Geochronology and geochemistry of the Zhangjia granitic pluton in the Miaoershan uranium orefield, Northeastern Guangxi Province
-
摘要:
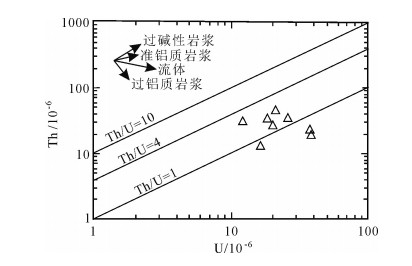
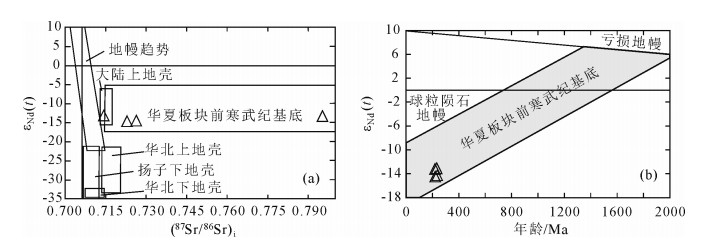
对张家岩体乍古田矿床及张家矿床的2件赋矿围岩样品,开展LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素定年,获得乍古田矿床赋矿围岩形成年龄为218.0±1.4Ma,张家矿床赋矿围岩形成年龄为226.8±5.7Ma。另外,对张家岩体8件样品的主量、微量元素及Sr-Nd同位素分析测试显示,张家花岗岩富硅(SiO2=74.35%~76.29%)、高铝(Al2O3=12.54%~14.03%)、高碱(Na2O+K2O=6.95%~9.17%)、低镁(MgO=0.34%~0.45%)、低钙(CaO=0.68%~1.03%)、低钛(TiO2=0.106%~0.18%),属高钾钙碱性花岗岩;富集Rb,亏损Ba、Sr,Rb/Sr值高,属于低Ba-Sr花岗岩;轻稀土元素富集,负Eu异常;富U(平均21.5×10-6),Th/U值低(平均1.63),有利于铀矿化;(87Sr/86Sr)i高(约0.7247),低εNd(t)值(平均-13.95),二阶段Nd模式年龄为2.07~2.19Ga。张家花岗岩属于强过铝质S型花岗岩,可能是华夏板块古元古代基底变泥质岩经部分熔融形成的。
-
关键词:
- 产铀岩体 /
- LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄 /
- 地球化学 /
- 张家花岗岩
Abstract:Two samples were collected near the Zhagutian uranium ore deposit and Zhangjia uranium ore deposit respectively to carry out LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb isotopic dating. The analytical result demonstrates that the formation age of the host rock in the Zhagutian uranium ore district is 218.0±1.4Ma, whereas the formation age of the host rock in the Zhangjia uranium ore district is 226.8±5.7Ma. Furthermore, the Zhangjia granite is characterized by high SiO2 (74.35%~76.29%), Al2O3 (12.54%~14.03%) and (Na2O+K2O) (6.95%~9.17%), but low MgO (0.34%~0.45%), CaO (0.68%~1.03%) and TiO2 (0.106%~0.18%), so it belongs to high-K calc-alkaline series granite. The Zhangjia granite is rich in Rb, and poor in Ba, Sr with high Rb/Sr ratio, so it belongs to low Ba-Sr granite series. The granite is rich in LREEs with negative Eu anomalies. Meanwhile, The granite is rich in U (21.5×10-6 on average)with low Th/U ratio (1.63 on average), so it is very favourable for uranium mineralization. The granite has high (87Sr/86Sr)i (~0.7247), low εNd (t) (-13.95 on average) and its two-stage Nd isotopic model ages are (2.07~2.19Ga). The Zhangjia granite belongs to strongly peraluminous S-type granite. It probably originated from partial melting of Proterozoic sedimentary metamorphic rocks.
-
新生代印度-欧亚大陆的碰撞汇聚作用,导致晚始新世—中新世喜马拉雅地壳物质发生大规模的熔融作用,并形成巨量的淡色花岗岩、花岗岩体[1]。这些岩体沿碰撞造山作用有关的伸展构造分布[2-11],并与造山带演化过程密切相关,是探索构造-岩浆相互作用关系和机制的重要“岩石探针”[12]。
在喜马拉雅山脉的脊部,自西向东出露一系列不连续的淡色花岗岩侵入体,岩体的分布受区域性伸展构造藏南拆离系(STDS)控制,并构成STDS韧性剪切带的一部分[13-14],因此,又称其为STDS淡色花岗岩。前人对造山带西部的淡色花岗岩进行了较多的年代学和成因机制方面的研究,取得的主要认识和存在的争议包括:①淡色花岗岩的时代,基本厘定STDS淡色花岗岩的年代格架,时代集中于36~13Ma[2, 4-5, 7, 9, 15-22],暗示长时间的地壳深熔作用;但多数年龄来自喜马拉雅中西部地区的岩体,缺少东部岩体年龄的补充和限定。②淡色花岗岩的源区和源岩,大多数学者认为,STDS淡色花岗岩源区和源岩为大喜马拉雅变质沉积岩[23-26];而杨晓松等[27]根据部分熔融实验研究,认为源岩为大喜马拉雅中的黑云斜长片麻岩;Guo等[28]通过系统的地球化学和实验岩石学模拟研究,认为源区为大喜马拉雅变质沉积岩和来自小喜马拉雅流体的两端元混合区。③淡色花岗岩的形成机制,淡色花岗岩源自白云母脱水熔融这一结论已基本达成共识[29-30],但对触发部分熔融的因素仍有争议;Le Fort等[31]认为,流体(如水)是导致部分熔融的因素,然而,实验岩石学研究表明,在无流体参与时,部分熔融行为仍可进行[24];Har⁃ris等[25]、Davidson等[32]认为,构造减压是部分熔融的直接触发因素。后期,又有学者提出断裂的剪切摩擦生热和放射性同位素生热可以导致部分熔融[17, 30-33],但理论计算表明,单纯的剪切摩擦热或地壳放射性元素生热难以触发大规模的岩浆作用[34]。由此可见,STDS淡色花岗岩的研究仍存在不足,已取得的部分认识多基于对造山带中西部岩体的分析,而缺少来自东部岩体的年代学、地球化学等的约束。
本次研究采集喜马拉雅造山带东部错那地区淡色花岗岩样品,进行锆石U-Pb年龄、全岩地球化学和Sr-Nd同位素研究,为STDS淡色花岗岩研究提供了新的数据,以期厘定深熔作用时代,查明其源区和源岩,并探讨成因机制和构造意义。
1. 区域地质背景
狭义的喜马拉雅造山带指雅鲁藏布江缝合带与主前锋逆冲断裂(MFT)之间的、由新生代印度-欧亚大陆碰撞形成的强烈变形、变质带。造山带自北向南发育的构造-岩石单元依次为特提斯喜马拉雅沉积系(THS)、STDS、大喜马拉雅结晶杂岩(GHC)、主中央逆冲断裂(MCT)、小喜马拉雅沉积岩系(LHS)、主边界逆冲断裂(MBT)、西瓦里克前陆盆地沉积(SS)和MFT(图 1)[35]。THS位于最北部,南北分别以STDS和雅鲁藏布江缝合带为界,主要发育一套古生代—始新世、经历极低级变质的硅质碎屑岩和碳酸盐岩沉积,在中部自西向东分布一系列片麻岩穹窿——北喜马拉雅片麻岩穹窿(NH⁃GD),是北喜马拉雅伸展构造的重要组成部分[36]。GHC位于MCT和STDS之间,由一套源岩时代为古元古代—奥陶纪的中高级变质结晶杂岩系组成[37],上部紧邻STDS处出露大量淡色花岗岩。LHS位于MBT和MCT之间,主要由碎屑沉积岩和低级变质岩组成。最南部为SS,由古近纪—中新世的海相和陆相沉积组成。
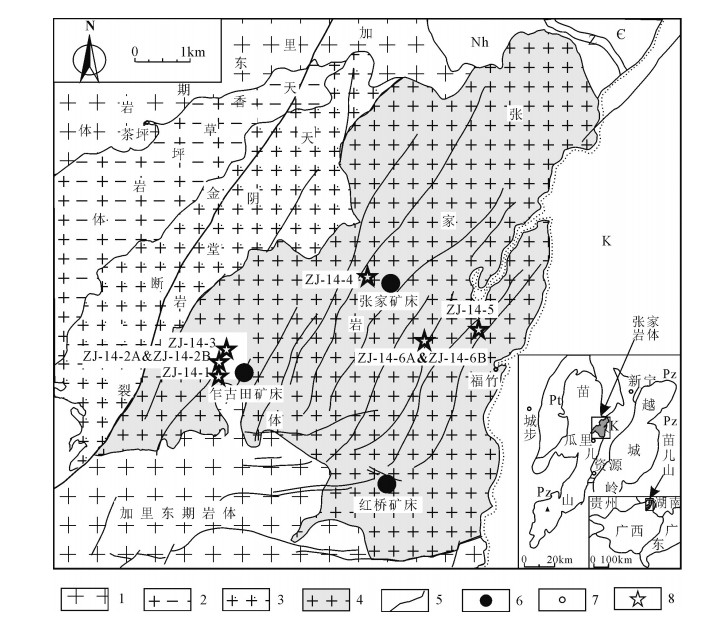
![]() 图 1 喜马拉雅造山带中东段地质简图(据参考文献[35]修改)GCT—大反冲断层;STDS—藏南拆离系;MCT—主中央逆冲断裂;MBT—主边界逆冲断裂;MFT—主前锋逆冲断裂;NHGD—北喜马拉雅片麻岩穹窿Figure 1. Sketch geological map of the middle and east Himalayan orogen
图 1 喜马拉雅造山带中东段地质简图(据参考文献[35]修改)GCT—大反冲断层;STDS—藏南拆离系;MCT—主中央逆冲断裂;MBT—主边界逆冲断裂;MFT—主前锋逆冲断裂;NHGD—北喜马拉雅片麻岩穹窿Figure 1. Sketch geological map of the middle and east Himalayan orogen研究区位于喜马拉雅造山带东部的错那地区(图 1)。研究区以STDS为界,北部为THS,由三叠纪—白垩纪沉积岩组成,主要岩性为砂岩、粉砂岩、泥页岩,以及低级变质的板岩和千枚岩(图 2)。南部为GHC中高级变质的肉切村群和聂拉木群,其中,肉切村群主要岩石包括钙质石英片岩、泥质片岩、大理岩等(图 2),内部发育少量切层的淡色花岗岩脉(图 3-a、3-b)。聂拉木群主要由黑云斜长片麻岩、透辉大理岩、含石榴子石矽线黑云斜长变粒岩、含矽线黑云石英片岩、石英岩等组成。在STDS附近出露淡色花岗岩体(图 2、图 3-c),岩石整体呈灰白色,显微镜下观察主要矿物成分为石英(40%)、斜长石(25%)、钾长石(20%)、白云母(10%),以及少量的黑云母和石榴子石(图 3-d)。
2. 实验方法
2.1 LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年
采用常规方法分选出锆石单矿物并制作成环氧树脂靶,打磨靶面使锆石中心暴露,拍摄锆石的可见光和阴极发光显微照片,然后进行LA-MCICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素测试。锆石阴极发光图像(CL)在北京大学造山带与地壳演化教育部重点实验室的扫描电镜上完成。LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素测试在天津地质矿产研究所同位素实验室进行。所用仪器为Thermo Fisher公司生产的Neptune型多接受器等离子体质谱仪(MC-ICPMS),并结合美国ESL公司生产的UP193-FX ArF准分子激光器,激光剥蚀束斑直径为35μm,激光能量密度为2.5J/cm2,频率为10Hz,激光剥蚀物质以氦为载气送入Neptune的电感耦合等离子体,GJ-1作为外部锆石年龄标准进行U-Pb同位素分馏校正。在测试过程中,每测定7个样品点之前、之后各测定2次锆石标样GJ-1。数据的离线处理采用ICPMS⁃DataCal程序[38]完成,锆石U-Pb谐和图用Isoplot/ Ex3.00程序绘制[39]。
2.2 主量和微量元素
野外采集的样品挑选较新鲜、无蚀变的部分碎至200目,在加拿大ACME实验室完成全岩主量和微量元素测定。主量元素采用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(ICP-ES)测定,测试精度优于5%;微量元素采用Agilent 7500a型电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS)测定,测试精度优于5%~10%。
2.3 Sr-Nd同位素
Rb-Sr、Sm-Nd同位素测试样品的化学分离在北京大学造山带与地壳演化教育部重点实验室完成,Sr、Nd同位素比值测定在天津地质矿产研究所热电离质谱仪TRITON上完成。同位素比值测试过程中,扇形磁分析器的有效半径为81cm,加速电压为10kV时分析质量数范围为3~320amu,分辨率大于450(10%峰谷定义),灵敏度大于3ion/100μmol,丰度灵敏度≤10×10-9。在样品测试过程中,测定的JN-DI Nd同位素标样和NBS-987 Sr同位素标样的同位素值分别为143Nd/144Nd=0.512107±0.000004 (2σ)和87Sr/86Sr=0.710265±0.000004 (2σ)。
3. 测试结果
3.1 LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄
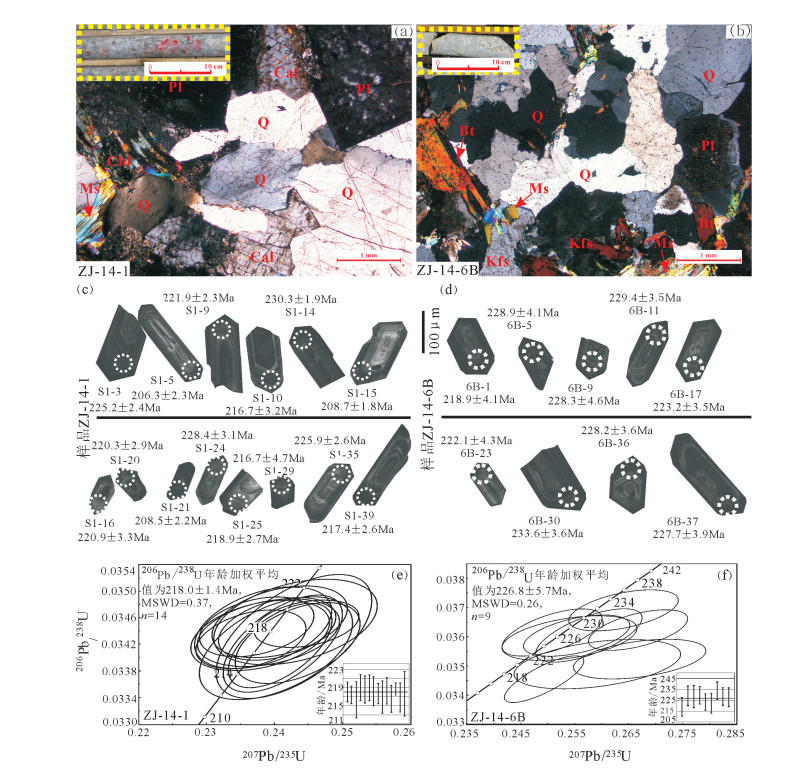
错那淡色花岗岩样品CN-06的锆石阴极发光图像显示,锆石颗粒自形,长柱状,棱角清晰,颗粒长度为200~400μm,长宽比介于2∶1~4∶1之间。大多数锆石发育核-幔-边结构,核部和幔部为继承锆石,核部色调较暗,幔部形状不规则,色调灰白;边部宽度为40~60μm,色调黑暗并显示密集的韵律生长环带,表明为岩浆成因。少数锆石仅发育核-边结构,核部色调较亮,围绕核部发育具有韵律环带的暗色生长边(图 4-a)。
对样品CN-06共选取23个点位进行U-Pb同位素测试,全部分析点均位于锆石边部的暗色韵律环带上,测试数据列于表 1。23个分析点的Th和U含量分别为187×10-6~509×10-6和8186×10-6~8970×10-6,Th/U值极低,为0.02~0.06,均不大于0.10,与深熔成因的锆石特征吻合[40]。23个分析点的206Pb/ 238U年龄介于18.9~16.4Ma之间,给出的年龄加权平均值为17.7±0.3Ma(MSWD=2.0)(图 4-b),代表错那淡色花岗岩的最终结晶年龄。
表 1 藏南错那淡色花岗岩样品(CN-06)LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素测试数据Table 1. LA-MC-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb isotopic data of the leucogranite sample CN-06 from Cuona, southern Tibet分析点号 Pb Th U Th/U 同位素比值 表观年龄/Ma 10-6 207Pb/235U ±1σ 206Pb/238U ±1σ 208Pb/232Th ±1σ 207Pb/235U ±1σ 206Pb/238U ±1σ 208Pb/232Th ±1σ 01 2598 339 8357 0.04 0.0170 0.0009 0.00255 0.00013 0.00108 0.00006 17.1 0.9 16.4 0.8 21.9 1.3 02 2687 208 8481 0.02 0.0177 0.0009 0.00275 0.00014 0.00087 0.00010 17.8 0.9 17.7 0.9 17.6 2.0 03 2716 213 8475 0.03 0.0181 0.0010 0.00279 0.00014 0.00086 0.00009 18.2 0.9 17.9 0.9 17.5 1.9 04 2889 226 8970 0.03 0.0175 0.0009 0.00267 0.00013 0.00085 0.00007 17.7 0.9 17.2 0.9 17.3 1.3 05 2612 275 8418 0.03 0.0174 0.0009 0.00270 0.00014 0.00086 0.00007 17.5 0.9 17.4 0.9 17.5 1.4 06 2944 309 8375 0.04 0.0201 0.0010 0.00284 0.00014 0.00177 0.00011 20.2 1.0 18.3 0.9 35.7 2.3 07 2826 187 8499 0.02 0.0185 0.0011 0.00287 0.00015 0.00166 0.00027 18.6 1.1 18.5 1.0 33.6 5.4 08 2630 298 8395 0.04 0.0177 0.0009 0.00275 0.00014 0.00083 0.00006 17.9 0.9 17.7 0.9 16.7 1.1 09 2634 350 8344 0.04 0.0180 0.0009 0.00267 0.00014 0.00103 0.00007 18.1 0.9 17.2 0.9 20.9 1.3 10 2747 207 8481 0.02 0.0182 0.0010 0.00283 0.00014 0.00111 0.00010 18.3 1.0 18.2 0.9 22.4 2.0 11 3001 250 8433 0.03 0.0202 0.0011 0.00277 0.00014 0.00284 0.00022 20.3 1.1 17.9 0.9 57.3 4.5 12 2707 439 8254 0.05 0.0181 0.0010 0.00264 0.00014 0.00136 0.00010 18.2 1.0 17.0 0.9 27.4 2.1 13 2834 371 8321 0.04 0.0195 0.0010 0.00257 0.00013 0.00232 0.00015 19.6 1.0 16.5 0.9 46.8 2.9 14 2721 354 8336 0.04 0.0181 0.0009 0.00274 0.00014 0.00102 0.00007 18.2 0.9 17.6 0.9 20.7 1.4 15 2719 193 8496 0.02 0.0182 0.0009 0.00277 0.00014 0.00117 0.00012 18.3 0.9 17.8 0.9 23.7 2.4 16 3128 225 8456 0.03 0.0192 0.0019 0.00275 0.00014 0.00430 0.00048 19.3 1.9 17.7 0.9 86.7 9.6 17 2612 192 8501 0.02 0.0174 0.0010 0.00271 0.00014 0.00090 0.00025 17.5 1.0 17.4 0.9 18.3 5.0 18 2699 337 8354 0.04 0.0185 0.0010 0.00276 0.00014 0.00106 0.00008 18.6 1.0 17.8 0.9 21.4 1.6 19 2704 278 8412 0.03 0.0187 0.0010 0.00282 0.00014 0.00112 0.00009 18.8 1.0 18.1 0.9 22.7 1.7 20 2832 305 8379 0.04 0.0188 0.0010 0.00294 0.00015 0.00100 0.00009 18.9 1.0 18.9 1.0 20.2 1.8 21 3020 198 8483 0.02 0.0181 0.0010 0.00292 0.00015 0.00300 0.00024 18.2 1.0 18.8 1.0 60.6 4.8 22 2760 400 8290 0.05 0.0178 0.0009 0.00279 0.00014 0.00126 0.00011 18.0 0.9 18.0 0.9 25.4 2.3 23 2677 509 8186 0.06 0.0182 0.0011 0.00265 0.00014 0.00158 0.00022 18.3 1.1 17.1 0.9 32.0 4.4 3.2 主量和微量元素
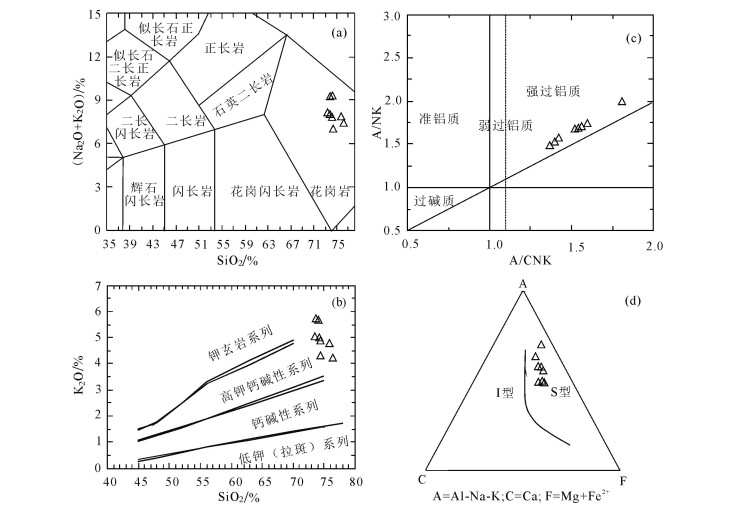
样品全岩主量和微量元素数据见表 2。错那淡色花岗岩具有较高的SiO2(74.46%~75.57%)、Al2O3 (14.07%~14.64%)和K2O(4.19%~4.85%),以及较低的CaO(0.51%~0.67%)、MgO(0.07%~0.10%)和TiO2(0.02% ~0.04%)含量。K2O/Na2O值较高,介于1.09~1.31之间。在SiO2-K2O图解中,样品点位于高钾钙碱性系列(图 5-a)。A/CNK值为1.15~1.25,均大于1.1,在A/CNK-A/NK图解中,样品点全部落入过铝质区域(图 5-b)中。总体来看,错那淡色花岗岩属于高钾钙碱性过铝质S型花岗岩。
表 2 藏南错那淡色花岗岩全岩主量、微量和稀土元素测试数据Table 2. Whole-rock major, trace and rare earth element analyses of the Cuona leucogranites in southern Tibet样品号 CN-01 CN-02 CN-03 CN-04 CN-05 SiO2 74.59 74.58 74.46 74.87 75.57 Al2O3 14.48 14.64 14.60 14.31 14.07 Fe2O3 0.70 0.83 0.90 0.77 0.69 MgO 0.08 0.09 0.10 0.07 0.08 CaO 0.51 0.53 0.59 0.64 0.67 Na2O 3.69 3.64 3.51 3.90 3.84 K2O 4.85 4.68 4.41 4.48 4.19 TiO2 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.03 0.03 P2O5 0.20 0.19 0.18 0.18 0.15 MnOz 0.04 0.04 0.06 0.05 0.04 烧失量 0.8 0.7 1.1 0.7 0.7 合计 99.16 99.25 98.85 99.30 99.33 A/NK 1.28 1.32 1.38 1.27 1.30 A/CNK 1.18 1.22 1.25 1.15 1.16 Na2O+K2O 8.54 8.32 7.92 8.38 8.03 K2O/Na2O 1.31 1.29 1.26 1.15 1.09 CaO/Na2O 0.14 0.15 0.17 0.16 0.17 Be 7 12 10 16 14 Sc 3 3 4 3 3 Co 0.4 0.2 0.4 0.5 1.1 Ni 0.1 0.1 0.3 0.2 0.2 Zn 5 9 13 11 9 Ga 16.9 18.5 20.8 18.9 19.5 Rb 377.6 413.5 381.7 353.8 353.0 Sr 12.8 23.3 18.2 15.3 15.2 Y 9.7 12.8 20.1 13.3 11.2 Zr 32.6 39.9 52.9 41.0 25.2 Nb 14.2 17.7 20.5 18.3 18.0 Cs 25.3 30.9 31.2 25.7 23.7 Ba 17 47 37 24 23 La 3.4 5.5 6.8 5.2 4.0 Ce 7.2 11.2 14.9 10.0 8.9 Pr 0.86 1.37 1.79 1.17 0.99 Nd 3.6 3.5 6.4 3.3 3.3 Sm 1.03 1.43 2.15 1.55 1.28 Eu 0.09 0.14 0.14 0.13 0.10 Gd 1.29 1.83 2.57 1.49 1.42 Tb 0.27 0.39 0.56 0.35 0.32 Dy 1.39 2.07 3.24 1.95 1.93 Ho 0.26 0.36 0.63 0.41 0.36 Er 0.78 1.11 1.78 1.09 0.92 Tm 0.12 0.19 0.30 0.20 0.15 Yb 0.86 1.28 1.94 1.18 1.11 Lu 0.13 0.19 0.28 0.19 0.16 Hf 1.0 1.3 2.3 1.7 1.3 Ta 4.0 4.4 5.4 6.1 4.8 Pb 6.3 6.7 7.2 6.3 6.7 Th 2.4 3.4 5.0 2.9 2.4 U 5.4 5.7 8.1 4.1 4.2 Sn 14 17 20 14 12 Rb/Sr 29.50 17.75 20.97 23.12 23.22 LREE 16.18 23.14 32.18 21.35 18.57 HREE 5.10 7.42 11.30 6.86 6.37 TREE 21.28 30.56 43.48 28.21 24.94 (La/Sm)w 2.13 2.49 2.04 2.17 2.02 (Gd/Yb)N 1.24 1.18 1.10 1.04 1.06 (La/Yb)N 2.84 3.08 2.52 3.16 2.59 δEu 0.24 0.26 0.18 0.26 0.23 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6;A/NK=摩尔Al2O3/ (Na2O+K2O),A/ CNK=摩尔Al2O3/ (CaO+Na2O+K2O);δEu=2EuN/ (SmN+GdN),其中N为球粒陨石标准化值[41] ![]() 图 5 藏南错那淡色花岗岩的SiO2-K2O (a)、A/CNK-A/NK分类图解(b)及原始地幔标准化蛛网图(c)和球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式图(d) (原始地幔和球粒陨石数值据参考文献[41])Figure 5. TAS diagram (a), A/CNK-A/NK diagram (b), primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagram (c) and chondrite-normalized REE patterns (d) of Cuona leucogranites, southern Tibet
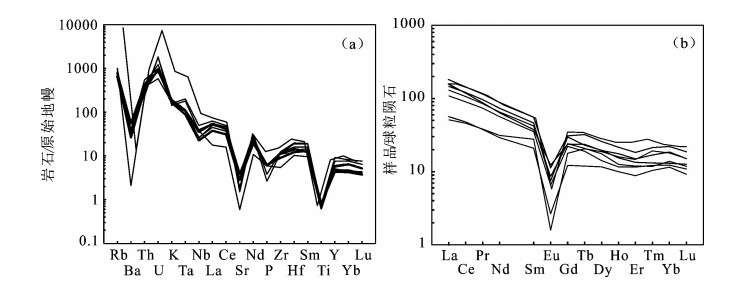
图 5 藏南错那淡色花岗岩的SiO2-K2O (a)、A/CNK-A/NK分类图解(b)及原始地幔标准化蛛网图(c)和球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式图(d) (原始地幔和球粒陨石数值据参考文献[41])Figure 5. TAS diagram (a), A/CNK-A/NK diagram (b), primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagram (c) and chondrite-normalized REE patterns (d) of Cuona leucogranites, southern Tibet在原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(图 5-c)中,显示Rb、Th、U和Pb的正异常,以及Ba、Nb、Sr和Zr的负异常。稀土元素总量较低,为21.28×10-6~ 43.48×10-6,轻、重稀土元素分馏较弱,(La/Yb)N为2.59~3.16。在球粒陨石标准化的稀土元素配分模式图(图 5-d)中,具有强烈的负Eu异常,δEu值为0.18~0.26。
3.3 Rb-Sr、Sm-Nd同位素
样品全岩Rb-Sr、Sm-Nd同位素测试结果列于表 3。经过t=18Ma校正后,4个样品的Isr值较高,为0.78982~0.79276,εNd(t)值较低,为-19.5~-18.2,SrNd同位素的初始比值变化不大。Nd同位素二阶段亏损地幔模式年龄为2469~2372Ma,表明淡色花岗岩可能源自古老地壳的重熔。
表 3 藏南错那淡色花岗岩全岩Rb-Sr和Sm-Nd同位素测试数据Table 3. Whole-rock Rb-Sr and Sm-Nd isotopic compositions of the Cuona leucogranites in southern Tibet样品号 t/Ma Rb/10-6 Sr/10-6 87Rb/86Sr 87Sr/86Sr 2σ Isr Sm/10-6 Nd/10-6 147Sm/144Nd 143Nd/144Nd 2σm TDM2/Ma εNd(t) CN-01 18.0 377.6 12.8 83.3240 0.81406 0.00020 0.79276 1.03 3.60 0.181524 0.511636 0.000004 2372 -19.5 CN-02 18.0 413.5 23.3 50.1266 0.81431 0.00006 0.80150 1.43 3.50 0.259220 0.511652 0.000004 2469 -19.4 CN-04 18.0 353.8 15.3 65.3153 0.80910 0.00001 0.79241 1.55 3.30 0.298001 0.511654 0.000004 2452 -19.4 CN-05 18.0 353.0 15.2 65.5963 0.80659 0.00001 0.78982 1.28 3.30 0.246091 0.511709 0.000006 2390 -18.2 注:87Rb/86Sr和147Sm/144Nd通过ICP-MS测试的微量元素Rb、Sr、Sm和Nd计算所得,计算公式为87Rb/86Sr=Rb/Sr×2.981,147Sm/144Nd=Sm/Nd×[0.531497+0.142521×(143Nd/144Nd)s]。ISr=(87Sr/86Sr)s+87Rb/86Sr(eλt–1),143Nd/144Nd(t)=(143Nd/144Nd)s+147Sm/144Nd (eλt-1);εNd(t)=[ (143Nd/144Nd)s/ (143Nd/144Nd)CHUR-1]×104。(143Nd/144Nd)CHUR=0.512638,(147Sm/144Nd)CHUR=0.1967,(143Nd/144Nd)DM=0.51315,(147Sm/144Nd)DM=0.2137;λRb=1.42×10-12/年[42],λSm=6.54×10-12/年[43];二阶段模式年龄TDM2的计算见参考文献[41] 4. 讨论
4.1 STDS淡色花岗岩的时代
喜马拉雅淡色花岗岩的形成时代一直是地学界研究的重点,准确获得各岩体的年龄,不仅有助于限定相关构造的活动时代,而且有利于重建造山过程中岩浆作用的时空格局,进而反演造山带的岩浆演化历史。近期,吴福元等[1]根据目前已发表的年龄数据,重新勾画了喜马拉雅淡色花岗岩的年代格架,大致划分为始喜马拉雅阶段(Eo-Himalayan:44~26Ma)、新喜马拉雅阶段(Neo-Himalayan:26~ 13Ma)和后喜马拉雅阶段(Post-Himalayan:13~ 7Ma)。以上3个时期的花岗岩最显著的区别在于受造山带内不同构造的控制:始喜马拉雅阶段的花岗岩多分布于THS中部的NHGD核部,新喜马拉雅阶段的淡色花岗岩主要沿STDS分布,而后喜马拉雅阶段的花岗岩受控于南北向裂谷(NSTR)。错那淡色花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄为17.7±0.3Ma (MSWD=2.0),且岩体沿STDS分布,应属于上述划分方案中的新喜马拉雅阶段淡色花岗岩。在造山带的中西部,相同峰期时代的STDS淡色花岗岩也广泛分布(图 1)。①在西部,玛纳斯鲁淡色花岗岩年龄为19.3~18.1Ma[30, 33, 45]。②在中部,吉隆STDS淡色花岗岩脉年龄为18.6~16.6Ma[14],聂拉木淡色花岗岩年龄为17.1~16.8Ma[9],希夏邦马淡色花岗岩年龄为17.3Ma[46],达扎卡淡色花岗岩年龄为16.7Ma[4],绒布淡色花岗岩年龄为16.8~16.2Ma[18, 47],珠峰淡色花岗岩年龄为16.9~16.4Ma[2, 30],定结淡色花岗岩年龄为16.9~15.1Ma[7, 48-49]。③在东部,东不丹地区淡色花岗岩年龄为17.6~16.8Ma[50]。这些淡色花岗岩均沿区域性伸展构造STDS分布,且具有近乎一致的峰期结晶年龄,暗示其形成可能与STDS的活动密切相关。
4.2 错那淡色花岗岩的源区和源岩
错那淡色花岗岩具有高SiO2和Na2O含量,铝过饱和,K2O>Na2O,为高钾钙碱性过铝质花岗岩。全岩的Isr值较高(0.78982~0.79276),εNd(t)值较低(-19.5~-18.2),Rb/Sr值(17.75~29.50)远高于大陆地壳的平均值(0.32),与典型壳源成因花岗岩特征吻合。而淡色花岗岩体内部及附近均未发现幔源包体和相关的岩石,因此,笔者认为错那淡色花岗岩应为壳源成因。
目前,关于STDS淡色花岗岩的源岩问题仍存在分歧。杨晓松等[51]的高温高压岩石学模拟研究发现,在温压分别为770~980℃和1.0~1.4GPa,且无外来流体的条件下,GHC中黑云斜长片麻岩发生部分熔融,形成的熔体与STDS淡色花岗岩成分类似,且熔融后的残留物质与GHC下地壳麻粒岩成分相当,据此认为,淡色花岗岩源岩为GHC黑云斜长片麻岩[27]。Knesel等[52]通过实验岩石学研究发现,GHC变泥质岩早期发生白云母脱水熔融,形成的花岗质熔体成分与前人获得的STDS淡色花岗岩的地球化学特征一致,因此,认为源岩应该为GHC变质沉积岩。考虑到淡色花岗岩的壳源成因特性,将错那淡色花岗岩样品的Sr、Nd同位素成分与潜在的可能源岩,包括GHC变泥质岩、LHS变质沉积岩和北喜马拉雅片麻岩[53-56],统一以t=18Ma重新进行计算并综合对比(图 6)。结果显示,4件样品均位于GHC变泥质岩区域。此外,错那淡色花岗岩的二阶段亏损地幔模式年龄TDM2值(2469~2372Ma)与GHC变泥质岩的相同,且与GHC变泥质岩中碎屑锆石获得的约2500Ma的峰值年龄重叠[57],暗示其可能来自GHC变泥质岩的部分熔融。综上所述,错那淡色花岗岩的源岩为GHC变泥质岩。
4.3 错那淡色花岗岩的形成机制
STDS淡色花岗岩是GHC变泥质岩部分熔融的产物,但部分熔融的机制仍有争议,争议点包括熔融的矿物是白云母还是黑云母?熔融过程是否有外来流体参与?
Knesel等[52]对GHC变泥质岩进行部分熔融实验研究发现,单一源区的变泥质岩在熔融的不同阶段具有不同的熔融机制,并产生化学成分迥异的熔体。早期在无水条件下,白云母发生脱水熔融,形成低Sr、高Isr的花岗质熔体。而后期伴随早期脱水熔融产生的含水流体的加入,主要发生水致部分熔融,形成高Sr、低Isr的熔体,分布于不同地区的花岗岩的Sr和Isr数据也证实了上述实验结论。本文搜集已发表的喜马拉雅花岗岩的Sr和Isr数据,统一以t=18Ma重新计算并归纳于图 7-a中。从该图可以看出,花岗岩主要集中分布于a1和a2两个截然不同的区域,其中a1区域内花岗岩表现出低Sr(10×10-6~ 80×10-6)、高Isr(0.75~0.80)的特征,与部分熔融实验中无水条件下白云母脱水熔融形成的熔体化学特征吻合。而a2区域内花岗岩显示高Sr(50×10-6~ 200×10-6)、低Isr(0.72~0.75)的特征,与水致部分熔融形成的熔体化学特征相符(图 7-a)。错那淡色花岗岩具有低Sr(12.8×10-6~23.3×10-6)和高Isr (0.78982~0.79276)的特征,在图 7-a中,与其他地区的STDS淡色花岗岩一样位于a1区域中,暗示其为无水条件下白云母脱水熔融的产物。
实验岩石学[52, 60]和理论计算结果[61-62]表明,随温压条件和含水量的变化,变泥质岩发生从白云母到黑云母的递进部分熔融,形成具有复杂RbSr组分的花岗质熔体[24, 52, 61]。在变泥质岩中,Rb主要赋存于云母类矿物中,而Sr主要赋存于长石矿物中,在有水参与的地壳熔融过程中,白云母和斜长石都发生部分熔融,且长石熔融的量远大于云母,导致熔体的Rb/Sr值偏低。在无水条件下,白云母大量熔融,形成的熔体Rb/Sr值较高[63]。因此,可以通过Rb/Sr值及其与Ba浓度的关系反推部分熔融机制。错那淡色花岗岩具有较高的Rb/Sr值(17.75~29.50),在Ba-Rb/Sr图解(图 7-b)中,Rb/ Sr值随着Ba浓度的增加而减小,二者呈负相关,与缺乏蒸汽相的白云母脱水熔融的趋势一致[63],也与上述Sr-Isr系统分析结果一致。同时,由于无水条件下参与熔融的矿物主要为白云母,斜长石未进入熔体而残留在源区,导致错那淡色花岗岩具有较强的负Eu异常。综上所述,错那淡色花岗岩是GHC变泥质岩在无水条件下白云母脱水熔融的产物。
4.4 构造动力学意义
喜马拉雅造山带内发育多种类型的花岗岩,其形成过程对应不同的造山阶段,反映不同的构造背景和动力学过程。如晚始新世—渐新世(45~28Ma)的花岗岩主要出露于NHGD,如然巴穹窿(44Ma)[64]、麻布迦穹窿(35Ma)[65]、萨迦穹窿(28.1Ma)[66]、佩枯错穹窿(28.2Ma)[67]等。这些花岗岩的形成年龄与喜马拉雅变质岩的进变质时代相同[68-69],是早期地壳逆冲增厚条件下部分熔融的产物[37],熔体的产生使地壳弱化,并直接影响与STDS相关的中下地壳的伸展拆离,是触发STDS启动的关键因素。另一类为晚渐新世—早中新世(26~13Ma)[1]的淡色花岗岩,以STDS淡色花岗岩为代表,其地球化学成分与始新世—渐新世花岗岩不同,以高Rb/Sr值和高Isr为特征,结晶时代与喜马拉雅峰期变质作用时代相同,其形成可能与地壳伸展背景下GHC的快速折返/隆升导致的减压熔融有关[25]。最后一类为晚中新世(13~7Ma)花岗岩,这类花岗岩的矿物和化学成分与STDS淡色花岗岩类似,主要的区别在于前者主要沿NSTR分布,其形成与造山后期的东西向伸展有关。
在GHC变泥质岩部分熔融的过程中,温度和压力是主控因素。错那淡色花岗岩的锆石饱和温度为657~715℃,这一温度低于白云母脱水熔融的温度(720~770℃)。在缺少深部热源证据和剪切摩擦生热,地壳中放射性同位素衰变生热无法产生大规模岩浆作用的情况下[34],减压成为部分熔融的必要条件,而STDS的启动不仅可以起到减压的作用,还可为岩浆上侵提供空间和通道,可能是触发熔融的重要因素。已有研究表明,STDS强烈活动的时间集中在28~13Ma[14],与STDS淡色花岗岩的时代基本一致,且淡色花岗岩主要沿STDS分布,佐证了以上结论。错那淡色花岗岩的年龄(17.7±0.3Ma)与STDS活动时代吻合,其地球化学特征也与晚渐新世—早中新世淡色花岗岩相同。从构造-岩浆作用角度综合考虑,笔者认为,错那淡色花岗岩可能形成于STDS启动之后的伸展减薄背景下,反映了构造减压导致的中下地壳变泥质岩中含水矿物(白云母)脱水熔融的动力学过程。
5. 结论
(1)藏南错那淡色花岗岩的结晶年龄为17.7±0.3Ma,岩石属于高钾钙碱性过铝质花岗岩,富集Rb、Th和U,亏损Ba、Nb、Sr和Zr,具有强烈的负Eu异常;Rb/Sr值较高,Isr和εNd(t)值分别为0.78982~0.79276和-19.5~-18.2。
(2)错那淡色花岗岩为壳源成因,源岩是GHC变泥质岩,是无水条件下白云母脱水熔融的产物。熔体的形成与STDS的启动有关,反映了地壳伸展减薄背景下,构造减压导致中下地壳变泥质岩中含水矿物脱水熔融并沿STDS上升侵位的动力学过程。
致谢: 成文过程中,得到南华大学冯志刚教授、核工业北京地质研究院刘军港、黄少华博士的帮助,审稿专家提出了很多中肯的建议,在此一并表示感谢。 -
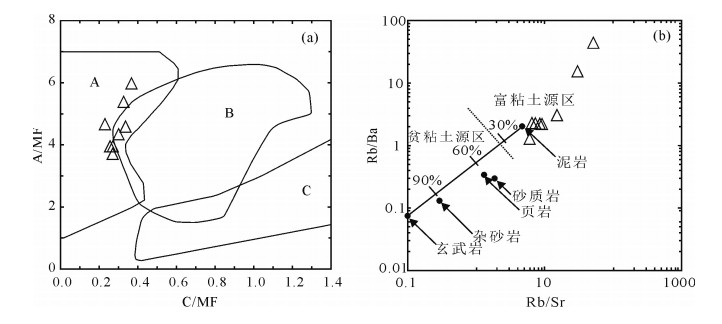
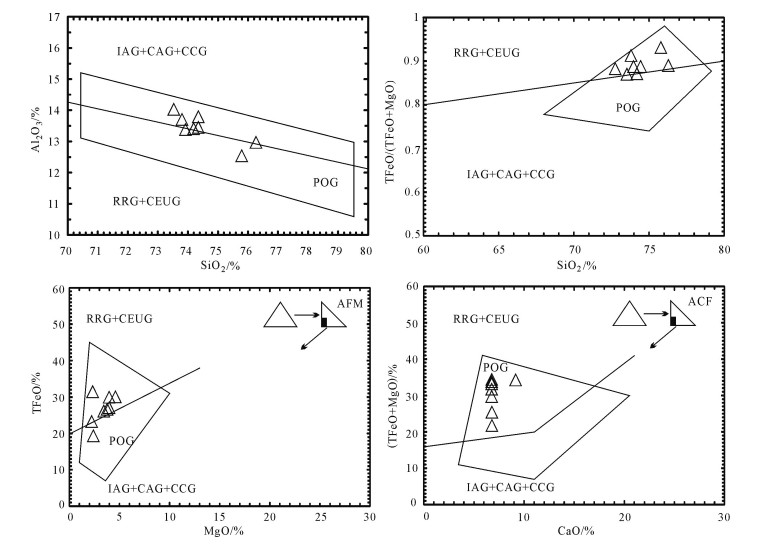
图 7 花岗岩源岩判别图解[34]
A—变质泥岩部分熔融;B—变质砂岩部分熔融;C—基性岩的部分熔融;坐标轴:C=CaO, MF=MgO+TFeO, A=Al2O3,均为分子数
Figure 7. Original rock discrimination diagrams of the Zhangjia granite
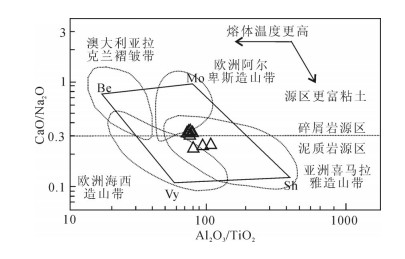
图 8 张家花岗岩CaO/Na2O-Al2O3/TiO2图[34]
Figure 8. CaO/Na2O-Al2O3/TiO2 plot for the Zhangjia granite Be-Bethanga; Mo-Moschumandl; Vy-Vysoky-Kanen; Sh-Shishapangma
图 9 张家花岗岩构造环境判别图解[23]
IAG—岛弧花岗岩;CAG—大陆弧花岗岩;CCG—大陆碰撞花岗岩;POG—后造山花岗岩;RRG—裂谷花岗岩;CEUG—大陆造陆隆升花岗岩;AFM—铝铁镁元素三角图;ACF—铝钙铁元素三角图
Figure 9. Tectonic discrimination diagrams for the Zhangjia granite
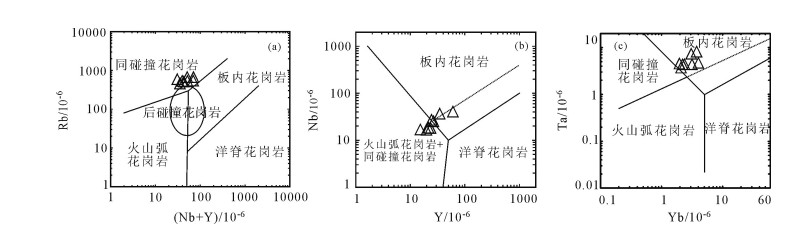
图 10 张家花岗岩(Nb+Y)-Rb(a)、Y-Nb(b)和Yb-Ta(c)元素含量大地构造环境判别图解[49]
Figure 10. (Nb+Y)-Rb (a), Y-Nb (b) and Yb-Ta (c) discrimination diagrams of the Zhangjia granite
表 1 张家花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb数据
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb data for the Zhangjia granite
测点 Pb/
10-6232Th/
10-6238U/
10-6232Th
/238U207Pb/
206Pb1σ
/10-4207Pb/
235U1σ
/10-4206Pb/
238U1σ/
10-4207Pb/235U年龄/Ma 1σ 206Pb/238U年龄/Ma 1σ ZJ-14-1 S1-3 277 1852 9188 0.20 0.04996 14 0.24893 70 0.03556 4 225.7 5.7 225.2 2.4 S1-5 237 1583 8126 0.19 0.04922 15 0.22324 66 0.03251 4 204.6 5.5 206.3 2.3 S1-9 194 2228 4166 0.53 0.04901 14 0.23928 69 0.03501 4 217.8 5.6 221.9 2.3 S1-10 244 2816 6931 0.41 0.05112 13 0.24078 62 0.03419 5 219.1 5.1 216.7 3.2 S1-14 203 1583 5683 0.28 0.05250 13 0.26597 66 0.03637 3 239.5 5.3 230.3 1.9 S1-15 246 2087 7848 0.27 0.05069 15 0.23242 63 0.03291 3 212.2 5.2 208.7 1.8 S1-16 143 1650 2573 0.64 0.05091 20 0.24546 98 0.03486 5 222.9 8.0 220.9 3.3 S1-20 339 2927 10256 0.29 0.05213 17 0.25206 86 0.03476 5 228.2 7.0 220.3 2.9 S1-21 618 3738 21470 0.17 0.05125 14 0.23533 64 0.03287 4 214.6 5.2 208.5 2.2 S1-24 185 1627 4386 0.37 0.05042 16 0.25035 82 0.03606 5 226.9 6.7 228.4 3.1 S1-25 142 1462 3051 0.48 0.05062 17 0.24072 81 0.03454 4 219.0 6.7 218.9 2.7 S1-29 432 5070 8012 0.63 0.05369 21 0.25253 92 0.03418 7 228.6 7.5 216.7 4.7 S1-35 148 1615 2707 0.60 0.05040 18 0.24889 85 0.03566 4 225.7 6.9 225.9 2.6 S1-39 582 1411 24927 0.06 0.05170 14 0.24883 69 0.03430 4 225.6 5.6 217.4 2.6 ZJ-14-6B 6B-1 435 2729 13430 0.20 0.05270 12 0.24933 60 0.03455 7 226.0 4.9 218.9 4.1 6B-5 318 2887 7069 0.41 0.05050 15 0.25081 76 0.03615 7 227.2 6.1 228.9 4.1 6B-9 358 2032 11688 0.17 0.05130 14 0.25762 80 0.03604 7 232.7 6.5 228.3 4.6 6B-11 443 2674 12029 0.22 0.05300 15 0.26671 75 0.03623 6 240.1 6.0 229.4 3.5 6B-17 153 1420 2866 0.50 0.05460 20 0.26701 100 0.03524 6 240.3 8.0 223.2 3.5 6B-23 81 768 1552 0.49 0.05390 27 0.25918 126 0.03506 7 234.0 10.2 222.1 4.3 6B-30 471 4913 7039 0.70 0.05160 16 0.26403 83 0.03690 6 237.9 6.7 233.6 3.6 6B-36 181 1405 4890 0.29 0.05130 16 0.25536 80 0.03604 6 230.9 6.5 228.2 3.6 6B-37 131 1352 2021 0.67 0.04960 19 0.25402 102 0.03595 6 229.8 8.3 227.7 3.9 表 2 张家花岗岩主量、微量和稀土元素组成
Table 2 Major, trace element and REE compositions of the Zhangjia granite
样品号 ZJ-14-1 ZJ-14-2A ZJ-14-2B ZJ-14-3 ZJ-14-4 ZJ-14-5 ZY-14-6A ZJ-14-6B SiO2 74.35 76.29 73.95 73.81 75.79 74.35 73.53 74.19 TiO2 0.13 0.11 0.17 0.14 0.16 0.18 0.18 0.18 Al2O3 13.79 12.97 13.39 13.70 12.54 13.45 14.03 13.41 Fe2O3 1.42 1.04 1.65 1.27 1.67 1.46 1.44 1.58 FeO 1.19 0.89 1.34 1.05 1.47 1.25 1.22 1.37 MnO 0.07 0.05 0.06 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.04 0.05 MgO 0.34 0.24 0.40 0.22 0.23 0.39 0.40 0.45 CaO 0.68 0.80 0.92 0.85 0.93 0.93 1.03 0.93 Na2O 2.62 3.21 2.96 3.44 3.06 2.95 3.10 2.89 K2O 4.33 4.22 5.71 5.73 4.79 4.94 5.04 5.03 P2O5 0.13 0.10 0.06 0.13 0.08 0.13 0.13 0.13 烧失量 2.05 0.89 0.74 0.59 0.63 1.08 0.98 1.08 总计 101.10 100.81 101.34 100.95 101.38 101.15 101.12 101.28 CaO/Na2O 0.26 0.25 0.31 0.25 0.30 0.32 0.33 0.32 Al2O3/TiO2 104.47 122.36 80.66 97.86 80.38 76.86 78.82 74.92 A/NK 1.98 1.75 1.54 1.49 1.60 1.70 1.72 1.69 A/CNK 1.81 1.58 1.40 1.37 1.43 1.52 1.53 1.52 Li 318.00 288 102 99.00 160.00 173.00 186.00 143.00 Be 5.33 16.5 5.27 2.61 6.85 6.96 7.99 15.70 Sc 5.13 3.58 7.28 2.85 3.58 3.94 4.56 4.67 Ti 791.34 636.00 996.00 839.30 935.22 1049.12 1067.11 1073.10 V 7.31 5.19 12.9 7.82 9.58 12.10 13.70 12.90 Cr 2.98 1.84 7.76 1.99 2.02 5.48 6.08 5.73 Co 1.62 1.11 1.9 1.45 1.99 2.05 2.67 2.41 Ni 1.10 1.05 3.27 1.09 0.94 2.41 2.61 2.45 Cu 2.62 3.05 8.67 0.99 1.80 5.03 6.00 14.80 Zn 57.60 31.2 35.9 15.20 20.40 42.20 47.30 50.30 Ga 25.10 20.3 17.4 20.30 21.60 18.40 22.00 21.70 Rb 641 557 604 494 526 413 483 489 Sr 12.40 18.4 39.7 81.60 79.40 59.60 59.70 57.40 Y 25.30 15.3 41.6 26.70 34.30 19.70 21.60 22.90 Zr 60.40 61.9 129 101.00 139.00 126.00 122.00 135.00 Nb 27.00 16.9 28.3 25.20 35.50 16.10 18.80 18.20 Mo 0.12 0.784 0.351 0.25 0.53 0.23 0.38 0.30 Cd 0.18 0.055 0.066 0.12 0.03 0.02 0.08 0.08 In 0.18 0.155 0.115 0.02 0.06 0.09 0.09 0.10 Sb 0.24 0.302 0.159 0.78 0.64 0.23 0.16 0.25 Cs 53.30 105 51.9 32.40 52.70 44.30 52.80 46.40 Ba 14.60 36.2 198 387.00 274.00 185.00 225.00 220.00 La 12.10 13.3 37.5 37.30 42.80 25.70 30.80 34.60 Ce 28.10 29.2 81.8 72.30 87.80 55.10 65.10 74.00 Pr 3.63 3.58 10.4 8.29 10.90 7.01 8.07 9.15 Nd 14.60 13.6 38 29.70 41.20 26.30 30.50 34.30 Sm 4.25 3.2 8.26 5.75 8.49 5.38 6.44 7.08 Eu 0.09 0.154 0.337 0.71 0.65 0.38 0.50 0.44 Gd 3.66 2.51 7.16 4.88 6.35 4.55 4.95 6.13 Tb 0.77 0.445 1.28 0.88 1.20 0.71 0.78 0.86 Dy 4.76 2.95 7.29 4.95 6.57 3.60 4.45 4.97 Ho 0.90 0.566 1.43 1.00 1.22 0.66 0.71 0.87 Er 2.43 1.46 4.17 2.47 3.03 1.91 1.97 2.22 Tm 0.49 0.265 0.708 0.43 0.54 0.31 0.30 0.34 Yb 3.06 1.96 4.01 3.16 3.75 2.09 2.35 2.21 Lu 0.39 0.234 0.56 0.38 0.47 0.28 0.30 0.32 Hf 3.15 2.49 5.79 3.76 6.08 4.46 4.16 4.90 Ta 7.35 4.55 4.69 4.38 8.20 3.63 4.28 4.37 W 9.02 5.73 2.26 10.40 12.30 3.47 3.46 3.40 Re 0.01 0.004 0.004 < 0.002 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 Tl 3.51 3.42 4.27 3.18 3.31 2.47 2.72 2.80 Pb 34.00 38 71.3 72.80 48.00 43.00 52.70 50.80 Bi 4.63 4.72 1.4 0.19 3.34 5.88 3.45 4.53 U 38.60 16.4 37.7 18.50 20.90 19.90 12.20 25.70 Th 19.80 13.1 23.2 35.30 46.40 27.70 32.20 37.30 Rb/Sr 51.69 30.27 15.21 6.05 6.62 6.93 8.09 8.52 Rb/Ba 43.90 15.39 3.05 1.28 1.92 2.23 2.15 2.22 Th/U 0.51 1.25 1.63 1.91 2.22 1.39 2.64 1.45 REE 79.23 73.42 202.91 172.20 214.98 133.97 157.22 177.48 TZr/℃ 731 722 770 746 779 776 772 781 δEu 0.07 0.16 0.13 0.40 0.26 0.23 0.26 0.20 (La/Yb)N 2.67 4.57 6.30 7.96 7.69 8.29 8.84 10.56 (Gd/Yb)N 0.97 1.03 1.44 1.25 1.37 1.76 1.70 2.24 (La/Sm)N 1.79 2.61 2.86 4.08 3.17 3.00 3.01 3.07 LREE/HREE 1.50 2.45 2.58 3.43 3.34 3.55 3.78 3.91 Rb/Nb 23.74 32.96 21.34 19.60 14.82 25.65 25.69 26.87 Zr/Hf 19.17 24.86 22.28 26.86 22.86 28.25 29.33 27.55 Nb/Ta 3.67 3.71 6.03 5.75 4.33 4.44 4.39 4.16 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素为10-6;A/CNK=Al2O3/(CaO+Na2O+K2O)(分子比);A/NK=Al2O3/(Na2O+ K2O)(分子比);TZr计算方法据参考文献[19-20] 表 3 张家花岗岩Sr-Nd同位素
Table 3 Sr-Nd isotopic composition of the Zhangjia granite
样品号 年龄/Ma Rb/10-6 Sr/10-6 87Rb/86Sr 87Sr/86Sr (87Sr/86Sr)i Sm/10-6 Nd/10-6 147Sm/144Nd 143Nd/144Nd εNd(t) T2DM/Ma ZJ-14-2A 218 557 18.4 90.17 0.993900 0.714337 3.20 13.60 0.1380 0.511879 -13.2 2066 ZJ-14-2B 218 648 39.7 47.19 0.941663 0.795342 8.72 38.50 0.1370 0.511869 -13.3 2080 ZJ-14-05 218 436 60.7 20.80 0.790881 0.726397 5.39 25.70 0.1265 0.511791 -14.6 2179 ZJ-14-6B 218 480 51.6 26.95 0.806504 0.722943 5.00 24.00 0.1260 0.511784 -14.7 2189 -
北京第三研究所, 广西核工业第十地质队. 苗儿山产铀岩体年龄[C]//第二届全国同位素地质会议论文集. 北京: 地质出版社, 1974: 1-308. 徐伟昌, 张洪运.苗儿山岗岩复式岩基年代学研究的进展及时代划分方案[J].岩石学报, 1994, 10(3):330-334. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/3ffddb0831126edb6e1a102a-3.html 谢晓华, 陈卫锋, 赵葵东, 等.桂东北豆乍山花岗岩年代学与地球化学特征[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(6):1302-1312. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/YSXB200806014.htm 石少华. 桂北沙子江铀矿床矿床地球化学[D]. 中国科学院地球化学研究所博士学位论文, 2011: 1-116. 胡欢, 王汝成, 陈卫锋, 等.桂东北豆乍山产铀花岗岩的铀源矿物研究[J].地质论评, 2012, 58(6):1056-1068. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91067X/201206/44159660.html 胡欢, 王汝成, 陈卫锋, 等.桂东北豆乍山产铀花岗岩热液活动时限的确定与铀成矿意义[J].科学通报, 2013, 36:3849-3858. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KXTB201336014.htm 方适宜, 范立亭, 陶志军, 等.豆乍山产铀花岗岩中暗色残留体特征及其成因[J].铀矿地质. 2014, 30(4):2012-2018. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_ykdz201404004 孙涛, 王志成, 陈培荣, 等.南岭地区晚中生代花岗岩成因与岩石圈动力学演化[M].北京:科学出版社, 2007:504-519. Anderson T. Correction of common Pb in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192:59-79. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00195-X
Liu X M, Gao S, Diwu C R. Simultaneous in situ determination of U-Pb age and trace elements in zircon by LA-ICP-MS in 20μm spot size[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2007, 52(9):1257-1264. doi: 10.1007/s11434-007-0160-x
Ludwig K R. User's Manual for Isoplot 3.0:a geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J]. Berkeley Geochron Center, Special, Publication, 2003:41-71. http://www.worldcat.org/title/users-manual-for-isoplot-300-a-geochronological-toolkit-for-microsoft-excel/oclc/695595118
周佐民, 谢才富, 孙文良, 等.江西乐安咸口花岗岩体的锆石LAICP-MS定年及构造意义[J].地质学报, 2015, 89(1):83-98. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZXE201501007.htm 王军, 万传辉, 赖湘濡, 等.粤北下庄矿田太平庵地区闪长玢岩的发现及其年代学特征[J].地质论评, 2016, C1:335-336. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10491-1012446513.htm 陈金勇, 范洪海, 王生云, 等.纳米比亚欢乐谷地区白岗岩型铀矿成矿物质来源分析[J].地质学报, 2016, 90(2):219-230. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201602002 王志成. 南岭湘桂段中生代壳源岩浆作用和铀成矿作用[D]. 南京大学博士学位论文, 2003. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y802121 吴元保, 郑永飞.锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J].科学通报, 2004, 49(16):1589-1604. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002 Belousova E, Griffin W, O'Reilly S, et al. Igneous zircon:trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type[J]. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol, 2002, 143(5):602-622. doi: 10.1007/s00410-002-0364-7
李妩巍, 王敢, 陈卫锋, 等.香草坪花岗岩体年代学和地球化学特征[J].铀矿地质, 2010, 26(4):215-221. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/91728X/201004/34412901.html Watson E B. Zicron saturation in felsic liquids:Experimental data and applications to trace element geochemistry[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1979, 70:407-419. doi: 10.1007/BF00371047
Watson E B, Hamson T M. Zicron saturation revisited:Temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth Planetary Science Letters, 1983, 64:295-304. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(83)90211-X
Middlemost E A K. Naming material in the magama/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Sci. Rev., 1994, 37:215-224. doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(94)90029-9
Peccerillo R, Taylor S R. Geochemistry of eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contrib. Mineral Petrol., 1976, 58:63-81. doi: 10.1007/BF00384745
Maniar P D, Piccolli P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoid[J]. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull., 1989, 101:635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
Nakada S, Takahashi M. Regional variation in chemistry of the Miocene intermediate to felsic magmas in the Outer Zone and the Setouchi province of southwest Japan[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of Japan, 1979, 85:57125-57182. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/110003022983
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and proeesses[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in Ocean Basins. London: Geological Society Publications, 1989, 42: 313-345.
Boynton W V. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite studies[C]//Henderson P. Rare earth element geochemistry. Elsevier, 1984: 63-114.
孙涛, 周新民, 陈培荣, 等.南岭东段中生代强过铝花岗岩成因及其大地构造意义[J].中国科学(D辑), 2003, 33(12):1209-1218. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/yj/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_zgkx-cd200312010 Gao S, Luo T C, Zhang B R. Structure and composition of the Continental crust in east China[J]. Science in China (Seires D), 1999, 42(2):129-140. doi: 10.1007/BF02878511
Rudnick R, Land Fountain D M. Nature and composition of the continental crust:A lower crustal Perspective[J]. Review of Geophysics, 1995, 33:267-309. doi: 10.1029/95RG01302
赵伦山, 张本仁.地球化学[M].北京:地质出版社, 1988:1-404. Zhao K D, Jiang S Y, Ling H F, et al. Late Triassic U-bearing and barren granites in the Miao'ershan batholith, South China:Petrogenetic discrimination and exploration significance[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 77:260-278. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.02.016
Janh B M, Wu F Y, Lo C H, et al. Crust-mantle interaction induced by deep subduction of the continental crust[J]. Chem. Geol., 1999, 157:119-146. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(98)00197-1
沈渭洲, 朱金初, 刘昌实, 等.华南基底变质岩的Sm-Nd同位素及其对花岗岩类物质来源的制约[J].岩石学报, 1993, 9:115-124. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1993.02.001 Sylvester P J. Post-collisional strongly peraluminous granites[J]. Lithos, 1998, 45(1/4):29-44. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493798000243
舒良树.华南构造演化的基本特征[J].地质通报, 2012, 31(7):1035-1053. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20120703&flag=1 谢才富, 朱金初, 丁式江, 等.海南尖峰岭花岗岩体的形成时代、成因及其与抱伦金矿的关系[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(10):2498-2508. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/create_pdf.aspx?file_no=2006010268&journal_id=ysxb&year_id=2006 周新民.对华南花岗岩研究的若干思考[J].高校地质学报, 2003, 9(4):556-565. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200304008.htm 郭福祥.中国南方中新生代大地构造属性和南华造山带褶皱过程[J].地质学报, 1998, 72(1):22-23. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95080X/199801/3014189.html Carter A, Roques D, Bristow C. Understanding Mesozoic accre-tion in Southeast Asia:Significance of Triassic thermotectonism (Indosinian orogeny)in Vietnam[J]. Geology, 2001, 29:211-214. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0211:UMAISA>2.0.CO;2
于津海, 王丽娟, 王孝磊, 等.赣东南富城杂岩体的地球化学和年代学研究[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(6):1441-1456. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/create_pdf.aspx?file_no=200706137&journal_id=ysxb 舒斌, 王平安, 李中坚, 等.海南抱伦金矿的成矿时代研究及其意义[J].现代地质, 2004, 18(3):316-320. https://t.docin.com/p-1123062754.html 邓希光, 陈志刚, 李献华, 等.桂东南地区大容山-十万大山花岗岩带SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年[J].地质论评, 2004, 50(4):426-432. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/DZLP200404016.htm 邱检生, McInnes B I A, 徐夕生, 等.赣南大吉山五里亭岩体的锆石LA-ICPMS定年及其与钨成矿关系的新认识[J].地质论评, 2004, 50(2):125-133. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4886693 张文兰, 华仁民, 王汝成, 等.江西大吉山五里亭花岗岩单颗粒锆石U-Pb同位素年龄及其地质意义[J].地质学报, 2004, 78(3):352-358. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4876452 徐夕生, 邓平, O'eifly S Y.华南贵东杂岩体单颗粒锆石激光探针ICPMS U-Pb定年及其成岩意义[J].科学通报, 2003, 48(12):1328-1334. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.12.020 Li X H, Li Z X, Li W X, et al. Initiation of the Indosinian orogeny in South China:Evidence for a Permian magmatic arc on Hainan Island[J]. J. Geo., 2006, 114:341-353. doi: 10.1086/501222
谢才富, 朱金初, 赵子杰, 等.三亚石榴霓辉石正长岩的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄:对海南岛海西-印支期构造演化的制约[J].高校地质学报, 2005, 11(1):47-57. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200304008.htm 谢才富, 朱金初, 丁式江, 等.琼中海西期钾玄质侵入岩的厘定及其构造意义[J].科学通报, 2006, 51(16):1944-1954. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2006.16.014 Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25:956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
Luo J C, Hu R Z, Shi S H. Timing of Uranium Mineralization and Geological Implications of Shazijiang Granite-Hosted Uranium Deposit in Guangxi, South China:New Constraint from Chemical U-Pb Age[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2015, 26(6):911-919. doi: 10.1007/s12583-015-0542-y




 下载:
下载: