Zircon U-Pb age and geochemistry of the dioritic rocks in Chuzhou area in Anhui Province: Petrogenesis and dynamics significance
-
摘要:
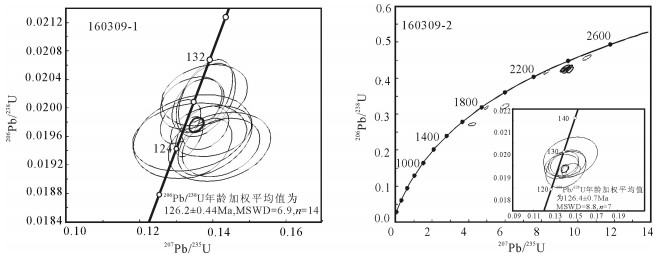
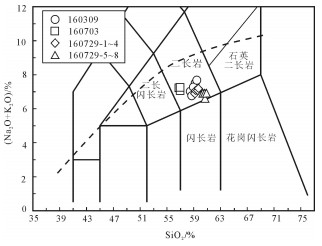
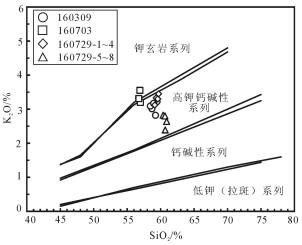
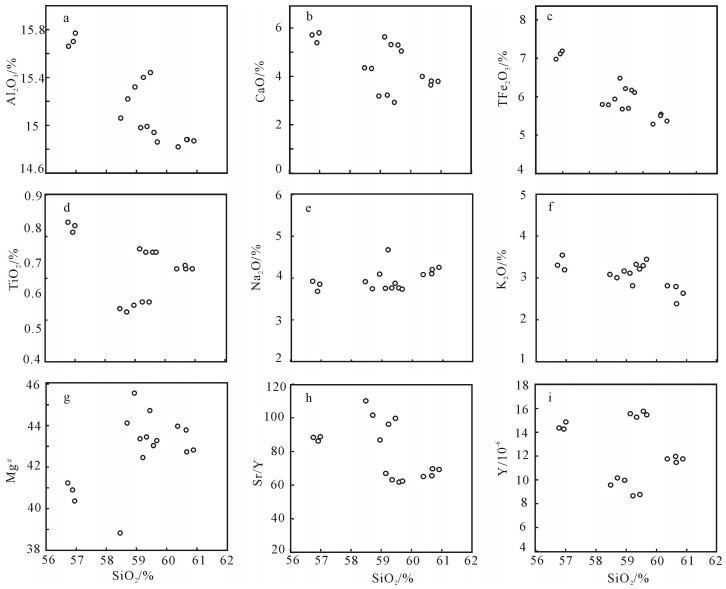
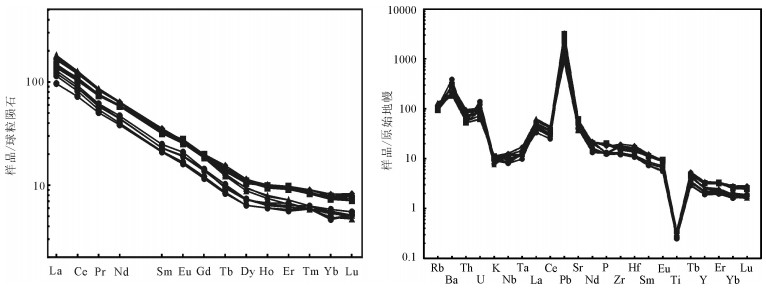
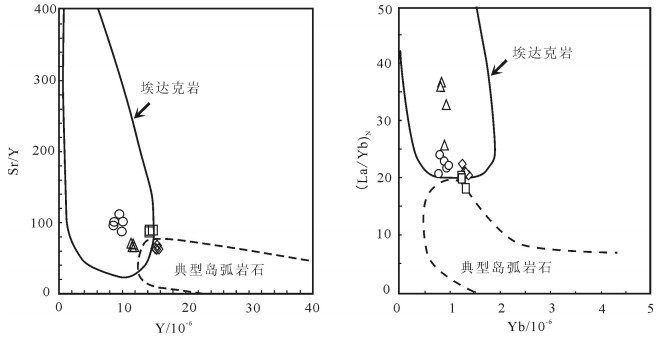
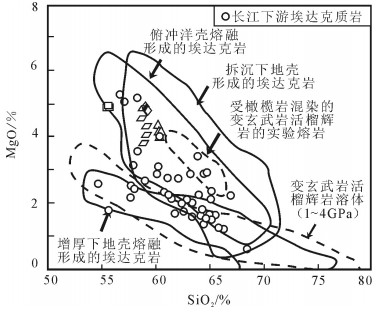
用LA-ICP-MS测得安徽滁州2个闪长玢岩样品中锆石206Pb/238U年龄为126.19±0.44Ma和126.4±0.7Ma,结合前人研究,得出滁州地区岩体的侵位时代应为120~130Ma之间,为早白垩世。岩石地球化学研究显示,SiO2含量变化范围为56.75%~60.90%,具有高Al2O3(14.82%~15.77%)、MgO(> 4%)、Sr(> 750×10-6)、Sr/Y(62~110)、La/Yb(20~36),低Y、Yb的特征,同时富集轻稀土元素和大离子亲石元素,亏损高场强元素,Eu异常不明显,属于典型的埃达克质岩。Mg#值为39~45,K2O/Na2O值为0.57~0.96,平均值为0.75,明显低于大别造山带加厚下地壳埃达克岩,Ce/Pb值较低,大多集中在3~5之间,类似于陆壳而明显低于洋壳。研究认为,安徽滁州地区埃达克质岩由拆沉下地壳部分熔融形成,埃达克质岩浆在上升过程中与地幔橄榄岩发生反应,导致熔体MgO、Cr、Ni等含量增加。早白垩世中国东部地壳伸展减薄导致下地壳拆沉,地幔物质的参与带来铜、金等成矿物质,埃达克质岩可作为该地区重要的找矿标志。
Abstract:LA-ICP-MS zircon 206Pb/238U ages of two diorite porphyrite samples from Chuzhou area of Anhui Province are 126.19±0.44Ma and 126.4±0.7Ma, respectively. Previous study shows that the emplacement age of dioritic rocks should be 120~130Ma, sug-gesting early Cretaceous. Geochemical study shows the values of SiO2 vary from 56.75% to 60.90%, with the characteristics of high Al2O3(14.82%~15.77%), MgO(>4%), Sr(>750×10-6), Sr/Y(62~110), and La/Yb(20~36) but low Y, Yb, LREE as well as enrichment of LREE and LILE but depletion of HREE, with indistinct Eu anomaly, indicating typical adakitic rocks. Mg# values range from 39 to 45, K2O/Na2O vary from 0.57 to 0.96, 0.75 on average, significantly lower than the values of the adakitic rocks in the thickened crustal of Dabie orogenic belt; Ce/Pb ratios are low, mostly concentrated in the range of 3~5, similar to the values of the continental crust but significantly lower than those of the oceanic crust. The authors hold that the adakitic rocks in Chuzhou area of Anhui was formed by partial melting of delaminated lower crust, and the reaction of upward migrating adakitic magmas and mantle peridotite led to the increase of MgO, Cr and Ni melt content. In Early Cretaceous, eastern China crustal extension thinning resulted in lower crust delamination, and mantle material was involved in bringing Cu, Au and other ore-forming elements; hence adakitic rocks can be used as an important prospecting indicator in this area.
-
致谢: 安徽省地矿局312地质队杨才波工程师帮助采集测试样品,中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所成矿作用与资源评价重点实验室侯可军、王倩等老师在锆石U-Pb同位素测试方面给予了很大的帮助,审稿专家提出了许多宝贵的意见和建议,在此一并表示感谢。
-
图 7 稀土元素配分曲线及微量元素蛛网图(标准化值据参考文献[35])
Figure 7. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagram
图 9 安徽滁州地区埃达克质岩的成因分类图解
(长江中下游埃达克质岩数据参考文献[27])
Figure 9. Petrogenetic diagrams of the adakitic rocks in Chuzhou area of Anhui
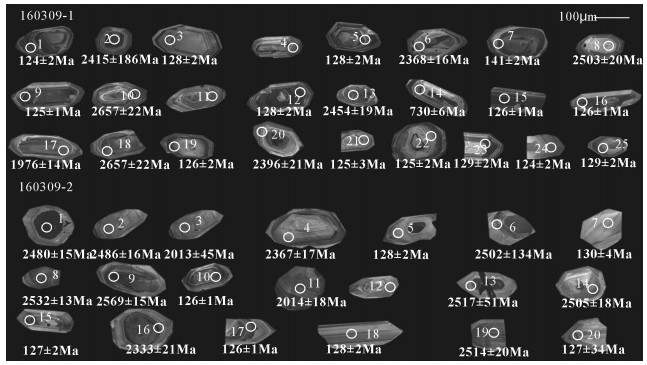
表 1 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素测定结果
Table 1 Results of the LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb dating
样品 含量/10-6 Th/U 207Pb/206Pb 206Pb/238U 207Pb/206Pb 206Pb/238U Pb 232Th 238U 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 160309-1-1 13 350 576 0.61 0.0517 0.0019 0.0194 0.0002 272 92 124 2 160309-1-2 190 14 459 0.03 0.1638 0.0013 0.3711 0.0037 2415 186 2035 18 160309-1-3 7 180 273 0.66 0.0524 0.0021 0.0201 0.0002 128 103 128 2 160309-1-5 8 293 313 0.94 0.0514 0.0022 0.0212 0.0003 209 90 128 2 160309-1-6 115 96 228 0.42 0.1594 0.0015 0.4145 0.0029 2368 16 2234 13 160309-1-7 11 377 367 1.03 0.0545 0.0028 0.0224 0.0003 276 122 141 2 160309-1-8 33 75 47 1.60 0.1636 0.0019 0.4575 0.0046 2503 20 2414 20 160309-1-9 24 527 1060 0.50 0.0526 0.0009 0.0212 0.0002 172 44 125 1 160309-1-10 6 210 257 0.82 0.0514 0.0025 0.0292 0.0003 332 101 124 2 160309-1-12 11 185 485 0.38 0.0575 0.0017 0.0214 0.0003 169 84 128 2 160309-1-13 151 248 258 0.96 0.1636 0.0018 0.4242 0.0035 2454 19 2283 16 160309-1-14 52 613 254 2.42 0.0754 0.0011 0.1251 0.0011 787 36 730 6 160309-1-15 14 719 531 1.35 0.0578 0.0013 0.0213 0.0002 102 65 126 1 160309-1-16 13 344 546 0.63 0.0507 0.0016 0.0245 0.0002 232 68 126 1 160309-1-17 126 337 276 1.22 0.1202 0.0013 0.3125 0.0034 1976 14 1755 17 160309-1-18 186 183 306 0.60 0.1812 0.0023 0.4645 0.0045 2657 22 2444 20 160309-1-19 3 105 137 0.76 0.0528 0.0027 0.0234 0.0002 272 120 126 1 160309-1-20 44 72 133 0.54 0.1515 0.0019 0.2775 0.0059 2396 21 1541 3 160309-1-21 4 126 155 0.82 0.0543 0.0041 0.0214 0.0004 217 179 125 2 160309-1-22 5 170 181 0.94 0.0531 0.0038 0.0236 0.0003 183 167 125 2 160309-1-23 11 281 469 0.60 0.0502 0.0015 0.0218 0.0003 161 72 129 2 160309-1-24 3 82 153 0.53 0.0537 0.0038 0.0248 0.0003 376 156 124 2 160309-1-25 5 150 191 0.79 0.0524 0.0035 0.0256 0.0003 195 137 129 2 160309-2-1 373 178 735 0.24 0.1625 0.0014 0.4475 0.0045 2480 15 2345 20 160309-2-2 73 95 130 0.73 0.1643 0.0016 0.4328 0.0033 2486 16 2321 15 160309-2-3 21 24 61 0.40 0.1216 0.0032 0.2946 0.0027 2013 45 1660 13 160309-2-4 40 49 73 0.68 0.1528 0.0016 0.4428 0.0039 2367 17 2344 18 160309-2-5 3 71 124 0.57 0.0575 0.0036 0.0201 0.0004 233 168 128 2 160309-2-6 98 121 175 0.69 0.1656 0.0014 0.4426 0.0046 2502 14 2340 21 160309-2-7 2 46 78 0.59 0.0585 0.0062 0.0209 0.0006 309 277 130 4 160309-2-8 167 174 307 0.57 0.1736 0.0014 0.4345 0.0046 2532 13 2321 21 160309-2-9 242 274 398 0.69 0.1715 0.0015 0.4805 0.0049 2569 15 2522 21 160309-2-10 27 1329 986 1.35 0.0515 0.0015 0.0207 0.0002 217 48 126 1 160309-2-11 76 72 193 0.37 0.1225 0.0013 0.3445 0.0034 2014 18 1886 16 160309-2-13 98 102 182 0.56 0.1775 0.0017 0.4316 0.0043 2517 51 2324 20 160309-2-14 45 69 79 0.87 0.1636 0.0017 0.4318 0.0044 2505 18 2323 20 160309-2-15 9 323 359 0.90 0.0545 0.0039 0.0218 0.0004 187 174 127 2. 160309-2-16 97 66 244 0.27 0.1425 0.0018 0.3438 0.0052 2333 21 1902 25 160309-2-17 7 151 276 0.55 0.0558 0.0022 0.0236 0.0002 354 93 126 1 160309-2-18 3 97 103 0.94 0.0563 0.0044 0.0279 0.0004 317 189 128 2 160309-2-19 113 157 192 0.82 0.1779 0.0019 0.4346 0.0051 2514 20 2318 23 160309-2-20 2 61 91 0.68 0.0548 0.0045 0.0228 0.0006 250 202 127 4 表 2 岩石主量、微量和稀土元素组成
Table 2 Composition of major, trace and rare earth elements in rocks
样号 160309-2-1 160309-2-2 160309-2-3 160309-2-4 160309-2-5 160703-1 160703-2 160703-3 160729-5 160729-6 160729-7 160729-8 160729-1 160729-2 160729-3 160729-4 SiO2 59.46 59.23 58.71 58.48 58.95 56.98 56.75 56.91 60.38 60.68 60.66 60.90 59.14 59.35 59.58 59.69 Al2O3 15.44 15.40 15.22 15.06 15.32 15.77 15.66 15.70 14.82 14.88 14.88 14.87 14.98 14.99 14.94 14.86 CaO 2.97 3.27 4.37 4.40 3.23 5.85 5.76 5.44 4.04 3.85 3.69 3.84 5.68 5.36 5.34 5.09 TFe2O3 5.71 5.69 5.80 5.81 5.95 7.19 6.98 7.12 5.30 5.56 5.52 5.38 6.49 6.22 6.18 6.12 K2O 3.22 2.82 3.01 3.09 3.17 3.20 3.31 3.55 2.82 2.39 2.80 2.64 3.12 3.33 3.30 3.45 MgO 4.62 4.20 4.58 3.69 4.98 4.87 4.90 4.93 4.16 4.15 4.30 4.03 4.97 4.78 4.67 4.67 MnO 0.07 0.08 0.08 0.07 0.08 0.12 0.11 0.11 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.11 0.10 0.10 0.10 Na2O 3.88 4.68 3.75 3.92 4.10 3.86 3.93 3.69 4.09 4.21 4.11 4.26 3.76 3.77 3.77 3.74 P2O5 0.29 0.28 0.28 0.27 0.28 0.44 0.46 0.46 0.28 0.27 0.28 0.28 0.41 0.39 0.38 0.37 TiO2 0.58 0.58 0.55 0.56 0.57 0.81 0.82 0.79 0.68 0.68 0.69 0.68 0.74 0.73 0.73 0.73 烧失量 3.72 4.07 3.77 4.54 3.31 0.70 0.86 1.00 3.62 3.33 3.13 3.01 0.93 0.94 0.86 0.75 总计 99.96 99.98 99.98 99.89 99.94 99.79 99.54 99.70 99.98 99.97 99.96 99.95 99.89 99.96 99.85 99.57 Mg# 45 42 44 39 46 40 41 41 44 43 44 43 43 43 43 43 Rb 69.2 58.8 64.9 69.4 67.6 58.4 66.2 62.7 72.6 77.0 84.0 77.6 58.9 63.0 65.7 68.1 Ba 1320 1455 1455 2710 1315 2140 1915 2000 1535 1255 1425 1410 1995 2040 2010 2030 Th 4.85 4.60 4.73 4.85 4.73 4.83 5.44 4.47 7.54 7.59 7.82 7.84 6.20 7.20 8.20 7.20 U 2.91 1.90 1.53 1.52 2.57 1.35 1.92 1.29 1.74 1.99 1.84 1.80 1.80 2.00 2.10 1.90 Nb 6.0 5.8 5.8 5.7 5.8 6.8 7.1 6.7 8.0 8.1 8.3 8.2 8.2 8.4 9.0 9.10 Ta 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.4 0.4 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.6 0.6 0.7 0.70 Pb 17 15 13 11 16 20 25 18 8 9 8 7 21 25 20 26 Sr 871 831 1030 1050 864 1320 1270 1230 767 800 786 816 1045 967 977 968 Nd 18.6 17.9 21.9 20.7 20.5 27.7 27.8 27.0 28.8 29.4 27.1 30.0 29.5 29.5 29.4 29.8 Zr 146 135 140 137 137 191 177 178 189 195 201 195 165 199 201 218 Hf 3.60 3.3 3.6 3.4 3.5 4.8 4.4 4.4 4.6 4.7 4.9 4.8 4.2 5.1 4.8 5.6 Tb 0.32 0.31 0.38 0.36 0.35 0.51 0.51 0.50 0.46 0.46 0.46 0.48 0.60 0.50 0.50 0.60 Er 0.96 0.93 1.05 1.01 1.11 1.61 1.54 1.50 1.20 1.08 1.19 1.19 1.50 1.60 1.60 1.60 La 27.1 22.8 30.5 28.8 28.8 34.6 35.1 33.7 43.5 41.6 32.5 42.9 38.8 38.8 39.3 39.6 Ce 49.9 44.2 56.5 53.5 53.4 67.2 66.4 64.5 77.8 75.7 62.8 78.0 74.4 73.3 75.3 75.5 Pr 5.13 4.79 5.84 5.65 5.49 7.23 7.17 7.11 7.93 8.02 6.97 8.2 7.97 7.91 7.88 7.95 Nd 18.6 17.9 21.9 20.7 20.5 27.7 27.8 27 28.8 29.4 27.1 30 29.5 29.5 29.4 29.8 Sm 3.26 3.2 3.8 3.5 3.51 5.07 5 4.83 5 4.86 4.83 5.25 5.26 5.43 5.01 5.42 Eu 0.97 0.93 1.21 1.1 1.12 1.61 1.54 1.56 1.46 1.47 1.51 1.48 1.59 1.47 1.52 1.56 Gd 2.48 2.38 2.93 2.82 2.9 4.08 4.01 4.05 3.82 3.77 3.97 3.94 4.09 4.04 4.08 4.09 Tb 0.32 0.31 0.38 0.36 0.35 0.51 0.51 0.5 0.46 0.46 0.46 0.48 0.58 0.53 0.51 0.55 Dy 1.62 1.62 1.86 1.85 1.82 2.78 2.64 2.74 2.4 2.24 2.41 2.37 2.9 2.85 2.81 2.87 Ho 0.34 0.34 0.37 0.36 0.38 0.54 0.56 0.53 0.45 0.42 0.44 0.45 0.56 0.55 0.56 0.57 Er 0.96 0.93 1.05 1.01 1.11 1.61 1.54 1.5 1.2 1.08 1.19 1.19 1.51 1.55 1.59 1.61 Tm 0.15 0.15 0.16 0.15 0.15 0.21 0.21 0.21 0.16 0.15 0.16 0.16 0.21 0.23 0.22 0.23 Yb 0.81 0.79 0.99 0.9 0.95 1.25 1.24 1.33 0.85 0.83 0.91 0.94 1.33 1.32 1.26 1.39 Lu 0.13 0.13 0.14 0.13 0.13 0.19 0.18 0.18 0.13 0.12 0.13 0.12 0.2 0.21 0.2 0.21 Y 8.7 8.6 10.1 9.5 9.9 14.8 14.3 14.2 11.7 11.4 11.9 11.7 15.5 15.2 15.7 15.4 Sr/Y 100.1 96.6 102.0 110.5 87.3 89.2 88.8 86.6 65.6 70.2 66.1 69.7 67.4 63.6 62.2 62.9 δEu 1.00 0.99 1.07 1.04 1.04 1.05 1.02 1.05 0.98 1.01 1.02 0.95 1.01 0.92 1.00 0.97 注:Mg#=100×Mg2+/(Mg2++TFe2+); 主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素为10-6 -
周力, 张均, 王健, 等.安徽张八岭地区管店岩体成因及其与上成金矿床的关系[J].地质科技情报, 2014, 33(1):32-40. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4573025 胡子龙. 皖东滁州地区燕山期岩浆岩地球化学特征与铜金成矿[D]. 中国科学技术大学硕士学位论文, 2015: 6-16. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10358-1015615550.htm 张旗, 王焰, 钱青, 等.中国东部燕山期埃达克岩的特征及其构造成矿意义[J].岩石学报, 2001(2):236-244. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20010228 张旗, 王元龙, 王焰.燕山期中国东部高原下地壳组成初探:埃达克质岩Sr, Nd同位素制约[J].岩石学报, 2001, 4:505-513. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200104000.htm 王元龙, 王焰, 张旗, 等.铜陵地区中生代中酸性侵入岩的地球化学特征及其成矿地球动力学意义[J].岩石学报, 2004, 2:325-338. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/DZXE201105013.htm 汪洋, 邓晋福, 姬广义.长江中下游地区早白垩世埃达克质岩的大地构造背景及其成矿意义[J].岩石学报, 2004, 2:297-314. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20040229 王强, 许继峰, 赵振华, 等.安徽铜陵地区燕山期侵入岩的成因及其对深部动力学过程的制约[J].中国科学(D辑), 2003, 4:323-334. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98491X/2003004/7697348.html 王强, 赵振华, 许继峰, 等.鄂东南铜山口、殷祖埃达克质(adakitic)侵入岩的地球化学特征对比:(拆沉)下地壳熔融与斑岩铜矿的成因[J].岩石学报, 2004, 2:351-360. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Column/Paper?Id=dl_010108&q=CLCShort%3a%22P*%22+%e6%97%a5%e6%9c%9f%3a2004-2004&f=sort&o=sortby+CitedCount+CoreRank+HasOriginalDoc+date%2fweight%3d5+relevance Wang Q, Xu J F, Zhao Z H, et al. Cretaceous high potassium intrusive rocks in the Yueshan-Hongzhen area of east China:adakites inan extension al tectonic regime within a continent[J]. Geochemical Journal, 2004, 38:417-434. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.38.417
Wang Q, Zhao Z H, Bao Z W, et al. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Tongshankou and Yinzu adakitic intrusive rocksand the associated porphyry copper-molybdenum mineralization in south-east Hubei, east China[J]. Resource Geology, 2004, 54:137-152. doi: 10.1111/rge.2004.54.issue-2
Wang Q, Wyman D A, Xu J F, et al. Petrogenesis of Cretaceous adakitic and shoshonitic igneous rocks in theLuzong area, Anhui Province (eastern China):implications for geodynamics and Cu-Au mineralization[J]. Lithos, 2006, 89:424-446. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2005.12.010
Wang Q, Xu J F, Jian P, et al. Petrogenesis of adakitic porphyries in an extensional tectonic setting, Dexing, South China:implications for the genesis of porphyry copper mineralization[J]. Journal of Petrology 2006, 47:119-144. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egi070
Wang Q, Wyman D A, Xu J F, et al. Early Cretaceous adakitic granites in the Northern Dabie Complex, central China:implications for partial melting and delamination of thickened lower crust[J]. Geochemical Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71:2609-2636. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.03.008
Wang Q, Wyman D A, Xu J F, et al. Partial melting of thickened or delaminated lower crust in the middle of Eastern China:implications for Cu-Au mineralization[J]. Journal of Geology, 2007, 115:149-161. doi: 10.1086/510643
Xu J F, Shinjo R, Defant M J, et al. Origin of Mesozoic adakitic intrusive rocks in the Ningzhen area of eastern China:partial melting of delaminated lower continental crust?[J] Geology, 2002, 30:1111-1114. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<1111:OOMAIR>2.0.CO;2
谢成龙, 朱光, 牛漫兰, 等.滁州中生代火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].地质论评, 2007, 53(5):642-655. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/yj/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_OA000004801 Xie G Q, Mao J W, Li L R, et al. Geochemistry and Nd-Sr isotopic studies ofLate Mesozoic granitoids in the southeastern Hubei province, Middle-Lower Yangtze River belt, Eastern China:petrogenesis and tectonic setting[J]. Lithos, 2008, 104:216-230. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2007.12.008
Ling M X, Wang F Y, Ding X, et al. Cretaceous ridge subduction along the lower Yangtze river belt, eastern China[J].Economic Geology, 2009, 104:303-321. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.104.2.303
Ling M X, Wang F Y, Ding X, et al. Different origins of adakites-from the Dabie Mountains and the Lower Yangtze River belt in eastern China:geochemical constraints[J]. International Geology Review, 2011, 53:727-740. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2010.482349
Li J W, Zhao X F, Zhou M F, et al. Late Mesozoic magmatism from the Daye region, eastern China:U-Pb ages, petrogenesis, and geodynamics implications[J]. Contribution to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2009, 157:383-409. doi: 10.1007/s00410-008-0341-x
Liu S A, Li S G, He Y S, et al. Geochemical contrasts between early Cretaceous ore-bearing and ore-barren high-Mg adakites in central-eastern China:implications for petrogenesis and Cu-Au mineralization[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2010, 74:7160-7178. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2010.09.003
孙卫东, 凌明星, 杨晓勇, 等.洋脊俯冲与斑岩铜金矿成矿[J].中国科学(D辑), 2010, 2:127-137. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201002001.htm Sun W D, Zhang H, Ling M X, et al. The genetic association of adakites and Cu-Au ore deposits[J]. International Geology Review, 2011, 53:691-703. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2010.507362
Sun W D, Ling M X, Chung S L, et al. Geochemical constraints on adakites of different origins and copper mineralization[J]. Journal of Geology, 2012, 120:105-120. doi: 10.1086/662736
谢建成, 陈思, 孙卫东, 等.安徽铜陵早白垩世埃达克质岩地球化学:成岩成矿制约[J].岩石学报, 2012, 10:3181-3196. http://www.irgrid.ac.cn/handle/1471x/749272?mode=full Chen B, Jahn B M, Suzuki K.Petrological and Nd-Sr-Os isotopic constraints onthe origin of high-Mg adakitic rocks from the North China Craton:tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 2013, 41:91-94. doi: 10.1130/G33472.1
Yang Y Z, Chen F K, Siebel W, et al. Age and composition of CuAu related rocks from the lower Yangtze River belt:Constraints on paleo-Pacific slab roll-back beneath eastern China[J].Lithos, 2014, 200/203:331-346. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/263202555_Age_and_composition_of_Cu-Au_related_rocks_from_the_lower_Yangtze_River_belt_Constraints_on_paleo-Pacific_slab_roll-back_beneath_eastern_China
Defant M J, Drummond M S.Derivation of some modern arc magmas by meltingof young subducted lithosphere[J]. Nature, 1990, 347:662-665. doi: 10.1038/347662a0
Defant M J, Kepezhinskas P.Evidence suggests slab melting in arc magmas[J].Eos Transactions, 2001, 82:62-65. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=16be5c5a30dc4598e67efcc5d877862d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Mungall J E.Roasting the mantle:slab melting and the genesis of major Au and Aurich Cu deposits[J]. Geology, 2002, 30:915-918. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0915:RTMSMA>2.0.CO;2
Oyarzun R, Márquez A, Lillo J, et al. Giant versus small porphyry-copper deposits of Cenozoic age in northern Chile:adakitic versus normal calcalkaline magmatism[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2001, 36:794-798. doi: 10.1007/s001260100205
Sajona F G, Maury R C.Association of adakites with gold and copper mineralization in the Philippines. Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences-Series ⅡA[J].Earth and Planetary Science, 1998, 326:27-34. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/223689518_Association_of_adakites_with_gold_and_copper_mineralization_in_the_Philippines
Thieblemont D, Stein G, Lescuyer J L. Gisementsepithermaux et porphyriques:laconnexionadakite. Comptes Rendus de l'Academie des Science-Series[J].Earth and Planetary Science, 1997, 325:103-109.
Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen:U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 20009, 51(1/2):537-571. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=6e670e94216d07dcd3c8ccc5b2989818&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics ofo-ceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in Oceanic-Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 1989, 42(1): 313-345.
李学明, 李彬贤, 张巽, 等.安徽管店岩体的同位素地质年龄和郯庐断裂带的动力学变质作用[J].中国科学技术大学学报, 1985, 15(增刊):254-261. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKQ201401006.htm 牛漫兰.张八岭地区中生代岩体中黑云母的40Ar-39Ar年龄及其地质意义[J].地质科学, 2006, 41(2):217-225. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzkx200602005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 资锋, 王强, 唐功建, 等.皖中管店岩体的锆石年代学与地球化学:岩石成因和动力学意义[J].地球化学, 2008, 37(5), 462-480. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKQ201401006.htm Wang Q, Wyman D A, Xu J F, et al. Early Cretaceous adakitic granites in the Northern Dabie Complex, central China:implications for partial melting and delamination of thickened lower crust[J].Geochemical Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71:2609-2636. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.03.008
Huang F, Li S G, Dong F, et al. High-Mg adakiticrocks in the Dabie orogeny, Central China:Implications for foundering mechanism of lower continental crust[J].Chemical Geology, 2008, 255(1/2):1-13.
Sen C, Dunn T.Dehydration melting of a basaltic compositionam-phibolite at 1.5 and 2.0GPa:Implications for the origin of adakite[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1994, 117(4):394-409. doi: 10.1007/BF00307273
Taylor S R, McLennan S M.The Continental Crust:Its Composition and Evolution[M]. Oxford:Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1985:1-100.
Rudnick R L, Gao S. Composition of the continental crust[C]//Rudnick R L, Holland H D, Turekian K K. The Crust Vol. 3 Treatiseon Geochemistry. Oxford: Elsevier-Pergamon, 2003: 1-64.
Zhu G, Xie C L, Xiang B W, et al. Genesis of the Hongzhen metamorphic core complex and its tectonic implications[J]. Science in China (D), 2007, 50:649-659. doi: 10.1007/s11430-007-0032-x
Sun W D, Ding X, Hu Y H, et al. The golden transformation of the Cretaceous plate subduction in the west Pacific[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 262(3/4):533-542. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=6a944fd74f65ac63838d6ef2e9c5ff43&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn



 下载:
下载: