First discovery of modern mud volcanoes in Qiangtang Basin and its petroleum geological significance
-
摘要:
在羌塘盆地唢呐湖地区发现现代泥火山,通过采集泥浆样、水样等样品,开展水化学离子、水溶烃类气体、碳氢氧稳定同位素等测试分析,对现代泥火山的油气地质意义进行了探讨。水化学类型和氢氧同位素表明,该地区地下可能存在油气藏;水溶烃类气体测试结果表明,气体成分为C1~C5,以甲烷为主,与常规气藏的气体成分一致;碳同位素判别结果表明,其为热解成因的油成气。结合泥火山的地质背景,表明泥火山为油气藏破坏渗漏的产物,在保存良好的未泄露地区,油气勘探具有良好前景。
Abstract:For the first time the modern mud volcanoes were found in Suonahu area of Qiangtang Basin. Through collecting water samples and mud samples and analyzing water chemical ions, water soluble hydrocarbon gas, and carbon and oxygen stable isotope, this paper discusses oil and gas geological significance of modern mud volcanoes. Hydrochemical types and hydrogen and oxygen iso-topes indicate that underground reservoirs may exist in this area. The test results of water-soluble hydrocarbon gas show that the gas composition is C1~C5, mainly methane, consistent with the gas composition of the conventional gas reservoir, and the carbon iso-tope discrimination result shows that it is oil gas of pyrolysis origin. Combined with geological background of the mud volcano, it is shown that mud volcano is the product of oil and gas reservoir seepage and leakage, and hence good prospects for oil and gas explora-tion lie in well preserved and non leaking areas.
-
泥火山是盆地地层深部含水(气)和混有砾石、砂的泥质物在高压作用下喷出地表形成的锥状沉积体[1-4]。泥火山是地层内部圈闭气体由于压力释放上冲的结果,也是流体向上运移的通道。1984年Ginsburg等地球物理学家第一次对天然气与海底泥火山的关系问题进行了探讨,此后大量的研究陆续在里海、黑海、挪威海、地中海、巴巴多斯近海、尼日利亚近海、墨西哥湾等油气分布区发现了泥火山,这些现象说明,泥火山与油气关系非常密切,在油气勘探早期可作为评价油气远景区的标志之一[5]。
中国对泥火山的研究主要集中在海洋地区,对分布于陆地的泥火山研究,目前主要在地质年代、分布构造及其与地震活动、油气藏的关系等方面。如梁杰等[6]发现,泥火山中心的气体水合物是由于水和甲烷渗滤驱动的低温热液过程而形成的;王道等[7]发现,泥火山多分布在地震频发区,且二者存在一定的动态效应;范卫平等[8]发现,泥火山的存在表明该区曾发生过油气的生成、运聚和破坏,可作为盆地早期油气评价的一项标志;高小其[9]总结了新疆独山子泥火山泥浆的物理化学指标;马小龙等[10]对新疆泥火山中的微生物分布规律进行了研究,通过对新疆泥火山的水体、气体采样分析,判断出水样为油田水,喷出气体主要为甲烷。台湾地区的泥火山研究较多, 对泥火山的分布特征、形成机理和生物地球化学都有较深入的研究[11-13]。
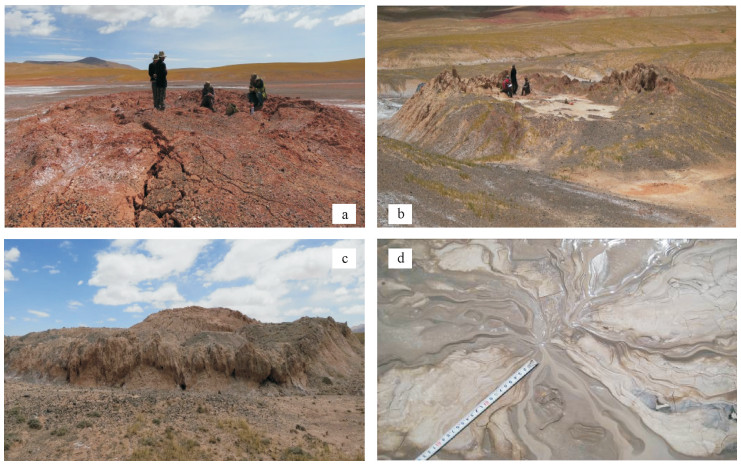
对羌塘盆地泥火山的报道研究目前集中于雀莫错地区[14-16],雀莫错地区以外的其他地区有少量报道[17],但目前报道的泥火山均为已经停止喷发泥浆的古泥火山,尚无正在喷发泥浆的现代泥火山的报道。笔者于2013年在唢呐湖地区进行了详细的1:5万地质调查,发现了正在喷发(喷溢)泥浆的“现代泥火山”,对喷出的泥浆进行了取样分析,通过水文、有机地球化学组分及同位素分析,探讨羌塘盆地现代泥火山的油气地质意义。
1. 地质背景
唢呐湖地区隶属于西藏藏族自治区阿里地区双湖县多玛乡,位于羌塘盆地中部,地理坐标东经86°33′20″~86°55′45″、北纬33°51′10″~34°02′10″。区内平均海拔5000m以上,空气稀薄,寒冷干燥,沙化严重,草场退化,湖泊严重萎缩,为典型的高原戈壁地貌。
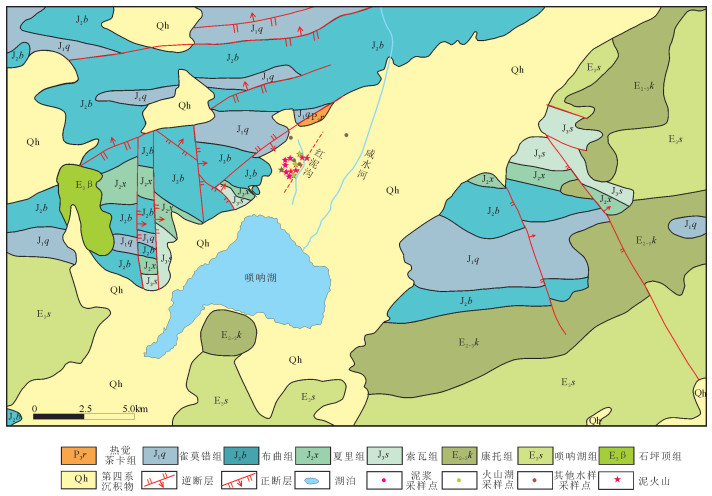
地质构造上研究区位于北羌塘盆地南缘(图 1),断裂和断层发育,断层主要发育NEE向、SN向、NW向和NE向4组。地层分布不规则,地层体间多呈断层接触,出露地层包括二叠系热觉茶卡组,侏罗系雀莫错组、布曲组、夏里组、索瓦组,古近系康托组、唢呐湖组,第四系(图 2)。其中,热觉茶卡组以浅黄色中层中粒钙质石英砂岩为主;侏罗系雀莫错组以含砾砂岩、砂岩为主;布曲组以灰黑色泥晶灰岩、生物屑泥晶灰岩、亮晶灰岩为主;夏里组以细粒石英砂岩为主;索瓦组以泥晶灰岩为主;古近系康托组主要为砾岩、含砾砂岩、砂岩组合;唢呐湖组主要为紫红色砾岩、含砾砂岩、砂岩、含膏灰岩、泥晶生屑灰岩、亮晶藻球粒灰岩组合;第四系广泛分布于工作区中部,少量分布于西北部。
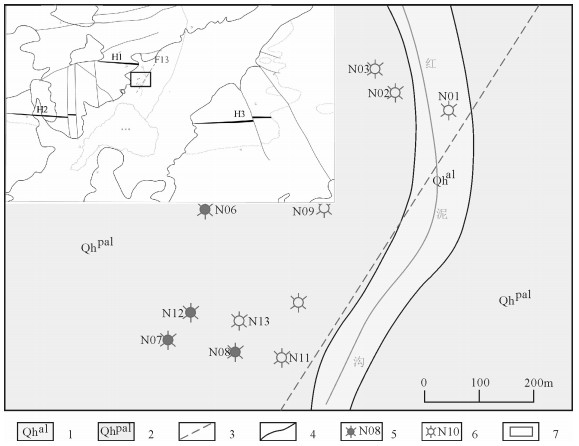
唢呐湖泥火山群分布在唢呐湖东北侧的红泥沟一带,沿NE向新构造(推测)展布(图 3)。泥火山共计13座,其中喷发较早的“古泥火山”7座,正在喷溢泥浆的“现代泥火山”6座,二者呈东西分带的特征,整体走向为NE30°方向。形态上主要分为盾状、盆状和复合状泥火山,盆状泥火山往往蓄水形成泥火山湖,在现代泥火山中还发育大量的小型喷发口(图 4)。
2. 样品采集及分析
2.1 样品采集
本次对泥火山的泥浆、湖水、非泥火山水体等共采集13件样品,样品均由密封罐保存,其中泥浆样品5件,泥火山湖水3件,其他5件。
2.2 分析方法及依据
分析方法和检出限依据SY/T6009—2003《石油天然气行业标准》,DZ/T 0184.17—1997《碳酸盐矿物或岩石中碳、氧同位素组成的磷酸法测定》,液体常规水地球化学测试依据为DZ/T 0064.28—1993、DZ/T 0064.51—1993《地下水质检验方法-离子色谱法测定》, DZ/T 0064.49-1993《地下水质检验方法-滴定法》, DZ/T 0184.19—1997《水中氢同位素锌还原法测定》, DZ/T 0184.21—1997《天然水中氧同位素二氧化碳-水平衡法测定》,测试由核工业北京地质研究院实验室完成。吸附气(水溶气)气成分含量主要由GC7890F气象色谱仪完成,稳定同位素由MAT253型稳定同位素质谱仪完成,常规水地球化学分析由DIONEX- 500离子色谱仪、METROHM全自动滴定仪器完成。在检测过程中,除常规的空白监控、标准样品仪器监控等手段外,还采取管理样监控、重复密码样监控、异常点复测等方法保证质量。部分因同位素样品中分离的气体含量较少而未测出。测试结果见表 1、表 2。
表 1 唢呐湖地区泥浆样和水样的水化学及氢氧同位素测试结果Table 1. The test results of water chemical and water mud samples as well as hydrogen and oxygen isotopes of Suonahu area序号 样品编号 离子含量/(mg·L-1) 氢氧稳定同位素/‰ 水的化学类型 泥火山编号 备注 Cl- SO42- Na+ K+ Mg2+ Ca2+ HCO3- δD δ18O 苏林分类 1 S-1 93.3 56.3 833 92.8 13.5 127 / -79.7 -9.3 重碳酸钠 N04 泥浆 2 S-2 258 92.1 1009 104 8.7 100 / -92 -10.5 重碳酸钠 N05 3 S-3 / / / / / / / / / / N06 4 S-4 168 86.7 412 25.4 3.83 4.94 / -75.2 -7.5 重碳酸钠 N8 5 S-5 227 93 465 18.2 1.73 3.42 / -81.3 -8 重碳酸钠 N12 6 S-6 16719 3735 12983 405 430 94.3 3417 -34.2 2.2 重碳酸钠 泥火山湖水 7 S-7 38444 7102 29106 992 393 / 5704 -55.4 -3.8 重碳酸钠 8 S-8 8534 1810 7059 259 184 / 2465 -63.5 -2.8 重碳酸钠 9 S-9 4727 1083 3806 160 46.2 257 2171 -24.2 2.3 重碳酸钠 非泥火山水体 10 S-10 -120.4 -13.1 11 S-11 4157 944 3413 137 49.3 208 2061 -102.5 -11 重碳酸钠 12 S-12 13105 2645 10250 389 225 / 2060 -117.1 -12.6 重碳酸钠 注:数据由核工业北京地质研究院测试提供 表 2 唢呐湖地区泥浆样、水样烃类气体及碳同位素测试结果Table 2. The test results of water samples, mud samples of hydrocarbon gas and carbon isotope in Suonahu area序号 样品编号 测试结果汇总(μL.kg-1) 碳同位素/‰ 泥火山编号 备注 甲烷 乙烷 丙烷 异丁烷 正丁烷 异戊烷 正戊烷 δ13C1 δ13C2 1 S-1 1194 86.3 35.3 4.35 5.84 3.67 2.42 -46.1 -29.1 N04 泥浆 2 S-2 684 36 13 1.66 2.09 1.31 0.970 -47.2 N05 3 S-3 2279 471 218 25 33 19.3 15.9 -46.0 -30.6 N06 4 S-4 594 37.90 14 1.89 2.250 1.6 1.18 -46.6 -28.1 N8 5 S-5 459 27.1 10.5 1.27 1.580 1.16 0.74 -46.9 N12 6 S-6 0.170 0.006 0.003 0.005 0.003 0.002 0.002 泥火山湖水 7 S-7 0.200 0.005 0.005 0.003 0.002 0.005 0.005 8 S-8 0.470 0.006 0.006 0.004 0.006 0.004 0.004 9 S-9 2.380 0.100 0.041 0.011 0.006 0.008 0.006 非泥火山水体 10 S-10 0.270 0.008 0.005 0.005 0.005 0.008 0.005 11 S-11 1.440 0.004 0.004 0.006 0.006 0.002 0.006 12 S-12 58.2 0.007 0.010 0.007 0.010 0.007 0.010 -45.0 注:数据由核工业北京地质研究院测试提供 3. 结果与讨论
3.1 泥浆、水体离子及同位素特征
本次对10件样品进行了离子的测试分析,包括K+、Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+、Cl-、SO42-、HCO3-七种常见离子,并进行了氢氧稳定同位素测试分析(表 1),用于进行水体化学类型分类,判断地下水化学环境,及其与油气藏存在的关系。
按照苏林油田水的计算方法和分类原则,10件样品全部是重碳酸钠型(NaHCO3型)。NaHCO3型水是油田水的典型类型,可存在于浅层和深层,但浅层水的矿化度一般较低。低矿化度NaHCO3型淡水为大量地表水补给的结果,而较高矿化度的NaHCO3型水则可能预示地下油田的存在;泥火山区水样的矿化度很高,一般达到盐水类型。综合考虑泥火山地区水样类型和矿化度,该地区的水可能预示地下油田的存在。
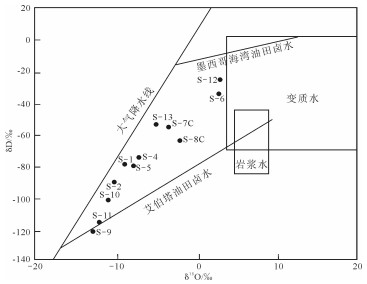
此外,水体氢氧稳定同位素(δ18O、δD)可以较有效地确定地下水的气源与形成过程,测试结果显示,δD分布在-120.4‰~-24.2‰之间,δ 18O在-13.1‰~2.3‰之间(图 5)。在分类判别图中,对比各种水体的氢氧同位素分布范围可以发现,研究区的水体样品来源主要为混合来源,氢氧同位素落在大气降水线右侧,靠近油气水,说明采集的水体样品除得到地表大气降水补给外, 也受地下油田水的补给。说明该地区地下可能有潜在的油气藏存在,与上述水型判别结果一致。
3.2 气体成分及同位素特征
通过对泥浆样和水样的水溶性烃类气体进行测试分析(表 2),泥火山泥浆样的烃类气体总含量为501.35~3061.2μL/kg,C1~C5均发育,主体成分为甲烷,含量在459~2279μL/kg之间,平均含量为1042μL/kg;其次为乙烷,含量介于27~471μL/kg之间,平均含量为131μL/kg;丙烷、丁烷和戊烷含量较少。各种烃类之间的相关性较高,相关系数均大于0.91,反映烃类组分之间的组成特征与油气藏或天然气水合物矿藏分解产生的烃类组成特征一致,其迁移形式具有共性。
其他样品中,除S-12外,水样中烃类气体平均含量为0.989μL/kg。水样S-8c甲烷含量较高,为58.20μL/kg,是其他水样平均值的59倍;可能与水样取自泥火山地区的上升泉有关。由于该上升泉位于泥火山分布区,并与现代泥火山呈线性分布,所以其甲烷含量和泥浆样一样相对富集。整体上,泥浆中气体的含量是背景水体中水溶气的1000倍左右。说明具有正在喷溢泥浆的现代泥火山是气体渗漏的主要通道,而其他水体样品甲烷含量都比较低,表明地下气体具有良好的保存条件,并未大面积逸出。
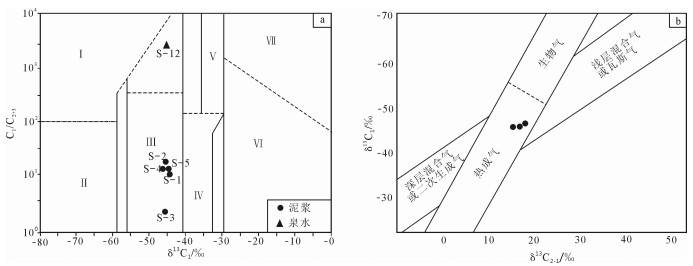
此外,将样品中甲烷气体抽离出来开展了碳同位素分析,分析这些气体的具体成因。测试结果显示,甲烷碳同位素δ 13C1介于-47.2‰ ~-45.0‰之间(表 1),较统一稳定,平均值为-46.3‰;乙烷碳同位素δ13C2介于-30.6‰~-28.1‰之间,平均值为-29.27‰。判断天然气成因方法有多种,本次选择2种方法进行判断。第一种是利用δ13C1与烃成分指标C1/(C2+C3)值作为划分依据,能很好地鉴别生物气、混合气、油型气、过成熟油型气、煤型气、无机气[18];第二种是用δ13C1和δ13C2-1值作为划分依据,可以鉴别出生物气、热成气、深源气、瓦斯气和深层混合气[19]。如图 6所示,工作区水样中的甲烷属于热解成因的油型气,说明气体来源于地下油气藏的泄漏。
4. 结论
(1)通过对泥火山群流体地球化学成分及同位素特征的研究,水体常规离子及同位素分析结果表明,泥火山群发育区的水体主要为重碳酸钠型的油田水类型。
(2)气体成分C1~C5均有发育,主体为甲烷,为常规气藏发育的气体成分结构,且同位素判别结果表明其为热解成因的油成气,而不是浅表生物成因的气藏。
(3)从地质背景分析,泥火山群位于研究区中生代地层组成的背斜与NE—SW向断裂的交会处。因此,泥火山群为地下油气藏受断裂破坏泄漏,并在地层压力作用下,携带下伏的流体喷出地表形成。表明在研究区目前正在发生油气渗漏,在保存良好的未泄露地区,应存在良好的油气圈闭,油气勘探具有良好前景。
致谢: 承蒙成都理工大学文华国教授和核工业二八〇研究所权建平研究员审阅全文并提出了宝贵的修改意见, 野外工作得到成都地质调查中心谭富文、陈明研究员的热情帮助,成都理工大学伊海生教授和核工业二八〇研究所魏继生、刘君豪、李金锋、仇季龙也给予了诸多帮助, 在此一并致谢。 -
表 1 唢呐湖地区泥浆样和水样的水化学及氢氧同位素测试结果
Table 1 The test results of water chemical and water mud samples as well as hydrogen and oxygen isotopes of Suonahu area
序号 样品编号 离子含量/(mg·L-1) 氢氧稳定同位素/‰ 水的化学类型 泥火山编号 备注 Cl- SO42- Na+ K+ Mg2+ Ca2+ HCO3- δD δ18O 苏林分类 1 S-1 93.3 56.3 833 92.8 13.5 127 / -79.7 -9.3 重碳酸钠 N04 泥浆 2 S-2 258 92.1 1009 104 8.7 100 / -92 -10.5 重碳酸钠 N05 3 S-3 / / / / / / / / / / N06 4 S-4 168 86.7 412 25.4 3.83 4.94 / -75.2 -7.5 重碳酸钠 N8 5 S-5 227 93 465 18.2 1.73 3.42 / -81.3 -8 重碳酸钠 N12 6 S-6 16719 3735 12983 405 430 94.3 3417 -34.2 2.2 重碳酸钠 泥火山湖水 7 S-7 38444 7102 29106 992 393 / 5704 -55.4 -3.8 重碳酸钠 8 S-8 8534 1810 7059 259 184 / 2465 -63.5 -2.8 重碳酸钠 9 S-9 4727 1083 3806 160 46.2 257 2171 -24.2 2.3 重碳酸钠 非泥火山水体 10 S-10 -120.4 -13.1 11 S-11 4157 944 3413 137 49.3 208 2061 -102.5 -11 重碳酸钠 12 S-12 13105 2645 10250 389 225 / 2060 -117.1 -12.6 重碳酸钠 注:数据由核工业北京地质研究院测试提供 表 2 唢呐湖地区泥浆样、水样烃类气体及碳同位素测试结果
Table 2 The test results of water samples, mud samples of hydrocarbon gas and carbon isotope in Suonahu area
序号 样品编号 测试结果汇总(μL.kg-1) 碳同位素/‰ 泥火山编号 备注 甲烷 乙烷 丙烷 异丁烷 正丁烷 异戊烷 正戊烷 δ13C1 δ13C2 1 S-1 1194 86.3 35.3 4.35 5.84 3.67 2.42 -46.1 -29.1 N04 泥浆 2 S-2 684 36 13 1.66 2.09 1.31 0.970 -47.2 N05 3 S-3 2279 471 218 25 33 19.3 15.9 -46.0 -30.6 N06 4 S-4 594 37.90 14 1.89 2.250 1.6 1.18 -46.6 -28.1 N8 5 S-5 459 27.1 10.5 1.27 1.580 1.16 0.74 -46.9 N12 6 S-6 0.170 0.006 0.003 0.005 0.003 0.002 0.002 泥火山湖水 7 S-7 0.200 0.005 0.005 0.003 0.002 0.005 0.005 8 S-8 0.470 0.006 0.006 0.004 0.006 0.004 0.004 9 S-9 2.380 0.100 0.041 0.011 0.006 0.008 0.006 非泥火山水体 10 S-10 0.270 0.008 0.005 0.005 0.005 0.008 0.005 11 S-11 1.440 0.004 0.004 0.006 0.006 0.002 0.006 12 S-12 58.2 0.007 0.010 0.007 0.010 0.007 0.010 -45.0 注:数据由核工业北京地质研究院测试提供 -
李锰, 王道, 李茂伟, 等.新疆独山子泥火山喷发特征的研究[J].内陆地震, 1996, 10(4):359-362. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LLDZ604.009.htm Aliyev A A, Guliyev I S, Belov I S. Catalogue of recorded eruptions of mud volcanoes of Azerbaijan[M]. Baku:Nafta Press, 2002.
Milkov A V. Worldwide distribution of submarine mud volcanoes and associated gas hydrates[J]. Marin. Geology, 2000, 167(12):29-42. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a0c67cdc1a2bb1a97681288c7f151431&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Dimitrov L I. Mud volcanoes:A significant source of atmospheric methane[J]. Geo. Marine Letters. 2003, 23(3/4):155-161. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=d719e4e2f978ee69782034c66f0d7cc7&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Milkov A V. Global distribution of mud volcanoes and their significance in petroleum exploration as a source of methane in the atmo-sphere and hydrosphere and as a geohazard[C]//Mud Volcanoes, Geodynamics and Seismicity, 2005, 51: 29-34.
梁杰, 龚建明, 陈建文.泥火山与天然气水合物[J].海洋地质动态, 2006, 22(12):20-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2006.12.006 王道, 李茂伟, 李锰, 等.新疆独山子泥火山喷发的初步研究[J].地震地质, 1997, 19(1):14-16. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ701.002.htm 范卫平, 郑雷清, 龚建华, 等.泥火山的形成及其与油气的关系[J].吐哈油气, 2007, 12(1):43-47. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/XJSD201003041.htm 高小其, 王海涛, 高国英, 等.霍尔果斯泥火山活动与新疆地区中强以上地震活动关系的初步研究[J].地震地质, 2008, 30(2):464-474. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KWXB2015S1696.htm 马小龙, 王芸, 杨红梅, 等.新疆泥火山群细菌遗传多样性[J].生态学报, 2009, 29(7):3722-3728. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jsnykx201102023 Sung Q C, Chang H C, Liu H C, et al. Mud volcanoes along the Chishan fault in southwestern Taiwan:Areleasebend model[J]. Geomorph., 2010, 118(1):188-198. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229394387_Mud_volcanoes_along_the_Chishan_fault_in_Southwestern_Taiwan_A_release_bend_model
Sun C H, Chang S C, Kuo C L, et al.Origins of Taiwan's mud volcanoes:Evidence from geochemistry[J]. J. Asian Earth Sci., 2010, 37(2):105-116. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2009.02.007
Hung C C, Ch en F Y, Sun C H. Gases in Taiwan mud volcanoes:Chemicalcomposition, methane carbon isotopes, andgas fluxes[J]. Applied Geochem., 2010, 25(3):428-436. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.12.009
解超明, 李才, 李林庆, 等.藏北羌塘中部首次发现泥火山[J].地质通报, 2009, 28(9):1319-1324. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090921&flag=1 解超明, 李才, 吴彦旺, 等.青藏高原羌塘中部泥火山喷发物中沥青脉饱和烃气相色谱特征及其油气地质意义[J].地质通报, 2012, 31(6):977-978. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20120616&flag=1 冯兴雷, 付修根, 谭富文, 等.羌塘盆地戈木错地区泥火山群沉积及浅表地球化学特征[J].沉积与特提斯地质, 2015, 35(1):50-56. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ttsd201501007&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 和源, 朱利东, 杨文光, 等.西藏改则东地区第四纪泥火山的首次发现[J].地质科技情报, 2016, 35(4):38-42. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzkq201604006&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 戴金星.各类烷烃气的鉴别[J].中国科学(B辑:化学·生命科学·地学), 1992, (2):185-193. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/88064X/199202/985597.html 张义纲, 章康复, 郑朝阳. 识别天然气的碳同位素方法[C]//有机地球化学论文集. 北京: 地质出版社, 1987.



 下载:
下载: