Geochronology, geochemistry and geological sig-nificance of the Early Cretaceous alkali feldspar granites in the Yilehuli Mountain, Da Hinggan, Mountain
-
摘要:
对大兴安岭伊勒呼里山早白垩世碱长花岗岩进行了岩相学、地球化学、LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年研究。伊勒呼里山地区碱长花岗岩主量元素具有富Si、富碱,贫Mg、Ca的特征;微量元素亏损Sr、P、Eu、Ti,富集K、Rb、Th等不相容元素,元素地球化学特征表明,岩体为铝质A型花岗岩(A/CNK=0.88~1.21,A/NK=0.94~1.49)。测年结果显示,粗中粒碱长花岗岩的锆石年龄为140.3±1.0Ma,细中粒碱长花岗岩锆石年龄为137.9±0.8Ma,均形成于早白垩世。结合区域研究资料,伊勒呼里山地区碱长花岗岩岩体的形成与蒙古-鄂霍茨克洋闭合后的岩石圈伸展密切相关,其岩浆源区可能为地壳物质的部分熔融。
Abstract:Petrographic and geochemical data and LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb ages were obtained for Early Cretaceous alkali feldspar granites of the Yilehuli Mountain. The major elements of Yilehuli alkali feldspar granites are high in Si, ALK, and low in Mg, Ca. Trace elements are enriched in incompatible elements such as K, Rb and Th, and depleted in Sr, P, Eu and Ti. Geochemical features indicate that alkali feldspar granites are aluminum A-type granites (A/CNK=0.88~1.21, A/NK=0.94~1.49). LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age data of coarse-medium alkali feldspar granites and fine-medium alkali feldspar granites are 140.3 ±1.0Ma and 137.9 ±0.8Ma, respectively, indicating that intrusive rocks were formed in Early Cretaceous. Combined with regional geological investiga-tion, the authors hold that the formation of Yilehuli plutons was closely related to lithospheric extension caused by closure of the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean, and that the primary magma was derived from partial melting of crustal materials.
-
Keywords:
- Early Cretaceous /
- geochemistry /
- zircon U-Pb age /
- A-type granite /
- Yilehuli Mountain
-
徐淮推覆-褶皱带位于华北板块东南缘、郯庐断裂西侧(图 1),为该区重要的陆内变形带。区域内徐淮断裂-褶皱系统由北向南走向由NNE—近NS—NW变化,也称为徐淮弧。弧顶位于萧县—淮北市一带, 与华北板块的其余构造形态具有明显差别(图 1)。早在20世纪90年代,徐树桐等[3]将其称为半圆形造山带或大型褶皱逆冲推覆体;王桂梁等[4]提出区域构造表现为弧形双冲-叠瓦状逆断层特点;彭凌日等[5]与Shu等[1]认为,区域构造属于挤压背景下的薄皮构造模型,表现为区域上普遍存在一系列弧形的斜歪褶皱、逆冲推覆构造。以上均为该区构造样式成因的研究,取得较多成果,而对于区域广泛存在的滑脱层研究不足[1, 1-5]。
滑脱层的存在影响盖层与基底间界面的剪切强度,使褶皱-冲断带构造传播方式及构造样式发生变化[6]。通常滑脱层能使构造变形传播距离更远,并且不同厚度滑脱层影响后冲断层的发育数量及构造的对称性,形成隔挡隔槽式褶皱、等间距逆冲断层、反冲断层等典型构造[7-9];滑脱层深度及强弱性质的改变将影响构造变形的传播特征及褶皱、断层构造的样式和间距变化[10-13]。
随着构造物理模拟手段的不断完善,它已成为地质学家认识构造变形过程、分析构造成因机制的重要手段[14-19]。本文选取徐淮推覆-褶皱带为研究对象,结合前人研究资料,采取物理模拟手段对区域滑脱层深度变化、滑脱层摩擦系数的控制作用进行探索,进而对区域构造样式的控制因素和形成机制进行研究。
1. 徐淮地区构造背景
1.1 区域地层
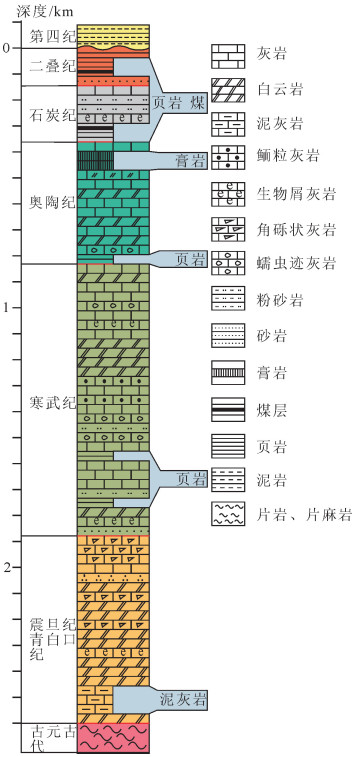
研究区沉积盖层在东西向剖面上表现为东侧盖层厚度大于西侧(图 2-b),基底为太古宇泰山群变质岩,盖层分为3个亚层,即青白口系—震旦系、寒武系—奥陶系、石炭系—二叠系,相应亚层的分布表现为下部的青白口系—震旦系多为碎屑岩-碳酸盐岩沉积,岩石组成多为叠层石灰岩与白云岩,中部的寒武系—奥陶系主要为浅海碳酸盐岩,石炭系—二叠系以滨海相灰岩及滨海湖泊-三角洲体系陆源碎屑岩沉积为主,其中山西组和上、下石盒子组是主要的含煤层系①[21-22]。结合前人野外调查,区域上滑脱层普遍发育,主要为页岩、膏岩泥灰岩及煤层,分别为青白口系泥灰岩、寒武系猴家山组与馒头组页岩、奥陶系贾汪组页岩与马家沟组膏岩、石炭系—二叠系页岩及煤层(图 3)[1, 23]。其中,青白口系泥灰岩、寒武系页岩、石炭系—二叠系页岩及煤层作为主要拆离层控制区域主要构造变形[24]。
1.2 构造特征
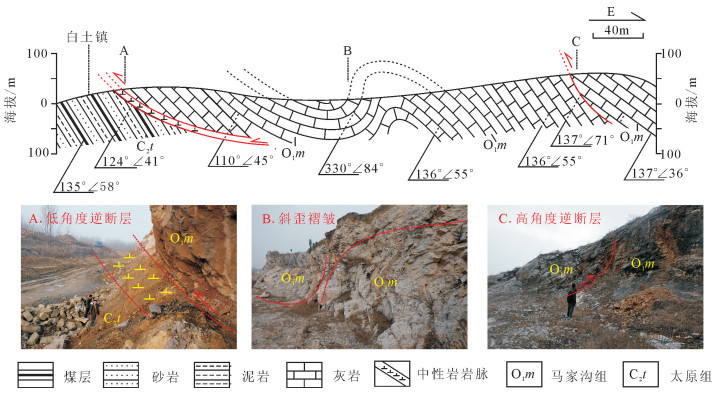
研究区以逆冲推覆构造为主,未卷入结晶基底,属于典型的薄皮构造(图 2-a),平面上逆冲推覆构造为一系列走向由北向南、由NNE—近NS—NW变化的逆断层及伴生斜歪褶皱[5],如白土镇东斜歪褶皱的轴面产状为144°∠75°,高角度逆断层的产状为137°∠71°,低角度逆断层的产状为124°∠41°(图 4),表明该区受到从南东向北西的挤压应力场作用。
结合前人在该区域进行的构造应力场研究[1, 25-26],区域受2期应力场作用,分别是早燕山期SE—NW向挤压及晚燕山期NNE—SSW向挤压力。本次研究通过61个野外共轭节理、断面擦痕求应力场,并利用赤平投影求得最大主应力轴(σ1)优势方位,2个极密点方位为200°∠6°、133°∠6°,表明该2期应力场方位与前人研究一致(图 5)。虽然晚燕山期受NNE向挤压,导致该区侏罗纪—白垩纪盆地发育,但仍以早燕山期SE—NW向挤压作用形成的构造格局为主[4, 27]。
以皇藏峪背斜为界将研究区构造划分为东部构造带与西部构造带(图 2-b),东部构造带主要为一系列斜歪褶皱,少量叠瓦状分支断层;西部构造带表现为强烈变形,发育一系列逆冲断层。总体构造具明显东西分带的特点[3, 20]。
2. 构造物理模拟实验设计
2.1 实验材料
构造物理模拟实验遵循相似原则,即几何学相似、动力学相似、运动学相似,实验材料物性、模型尺寸等需要与自然界中实际的相应参数保持一定比值[28-29]。本次实验中所用材料为石英砂、微玻璃珠及硅胶。
干燥石英砂用于模拟脆性的上覆岩层,其物理性质为脆性且遵循库伦-莫尔破坏准则,内摩擦角为31°左右,内聚力极小[30],变形过程中铺设的石英砂颗粒将出现从应变硬化-应变软化的过渡,导致影响断层角度的内摩擦系数稍小于未变形前岩石的内摩擦系数[31-32]。石英砂颗粒直径为200~300μm,根据不同的铺沙方式(筛或直接倒入模型中),密度会有差别,总体密度在1.3~1.6g/cm3之间。人工烧结的彩色石英砂颗粒一般物性不发生改变,铺设1mm厚彩色石英砂于模型中作为观察构造变形的标志层[33]。
微玻璃珠通常用于模拟强滑脱层,表面光滑且磨圆度好,玻璃珠内聚力几乎为零,内摩擦角为25°左右[34-35],应变软化幅度很小,变形前后内摩擦角变化不大。本次实验使用直径为300μm的微玻璃珠充当强滑脱层,铺设于模型最底部[36]。
硅胶为透明高粘度的材料,用于模拟上地壳的塑性变形,在低应变速率下具有牛顿流体性质且具有非常低的屈服强度[37]。测得室温下本实验材料粘度为1.2×104Pa.s, 密度为0.926g/cm3, 铺设2~3mm于基底之上,作为弱滑脱层,控制变形传播距离,产生各类褶皱-冲断构造[7, 38-39]。
2.2 相似条件
根据相似原理,模型与地质原型长度的相似因子L*为1×10-5(即实验室中模型1cm代表自然界中1km的长度);地质原型中沉积岩的平均密度为2.6g/cm3, 模型中石英砂与微玻璃珠的平均密度为1.4g/cm3, 所以实验设定的密度相似因子为0.5[40];模型与地质原型的重力加速度相同,为9.8m/s2, 重力加速度相似因子为1;关于硅胶滑脱层,粘度一般为1×104Pa.s, 而地质原型相应地层的粘度为1×1019Pa.s, 粘度相似因子为1×10-15(*代表相应模型参数与地质原型参数的比值)。
根据前人对徐淮地区变形的年代学数据及缩短率的研究[23, 25],推算出地质原型变形速率为1~10mm/a,因而设置实验室计步器推挤速率为0.005mm/s,结合速度相似因子v*=5×104,实验中模拟地质原型的挤压速率为3.2mm/a,与推算变形速率(1~10mm/a)大小为同一数量级,符合构造模拟相似条件。
2.3 实验装置
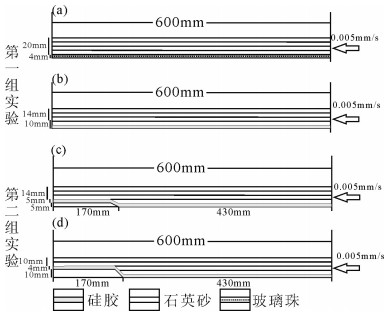
根据控制变量法来改变滑脱层深度及滑脱层物理性质[6, 17],设计2组实验。第一组实验设计2个模型分别为模型1与模型2,初始尺寸均为600mm×400mm×24mm,且底板水平。模型1使用4mm厚微玻璃珠作为强滑脱层,20mm厚的石英砂作为盖层,而模型2则用一层厚4mm的硅胶层为弱滑脱层,盖层材料与厚度均与模型1相同(图 6-a、b)。模型两侧为钢化玻璃,为减少边界效应的影响,在实验前用无水酒精将其擦拭干净。
第二组实验设计2个模型分别为模型3和模型4,尺寸均为600mm×400mm×24mm, 模型底板均保持水平,考虑到滑脱层深度变化的影响,模型中均设计有先存的台阶式隆起,模型3距离活动端430mm处设置有5mm高的台阶状基底隆起,而模型4则在距活动端430mm处设置为10mm高的台阶状隆起。模型3、4底部均有一层厚4mm的硅胶层作为滑脱层,盖层为石英砂,两模型材料厚度均为24mm(图 6-c、d)。
4个模型均从右侧施加挤压力,活动端推板运动速度均为0.005mm/s,根据前人对区域平衡剖面恢复所得缩短率[1, 25],本文模型缩短率取30%,每组实验过程通过照相机定时,每隔5min照相记录。
3. 实验结果及分析
3.1 第一组实验
3.1.1 模型1
实验过程分为4个阶段。阶段一,缩短率为2.00%时,在靠近活动端出现前冲断层1及断层相关褶皱,形成构造单元Ⅰ;阶段二,缩短率为13.50%时,构造单元Ⅰ中发育1号断层的分支断层2,以及从微玻璃珠滑脱层逐渐向地表延伸的断层3、4,此时该单元具逆冲叠瓦构造特点,位于构造单元Ⅰ前方1.6cm处发育受前冲断层5控制的构造单元Ⅱ;阶段三,缩短率为20.50%时,构造单元Ⅱ形成与构造单元Ⅰ相同的构造样式,其中断层6为断层5的分支断层,调节断层运动,位于构造单元Ⅱ前方3.8cm处(相比前者间距更远)发育受前冲断层7控制的构造单元Ⅲ;阶段四,缩短率为30.00%时,构造单元Ⅲ形成构造与前者相同,其中断层9为分支断层(图 7)。
实验所切剖面见3个间距明显不同的构造单元。构造单元Ⅰ主要受1~4前冲断层控制,形成堆垛式逆冲叠瓦构造及断层相关褶皱;构造单元Ⅱ与构造单元Ⅲ构造样式与构造单元Ⅰ相同,各个构造单元内断层间距变化均表现为朝固定端(前陆)逐渐增大,与前人研究结果一致[14, 41](图 7-e、图 8-f)。
![]() 图 8 徐淮推覆-褶皱带物理模拟中模型1(a)、模型2(b)的断层角度/缩短率关系图(1~9代表相应断层编号)、模型1与2楔长/缩短率(c)、楔高/缩短率(d)、楔角/缩短率(e)对比图及最终剖面上断层间距/断层顺序(f)对比图(断层顺序1~8代表活动端向固定端测量断层间距的顺序)Figure 8. Model 1(a), model 2(b) fault angle/shortening ratio diagram, model 1 and 2 wedge long/short ratio(c), wedge high/ short ratio(d), wedge angle/short ratio(e) contrast diagram and the final section on fault distance/order(f) contrast diagram
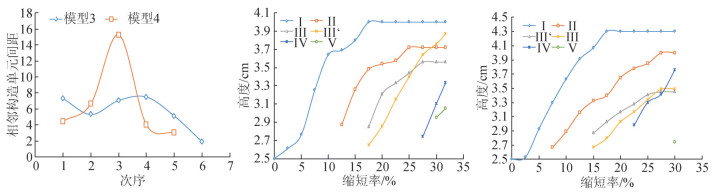
图 8 徐淮推覆-褶皱带物理模拟中模型1(a)、模型2(b)的断层角度/缩短率关系图(1~9代表相应断层编号)、模型1与2楔长/缩短率(c)、楔高/缩短率(d)、楔角/缩短率(e)对比图及最终剖面上断层间距/断层顺序(f)对比图(断层顺序1~8代表活动端向固定端测量断层间距的顺序)Figure 8. Model 1(a), model 2(b) fault angle/shortening ratio diagram, model 1 and 2 wedge long/short ratio(c), wedge high/ short ratio(d), wedge angle/short ratio(e) contrast diagram and the final section on fault distance/order(f) contrast diagram随着缩短率逐渐增加,楔长变化表现为增长至逐渐稳定的特点,楔长增加代表构造变形向固定端(前陆)传播,直至近稳定状态,最前端的断层前方未出现新构造使楔长不变或小幅减小;楔高则随缩短率增加逐渐增加,但增高速率逐渐减小(图 8-c、d),与前人观点一致[42]。组成构造单元Ⅰ的断层1、2、3、4角度变化具有较好的相关性,表现为晚出现的断层角度变化均会对早出现的断层角度产生影响;组成构造单元Ⅱ的断层5、6中,断层6角度逐渐小幅度增加,而断层5角度先增大后稳定,随后按该变化趋势发生变化;组成构造单元Ⅲ的断层7、8、9断层角度变化速率最慢,断层角度缓慢增加直至稳定,可见断层越远离力源,角度变化越容易达到稳定状态,并受晚期新构造影响越小(图 8-a)。
地表楔形隆起主要受到基底滑脱面性质及上覆材料强度的影响[14, 43]。随缩短率增加,活动端产生的楔状隆起角度达到临界角度之后,由于前缘未出现新断层,使角度继续增大向超临界角发展,直至前缘出现新断层,楔形隆起角度将减小,并向着次临界角值发展,达到相应次临界角后将再次增大(图 8-e),可见楔体达到临界角度后仍处于非稳定状态,而不是保持该状态向固定端方向稳定传播。模型1中,缩短率为8.75%时,楔角增大至相应超临界角,随后向一定次临界角值减小,缩短率为13.75%、23.75%时,相应状态下相应次临界角值再增大,符合前人观点[44-46]。
3.1.2 模型2
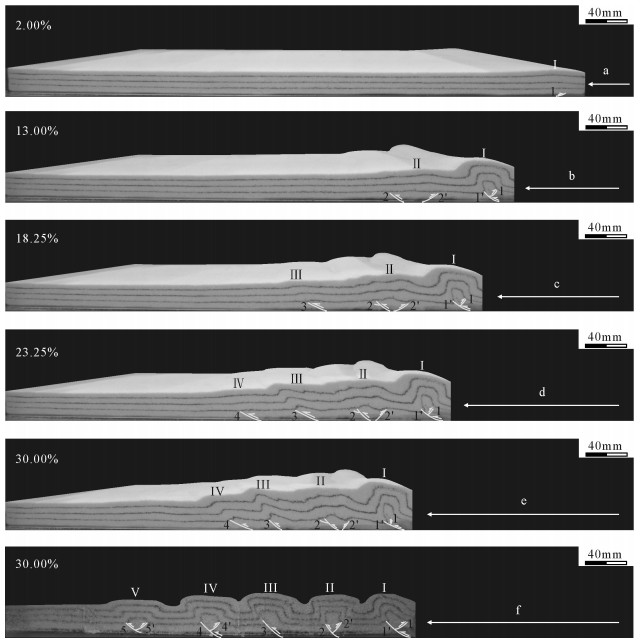
按构造单元将实验过程分为5个阶段。阶段一,缩短率为2.00%时,形成由前冲断层1与断层相关褶皱组成的构造单元Ⅰ;阶段二,缩短率为13.00%时,构造单元Ⅰ中发育后冲断层,此时断层相关褶皱形态为不对称箱状,位于构造单元Ⅰ前方,构造单元Ⅱ出现,主要由一对前后冲断层及断层相关褶皱组成;阶段三,缩短率为18.25%时,构造单元Ⅰ、Ⅱ继续发育,构造单元Ⅲ前方出现由只受前冲断层控制的构造单元Ⅲ;阶段四,缩短率为23.25%时,构造单元Ⅲ未出现后冲断层,断层相关褶皱形态为尖棱斜歪,并在其前方出现由前冲断层组成的构造单元Ⅳ;阶段五,缩短率为30.00%时,构造单元Ⅳ继续发育,表现为宽阔斜歪褶皱(图 9)。
实验所切剖面见5个明显构造单元。构造单元Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅳ、Ⅴ均由前、后冲断层及断层相关褶皱组成,其中褶皱为不对称箱状;构造单元Ⅲ由前冲断层及断层相关褶皱组成,其中褶皱表现为尖棱斜歪特点。断层间距均大于模型1,表现为先减小后增大的特点(图 8-f、图 9-f)。
实验过程中楔长变化主要为增长-稳定交替变化特点,其中稳定阶段时间略小于模型1,但模型2楔长普遍大于模型1,表明模型2构造变形传播的更远;楔高逐渐增大,至缩短率13.75%达到近稳定状态,随后楔高小幅度变化;活动端地表隆起楔角在缩短率为6.25%时,达到相应超临界角后,楔角下降,随缩短率增加,楔角减小速率逐渐变小,直至楔角趋于近稳定状态,达到临界值。实验过程中模型2楔角值均小于模型1,符合Davis等关于基底摩擦系数对库伦楔角影响的认识(图 8-c、d、e)[45]。各断层角度变化趋势相似,均表现为增大-稳定(图 8-b)的变化趋势。
3.2 第二组实验
3.2.1 模型3
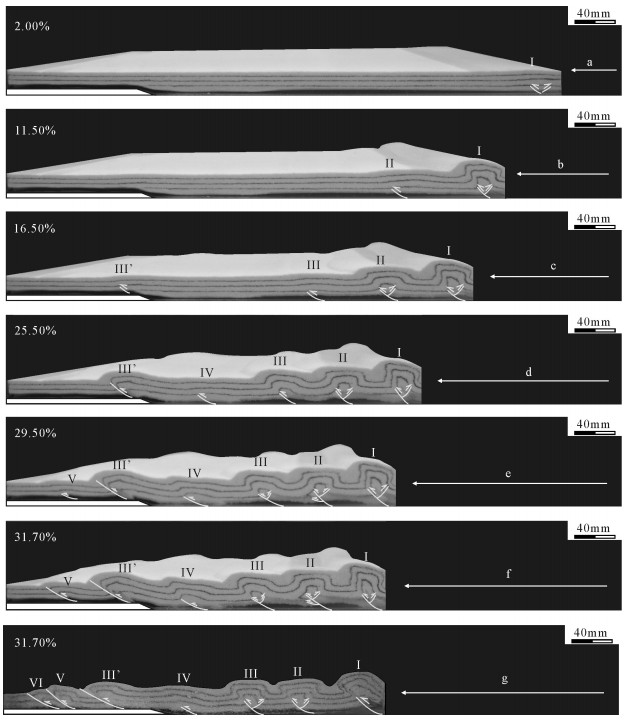
实验过程分为6个阶段。阶段一,缩短率为2.00%时,最先在活动端处出现构造单元Ⅰ,表现为一对前冲后冲断层,地表微微隆起;阶段二,缩短率为11.50%时,构造单元Ⅰ断层持续活动,断层相关褶皱表现为不对称箱状特点,在构造单元Ⅰ前方出现受前冲断层控制的构造单元Ⅱ;阶段三,缩短率为16.50%时,构造单元Ⅱ出现后冲断层,使断层相关褶皱表现为箱状特点,并在前方构造单元Ⅲ开始发育受前冲断层控制的断层相关褶皱,同时滑脱层深浅变化处发育构造单元Ⅲ’的断层转折褶皱;阶段四,缩短率为25.50%时,构造单元Ⅰ、Ⅱ持续活动,与Ⅰ、Ⅱ构造演化特点相同,在构造单元Ⅲ与Ⅲ’之间发育构造单元Ⅳ的受前冲断层控制的断层相关褶皱,褶皱形态宽缓;阶段五,缩短率为29.50%时,在构造单元Ⅲ’前方发育构造单元Ⅴ的前冲断层及断层相关褶皱,褶皱波长较小;阶段六,缩短率为31.70%时,构造单元Ⅳ持续活动,但未见后冲断层,构造单元Ⅴ的褶皱高度明显增加,相应断层延伸至地表(图 10)。
实验所切剖面见7个明显的构造单元,构造单元Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ主要受前冲断层及伴生的后冲断层控制,形成箱状褶皱;构造单元Ⅳ只受前冲断层控制,断层相关褶皱为宽缓斜歪褶皱,具明显不对称性;构造单元Ⅲ’、Ⅴ、Ⅵ受前冲断层控制,其中构造单元Ⅱ、Ⅰ’表现为断层转折褶皱,构造单元Ⅴ、Ⅵ组成逆冲叠瓦构造。深滑脱层区域各构造单元间距较大,平均间距为6.5cm,发育4个构造单元;浅滑脱层区域构造单元间距较小,从构造单元Ⅲ’至Ⅵ间距为先增大后减小;滑脱层深度变化处则对应剖面中波长最大的向斜(图 10-g、图 11-c)。
实验中随着缩短率逐渐增大,构造单元Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ隆起高度变化为增大-稳定不断循环的特点,证明模型中导致构造活动的应力集中过程是不稳定的,使得相应构造单元的活动具有乱序性,但处于滑脱层深浅变化附近的构造单元Ⅲ’与Ⅳ的隆起高度持续增加,未表现明显的稳定期,其中晚期出现的Ⅲ’构造单元最终隆起高度甚至超过了构造单元Ⅱ、Ⅲ(图 11-a)。
3.2.2 模型4
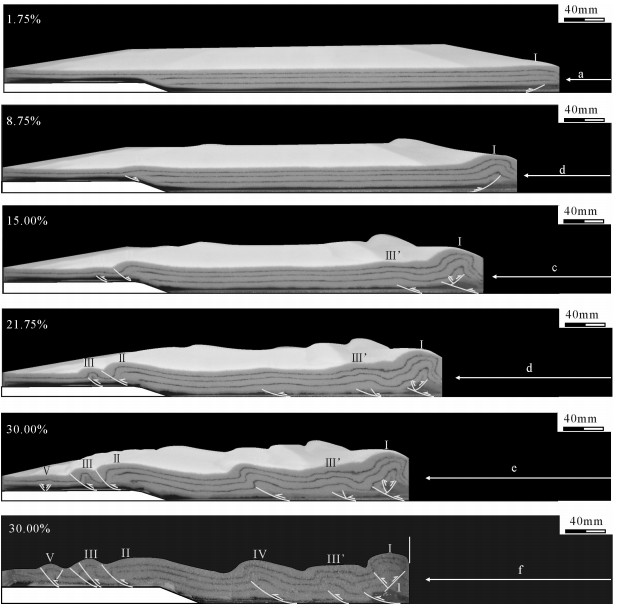
实验过程主要划分为5个阶段。阶段一,缩短率为1.75%时,构造单元Ⅰ发育由后冲断层控制的断层相关褶皱;阶段二,缩短率为8.75%时,构造单元Ⅰ持续活动,形成明显斜歪褶皱,位于滑脱层深浅变化处见构造单元Ⅱ的断层转折褶皱;阶段三,缩短率为15.00%时,在构造单元Ⅰ与Ⅱ前方同时发育构造单元Ⅲ、Ⅲ’,两者均表现为受前冲断层控制的断层相关褶皱,构造单元Ⅰ出现2条不同深度的前冲断层,表现出叠加褶皱的特点;阶段四,缩短率为21.75%时,构造单元Ⅱ与Ⅲ’之间出现构造单元Ⅳ,表现为断层相关褶皱;阶段五,缩短率为30.00%时,在构造单元Ⅲ前方出现构造单元Ⅴ,该构造受前后冲断层控制属于冲起构造,构造单元Ⅳ进一步发育,表现为尖棱斜歪的断层相关褶皱(图 12)。
实验所切剖面见6个明显的构造单元,构造单元Ⅰ中晚期低角度前冲断层将早期一对前后冲逆断层切断,最终表现褶皱为共轴叠加褶皱;构造单元Ⅲ’与Ⅳ主要受前冲断层控制,其中构造单元Ⅲ’为尖棱斜歪褶皱,Ⅳ为箱状斜歪褶皱;构造单元Ⅱ、Ⅲ受前冲断层控制,其构造单元Ⅱ主要表现为断层转折褶皱,构造单元Ⅲ为逆冲叠瓦构造及断层相关褶皱;构造单元Ⅴ受前后冲断层控制,属于冲起构造。深滑脱层区域各构造单元间距较大,向固定端间距逐渐增加,发育3个构造单元;浅滑脱层区域构造单元间距较小,且向固定端逐渐减小;滑脱层深度变化处也对应剖面中明显波长最大的向斜(图 11-c、图 12-f)。
随着缩短率的增加,构造单元Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ及Ⅲ’隆起高度先增大后趋于稳定,相应构造单元高度达到稳定状态后将不会改变,构造单元Ⅳ隆起高度增长最快,最终高度超过早于其出现的构造单元Ⅲ与Ⅲ’(图 11-b)。
4. 讨论
4.1 滑脱层强弱及深度对构造变形的影响
模型1基底之上为强滑脱层(微玻璃珠),随着缩短率增加,构造样式为逆冲叠瓦构造,表现为前展式传播形式,最终传播距离16.5cm,而模型2基底之上为弱滑脱层(硅胶),构造主要表现为不对称箱状褶皱及尖棱褶皱,构造传播方式与模型1相同,但变形向前缘方向传递距离明显大于模型1(图 7、图 9)。可见,滑脱层强弱差异控制着不同的构造样式。
模型3、4所设置装置底部不同高度台阶式抬升,使滑脱层深度发生变化,从而改变上覆盖层厚度与脆性层强度,使构造变形传播不再是传统的前展式,而呈乱序式,且在滑脱层深浅变化处容易应力集中而较早发生变形[17],变形传播距离相较于模型2更远。对于模型3与4,由于基底隆起高度大小差异,模型3(低基底隆起条件)在深滑脱层区域将出现更多的构造单元;模型3在深滑脱层区域普遍出现受前后冲断层控制的箱状断层相关褶皱,模型4除构造单元Ⅰ发育共轴叠加褶皱外,均表现为受前冲断层控制的斜歪褶皱特点,在浅滑脱层区域两者构造样式基本相同,主要为断层相关褶皱与逆冲断层(图 10、图 12)。因此,滑脱层深度变化对盖层相关构造变形具有明显影响。
4.2 实验结果与实际构造变形对比
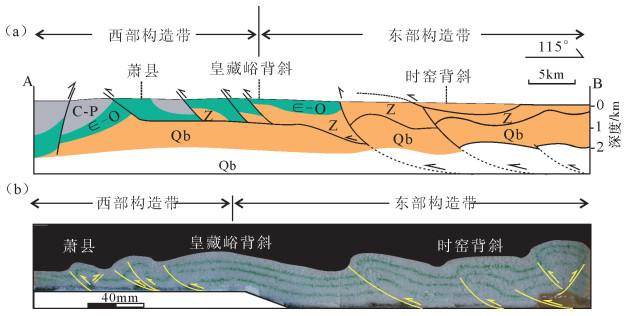
徐淮地区构造变形属于典型挤压背景下的薄皮构造,发育于早燕山期的滑脱构造,具有明显东西分带的特点,由东向西变形强度逐渐增强。以皇藏屿背斜为界,该界以西构造变形涉及盖层主要为寒武系—奥陶系与石炭系—二叠系,盖层厚度较小,发育一系列逆冲断层;该界以东构造变形涉及盖层主要为震旦系—奥陶系,盖层较厚,广泛发育轴面向SE方向倾斜的斜歪褶皱,叠瓦状分支断层较少[1]。
通过4个模型所切剖面与实际构造变形对比,认为实验模型4与区域上剖面具有较好的相似性,模型基底抬升处产生的背斜与皇藏峪背斜位置相当,虽然区域上变形含有多层滑脱层,但结合构造变形变化特点与物理模拟实验结果,认为区域上构造变形主要受2层不同深度滑脱层控制,分别是青白口系泥灰岩与寒武系页岩。以滑脱层抬升处(皇藏屿背斜)为界线,出现的褶皱间距及构造强弱的变化在模型4中有良好表现。滑脱层深度小,出现较密集的逆断层;滑脱层深度大,则构造形态以大波长的斜歪褶皱为主,断层未延伸至地表(图 13)。
本文对徐淮地区构造地质原型设计了2组实验,通过改变模型的材料及边界条件,研究了滑脱层性质及滑脱层深度变化对构造变形的控制作用,取得了与地质原型相似的模拟结果。然而自然界构造变形复杂,如多期构造叠加、沉积与剥蚀作用、多层滑脱层等。本次研究从主要控制因素入手,对地质原型进行模型化与理想化。该区存在多层滑脱层,滑脱层平面展布未能考虑,因而对于盖层变形控制不全面,有待进一步探讨滑脱层平面展布等因素对区域构造的影响。
5. 结论
(1) 滑脱层控制徐淮地区薄皮构造的形成,滑脱层的存在使得变形向前传播距离更远,是形成徐淮地区构造样式的主控因素,缺少滑脱层构造变形则表现出一系列堆垛式逆冲断层特点。
(2) 徐淮地区存在多套滑脱层,模拟实验表明,控制区域上东西构造样式变化的滑脱层主要有2套,分别为青白口系泥灰岩(深滑脱层)和寒武系页岩(浅滑脱层)。以皇藏屿背斜为界线,界线以西,滑脱层深度较浅,构造变形强烈,构造间距密集,逆冲断层普遍发育;界线以东,滑脱层深度较深,构造间距较大,主要发育斜歪褶皱,断层未能延伸至地表。
-
图 1 伊勒呼里山地区中生代侵入岩分布地质简图(据参考文献[5]修改)
Figure 1. Distribution diagram of Mesozoic intrusive rocks of the Yilehuli Mountain
表 1 伊勒呼里山早白垩世花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb定年结果(D0410)
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb data for Early Cretaceous granites in Yilehuli Mountain
分析序号 含量/10-6 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Pb U 206Pb/238U 1σ err% 207Pb/235U 1σ err% 207Pb/206Pb 1σ err% 208Pb/232Th 1σ err% 232Th/238U 1σ err% 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 中粗粒碱长质花岗岩,D0410 1 9 342 0.0225 0.0001 0.54 0.1574 0.0041 2.60 0.0507 0.0013 2.59 0.0079 0.0001 0.73 0.8196 0.0061 0.75 143 1 148 4 227 60 2 3 133 0.0227 0.0002 0.88 0.1487 0.0080 5.36 0.0474 0.0025 5.32 0.0075 0.0001 1.58 0.6675 0.0034 0.51 145 1 141 8 68 127 3 4 174 0.0221 0.0002 0.72 0.1495 0.0057 3.80 0.0490 0.0018 3.76 0.0078 0.0001 0.90 0.6852 0.0024 0.36 141 1 141 5 147 88 4 7 268 0.0222 0.0001 0.57 0.1565 0.0041 2.61 0.0510 0.0013 2.57 0.0078 0.0001 0.60 0.9643 0.0052 0.53 142 1 148 4 240 59 5 15 623 0.0224 0.0001 0.49 0.1561 0.0019 1.22 0.0506 0.0006 1.20 0.0080 0.0001 0.46 0.4852 0.0017 0.36 143 1 147 2 222 28 6 5 206 0.0223 0.0001 0.62 0.1475 0.0052 3.55 0.0479 0.0017 3.45 0.0087 0.0001 0.92 0.6622 0.0026 0.40 142 1 140 5 94 82 7 5 175 0.0216 0.0002 0.79 0.1516 0.0064 4.20 0.0507 0.0021 4.09 0.0079 0.0001 0.94 0.8952 0.0060 0.67 138 1 143 6 226 95 8 3 131 0.0209 0.0002 0.93 0.1474 0.0073 4.94 0.0511 0.0024 4.79 0.0071 0.0002 2.22 0.6022 0.0084 1.40 133 1 140 7 246 110 9 6 244 0.0217 0.0001 0.62 0.1439 0.0047 3.25 0.0481 0.0015 3.20 0.0081 0.0001 0.88 0.6602 0.0027 0.40 138 1 136 4 104 76 10 5 207 0.0218 0.0002 0.80 0.1493 0.0059 3.95 0.0497 0.0020 3.93 0.0082 0.0001 1.59 0.6368 0.0024 0.38 139 1 141 6 180 92 11 9 352 0.0224 0.0001 0.60 0.1466 0.0025 1.70 0.0474 0.0008 1.63 0.0084 0.0001 0.43 0.7885 0.0039 0.50 143 1 139 2 68 39 12 7 255 0.0226 0.0001 0.60 0.1502 0.0039 2.57 0.0482 0.0012 2.53 0.0081 0.0001 0.70 0.7232 0.0029 0.40 144 1 142 4 109 60 13 8 319 0.0215 0.0001 0.53 0.1517 0.0035 2.31 0.0511 0.0012 2.26 0.0081 0.0001 0.67 0.8151 0.0077 0.95 137 1 143 3 243 52 14 5 211 0.0219 0.0001 0.61 0.1473 0.0049 3.35 0.0487 0.0016 3.26 0.0086 0.0001 0.95 0.6870 0.0089 1.29 140 1 140 5 135 77 15 24 770 0.0222 0.0002 1.01 0.1518 0.0017 1.14 0.0495 0.0005 1.00 0.0083 0.0001 0.65 1.4382 0.0062 0.43 142 1 143 2 171 23 16 5 201 0.0223 0.0001 0.65 0.1545 0.0045 2.93 0.0502 0.0014 2.85 0.0085 0.0001 1.07 0.6102 0.0084 1.38 142 1 146 4 204 66 17 3 111 0.0217 0.0003 1.16 0.1533 0.0091 5.93 0.0513 0.0029 5.60 0.0091 0.0001 1.22 0.9005 0.0047 0.52 138 2 145 9 252 129 18 11 447 0.0219 0.0001 0.53 0.1465 0.0019 1.30 0.0486 0.0006 1.26 0.0084 0.0001 0.64 0.7845 0.0037 0.47 140 1 139 2 126 30 19 8 329 0.0219 0.0001 0.50 0.1479 0.0031 2.08 0.0491 0.0010 1.99 0.0091 0.0001 0.58 0.7240 0.0024 0.33 139 1 140 3 152 47 20 9 325 0.0215 0.0001 0.53 0.1545 0.0035 2.24 0.0521 0.0011 2.20 0.0081 0.0001 0.67 1.2785 0.0208 1.62 137 1 146 3 290 50 21 2 86 0.0215 0.0003 1.17 0.1508 0.0122 8.11 0.0506 0.0041 8.09 0.0084 0.0002 2.37 0.6421 0.0030 0.46 137 2 143 12 224 187 22 5 198 0.0216 0.0001 0.63 0.1419 0.0049 3.47 0.0475 0.0016 3.43 0.0079 0.0001 0.95 0.6191 0.0056 0.91 138 1 135 5 74 81 23 6 231 0.0224 0.0002 0.83 0.1588 0.0043 2.71 0.0514 0.0013 2.57 0.0082 0.0001 0.63 1.0333 0.0105 1.01 143 1 150 4 258 59 24 6 254 0.0216 0.0002 0.77 0.1526 0.0037 2.40 0.0513 0.0012 2.26 0.0081 0.0001 0.62 0.8131 0.0051 0.63 138 1 144 3 252 52 25 5 217 0.0222 0.0001 0.64 0.1525 0.0045 2.94 0.0499 0.0015 2.91 0.0084 0.0001 0.80 0.6496 0.0028 0.43 141 1 144 4 189 68 中粗粒碱长质花岗岩,D0410 1 23 795 0.022 0.0002 0.94 0.1557 0.0035 2.23 0.0512 0.001 2.01 0.0072 0.0001 0.75 1.3066 0.0022 0.17 141 1 147 3 252 46 2 2 87 0.022 0.0004 1.75 0.1591 0.0105 6.58 0.0525 0.0037 7.14 0.0064 0.0002 3.86 1.1638 0.0134 1.15 140 2 150 10 306 163 3 5 186 0.0216 0.0003 1.25 0.1446 0.0085 5.9 0.0485 0.0028 5.79 0.0069 0.0001 2.09 0.8203 0.0012 0.15 138 2 137 8 124 136 4 4 148 0.022 0.0003 1.28 0.1553 0.0106 6.84 0.0513 0.0034 6.61 0.0069 0.0002 2.65 0.8119 0.0077 0.95 140 2 147 10 254 152 5 2 68 0.0211 0.0003 1.5 0.1607 0.0129 8.04 0.0551 0.0041 7.52 0.0067 0.0002 3.33 1.3812 0.0165 1.2 135 2 151 12 417 168 6 7 240 0.0218 0.0002 1.08 0.1553 0.0073 4.68 0.0518 0.0023 4.53 0.0065 0.0001 0.89 1.6087 0.0081 0.51 139 1 147 7 275 104 7 13 390 0.0219 0.0002 0.73 0.1519 0.0041 2.69 0.0504 0.0013 2.65 0.0069 0 0.45 2.436 0.0177 0.73 140 1 144 4 211 62 8 5 206 0.0212 0.0002 1.09 0.1595 0.0089 5.6 0.0545 0.003 5.47 0.0066 0.0002 2.58 0.6629 0.0007 0.11 135 1 150 8 393 123 9 5 183 0.0217 0.0005 2.12 0.1634 0.015 9.19 0.0545 0.005 9.13 0.0067 0.0002 2.74 0.9998 0.0068 0.68 139 3 154 14 393 205 10 2 76 0.0214 0.0003 1.46 0.1608 0.011 6.86 0.0544 0.004 7.41 0.0065 0.0003 4.03 1.0006 0.0061 0.61 137 2 151 10 388 166 11 2 61 0.0219 0.0004 1.71 0.1391 0.0131 9.44 0.046 0.005 10.78 0.0075 0.0004 5.56 0.8453 0.0017 0.2 140 2 132 12 0 260 12 12 478 0.0212 0.0002 0.84 0.1422 0.006 4.21 0.0487 0.002 4.09 0.0062 0.0001 0.96 1.1916 0.0014 0.12 135 1 135 6 131 96 13 2 90 0.0218 0.0006 2.78 0.1555 0.0112 7.2 0.0516 0.0039 7.59 0.0068 0.0003 4.62 0.9944 0.005 0.5 139 4 147 11 268 174 14 3 108 0.0211 0.0004 1.96 0.1579 0.0154 9.73 0.0542 0.0055 10.08 0.0063 0.0003 4.02 0.7825 0.0021 0.27 135 3 149 14 378 227 15 1 56 0.021 0.0008 3.65 0.1665 0.0194 11.67 0.0576 0.0063 10.88 0.0062 0.0004 6.64 0.852 0.0033 0.39 134 5 156 18 515 239 16 1 54 0.0218 0.0006 2.75 0.1573 0.0147 9.38 0.0524 0.0062 11.76 0.0039 0.0008 20.03 0.8927 0.0045 0.5 139 4 148 14 304 268 17 5 198 0.0216 0.0003 1.25 0.1435 0.0079 5.52 0.0482 0.0026 5.46 0.0059 0.0001 1.29 1.4964 0.0145 0.97 138 2 136 8 111 129 18 3 109 0.022 0.0004 1.97 0.1302 0.0113 8.67 0.0429 0.0053 12.41 0.0068 0.0002 2.96 1.0084 0.0054 0.54 140 3 124 11 -175 309 19 6 222 0.0214 0.0002 1.02 0.1467 0.0072 4.93 0.0498 0.0023 4.67 0.0068 0.0001 1.6 0.9028 0.0072 0.79 136 1 139 7 185 109 20 5 196 0.0214 0.0002 1.14 0.1722 0.0085 4.91 0.0583 0.0028 4.76 0.0061 0.0001 2.34 0.7509 0.0015 0.2 137 2 161 8 540 104 21 1 56 0.0216 0.0004 2.08 0.1423 0.0111 7.78 0.0479 0.0045 9.37 0.0085 0.0006 7.42 0.7843 0.0041 0.52 137 3 135 11 93 222 22 1 25 0.0216 0.0006 2.94 0.1642 0.0181 11.05 0.055 0.0055 9.94 0.0087 0.0016 18.59 0.9261 0.0024 0.26 138 4 154 17 413 222 23 5 217 0.0214 0.0003 1.25 0.1549 0.0091 5.87 0.0525 0.0031 5.98 0.0065 0.0001 2.18 0.8261 0.0024 0.3 137 2 146 9 307 136 24 3 114 0.0218 0.0004 1.8 0.1635 0.0138 8.42 0.0544 0.0052 9.62 0.0071 0.0006 7.88 0.8378 0.0034 0.41 139 3 154 13 386 216 25 10 375 0.022 0.0002 0.93 0.1482 0.0055 3.68 0.0489 0.0017 3.57 0.0069 0.0001 1.17 1.1747 0.0029 0.25 140 1 140 5 143 84 表 2 伊勒呼里山碱长花岗岩体主量、微量和稀土元素组成
Table 2 Major, trace element and REE data components for Yilehuli intrusion
岩性 粗中粒、细粒似斑状碱长花岗岩 样品号 D0410 D1396 D1397 P12TC29 P12TC39 P12TC94 P15TC34 P15TC38 P15TC96 P22LT58 P22TC20 P25TC360 SiO2 74.26 76.2 75.58 65.21 69.78 67.88 75.64 75.84 74.38 75.04 75.98 75.62 TiO2 0.19 0.17 0.16 0.12 0.22 0.21 0.21 0.24 0.37 0.23 0.19 0.54 Al2O3 12.59 12.2 12.13 15.51 15.13 15.14 11.27 11.61 12.08 11.77 12.66 11.97 Fe2O3 1.22 0.79 1.03 2.78 1.96 2.4 2.04 1.47 1.49 1.75 0.93 1.33 FeO 0.66 1.36 2.09 3.18 2.62 3.16 1.62 1.84 1.54 1.3 1.18 1.54 MnO 0.04 0.02 0.05 0.03 0.07 0.05 0.02 0.01 0.06 0.04 0.04 0.05 MgO 0.48 0.33 0.35 1.15 0.68 0.67 0.03 0.02 0.2 0.3 0.24 0.36 CaO 0.37 0.22 0.23 1.89 0.91 1.18 0.41 0.39 0.59 0.7 0.54 0.14 Na2O 4.62 3.93 3.94 3.7 3.87 4.47 4.36 3.92 4.29 4.21 3.79 4.28 K2O 4.5 4.62 4.63 4 4.17 4.26 4.49 4.78 4.32 4.69 4.63 3.78 P2O5 0.02 0.03 0.01 0.02 0.08 0.06 0.06 0.13 0.1 0.05 0.05 0.32 烧失量 0.36 0.11 0.02 2.28 0.02 0 0.04 0.02 0.22 0 0.08 0.12 总计 99.31 99.98 100.22 99.87 99.51 99.48 100.19 100.27 99.64 100.08 100.31 100.05 K2O/Na2O 0.97 1.18 1.18 1.08 1.08 0.95 1.03 1.22 1.01 1.22 1.11 0.88 K2O+Na2O 9.12 8.55 8.57 7.7 8.04 8.73 8.85 8.7 8.61 8.9 8.42 8.06 A/CNK 0.96 1.03 1.02 1.12 1.21 1.07 0.88 0.94 0.94 1.04 0.89 1.05 A/NK 1.01 1.06 1.05 1.49 1.39 1.26 0.94 1.00 1.03 0.98 1.12 1.07 Mg# 56.27 30.21 23.01 39.22 31.65 27.45 3.2 1.9 18.81 26.63 29.17 29.43 Ba 296 91.6 104 27.6 15.9 243 607 359 280 277 83 131 Rb 127 142 122 125 140 115 118 132 121 122 151 121 Sr 98.4 15.2 13.3 19.2 21.4 80.1 60.3 42.4 40.4 46.1 14.6 23.3 Zr 273 140 116 237 218 174 185 137 280 179 159 250 Cr 33 7.73 5.32 7.13 7.67 6.71 7.23 6.83 6.46 6.43 7.08 7.53 Sc 2.5 2.78 1.1 2.4 3.11 3.03 3.11 2.09 5.86 2.92 2.32 0.92 Nb 17.3 14.2 13.4 18.6 18.9 13.4 14.3 13.1 17.3 14.9 15.8 19.5 Hf 5.33 5.59 5.81 9.12 8.02 6.17 6.35 5.01 8.37 5.53 9.7 7.18 Ta 1.46 1 1.54 1.6 1.12 1.16 1.14 0.99 2.42 1.56 8.93 1.4 Th 1.76 9.16 5.9 17.5 19.7 15.4 11.9 8.97 16.5 11.6 16.7 9.94 Y 14.7 9.13 12.1 11.6 10.4 16.6 11.9 12.1 37.2 24.6 33.1 14.1 V 15.2 3.39 0.14 2.23 1.11 12.8 7.39 5.55 13.4 9.56 1.86 8.7 La 28.8 9.73 20.5 16.3 24.6 30.2 19.3 10.2 47.2 30.7 54.5 13.5 Ce 69.3 19.1 43.4 29.2 37.6 63.3 40 17.4 101 78.9 122 61.2 Pr 6.25 2.29 5.6 2.68 3.41 7.35 5.23 2.37 12.9 9.4 11.8 2.31 Nd 20.7 6.59 16.5 7.14 8.15 22 15.7 6.98 42.1 30 34.2 6.23 Sm 3.61 1.22 2.92 1.23 1.16 3.69 2.82 1.23 7.78 5.62 5.82 1.19 Eu 0.46 0.2 0.3 0.16 0.15 0.59 0.64 0.39 1.02 0.6 0.96 0.4 Gd 2.84 1.15 2.56 1.32 1.41 3.51 2.52 1.29 7.21 4.95 5.91 1.45 Tb 0.45 0.21 0.4 0.21 0.2 0.5 0.39 0.25 1.12 0.78 0.92 0.26 Dy 2.7 1.45 2.26 1.43 1.22 2.7 2.16 1.69 6.22 4.14 5.4 1.8 Ho 0.54 0.32 0.44 0.34 0.29 0.54 0.42 0.37 1.23 0.79 1.08 0.41 Er 1.58 1.2 1.52 1.33 1.16 1.76 1.38 1.31 3.99 2.42 3.62 1.47 Tm 0.28 0.22 0.26 0.26 0.23 0.28 0.24 0.23 0.63 0.36 0.63 0.26 Yb 1.86 1.55 1.71 1.93 1.71 1.81 1.6 1.58 3.92 2.18 4.47 1.79 Lu 0.28 0.29 0.32 0.36 0.35 0.33 0.29 0.29 0.7 0.37 0.84 0.33 ∑REE 154.35 54.65 110.79 75.49 92.04 155.16 104.59 57.68 274.22 195.81 285.25 106.7 LR/HR 12.26 6.12 9.42 7.9 11.43 11.12 9.3 5.5 8.47 9.71 10.03 10.92 (La/Yb)N 10.44 4.23 8.08 5.7 9.7 11.25 8.13 4.35 8.12 9.49 8.22 5.09 δEu 0.42 0.51 0.33 0.38 0.36 0.49 0.72 0.94 0.41 0.34 0.5 0.93 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量为10-6 -
潘少逵. 大兴安岭地区岩石圈地幔的性质及其形成演化过程[D]. 中国地质大学(武汉)博士学位论文, 2013. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10491-1014158069.htm 武广. 大兴安岭北部区域成矿背景与有色, 贵金属矿床成矿作用[D]. 吉林大学博士学位论文, 2005. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10183-2006094308.htm 张福江.大兴安岭伊勒呼里山成矿亚带典型矿床特征及找矿方向[J].西部资源, 2014, (2):167-169. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/74c97d26e2bd960590c67735-4.html 董坤鹏. 伊勒呼里山中生代火山岩岩石化学特征及其地质意义[D]. 吉林大学硕士学位论文, 2012. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10183-1013118844.htm 尹志刚, 王文材, 张跃龙, 等.伊勒呼里山中生代火山岩:锆石UPb年代学及其对岩浆事件的制约[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2016, 46(3):766-780. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ccdz201603013&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ Yuan H, Gao S, Liu X, et al. Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinations of zircon by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2004, 28(3):353-370. doi: 10.1111/ggr.2004.28.issue-3
唐杰, 许文良, 王枫, 等.张广才岭帽儿山组双峰式火山岩成因:年代学与地球化学证据[J].世界地质, 2011, 30(4):508-520. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB201309001.htm 吴元保, 郑永飞.锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J].科学通报, 2004, 49(16):1589-1604. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002 Belousova E, Griffin W L, O'Reilly S Y, et al. Igneous zircon:trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2002, 143(5):602-622. doi: 10.1007/s00410-002-0364-7
Yan M, Chi Q. The chemical compositions of the continental crust and rocks in the eastern part of China[M]. Science Press, 2005.
宋维民, 庞雪娇, 付俊彧, 等.内蒙古科尔沁右翼中旗碱长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学, 岩石地球化学及其动力学意义[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2015, (3):847-859. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/yj/DetailCorrelated/Reference?id=ysxb98200602006&title=%25e8%25be%25bd%25e8%25a5%25bf%25e4%25b8%259c%25e5%258d%2597%25e9%2583%25a8%25e4%25b8%25ad%25e7%2594%259f%25e4%25bb%25a3%25e8%258a%25b1%25e5%25b2%2597%25e5%25b2%25a9%25e6%2597%25b6%25e4%25bb%25a3&resourceType=Periodical 邓晋福, 罗照华, 苏尚国, 等.岩石成因, 构造环境与成矿作用[M].北京:地质出版社, 2004. 邓晋福, 刘翠, 冯艳芳, 等.关于火成岩常用图解的正确使用:讨论与建议[J].地质论评, 2015, 61(4):717-734. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91067X/201504/665535688.html 纪政, 葛文春, 杨浩, 等.大兴安岭中段塔尔气地区早白垩世花岗岩成因及形成构造环境[J].世界地质, 2016, 35(2):283-296. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB200706000.htm 刘艳君. 大兴安岭北段卧都河地区中生代花岗岩地球化学特征及其构造意义[D]. 吉林大学硕士学位论文, 2016. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10183-1016089624.htm 张旗. A型花岗岩的标志和判别——兼答汪洋等对"A型花岗岩的实质是什么"的质疑[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2013, 32(2):267-274. 孙德有, 吴福元, 高山, 等.吉林中部晚三叠世和早侏罗世两期铝质A型花岗岩的厘定及对吉黑东部构造格局的制约[J].地学前缘, 2005, 12(2):263-275. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4875842 苟军, 孙德有, 赵忠华, 等.满洲里南部白音高老组流纹岩锆石U-Pb定年及岩石成因[J].岩石学报, 2010, (1):333-344. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/create_pdf.aspx?file_no=20160517&year_id=2016&quarter_id=5&falg=1 宋维民, 庞雪娇, 付俊彧, 等.内蒙古科尔沁右翼中旗碱长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学, 岩石地球化学及其动力学意义[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2015, 45(3):847-859. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/yj/DetailCorrelated/Reference?id=ysxb98200602006&title=%25e8%25be%25bd%25e8%25a5%25bf%25e4%25b8%259c%25e5%258d%2597%25e9%2583%25a8%25e4%25b8%25ad%25e7%2594%259f%25e4%25bb%25a3%25e8%258a%25b1%25e5%25b2%2597%25e5%25b2%25a9%25e6%2597%25b6%25e4%25bb%25a3&resourceType=Periodical 张旗, 冉皞, 李承东. A型花岗岩的实质是什么?[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2012, 31(4):621-626. http://www.cnki.com.cn/xuexi/xuexi-yanjiuxingxuexi-1.html 钱兵, 高永宝, 李侃, 等.新疆东昆仑于沟子地区与铁-稀有多金属成矿有关的碱性花岗岩地球化学、年代学及Hf同位素研究[J].岩石学报, 2015, 31(9):2508-2520. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Magazine?magazineId=ysxb98&yearissue=2015_9 张旗, 王焰, 李承东, 等.花岗岩的Sr-Yb分类及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(9):2249-2269. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=200609238 张旗, 金惟俊, 李承东, 等.再论花岗岩按照Sr-Yb的分类:标志[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(4):985-1015. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB201004002.htm 林强, 葛文春, 吴福元, 等.大兴安岭中生代花岗岩类的地球化学[J].岩石学报, 2004, 20(3):403-412. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200503016.htm 杨高学, 李永军, 张兵, 等.新疆西准噶尔接特布调A型花岗岩年代学、地球化学及岩石成因[J].地球学报, 2015, (3):41-52. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQXB201303008.htm 刘杰勋, 郭巍, 朱凯.辽东岫岩地区早白垩世侵入岩的年代学、地球化学及地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2016, 32(9):2889-2900. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/magadetail/YSXB201609.htm 张旗, 王焰, 潘国强, 等.花岗岩源岩问题——关于花岗岩研究的思考之四[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(6):1193-1204. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20080604&journal_id=ysxb Xu W L, Ji W Q, Pei F P, et al. Triassic volcanism in eastern Heilongjiang and Jilin Provinces, NE China:chronology, geochemistry, and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 34(3):392-402. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.07.001
尹志刚, 张跃龙, 杜玉春.大兴安岭北部早白垩世上库力组流纹岩的地球化学特征及成因[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2013, (3):788-796. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4355425 王德滋, 刘昌实, 沈渭洲, 等.桐庐I型和相山S型两类碎斑熔岩对比[J].岩石学报, 1993, 9(1):44-54. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4888962 高阳, 张招崇, 杨铁铮.黑龙江宝山一带海西晚期强过铝花岗岩地质地球化学及岩石成因[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2009, 28(5):433-449. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-EGVD201212001043.htm Taylor S R, McLennan S M. The chemical composition of the Archaean crust[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1986, 24(1):173-178. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1986.024.01.16
Lightfoot P C, Hawkesworth C J, Sethna S F. Petrogenesis of rhyolites and trachytes from the Deccan Trap:Sr, Nd and Pb isotope and trace element evidence[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95(1):44-54. doi: 10.1007/BF00518029
李佐臣, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等.西秦岭糜署岭花岗岩体年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(8):2617-2634. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/YSXB201308001.htm Liegeois J P, Navez J, Hertogen J, et al. Contrasting origin of postcollisional high-K calc-alkaline and shoshonitic versus alkaline and peralkaline granitoids. The use of sliding normalization[J]. Lithos, 1998, 45(1):1-28. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a26664e9c78e99b262768e0045ccb4a9&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Barbarin B. A review of the relationships between granitoid types, their origins and their geodynamic environments[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46(3):605-626. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00085-1
肖庆辉, 邓晋福, 马大铨, 等.花岗岩研究思维与方法[M].北京:地质出版社, 2002:1-294. Zhao X, Coe R S, Gilder S A, et al. Palaeomagnetic constraints on the palaeogeography of China:Implications for Gondwanal[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 1996, 43(6):643-672. doi: 10.1080/08120099608728285
赵振华.关于岩石微量元素构造环境判别图解使用的有关问题[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2007, 31(1):92-103. http://www.docin.com/p-1301632803.html 孟凡超, 刘嘉麒, 崔岩, 等.中国东北地区中生代构造体制的转变:来自火山岩时空分布与岩石组合的制约[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(12):3569-3586. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Fanchao_Meng4/publication/286231530_Mesozoic_tectonic_regimes_transition_in_the_Northeast_China_Constriants_from_temporal-spatial_distribution_and_associations_of_volcanic_rocks/links/572052ab08aead26e71b816d.pdf?origin=publication_detail Tomurtogoo O, Windley B F, Kröner A, et al. Zircon age and occurrence of the Adaatsag ophiolite and Muron shear zone, central Mongolia:constraints on the evolution of the Mongol-Okhotsk ocean, suture and orogen[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2005, 162(1):125-134. doi: 10.1144/0016-764903-146
徐美君, 许文良, 王枫, 等.小兴安岭中部早侏罗世花岗质岩石的年代学与地球化学及其构造意义[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(2):354-368. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130202 Wang F, Zhou X H, Zhang L C, et al. Late Mesozoic volcanism in the Great Xing'an Range (NE China):timing and implications for the dynamic setting of NE Asia[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 251(1):179-198. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=d1660018b51444bdcc4baaaad24c7e8e&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Xu W L, Pei F P, Wang F, et al. Spatial-temporal relationships of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in NE China:constraints on tectonic over-printing and transformations between multiple tectonic regimes[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 74:167-193. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.04.003
Maruyama S, Send T. Orogeny and relative plate motions:example of the Japanese Islands[J]. Tectonophysics, 1986, 127(3/4):305-329. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=83c470d4946bee08a381a34e6fc5d848&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn




 下载:
下载: