Constraints on tectonic, fluid and metallogenic system evolution for the formation of Sareke sandstone copper deposit in northwestern Tarim block
-
摘要:
塔里木陆块西北缘萨热克砂岩型铜矿床构造演化、流体演化与成矿之间具有密切关系,处于一个统一系统中。矿床成岩期方解石中包裹体水的δD值为-65.3‰~-99.2‰,改造成矿期石英包裹体水的δD值为-77.7‰~-96.3‰,成岩成矿期成矿流体δ18OH2O变化范围为-3.22‰~1.84‰,改造成矿期成矿流体δ18OH2O变化范围为-4.26‰~5.14‰,指示萨热克铜矿成岩期、改造期成矿流体主要为中生代大气降水及其经水岩作用而成的盆地卤水。矿石中辉铜矿δ34S值为-24.7‰~-15.4‰,指示硫主要源自硫酸盐细菌与有机质还原,部分源于有机硫。构造与成矿流体演化对砂岩铜矿成矿起关键制约作用。盆地发展早期强烈的抬升运动使盆地周缘基底与古生界剥蚀,为富铜矿源层的形成提供了丰富物源,至晚侏罗世盆地发展晚期,长期演化积聚的巨量含矿流体在库孜贡苏组砾岩胶结物及裂隙中富集,在萨热克巴依盆地内形成具有经济意义的砂岩型铜矿床。
Abstract:There exist close relationships between tectonics, fluid evolution and formation of copper ore in the Sareke sandstone deposit in northwestern Tarim block, which constitute an integrated system. The δD values of inclusion water in the calcite of diagenetic stage are in the range of -65.3‰~-99.2‰, and the δD values of inclusion water in the quartz of metallogenic epoch are in the range of -65.3‰~-99.2‰, the δ18OH2O values of the ore-forming fluid in the diagenetic stage are in the range of -3.22‰~1.84‰, and the δ18OH2O values of the ore-forming fluid in the metallogenic epoch are in the range of-4.26‰~5.14‰, suggesting that the ore-forming fluid in the diagenetic stage and transformation period of the Sareke copper deposit mainly originated from the atmospheric water in the Mesozoic period and basin brine evolved from the water-rock interaction of the rainfall. The δ34S values of the chalcocite in the ore are in the range of-15.4‰~-24.7‰, suggesting that most of the sulfur originated from the bacteria and reduced organic carbon in the strata, with the addition of minor organic sulfur. The evolution of the tectonics and ore-forming fluid controlled the formation of sandstone copper deposits. In the early period of the basin development, the strong uplift movement caused the erosion of the basement and Paleozoic strata in the periphery of Sareke basin, which offered abundant provenance to the formation of copper-rich source layer. Toward the late period, i.e., Late Jurassic epoch, large amounts of ore-forming fluid after long-term evolution was concentrated in the agglutinate and fissures of conglomerate in Kuzigongsu Formation, forming sandstone copper deposits with economic value in Sareke basin.
-
Keywords:
- Tarim block /
- Sareke /
- sandstone copper deposit /
- tectonic /
- fluid /
- metallogenic system
-
致谢: 成文过程中得到中国地质调查局西安地质调查中心陈隽璐、贾群子研究员、王志海高级工程师、叶美芳工程师的热心指导,野外工作中得到萨热克铜矿的大力支持,审稿专家提出宝贵的意见,在此一并致以衷心的感谢。
-
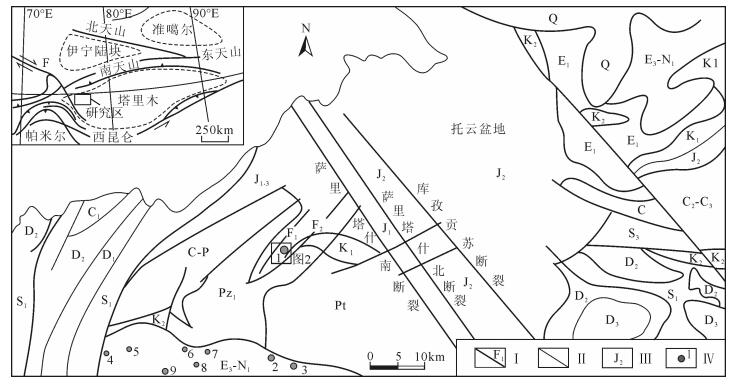
图 1 萨热克铜矿区域地质略图(据参考文献[7]修改)
Ⅰ—断裂:F—费尔干纳断裂;F1—萨热克巴依北逆断裂;F2—萨热克巴依南逆断裂;Ⅱ—地层界线;Ⅲ—地层及时代;Ⅳ—砂(砾)岩型铜矿床(点)及编号:1—萨热克铜矿;2—杨叶铜矿;3—花园铜矿;4—沙哈尔铜矿点;5—托克乔尔铜矿点;6—喀拉丹铜矿点;7—卡巴加特铜矿点;8—吉里德热铜矿点;9—丹格-恰比尔铜矿点;Q—第四系;E3-N1—渐新统;E1—古新统;K2—上白垩统;K1—下白垩统;J2—中侏罗统;J1—下侏罗统;C-P—石炭系-二叠系;D3—上泥盆统;D2—中泥盆统;D1—下泥盆统;S3—上志留统;S1—下志留统
Figure 1. Regional geological map of the Sareke copper deposit
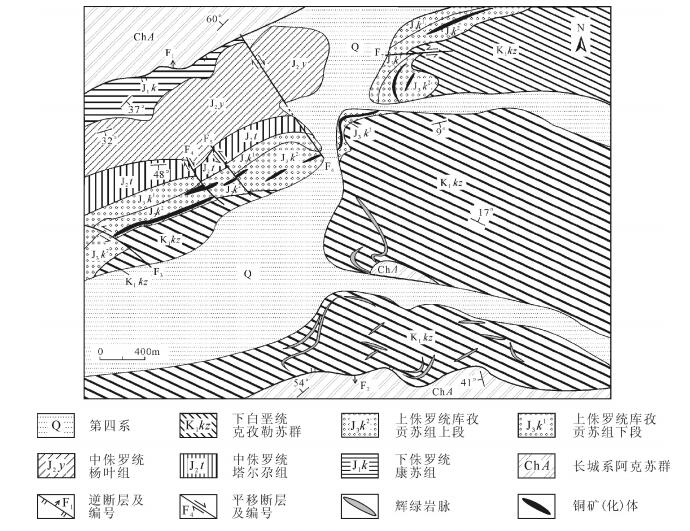
图 2 萨热克铜矿床地质图(据参考文献[7]修改)
Figure 2. Geological map of the Sareke copper deposit
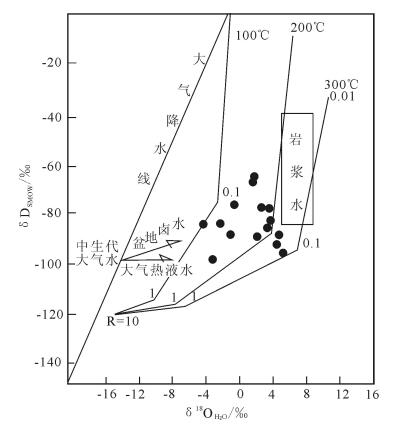
图 5 萨热克铜矿成矿流体水/岩同位素δ18O-δD交换图(底图据参考文献[20])
Figure 5. Plot of δ18O-δD for water/rock isotopic exchange of ore-forming fluids in the Sareke copper deposit
表 1 萨热克铜矿床氢-氧同位素组成
Table 1 H-O isotopic data of the Sareke copper deposit
样号 样品对象 成矿期 δDV-SMOW/‰ δ18OV-SMOW/‰ 均一温度/K δ18OH2O/‰ SRK-W1 方解石 成岩成矿期 -64.4 21.3 352.7 1.84 SRK-W3 -66.8 21.0 352.6 1.52 SRK-W4 -98.8 17.0 346.9 -3.22 SRK-W6 -76.4 19.9 343.6 -0.76 SRK-T1 石英 改造成矿期 -88.9 17.6 441.7 2.03 SRK-T2 -84.3 18.3 391.5 -2.27 SRK-T3 -78.4 18.9 448.6 3.89 SRK-T4 -89.4 18.4 467.0 4.76 SRK-T5 -77.7 19.4 428.6 2.69 SRK-T6 -82.8 17.7 462.1 3.71 SRK-T7 -84.5 18.2 376.5 -4.26 SRK-T9 -86.6 19.1 439.8 3.37 SRK-T10 -96.3 19.7 454.4 5.14 SRK-T11 -92.1 18.5 458.6 4.25 SRK-T12 -88.3 17.6 408.8 -1.04 表 2 萨热克铜矿床辉铜矿单矿物硫同位素组成
Table 2 Sulfur isotopic compositions of chalcocite single mineral from the Sareke copper deposit
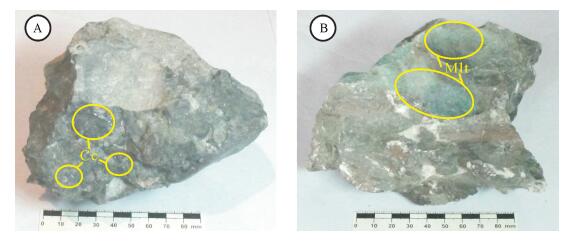
样号 矿物 样品特征 δ34SV-CDT/‰ SRK-TW1 辉铜矿 灰色稀疏浸染状含孔雀石、辉铜矿矿石 -22.2 SRK-TW2 辉铜矿 灰色细脉状辉铜矿矿石 -18.5 SRK-TW3 辉铜矿 灰色团块状辉铜矿矿石 -16.9 SRK-TW4 辉铜矿 灰色稀疏团块状含孔雀石、辉铜矿矿石 -22.1 SRK-TW5 辉铜矿 灰色细脉状含孔雀石、辉铜矿矿石 -18.9 SRK-TW7 辉铜矿 灰色块状辉铜矿矿石 -15.9 SRK-TW8 辉铜矿 灰色块状含孔雀石、辉铜矿矿石 -15.4 SRK-TW9 辉铜矿 灰色稀疏浸染状含孔雀石、辉铜矿矿石 -17.3 SRK-TW10 辉铜矿 灰色团斑状含孔雀石、辉铜矿矿石 -24.7 表 3 萨热克铜矿床流体包裹体气相成分激光拉曼探针分析结果
Table 3 Laser Raman data of gas components of the fluid inclusions in the Sareke copper deposit
样号 成矿期 x气相/% CO2 H2S CH4 N2 H2 总和 SRK-LT1 4.00 39.9 56.1 100.0 SRK-LT2 59.7 40.3 100.0 SRK-LT3 71.8 28.2 100.0 SRK-LT5 52.5 47.5 100.0 SRK-LT6 成岩成 27.3 72.7 100.0 SRK-LT7 矿期 76.0 24.0 100.0 SRK-LT8 13.3 86.7 100.0 SRK-LT9 14.4 85.6 100.0 SRK-LT11 23.5 76.5 100.0 SRK-LT14 93.3 6.7 100.0 SRK-LT4 9.6 82.6 7.8 100.0 SRK-LT10 49.2 50.8 100.0 SRK-LT11 75.9 6.5 17.6 100.0 SRK-LT12 83.7 10.0 6.2 100.0 SRK-LT13 改造成 45.6 6.4 48.0 100.0 SRK-LT15 矿期 83.3 16.7 100.0 SRK-LT16 7.9 92.1 100.0 SRK-LT18 69.2 30.8 100.0 SRK-LT19 84.5 15.5 100.0 SRK-LT20 81.3 18.7 100.0 表 4 萨热克铜矿床流体包裹体液相成分激光拉曼探针分析结果
Table 4 Laser Raman data of liquid components of the fluid inclusions in the Sareke copper deposit
样号 成矿期 x液相/% CO2 H2S CH4 H2O 总和 SRK-LT1 0.01 99.99 100.0 SRK-LT2 100.00 100.0 SRK-LT3 0.30 0.01 0.01 99.67 100.0 SRK-LT5 100.00 100.0 SRK-LT6 成岩成 100.00 100.0 SRK-LT7 矿期 100.00 100.0 SRK-LT8 100.00 100.0 SRK-LT9 100.00 100.0 SRK-LT11 100.00 100.0 SRK-LT14 100.00 100.0 SRK-LT4 0.01 99.99 100.00 SRK-LT10 0.09 99.91 100.00 SRK-LT11 0.43 99.57 100.00 SRK-LT12 100.00 100.00 SRK-LT13 改造成 100.00 100.00 SRK-LT15 矿期 100.00 100.00 SRK-LT16 100.00 100.00 SRK-LT18 0.10 99.9.00 100.00 SRK-LT19 100.00 100.00 SRK-LT20 0.08 99.92 100.00 表 5 不同期次流体特征参数
Table 5 The characteristic parameters for different stages of fluid inclusions
测试参数 成岩成矿期(35个测试点) 改造成矿期(38个测试点) 冰点温度/℃ 范围 -7.7 ~ -1.2 -6.5 ~ -0.1 均值 -4.4 -3.6 均一温度/℃ 范围 72.2~173.5 120.3~260.7 均值 119.8 192.4 盐度/wt%,NaCl 范围 2.07~11.34 0.18~9.86 均值 7.04 5.73 流体密度/g·cm-3 范围 0.92~1.03 0.81~1.00 均值 0.99 0.91 流体压力/MPa 范围 246.16~500.46 222.34~461.14 均值 386.59 358.81 -
谭凯旋.砂岩铜矿地球化学和成矿动力学[M].北京:地震出版社, 1998. 祝新友, 王京彬, 王玉杰, 等.新疆萨热克铜矿——与盆地卤水作用有关的大型矿床[J].矿产勘查, 2011, 2(1):28-35. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytgcj201101007 刘增仁, 漆树基, 田培仁, 等.塔里木盆地西北缘中新生代砂砾岩型铅锌铜矿赋矿层位的时代厘定及意义[J].矿产勘查, 2014, 5(2):149-158. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ysjs201402006&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 张振亮, 冯选洁, 董福辰, 等.西南天山砂砾岩容矿矿床类型及找矿方向[J].西北地质, 2014, 47(3):70-82. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=xbdi201403010&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 白洪海, 石玉君.西南天山砂岩型铜矿地质特征及成因分析[J].新疆有色金属, 2008, 4:14-18. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/98333X/200804/27822270.html 胡庆雯, 刘宏林.新疆乌恰县萨热克砂岩铜矿床地质特征与找矿前景[J].矿产与地质, 2008, 22(2):131-134. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=kcyd200802008&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 李志丹, 薛春纪, 辛江, 等.新疆乌恰县萨热克铜矿床地质特征及硫、铅同位素地球化学[J].现代地质, 2011, 25(4):720-729. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/96868X/201104/39175948.html 辛江.新疆乌恰县杨叶砂岩型铜矿地质特征及成因浅析[J].矿床地质, 2010, 29(S1):393-394. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-XBTK201510053.htm 高珊, 高纬, 赵良军, 等.新疆乌恰县花园铜矿遥感近矿找矿标志分析[J].测绘与空间地理信息, 2016, 39(8):42-44+48. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dbch201608012&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 高珍权, 方维萱, 王伟, 等.沟系土壤测量在新疆乌恰县萨热克铜矿勘查中的应用效果[J].矿产与地质, 2005, 6:669-673. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2005.06.017 胡剑辉, 吉蕴生, 曾志钢, 等.新疆萨热克铜矿床地球化学异常评价研究[J].矿产勘查, 2014, 5(2):281-292. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ysjs201402021&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 刘宏林, 胡庆雯, 田培仁.关于新疆乌恰盆地中新生代砂岩型铅锌铜铀层次成矿问题浅析[J].矿产与地质, 2010, 24(2):113-119. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=34538927 陆俊吉, 胡煜昭, 江小均, 等.新疆乌恰萨热克铜矿北矿带库孜贡苏组沉积相、古流向、物源区及其找矿意义——来自砾石统计分析的证据[J].地质通报, 2016, 35(6):963-970. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160613&flag=1 方维萱, 贾润幸, 王磊, 等.新疆萨热克大型砂砾岩型铜多金属矿床的成矿控制规律[J].矿物学报, 2015, 35(S1):202-204. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=kwxb2015s1150&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 刘中华, 陆俊吉, 胡煜昭, 等.新疆萨热克铜矿控矿因素的探索[J].矿产与地质, 2017, 31(01):23-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2017.01.003 罗金海, 周新源, 邱斌, 等.塔里木盆地西部中、新生代5次构造事件及其石油地质学意义[J].石油勘探与开发, 2005, 1:18-22. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.01.005 冉祟英, 刘卫华.康滇地轴铜矿床地球化学和矿床层楼结构机理[M].北京:科学出版社, 1993. 张理刚.稳定同位素在地质科学中的应用[M].西安:陕西科学技术出版社, 1985. 郑永飞, 陈江峰.稳定同位素地球化学[M].北京:科学出版社, 2000. 谭凯旋, 龚文君, 李小明, 等.地洼盆地砂岩铜矿床的构造-流体-成矿体系及演化[J].大地构造与成矿学, 1999, 1:35-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.1999.01.005 王思程, 薛春纪, 李志丹.新疆伽师砂岩型铜矿床地质及S、Pb同位素地球化学[J].现代地质, 2011, 25(2):219-227. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/96868X/201102/37935139.html Bodnar R J. Reviced equation and table for determining the freezing point depression of H2O-NaCl solutions[J]. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 1993, 57:683-684. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(93)90378-A
刘斌, 朱思林, 沈昆.流体包裹体热力学参数计算软件及算例[M].北京:地质出版社, 2000. 新疆华维地矿工程技术有限公司. 新疆维吾尔自治区乌恰县萨热克铜矿勘探报告. 2013.



 下载:
下载: