry of Eocene cala-alkallne volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area. Northern Turkey[J]. Contrib. Mineral. and Petrol., 1976, 58:63-81. doi: 10.1007%2FBF00384745
Boynton W V. Chapter 3-Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements:meteorite studies[J]. Developments in Geochemistry, 1984, 2(2):63-114. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a86bc72c95d06bcdf62c0e1eb55bf851&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Mcdonough W F, Sun S S. The composition of the Earth[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120(3/4):223-253. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_fb4dd133285d7a6db94ef688ee319429
Bacon C R, Druitt T H. Compositional evolution of the zoned calcalkaline magma chamber of Mount Mazama, Crater Lake, Oregon[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1988, 98(2):224-256. doi: 10.1007/BF00402114
Bonin B. Do coeval mafic and felsic magmas in post-collisional to within-plate regimes necessarily imply two contrasting, mantle and crustal, sources? A review[J]. Lithos, 2004, 78(1/2):1-24. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493704002014
林强, 葛文春, 曹林, 等.大兴安岭中生代双峰式火山岩的地球化学特征[J].地球化学, 2003, 32(3):208-222. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2003.03.002 Guffanti M, Clynne M A, Muffler L. Thermal and massmimplications of magmatic evolution in the Lassen volcanic region, California, and minimum constraints on basalt influx to the lower crust[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth (1978-2012), 1996, 101(B2):3003-3013. doi: 10.1029/95JB03463
Wilson M. Magmatism and the geodynamics of basin formation[J]. Sediment Geology, 1993, 86(1/2):5-29. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/003707389390131N
Shinjo R, Kato Y. Geochemical constraints on the origin of bimodal magmatism at the Okinawa Trough, an incipient back-arc basin[J]. Lithos, 2000, 54(3/4):117-137. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=95a4abbef83657faadfe7ef9b6f5eac3&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Tischendorf G, Paelchen W. Zur Klassifikation von Granitoiden/Classification of granitoids[J]. Zeitschrift fuer Geologische Wissenschaften, 1985, 13(5):615-627.
单强, 曾乔松, 罗勇, 等.新疆阿尔泰康布铁堡组钾质和钠质流纹岩的成因及同位素年代学研究[J].岩石学报, 2011, 7(12):3653-3665. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201112012 Green T H. Experimental studies of trace-element partitioning applicable to igneous petrogenesis-Ssdona 16 years later[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 117:1-36. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(94)90119-8
Janousek V, Finger F, Roberts M, et al. Deciphering the petrogenesis of deeply buried granites:whole-rock geochemical constraints on the origin of largely undepleted felsic granulites from the Moldanubian Zone of the Bohemian Massif[J]. Earth & Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 2004, 95:141-159.
刘德来, 马莉.松辽盆地裂谷期前火山岩与裂谷盆地关系及动力学过程[J].地质论评, 1998, 44(2):130-135. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1998.02.003 赵海玲, 邓晋福, 陈发景, 等.中国东北地区中生代火山岩岩石学特征与盆地形成[J].现代地质, 1998, 12(1):56-59. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ801.006.htm 吴福元, 叶茂, 张世红.中国满洲里-绥芬河地学断面域的地球动力学模型[J].地球科学, 1995, 20(5):535-539. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/94035X/199505/1710801.html Wang P J, Liu W Z, Wang S X, et al. 40Ar/39Ar and K/Ar dating on the volcanic rocks in the Songliao basin, NE China:mConstraints on stratigraphy and basin dynamics[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2002, 91(2), 331-340. doi: 10.1007%2Fs005310100219
Zhang J H, Gao S, Ge W C, et al. Geochronology of the Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the Great Xing'an Range, northeastern China:Implications for subduction-induced delamination[J]. Chemical Geology, 2010, 276(3/4):144-165. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=6b906d24275831ba60cd504fbab119b0&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
林强, 葛文春, 孙德有, 等.中国东北地区中生代火山岩的大地构造意义[J].地质科学, 1998, 33(2):129-139. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-80165-2007101613.htm 邵济安, 张履桥, 牟保磊.大兴安岭中生代伸展造山过程中的岩浆作用[J].地学前缘, 1999, (4):339-346. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1999.04.017 Wang P J, Chen F K, Chen SM, et al. Geochemical and Nd-Sr-Pb isotopic composition of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the Songliao basin, NE China[J]. Geochemical Journal, 2006, 40(2):149-159. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.40.149
Xu W L, Pei F P, Wang F, et al. Spatial-temporal relationships of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in NE China:Constraints on tectonic overprinting and transformations between multiple tectonic regimes[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 74:167-193. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/268151863_Spatial-temporal_relationships_of_Mesozoic_volcanic_rocks_in_NE_China_Constraints_on_tectonic_overprinting_and_transformations_between_multiple_tectonic_regimes
张超, 吴新伟, 张渝金, 等.大兴安岭北段龙江盆地光华组碱流岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2017, 36(9):1531-1541. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.09.005 Wu F Y, Lin J Q, Wilde SA, et al. Nature and significance of the Early Cretaceous giant igneous event in eastern China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 233(1/2):103-119. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X05001214
高晓峰, 郭锋, 范蔚茗, 等.南兴安岭晚中生代中酸性火山岩的岩石成因[J].岩石学报, 2005, 21(3):737-748. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200503014 隋振民, 葛文春, 吴福元, 等.大兴安岭东北部侏罗纪花岗质岩石的锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及成因[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(2):461-468. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200702023 陈志广, 张连昌, 周新华, 等.满洲里新右旗火山岩剖面年代学和地球化学特征[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(12):2971-2986. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200612014 李长华, 卫三元, 陈贵海, 等.内蒙古满洲里地区中生代中基性火山岩成因及构造地质背景[J].世界核地质科学, 2009, 27(1):19-24. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sjhdzkx201001004 Pitcher W S. Granite type and tectonic environment[C]//Hsu K. Mountain Building Processes. London: AcademicPress, 1983: 19-40.
Davidson J P, Stern C R. Comment and Reply on "Role of subduction erosion in the generation of Andean magmas"[J].Geology, 1991, 19(10):1054-1056. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1991)019<1054:CARORO>2.3.CO;2
Pearce J A. Sources and settings of granitic rock[J]. Episodes, 1996, 19(4):120-125. http://www.episodes.co.in/www/backissues/194/Articles--120.pdf
Foster H J, Tischendorf G, Trumbull R B. An evaluation of the R. (Y+Nb) discrimination diagram to infer tectonic setting of silicic igneous rocks[J]. Lithos, 1997, 40:261-293. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(97)00032-7
张旗.中国东部中生代岩浆活动与太平洋板块向西俯冲有关吗?[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2013, 32(1):113-128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2013.01.010 张旗, 王元龙, 金惟俊, 等.造山前、造山和造山后花岗岩的识别[J].地质通报, 2008, 27(1):1-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.01.001 李锦轶, 莫申国, 和政军, 等.大兴安岭北段地壳左行走滑运动的时代及其对中国东北及邻区中生代以来地壳构造演化重建的制约[J].地学前缘, 2004, 11(3):157-168. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.03.017 许文良, 王枫, 裴福萍, 等.中国东北中生代构造体制与区域成矿背景:来自中生代火山岩组合时空变化的制约[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(2):339-353. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201302001 Kravchinsky V A, Cogné J P, Harbert W P, et al. Evolution of the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean as constrained by new palaeomagnetic data from the Mongol-Okhotsk suture zone, Siberia[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2002, 148(1):34-57. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246x.2002.01557.x
Sorokin A A, Yarmolyuk V V, Kotov A B, et al. Geochronology of Triassic-Jurassic granitoids in the southern framing of the Mongol-Okhotsk fold belt and the problem of Early Mesozoic granite formation in central and eastern Asia[J]. Doklady Earth Sciences, 2004, 399(8):1091-1094.




 下载:
下载: