Geochemical characteristics and geological signifi-cance of Binggounan Formation meta-volcanic rocks on the northern side of Yusupualeketage at the southern edge of the Al-tun Mountains
-
摘要:
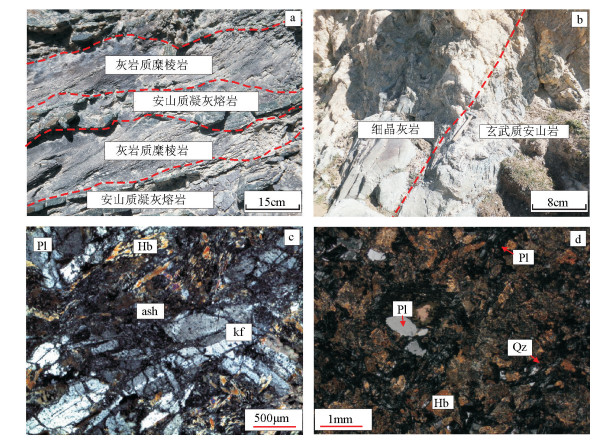
阿尔金南缘玉苏普阿勒克塔格北侧青白口系冰沟南组变质火山岩为一套与滨浅海相细粒陆源碎屑岩和碳酸盐岩共生的基性火山岩,主要岩性为蚀变玄武安山岩和安山质凝灰熔岩。岩石地球化学结果显示,SiO2含量在48.28%~51.98%之间,平均为50.31%,富碱、低钛,里特曼指数δ为0.33~2.30,铝饱和指数A/CNK为0.45~0.88,属于低钾(拉斑)系列。Mg#值介于40.46~56.28之间,平均值为50.12,表明基性火山岩岩浆经历了较弱程度的结晶分异作用。稀土元素弱富集、弱负Eu异常,呈右倾型。大离子亲石元素Rb、Ba、K、Sr亏损,高场强元素P、Ti、Nb、Hf亏损,强不相容元素Th、U富集,为强不相容富集型。岩石微量与稀土元素具有板内玄武岩的特征。根据构造环境判别系列图解综合分析认为,基性火山岩形成于板内裂谷环境。结合区域地质背景,研究区古元古代古大陆的裂解从长城纪一直持续到青白口纪早期,形成基性火山岩,从青白口纪中晚期开始转为罗迪尼亚超大陆的挤压汇聚阶段。
Abstract:The Binggounan Formation volcanic rocks on the northern side of Yusupualeketage at the southern edge of the Altun Mountains are a suite of basic volcanic rocks associated with littoral neritic facies terrigenous clastic rocks and carbonate rock. The gneiss rocks are composed mainly of basalt-andesite and andesitic tuff lava. Geochemical analysis shows that the SiO2 content of the rocks is between 48.28% and 51.98% with an average of 50.31%. The rocks have rich alkal and low titanium. The Rittman index(δ) is 0.33~2.30 and the aluminum saturation index(A/CNK) is 0.45~0.88, suggesting calc-alkaline series.The value of Mg# is between 40.46 and 56.28, with an average of 50.12. It is shown that the basic volcanic rocks experienced higher crystallization differentiation, suggesting a weaker right-inclined LREE enrichment type. Eu anomaly is not obvious, and δEu is between 0.81 and 1.17. Lithophile elements Rb, Ba, K, Sr and high field strength elements P, Ti, Nb, Hf are depleted, and incompatible elements Th, U are enriched, implying incompatible enrichment type. The trace elements and rare earth elements have the characteristics of intraplate basalt. Ac-cording to the tectonic environment discrimination series diagram and the comprehensive analysis, the basic volcanic rocks were formed in an inner-plate rift environment. The regional plate breakup of the Paleoproterozoic continent occurred from Changcheng period to the early Qingbaikou period, forming basic volcanic rocks. In the late Qingbaikou period, the evolution began to turn to the Rodinia supercontinent squeeze convergence stage.
-
致谢: 岩石地球化学数据分析得到咸阳核工业二○三研究所分析测试中心林桂芝工程师的大力支持和热心帮助;审稿专家提出了诸多宝贵而中肯的修改意见,在此一并谨致谢忱。
-
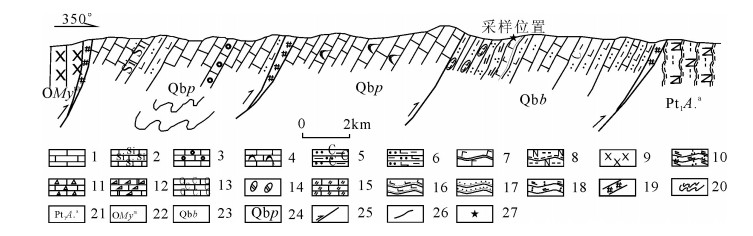
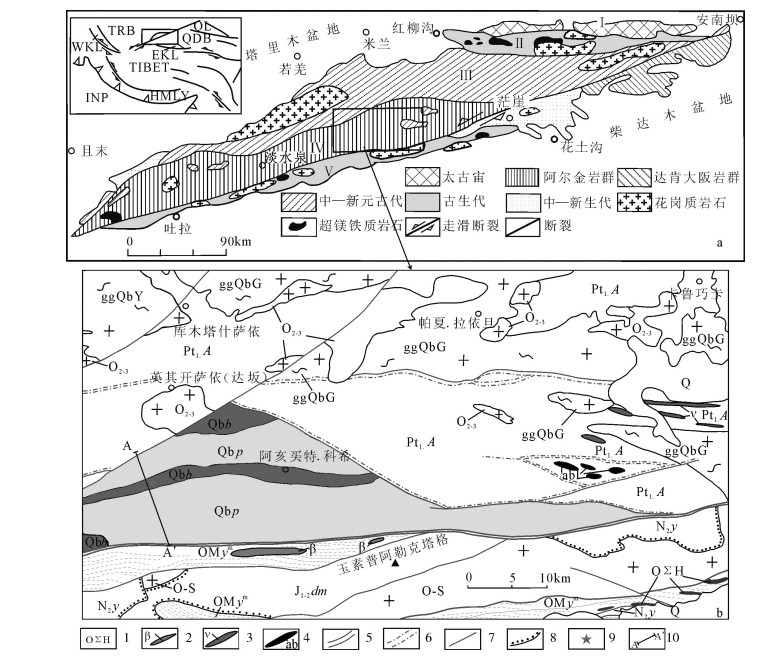
图 1 阿尔金造山带地质构造图(a)及研究区地质简图(b)
TRB―塔里木盆地;QL―祁连山;QDB―柴达木盆地;WKL―西昆仑;EKL―东昆仑;HMLY―喜马拉雅山;INP―印度板块;Ⅰ ―阿北变质地块;Ⅱ―红柳沟-拉配泉混杂岩带;Ⅲ―阿中地块;Ⅳ―南阿尔金超高压变质岩带;Ⅴ―阿南蛇绿构造混杂岩带;Q―第四系;N2y―新近系油砂山组;J1-2dm―侏罗系大煤沟组;QMym―奥陶系茫崖蛇绿混杂岩;Qbb―青白口系索尔库里群冰沟南组;Qbp―青白口系索尔库里群平洼沟组;Pt1.A―古元古界阿尔金岩群;Q-S―玉苏普阿勒塔格岩体;O2-3―帕夏拉依档岩体;ggQbY―亚干布阳片麻岩;ggQbG―盖里克片麻岩;1―超基性岩块体;2―玄武岩块体;3―辉长岩脉;4―斜长角闪岩;5―区域大断裂;6―韧性剪切带;7―断层;8―不整合界限;9―采样地点;10―实测剖面位置
Figure 1. Geological and tectonic map of Altun orogenic belt(a) and geological sketch map of the study area(b)
图 2 索尔库里群实测地质剖面
1―灰岩;2―硅质条带灰岩;3―鲕粒灰岩;4―含叠层石灰岩;5―含炭泥质粉砂岩;6―含钙泥质粉砂岩;7―变玄武-安山质火山岩;8―黑云斜长片麻岩;9―蚀变辉长岩;10―绢云石英千枚岩;11―含白云质角砾灰岩;12―碎裂岩化白云岩化微晶灰岩;13―含炭质灰岩;14―白云质灰岩滑塌岩块;15―白云质灰岩;16―钙质板岩;17―变质砂岩;18―凝灰质绢云母板岩;19―断层破碎带;20―宽缓褶皱;21―奥陶纪茫崖蛇绿混杂岩;22―青白口系索尔库里群冰沟南组;23―青白口系索尔库里群平洼沟组;24―古元古代阿尔金岩群;25―逆冲断层;26―分层界线;27―采样位置
Figure 2. Measured geological section of Suorkuli Group
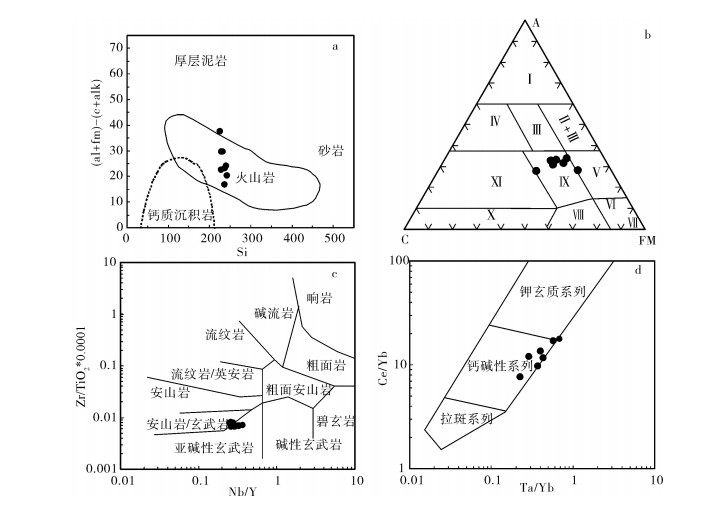
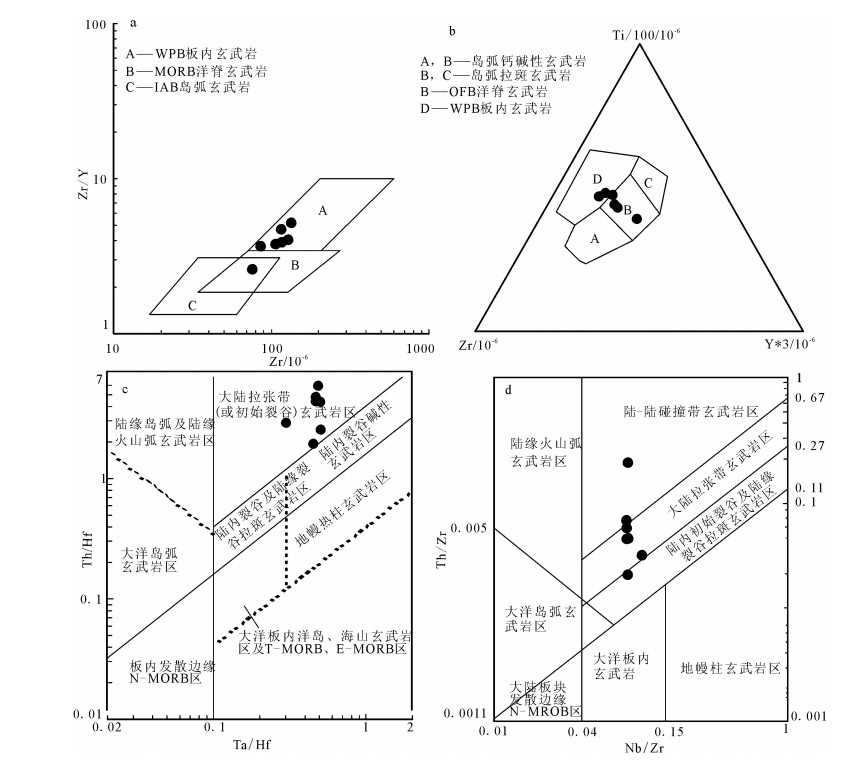
图 4 冰沟南组变质火山岩Si-[(al+fm)-(c-alk)](a)[37]、A-C-FM(b)[38]、Nb/Y-Zr/TiO2*0.0001(c)[39]及Ta/Yb-Ce/Yb(d)图解
Ⅰ—纯泥质岩;Ⅱ—铁质泥质岩;Ⅲ—中酸性火山岩;Ⅳ—钙质泥质岩;Ⅴ—胶体化学沉积及质岩;Ⅵ—胶体化学沉积;Ⅶ—超基性岩;Ⅷ—超基性火山岩及部分白云质岩石;Ⅸ—基性火山岩及部分沉积灰质岩石;Ⅹ—碳酸盐岩沉积岩;Ⅺ—泥灰质沉积岩
Figure 4. Si-[(al+fm)-(c-alk)](a), A-C-FM (b), Nb/Y-Zr/TiO2*0.0001 (c)and Ta/Yb-Ce/Yb (d) diagrams for the Binggounan Formation meta-volcanic rocks
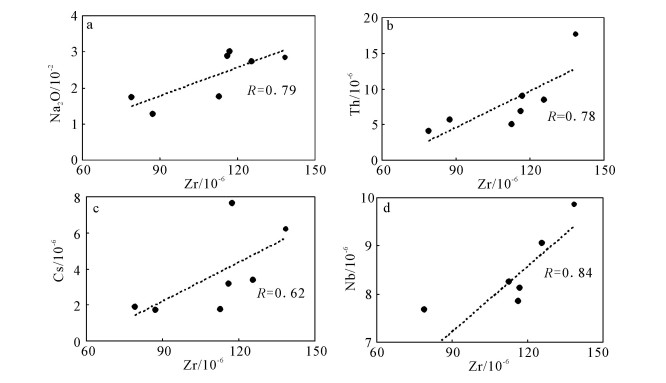
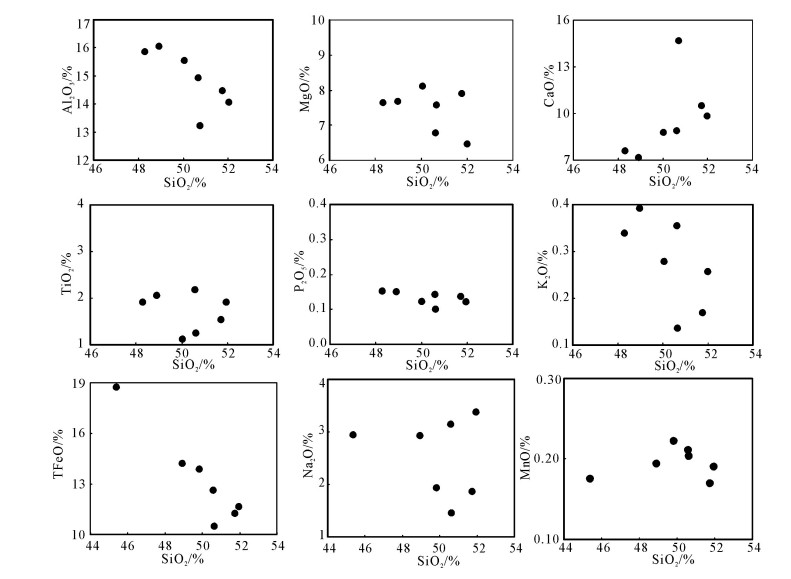
图 5 冰沟南组变质火山岩主量元素哈克图解[40]
Figure 5. Harker diagrams for the Binggounan Formation meta-volcanic rocks
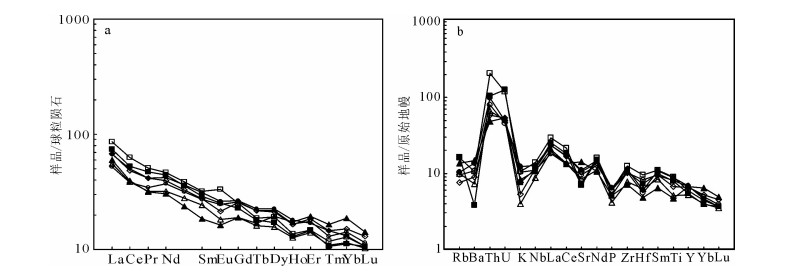
图 6 冰沟南组变质火山岩稀土元素配分型式图(a)和微量元素蛛网图(b)[44]
Figure 6. The REE patterns (a) and spider diagram (b) for the Binggounan Formation meta-volcanic rocks
表 1 冰沟南组变质火山岩主量、微量和稀土元素测试结果及相关参数
Table 1 Major, trace and REE analytical results and related parameters of the Binggounan Formation meta-volcanic rock
样品编号 PM002/21-1 PM002/21-2 PM002/23-1 PM002/23-2 PM002/30-1 PM002/30-2 PM002/36-1 岩性 安山质凝灰熔岩 安山质凝灰熔岩 安山质凝灰熔岩 安山质凝灰熔岩 蚀变玄武安山岩 蚀变玄武安山岩 蚀变玄武安山岩 SiO2 45.53 46.48 44.08 45.32 48.89 44.73 44.92 TiO2 1.96 1.72 1.75 1.91 1.46 1.11 1.01 Al2O3 13.39 12.6 14.47 14.87 13.65 11.74 13.95 Fe2O3 1.41 1.04 9.39 1.74 2.26 1.28 2.65 FeO 10.10 9.49 4.11 11.62 8.61 8.13 9.80 MgO 6.09 5.77 7.01 7.15 7.47 6.70 7.28 MnO 0.19 0.17 0.17 0.18 0.16 0.18 0.20 CaO 8.01 8.8 6.99 6.64 9.93 12.99 7.87 Na2O 2.83 3.01 2.87 2.72 1.76 1.28 1.74 K2O 0.32 0.23 0.31 0.37 0.16 0.12 0.25 P2O5 0.13 0.11 0.14 0.14 0.13 0.09 0.11 烧失量 8.79 9.07 8.03 5.86 4.29 10.52 8.99 总计 98.75 98.49 99.32 98.52 98.77 98.87 99.86 σ 3.92 3.02 9.36 4.12 0.63 1.13 2.06 K2O/Na2O 0.11 0.08 0.11 0.14 0.09 0.09 0.14 AR 1.35 1.36 1.35 1.34 1.18 1.12 1.20 SI 1.28 1.22 1.01 1.08 1.24 1.64 1.37 Mg# 49.65 48.85 56.28 40.46 49.16 55.57 50.89 La 20.40 17.60 12.40 15.90 16.00 13.20 14.20 Ce 38.50 32.30 23.40 30.60 29.80 23.60 24.10 Pr 4.85 4.46 3.27 3.95 3.98 3.06 3.01 Nd 21.90 20.60 17.30 19.80 18.40 15.00 14.30 Sm 4.87 4.42 4.14 4.76 4.21 3.70 2.84 Eu 1.94 1.47 1.43 1.52 1.25 1.06 0.94 Gd 5.16 4.68 5.29 5.47 5.25 3.87 3.89 Tb 0.70 0.67 0.81 0.84 0.81 0.60 0.63 Dy 4.86 4.33 5.51 5.76 5.40 4.01 4.95 Ho 0.77 0.74 0.95 1.02 0.93 0.72 0.98 Er 2.45 2.41 2.91 2.81 3.04 2.31 3.22 Tm 0.30 0.27 0.33 0.37 0.37 0.28 0.42 Yb 2.17 1.90 2.40 2.25 2.56 1.96 3.16 Lu 0.27 0.27 0.29 0.27 0.33 0.26 0.36 Y 26.70 24.80 30.20 31.00 29.50 23.90 30.20 ∑REE 109.14 96.12 80.43 95.32 92.33 73.63 76.99 LREE 92.46 80.85 61.94 76.53 73.64 59.62 59.38 HREE 16.68 15.27 18.49 18.79 18.69 14.01 17.61 LREE/HREE 5.54 5.29 3.35 4.07 3.94 4.26 3.37 δEu 1.17 0.98 0.93 0.91 0.81 0.85 0.86 δCe 0.92 0.87 0.88 0.92 0.89 0.88 0.86 (La/Yb)N 6.74 6.64 3.71 5.07 4.48 4.83 3.22 (Gd/Yb)N 1.97 2.04 1.82 2.01 1.70 1.63 1.02 Cu 15.20 15.10 166.80 221.00 77.30 75.70 215.20 Pb 14.10 10.50 11.40 13.00 16.50 13.00 22.50 Zn 116.10 106.80 108.50 120.70 130.70 135.40 115.50 Ni 41.00 40.60 46.60 49.10 37.70 31.10 51.20 Cr 12.90 12.50 81.10 68.00 82.80 70.40 80.00 V 92.00 84.30 266.20 213.60 355.20 329.90 181.00 Ga 337.20 313.30 370.40 363.40 281.70 241.10 358.00 Sr 20.80 19.40 21.10 22.10 19.60 16.40 16.10 Ba 154.40 147.40 199.20 230.40 223.50 178.70 298.90 Nb 74.40 26.80 74.90 94.90 62.00 50.80 103.10 Ta 10.20 10.30 6.10 6.60 4.80 6.30 8.60 Zr 9.86 8.12 7.85 9.05 8.25 6.28 7.67 Hf 1.49 1.10 0.90 0.91 1.11 0.57 0.72 U 138.60 117.00 116.20 125.70 112.80 87.40 79.10 Th 2.94 2.26 1.70 1.86 2.54 1.93 1.48 Ag 2.48 2.67 0.95 1.05 1.12 1.07 1.13 Au 17.6 9.01 6.85 8.46 5.02 5.66 4.1 Cs 0.35 0.33 0.32 0.45 0.39 0.44 0.19 Rb/Sr 0.07 0.07 0.03 0.03 0.02 0.04 0.03 K/Rb 260.44 185.37 421.88 465.39 276.72 158.12 241.32 Ba/Sr 0.48 0.18 0.38 0.41 0.28 0.28 0.34 Th/Ta 11.81 8.19 7.61 9.30 4.52 9.93 5.69 K 2656.48 1909.34 2573.46 3071.55 1328.24 996.18 2075.37 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量为10-6 -
车自成, 刘良, 刘洪福, 等.阿尔金山地区高压变质泥质岩石的发现及其产出环境[J].科学通报, 1995, 40(14): 1298-1300. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1995.14.015 车自成, 刘良, 刘洪福, 等.阿尔断裂系的组成及相关中新生代含油气盆地的成因特征[J].中国区域地质, 1998, 7(4): 375-384. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD804.006.htm 刘良, 车自成, 罗金海, 等.阿尔金西段榴辉岩的确定及其地质意义[J].科学通报, 1996, 41(16): 1458-1488. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=kxtb199616012&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 刘良, 车自成.阿尔金高压变质岩带的特征及其构造意义[J].岩石学报, 1999, 15(1): 57-64. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/jt/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_ysxb98199901006 Zhang J X, Zhang Z M, Xu Z Q, et al. The Sm-nd and U-Pb agesofeclogite[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1999, 44: 1109-1112.
Zhang J X, Zhang Z M, Xu Z Q, et al. Petrology and geochronology of eclogite from the western segment of the Altyn Tagh, northwestern China[J]. Lithos, 2001, 56: 187-206. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(00)00052-9
许志琴, 杨经绥, 张建新, 等.阿尔金断裂两侧构造单元的对比及岩石圈剪切机制[J].地质学报, 1999, 73(3): 193-205. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzxe199903000&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 崔军文, 唐哲民, 邓晋福, 等.阿尔金断裂系[M].北京:地质出版社, 1999, 137-213. Liu L, Wang C, Chen D L, et al. Petrology and geochronology of HP-UHP rocks from the South Altyn Tagh, northwestern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 35(3/4): 232-244. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912008001582
Liu L, Che Z C, Luo J H, et al. Recognition and implication of eclogite in the western Altun Mountains, Xinjiang[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1997, 42(11): 931-934. doi: 10.1007/BF02882551
Liu L, Sun Y, Xiao P X, et al. Discovery of ultrahigh-pressure magnesite-bearing garnet Iherzolite(>3.8GPa)in the Altyn Tagh, Northwest China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2002, 47: 881-886. doi: 10.1360/02tb9197
Liu L, Sun Y, Luo J H, et al. Ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism of granitic gneiss in the Yinggelisayi area, Altun Monutains, NW China[J]. Science in China (Series D), 2003, 47(4): 338-346. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=jdxg200404004&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Liu L, Chen D L, Zhang A D. Ultrahigh pressure gneissic K-feldspar garnet clinopyroxenite in the Altyn Tagh, NW China:Evidence from clinopyroxene exsolution in garnet[J]. Science in China (Series D), 2005, 48(7): 1000-1010. doi: 10.1360/04yd0166
Liu L, Zhang A D, Chen D L, et al. Implications based on LAICP-MS zircon U-Pb ages of eclogite and its country rock from Jianggalesayi area, Altyn Tagh[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2007, 14 (1): 98-107. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5791(07)60004-9
Liu L, Chen D L, Wang C, et al. New progress on geochronology of high-pressure/ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks from the South Altyn Tagh, the North Qaidam and the North Qinling orogenic, NW China and their geological significance[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2009, 39(3): 472-479.
刘良, 张安达, 陈丹玲, 等.阿尔金江尕勒萨依榴辉岩和围岩锆石LA-ICP-MS微区原位定年及其地质意义[J].地学前缘, 2007, 14 (1): 98-107. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_dxqy200701009.aspx Wang C, Liu L, Chen D L, et al. Petrology, geochemistry, geochronology and metamorphic evolution of garnet peridotites from South Altyn UHP terrane, NW China: Records related to crustal slab subduction and exhumation history[C]//Dobrzhinetskaya L, Cuthbert S, Faryad W, et al. Uhpm: 25 Years after Discovery of Coesite and Diamond[J]. New York: Elsevier, 2011: 541-577.
Zhang J X, Zhang Z M, Xu Z Q, et al. The Sm-nd and U-Pb agesofeclogite[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1999, 44: 1109-1112.
Zhang J X, Zhang Z M, Xu Z Q, et al. Petrology and geochronology of eclogite from the western segment of the Altyn Tagh, northwestern China[J]. Lithos, 2001, 56: 187-206. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(00)00052-9
Zhang J X, Xu Z Q, Yang J S, et al. Petrology geochemistry and geochronology of eclogites from the western segment of the Altum tectonic belt northwestern China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2001, 75(2): 186-197. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZXE200102007.htm
Zhang J X, Yang J S, Xu Z Q, et al. Evidence for UHP metamorphism of eclogites from the Altun Mountains[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2002, 47(9): 751-755. doi: 10.1360/02tb9170
Zhang J X, Meng F C. Sapphirine-bearing high pressure mafic granulite and its implications in the south Altyn Tagh[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2005, 50(3): 265-269. doi: 10.1007/BF02897537
Zhang J X, Meng F C, Yang J S. A new HP/LT metamorphic terrane in the northern Altyn Tagh, western China[J]. Int. Geol. Rev., 2005, 47(4): 371-386. doi: 10.2747/0020-6814.47.4.371
曹玉亭, 刘良, 王超, 等.阿尔金淡水泉早古生代泥质高压麻粒岩及其P-T演化轨迹[J].岩石学报, 2009, 25(9): 2260-2270. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090918&journal_id=ysxb 校培喜, 高晓峰, 胡云绪, 等.阿尔金-东昆仑西段成矿带地质背景研究[M].北京:地质出版社, 2014. 李向民, 马中平, 孙吉明, 等.阿尔金断裂南缘约马克其镁铁-超镁铁岩的性质和年代学研究[J].岩石学报, 2009, 25(4): 862-872. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090411 马中平, 李向民, 孙吉明, 等.阿尔金断裂南缘长沙沟镁铁-超镁铁质层杂岩体的发现及地质意义——岩石学和地球化学初步研究[J].岩石学报, 2009, 4: 793-804. 曹玉亭, 刘良, 王超, 等.阿尔金南缘塔特勒克布拉克花岗岩的地球化学特征、锆石U-Pb定年及Hf同位素组成[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(11): 3259-3271. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201011009.htm 孙吉明, 马中平, 唐卓, 等.阿尔金南缘鱼目泉岩浆混合花岗岩LA-ICP-MS测年与构造意义[J].地质学报, 2012, 2: 247-257. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dzxe201202005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 杨文强, 刘良, 丁海波, 等.南阿尔金迪木那里克花岗岩地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学与Hf同位素特征及其构造地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2012, 12: 4139-4150. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20121226&journal_id=ysxb 张建新, 许志琴, 杨经绥, 等.阿尔金西段榴辉岩岩石学、地球化学和同位素年代学研究及其构造意义[J].地质学报, 2001, 75(2): 186-197. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200102007 张建新, 杨经绥, 许志琴, 等.阿尔金榴辉岩中超高压变质作用证据[J].科学通报, 2002, 47(3): 231-234. http://edu.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/Detail/kxtb200203016 张建新, 孟繁聪, Mattinson C G.南阿尔金-柴北缘高压-超高压变质带研究进展、问题及挑战[J].高校地质学报, 2007, 13(3): 526-545. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxdzxb200703021 Calanchi N, Peccerillo A, Tranne CA, et al. Petrology and geochemistry of volcanic rocks from the island of Panarea:Impliccations for manntle evolution beneath the Aeolian island arc(southern Tyrrhenian sea)[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Researth, 2002, 115: 367-395. doi: 10.1016/S0377-0273(01)00333-X
Hollanda M H B M, Pimentel M M, Oliveira D C, et al. Lithosphere-asthenosphere interaction and the origin of Cretaceous tholeiitic manmatism in Northeastern Brazil:Sr-Nd-PbIsotopic evidence[J]. Lithos, 2006, 86: 34-49. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2005.04.004
徐通, 裴先治, 刘成军, 等.南秦岭勉略构造带张儿沟新元古代变安山岩地球化学特征及锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄[J].地质论评, 2016, 62(6): 434-450. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/create_pdf.aspx?file_no=20130106&journal_id=ysxb&year_id=2013 王仁民, 贺高品, 陈珍珍, 等.变质岩原岩图解判别法[M].北京:地质出版社, 1987: 1-199. Simonen A. Stratigraphy and sedimentation of the Svecofennidic, early Archean supracrustal rocks in southestern Finland[J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society, 1953, 160: 1-64. http://www.oalib.com/references/17372643
Winchester J A, Floyd P A. Geochemical magma type discrimination: Application to altered and metamorphosed igneous rocks[J]. Earthand Planetary Science Letters, 1976, 28: 459-469. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(76)90207-7
Bhatia M R. Plate tectonics and geochemical composition of sandstones[J]. J. Geol., 1983, 91: 611-627. doi: 10.1086/628815
Frey F A, Green D H, Roy S D. Integrated models of basaltpetro genesis: A study of quartz tholeiies to olivine melilites from south eastem Australia utillzing geochemical and experimental petrological data[J]. J. Petrol., 1978, 19: 463-513. doi: 10.1093/petrology/19.3.463
Ellam R M, Hawkesworth C J. Elemental and isotopic variations in subduction related basalts: Evidence for a three component model[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1988, 98(1): 72-80. doi: 10.1007/BF00371911
Holm P E. The Geochemical fingerprints of different tectonomagmatic environments using hydromagmatophile element abundances of tholelitic basalts and basaltic andesites[J]. Chem. Geol., 1985, 51: 303-323. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(85)90139-1
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the OceanBasins. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345.
Wilson M. Igneous Petrogenesis[M]. London: Unwin Hyman Press, 1989.
王银喜, 顾连兴, 张遵忠, 等.博格达裂谷双峰式火山岩地质年代学与Nd-Sr-Pb同位素地球化学特征[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(5): 1215-1224. https://www.cnki.com.cn/qikan-YSXB200605013.html Weaver B L. The origin of oceanic basalt end-member compositions: Trace element and isotopic constrains[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1991, 104(2/4): 381-397. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0012821X91902176
张招崇, 肖序常, 王军, 等.西昆仑山普鲁新生代火山岩中包体的发现及其地质意义[J].地球科学, 2002, 04: 386-390. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2002.04.005 Saunders A D, Storey M, Kent R W, et al. Consequences of Plume-Lithosphere Interaction[C]//Storey B C, Alabaster T, Pankhurst R J, et al. Magmatism and the Causes of Continental Breakup. London: Geol. Soc. Spec. Pub., 1992, 68: 41-60.
Kieffer B, Arndt N, Lapierre H, et al. Flood and shield basalts from Ethiopia: magmas from the African superswell[J]. J. Petrol., 2004, 45(4): 793-834. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egg112
夏林圻, 夏祖春, 徐学义, 等.利用地球化学方法判别大陆玄武岩和岛弧玄武岩[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2007, 26(1): 77-89. http://www.doc88.com/p-2038219345045.html Lightfoot P C, Naldrett A J, Gorbachev N S, et al. Geochemistry of the Siberian Trap of the Noril' s Karea, USSR, with Implications for the Relative Contributions of Crust and Mantle to Flood Basalt Magmatism[J]. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 1990, 104(6): 631-644. doi: 10.1007/BF01167284
赵振华.微量元素地球化学原理[M].北京:科学出版社, 1997. Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. J. Petrol., 1984, 25: 956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
Pearce J A, Cann J R. Tectonic Setting of Basic Volcanic Rocks Determined Using Trace Element Analyses[J]. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1973, 19: 290-300. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(73)90129-5
汪云亮, 张成江, 修淑芝.玄武岩类形成的大地构造环境的Th/Hf-Ta/Hf图解判别[J].岩石学报, 2001, 17(3): 413-421. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200103008.htm 孙书勤, 张成江, 赵松江.大陆板内构造环境的微量元素判别[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2007, 1: 104-109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2007.01.012 校培喜, 张海泉, 王永和, 等.阿中地块南缘晚元古代火山岩地质特征及构造环境分析[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 31(5): 461-466. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_cdlgxyxb200405004.aspx 李琦, 曾忠诚, 陈宁, 等.阿尔金南缘新元古代盖里克片麻岩年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J].现代地质, 2015, 29(6): 1271-1283. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201506002.htm 广西壮族自治区地质调查院. 1: 25万瓦石峡幅、古尔嘎幅区域地质调查报告. 2002. 西安地质调查中心. 1: 25万苏吾什杰幅区域地质调查报告. 2002. 西安地质调查中心. 1: 25万巴什库尔干幅、茫崖镇幅区调修侧报告. 2012. 湖南省地质调查院. 1: 25万且末县一级电站幅、银石山幅区域地质调查报告. 2002. 中国地质调查局西安地调中心. 新疆清水泉地区四幅1: 5万区域地质调查报告. 2011.



 下载:
下载: