A study of the coupling relationship be-tween fractal characteristics of river, geomorphology and tectonic activity in areas around the Tibetan Plateau
-
摘要:
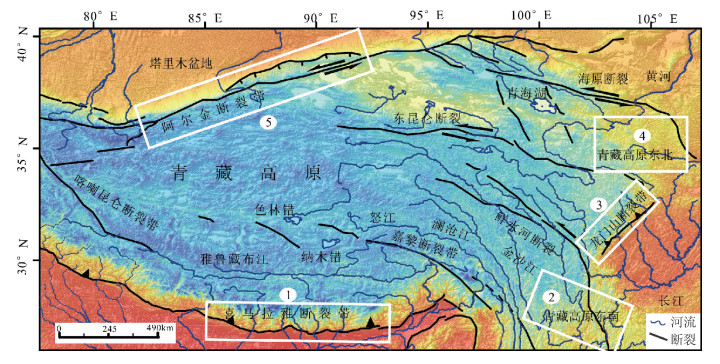
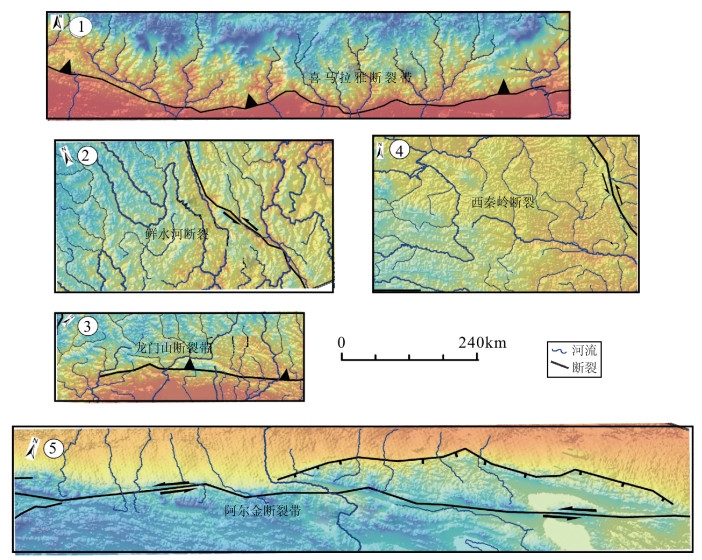
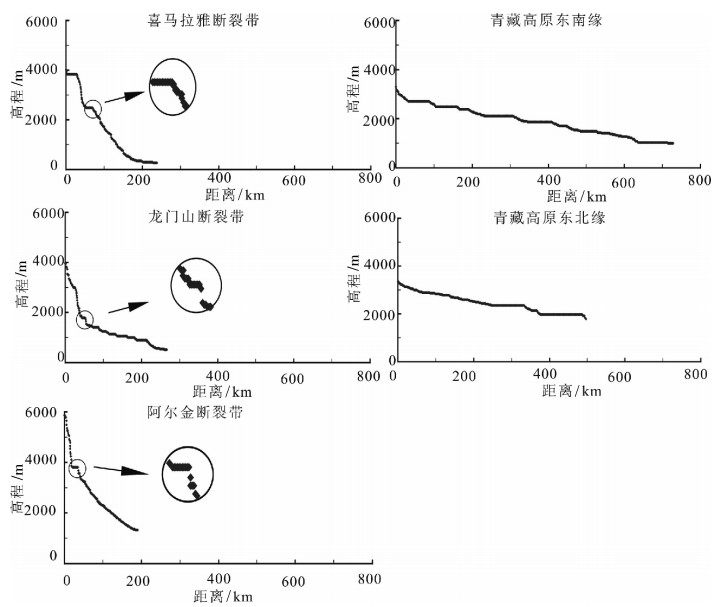
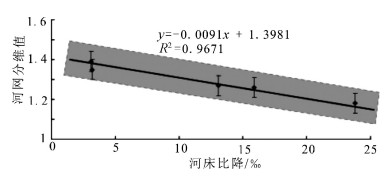
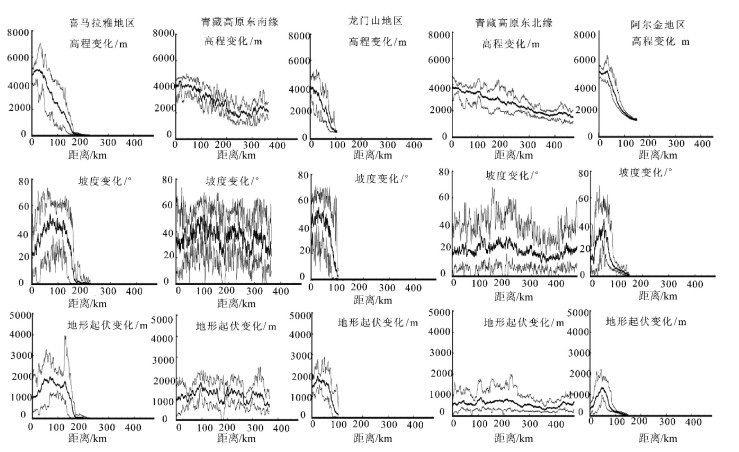
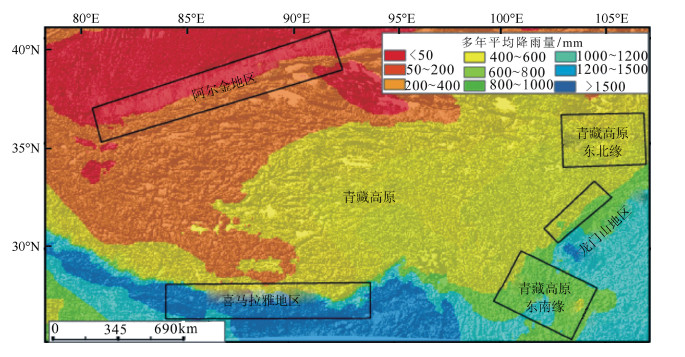
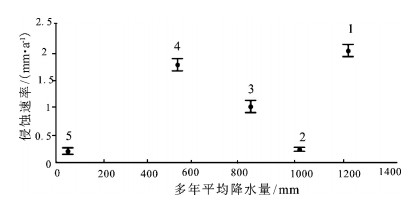
青藏高原周边地区的地貌特征与形成演化机制一直是科学界研究的热点。选择青藏高原周边典型地区河流分形特征、地貌特征及构造活动性进行研究,发现喜马拉雅断裂带、龙门山断裂带和阿尔金断裂带控制的区域构造活动性强烈,历史地震记录频繁,大震较多,河流形态与地貌演化特征也非常相似,河流纵剖面变化很快,长波长下凹型,河流坡降比大,地形起伏度大,河流形态变化简单,河流分维值低;青藏高原东北缘构造活动性不强烈,历史地震记录偏低,大震极少,河流纵剖面变化缓慢,近似长波长微振幅上凸型,河流坡降比小,地形起伏度较小,河流形态错综复杂、分维值高;青藏高原东南缘,构造活动性较强烈,历史地震记录频繁,大震较多,但由于该区域平均多年侵蚀速率比较低,同时河流下切深度大,河流纵剖面变化缓慢,也是近似长波长微振幅上凸型,河流坡降比小,河网发育较成熟,河网分维值较高。通过对比发现,降水量的变化对该区域侵蚀速率的影响远小于构造活动性的作用,在分析河网形态特征时可以不考虑降水量空间变化的影响。
Abstract:The research on the geomorphological characteristics and the mechanism of the formation and evolution in areas around the Tibetan Plateau has been a hot issue in recent years. In this paper, the authors studied the fractal characteristics of the river net-work, geomorphic features and tectonic activity in areas around the Tibetan Plateau. There are strong tectonic activities, frequently strong historical earthquakes, many large earthquakes in the Himalaya fault zone, Longmenshan Mountain fault zone and Altun fault zone, and there are many similarities in river pattern characteristics and geomorphic evolution, such as quick changes of the longitudi-nal profile and concave shape with long wavelength, steep stream gradient ratio, high relief, simple river pattern and low fractal dimen-sion of river. Tectonic activities are not strong on the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau as compared with features of the Hi-malaya fault zone in this aspect, as shown by rare strong historical earthquakes, slow changes of the longitudinal profile and convex shape with long wavelength and micro-amplitude, slow stream gradient ratio, small relief, complex river pattern and high fractal di-mension of river. There are strong tectonic activities, frequent strong historical earthquakes, many large earthquakes on the southeast-ern margin of the Tibetan Plateau, but because the regional average annual erosion rate is very low, and stream trenching is very deep, the change of the longitudinal profile is slow, its shape is convex with long wavelength and micro-amplitude, the stream gradi-ent ratio is slow, the river pattern is complex, and the fractal dimension of the river is high. The authors hold that the regional erosion rate is much more controlled by the tectonic activity than by the precipitation, and therefore the influence of the spatial variation of precipitation can be largely ignored in the analysis of river pattern characteristics.
-
Keywords:
- Tibetan Plateau /
- fractal characteristics /
- longitudinal profile /
- tectonic activity
-
阶地指由于地壳上升,河流下切形成的阶梯状地貌。北京西山的隆升影响了大石河阶地的形成,阶地的研究对全面解析新构造运动的隆升意义重大。
北京西山从北向南依次分布永定河、大石河和拒马河3条河流,其中大石河形成时代最新,目前尚未见到公开发表的研究文献,对大石河阶地的研究对北京西山的新构造运动隆升有实际意义。
大石河属海河流域大清河水系北拒马河支流。发源于霞云岭乡堂上村西北,是唯一发源于房山境内的河流,《水经注》称“圣水”。大石河总流域面积为1280km2,河道全长129km,其中辛开口村以上山区河道长85km(平均比降为6.4‰),辛开口村至夏村长15km(平均比降为3‰),夏村至北京市界长21km(平均比降为0.3‰)[1]。流域内多年平均降水量600mm左右,多年平均天然径流量9570 × 104m3,枯水年天然径流量4785×104m3。建国后大石河下游发生过多次洪水灾害,1956年洪水流量为1860m3/s,是漫水河水文站实测最大洪峰流量[2]。
大石河是北京西山发育的一条未侵蚀至分水岭的河流,其阶地发育特征代表了北京西山隆升的发展过程,对北京地区现今地形地貌、新构造运动和平原区堆积物层序研究具有重要意义。
北京西山的基础地质[3]和新生代地质研究详细[4],也曾研究过永定河阶地[5],1:5万周口店幅曾测制陈家台河谷剖面[6],为大石河阶地的全面研究奠定了基础。本文对陈家台村—霞云岭乡堂上村河谷阶地进行了调查(图 1),对不同位置阶地发育特征进行了研究,结合沉积地层分析和阶地面高程测量,初步计算了大石河流域不同时代阶地的垂直落差,探讨了大石河流域山体中更新世以来隆升的速率。
1. 大石河阶地剖面特征
大石河流域陈家台村至霞云岭乡堂上村(山区)穿切的地层主要为长城系、蓟县系、青白口系和寒武系、奥陶系及少量二叠系,岩性主要为碳酸盐岩类的灰岩、白云岩类及陆相碎屑沉积岩(图 2)。河流阶地普遍发育,依序介绍如下。
1.1 陈家台河谷阶地特征(P01)
阶地地处房山区佛子庄乡陈家台村,阶地发育在河床左侧,共发育4级(图 3)。
河床宽56.6m,海拔125m,主要为砾石,含少量粗砂。砾石大小5~20cm,大者大于20cm,磨圆度较好,岩性以灰岩为主,含少量火山岩、砂岩砾石。
一级阶地(T1)为堆积型阶地,宽63.4m,主要为砾石,砾石特征与河床砾石相近。
二级阶地(T2)为基座型阶地,宽51.7m,阶高15.5m,基座为下马岭组千枚状板岩,向东追索,基座可见昌平组灰岩。二级阶地前缘上部为全新统河流洪积物,岩性为泥质砾石。泥质为土黄色,含量30%~40%,局部含量较高,砾石分选性中等,磨圆度中等,大小以小于5cm为主,10~20cm次之,成层性一般,砾石成分较复杂,灰岩砾石为主,见少量石英砂岩和火山岩砾石。底部见棕黄色粉砂质粘土透镜体,厚约60cm,长5.6m,走向320°,上覆泥质砾石,厚约3m。二级阶地后缘岩性为砾石层和土黄色粘土。砾石层含少量泥质,砾石大小约5cm,分选性、磨圆度中等,砾石成分同前缘一致,分选性、磨圆度中等。土黄色粘土粒度细,不含砾石,钙质含量较高,土质较硬,顶部20cm含少量砾石,砾石分选性、磨圆度均较差。
三级阶地(T3)为基座型阶地,阶宽15.3m,阶高2.8m,基座为下马岭组千枚状板岩。底部为砾石层,砾石大小约为5cm,分选性、磨圆度较好,为复成分砾石,主要为灰岩砾石;中部为土黄色含砾粘土,厚约80cm,砾石含量较少,均为千枚岩岩片,小于2cm,无磨圆;上部为土黄色粘土,厚约40cm,粒度细,手搓有滑感,湿时可搓成细条,不易断,为较典型的河流冲积、洪积产物。
四级阶地(T4)为基座型阶地,阶高9.5m,主要为砾石。砾石大小约为10cm,分选性、磨圆度中等,岩性以灰岩为主,含少量火山岩、砂岩砾石。基底为下马岭组千枚状板岩。
1.2 红煤厂河谷阶地特征
1.2.1 红煤厂公路边阶地特征(P02)
阶地地处房山区佛子庄乡红煤厂村,阶地发育在河床左侧,共发育3级。
河床宽135m,海拔167.1m,主要为砾石,大小不等,大者大于20cm,一般为5~10cm,磨圆度较好,岩性以灰岩、火山岩、砂岩砾石为主(图 4)。
一级阶地(T1)为基座型阶地,阶宽19.2m,阶高21.1m,基座为下马岭组灰黑色页岩,基座上主要为粗砂质砾石,砂含量20%~30%,砾石大小约10cm,分选性、磨圆度中等,成分主要为灰岩,见少量火山岩、砂岩砾石。为较典型的河流冲积、洪积物。
二级阶地(T2)为基座型阶地,阶宽10.8m,阶高3m,基座为下马岭组灰黑色页岩。基座之上覆盖较严重,零星可见砾石发育,含泥质成分,含量约15%,泥质为土黄色,手搓有滑感,粒度细。砾石砾径10cm左右,分选性、磨圆度一般,以灰岩砾石为主,含少量火山岩和砂岩。为河流洪积产物。
三级阶地(T3)为基座型阶地,阶宽大于10m,阶高7.1m,基座为下马岭组灰黑色页岩,产状20°∠30°。按岩性分为4层。
1层:土黄色粘土,粒度细,砾石含量少,层状,厚约1.5m,延伸稳定,为水平层。
2层:含泥质砾石,延走向厚度不稳定,最薄处厚约1.5m,最厚为3m。砾石未胶结或松散胶结,分选性、磨圆度中等,砾径以5~10cm为主,大者可达20cm,砾石岩性为灰岩、页岩和少量火山岩。
3层:土黄色粘土,岩性与1层一致。延伸不稳定,厚0.5~1.5m,透镜体状产出。
4层:含泥质砾石,沿走向厚度有变化,厚1.1~ 3.6m,砾石胶结差,分选性、磨圆度中等,砾径多小于5cm,成分为灰岩、火山岩和页岩。
三级阶地上发育较典型的河流冲积、洪积物。
1.2.2 红煤厂西黄土台阶地特征(P03)
阶地地处房山区佛子庄乡红煤厂村西,阶地发育在河床右侧,为河流四级阶地,海拔230m(图 5)。
该阶地属基座型阶地,基座为下马岭组页岩,基座上为3套岩性,由上而下描述如下。
1层:土黄色粘土,粒度细,手搓有滑感,硬度较大,含钙质,未见砾石发育。厚约3m。
2层:棕红色黄土,粒度细,较硬,发育垂直节理,手搓有滑感,湿时可搓成条,不易断,未见砾石发育。厚3~4m。
3层:含砂泥质砾石,底部见薄层棕红色含砾泥质粉细砂。泥质为棕红色,粒度细,节理不发育,硬度较大。上部砂质含量相对较少,砾石磨圆度较好,分选性一般,砾径5cm左右,大者10~20cm,成分以灰岩、页岩为主。厚2~3m。
该阶地发育的岩石类型具有河流沉积和风积混合成因特点。
1.3 长操北岸二级阶地特征
阶地位于房山区佛子庄乡长操村西北,阶地发育在河床左侧,为二级阶地,海拔185m,河床海拔约175m。阶地属于基座型阶地,基座为下马岭组页岩,由上而下共分为5层。
1层:粉砂质粘土,土灰色、土黄色,粒度较细,手搓略有涩感,未见砾石,植物根系发育。
2层:含砾粗砂质细砂,土灰色,粒度不均匀,砂质含量约占80%,砾石大小约为2cm,分选性、磨圆度较好,以灰岩、页岩砾石为主,含少量泥质。
3层:土黄色粉砂质粘土,粒度均匀,较细,硬度大,手搓略有涩感,砾石很少。
4层:土灰色细砂,无胶结或松散胶结,硬度小,层状,分选性、磨圆度较好,砾石少见。
5层:砾石层,砾石大小2~10cm,分选性差。大砾石磨圆度中等,小砾石磨圆度较差,砂质充填。
该剖面岩石成层性较好,发育泥、砂二元结构,为较典型的河流冲积产物。
1.4 贾峪口村西三级阶地特征
阶地位于房山区佛子庄乡贾峪口村,阶地发育在河床左侧,为河流三级阶地,阶地属于基座型阶地,河床海拔282m。该剖面由上而下共分为16层,为土黄色粘土和砾石层互层状产出,其中8层砾石,8层土黄色粘土。上部砾石层和黄土层较厚,最厚处为1~1.5m,底部粘土层较厚,砾石层多为薄层,沿走向延伸较稳定。
粘土为土黄色,质地较硬,钙质含量较高,局部粉砂质含量略高,手搓较细,有砂感,局部含少量砾石。
砾石松散,砾径以5~10cm居多,大者可达20cm,分选性差,次棱角状磨圆,局部泥质充填。砾石成分较复杂,以白云岩为主,含少量火山岩和砂岩,为近源沉积的产物。
1.5 庄户台村一级阶地特征(P04)
阶地位于房山区霞云岭乡庄户台村,阶地发育在河床右侧,为河流一级阶地,阶地高30m,属基座阶地,基座为龙山组纹层状砂岩,产状平缓,倾角4°~5°,阶地海拔665m,河床海拔635m。
基座上为砾石层,泥砂质充填,松散胶结,砾石为次圆状-圆状磨圆,分选性差。大小以10~20cm为主,小者约5cm,大者50~80cm。砾石层厚3~4m,主要为河流洪积搬运的产物(图 6)。
1.6 龙门台村一级阶地特征
阶地位于房山区霞云岭乡龙门台村,发育在河床左侧,为河流一级阶地,阶地高约10m,属于基座型阶地,基座为龙山组砂岩,产状平缓,阶地海拔645m,河床海拔635m。
根据不同岩性,由上而下可分为4层。
1层:砾石层,泥砂充填,砾径以5~10cm居多,大者逾20cm,岩性以砂岩为主,分选性差,磨圆度中等,为流水搬运成因。
2层:土黄色粘土,粒度细,硬度中等,局部粉砂含量较高,见少量残积碎石,大小为5cm,岩性均为砂岩。
3层:残坡积物,由粘土、残积碎石及少量砂质组成。粘土为棕红色,砂质以中细砂为主,碎石无分选、无磨圆,砾径为5~20cm,大者达50cm,岩性单一,均为砂岩。
4层:棕红色粘土,粒度细,手搓较滑,硬度大,内部见少量残积碎石。
根据该剖面物质组成分析,龙门台村一级阶地早期为河流洪积粘土层,之后为近源的残坡堆积,晚期经历流水搬运沉积的粘土层和砾石层。
2. 样品采集与测试
2.1 样品采集
样品采自红煤厂西黄土台河流四级阶地之上(P03),样品号为DS005-ESR-01(图 5),位于剖面第3层底部,采样层厚度约20cm。采样处泥砂质成分较高,岩性为棕红色含砾泥质粉细砂。
2.2 样品测试
2.2.1 测年方法及原理
ESR是电子自旋共振(Electron Spin Reso⁃ nance)的简称,由德国科学家Zeller在1967年提出,是根据样品吸收自然辐照剂量来推导样品形成年代的测年方法[7]。ESR方法是一种非破坏性测量方法,其测年原理是用电子自旋共振方法直接测量晶体样品在自然环境中由于辐照损伤所产生的顺磁中心数目。测量谱仪为德国布鲁克公司生产的EMXBRUKERX-BandESR波谱仪。
2.2.2 实验过程
样品前处理流程如下:根据样品性状不同,取一定数量的原样品称重,放入干燥箱中烘干(温度40℃)。烘干前后记重量,并计算含水量。然后碎样,过筛分选出100~140μm粒径的样品约120g,放入1000ml烧杯中进行化学处理,获取石英矿物。① 用双氧水浸泡处理去除样品中的有机质;② 盐酸浸泡处理去除样品中的碳酸盐类;③ 氢氟酸浸泡处理(蚀刻)去除长石等矿物。
每一步处理完成后都要用清水反复清洗至中性再进行下一步处理。将处理好的样品放入(40℃)烘箱内烘干后待磁选。对该样品进行磁选(去除磁性矿物):每个样品称小样10份(每份称重0.25g),送北京大学分子化学院钴源实验室进行样品人工辐照;根据样品岩性、地质地貌信息及估计时代,辐照剂量为0、200、400、800、1400、2000、2800、3600、4600、6000(Gy);辐照后的样品需放置一段时间去除辐照后产生的不稳定信号。
2.2.3 古剂量和环境剂量测定
古剂量测定是在德国布鲁克公司生产的EMX1/6型ESR信号测量谱仪上对辐照后的样品进行信号测量。根据样品岩性、地质地貌信息及估计时代选择样品,测量功率为2.0MW(E`)和(Ge)`信号。根据ESR信号测量结果带入计算相应软件,计算古剂量。
环境剂量率测量是电子自旋共振测年的重要参数之一,样品所吸收的环境辐射剂量是其本身及周围物质中放射性核素(U238、Th232和K40)的α、β和γ衰变产生的电离辐射所提供的,同时也有宇宙射线的少量贡献。样品的环境剂量(铀、钍、钾)含量分析,委托核工业北京地质研究院分析测试中心完成,仪器型号为ELEMENT等离子体质谱分析仪。
样品埋藏层的水含量对样品所接收的剂量率有不可忽视的影响,水对α、β和γ辐射有一定的吸收作用。样品埋藏期间含水量的变化,对样品年龄结果有直接的影响。根据样品的铀、钍、钾含量和样品埋深宇宙射线的少量贡献、含水量等参数,计算样品年剂量。
2.2.4 计算结果
根据公式:A=P/D,计算样品的ESR年龄。其中,A表示年龄(ka);P表示古剂量(Gy);D表示年剂量(Gy/ka)。
样品测量信号总体较好,年龄结果为567±56ka(表 1),误差为10%~20%。
表 1 Diagram of the longitudinal river slope in Dashi River valleyTable 1. Analytical results of samples实验
室号野外号 样品
物质U
/10-6Th
/10-6K2O
/%含水量
/%古剂量
/Gy年剂量
/(Gy· ka-1)年龄
/ka15272 DS005-ESR-01 泥质含砂物质 2.46 12.3 2.68 4.90 2268±226 4.00 567±56 3. 讨论
红煤厂西黄土台四级阶地棕红色含砾粉砂经ESR测试年龄为567±56ka,推断大石河河谷在第四纪中更新世早期开始发育,由于新构造运动产生间歇性隆升,在高位宽谷之下发育4级阶地,形成了如今的地貌特征。
3.1 大石河阶地发育特征
通过本次调查发现,大石河流域河北镇陈家台村—霞云岭乡堂上村(山区)河谷阶地普遍发育,河北镇至贾峪口,河流一级至三级阶地保留较完整,而且在河北镇还保留清晰的四级阶地。至庄户台地区,河流下切较深,一级阶地阶高达30m,一级以上阶地保留不完整,庄户台-龙门台普遍发育砾石,至上游霞云岭乡堂上村,仅见巨砾发育。
3.2 河床纵比降特征
大石河流域地质构造为箱状背斜,上新世形成宽谷地貌,宽谷两侧发育放射性沟谷,形成现今的高位宽谷系统。
唐县期大石河高位宽谷系统是北京西山的特色地貌,从陈家台溯源而上至龙门台附近,明显发育宽谷地貌,如南窖、校军厂宽谷与大石河连通,组成宽谷系统。宽谷结束于下石堡,宽谷谷底高度从上游向下游,河床海拔高度依次为龙门台635m、庄户台535m、贾峪口282m、长操175m、红煤厂167m、陈家台125m、辛开口80m,至夏村以北田各庄一带,海拔降至40m。从龙门台至辛开口河流曲线长度约72km,高差555m,平均纵比降约为7.71‰(图 7)。
4. 结论
(1)大石河流域河北镇陈家台村—霞云岭乡堂上村(山区)河谷阶地普遍发育,且较完整,不同区段的各级阶地均可进行对比。
(2)通过阶地面的对比研究,得出大石河流域辛开口—龙门台(山区)平均比降为7.71‰。
(3)根据阶地发育和物质成分成因,以及ESR测年数据初步推断,大石河在中更新世早期初始发育,600ka以来,大石河流域山区隆升速率约为0.96mm/a。
-
表 1 青藏高原周边水系河网分维值
Table 1 The river network fractal dimension value in areas around the Tibetan Plateau
区域名称 区域面积/km2 河流长度/km 格网分维值 河系分维值 喜马拉雅地区 147622 3091 1.21~1.25 1.31 青藏高原东南缘 122610 4530 1.33~1.37 1.44 龙门山地区 36068 1028 1.22~1.26 1.32 青藏高原东北缘 98853 2986 1.30~1.33 1.40 阿尔金地区 219090 1525 1.10~1.13 1.19 阿尔金地区(修正) 164318 1525 1.13~1.16 1.22 表 2 各子区域地震记录次数及不同震级分布情况
Table 2 The frequency of earthquake records and the distribution of different magnitudes in each subregion
区域名称 区域面积/km2 地震记录次数 次数/104km2 7级以上 6~6.9 5~5.9 4~4.9 3~3.9 3级以下 喜马拉雅地区 147622 333 23 3 5 22 219 94 0 青藏高原东南缘 122610 1015 83 1 8 37 229 739 1 龙门山地区 36068 1501 416 3 4 37 299 1148 10 青藏高原东北缘 98853 320 32 0 1 6 38 272 3 阿尔金地区 219090 893 41 2 4 26 317 544 0 -
Molnar P, Tapponnier P. Cenozoic teconics of Asia:effect of conti-nental collision[J]. Science, 1975, 189:419-426. doi: 10.1126/science.189.4201.419
钟大赉, 丁林.青藏高原隆升过程及其机制的探讨[J].中国科学(D辑), 1996, 26(4):289-295. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/JDXK199604000.htm Royden L H, Burchfiel B C, King R W, et al. Surface deformation and lower crustal flow in eastern Tibet[J]. Science, 1997, 276:788-790. doi: 10.1126/science.276.5313.788
李吉均, 方小敏.青藏高原隆起与环境变化研究[J].科学通报, 1998, 43(15):1569-1574. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1998.15.001 Clark M K, Royden L H. Topographic ooze:Building the eastern margin of Tibet by lower crustal flow[J]. Geology, 2000, 28:703-706. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<703:TOBTEM>2.0.CO;2
Tapponnier P, Xu Z Q, Roger F, et al. Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Science, 2001, 294:1671-1677. doi: 10.1126/science.105978
Burchfiel B C, Wang E C. Northwest-trending, middle Cenozoic, left-lateral faults in southern Yunnan, China, and their tectonic sig-nificance[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2003, 25:781-792. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(02)00065-2
Clark M K, House M A, Royden L H, et al. Late Cenozoic uplift of southeastern Tibet[J]. Geology, 2005, 33:525-528. doi: 10.1130/G21265.1
Shen Z K, Lu J N, Wang M, et al. Contemporary crustal deforma-tion around the southeast borderland of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Jour-nal of Geophysical Research-Solid Earth, 2005, 110(11):1-17.
李海兵, 杨经绥, 许志琴, 等.阿尔金断裂带对青藏高原北部生长、隆升的制约[J].地学前缘, 2006, 13(4):59-80. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200604005.htm 秦耀辰, 刘凯.分形理论在地理学中的应用研究进展[J].地理科学进展, 2003, 22(4):426-436. doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2003.04.011 艾南山, 陈嵘.走向分形地貌学[J].地理学与国土研究, 1999, 15(1):92-96. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLGT901.017.htm 艾南山, 李后强.从曼德尔布罗特景观到分形地貌学[J].地理学与国土研究, 1993, 16(1):13-17. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/92655X/199301/1008816.html 艾南山, 朱治军, 李后强.外营力作用随机特性和分形布朗地貌的稳定性[J].地理研究, 1998, 17(1):23-29. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKJ201306004.htm 沈晓华, 邹乐君, 阳峰, 等.长江河道分形与流域构造特征的关系[J].浙江大学学报(理学版), 2001, 28(1):107-111. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHKD200505007.htm 石峰, 何宏林, Densmore A L, 等.二维分形参数与构造活动关系研究——以滇西南块体为例[J].地震地质, 2016, 38(4):862-873. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-85402-1015543027.htm 刘传正.活动断裂系统的分段性及其分形几何特征[J].水文地质工程地质, 1993(6):16-19. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX199302007.htm 谭凯旋, 郝新才, 戴塔根.中国断裂构造的分形特征及其大地构造意义[J].大地构造与成矿学, 1998(1):17-20. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD904.004.htm 文力, 刘静, M Oskin, 等.活动构造对高原边界侵蚀速率空间分布的控制作用; 以龙门山地区为例[J].第四纪研究, 2012, 32(5):968-985. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dsjyj201205014 Liuzeng J, Tapponnier P, Gaudemer Y, et al. Quantifying land-scape differences across the Tibetan plateau:Implications for topo-graphic relief evolution[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Earth Surface, 2008, 113(F4):F04018. DOI: 10.1029/2007JF000897.
王林, 陈兴伟.基于DEM的流域水系分维计算与结果分析[J].地球信息科学, 2007, 9(4):133-137. http://www.dqxxkx.cn/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=23538 Horton R E. Erosional development of streams and their drainage basins; hydrophysical approach to quantitative morphology. Jour-nal of the Japanese Forestry Society, 1945, 56(3):275-370.
沈玉昌, 龚国元.河流地貌学概论[M].北京:科学出版社, 1986. Mandelbrot B B. The fractal geometry of nature[M]. New York:WH Freeman and Company, 1983.
Mesa O J, Gupta V K. On the main channel length-area relation-ship for channel networks[J]. Water Resource Research, 1987, 23(11):2119-2122. doi: 10.1029/WR023i011p02119
冯平, 冯焱.河流形态特征的分维计算方法[J].地理学报, 1997, 52(4):324-330. doi: 10.11821/xb200302016 贾绍凤.构造运动影响河流纵剖面及河道冲淤的数学模型[J].地理学报, 1994, 49(4):324-331. http://www.geog.com.cn/CN/abstract/abstract20841.shtml 陆中臣, 周金星, 陈浩.黄河下游河床纵剖面形态及其地文学意义[J].地理研究, 2003, 22(1):30-38. http://www.dqxxkx.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9154.shtml 张会平, 杨农, 张岳桥, 等.岷江水系流域地貌特征及其构造指示意义[J].第四纪研究, 2006, 26(1):126-135. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/DSJJ200601015.htm 张会平, 张培震, 吴庆龙, 等.循化-贵德地区黄河水系河流纵剖面形态特征及其构造意义[J].第四纪研究, 2008, 28(2):299-310. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/0fd941195acfa1c7aa00ccf8-2.html 赵洪壮, 李有利, 杨景春, 等.天山北麓河流纵剖面与基岩侵蚀模型特征分析[J].地理学报, 2009, 64(5):563-570. doi: 10.11821/xb200905005 阚瑷珂, 朱利东, 龚建辉, 等.基于ArcView的带状剖面工具开发及在地貌分析中的应用[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 33(1):64-69. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cdlgxyxb200601012 Clark M K, Royden L H, Whipple K X, et al. Use of a regional, relict landscape to measure vertical deformation of the eastern Ti-betan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Earth Surface, 2006, 111(F3):338-345.
Clark S J P, Dempster T J. The record of tectonic denudation and erosion in an emerging orogen:an apatite fission-track study of the Sierra Nevada, southern Spain[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2009, 166:87-100. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492008-041
Chappell J, Zheng H B, Fifield K.Yangtse River sediments and erosion rates from source to sink traced with cosmogenic Be-10:Sediments from major rivers[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatolo-gy, Palaeoecology, 2006. 241:79-94. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2006.06.010
Whipple K X, Tucker G E. Dynamics of the stream-power river incision model:Implications for height limits of mountain ranges, landscape response timescales, and research needs[J]. Journal of Geo-physical Research-Earth Surface, 1999, 104:17661-17674. doi: 10.1029/1999JB900120
Galy A, France-lanord C. Higher erosion rates in the Himalaya:Geochemical constraints on riverine fluxes[J]. Geology, 2001, 29:23-26. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0023:HERITH>2.0.CO;2
Garzanti E, Vezzoli G, Ando S, et al. Quantifying sand provenance and erosion (Marsyandi River, Nepal Himalaya)[J]. Earth and Plane-tary Science Letters, 2007, 258:500-515. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2007.04.010
Kirby E, Reiners P W, Krol M A, et al. Late Cenozoic evolution of the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau:inferences from 40Ar/39Ar and U-Th/He thermochronology[J]. Tectonics, 2002, 21(1):1-20.
Kirby E, Whipple K X, Tang W, et al. Distribution of active rock uplift along the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau:infer-ences from bedrock channel longitudinal profiles[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2003, 108(B4):215-231.
Godard V, Pik R, Lavé J, et al. Late Cenozoic evolution of the Central Longmen Shan (Eastern Tibet), insight from (U-Th)/He thermochronometry[J]. Tectonics, 2009, 28:TC5009.




 下载:
下载: