Material composition, age and significance of the Dong Co Melange in the Bangong Co-Nujiang suture zone
-
摘要:
班公湖-怒江缝合带中段洞错混杂岩保存了完整的与大洋演化相关的混杂岩系,包括蛇绿岩岩块、洋岛残片,以及复理石岩片、大陆边缘沉积等沉积岩块体,是恢复和反演班公湖-怒江洋演化的理想地区。在综述前人研究的基础上,结合近年来的研究成果,归纳和总结洞错混杂岩的物质组成和时代,初步阐述洞错混杂岩对班公湖-怒江洋演化的指示意义。结果表明,洞错混杂岩中无论是蛇绿岩残块、洋岛残片还是次深海-深海复理石岩片等,均是不同时代多期次构造混杂的混杂体。最早的年龄记录可追溯至晚二叠世末期,最晚可延至早白垩世中晚期,是班公湖-怒江洋晚二叠世末期-早白垩世中晚期连续演化的记录。洞错混杂岩早白垩世中晚期大陆边缘沉积与蛇绿岩等的不整合仅是弧前楔顶盆地沉积的产物,不能约束班公湖-怒江洋的最终消亡。
Abstract:The Dong Co Melange, which contains various Ophiolitic blocks, ocean island fragments, flysch deposits, and continental marginal sediments, is an ideal object for restoring the evolution of the Bangong Co-Nujiang Ocean. In this paper, the authors present a detailed review and in-depth analysis of previous studies about the Dong Co Melange with the purpose of clarifying the material composition and age of the Dong Co Melange and discussing the significance of the Dong Co Melange. The authors hold that the ophiolitic blocks, ocean island fragments and flysch deposits in the Dong Co Melange are all multi-stage tectonic mélange, with their earliest age probably being the latest Late Permian and the latest age being the Early Cretaceous, indicating that the Bangong Co-Nujiang Ocean was continuous from the latest Late Permian to Early Cretaceous. The unconformity between the Early Cretaceous continental marginal sediments and the flysch deposits in the Dong Co Melange is only a record of fore-arc basin located on the accretion wedge.
-
Keywords:
- Tibetan Plateau /
- Bangong Co-Nujiang suture zone /
- Dong Co Melange
-
班公湖-怒江结合带(BNS)位于青藏高原北部, 西起班公湖, 向东经改则、东巧、丁青与昌宁-孟连带相连, 向西延伸向克什米尔, 与东地中海特提斯蛇绿岩相连, 在中国境内长达2000km, 是青藏高原一条重要的结合带[1]。班公湖-怒江结合带中存在规模巨大的蛇绿岩、增生杂岩, 以及夹持其中的残余弧或岛弧变质地块, 发育韧性剪切带、逆冲断层、构造混杂岩、复杂褶皱等多种构造行迹, 沿断裂还发育晚白垩世-新近纪陆相火山岩、新生代陆相走滑拉分盆地和第四纪谷地[2]。为更好地认识班公湖-怒江结合带内物质的形成机制及相关的构造背景, 需要对其开展深入的研究。
通过对沉积岩中的碎屑锆石进行U-Pb定年分析, 可有效地探讨其源区并开展历史时期的古大陆重建。本文对该地区早白垩统多尼组(原1:25万区调划为上三叠统巫嘎组)砂岩的碎屑锆石开展了形态学及U-Pb年代学研究, 为揭示班公湖-怒江缝合带内该地层单元的物源区提供新的证据, 同时为探讨班公湖-怒江结合带的构造演化史提供一定的依据。
1. 地质特征
多尼组出露于改则县南西的洞错一带(图 1), 呈近东西向带状分布, 区域上为一套灰色-深灰色含煤碎屑岩地层。岩性主要为泥岩、砂岩、板岩、页岩、粉砂岩、石英砂岩、长石石英砂岩, 局部含火山岩, 产植物、菊石、双壳类、腹足类、珊瑚、层孔虫、海胆、腕足类、介形类等化石。根据野外实测剖面特征, 研究区多尼组主要岩性为深灰色、灰色泥质粉砂岩、粉砂岩, 局部夹灰色钙质岩屑石英砂岩、长石石英砂岩及少量灰岩等, 在灰岩中局部可见生物碎屑, 未见完整化石。
2. 样品采集与分析方法
样品采集于西藏改则县洞错乡南约15km处欧仁一带的PM009地层剖面上。样品岩性主要为灰色中细粒长石石英砂岩, 主要由石英(84%)、长石(13%)、岩屑(2%)、胶结物等组成, 颗粒大小以0.15~ 0.60mm为主, 分选性好, 磨圆度一般, 呈次棱角状, 次圆状。石英主要为单晶石英, 长石类以斜长石为主, 岩屑成分主要为灰岩、泥岩、粉砂岩等, 孔隙式胶结(图 2)。
样品锆石的分离和挑选由廊坊市地岩矿物分选有限公司完成, 在双目镜下挑选出晶形和透明度好的锆石颗粒, 粘贴在环氧树脂表面, 抛光后将锆石进行透射光、放射光和阴极发光显微照相。锆石制靶及阴极发光图像制备由北京中美美科科技有限公司完成, LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年测试分析在中国地质大学(武汉)地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室完成。其中LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素年龄分析仪器为Elan6100DRC型激光剥蚀系统, 激光器为193nmArF准分子激光器。激光剥蚀斑束直径为32μm, 激光剥蚀深度为20~40μm。实验中采用氦气为剥蚀物质的载气, 采用标准锆石91500为外标, 采用美国国家标准物质局人工合成硅酸盐玻璃NIST SRM610为内标。详细的实验原理、流程和仪器参数见Yuan等[3]的文献。
3. 分析结果
多尼组砂岩碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄数据见表 1。在多尼组砂岩样品中, 随机挑选71粒锆石进行分析。从阴极发光(CL)图像(图 3)看出, 锆石颗粒大小在50~180μm之间。研究表明, 不同成因的锆石具有不同的Th/U值, 岩浆锆石的Th/U值较大(一般大于0.4);而变质锆石的Th/U值较小(一般小于0.1)[4]。多尼组砂岩碎屑锆石的Th/U值较大, 51颗锆石的Th/U值大于0.4, 平均值约为0.64, 说明锆石大部分为岩浆成因, 部分可能为变质成因。
表 1 洞错地区多尼组砂岩碎屑锆石U-Th-Pb同位素年龄数据Table 1. Detrital zircons U-Th-Pb data of sandstones in the Duoni Formation from Dongcuo area


4. 分析与讨论
4.1 测年结果
对于年轻锆石而言, 207Pb/206Pb年龄误差较大, 而对于古老锆石而言, 206Pb/238U年龄的误差较大。本文在年龄选取时, 对小于1000Ma的锆石, 选取206Pb/238U计算年龄值; 年龄大于1000Ma的锆石, 选取207Pb/206Pb计算年龄值[5]。从碎屑锆石年龄分布频率直方图(图 4)可以看出, 多尼组砂岩碎屑锆石年龄值分布在125~3261Ma之间。其中125~1000Ma的锆石有37粒, 最年轻年龄值为125Ma(测点号为PM009/26-17, 和谐度为97%); 大于1000Ma的年龄值为34个, 最老年龄值为3261Ma(测点号为PM009/26-35, 和谐度为96%)。碎屑锆石主要年龄区间(或峰值)为3261Ma、2739~2335Ma、1880~ 1750Ma、1006~657Ma、577~510Ma、456~409Ma和252~202Ma(表 1)。
![]() 图 4 青藏高原碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄频率图(据参考文献[15]修改)Figure 4. Age distributions of detrital zircons from the Tibetan Plateau
图 4 青藏高原碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄频率图(据参考文献[15]修改)Figure 4. Age distributions of detrital zircons from the Tibetan Plateau4.2 讨论
多尼组的碎屑锆石年龄数据跨度较大, 不同的年龄峰值代表不同的地质意义。
(1) 3261Ma, 大于3000Ma的碎屑锆石在样品中仅出现1粒, 表明物源区存在古老地壳的残留[6], 为研究班怒带物源区的形成和演化奠定了物质基础。
(2) 2739~2335Ma年龄组包含10颗碎屑锆石, 代表物源区可能存在构造-岩浆事件。从全球地质背景看, 华北、北美、瑞芬及其他克拉通在2.5Ga左右发生了大规模的拼合事件(如Grenville事件、Pan-Afriean事件等), 形成有记载的最古老的超级大陆[7]。近年来, 众多学者在羌塘盆地发现1.8~ 2.7Ga的锆石, 如盆地中央隆起带差桑-茶布一带的戈木日群[8], 盆地西南部龙木错-双湖缝合带南侧荣玛温泉地区石英岩[9], 以及羌塘盆地北部唐古拉山温泉地区雁石坪群[10]。暗示羌塘盆地有太古宙的地壳物质, 支持羌塘盆地存在前寒武纪结晶基底的可能性。这也说明, 研究区多尼组的物源很可能为北部的南羌塘地块。
(3) 1880~1750Ma年龄组包含16颗碎屑锆石, 指示源区存在古元古代早期的构造热事件。研究表明[11-12], Columbia超级大陆各个组成陆块是在2.1~ 1.8Ga碰撞事件中拼合在一起的, 并在中元古代早-中期Columbia超级大陆边缘向外增生, 随后开始裂解, 1880~1750Ma可能也是羌塘结晶基底的主期变质年龄。
(4) 1006~657Ma年龄组包含13颗碎屑锆石, 该期是全球构造运动演化的一系列重大热事件时期, Grenvillian碰撞造山期(1000~900Ma)形成了罗迪尼亚超大陆, 在850~750Ma开始隆升、裂解[13]。在700Ma发生分解, 反映了早期的泛非碰撞, 中国大陆主要的构造表现为普遍存在张裂, 在羌塘结晶基底的戈木日群中发现1016~929Ma的热事件, 说明此时羌塘地块存在构造热事件[1]。
(5) 577~510Ma年龄组包含5颗碎屑锆石, 指示了新元古代晚期的一次构造热事件, 该组年龄值可能是泛非造山运动(550±100Ma)在物源区的记录。
(6) 456~409Ma年龄组包含8颗碎屑锆石, 可能指示了冈瓦纳大陆北缘在早泥盆世-奥陶纪的增生过程[14]。
(7) 252~202Ma年龄组包含5颗碎屑锆石, 指示拉萨地块与羌塘地块之间发生了俯冲消减及碰撞与缝合作用。
(8) 最小年龄125Ma和126Ma, 可能代表该套地层的沉积时代, 说明该套地层于早白垩世沉积形成。
班公湖地区中生代沙木罗组和日松组碎屑锆石显示, 其沉积物的物源区可能为北部的羌塘地块[1]。商旭地区中生代沉积物中含有部分来自其北部南羌塘地块中的物质, 暗示班公湖-怒江洋壳在中生代向北俯冲[15]。南羌塘与特提斯喜马拉雅沉积变质岩的碎屑锆石年龄具有相似的频率分布特征, 且二者的主要年龄峰值为530Ma、950Ma, 其与高喜马拉雅新元古代沉积变质岩碎屑锆石的年龄主峰一致, 表明其在古生代与高喜马拉雅相邻; 同时, 拉萨地块与澳大利亚西部的碎屑锆石具有一致的年龄峰值1170Ma, 表明拉萨地块可能在石炭纪-二叠纪与澳大利亚西北部毗邻[16]。从锆石年龄分布频率图可见, 研究区碎屑锆石年龄分布直方图与南羌塘更具相似性, 西藏洞错地区班公湖-怒江结合带早白垩世沉积物的物源可能来自北部的南羌塘地块。
5. 结论
(1) 班公湖地区早白垩世多尼组砂岩碎屑锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb测年结果显示, 碎屑锆石最年轻颗粒的年龄值为125Ma, 说明其形成时代晚于早白垩世; 最老碎屑锆石年龄值为3261Ma, 表明物源区存在古老地壳的残留。
(2) 将研究区早白垩世碎屑锆石的年龄分布频率图与南部的拉萨地块及北部的南羌塘地块对比, 其与南羌塘地块更具相似性, 说明研究区的早白垩世沉积物的物源可能来自北部的南羌塘地块。
致谢: 野外工作得到河海大学吴浩博士、中国海洋大学刘一鸣博士、中国地质大学(北京)许伟博士、吉林大学张天羽博士、南京大学李兴奎博士等的帮助和支持,审稿专家对本文提出了建设性的修改意见,在此一并表示感谢。 -
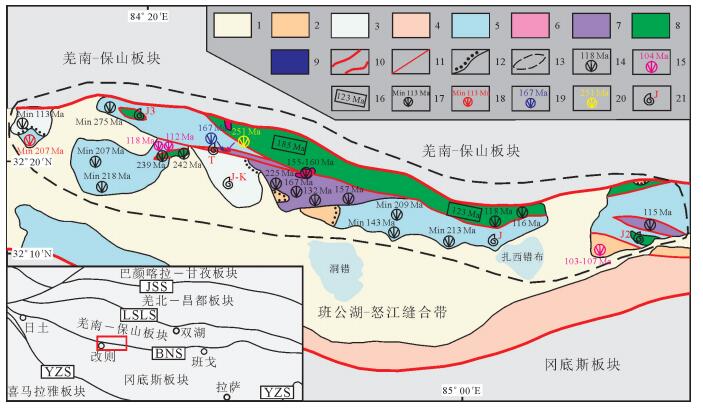
图 1 藏北改则洞错地区地质简图
(晚三叠世或早白垩世?);5—复理石岩片;6—岩浆岩;7—蛇绿岩;8—洋岛残片;9—榴辉岩;10-班公湖-怒江缝合带主干断裂;11—缝合带内主干断裂;12—角度不整合;13—洞错混杂岩范围;14—蛇绿岩和洋岛残片中的岩浆岩锆石U-Pb测年;15—地层中火山岩夹层锆石U-Pb测年;16—Ar-Ar年龄;17—已发表碎屑锆石最小锆石U-Pb年龄[23-24];18—待发表碎屑锆石最小锆石U-Pb年龄;19—洞错榴辉岩变质年龄;20—洞错榴辉岩原岩年龄;21—地层中的生物化石;JSS—金沙江缝合带;LSLS—龙木错-双湖-澜沧江缝合带;BNS—班公湖-怒江缝合带;YZS—雅鲁藏布江缝合带
Figure 1. Geological map of the Dong Co area, Gerze County, Northern Tibet
-
潘桂棠, 陈智梁, 李兴振, 等.东特提斯地质构造形成演化[M].北京:地质出版社, 1997. Shi R D, Griffin W L, Reilly S Y, et al. Melt/mantle mixing products podiform chromite deposits in ophiolites:Implication of Re-Os systematics in the Dongqiao Neo-tethyan ophiolite northern Tibet[J]. Gondwana Research, 2012, 21:194-206. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.05.011
Zhu D C, Li S M, Cawood P A, et al. Assembly of the Lhasa and Qiangtang terranes in central Tibet by divergent double subduction[J]. Lithos, 2016, 245:7-17. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.06.023
耿全如, 彭智敏, 张璋, 等.班公湖-怒江成矿带及邻区特提斯演化与成矿地质背景[M].北京:地质出版社, 2012. Geng Q R, Zhang Z, Peng Z M, et al. Jurassic-Cretaceous granitoids and related tectono-metallogenesis in the Zapug-Duobuza arc, western Tibet[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 77:163-175. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=6968b5853ea1728716252ce63aaeea5d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Li G M, Qin K Z, Li J X, et al. Cretaceous magmatism and metallogeny in the Bangong-Nujiang metallogenic belt, central Tibet:Evidence from petrogeochemistry, zircon U-Pb ages, and Hf-O isotopic compositions[J]. Gondwana Research, 2017, 41:110-127. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.09.006
潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 侯增谦, 等.冈底斯造山带的时空结构及演化[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(3):521-533. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200603001 范建军, 李兴奎, 张天羽, 等.班公湖-怒江洋中西段汇聚消亡时空重建[M].北京:地质出版社, 2017. Yin A, Harrison T M. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences 2000, 28:211-280. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.211
Allègre C J, Courtillot V, Tapponnier P, et al. Structure and evolution of the Himalaya-Tibet orogenic belt[J]. Nature, 1984, 307:17-22. doi: 10.1038/307017a0
Dewey J F, Shackelton R M, Chang C, et al. The tectonic evolution of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 1988, A327:379-413. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy200906024
Coulon C, Maluski H, Bollinger C, et al. Mesozoic and Cenozoic volcanic rocks from central and southern Tibet:39Ar/40Ar dating, petrological characteristics and geodynamical significance[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1986, 79:281-302. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(86)90186-X
Kapp P, Yin A, Harrison T M, et al. Cretaceous-Tertiary shortening, basin development, and volcanism in central Tibet[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2005, 117:865-878. doi: 10.1130/B25595.1
Kapp P, DeCelles P G, Gehrels G E, et al. Geological records of the Lhasa-Qiangtang and Indo-Asian collisions in the Nima area of central Tibet[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2007, 119:917-932. doi: 10.1130/B26033.1
Fan J J, Li C, Xie C M, et al. Petrology, geochemistry, and geochronology of the Zhonggang ocean island, northern Tiber:implications for the evolution of the Bangongco-Nujiang oceanic arm of Neo-Tethys[J]. International Geology Review, 2014, 56:1504-1520. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2014.947639
Fan J J, Li C, Wang M, et al. Reconstructing in space and time the closure of the middle and western segments of the Bangong-Nujiang Tethyan Ocean in the Tibetan Plateau[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2017, 107:231-249. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a5768c11380a5c8e0b60eea132ec8e74&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Li J X, Qin K Z, Li G M, et al. Geochronology, geochemistry, and zircon Hf isotopic compositions of Mesozoic intermediate-felsic intrusions in central Tibet:Petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Lithos, 2014, 198/199:77-91. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.03.025
Li Y L, He J, Wang C S, et al. Cretaceous volcanic rocks in south Qiangtang Terrane:Products of northward subduction of the Bangong-Nujiang Ocean?[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 104:69-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.09.033
Liu D L, Huang Q S, Fan S Q, et al. Subduction of the BangongNujiang Ocean:constraints from granites in the Bangong Co area, Tibet[J]. Geological Journal, 2014, 49:188-206. doi: 10.1002/gj.v49.2
Volkmer J E, Kapp P, Horton B K, et al. Northern Lhasa thrust belt of central Tibet:evidence of Cretaceous-early Cenozoic shortening within a passive roof thrust system?[J] Geological Society of America, Special Paper, 2014, 507:59-70. doi: 10.1130/2014.2507(03)
Hao L L, Wang Q, Wyman D A, et al. Underplating of basaltic magmas and crustal growth in a continental arc:Evidence from Late Mesozoic intermediate-felsic intrusive rocks in southern Qiangtang, central Tibet[J]. Lithos, 2016, 245:223-242. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.09.015
Xu W, Li C, Wang M, et al. Subduction of a spreading ridge within the Bangong Co-Nujiang Tethys Ocean:Evidence from Early Cretaeous mafic dykes in the Duolong porphyry Cu-Au deposit, western Tibet[J]. Gondwana Research, 2017, 41:128-141. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.09.010
Li S, Guilmette C, Ding L, et al. The subduction-accretion history of the Bangong-Nujiang Ocean:Constraints from provenance and geochronology of the Mesozoic strata near Gaize, central Tibet[J]. Tectonophysics, 2017, 702:42-60. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2017.02.023
Huang T T, Xu J F, Chen J L, et al. Sedimentary record of Jurassic northward subduction of the Bangong-Nujiang Ocean:insights from detrital zircons[J]. International Geology Review, 2017, 59:166-184. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2016.1218801
邱瑞照, 周肃, 邓晋福, 等.西藏班公湖-怒江带西段舍马拉沟蛇绿岩中辉长岩年龄测定:兼论班公湖-怒江蛇绿岩带形成时代[J].中国地质, 2004, 31(3):262-268. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2004.03.004 曾庆高, 毛国政, 王保弟, 等. 1:25万改则县幅等4幅区域地质调查报告[M].北京:地质出版社, 2010. Fan J J, Li C, Xu J X, et al. Petrology, geochemistry, and geological significance of the Nadong ocean island, Banggongco-Nujiang suture, Tibetan plateau[J]. International Geology Review, 2014, 56:915-928. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2014.900651
Fan J J, Li C, Liu J H, et al. The Middle Triassic evolution of the Bangong-Nujiang Tethyan Ocean:Evidence from analyses of OIB-type basalts and OIB-derived phonolites in northern Tibet[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2018, 107(5):1755-1775. doi: 10.1007/s00531-017-1570-x
Xu W, Xu M J, Wu Y W, et al. Petrology geochemistry and geochronology of boninitic dykes from the Kangqiong ophiolite:implications for the Early Cretaceous evolution of Bangong-Nujiang Neo-Tethys Ocean in Tibet[J]. International Geology Review 2015, 57:2028-2043. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2015.1050464
Fan J J, Li C, Xie C M, et al. The evolution of the Bangong-Nujiang Neo-Tethys ocean:evidence from zircon U-Pb and Lu-Hf isotopic analyses of Early Cretaceous oceanic islands and ophiolites[J]. Tectonophysics, 2015, 655:27-41. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2015.04.019
Zhang K J, Xia B, Zhang Y X, et al. Central Tibetan Meso-Tethyan oceanic plateau[J]. Lithos, 2014, 210/211:278-288. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.09.004
付佳俊, 丁林, 许强, 等.西藏改则洞错地区白垩纪火山岩锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素组成及对班公湖-怒江洋俯冲闭合的制约[J].地质科学, 2015, 50(1):182-202. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2015.01.011 陈志.西藏改则地区仲岗洋岛火山-沉积序列与地球化学特征[D].成都理工大学硕士学位论文, 2016. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10616-1016226962.htm 徐建鑫, 李才, 范建军, 等.藏北班公湖-怒江板块缝合带内的侏罗纪洋岛型岩石组合——来自岩石学及地球化学的证据[J].地质通报, 2014, 33(11):1793-1803. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.11.015 Mourão C, Mata J, Doucelance R, et al. Quaternary extrusive calciocarbonatite volcanism on Brava Island (Cape Verde):A nephelinite-carbonatite immiscibility product[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2010, 56:59-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2009.06.003
鲍佩声, 肖序常, 苏犁, 等.西藏洞错蛇绿岩的构造环境:岩石学、地球化学和年代学制约[J].中国科学(D辑), 2007, 37(3):298-307. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd200703002 张玉修.班公湖-怒江缝合带中西段构造演化[D].中国科学院研究生院博士学位论文, 2007. http://www.irgrid.ac.cn/handle/1471x/339607?mode=full&submit_simple=Show+full+item+record 李建峰, 夏斌, 王冉, 等.洞错地幔橄榄岩、均质辉长岩矿物化学特征及其构造意义[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2013, 37(2):308-319. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2013.02.013 Wang B D, Wang L Q, Chung S L, et al. Evolution of the Bangong-Nujiang Tethyan ocean:Insights from the geochronology and geochemistry of mafic rocks within ophiolites[J]. Lithos, 2016, 245:18-33. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.07.016
武勇.西藏洞错蛇绿岩成因及构造环境研究[D].中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2016. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1016184333.htm Fan J J, Li C, Liu Y M, et al. Age and nature of the late Early Cretaceous Zhaga Formation, northern Tibet:constraints on when the Bangong-Nujiang Neo-Tethys Ocean closed[J]. International Geology Review, 2015, 57:342-353. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2015.1006695
Zeng M, Zhang X, Cao H, et al. 2014. Late Triassic initial subduction of the Bangong-Nujiang Ocean beneath Qiangtang revealed:stratigraphic and geochronological evidence from Gaize, Tibet[J]. Basin Research, 2016, 28:147-157. doi: 10.1111/bre.12105
Li S, Ding L, Guilmette C, et al. The subduction-accretion history of the Bangong-Nujiang Ocean:Constraints from provenance and geochronology of the Mesozoic strata near Gaize, central Tibet[J]. Tectonophysics, 2017, 702:42-60. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2017.02.023
Fan J J, Li C, Sun Z M, et al. Early Cretaceous MORB-type basalt and A-type rhyolite in northern Tibet:Evidence for ridge subduction in the Bangong-Nujiang Tethyan Ocean[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 154:187-201. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.12.020
Li S, Guilmette C, Ding L, et al. Provenance of Mesozoic clastic rocks within the Bangong-Nujiang suturezone, central Tibet:Implications for the age of the initial Lhasa-Qiangtang collision[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 147:469-484. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.08.019
邓金火, 袁振国, 余江, 等.班公湖-怒江结合带西段底砾岩的新发现及地质意义[J].地质论评, 2017, 63(2):302-310. http://qikan.cqvip.com/article/detail.aspx?id=671727492 吴浩, 李才, 胡培远, 等.西藏尼玛县塔色普勒地区去申拉组火山岩的发现及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2013, 32(7):1014-1026. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2013.07.007 吴浩, 李才, 胡培远, 等.藏北班公湖-怒江缝合带早白垩世双峰式火山岩的确定及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2014, 33(11):1804-1814. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.11.016 Wu H, Li C, Xu M J, et al. Early Cretaceous adakitic magmatism in the Dachagou area, northern Lhasa terrane Tibet:implications for slab roll-back and subsequent slab break-off of the lithosphere of the Bangong-Nujiang Ocean[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 97(1):51-66. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1f9d412ae772b8dbaf0ceac82fb0d61c&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Chen W W, Zhang S H, Ding J K, et al. Combined paleomagnetic and geochronological study on Cretaceous strata of the Qiangtang terrane, central Tibet[J]. Gondwana Research, 2017, 41:373-389. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.07.004
Fan J J, Li C, Wu H, et al. Late Jurassic adakitic granodiorite in the Dong Co area, northern Tibet:Implications for subduction of the Bangong-Nujiang oceanic lithosphere and related accretion of the Southern Qiangtang terrane[J]. Tectonophysics, 2016, 691:345-361. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2016.10.026
王保弟, 王立全, 许继峰, 等.班公湖-怒江结合带洞错地区舍拉玛高压麻粒岩的发现机器地质意义[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(9):1605-1616. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.09.002 Zhang Y X, Li Z W, Zhu L D, et al. Newly discovered eclogites from the Bangong Meso-Tethyan suture zone (Gaize, central Tibet, western China):mineralogy, geochemistry, geochronology, and tectonic implications[J]. International Geology Review, 2015, 58:1-14. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=04aa3f2fd15ec5bc4cfd266de6653f25&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Zhang X Z, Wang Q, Dong Y S, et al. High pressure granulite-facies overprinting during the exhumation of eclogites in the Bangong-Nujiang suture zone, central Tibet:link to flat-slab subduction[J]. Tectonics, 2018, doi:10. 1002/2017TC004774.
陈国荣, 刘鸿飞, 蒋光武, 等.西藏班公湖-怒江结合带中段沙木罗组的发现[J].地质通报, 2004, 23(2):193-194. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.02.015 谢冰晶, 程捷, 黄传冠.班公湖-怒江结合带西段沙木罗组的发现及意义[J].东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 33(2):159-164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3504.2010.02.008 王建平.西藏东部特提斯地质[M].北京:科学出版社, 2003. Pan G T, Wang L Q, Li R S, et al. Tectonic evolution of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 53:3-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.12.018
Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, Niu Y L, et al. The origin and pre-Cenozoic evolution of the Tibetan Platean[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 23:1429-1454. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.02.002
Smith A B, Xu J T. Paleontology of the 1985 Tibet geotraverse, Lhasa to GolmudThe Geological Evolution of Tibet[M]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, London, 1988:53-106.
任纪舜, 肖黎薇. 1:25万地质填图进一步揭开了青藏高原大地构造的神秘面纱[J].地质通报, 2003, 23(1):1-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2003.01.001 Shi R D, Yang J S, Xu Z Q, et al. The Bangong Lake ophiolite (NW Tibet) and its bearing on the tectonic evolution of the Bangong-Nujiang suture zone[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2008, 32:438-457. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2007.11.011
黄启帅, 史仁灯, 丁炳华, 等.班公湖MOR型蛇绿岩Re-Os同位素特征对班公湖-怒江特提斯洋裂解时间的制约[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2012, 31(4):465-478. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2012.04.001 Girardeau J, Marcoux J, Allegre C J, et al. Tectonic environment and geodynamic significance of the Neo-Cimmerian Dongqiao ophiolite, Bangong-Nujiang suture zone, Tibet[J]. Nature, 1984, 307:27-31. doi: 10.1038/307027a0
Zhou M F, Malpas J, Robinson P T, et al. The dynamothermal aureole of the Donqiao ophiolite (northern Tibet)[J]. Canada Journal of Earth Sciences, 1997, 34:59-65. doi: 10.1139/e17-005
雍永源, 贾宝江.板块剪式汇聚加地体拼贴——中特提斯洋消亡的新模式[J].沉积与特提斯地质, 2000, 20(1):85-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2000.01.007 Wang W L, Aitchison J C, Lo C H, et al. Geochemistry and geochronology of the amphibolite blocks in ophiolitic mélanges along Bangong-Nujiang suture, central Tibet[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2008, 33:122-138. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2007.10.022
夏斌, 徐力峰, 韦振权, 等.西藏东巧蛇绿岩中辉长岩锆石SHRIMP定年及其地质意义[J].地质学报, 2008, 82(4):528-531. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb200804010 曲晓明, 辛洪波, 赵元艺, 等.西藏班公湖中特提斯洋盆的打开时间:镁铁质蛇绿岩地球化学与锆石U-Pb LAICPMS定年结果[J].地学前缘, 2010, 17(3):53-63. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201003005 卢书炜, 任建德, 杜凤军, 等.从尼玛地区地质新资料看中特提斯洋的构造演化[J].沉积与特提斯地质, 2003, 23(3):35-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2003.03.004 赵文津, 刘葵, 蒋忠惕, 等.西藏班公湖-怒江缝合带——深部地球物理结构给出的启示[J].地质通报, 2004, 23(7):623-635. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.07.001 王玉净, 王建平, 刘彦明, 等.西藏丁青蛇绿岩特征、时代及其地质意义[J].微体古生物学报, 2002, 19(4):417-420. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0674.2002.04.009 Fan J J, Li C, Wang M, et al. Remnants of a Late Triassic ocean island in the Gufeng area, northern Tibet:implications for the opening and early evolution of the Bangong-Nujiang Tethyan Ocean[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 135:35-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.12.015
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(4)




 下载:
下载: