Geochemical characteristics and zircon U-Pb ages of the granite in Xiji basin of Ningxia
-
摘要:
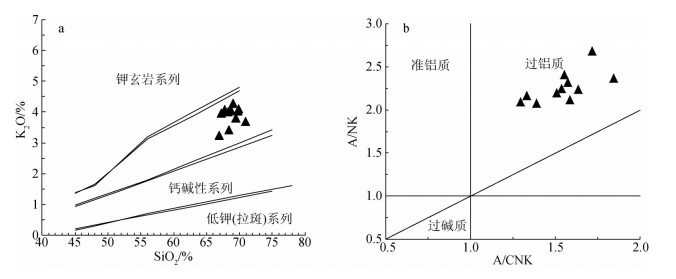
对北祁连山东段宁夏西吉盆地花岗岩地球化学特征和U-Pb年龄进行研究,并与区域上中酸性岩体进行对比。西吉盆地花岗岩属高钾钙碱性系列,具有富钠、过铝质的特征,LREE/HREE=10.89~11.93,轻稀土元素相对富集,分馏明显,重稀土元素分馏不明显,具有陆缘弧岩石的特点。岩石负Eu异常不明显,轻、重稀土元素分馏明显(LaN/YbN=10.90~15.41)。在微量元素组成上,花岗岩富集大离子亲石元素Rb、Th、Pb、La,亏损Sr、Ta、Nb、Ce、Ti元素,Pr、Nd、Sm、Dy弱富集,曲线形态具有造山花岗岩的特征,并具有负Nb异常,属正常大陆弧花岗岩。西吉盆地花岗岩成因类型为I型,形成于陆缘弧环境,为板块碰撞造山作用的产物,岩浆来源于下地壳的部分熔融。通过锆石U-Pb定年获得花岗岩结晶年龄为434.3±9.0Ma,为早志留世,属加里东期岩浆侵入活动的产物。西吉盆地花岗岩与北祁连造山带东段南华山-屈吴山一线的花岗闪长岩体及甘肃老虎山闪长岩体同属北祁连岩浆弧带,是同期岩浆活动的产物,与板块俯冲消减作用有关,间接证明了西吉盆地属于北祁连造山带。
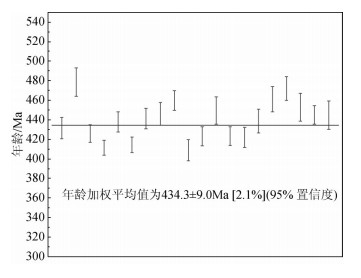
Abstract:In this paper, the authors studied geochemical characteristics and U-Pb age of the granite in Xiji basin of Ningxia in North Qilian Mountains and made a comparative research on the acid rocks of this area. The granite in the Xiji basin is a series of high potassium calc-alkaline rocks and shows sodium-rich and aluminium characteristics. LREE/HREE=10.89~11.93, LREE are relatively rich, LREE fractionation is obvious, and HREE earth distillation is not obvious with characteristics of the continental arc rock. The negative anomaly of Eu is not obvious, REE data for the granodiorite show strongly fractionated REE patterns (LaN/YbN=10.90~15.41). As for the composition of trace elements, the granite is rich in LILE Rb, Th, Pb and La, but poor in Sr, Ta, Nb, Ce and Ti, with weak enrichment of Nd, Sm and Dy. The curve of trace elements has the characteristics of orogenic granite with Nb negative anomaly, suggesting normal continental arc granite. The genetic type of granite in the Xiji basin is of I type, which formed in the continental arc environment and was the product of the collision of plates. Its magma was derived from the partial melting of the lower crust. U-Pb zircon dating by LA-ICP-MS shows that magma crystallization age is 434.3±9.0Ma, suggesting early adakite and a product of the magma intrusion of Caledonian period. The granite in the Xiji basin, the granodiorite in Nahuashan-Juewushan area of eastern North Qilian Mountain and the diorite of Laohushan area in Gansu Province are the same products as the northern Qilian magmatic arc belt and were formed by lava activity related to the plate subduction. It is thus proved that the Xiji basin belonged to the North Qilian orogenic belt indirectly.
-
Keywords:
- the Xiji basin /
- granite /
- geochemical characteristics /
- zircon U-Pb ages /
- North Qilian Mountain
-
-
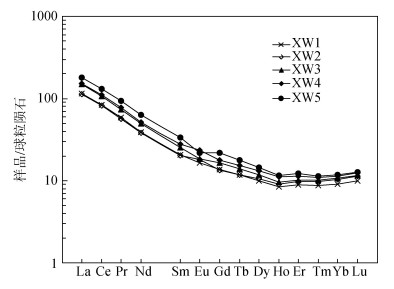
图 4 西吉盆地花岗岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化曲线[27]
Figure 4. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns of the granite in the Xiji basin
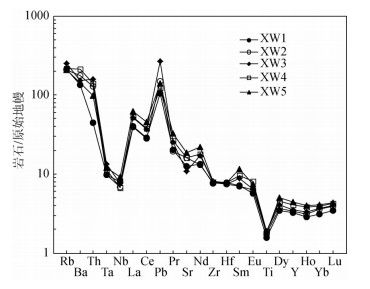
图 5 西吉盆地花岗岩微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图[27]
Figure 5. Trace elements spider diagram of the granite in the Xiji basin
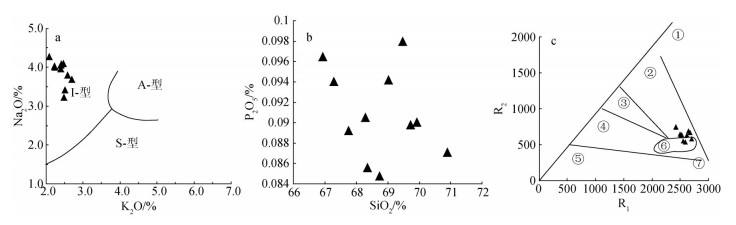
图 6 K2O-Na2O图解[29](a)、SiO2-P2O5图解(b)和R1-R2构造判别图(c)
①—地幔斜长花岗岩;②—活动板块边缘(板块碰撞前)花岗岩;③—板块碰撞后隆起期花岗岩;④—晚造期花岗岩;⑤—非造山区A型花岗岩;⑥—同碰撞(S型)花岗岩;⑦—造山期后A型花岗岩
Figure 6. K2O-Na2O(a), SiO2-P2O5(b) and R1-R2 diagrams(c)
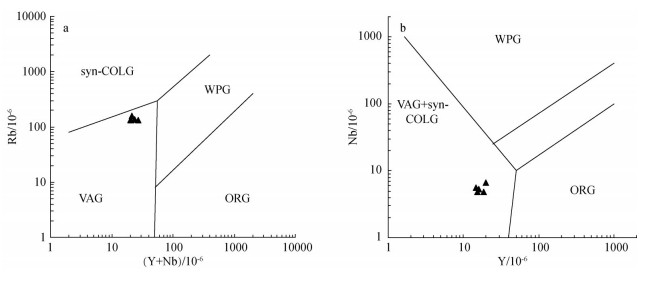
图 7 西吉盆地花岗岩微量元素构造环境判别图解[30]
syn-GOLG—同碰撞花岗岩;WPG—板内花岗岩;VAG—火山弧花岗岩类;ORG—洋脊花岗岩
Figure 7. Diagrams of tectonic setting of trace elements for Xiji basin granite
表 1 西吉盆地花岗岩主要氧化物含量及特征参数
Table 1 Main oxide content and characteristic parameters of the granite in the Xiji basin
% 序号 样品号 岩石名称 SiO2 CaO MgO Al2O3 FeO Fe2O3 K2O Na2O TiO2 P2O5 MnO H2O- H2O+ 1 GS1 花岗岩 70.90 14.32 3.70 2.70 2.36 0.92 0.087 0.26 0.098 0.087 1.49 0.49 1.56 2 XW1 花岗岩 67.76 13.62 4.08 2.42 4.00 0.86 0.089 0.24 0.10 0.089 1.47 0.17 2.78 3 GS3 花岗岩 66.94 15.32 3.23 2.48 3.20 0.92 0.096 0.29 0.099 0.096 1.57 0.17 3.58 4 XW2 花岗岩 69.72 14.06 4.03 2.23 2.88 0.91 0.090 0.25 0.11 0.090 1.47 0.19 3.01 5 GS5 花岗岩 67.28 13.78 3.97 2.40 3.99 0.99 0.094 0.26 0.15 0.094 1.62 0.40 2.55 6 XW3 花岗岩 69.02 13.99 4.27 2.10 2.91 0.78 0.094 0.25 0.13 0.094 1.65 0.19 3.35 7 GS7 花岗岩 68.74 13.43 4.05 2.40 3.21 0.72 0.085 0.22 0.16 0.085 1.13 0.37 2.48 8 XW4 花岗岩 69.92 13.92 4.09 2.47 2.21 0.81 0.090 0.24 0.11 0.090 1.34 0.18 3.52 9 GS9 花岗岩 69.48 15.12 3.80 2.58 1.82 0.88 0.098 0.26 0.091 0.098 1.54 0.06 2.79 10 XW5 花岗岩 68.36 14.30 3.42 2.52 3.27 0.71 0.086 0.24 0.11 0.086 1.36 0.03 3.27 11 GS11 花岗岩 68.28 14.46 4.00 2.24 2.95 0.71 0.091 0.25 0.11 0.091 1.42 0.17 2.42 表 2 西吉盆地花岗岩微量和稀土元素含量
Table 2 Trace and rare earth elements contents of the granite in the Xiji basin
10-6 含量 XW1 XW2 XW3 XW4 XW5 Sc 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 Ba 946 1223 1066 1493 1009 Ti 2053 2319 2445 2469 2352 V 104 96.0 94.3 88.9 96.3 Cr 66.3 67.4 68.6 71.5 69.2 Co 8.6 8.5 8.7 8.1 8.0 Ni 4.7 1.8 2.0 2.6 2.2 Pb 7.4 10.5 19.1 8.8 10.0 Th 3.8 10.9 13.6 11.8 8.4 Rb 134 132 160 139 132 Zr 85.9 87.5 88.9 88.3 91.1 Hf 2.4 2.3 2.3 2.4 2.4 Nb 5.6 4.8 5.4 4.8 6.6 Ta 0.4 0.4 0.6 0.5 0.5 Sr 264 340 228 341 389 Cu 26.7 27.3 27.6 26.4 26.4 La 27.5 26.8 35.5 35.9 43.0 Ce 51.0 50.4 65.7 67.7 80.7 Pr 5.57 5.37 6.99 7.35 8.91 Nd 18.2 17.8 23.0 24.1 29.5 Sm 3.18 3.1 3.89 4.24 5.15 Eu 0.96 1.05 1.08 1.35 1.26 Gd 2.83 2.78 3.37 3.65 4.47 Tb 0.44 0.44 0.52 0.58 0.66 Dy 2.55 2.7 2.98 3.36 3.7 Ho 0.47 0.51 0.54 0.63 0.66 Er 1.47 1.62 1.69 1.87 2.01 Tm 0.22 0.25 0.26 0.28 0.29 Yb 1.54 1.76 1.82 1.93 2.00 Lu 0.25 0.29 0.3 0.31 0.32 Y 14.8 15.4 16 18.6 20.1 ΣREE 116.27 114.84 147.65 153.25 182.59 LREE 106.49 104.48 136.18 140.65 168.48 HREE 9.78 10.35 11.46 12.61 14.12 LREE/HREE 10.89 10.09 11.88 11.16 11.93 (La/Yb)N 12.8 10.9 14.03 13.36 15.41 δEu 0.95 1.07 0.89 1.03 0.78 表 3 花岗岩锆石U-Th-Pb测试结果
Table 3 Zircon U-Th-Pb data of granite
样品编号 含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma 232Th 238U 207Pb/06Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ TW1-02 345 660 0.52 0.05586 0.00128 0.5350 0.0133 0.06921 0.00090 456 51.8 435 8.8 431 5.4 TW1-03 341 821 0.42 0.05519 0.00131 0.5877 0.0160 0.07710 0.00121 420 53.7 469 10.3 479 7.3 TW1-05 1337 3890 0.34 0.05588 0.00096 0.4559 0.0096 0.05888 0.00068 456 37.0 381 6.7 369 4.1 TW1-06 142 359 0.40 0.05973 0.00152 0.7207 0.0187 0.08751 0.00100 594 54.5 551 11.0 541 5.9 TW1-07 610 784 0.78 0.05500 0.00126 0.5183 0.0120 0.06830 0.00073 413 50.0 424 8.0 426 4.4 TW1-08 460 1373 0.33 0.05659 0.00108 0.4565 0.0105 0.05863 0.00108 476 42.6 382 7.3 367 6.6 TW1-09 352 838 0.42 0.05879 0.00145 0.5364 0.0135 0.06589 0.00062 567 53.7 436 8.9 411 3.8 TW1-10 358 702 0.51 0.05510 0.00136 0.5355 0.0136 0.07028 0.00086 417 58.3 435 9.0 438 5.2 TW1-11 940 2515 0.37 0.05675 0.00115 0.5221 0.0107 0.06637 0.00066 483 46.3 427 7.2 414 4.0 TW1-12 134 287 0.47 0.05611 0.00166 0.5502 0.0166 0.07085 0.00088 457 64.8 445 10.9 441 5.3 TW1-13 128 222 0.58 0.05507 0.00176 0.5457 0.0180 0.07166 0.00097 417 70.4 442 11.8 446 5.8 TW1-14 327 926 0.35 0.05540 0.00111 0.5693 0.0125 0.07392 0.00083 428 44.4 458 8.1 460 5.0 TW1-15 1327 1662 0.80 0.05579 0.00114 0.5073 0.0113 0.06546 0.00088 443 44.4 417 7.6 409 5.4 TW1-16 568 1115 0.51 0.05620 0.00122 0.5296 0.0119 0.06783 0.00082 461 48.1 432 7.9 423 5.0 TW1-17 164 368 0.45 0.05630 0.00166 0.5624 0.0173 0.07220 0.00116 465 64.8 453 11.2 449 7.0 TW1-18 868 2281 0.38 0.05661 0.00101 0.5350 0.0111 0.06784 0.00079 476 40.7 435 7.4 423 4.8 TW1-19 2291 3390 0.68 0.05745 0.00106 0.5406 0.0115 0.06762 0.00085 509 36.1 439 7.6 422 5.1 TW1-20 158 281 0.56 0.05680 0.00193 0.5535 0.0189 0.07041 0.00100 483 80.5 447 12.4 439 6.1 TW1-21 450 905 0.50 0.05571 0.00133 0.5749 0.0156 0.07415 0.00106 439 53.7 461 10.1 461 6.3 TW1-22 856 1404 0.61 0.05529 0.00114 0.5837 0.0137 0.07599 0.00102 433 50.9 467 8.8 472 6.1 TW1-23 145 411 0.35 0.05783 0.00168 0.5852 0.0190 0.07277 0.00119 524 64.8 468 12.2 453 7.1 TW1-24 321 596 0.54 0.05601 0.00132 0.5519 0.0124 0.07146 0.00081 454 53.7 446 8.1 445 4.9 TW1-25 1054 1812 0.58 0.05556 0.00113 0.5505 0.0141 0.07140 0.00120 435 46.3 445 9.2 445 7.2 -
杜远生, 朱杰, 韩欣, 等.从弧后盆地到前陆盆地-北祁连造山带奥陶纪-泥盆纪的沉积盆地与构造演化[J].地质通报, 2004, 23(9/10):911-917. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=200409163&flag=1 冯益民, 何世平.祁连山大地构造与造山作用[M].北京:地质出版社, 1996:81-82. 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 徐学义.北祁连山早古生代洋脊-洋岛和弧后盆地火山作用[J].地质学报, 1998, 72(4):301-312. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzxe199804001&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 冯益民.祁连造山带研究概况——历史、现状及展望[J].地球科学进展, 1997, 12(4):307-314. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/94287X/199704/2575789.html 葛肖虹, 刘俊来.北祁连造山带的形成与背景[J].地学前缘, 1996, 6(4):223-230. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy199904004 宋述光.北祁连山俯冲杂岩带的构造演化[J].地球科学进展, 1997, 12(4):340-350. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dxjz704.007&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 李文渊, 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 等.北祁连早古生代弧后盆地火山作用及成矿特点[J].地质论评, 1999, 45:1048-1053. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/294897 张建新, 许志琴, 徐惠芬, 等.北祁连加里东俯冲增生楔结构及动力学[J].地质科学, 1998, 33(3):290-301. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzkx803.003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 张旗, 王焰, 钱青.北祁连早古生代是裂陷槽还是大洋盆——与葛肖虹讨论[J].地质科学, 2000, 35(1):121-128. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzkx200001015&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 左国朝.北祁连中段早古生代双向俯冲碰撞造山模式剖析[J].地球科学进展, 1997, 12(4):315-323. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=2575790 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 徐学义.北祁连山构造-火山岩浆演化动力学[J].西北地质科学, 1995, 16(1):1-28. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=xbfk501.000&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 张建新, 许志琴, 李海兵.北祁连加里东造山带从挤压到伸展造山机制的转换[J].长春地质学院学报, 1997, 27(3):277-283. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ccdz703.006&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 李天斌, 张学文, 王成, 等.北祁连山东段海原一带海原群变质岩原岩恢复及其构造背景[J].地质通报, 2006, 25(1/2):194-203. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060131&flag=1 吴才来, 杨经绥, 杨宏仪, 等.北祁连东部两类I型花岗岩定年及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2004, 20(30):425-432. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzxe200502019&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 徐卫东, 岳世东, 张国成.北祁连西段黑下佬同碰撞花岗岩地质特征[J].地质调查与研究, 2007, 30(2):110-114. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qhwjyjjz200702004 吴才来, 徐学义, 高前明, 等.北祁连早古生代花岗质岩浆作用及构造演化[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(4):1027-1044. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ysxb201004004&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 秦海鹏. 北祁连造山带早古生代花岗岩岩石学特征及其与构造演化的关系[D]. 中国地质科学院博士学位论文, 2012. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-82501-1012371270.htm 霍福臣, 郑昭昌.宁夏海原地区海原群的时代对比[J].地质论评, 1988, 34(1):1-9. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/OA000003978 闫志强, 李天斌.宁夏南华山-西华山大型韧性剪切带特征[J].西北地质, 1991, 12(2):13-18. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=xbdi199102002&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 王崇礼, 李厚民, 等.海原群变质地质及含矿性研究[M].西安:陕西科学技术出版社, 1996:1-60. 李天斌.宁夏南华山-西华山北麓断裂最大水平位移质疑[J].中国区域地质, 1999, 18(4):359-365. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz199904004 闫志强.宁夏海原地区的元古宇[J].地层学杂志, 1994, 18(1):30-38. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=1308097 王成, 李明涛, 马彦云.海原岩群锆石SHRIMP U-Pb测年及时代归属讨论[J].地质论评, 2014, 13(1):13-17. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nxgcjs201401003 Rickwood P C. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J]. Lithos, 1989, 22(4):247-263. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(89)90028-5
Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5):635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
李佐臣, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等.西秦岭糜署岭花岗岩体年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(8):2617-2634. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_ysxb98201308001.aspx Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for Mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, 1989, 42(1):313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Chappell B W. Aluminium saturation in I and S-type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46:535-551. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00086-3
Collins W J, Beams S D, White A J R. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to Southeastern Australia Contrib[J]. Miner. Petro., 1982, 80:189-200. doi: 10.1007/BF00374895
Barbarin B. A review of the relationships between granitoid types, their oirgins and their geodynamic environmets[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46:605-626. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00085-1
Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Gao S, et al. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chem. Geol., 2008, 257:34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004
Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen:U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51(1/2):537-571.
常华进, 储雪蕾, 王金荣, 等.被祁连山东段埃达克岩带Cu、Au成矿初探[J].西北地质, 2008, 41(3):30-37. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=xbdi200803003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 钱青, 王岳明, 李蕙民, 等.甘肃老虎山闪长岩的地球化学特征及其成因[J].岩石学报, 1998, 14(4):520-528. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98199804011 王成, 陈国新, 杨军宁, 等. 1: 25万固原市幅区域地质调查报告. 宁夏回族自治区地质调查院, 2004.



 下载:
下载: