Baddeleyite U-Pb geochronology of Maliucun diabase from Tangwangzhai-Yangtianwo syncline in the northern segment of Longmen Mountain, Sichuan, and its geological significance
-
摘要:
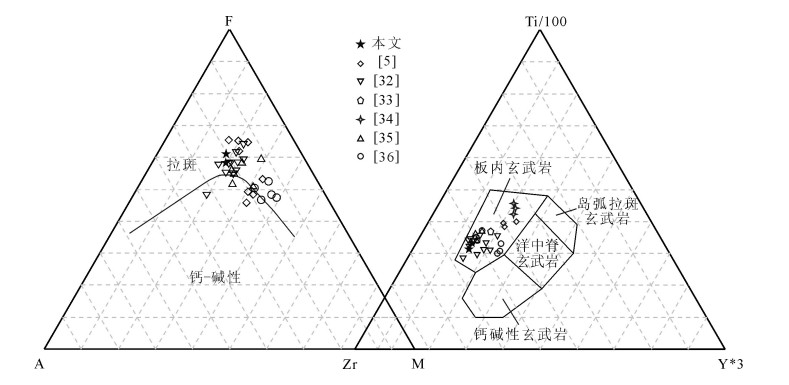
为确定龙门山北段唐王寨-仰天窝向斜内发育的NE向辉绿岩脉的侵位时代、构造背景,探讨其是否与峨眉山地幔柱活动相关,对向斜内麻柳村处的辉绿岩样品进行了斜锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb同位素测年、主量和微量元素分析。结果表明,辉绿岩斜锆石U-Pb同位素年龄为261.1±1.8Ma;属于高钛型拉斑玄武岩,高铝(13.39%~14.02%)、高铁(13.88%~14.67%)、低镁(4.43%~4.56%),富集大离子亲石元素和轻稀土元素,Nb/La=0.84~0.85、Th/Ta=2.40~2.45、Ta/Hf>0.25,具有与洋岛玄武岩相似的地球化学特征,Nb-Ta略微负异常,暗示其可能源于富集型地幔并受到少量陆壳物质混染,形成于大陆板内环境。与峨眉山玄武岩质火成岩对比发现,两者具有高度一致的形成时代及相似的地球化学特征。据此认为,该区辉绿岩为峨眉山地幔柱活动的产物,峨眉山玄武质岩浆的活动已经波及至龙门山北段及川西北地区,可能影响了该区的生物环境及油气成藏。
Abstract:To confirm the emplacement age and tectonic setting of the NE-striking diabase dykes developed in the Tangwangzhai-Yangtianwo syncline of northern Longmen Mountain as well as to reveal whether or not the diabases were associated with the Emeishan mantle plume activity, the authors investigated U-Pb baddeleyite age, major element content and trace element abundances of the diabase samples collected from the Maliucun area within the syncline. The results showed that the diabases yielded a baddeleyite concordant U-Pb age of 261.1±1.8Ma; they belong to the high-Ti (Ti/Y>500) tholeiitic series, and are characterized by high Al (13.39%~14.02%), high Fe (13.88%~14.02%), and low Mg (4.43%~4.56%) values as will as enrichment of the large iron lithophile ele-ments and light rare earth elements; coupled with the data Nb/La (0.84~0.85), Th/Ta (2.40~2.45), and Ta/Hf>0.25, the features of the diabases are similar to the geochemical characteristics of ocean island basalt; the slightly negative anomaly of Nb-Ta indicates that they were probably derived from the enriched mantle with minor contamination by crust materials. A comparison with the Emeishan basaltic rocks shows that they are consistent highly with each other in ages and geochemical characteristics. It is considered that the diabases were formed by Emeishan mantle plume activity and the activity of Emeishan basaltic magma was spread to the northern section of Longmen Mountain and northwestern Sichuan, which had an impact on the biotic environment and hydrocarbon accumulation of this area.
-
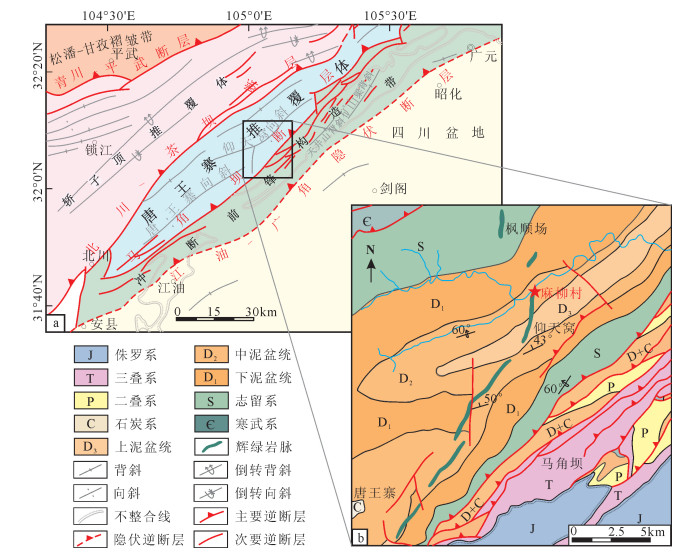
阿尔金山特殊的大地构造属性使该地区的基础地质、区域构造演化、地质找矿研究成为最近十几年的研究热点[1-8]。阿尔金北缘地区发育红柳沟-拉配泉蛇绿混杂岩带,代表了北阿尔金曾经存在古洋盆(北阿尔金洋)。喀腊大湾地区位于蛇绿混杂岩带中东段,区内广泛发育浅变质火山-沉积岩组合,是研究阿尔金北缘构造演化的重要窗口。有学者曾对该火山-沉积岩系内岩浆岩的时代做过研究,得到了早古生代存在岩浆活动的认识[9-12]。近年来根据碎屑岩的物质组成,特别是碎屑锆石的年龄来限定碎屑物源、沉积时代和沉积环境已发展成为盆地与造山带研究的重要方法。所以对研究区北部的沉积岩系开展碎屑锆石年代学的研究,不仅可以限定该地层的形成时代,还有利于正确认识阿尔金喀腊大湾地区早古生代的构造演化历史。因此,本文选择喀腊大湾沟沉积岩系中的砾岩进行高精度的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年,结合古生代区域地质背景及邻区早古生代岩浆活动分析,对该沉积岩系的时代、物质来源和构造属性进行初步探讨,同时为北阿尔金和北祁连演化的相似性提供进一步依据。
1. 区域地质背景
阿尔金山是青藏高原北缘的重要组成部分,向东与北祁连相连,西侧插入西昆仑。从大地构造看,阿尔金山南北两侧分别以阿尔金南缘断裂(阿尔金主断裂)和阿尔金北缘断裂(西北缘断裂)2条深大断裂为界,分割了柴达木地块、昆仑-祁连造山带和塔里木地块。阿尔金山东段喀腊大湾地区位于北东向阿尔金走滑断裂北侧与东西向阿尔金北缘断裂所夹持的索尔库里走廊北侧区域,属于阿尔金山山脉中金雁山的西段。
研究区所在的阿尔金北缘地区发育红柳沟-拉配泉蛇绿混杂岩带,走向近东西,宽约20km,主要由蛇绿岩、具复理石特征的深海-半深海碎屑岩、碳酸盐岩和变质岩组成[13]。多位学者研究认为,红柳沟-拉配泉裂谷带在震旦纪晚期—早古生代早期经历了扩张,晚寒武世开始发生板块俯冲作用,至中奥陶世发生板块碰撞作用[14-18]。晚中生代以来阿尔金断裂带发生了大规模的左行走滑[19-20]。研究区内构造线以近东西向为特征(图 1),主干断裂主要为东西向,一级断裂有喀腊达坂断裂和阿尔金北缘断裂(阿北断裂),呈东西向横贯南北两侧;二级断裂有白尖山断裂,呈东西向贯穿中北部;次级小断裂呈北东东向和北西向,断裂性质以压性、压扭性为主。其中阿尔金北缘断裂规模巨大,出露于研究区北部,是太古宇与下古生界奥陶系的界线。喀腊达坂断裂位于研究区南部,是下古生界与震旦系(西段)或下古生界与新生界(东段)的界线。白尖山断裂位于研究区中北部的白尖山南侧,该断裂部分为卓阿布拉克组与斯米尔布拉克组的界线。研究区地层属于塔里木地层区中塔南地层分区的阿尔金山地层小区①[21],根据已有的火山-沉积岩系测年资料[6],区内自老到新依次出露太古界达格拉格布拉克组(Ardg)的一套中、高温变质的高角闪岩相-麻粒岩相变质岩系;中元古界蓟县系金雁山组(Jx j)碳酸盐岩;下古生界卓阿布拉克组(Є3-Ozh)、斯米尔布拉克组(Є3-Os);上石炭统因格布拉克组(C3y),主要由石英砂岩、砂砾岩、粉砂岩组成;古近系渐新统下干柴沟组(E3g),新近系中新统上干柴沟组(N1g)、中新统下油砂山组(N1y)和第四系(Q)。
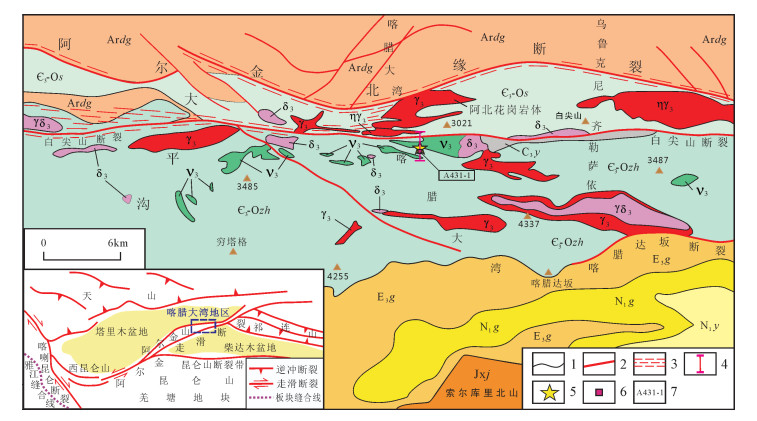
![]() 图 1 阿尔金山东段喀腊大湾地区地质构造图N1y—中新世下油砂山组;N1g—中新世上干柴沟组;E3g—渐新世下干柴沟组;C3y—上石炭统因格布拉克组;Є3-Os—早古生界斯米尔布拉克组;Є3-Ozh—早古生界卓阿布拉克组;Jx j—金雁山组;Ardg—太古宇达格拉格布拉克组;δ3—早古生代闪长岩;γδ3—早古生代花岗闪长岩;γ3—早古生代花岗岩;ηγ3—早古生代似斑状二长花岗岩;v3—早古生代辉长岩;1—地质界线;2—断裂;3—韧脆性变形带;4—火山-沉积岩系剖面位置;5—图 2、图 4沉积岩系剖面位置;6—采样点;7—样品编号Figure 1. Map of geological structure in Kaladawan area, eastern part of Altun Mountains
图 1 阿尔金山东段喀腊大湾地区地质构造图N1y—中新世下油砂山组;N1g—中新世上干柴沟组;E3g—渐新世下干柴沟组;C3y—上石炭统因格布拉克组;Є3-Os—早古生界斯米尔布拉克组;Є3-Ozh—早古生界卓阿布拉克组;Jx j—金雁山组;Ardg—太古宇达格拉格布拉克组;δ3—早古生代闪长岩;γδ3—早古生代花岗闪长岩;γ3—早古生代花岗岩;ηγ3—早古生代似斑状二长花岗岩;v3—早古生代辉长岩;1—地质界线;2—断裂;3—韧脆性变形带;4—火山-沉积岩系剖面位置;5—图 2、图 4沉积岩系剖面位置;6—采样点;7—样品编号Figure 1. Map of geological structure in Kaladawan area, eastern part of Altun Mountains2. 沉积岩系夹层地层剖面
早古生界卓阿布拉克组和斯米尔布拉克组火山-沉积岩系分布于研究区的中部,呈东西向延伸,厚度巨大,在南北两侧分别以喀腊达坂断裂和阿尔金北缘断裂与新生界及太古宇呈断层接触。底部与蓟县系浅变质岩呈角度不整合接触或断层接触,顶与奥陶系砾岩整合接触。东部喀腊大湾地区斯米尔布拉克组为一套火山-沉积岩系,厚度1139~ 3232m。其中火山岩以中基性火山岩为主,由于临近阿北断裂带并分布于阿北断裂带与白尖山断裂之间,受后期构造的强烈改造,火山-沉积岩几乎全部呈直立状态,并经历低绿片岩相动力变质作用。卓阿布拉克组也是一套火山-沉积岩系,厚562~ 1876m。其中火山岩在北部以中基性火山岩为主,中南部以中酸性火山岩为主。虽然发生一定程度构造变形,但是比斯米尔布拉克组构造变形要弱得多,变质作用以低绿片岩相为特点,变形变质作用较低,火山喷发-沉积旋回较清楚,因此作为岩性研究剖面和定年样品的主要采样点。
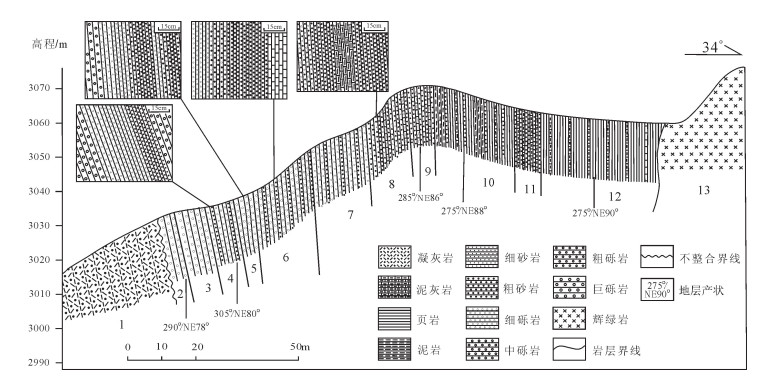
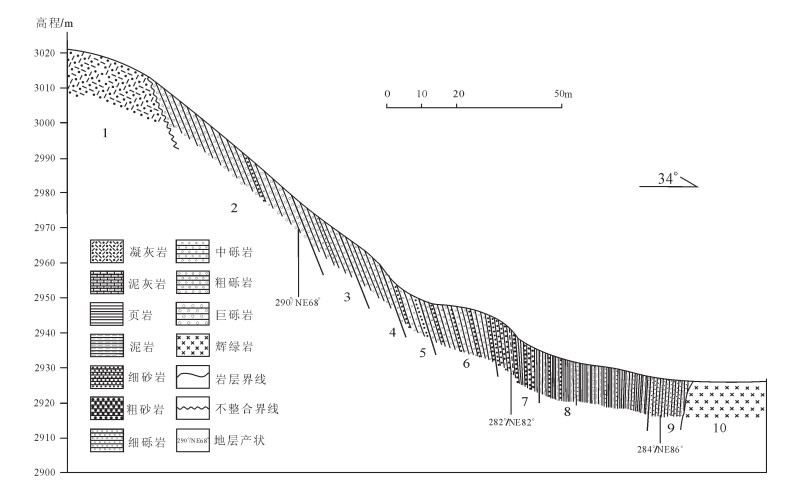
在阿尔金北缘断裂南侧4km的3021高地西南侧的喀腊大湾沟东剖面,发育156m厚的沉积岩系夹层,夹层以南为火山岩,以北为辉长岩体(图 2)。沉积岩剖面南段为砾岩,不整合覆盖于安山质火山岩之上,近南端砾石粒径达5~10cm,局部最大达20cm,向北20~30m后,砾石的粒径减小,为2~ 5cm,再向北变化为含砾砂岩、砂岩,接近辉长岩体的位置出露粉砂岩、泥岩甚至泥灰岩(图 2)。同时在大旋回序列内,还存在次一级的微层序列变化。如在层4内部,发育厚度为40~50cm的微层序列,岩性从巨-粗砾岩到细砾岩,再到砂岩(图 3-a);在层5内部,微层序列岩性从中-粗砾岩,到细砾岩、含砾砂岩,再到粗砂岩、中砂岩、细砂岩(图 2、图 3-b);而在层6内部,微层序列岩性从细砾岩、含砾砂岩,到粗砂岩、中砂岩,再到粉砂岩、泥岩、泥灰岩;该火山岩中沉积岩夹层的沉积序列特点非常清楚地反映了沉积层自南向北的变化特点。同时,喀腊大湾沟西侧剖面,发育126m的沉积岩系夹层,沉积岩夹层以南为火山岩,以北为辉长岩体。剖面南段为砾岩,不整合覆盖于安山质火山岩之上,近南端砾石粒径达5~10cm,局部最大达20cm,往北砾石的粒径减小,为2~5cm,再向北变化为含砾砂岩、砂岩;110m(斜距)后,则主要出露粉砂岩、泥岩甚至泥灰岩(图 4)。同时在大旋回序列内,也存在次一级的微层序列变化。该砂砾岩层(砾岩占多数)向东断续延伸可达近10km,其南侧为具有典型枕状构造的玄武岩,砂砾岩层不整合覆盖于枕状玄武岩之上。
3. 样品和测试方法
3.1 测试方法
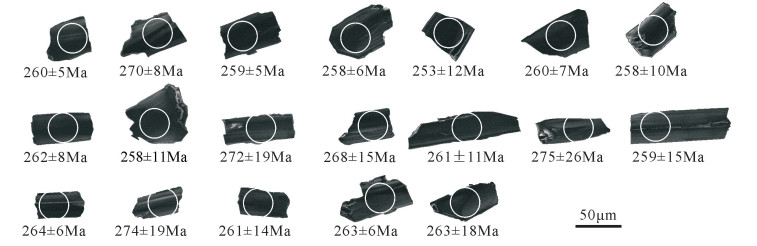
本次采集的样品为北阿尔金喀腊大湾地区北部卓阿布拉克组中沉积岩系的砾岩,采样点GPS坐标为北纬39°08′04.68″、东经91°41′56.91″(图 1),野外编号A431-1,对其进行LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄测试。锆石的分选工作由河北省廊坊市地质勘探技术服务有限公司完成,采用常规方法将样品粉碎,经人工水淘洗分选出锆石,在实体双目镜下挑选出晶形和透明度较好的锆石颗粒作为测定对象。将锆石颗粒粘在双面胶上,然后用无色透明的环氧树脂固定,待环氧树脂充分固化后,对其表面进行抛光至锆石内部暴露,然后进行锆石显微照相(反射光和透射光)、阴极发光(CL)图像研究及LAICP-MS测试分析。锆石原位U-Th-Pb同位素年龄分析在吉林大学东北亚矿产资源评价国土资源部重点实验室完成,测试仪器为美国Agilent公司7900型四极杆等离子质谱仪和激光剥蚀系统(COMPExPro)联机,激光器为193nmArF准分子激光器,激光剥蚀束斑直径为32μm,剥蚀样品的深度为20~40μm。测试过程中使用标准锆石91500(206Pb/238U年龄为1065.4±0.6Ma)作为外标进行同位素比值校正,以标准锆石GJ(206Pb/238U年龄为600Ma)控制盲样。元素含量采用美国国家标准物质局人工合成硅酸盐玻璃NIST SRM610作为外标,29Si作为内标进行校正。实验数据采集选用一个质量峰一点的跳峰方式,每完成7个待测样品点,测定一次标样。样品的同位素比值及元素含量的数据处理采用中国地质大学刘勇胜教授研发的ICPMSDataCal7.7程序,年龄计算及U-Pb谐和图的绘制采用Isoplot3.0程序[22],单个点的同位素比值及年龄误差均为1σ。
3.2 测试结果
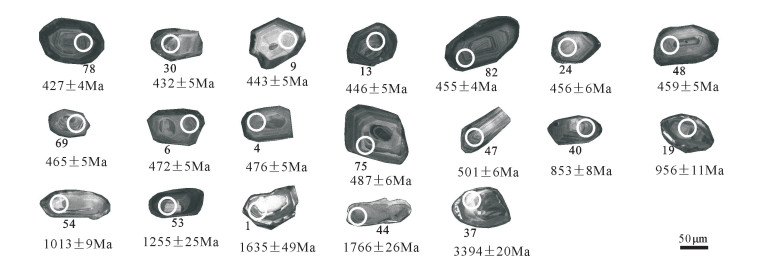
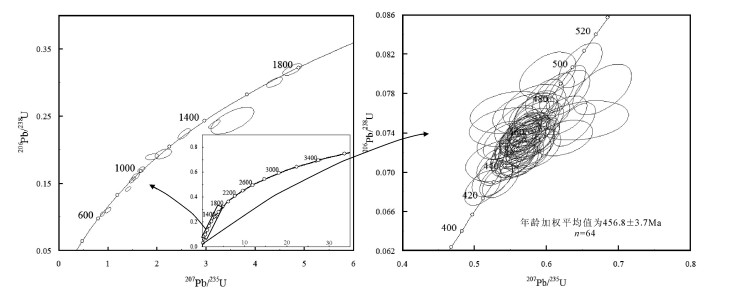
对所采样品共测试了84颗锆石,碎屑锆石阴极发光图像见图 5,分析结果列于表 1。采用谐和度高的数据点统计,其中谐和度定义为206Pb/238U与207Pb/235U的表面年龄之比,剔除谐和度小于90%的数据,可得到80个数据点。对于年龄大于1000Ma的锆石,采用207Pb/206Pb表面年龄,小于1000Ma的锆石,采用更精确的206Pb/238U表面年龄。在U-Pb年龄谐和图中,绝大多数数据点都落在谐和线上或其附近,表明样品中的锆石U-Pb体系基本保持封闭,绝大多数锆石具有谐和年龄(图 6)。
表 1 卓阿布拉克组砾岩(A431-1)碎屑锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb分析结果Table 1. LA-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb isotope composition of zircons from conglomerate in sedimentary series of Zhuo'abulake Formation点号 含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma 谐和度 Th U 207Pb/206Pb ±1σ 207Pb/235U ±1σ 206Pb/238U ±1σ 207Pb/206Pb ±1σ 207Pb/235U ±1σ 206Pb/238U ±1σ 1 159 253 0.63 0.1005 0.0029 3.541 0.180 0.2433 0.0081 1635 49 1536 40 1404 42 90% 2 952 1042 0.91 0.0567 0.0013 0.587 0.015 0.0751 0.0009 480 50 469 10 467 5 99% 3 950 1124 0.85 0.0548 0.0014 0.602 0.016 0.0799 0.0010 406 56 478 10 495 6 96% 4 906 1226 0.74 0.0550 0.0014 0.583 0.018 0.0767 0.0009 413 62 467 11 476 6 97% 5 2413 1768 1.36 0.0729 0.0019 1.903 0.057 0.1893 0.0019 1010 55 1082 20 1117 10 96% 6 675 1170 0.58 0.0552 0.0019 0.579 0.022 0.0759 0.0009 420 76 464 14 472 5 98% 7 814 907 0.90 0.0524 0.0020 0.549 0.023 0.0761 0.0009 302 87 445 15 473 5 93% 8 1460 1196 1.22 0.0533 0.0020 0.547 0.022 0.0746 0.0008 343 90 443 15 464 5 95% 9 543 525 1.03 0.0554 0.0021 0.539 0.021 0.0712 0.0009 428 83 437 14 443 5 98% 10 535 1335 0.40 0.0585 0.0016 0.679 0.020 0.0843 0.0009 550 61 526 12 522 5 99% 11 1037 1380 0.75 0.0565 0.0014 0.572 0.016 0.0734 0.0008 472 54 460 10 456 5 99% 12 1484 1990 0.75 0.0565 0.0012 0.567 0.013 0.0728 0.0009 472 42 456 9 453 5 99% 13 2444 2394 1.02 0.0565 0.0010 0.559 0.012 0.0716 0.0008 472 45 451 8 446 5 98% 14 893 1068 0.84 0.0570 0.0012 0.578 0.014 0.0734 0.0009 500 79 463 9 456 5 98% 15 591 705 0.84 0.0575 0.0015 0.582 0.015 0.0735 0.0008 522 57 466 9 457 5 98% 16 500 660 0.76 0.0667 0.0014 1.011 0.023 0.1101 0.0016 828 44 709 12 673 9 94% 17 1004 1087 0.92 0.0574 0.0011 0.581 0.012 0.0733 0.0008 506 44 465 8 456 5 98% 18 2682 2256 1.19 0.0578 0.0009 0.627 0.011 0.0785 0.0010 520 40 494 7 487 6 98% 19 487 683 0.71 0.0708 0.0014 1.565 0.032 0.1599 0.0019 954 34 957 13 956 11 99% 20 912 962 0.95 0.0579 0.0013 0.626 0.014 0.0780 0.0010 524 48 493 9 484 6 98% 21 278 1785 0.16 0.0702 0.0011 1.507 0.025 0.1551 0.0018 933 31 933 10 929 10 99% 22 1002 1252 0.80 0.0578 0.0012 0.580 0.013 0.0725 0.0008 520 48 465 8 451 5 97% 23 1473 1442 1.02 0.0964 0.0013 3.175 0.047 0.2379 0.0027 1567 25 1451 12 1376 14 94% 24 747 1490 0.50 0.0563 0.0010 0.571 0.012 0.0732 0.0009 465 36 459 8 456 6 99% 25 1442 1540 0.94 0.0566 0.0010 0.565 0.010 0.0722 0.0008 476 39 455 7 450 5 98% 26 543 638 0.85 0.0587 0.0014 0.585 0.014 0.0723 0.0008 554 52 468 9 450 5 96% 27 892 1133 0.79 0.0565 0.0011 0.576 0.011 0.0741 0.0008 472 47 462 7 461 5 99% 28 1364 2145 0.64 0.0553 0.0010 0.566 0.011 0.0741 0.0008 433 39 456 7 461 5 98% 29 740 1122 0.66 0.0536 0.0011 0.541 0.012 0.0731 0.0008 354 46 439 8 455 5 96% 30 613 1349 0.45 0.0549 0.0011 0.525 0.012 0.0693 0.0007 409 46 429 8 432 5 99% 31 965 1398 0.69 0.0557 0.0011 0.585 0.012 0.0762 0.0009 439 44 468 8 473 5 98% 32 809 959 0.84 0.0553 0.0010 0.562 0.011 0.0737 0.0008 433 38 453 7 458 5 98% 33 1734 1855 0.93 0.0553 0.0010 0.563 0.011 0.0736 0.0008 433 39 454 7 458 5 99% 34 1272 1470 0.87 0.0554 0.0011 0.557 0.012 0.0729 0.0008 428 44 450 8 453 5 99% 35 526 1376 0.38 0.1595 0.0022 10.10 0.161 0.4582 0.0051 2450 23 2444 15 2432 23 99% 36 2497 1976 1.26 0.0556 0.0009 0.569 0.010 0.0740 0.0008 435 37 457 7 460 5 99% 37 963 845 1.14 0.2857 0.0037 27.47 0.485 0.6932 0.0084 3394 20 3400 17 3395 32 99% 38 1010 1190 0.85 0.0559 0.0012 0.558 0.012 0.0725 0.0007 456 48 450 8 451 4 99% 39 979 1019 0.96 0.0566 0.0011 0.555 0.011 0.0713 0.0007 476 43 448 7 444 4 98% 40 388 1457 0.27 0.0725 0.0010 1.417 0.023 0.1414 0.0014 1011 29 896 10 853 8 95% 41 782 1545 0.51 0.0555 0.0010 0.550 0.011 0.0717 0.0008 432 41 445 7 447 5 99% 42 1027 1033 0.99 0.0577 0.0013 0.578 0.014 0.0726 0.0008 517 44 463 9 452 5 97% 43 98 95 1.03 0.0810 0.0027 2.132 0.070 0.1938 0.0030 1233 66 1159 23 114 16 98% 44 796 997 0.80 0.1080 0.0015 4.760 0.079 0.3192 0.0036 1766 26 1778 14 178 17 99% 45 800 811 0.99 0.0548 0.0013 0.535 0.013 0.0708 0.0008 467 52 435 9 441 5 98% 46 749 1378 0.54 0.0567 0.0011 0.578 0.012 0.0738 0.0008 480 41 463 8 459 5 99% 47 1358 1831 0.74 0.0582 0.0011 0.647 0.012 0.0809 0.0009 600 44 507 8 501 6 98% 48 1568 2276 0.69 0.0551 0.0010 0.561 0.010 0.0737 0.0008 417 39 452 7 459 5 98% 49 652 926 0.70 0.0554 0.0013 0.582 0.014 0.0758 0.0008 428 45 466 9 471 5 98% 50 887 1221 0.73 0.0568 0.0011 0.610 0.012 0.0779 0.0009 483 43 483 8 483 5 99% 51 820 1073 0.76 0.0562 0.0013 0.580 0.014 0.0745 0.0008 461 48 465 9 463 5 99% 52 819 896 0.91 0.0740 0.0029 0.837 0.041 0.0788 0.0010 1043 79 617 23 489 6 76% 53 1198 1520 0.79 0.0824 0.0011 2.558 0.051 0.2235 0.0032 1255 25 1289 15 130 17 99% 54 624 724 0.86 0.0717 0.0012 1.685 0.031 0.1701 0.0017 977 35 1003 12 101 9 99% 55 1971 2710 0.73 0.0592 0.0010 0.624 0.013 0.0758 0.0008 576 35 492 8 471 5 95% 56 969 970 1.00 0.0619 0.0020 0.651 0.026 0.0753 0.0008 672 64 509 16 468 5 91% 57 1040 1496 0.70 0.0561 0.0011 0.576 0.012 0.0744 0.0007 457 43 462 7 462 4 99% 58 1031 1371 0.75 0.0541 0.0011 0.558 0.012 0.0748 0.0008 376 46 451 8 465 5 96% 59 1110 1690 0.66 0.0557 0.0010 0.597 0.011 0.0776 0.0008 443 6 475 7 482 5 98% 60 2143 2191 0.98 0.0550 0.0009 0.548 0.010 0.0720 0.0007 413 37 444 7 448 4 99% 61 915 1141 0.80 0.0556 0.0011 0.583 0.011 0.0762 0.0008 435 44 466 7 473 5 98% 62 1024 877 1.17 0.0576 0.0013 0.566 0.012 0.0714 0.0008 522 48 456 8 445 5 97% 63 1234 1393 0.89 0.0654 0.0014 0.650 0.014 0.0721 0.0007 787 44 509 8 449 4 87% 64 657 1439 0.46 0.0546 0.0010 0.533 0.011 0.0704 0.0007 398 43 434 7 438 4 98% 65 932 1055 0.88 0.0615 0.0015 0.494 0.013 0.0578 0.0006 657 52 408 9 362 4 88% 66 867 861 1.01 0.0562 0.0012 0.554 0.012 0.0713 0.0008 461 48 448 8 444 5 99% 67 287 843 0.34 0.0621 0.0013 0.891 0.020 0.1041 0.0013 676 44 647 11 638 8 98% 68 900 1331 0.68 0.0571 0.0011 0.564 0.012 0.0712 0.0006 498 43 454 8 443 4 97% 69 1186 1476 0.80 0.0620 0.0012 0.639 0.012 0.0748 0.0009 676 43 501 7 465 5 92% 70 777 1011 0.77 0.0579 0.0013 0.575 0.013 0.0719 0.0008 524 48 461 8 448 5 97% 71 2299 2003 1.15 0.0561 0.0010 0.536 0.010 0.0691 0.0007 454 41 436 7 431 4 98% 72 490 1340 0.37 0.0612 0.0015 0.624 0.017 0.0735 0.0007 656 54 492 10 457 4 92% 73 763 4885 0.16 0.0773 0.0013 1.283 0.039 0.1171 0.0023 1128 33 838 17 714 14 84% 74 1564 2180 0.72 0.0559 0.0009 0.567 0.010 0.0734 0.0007 456 37 456 6 457 4 99% 75 1088 1301 0.84 0.0620 0.0012 0.677 0.017 0.0784 0.0010 676 41 525 10 487 6 92% 76 384 709 0.54 0.1059 0.0014 4.398 0.067 0.3001 0.0031 1731 24 1712 13 169 15 98% 77 1847 1759 1.05 0.0578 0.0011 0.590 0.012 0.0738 0.0007 524 43 471 7 459 4 97% 78 1262 1801 0.70 0.0540 0.0010 0.512 0.010 0.0684 0.0007 372 39 420 7 427 4 98% 79 757 784 0.97 0.0534 0.0014 0.539 0.014 0.0732 0.0008 346 59 438 9 456 5 95% 80 1123 1262 0.89 0.0558 0.0011 0.581 0.015 0.0748 0.0011 443 10 465 10 465 7 99% 81 528 924 0.57 0.0567 0.0013 0.562 0.012 0.0721 0.0007 483 50 453 8 449 4 99% 82 1134 2122 0.53 0.0563 0.0009 0.570 0.010 0.0732 0.0007 465 35 458 6 455 4 99% 83 2375 2213 1.07 0.0556 0.0010 0.530 0.009 0.0692 0.0007 435 41 432 6 432 4 99% 84 1009 1360 0.74 0.0551 0.0011 0.554 0.011 0.0729 0.0007 417 44 448 7 454 4 98% 研究表明,岩浆锆石的Th/U值一般高于0.4,变质成因锆石的Th/U值一般低于0.1[23-24],快速生长的变质锆石含有相对高的Th/U值[25-26]。所获取的碎屑锆石的Th/U值为0.16~1.36,其中75颗锆石的Th/U值高于0.4,占锆石总数的93.75%;其余5颗锆石的Th/U值介于0.16~0.38之间;碎屑锆石为浅黄色-无色透明,多呈卵形、短柱状、菱形锥状,以次棱角状-次圆状为主,被不同程度地磨圆。大多数颗粒具有韵律环带,锆石的粒径大多在50~ 140μm之间,长宽比介于2.0~1.0之间。通过Th/U值并结合锆石的形态特征,认为本次研究的锆石大部分为岩浆成因锆石。样品中所测得的最年轻和最古老的锆石年龄分别为427Ma和3394Ma。
从锆石年龄频谱图(图 7)和表 1可以看出,所获碎屑锆石年龄可以分为2组:427~522Ma、638~ 1766Ma。其中427~522Ma年龄组有65颗锆石,约占锆石总数的81%,它们构成年龄谱中最大的碎屑锆石群体,且年龄相对集中,呈现出仅有的最强烈的峰值特征,峰值年龄为456Ma,可进一步细分为495~522Ma(3颗)、472~487Ma(12颗)、468~441Ma(45颗)、427~438Ma(5颗)4个亚组;673~1766Ma的同位素年龄数据有14个,占锆石总数的17.5%,可以进一步分为2个亚组:638~1255Ma和1635~ 1766Ma,这些锆石颗粒年龄分布较分散,数量较少,因此该年龄段无明显的峰值。除这些主要锆石颗粒外,还存在2颗年龄大于2400Ma的锆石,其锆石同位素年龄数据分别为2450Ma、3394Ma。
4. 讨论
4.1 形成时代的限定
对于喀腊大湾地区这套火山-沉积岩系,早先的研究,包括20世纪80年代初期完成的1:20万索尔库里幅区域地质矿产调查①将区内的火山-沉积岩系确定为震旦系,90年代初地层清理后改为中元古界[21]。王小凤等[28]依据Gehrels等[9]在红柳沟和卡拉塔格两地沉积岩(砂岩)中的2个碎屑锆石的年龄(分别为482Ma和487Ma)将红柳沟—拉配泉一带大面积发育火山岩的中元古界划归为奥陶系;韩凤彬等[10]对喀腊大湾地区中酸性侵入岩进行SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄测定,得到卓阿布拉克组火山-沉积岩系内的侵入岩年龄为417~506Ma。陈柏林等[11]运用SHRIMP法对区内火山-沉积岩系南部的中酸性火山岩进行定年,获得477~485Ma的年龄。上述测年结果将该套火山-沉积岩系的时代限定在晚寒武世—奥陶纪末期。
由于地层的沉积时代比碎屑形成的时代年轻,因此碎屑锆石的年龄常被用来约束地层沉积时代的下限。本次研究对喀腊大湾地区卓阿布拉克组火山-沉积岩组合中的沉积岩夹层的砾岩开展碎屑锆石U-Pb定年,测年结果显示,测试样品中碎屑锆石最主要的年龄谱段为427~522Ma,约占锆石总数的81%,并呈现出最强烈的峰值年龄456Ma。最年轻的碎屑锆石谐和年龄为427±4Ma,为典型的岩浆锆石,其谐和度达98%,说明该地层的沉积时代晚于427Ma。该年龄段中最年轻的5个锆石颗粒的年龄加权平均值为432±3.8Ma。研究区内广泛分布的岩浆岩年龄普遍在417~520Ma之间,与碎屑锆石的427~522Ma年龄数据吻合。且沉积岩系西侧200m处的细粒闪长岩运用SHRIMP锆石U-Pb方法得到的测年结果为472.5±7.4Ma和458.1±5.4Ma②,该砾岩的碎屑锆石峰值年龄与该段地层岩浆岩的形成年龄也非常类似,表明它们可能属于岩浆岩再循环形成的碎屑锆石,是岩浆岩形成后不久剥蚀、近距离搬运、沉积的产物。该沉积岩系北侧阿北花岗岩体中的黑云母二长花岗岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄为427.3±5.7Ma,地球化学特征和成因特征显示是同碰撞阶段(挤压)向后碰撞阶段(伸展)转换的特征产物[29]。阿北花岗岩体中黑云母二长花岗岩的年龄与砾岩中最年轻的碎屑锆石年龄一致,说明在沉积时期该二长花岗岩已经被抬升至地表。阿北岩体中似斑状二长花岗岩的年龄为417±5Ma[10],但是在碎屑锆石的年龄谱中并没有反映出这一期岩浆事件,表明在该段地层沉积时年轻的似斑状二长花岗岩还未大面积出露。根据上述内容,本文将该卓阿布拉克组沉积岩系的形成时代大致限定在晚志留世—早泥盆世(410~427Ma)。由前文可知,该沉积岩系具有明显的陆相沉积环境特征,暗示此时洋盆已经闭合。北阿尔金造山带构造体制转换的时限为420~440Ma,420Ma之后发生了广泛的下地壳拆离与减薄[29],进入后碰撞阶段。表明沉积岩系形成时已经进入了造山阶段的晚期。
4.2 碎屑锆石年龄信息
4.2.1 早古生代年龄信息
本次砾岩层的测试样品中,共有65颗锆石同位素年龄属于早古生代(427~522Ma),占锆石总数的81%,说明早古生代形成的岩浆岩是该沉积岩系最主要的物源,同时也反映研究区在加里东期发生了构造岩浆热事件。样品碎屑锆石的峰值年龄为456Ma,表明喀腊大湾地区在该时期发生过强烈的岩浆活动。
敦煌地块在早古生代沿阿尔金北缘红柳沟—拉配泉一带发生俯冲碰撞,由此产生了一系列复杂的构造-岩浆活动。阿尔金构造带北缘红柳沟-拉配泉混杂岩带西段的红柳沟钾长花岗岩LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb年龄为500.3±1.2Ma,形成于与洋壳俯冲作用相关的陆缘火山弧环境[30];喀腊大湾以西120km的恰什坎萨依沟蛇绿混杂岩带中变玄武岩和枕状玄武岩年龄分别为508.3 ± 41~512 ± 30Ma、524.4 ± 44Ma和448.6 ± 3.3Ma[31-32];喀腊大湾以西15km处的阔什布拉克杂岩体中似斑状黑云母花岗岩的单颗粒TIMS锆石U-Pb年龄为443±5Ma[33]。喀腊大湾以西约200km的巴什考供地区的花岗岩类锆石年龄为435~475Ma[34-36];喀腊大湾一带出露的火山岩年龄在477~485Ma之间,显示活动大陆边缘(岛弧)构造环境,且也获得了喀腊大湾地区侵入岩岩体417~514Ma的锆石U-Pb年龄[10-11, 37]。
通过上述岩浆活动事件与早古生代年龄谱(427~522Ma)的对比可以看出,这些锆石年龄与阿尔金北缘俯冲带的俯冲碰撞产生岩浆活动具有较好的对应性,因此,红柳沟—拉配泉一带早古生代岩浆岩为沉积岩系提供了主要物源。同时,前人在北祁连也得到与北阿尔金近同期(420~510Ma)的岩浆岩年龄[38-40];吴才来等[41]对北祁连西段多个岩体进行研究后得到一系列岩体的年龄和地球化学数据,表明北祁连岩浆活动也包括501~512Ma、463~ 477Ma、424~435Ma三期重要的岩浆作用,且花岗岩具有火山岛弧性质;李兆等[42]对北祁连河流沉积物的碎屑锆石研究后指出,北祁连造山带最强的岩浆作用发生于新元古代—晚古生代早期(400~ 650Ma),主要记录了北祁连洋壳的俯冲消减、陆-陆碰撞及碰撞后的壳内岩浆作用过程。因此,北祁连与阿尔金北缘构造环境极相似,这也许意味着两者之间存在某种可对比性,或者说为同一洋盆体系,北祁连作为北阿尔金东延的部分也有为其提供一定物源的可能性。
4.2.2 元古宙—太古宙年龄信息
卓阿布拉克组砾岩样品中获得该时期的测点共有14个,占锆石颗粒总数的17.5%,可以分为新元古代早期—中元古代(638.3~1255Ma)和古元古代末(1635~1766Ma)2个年龄段。锆石年龄在新元古代—中元古代的测点有10个,年龄为638.3~ 1255Ma。古元古代年龄组信息的碎屑锆石仅有3颗,年龄分别为1635Ma、1731Ma、1766Ma。Rodinia超大陆的汇聚及相应的后期造山事件始于1300Ma,到900Ma左右结束[43],之后在700~800Ma发生裂解[44]。在阿尔金有900~1100Ma的岩浆活动[45-49],对构成中阿尔金地块主体的阿尔金群碎屑锆石研究表明,其形成于新元古代900~940Ma之间,之后经历了新元古代晚期(760Ma左右)、早古生代(450~500Ma)的构造热事件[50];而在相邻的祁连造山带、柴北缘同样有中元古代末期—新元古代早期岩浆事件的报道[51-54]。在北阿尔金还发现有700~ 780Ma的岩浆活动,可能代表了北阿尔金陆内初始裂解阶段[55-56];北祁连在该时期也存在类似的岩浆活动[57-58]。在北阿尔金蛇绿构造混杂岩带北侧分布太古宇米兰群,构成敦煌地块的主体。在敦煌地块的米兰岩群中记录了2.35~2.45Ga深成花岗岩侵入的热事件[59],这与年龄为2450Ma的锆石有较好的对应性。米兰群是阿尔金山出露的最老变质基底,曾获得过3605Ma、3407±62Ma的锆石U-Pb年龄信息[56, 60]。碎屑锆石中最古老的年龄为3394Ma,意味着源区存在古太古代地层。
依据碎屑锆石内元古宙的年龄值,并结合区域热事件分析对比可以判断,元古宙2个年龄段的碎屑锆石最有可能来自南部的中阿尔金地块和北部的敦煌地块。427~521Ma的锆石与喀腊大湾岛弧岩浆岩和同碰撞及碰撞后岩浆活动的时间一致。另外,还有极少数来自结晶基底的锆石(老于1800Ma的锆石)。综上所述,喀腊大湾地区卓阿布拉克组北部沉积岩系夹层中砾岩的物源主要来自岛弧岩浆岩和同碰撞及碰撞后花岗岩,其次少量来自南部的中阿尔金地块和北部的敦煌地块,源自北部古老结晶基底的沉积物极少。
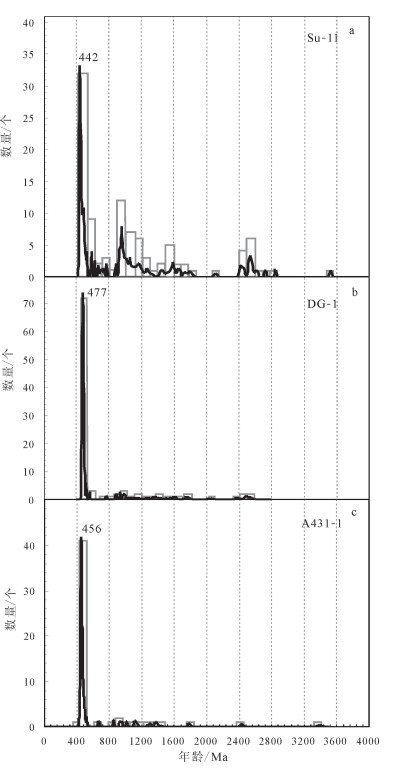
4.3 与鹿角沟组和天祝组砾岩中碎屑锆石的对比
北祁连东段武威斜豪地区上奥陶统天祝组主要为紫红色-灰绿色砂砾岩、砂岩、粉砂岩及页岩,底部局部见厚达百米的底砾岩。其与中奥陶统之间的不整合面,代表了中祁连地块与华北板块之间的初始碰撞[27]。北祁连西段肃南地区下志留统鹿角沟组以灰绿色砾岩、砂砾岩为主,夹含砾砂岩和砂岩,厚度可达350m以上。Xu等[61]对北祁连东段天祝组底部砾岩(DG-1)和西段鹿角沟组砾岩(Su- 11)进行了碎屑锆石的年代学研究,得到了年龄分布频谱图(图 7)。通过对比三者的年龄谱可以看出,天祝组底部砾岩、鹿角沟组砾岩和卓阿布拉克组沉积岩中砾岩的碎屑锆石具有相似的年龄谱峰,在420~520Ma区域显示出锆石年龄最强烈的峰值特征,由北祁连岛弧为其提供最主要的物源。其中,天祝组底部砾岩样品峰值年龄为477Ma,最年轻锆石年龄为467Ma,其沉积时代为450~467Ma[61],限定了华北板块和中祁连地块在此期间已完成初始碰撞。鹿角沟组砾岩样品峰值年龄为442Ma,最年轻锆石年龄为428Ma,其沉积期在435Ma左右[62]。上文已提及,卓阿布拉克组沉积岩中砾岩的碎屑锆石峰值年龄为456Ma,最年轻锆石年龄为427Ma。前述碎屑锆石物源分析表明,砾岩中碎屑锆石来自早古生代的岩浆岩,进一步表明碎屑沉积物的物源具有相似特征。由此可见,卓阿布拉克组和天祝组、鹿角沟组中碎屑沉积物的沉积时代、沉积物源基本相近,暗示三者的构造环境可能具有相似性,即研究区内该套沉积岩系可能形成于早古生代晚奥陶世中阿尔金地块与敦煌地块汇聚作用相关的造山时期。
4.4 构造意义
本文获得的卓阿布拉克组沉积岩系内砾岩碎屑锆石的峰值年龄区间为440~470Ma,说明喀腊大湾地区在此阶段依然存在大量的岩浆活动,应是俯冲、碰撞造山的结果。这一过程中有大量新生地壳产生,可能由于受俯冲碰撞的影响,使下部软流圈部分熔融而上涌的地幔物质。岩浆岩在形成之后很快被风化剥蚀,近距离搬运、沉积成岩。喀腊大湾地区火山-沉积岩系中的中酸性侵入岩年龄为413~443Ma、474~514Ma[10];区内中酸性火山岩的年龄在477~485Ma之间[11]。本文碎屑锆石的年龄研究反映出456Ma的岩浆活动,将岩浆活动在时间上串联起来,反映了喀腊大湾地区寒武纪晚期—志留纪末期中酸性岩浆喷发活动的持续性。
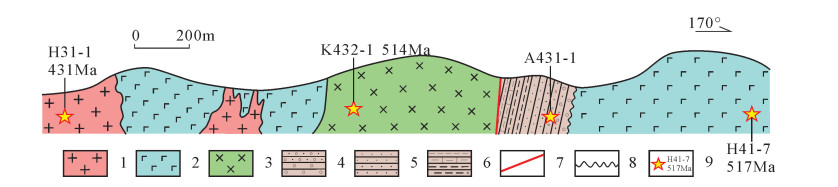
在喀腊大湾东叉沟东侧2km处的地质剖面中,该套沉积岩系北侧出露堆晶辉长岩,两者呈断层接触,与枕状玄武岩呈互层状产出,走向为东西向,南北向出露宽度400~500m,堆晶辉长岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄为514~516Ma(陈柏林等,另文报道);沉积岩系南为枕状玄武岩,二者也呈不整合接触,陈柏林等[12]获得该枕状玄武岩的SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄为517±7Ma,堆晶辉长岩与玄武岩的年龄非常相近;堆晶辉长岩北侧与玄武岩呈渐变关系,玄武岩被中粗粒似斑状二长花岗岩侵入接触(图 8),韩凤彬等[10]测得该似斑状二长花岗岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄为431±4Ma。在喀腊大湾西叉沟,堆晶辉长岩呈较大的捕虏体或包体出露于玄武岩中。笔者发现在卓阿布拉克组中岩浆岩的年龄范围在431~506Ma之间,在该沉积岩系南部的沉积地层中获得砾岩的最年轻碎屑锆石年龄为487Ma(何江涛等,未发表),而本文获得砾岩的形成时代晚于427Ma。因此卓阿布拉克组火山-沉积岩组合中,存在晚寒武世—早泥盆世陆缘弧物质、蛇绿岩、洋壳碎片、陆相碎屑岩等,为一混杂岩带,建议将其解体。在以后的区域地质调查工作中,要注意对卓阿布拉克组进行进一步划分。
郝杰等[63]获得阿尔金北缘红柳沟-拉配泉蛇绿混杂岩变质基质绢云母石英片岩455±2Ma和450± 11Ma的40Ar-39Ar高温坪年龄和等时线年龄,指示了红柳沟-拉配泉蛇绿岩最终构造就位(俯冲结束)的时间,暗示在450Ma左右,北阿尔金地区洋壳俯冲基本结束,之后可能陆续发生碰撞造山作用。北阿尔金巴什考供盆地北缘巴什考供-斯米尔布拉克杂岩体中存在440Ma左右的花岗岩,具有S型花岗岩特征,被认为形成于碰撞环境后[35],说明北阿尔金地区的碰撞时限可能早于440Ma。Xu等[61]认为,在北祁连东段武威地区华北板块和中祁连地块于467~ 450Ma已完成初始碰撞;西段肃南地区鹿角沟组碎屑锆石研究表明,在约435Ma发生了碰撞[62]。笔者参照目前北祁连造山带的研究进展,结合本次碎屑锆石的研究结果,初步认为在早古生代存在北祁连-北阿尔金局限洋盆,二者在演化历史上具有可比性,在中—晚奥陶世可能共同经历碰撞造山、洋盆闭合事件。碰撞阶段产生的新生地壳发生剥蚀、搬运、沉积成岩,随之在北祁连造山带和北阿尔金造山带发育具有相似环境的沉积岩。
结合本文研究结果可见,喀腊大湾地区经历了洋壳扩张期、洋壳板块俯冲碰撞期和碰撞后伸展期3个构造演化阶段。在晚寒武世仍然存在洋壳的俯冲,晚奥陶世北阿尔金有限洋盆发生碰撞造山,蛇绿岩就位到红柳沟—拉配泉一带,同时产生一系列的岩浆活动,形成新生地壳。志留纪后期碰撞隆升导致新生地壳陆续发生剥蚀、搬运,在碰撞带内沉积了一套碎屑岩系;在志留纪末碰撞后伸展期,再次发生构造-岩浆活动,形成了区内出露的中酸性侵入岩,伴随着二长花岗岩侵入。
5. 结论
(1) 运用LA-ICP-MS方法,对北阿尔金喀腊大湾地区卓阿布拉克组火山-沉积岩组合中沉积岩系的砾岩进行锆石U-Pb测年。砾岩样品中最年轻的碎屑锆石年龄为427±4Ma,说明该砾岩的形成时代晚于427Ma,即沉积时代晚于中志留世;结合区域地质资料,暗示地层可能形成于晚志留世—早泥盆世(410~427Ma)。该地区原划为奥陶系的火山-沉积岩组合存在不同时代的物质组成,应对卓阿布拉克组进行解体,需要进一步详细的划分厘定。
(2) 砾岩样品的碎屑锆石U-Pb同位素年龄可分为2组,介于427~521Ma时间段的锆石颗粒,构成砾岩中最大的碎屑锆石群体,说明在早古生代,尤其是晚寒武世—奥陶纪形成的岩浆岩是该砾岩最重要的一个物源;其峰值年龄为456Ma,表明喀腊大湾地区存在该时期的岩浆活动。沉积岩中出现600~1800Ma年龄段的锆石颗粒,说明古元古代中、晚期形成的岩浆岩也为其提供了部分物源,暗示该时期可能经历过一次重要的构造-岩浆-热事件;砾岩内古元古代早期,甚至太古宙碎屑锆石的出现,说明源区可能存在古元古代—太古宙的结晶基底。
(3)碎屑锆石谐和年龄分布特征表明,其沉积物主要来自喀腊大湾地区岛弧和同碰撞-碰撞后花岗岩(425~520Ma),少量来自南部的中阿尔金地块和北部的敦煌地块(800~1000Ma,1600~1800Ma),而源自北部古老结晶基底的沉积物(老于1800Ma的锆石)则极少。
(4)喀腊大湾地区卓阿布拉克组沉积岩系和北祁连天祝组、鹿角沟组具有相似的沉积环境和物质来源,它们可能同为北祁连-北阿尔金局限洋盆闭合后,陆-陆或弧-陆碰撞造山的产物。
致谢: 锆石U-Pb定年测试和论文修改得到南京大学王孝磊老师的大力协助,谨致谢忱。 -
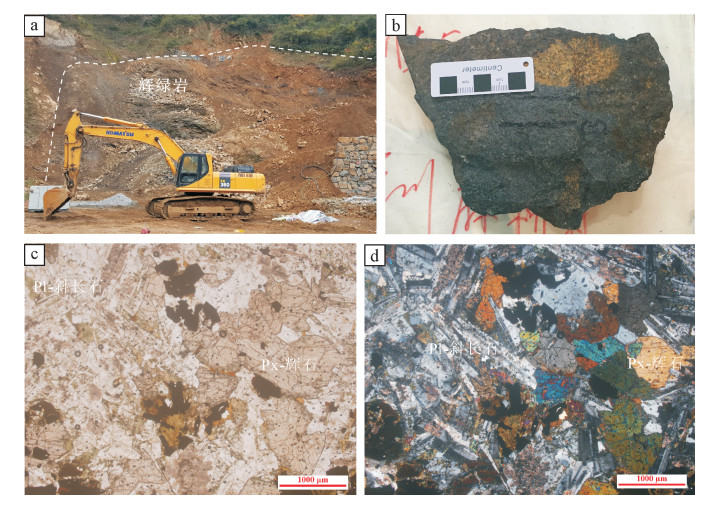
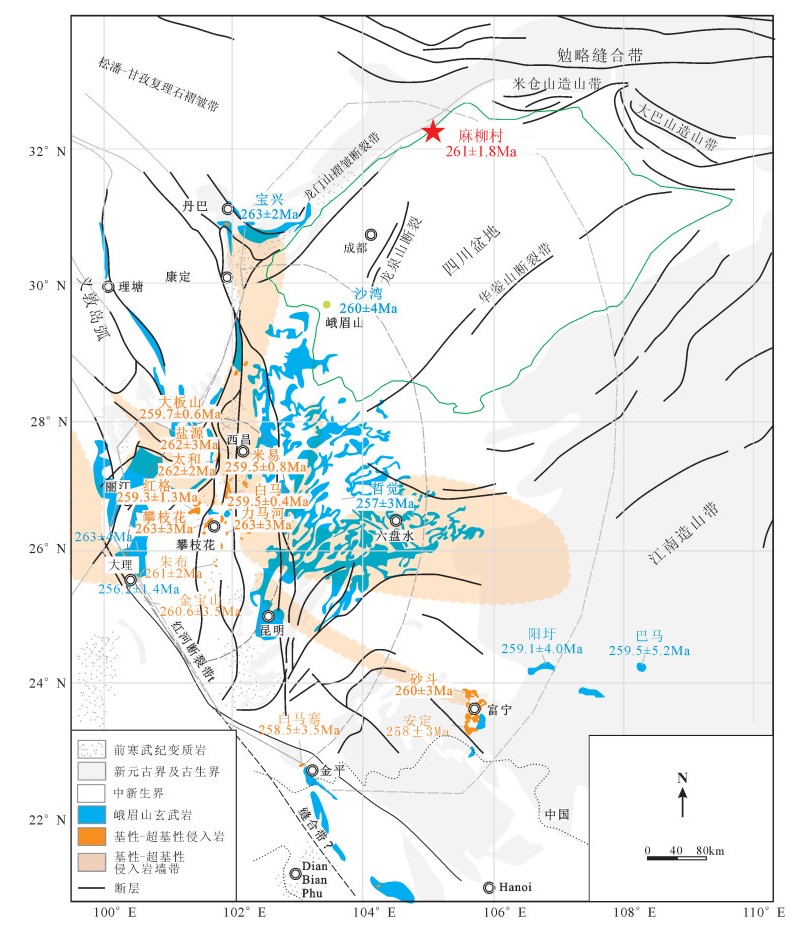
图 1 龙门山北段地质构造简图(a)[4]和麻柳村辉绿岩地质图(b)
Figure 1. Geological map of northern Longmen Mountain (a) and Maliucun diabases (b)
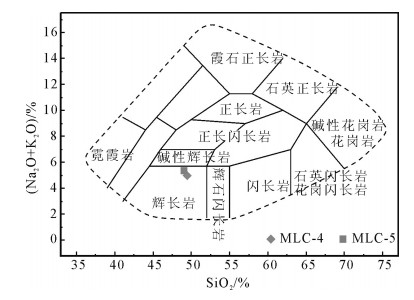
图 5 麻柳村辉绿岩硅碱图[30]
Figure 5. SiO2 versus (Na2O+K2O) diagram for the diabase in Maliucun
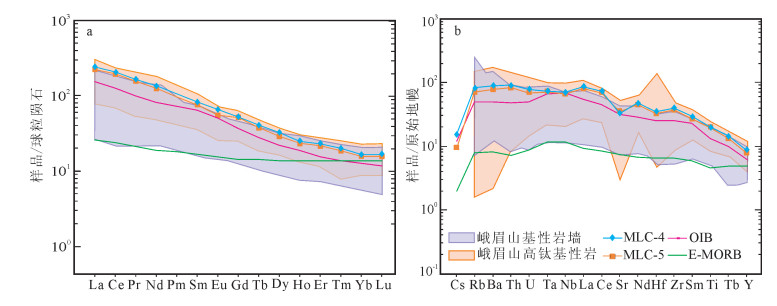
图 7 不同岩石类型稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线图(a)和不相容元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)[39]
Figure 7. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized incompatible element patterns (b) for different rock types
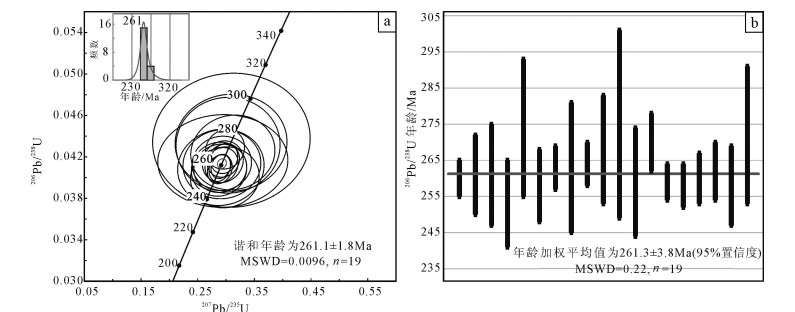
表 1 麻柳村辉长岩斜锆石U-Th-Pb年龄测试结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb dating results of baddeleyites from the diabase in Maliucun
测点号 232Th 238U Th/U 同位素比值 同位素年龄/Ma /10-6 /10-6 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ MLC4-1 147 692 0.21 0.05140 0.00209 0.2910 0.0116 0.04108 0.00077 259 91 259 9 260 5 MLC4-2 36 819 0.04 0.05058 0.00399 0.2982 0.0227 0.04273 0.00126 222 173 265 18 270 8 MLC4-3 54 1340 0.04 0.05121 0.00224 0.2889 0.0125 0.04093 0.00086 251 97 258 10 259 5 MLC4-4 22 727 0.03 0.05137 0.00263 0.2890 0.0145 0.04080 0.00092 258 114 258 11 258 6 MLC4-5 70 660 0.11 0.05400 0.00759 0.2980 0.0400 0.04002 0.00194 371 289 265 31 253 12 MLC4-6 51 1272 0.04 0.05144 0.00350 0.2921 0.0193 0.04120 0.00112 261 149 260 15 260 7 MLC4-7 30 396 0.08 0.05142 0.00569 0.2899 0.0309 0.04090 0.00154 260 236 258 24 258 10 MLC4-8 34 861 0.04 0.05144 0.00433 0.2943 0.0239 0.04153 0.00133 261 182 262 19 262 8 MLC4-9 24 762 0.03 0.05109 0.00601 0.2877 0.0323 0.04081 0.00172 245 250 257 25 258 11 MLC4-10 12 600 0.02 0.05102 0.01079 0.3036 0.0606 0.04312 0.00305 242 426 269 47 272 19 MLC4-11 40 393 0.10 0.05332 0.00871 0.3120 0.0490 0.04242 0.00238 343 333 276 38 268 15 MLC4-12 26 302 0.09 0.05133 0.00635 0.2926 0.0346 0.04137 0.00173 256 262 261 27 261 11 MLC4-13 13 176 0.08 0.05161 0.01598 0.3094 0.0918 0.04360 0.00427 268 588 274 71 275 26 MLC4-14 46 300 0.15 0.05148 0.00925 0.2909 0.0504 0.04099 0.00243 262 367 259 40 259 15 MLC4-15 77 585 0.13 0.05150 0.00280 0.2969 0.0158 0.04184 0.00096 263 120 264 12 264 6 MLC4-16 15 234 0.06 0.05173 0.01145 0.3089 0.0652 0.04336 0.00309 273 441 273 51 274 19 MLC4-17 20 374 0.05 0.05150 0.00834 0.2928 0.0454 0.04129 0.00220 263 335 261 36 261 14 MLC4-18 16 313 0.05 0.05142 0.00339 0.2952 0.0189 0.04163 0.00105 260 145 263 15 263 7 MLC4-19 2 30 0.05 0.05135 0.01366 0.2944 0.0758 0.04160 0.00295 257 518 262 59 263 18 表 2 麻柳村辉长岩主量、微量和稀土元素含量
Table 2 Major, trace and rare earth element for the diabase in Maliucun
样品号 SiO2 TiO2 Al2O3 TFe2O3 MnO MgO CaO Na2O K2O P2O5 烧失量 总计 Na2O+K2O MLC-4 49.04 4.35 13.39 14.67 0.19 4.43 7.50 2.92 1.97 0.54 1.08 100.08 4.89 MLC-5 47.90 4.39 14.02 13.88 0.18 4.56 6.99 3.50 1.68 0.49 1.81 99.40 5.18 样品号 Be Sc Ti V Cr Mn Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Rb Sr Y MLC-4 2.1 22 2.58 380 44 1340 40 61 311 138 27.8 52.3 687 39.6 MLC-5 1.7 21 2.54 367 51 1220 40 72 256 123 25.2 44.0 741 35.7 样品号 Zr Nb Mo Cd Sn Cs Ba La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd MLC-4 447 49.5 2 < 0.5 4 0.49 632 58.8 129.0 16.05 64.4 12.90 3.87 11.00 MLC-5 409 46.3 2 < 0.5 3 0.30 583 54.1 121.0 15.15 59.7 11.70 3.24 10.80 样品号 Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Hf Ta W Pb Bi Th U MLC-4 1.55 8.40 1.43 3.88 0.52 2.86 0.43 10.8 3.0 1 10 8 7.62 1.63 MLC-5 1.42 7.49 1.33 3.61 0.48 2.71 0.40 10.0 2.9 1 5 < 2 6.96 1.43 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素为10-6 -
张宗命, 胡明.龙门山唐王寨地区逆冲推覆体构造特征[J].西南石油学院学报, 1990, (3):46-70. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93402X/199003/385356.html 许志琴.中国松潘-甘孜造山带的造山过程[M].北京:地质出版社, 1992. 贾东, 陈竹新, 贾承造, 等.龙门山前陆褶皱冲断带构造解析与川西前陆盆地的发育[J].高校地质学报, 2003, (3):402-410. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/GXDX200303010.htm 陈竹新, 贾东, 魏国齐, 等.龙门山北段冲断前锋构造带特征[J].石油学报, 2008, 29(5):657-662. doi: 10.7623/syxb200805005 Xu Y G, Chung S L, Jahn B M, et al. Petrologic and geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of Permian-Triassic Emeishan flood basalts in southwestern China[J]. Lithos, 2001, 58(3/4):145-168. http://ntur.lib.ntu.edu.tw/bitstream/246246/172609/1/28.pdf
赖绍聪, 秦江锋.勉略缝合带三岔子辉绿岩墙锆石U-Pb年龄及Hf同位素组成——古特提斯洋壳俯冲的年代学证据[J].地球科学与环境学报, 2010, (1):27-33. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/XAGX201001007.htm Dong Y, Zhang G, Neubauer F, et al. Tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogen, China:Review and synthesis[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 41(3):213-237. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.03.002
Guo X, Gao R, Xu X, et al. Longriba fault zone in eastern Tibet:An important tectonic boundary marking the westernmost edge of the Yangtze block[J]. Tectonics, 2015, 34(5):970-985. doi: 10.1002/2015TC003880
Zi J, Cawood P A, Fan W, et al. Triassic collision in the Paleo-Tethys Ocean constrained by volcanic activity in SW China[J]. Lithos, 2012, 144/145:145-160. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.04.020
Wang J, Yin A, Harrison T M, et al. A tectonic model for Cenozoic igneous activities in the eastern Indo-Asian collision zone[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2001, 188(1):123-133. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X01003156
管涛, 黄智龙, 许成, 等.云南白马寨镍矿区煌斑岩40Ar-39Ar定年和地球化学特征[J].岩石学报, 2006, (4):873-883. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB200604011.htm 梁斌.龙门山北段唐王寨-仰天窝地区伸展构造解析[J].四川地质学报, 1998, (3):6-9. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCDB803.001.htm He B, Xu Y G, Chung S L, et al. Sedimentary evidence for a rapid, kilometer-scale crustal doming prior to the eruption of the Emeishan flood basalts[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2003, 213(3/4):391-405. https://www.deepdyve.com/lp/elsevier/sedimentary-evidence-for-a-rapid-kilometer-scale-crustal-doming-prior-Egr5OyB5Rb
沈浩, 汪华, 文龙, 等.四川盆地西北部上古生界天然气勘探前景[J].天然气工业, 2016, (8):11-21. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2016.08.002 Kamo S L, Gower C F, Krogh T E. Birthdate for the lapetus Ocean? A precise U-Pb zircon and baddeleyite age for the Long Range dikes, southeast Labrador[J]. Geology, 1989, 17(7):602-605. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1989)017<0602:BFTLOA>2.3.CO;2
Ibanez-Mejia M, Gehrels G E, Ruiz J, et al. Small-volume baddeleyite (ZrO2) U-Pb geochronology and Lu-Hf isotope geochemistry by LA-ICP-MS. Techniques and applications[J]. Chemical Geology, 2014, 384:149-167. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.07.011
Klemme S, Meyer H. Trace element partitioning between baddeleyite and carbonatite melt at high pressures and high temperatures[J]. Chemical Geology, 2003, 199(3):233-242. https://www.deepdyve.com/lp/elsevier/trace-element-partitioning-between-baddeleyite-and-carbonatite-melt-at-0JWgQMeEpS
Keil K, Fricher P E. Baddefeyite (ZrO2) in Gabbroic Rocks from Axel Heiberg lsland, Canadian Arctic Archipelago[J]. American Mineralogist, 1974, 59:249-253. http://rruff.info/doclib/am/vol59/AM59_249.pdf
Wang X, Peng P, Wang C, et al. Petrogenesis of the 2115Ma Hai-cheng mafic sills from the Eastern North China Craton:Implications for an intra-continental rifting[J]. Gondwana Research, 2016, 39:347-364. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2016.01.009
Söderlund U, Isachsen C E, Bylund G, et al. U-Pb baddeleyite ages and Hf, Nd isotope chemistry constraining repeated mafic magmatism in the Fennoscandian Shield from 1.6 to 0.9Ga[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2005, 150(2):174-194. doi: 10.1007/s00410-005-0011-1
贾秋鹏, 贾东, 朱艾斓, 等.青藏高原东缘龙门山冲断带与四川盆地的现今构造表现:数字地形和地震活动证据[J].地质科学, 2007, (1):31-44. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkx200701004 陈竹新, 李本亮, 贾东, 等.龙门山冲断带北段前锋带新生代构造变形[J].地质学报, 2008, 82(9):1178-1185. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200809003.htm 四川省地质矿产局.四川省区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社, 1991:1-730. Renna M R, Tiepolo M, Tribuzio R. In situ U-Pb geochronology of baddeleyite-zircon pairs using laser-ablation ICPMS:the case-study of quartz gabbro from Varney Nunatak (central Victoria Land, Antarctica)[J]. European Journal of Mineralogy, 2011, 23(2):223-240. doi: 10.1127/0935-1221/2011/0023-2083
Jackson S E, Pearson N J, Griffin W L, et al. The application of laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry to in situ U-Pb zircon geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 211(1/2):47-69. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254104002074
Griffin W L, Belousova E A, Shee S R, et al. Archean crustal evolution in the northern Yilgarn Craton:U & ndash; Pb and Hf-isotope evidence from detrital zircons[J]. Precambrian Research, 2004, 131(3/4):231-282.
Ludwig K R. Isoplot/Ex, Version 4. 15: A geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel: v. 4[M]. Geochronology Center Berkeley, 2011: 1-70.
Corfu F, Hanchar J M, Hoskin P, et al. Atlas of zircon textures[M]. Chantilly:Mineralogical Soc Amer, 2003.
Ludwig K R. On the treatment of concordant uranium-lead ages[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1998, 62(4):665-676. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00059-3
Cox K C, Boryta J D, Pankhurst R J. The interpretation of igneous rocks[M]. London:George Allen & Unwin, 1979.
Irvine T, Baragar W. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 1971, 8(5):523-548. doi: 10.1139/e71-055
肖龙, 许继峰.川西北松潘-甘孜地块大石包组玄武岩成因及其形成构造背景[J].岩石学报, 2005, (6):1539-1545. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/create_pdf.aspx?file_no=200506157&year_id=2005&quarter_id=6&falg=1 He B, Xu Y, Huang X, et al. Age and duration of the Emeishan flood volcanism, SW China:Geochemistry and SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating of silicic ignimbrites, post-volcanic Xuanwei Formation and clay tuff at the Chaotian section[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 255(3/4):306-323. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X06009149
Fan W, Zhang C, Wang Y, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of Permian basalts in western Guangxi Province, Southwest China:Evidence for plume-lithosphere interaction[J]. Lithos, 2008, 102(1/2):218-236. doi: 10.1007%2Fs00531-016-1326-z
Zi J W, Fan W M, Wang Y J, et al. U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of the Dashibao Basalts in the Songpan-Ganzi Terrane, SW China, with implications for the age of Emeishan volcanism[J]. American Journal of Science, 2010, 310(9):1054-1080. doi: 10.2475/09.2010.11
Shellnutt J G, Jahn B M. Origin of Late Permian Emeishan basaltic rocks from the Panxi region (SW China):Implications for the Ticlassification and spatial-compositional distribution of the Emeishan flood basalts[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2011, 199(1/2):85-95. https://www.deepdyve.com/lp/elsevier/origin-of-late-permian-emeishan-basaltic-rocks-from-the-panxi-region-a1KhjlHcgy
Xu Y G, Chung S L, Jahn B M, et al. Petrologic and geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of Permian-Triassic Emeishan flood basalts in southwestern China[J]. Lithos, 2001, 58(3/4):145-168. http://ntur.lib.ntu.edu.tw/bitstream/246246/172609/1/28.pdf
Zhang Z C, Wang F S. Geochemistry of Two Types of Basalts in the Emeishan Basaltic Province:Evidence for Mantle Plume-Litho-sphere Interaction[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2002, 76(2):229-237.
Sun S S, Mcdonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 1989, 42(1):313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Li H, Zhang Z, Ernst R, et al. Giant radiating mafic dyke swarm of the Emeishan Large Igneous Province:Identifying the mantle plume centre[J]. Terra Nova, 2015, 27(4):47-257. doi: 10.1111/ter.12154/suppinfo
Pearce J A, Cann J R. Tectonic setting of basic volcanic rocks determined using trace element analyses[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1973, 19(2):290-300. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(73)90129-5
Rodionov N V, Belyatsky B V, Antonov A V, et al. Comparative in-situ U-Th-Pb geochronology and trace element composition of baddeleyite and low-U zircon from carbonatites of the Palaeozoic Kovdor alkaline-ultramafic complex, Kola Peninsula, Russia[J]. Gondwana Research, 2012, 21(4):728-744. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.10.005
Condie K C. Chemical composition and evolution of the upper continental crust:Contrasting results from surface samples and shales[J]. Chemical Geology, 1993, 104(1/4):1-37. doi: 10.1007%2Fs00531-010-0635-x
Wooden J L, Czamanske G K, Fedorenko V A, et al. Isotopic and trace-element constraints on mantle and crustal contributions to Siberian continental flood basalts, Noril'sk area, Siberia[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 1993, 57(15):3677-3704. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(93)90149-Q
Lightfoot P C, Naldrett A J, Gorbachev N S, et al. Geochemistry of the siberian trap of the noril'sk area, ussr, with implications for the relative contributions of crust and mantle to flood basalt magmatism[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1990, 104(6):631-644. doi: 10.1007/BF01167284
Campbell I H. The Mantle's Chemical Structure: Insights from the Melting Products of Mantle Plumes[C]//Jackson I. The Earth's Mantle: Composition, Structure, and Evolution. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1998: 259-310.
徐义刚.地幔柱构造、大火成岩省及其地质效应[J].地学前缘, 2002, (4):341-353. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/98600x/2002004/8499925.html 贺世杰, 郭锋.地幔柱的识别和演化研究述评[J].地球科学进展, 2003, (3):433-439. http://www.adearth.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract389.shtml Boven A, Pasteels P, Punzalan L E, et al. 40Ar/39Ar geochronological constraints on the age and evolution of the Permo-Triassic Emeishan Volcanic Province, Southwest China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2002, 20(2):157-175. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(01)00031-1
Lo C, Chung S, Lee T, et al. Age of the Emeishan flood magmatism and relations to Permian & ndash; Triassic boundary events[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 198:449-458. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00535-6
Zhou M, Malpas J, Song X, et al. A temporal link between the Emeishan large igneous province (SW China) and the end-Guadalupian mass extinction[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 196(3/4):113-122. https://www.deepdyve.com/lp/elsevier/a-temporal-link-between-the-emeishan-large-igneous-province-sw-china-2x0bIWLHa0
Fan W, Wang Y, Peng T, et al. Ar-Ar and U-Pb geochronology of Late Paleozoic basalts in western Guangxi and its constraints on the eruption age of Emeishan basalt magmatism[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(21):2318-2327. doi: 10.1360/04wd0201
Guo F, Fan W, Wang Y, et al. When Did the Emeishan Mantle Plume Activity Start? Geochronological and Geochemical Evidence from Ultramafic-Mafic Dikes in Southwestern China[J]. International Geology Review, 2004, 46(3):226-234. doi: 10.2747/0020-6814.46.3.226
范蔚茗, 王岳军, 彭头平, 等.桂西晚古生代玄武岩Ar-Ar和UPb年代学及其对峨眉山玄武岩省喷发时代的约束[J].科学通报, 2004, 49(18):1892-1900. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.18.013 Zhong H, Zhu W G. Geochronology of layered mafic intrusions from the Pan-Xi area in the Emeishan large igneous province, SW China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2006, 41(6):599-606. doi: 10.1007/s00126-006-0081-7
Zhou M, Zhao J, Qi L, et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and elemental and Sr-Nd isotope geochemistry of Permian mafic rocks in the Funing area, SW China[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 2006, 151(1):1-19. doi: 10.1007%2Fs00531-016-1338-8
He B, Xu Y, Huang X, et al. Age and duration of the Emeishan flood volcanism, SW China:Geochemistry and SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating of silicic ignimbrites, post-volcanic Xuanwei Formation and clay tuff at the Chaotian section[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 255(3/4):306-323.
Luo Z Y, Yigang X U, Bin H E, et al. Geochronologic and petrochemical evidence for the genetic link between the Maomaogou nepheline syenites and the Emeishan large igneous province[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2007, 52(7):949-958. doi: 10.1007/s11434-007-0112-5
Wang D H, Jiankang L I, Wang C H, et al. New advances in geochronologic study related to Emei mantle plume and their significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2007, 26(5):550-556. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-KCDZ200705008.htm
Zhong H, Zhu W G, Chu Z Y, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology, geochemistry, and Nd-Sr isotopic study of contrasting granites in the Emeishan large igneous province, SW China[J]. Chemical Geology, 2007, 236(1/2):112-133. https://www.deepdyve.com/lp/elsevier/shrimp-u-pb-zircon-geochronology-geochemistry-and-nd-sr-isotopic-study-t0J3Nifo9c
Fan W, Zhang C, Wang Y, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of Permian basalts in western Guangxi Province, Southwest China:Evidence for plume-lithosphere interaction[J]. Lithos, 2008, 102(1/2):218-236. doi: 10.1007%2Fs00531-016-1326-z
Shellnutt J G, Zhou M, Wang D Y Y. Longevity of the Permian Emeishan mantle plume (SW China):1 Ma, 8 Ma or 18 Ma?[J]. Geological Magazine, 2008, 145(3):373-388. http://www.academia.edu/412289/Longevity_of_the_Permian_Emeishan_mantle_plume_SW_China_1_million_years_8_million_years_or_18_million_years
Sun X, Wang S, Sun W, et al. PGE geochemistry and Re-Os dating of massive sulfide ores from the Baimazhai Cu-Ni deposit, Yunnan province, China[J]. Lithos, 2008, 105(1):12-24.
Xu Y G, Luo Z Y, Huang X L, et al. Zircon U-Pb and Hf isotope constraints on crustal melting associated with the Emeishan mantle plume[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 2008, 72(13):3084-3104. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2008.04.019
Zhou M, Arndt N T, Malpas J, et al. Two magma series and associated ore deposit types in the Permian Emeishan large igneous province, SW China[J]. Lithos, 2008, 103(3/4):352-368. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493707002472
韩伟, 罗金海, 樊俊雷, 等.贵州罗甸晚二叠世辉绿岩及其区域构造意义[J].地质论评, 2009, 55(6):795-803. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4886136 Zheng L, Yang Z, Tong Y, et al. Magnetostratigraphic constraints on two-stage eruptions of the Emeishan continental flood basalts[J].Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2010, 11(12):1-19. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2010GGG....1112014Z
Zi J W, Fan W M, Wang Y J, et al. U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of the Dashibao Basalts in the Songpan-Ganzi Terrane, SW China, with implications for the age of Emeishan volcanism[J]. American Journal of Science, 2010, 310(9):1054-1080. doi: 10.2475/09.2010.11
王萌, 张招崇, 侯通, 等.攀西地区大板山岩体的年代学、元素地球化学及其对铜镍硫化物矿床成因的约束[J].岩石学报, 2011, 27(9):2665-2678. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201109016 Shellnutt J G, Denyszyn S W, Mundil R. Precise age determination of mafic and felsic intrusive rocks from the Permian Emeishan large igneous province (SW China)[J]. Gondwana Research, 2012, 22(1):118-126. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.10.009
李宏博. 峨眉山大火成岩省地幔柱动力学: 基性岩墙群、地球化学及沉积地层学证据[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2012. Tang Q, Li C, Zhang M, et al. U-Pb age and Hf isotopes of zircon from basaltic andesite and geochemical fingerprinting of the associated picrites in the Emeishan large igneous province, SW China[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2015, 109(1):103-114. doi: 10.1007/s00710-014-0349-z
Ali J R, Thompson G M, Zhou M F, et al. Emeishan large igneous province, SW china[J]. Lithos, 2005, 79(3/4):475-489. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493704003196
Chung S L, Jahn B M. Plume-lithosphere interaction in generation of the Emeishan flood basalts at the Permian-Triassic boundary[J]. Geology, 1995, 23(10):889-892. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<0889:PLIIGO>2.3.CO;2
卢记仁.峨眉地幔柱的动力学特征[J].地球学报, 1996, 17(4):424-438. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB604.007.htm Song X, Zhou M, Hou Z, et al. Geochemical Constraints on the Mantle Source of the Upper Permian Emeishan Continental Flood Basalts, Southwestern China[J]. International Geology Review, 2001, 43(3):213-225. doi: 10.1080/00206810109465009
徐义刚, 钟孙霖.峨眉山大火成岩省:地幔柱活动的证据及其熔融条件[J].地球化学, 2001, (1):1-9. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200101001.htm 宋谢炎, 侯增谦, 汪云亮, 等.峨眉山玄武岩的地幔热柱成因[J].矿物岩石, 2002, 22(4):27-32. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/KWYS200204005.htm Song X, Zhou M, Cao Z, et al. Late Permian rifting of the South China Craton caused by the Emeishan mantle plume?[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2004, 161(5):773-781. doi: 10.1144/0016-764903-135
Shellnutt J G. The Emeishan large igneous province:A synthesis[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2014, 5(3):369-394. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2013.07.003
Xu Y G, Luo Z Y, Huang X L, et al. Zircon U-Pb and Hf isotope constraints on crustal melting associated with the Emeishan mantle plume[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 2008, 72(13):3084-3104. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2008.04.019
Zheng L, Yang Z, Tong Y, et al. Magnetostratigraphic constraints on two-stage eruptions of the Emeishan continental flood basalts[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2010, 11(12):1-19. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2010GGG....1112014Z
张晓静, 肖加飞.桂西北玉凤、巴马晚二叠世辉绿岩年代学、地球化学特征及成因研究[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2014, 33(2):163-176. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2014.02.003 洪庆玉, 张宗命, 蒋武, 等.论龙门山唐王寨地区逆冲推覆体及其含油气性[J].天然气工业, 1990, 10(6):1-8. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4978056 赵松林.龙门山唐王寨地区逆冲推覆体及其前缘带含油性[J].西南石油学院学报, 1990, 12(03):71-82. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNSY199003003.htm Zhou M, Malpas J, Song X, et al. A temporal link between the Emeishan large igneous province (SW China) and the end-Guadalupian mass extinction[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 196(3/4):113-122. https://www.deepdyve.com/lp/elsevier/a-temporal-link-between-the-emeishan-large-igneous-province-sw-china-2x0bIWLHa0
He B, Xu Y, Zhong Y, et al. The Guadalupian-Lopingian boundary mudstones at Chaotian (SW China) are clastic rocks rather than acidic tuffs:Implication for a temporal coincidence between the end-Guadalupian mass extinction and the Emeishan volcanism[J]. Lithos, 2010, 119(1/2):10-19.
Xu Y, Chung S, Shao H, et al. Silicic magmas from the Emeishan large igneous province, Southwest China:Petrogenesis and their link with the end-Guadalupian biological crisis[J]. Lithos, 2010, 119(1/2):47-60.
Wignall P B. Large igneous provinces and mass extinctions[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2001, 53(1/2):1-33. http://www.academia.edu/5798236/Large_igneous_provinces_and_mass_extinctions
冯乔, 汤锡元.岩浆活动与油气成藏地质条件的关系[J].西北地质科学, 1997, 18(1):56-62. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/DZKQ704.010.htm Galushkin Y I. Thermal effects of igneous intrusions on maturity of organic matter:A possible mechanism of intrusion[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1997, 26(11):645-658. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222803033_Thermal_effects_of_igneous_intrusions_on_maturity_of_organic_matter_A_possible_mechanism_of_intrusion
Othman R, Arouri K R, Ward C R, et al. Oil generation by igneous intrusions in the northern Gunnedah Basin, Australia[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2001, 32(10):1219-1232. doi: 10.1016/S0146-6380(01)00089-4
马野牧. 地热流体水化学、岩浆活动热效应及其油气资源意义[D]. 南京大学博士学位论文, 2012. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y2260595 张旗, 金维浚, 王金荣, 等.岩浆热场对油气成藏的影响[J].地球物理学进展, 2016, 31(4):1525-1541. doi: 10.6038/pg20160416 朱传庆, 田云涛, 徐明, 等.峨眉山超级地幔柱对四川盆地烃源岩热演化的影响[J].地球物理学报, 2010, 53(1):119-127. http://manu39.magtech.com.cn/Geophy/CN/abstract/abstract1252.shtml -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 任雯倩,刘园园. 地质调查野外数据采集类APP集成框架设计与实现. 华北地质. 2022(04): 75-79+90 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: