Zircon U-Pb dating of the Shijiangshan Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous A-type granite in Xi Ujimqin Banner of Inner Mongolia and its tectonic setting
-
摘要:
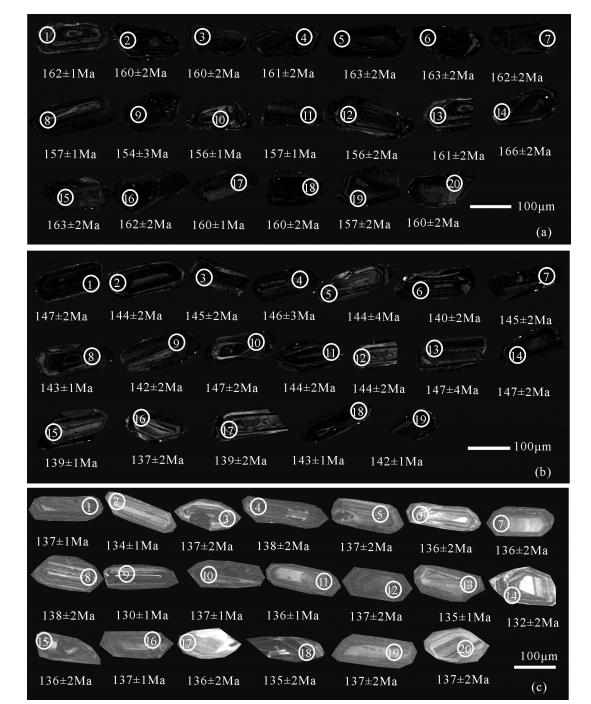
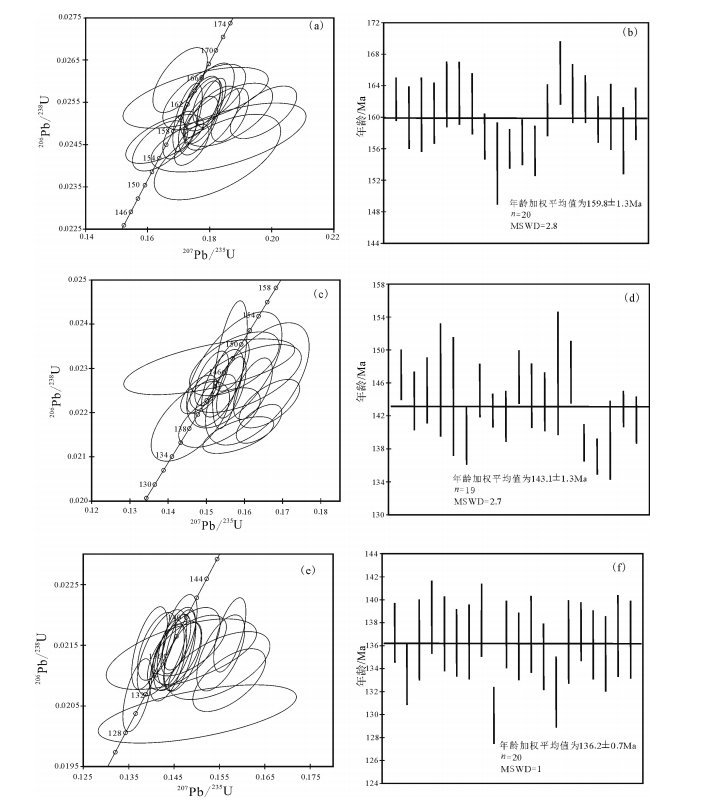
内蒙古西乌旗石匠山A型花岗岩位于贺根山缝合带内,侵位于早石炭世迪彦庙-白音布拉格蛇绿岩带和下二叠统寿山沟组与大石寨组中,岩性为二长花岗岩。石匠山A型花岗岩富硅(SiO2=74.18%~77.16%)、富钾(K2O=4.31%~5.07%)、富碱(Na2O+K2O=8.44%~9.16%),贫Al2O3、CaO、MgO、TiO2、P2O5、Sr、Ba、Eu、Ti和P,具有较高的Ga/Al(3.98~6.09)、(Na2O+K2O)/CaO、K2O/MgO、TFeO/MgO、Rb/Nb、Y/Nb、Sc/Nb值,稀土元素配分曲线为典型的海鸥式分布,δEu为0.01~0.19,负Eu异常显著,明显不同于I、S和M型花岗岩,为典型的铝质A型花岗岩。在地球化学分类判别图解上,石匠山A型花岗岩显示A2型后造山铝质花岗岩特征,反映其形成于后造山伸展环境。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年结果表明,该花岗岩的侵位年龄为159.8±1.3Ma、143.1±1.3Ma、136.20±0.69Ma,即形成时代为晚侏罗世-早白垩世,揭示贺根山缝合带在晚侏罗世-早白垩世为后造山伸展阶段。
-
关键词:
- 铝质A型花岗岩 /
- LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年 /
- 晚侏罗世-早白垩世 /
- 后造山伸展环境 /
- 内蒙古西乌旗
Abstract:Lying along the Hegenshan collisional orogenic suture zone in Xi Ujimqin Banner of Inner Mongolia, the Shijiangshan Atype granite intruded into Early Carboniferous Diyanmiao-Baiyinbulage ophiolite as well as Early Permian Shoushangou Formation and Dashizhai Formation, and consists mainly of monzogranites. The granite is geochemically characterized by high SiO2 (74.18%~77.16%), K2O (4.31%~5.07%), high absolute alkali values (Na2O+K2O=8.44%~9.16%), low Al2O3, CaO, MgO, TiO2, P2O5, Sr, Ba, Eu, Ti, P values, and higher Ga/Al (3.98~6.09), (Na2O+K2O)/CaO, K2O/MgO, TFeO/MgO, Rb/Nb, Y/Nb, Sc/Nb ratios. It is characterized by typical flat or slight right-inclined gull-wing shaped REE distribution patterns with obvious negative Eu anomalies (δEu=0.01~0.19). The Shijiangshan monzogranite exhibits typical geochemical characteristics of A-type granite, being significantly different from I, S and M type granites in geochemistry. According to the chemical subdivision diagrams of the A-type granitoids, the Shijiangshan A-type granite belongs to aluminous A2-type granitoid, formed and emplaced in a post-orogenic extension setting. LAICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating shows that the ages of the granite are 159.8±1.3Ma, 143.1±1.3Ma and 136.20±0.69Ma, suggesting that it was produced during Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous and that the Hegenshan suture zone was at the post orogenic extension stage in the Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous period.
-
地质数据是地质工作中形成的重要信息资源,多年累积形成的海量地质数据信息为国民经济和社会发展提供了重要支撑[1]。地质行业历史悠久,地质资料积累丰厚[2],因此,实现海量地质数据存储具有重要的现实意义。中国的地质数据库建设工作自20世纪80年代中后期起步,时间上晚于西方国家。目前为止,建立的地质数据库主要包括油气及固体矿产资源勘探、地质环境调查、水文地质、矿产资源潜力评价等内容,数量也已经具有一定的规模[3],采取的方法主要为关系数据库。张博[4]以ArcGIS为基础信息系统,通过ArcCatalog自带功能,建立基于Personal Geodatabase的陕西府谷县地质灾害空间数据库。蒲凯[5]在创建地质空间数据库系统时,把Oracle当做存储管理所有空间数据的基础工具,在ArcSDE的支持下,实现了空间数据的统一存储和管理,并进行应用示范。刘灿娟[6]在Microsoft Visual Studio.NET环境下,结合Oracle 10G数据库系统相关技术,根据应用要求,设计并完成地质数据的存储管理工作。然而,数据的不断积累,海量数据的出现,使得通用的关系型数据库无法很好地应对数据规模剧增时系统扩展性和性能问题,Hadoop的出现,则很好地解决了大数据存储的问题。由于Hadoop处理过程主要是通过Hadoop分布式文件系统(HDFS)来实现的[7], 因此本文采用Hadoop中的HDFS为底层存储架构,HBase为元数据存储机制的方式存储地质矿产大数据。实验证明,该存储方式明显优于传统关系数据存储方式。
1. Hadoop系统框架
地质数据具有多源、多元、异构、时空性、方向性、相关性、随机性、模糊性、非线性等特性[8],因此地质大数据具有多样性,存在多维度、结构化与非结构化并用的特点。HDFS[9]作为Hadoop的分布式文件系统,可用于保存基本是顺序访问的海量结构化、非结构化等数据,并且适合运行在普通硬件上[10],而HBase的主要优势为快速随机访问数据。因此,只有将两者结合起来才能更好地实现影像、矢量、文本等海量地质矿产数据的存储与检索。本文存储方法设计如下:将实际地质矿产数据存储到HDFS中(对于存储大的(基于MB、GB)影像地质数据条目直接存储到HDFS中,小的(KB)文本、矢量地质数据条目,先进行小文件合并等措施,再存储到HDFS中),HBase存储其索引数据。应用程序在一个新的HDFS文件中写入结果,同时更新基于HBase的元数据。
Hadoop为用户提供了一个开源的大数据分布式处理框架,包括分布式文件系统HDFS、分布式处理模型MapReduce、非关系型数据库HBase,该框架帮助用户在了解底层实现的基础上,通过函数编程和操作接口,完成对大数据的存储和处理[11]。其系统框架如图 1所示。
(1)HDFS:分布式文件系统,在整个软件生态系统中提供数据存储的功能,并提供数据的流式访问接口,相比集中式数据存储机制,它可以有效地提高系统数据访问的吞吐量。HDFS部署在一个由大量普通PC服务器组成的集群中,采用一次写入、多次读取的文件访问模型,并具有很强的容错处理能力和良好的平台可移植性。
(2)MapReduce:一个处理大数据的编程模型[12],采用Map和Reduce两个简化过程将复杂的任务分成相互独立的子问题,并自动调度计算处理节点来处理这些子问题。利用数据/代码互定位技术有效地减少节点间的数据通信,还能够为应用开发者隐藏系统层的功能实现细节。
(3)HBase:一种提供列存储、实时读写,高性能的分布式数据库,是非关系型数据库NoSQL的一种具体实现,用于存放非结构化和半结构化的松散数据,并且可以通过主键(RowKey)和主键range来实现检索功能。
2. 地质矿产大数据存储模型
2.1 基于关系型数据库的存储模型
关系型数据库指采用关系模型来组织数据的数据库,模型由IBM研究员Codd在1970年首次提出[13]。地理信息系统(Geographic Information System, 简称GIS)以计算机科学为主要支撑技术,专门针对空间数据的应用问题[14],能够用于地质数据的查询管理、空间分析、可视化等操作,将其与Oracle大型空间数据库结合并基于一定的标准进行数据库系统开发,是海量地质数据存储管理的现有存储方案。近半个世纪以来,中国针对国家级基础地质数据库的投资种类达到上百种,投资的数据总量也已超过100TB,并且目前数量还在急剧增长[15]。这些数据管理大多以GIS为基础实现平台,集合大型数据库存储技术、计算机技术进行组织、生产和展示,部分甚至采取三维建模等技术进行一体化管理。然而,这些管理应用中很少能充分利用数据库的功能,因此,面对海量数据的存储,将变得不堪重负。
2.2 基于非关系型数据库的存储模型
随着地质数据的快速增长,基于关系型数据库的存储模式已经很难高效地满足大量地质数据的存储要求。目前,云平台的出现及“大数据”的发展使得越来越多的学者倾向于运用Hadoop相关技术进行数据存储的研究。本文目标是结合HDFS与HBase的优点,设计一个复合式的地质大数据存储系统,将原始地质数据资料存储在HDFS中,将地质矿产元数据存储于HBase中,以实现大数据存储与高效率检索,系统架构如图 2所示。
HDFS主要由NameNode和一系列DataNode组成,其体系结构见图 3,其中,NameNode和Secondary NameNode协同合作管理HDFS的目录树和相关的元数据文件。NameNode的fsimage是元数据镜像文件,存储着整个文件系统的目录树,edits则是元数据的操作日志,且其大小影响NameNode的启动和运行速度,所以需要Secondary NameNode定期通过http get从NameNode中获取上述2个文件,并合并生成新的fsimage文件返回给NameNode,随后NameNode更新本地的fsimage文件,并清空edit操作日志内容,从而提升HDFS节点管理性能[16]。
2.2.1 基于HDFS的地质大数据存储
HDFS的文件操作主要包括读、写2个主要流程,两者均由HDFS客户端发起。
(1)文件写入:①客户端通过调用Distributed File System对象中的create()方法,初始化写入文件实例。②NameNode首先会验证系统中没有要创建的文件,并确保客户端有创建文件的权限,否则会抛出I/O异常。③若校验通过,FSData Output Stream会将文件切割成多个packets,并协调NameNode和DataNode,通过write packet方法将对象写入DataNode。④最后一个文件写入成功后会返回一个ack packet给客户端,客户端则调用close方法关闭所有数据流,并将完成的信息汇报给NameNode。
本文选取重庆市矿产潜力评价数据中的“重庆市城口南大巴山式侵入岩型金矿预测工作区遥感影像图GEOTIFF”(230MB)为测试数据将其存储到HDFS中,核心代码如下:
FSDataOutputStream fsDataOutputStream = fs. create(new Path(“/opt/hadoop/dfs/Data/重庆市/金矿/重庆市城口南大巴山式侵入岩型金矿预测工作区遥感影像图GEOTIFF.tif”));//在hdfs上打开一个文件输出流FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(“/home/hadoop/Desktop/重庆市城口南大巴山式侵入岩型金矿预测工作区遥感影像图GEOTIFF.tif”);//在hdfs上打开一个文件输入流IOUtils.copy(file Input Stream,fs Data Output Stream)。
(2)文件读取:①客户端调用open函数,向远程的NameNode发起RPC请求,调用元数据节点,得到文件的数据块信息。②客户端在打开的文件流上调用read()函数。DFSInputStream连接保存距离此文件最近的DataNode,并把要读的数据返回客户端。③读取完当前block的数据后,就会断开到DataNode的链接,然后选择下一个DataNode来获取下一个数据块。④所有数据读取完毕后,调用close函数来关闭数据流。
本文选取hdfs中data下的矢量数据为读取对象,核心代码如下:
RemoteIterator <LocatedFileStatus> listFiles = fs.listFiles(new Path(“/opt/hadoop/dfs/data”), true);
While(ListFiles.hasNext()){
LocatedFileStatus file = ListFiles.next();
System.out.println(file.getPath().getName()); }
2.2.2 基于HBase的地质元数据存储
HBase是一个分布式的、面向列的开源数据库,是基于Google论文《Bigtable:A distributed storage syatems for structured data》 [17]开源实现,HBase将HDFS作为其底层存储系统;以HadoopMapReduce进行海量数据分析;采用Zookeeper进行数据的统一管理。
以矢量地质数据为例,本文采用每个省份数据作为一个表,每个矿种对应一行,用行健表示各省份对应的矿种信息;用不同的列族代表“综合研究成果资料”、“省级矿产资料”;用不同的列代表不同的要素图(表 1)。
表 1 HBase列式存储设计Table 1. HBase column storage design table行健 时间戳 列族SPE 列族S_SPE 矿种ID 专题ID 图件ID 路径 其他属性 矿种ID 专题ID 图件ID 路径 其他属性 矿种RowKey TimeStamp MID SID FID LCT … MID SID FID LCT … 在表中,列族“SPE”代表“综合研究成果资料”,列族“S_SPE ”代表“省级矿产资料”。列族“SPE”下的‘MID’代表矿种的编码信息(编码信息由国家统一规定),如01代表“铁”,02代表“锰”等,后面命名规则参照前述方式。该事例表示的为“湖南省硫矿种”的编码信息和存储路径信息:
4319 column=SPE: MID, timestamp= 1478462443280, value=4319
4319 column=SPE: LCT, timestamp= 1478462443280, value=hdfs://192.168.20.51/opt/
hadoop/dfs/data/HUNAN
2.3 小文件存储问题
HDFS是一个具有高容错性、成本低廉性等特点的分布式文件系统,被设计用来对大文件进行流式存储,而在处理小文件时则会产生一些问题[18]。地质空间数据与其他空间数据相比,具有数据量大、专题内容多、信息量大等特点,且以矢量图层、遥感影像等大文件数据为主,非常适合于HDFS存储方法。以重庆市的金矿种为例,矿产潜力评价数据如图 4。
经实验发现,矢量图层存储时并非以各地区的“图件”为存储单元存储到一个至几个Block内存中,而是以WL、WT等文件单独进行存储,分别占据一个Block内存,形成无数小文件,造成HDFS存储瓶颈(图 5)。
图 4显示“重庆市城口石门口南大巴山岩浆热液型金矿区典型成矿要素图”中的一个矢量要素。该图只有15892个字节,却占据了一个Block节点,分配单独的split,给集群带来了存储压力。
2.4 Hadoop自带小文件优化方案
对于小文件问题,Hadoop系统自身提供了3个解决方案,分别是Hadoop Archive[19],Sequence File[20],CombineFileInputFormat。
HAR(Hadoop Archive)文件归档技术主要通过将HDFS上的小文件打包成HAR,缓解大量小文件消耗NameNode内存的问题。但是读取HAR中的文件需要读取两层index文件及文件本身数据,且HAR不支持存档文件的压缩,因此使用HAR处理小文件效率较低。
SequenceFile是HDFS提供的一种二进制文件技术,通过 <key, value>对序列化到SequenceFile文件实现多个小文件合并,同时支持数据块的压缩,显著减少了NameNode的内存及数据节点的磁盘空间。然而该方法没有建立相应的小文件到大文件的映射,读取效率低。
CombineFileInputFormat是一种新的输入格式,将HDFS上的多个文件合并成一个单独的split进而提高效率。该方法适用于HDFS中已经存在大量小文件的情况,并且CombineFileInputFormat是一个抽象类,需要用户自己实现实体类。
参考以上方法,CombineFileInputFormat方案更可行,然而,大量小文件数据尚未存到Hadoop平台,若先进行存储,再优化,效率则更低,所以最理想的策略是将“图层”下的各矢量因素合并为一个大文件,以此来提高小文件的存储性能。
2.5 IPutMerge解决方案
针对HDFS小文件存储,《hadoop实战》 [21]提供了一个PutMerge程序,用于将本地磁盘文件合并,然后再复制到HDFS。然而该方案仅面向本地单个文件夹下的数据,对于大量不同路径的数据存储,效率则较低,因此,本文设计了一种IputMerge(Improved PutMerge)程序,该方法可以实现数据的跨路径存储,操作更便捷。
管理split的总时间和构建map任务的总时间决定作业的执行时间,因此合理的分片大小决定负载平衡的质量,本文将分片大小设置为Block的大小128MB。其次,调用Configuration conf得到所需要的FileSystem实例。Configuration对象封装了客户端或服务器的配置,通过设置配置文件读取类路径实现core-site.xml。有了FileSystem实例后,调用factory方法FileSystem.getLocal(Configuration conf)。Hadoop文件API使用Path对象编制文件和目录名,使用FileStatus对象存储文件和目录的元数据。IPutMerge程序将调用递归算法合并本地不同目录中的所有文件。使用FileSystem的ListStatus()方法得到本地的目录。FSDataInputStream是Java标准类java.io.DataInputStream的子类,可以提供随机访问的功能,本文用该方法将数据写入HDFS。为实现IPutMerge,创建一个for循环逐一读取inputFiles中的所有文件。部分代码如下所示:
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
......
Path localPath = new Path((“/home/hadoop/Desktop/重庆市/金矿典型矿床成矿要素图”));
Path hdfsPath = new Path((“/opt/hadoop/dfs/data/重庆市/金矿种潜力评价图库/矿产及其预测/金矿典型矿床成矿要素图”));
if(out==null){
out = hdfsFS.create(hdfsPath);
}
readLocalFileWriteToHDFS(localPath, localFS);
......
FileStatus[] inputFiles = localFS.listStatus(localPath);
for(int i =0; i < inputFiles.length; i++){
boolean isDir = inputFiles[i].isDirectory();
if(isDir){
readLocalFileWriteToHDFS(inputFiles[i].getPath(), localFS);
}
if(inputFiles[i].isFile()){
……
}
}
}
最后,调用MapReduce程序,将数据上传到HDFS之上。Shell命令为:
[hadoop@hdmaster1 Desktop] $ hadoop jar HDFSpd.jar数据.HDFSpd2
3. 实验验证
3.1 小文件优化对比实验
为了验证优化后的方案更具优势,本文从2个方面进行对比测试:①实验数据在HDFS上的写入性能;②文件操作过程中HDFS的NameNode内存占用结果。
(1)实验环境
本文实验采用4个节点的Hadoop集群,其中包括1个NameNode和3个DataNode,具体配置如表 2。
表 2 集群配置情况Table 2. Cluster configuration组件 配置 Hadoop版本 Hadoop2.7.2 操作系统 Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server release 6.7(Santiago) Linux内核版本 2.6.32-573.e16.x86_64 JDK 1.7.0_91 网络带宽 100MB NameNode 八核2.4.0GHzCPU, 16G内存,600G硬盘,数量1 DataNode 八核2.4.0GHzCPU, 8G内存,600G硬盘,数量3 (2)写操作性能对比测试
本实验分别选取500, 1000, 10000, 20000, 30000, 40000个大小为1~1000KB的小文件为存储数据,分别进行数据存储,记录它们各自的存储时间,取3次实验结果的平均值,实验结果见图 6。
图 6表明,采用IPutMerge方法优化后的HDFS的写操作明显快于原始HDFS。这是因为,每写入一个文件到HDFS,NameNode都要对其进行创建和分配数据块的操作,而本文优化后的HDFS中,当n个小文件组成的大文件写入时,NameNode仅被调用一次。另外,Client对大文件使用的缓存机制,每128MB数据的请求被发送到NameNode,而不是发送每个小文件。
(3)内存占用对比测试
海量小文件会耗费主节点内存,造成NameNode瓶颈问题,进而严重影响HDFS的性能,为了分析基于HDFS的分布式文件存储系统中的NameNode占用情况并设计实验。
本实验分别选取500, 1000, 10000, 20000, 30000, 40000个大小为1~1000KB的小文件作为实验数据,在半小时内不断写入各文件到HDFS,并观察NameNode所占系统内存变化,取3次实验结果的平均值。内存使用量结果如图 7所示。
图 7显示了2种情况下的内存使用情况,从结果可以看出,在小文件数量小于1000个的情况下,优化效果并不明显,然而随着小文件数量的急剧增长,优化后的NameNode所占内存量远远低于优化前的HDFS中。这是因为,NameNode主要保存文件元数据及文件所在块的元数据。优化前的HDFS进行数据存储时,每个小文件占据了一个Block,则NameNode需占用大量内存来保存这些数据。而优化后的HDFS,NameNode保存了单个组合文件及Block的元数据,因此,系统内存占用量则会大幅度降低。
3.2 Hadoop与Oracle对比实验
本文实验通过对比2种空间数据存储方式:①传统空间数据存储方式,即采用Oracle与MapGis相结合进行空间数据存储。② Hadoop平台,通过HDFS进行数据存储。分析实验结果,验证本文方法更具优势。
(1)实验环境
表 3给出了测试用到的硬件环境,其中Oracle采用单节点,Hadoop则是在4台电脑上部署的集群。
表 3 测试数据库硬件环境Table 3. Test database hardware environment组件 Oracle Hadoop 操作系统 Windows7专业版 Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server release 6.7(Santiago) 服务器数量 1台(单节点) 4台(Hadoop集群) 网络带宽 100MB 100MB CPU性能 四核 八核 CPU主频 2.80GHz 2.40GHz 内存 8GB 8GB (2)数据导入对比实验
本实验以重庆市矿产资源潜力评价数据作为研究对象,选取100, 1000,10000, 50000, 100000个大小为1~1000KB的小文件为存储数据,分别采用Oracle与Hadoop先后进行数据存储,求取3次对比实验结果的平均值(图 8)。
从图 8可以看出,当文件数量较少时,2种存储方式效率持平,改进后的Hadoop存储方式则略占优势;当数据量很少时,较之传统的Hadoop存储,Oracle效率可能更高,这是因为使用Hadoop进行数据存储时,涉及到NameNode的元数据存储及DataNode的选取,耗费时间较长,优化后的Hadoop则仅需要调用少量的NameNode,大大节省了系统开销时间;当数据量较大时,尤其达到10000个以后,Hadoop在地质数据存储方面则显示出了巨大优势,写入数据所需时间大为缩短。而传统的Oracle数据库,数据存储由于主要集中在一台物理存储节点上,随着数据量不断增加大致呈线性增长。
3.3 数据导出对比实验
本实验以重庆市矿产资源潜力评价数据作为研究对象,选取100, 1000,10000, 50000, 100000个大小为1~1000KB的小文件为研究数据,将Oracle与Hadoop中存储的数据分别进行下载,记录它们各自的响应时间,对比3次实验结果,求取其平均值。
对比2种方式,从实验结果(图 9)可以看出,在数据量很小时,使用Hadoop进行数据读取并没有太大优势,比起传统Oracle仅略占优势。这是因为,当数据量少时,Hadoop本身的系统开销需要花费更多的数据处理时间,然而改进后的Hadoop将多个小文件合并为一个大文件,大大减少了访问数据量。因此,比起存储小数据量更占优势的Oracle来说,效率还要稍高。当数据量大幅度上升时,尤其数据量超过10000个时,Oracle的单节点数据输出则较吃力,系统响应时间大致呈线性增长,而Hadoop的多节点并行工作突显出了更大的优势。
4. 结语
大数据时代的到来带动了地质大数据的发展,而地质数据对城市规划、建设、安全等都具有重要的指导意义,如何有效存储地质数据成为了亟待解决的现实问题。本文针对海量地质矿产数据的存储问题,提出了一种全新的数据存储方案,对地质行业的发展具有一定的参考价值。实验表明:
(1)HDFS不适合海量地质小文件的存储,而优化后的HDFS数据存储则具有显著优势;
(2)当数据量很少时,基于Hadoop的存储效率优势并不明显,而当数据量急剧增长时,Hadoop则展示出了海量数据的存储优势;
(3)本文提出的方案是有效的,为地质数据的存储与管理提供了一种可行的技术方案。
致谢: 野外调查中得到中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心谷永昌研究员和辛后田、刘永顺副研究员等的热情指导和帮助,在此一并表示衷心的感谢。 -
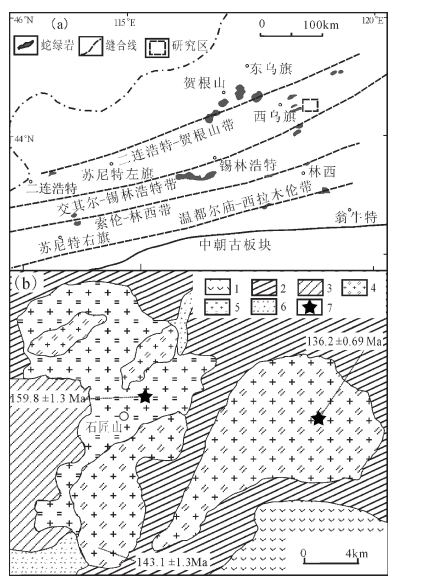
图 1 内蒙古西乌旗石匠山A型花岗岩区域构造(a)和地质简图(b)[29]
1—上侏罗统满克头鄂博组;2—下二叠统寿山沟组;3—下二叠统大石寨组;4—早白垩世二长花岗岩;5—晚侏罗世二长花岗岩;6—早石炭世白音布拉格蛇绿岩;7—采样位置
Figure 1. Sketch tectonic(a) and geological (b) map of the Shijiangshan A-type granite in Xi Ujimqin Banner, Inner Mongolia
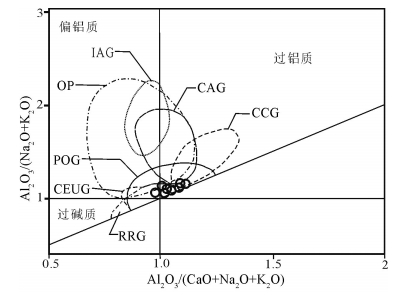
图 5 石匠山A型花岗岩铝饱和指数(A/CNK-A/NK)图解[42]
IAG—岛弧;CAG—大陆弧;CCG—大陆碰撞;RRG—裂谷;CEUG—大陆造陆抬升;POG—后造山;OP—大洋
Figure 5. Shand's index of the Shijiangshan A-type granite
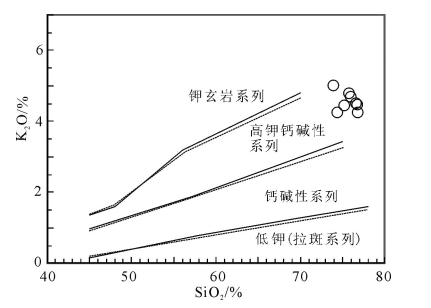
图 6 石匠山A型花岗岩SiO2-K2O分类图解[43]
Figure 6. SiO2-K2O classification diagram of the Shijiangshan A-type granite
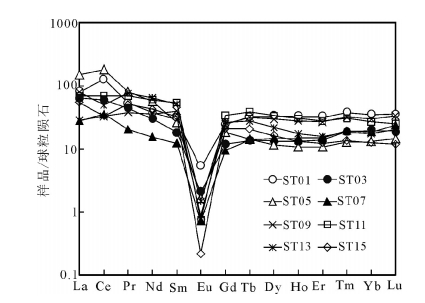
图 7 石匠山A型花岗岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分模式[44]
Figure 7. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns of the Shijiangshan A-type granite
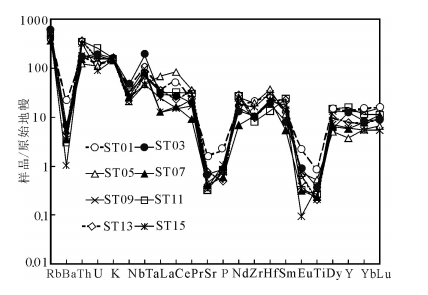
图 8 石匠山A型花岗岩微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图[45]
Figure 8. Primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagram of the Shijiangshan A-type granite
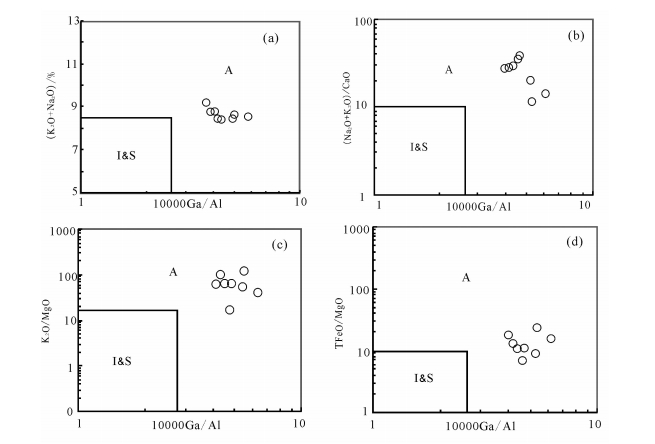
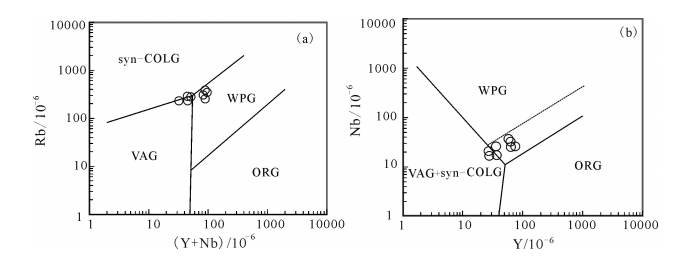
图 9 石匠山A型花岗岩10000×Ga/Al对(K2O+Na2O)、(K2O+Na2O)/CaO、K2O/MgO、TFeO/MgO判别图[3]
Figure 9. K2O+Na2O, (K2O+Na2O)/CaO, K2O/MgO and TFeO/MgO versus 10000×Ga/Al discrimination diagrams of the Shijiangshan A-type granite
图 10 石匠山A型花岗岩K2O-Na2O图解[2]
Figure 10. K2O-Na2O plot of the Shijiangshan A-type granite
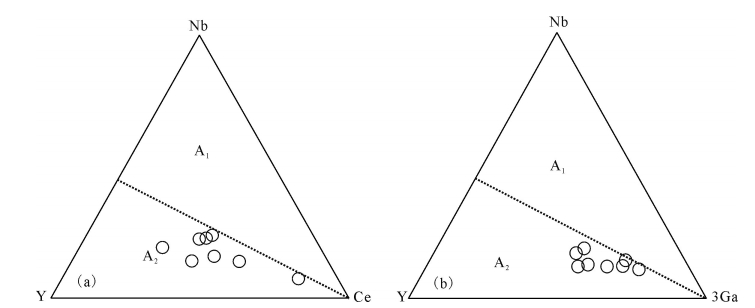
图 11 石匠山A1和A2型花岗岩类Y-Nb-Ce和Y-Nb-3Ga三角形判别图解[5]
Figure 11. Y-Nb-Ce and Y-Nb-3Ga triangular plots for distinguishing between A1 and A2 granitoids from the Shijiangshan A-type granite
图 12 石匠山A1和A2型花岗岩Y/Nb-Rb/Nb和Y/NbSc/Nb图解[5]
Figure 12. Y/Nb-Rb/Nb and Y/Nb-Sc/Nb plots for distinguishing between A1 and A2 granitoids from the Shijiangshan A-type granite
表 1 石匠山A型花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb测试结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb dating of zircons from the Shijiangshan A-type granite
测点 元素含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素原子比值 表面年龄/Ma Pb U Th 206Pb/238U ±% 207Pb/235U ±% 207Pb/206Pb ±% 206Pb/238U TWS01 1 53 2112 734 0.35 0.0510 15 0.179 1.2 0.0255 2.1 162 ±1 2 44 1708 610 0.36 0.0522 15 0.181 1.2 0.0251 2.0 160 ±2 3 32 1235 834 0.68 0.0510 7.5 0.177 2.4 0.0252 1.1 160 ±2 4 20 547 342 0.63 0.0535 8.6 0.186 2.2 0.0252 1.2 161 ±2 5 11 425 198 0.47 0.0509 11 0.180 1.7 0.0256 1.5 163 ±2 6 58 2083 1158 0.56 0.0505 9.1 0.178 2.0 0.0256 1.3 163 ±2 7 17 638 253 0.40 0.0505 13 0.177 1.4 0.0254 1.8 162 ±2 8 14 551 197 0.36 0.0500 14 0.170 1.2 0.0247 2.0 157 ±1 9 7 275 409 1.49 0.0548 3.6 0.183 5.1 0.0242 0.47 154 ±3 10 36 1481 750 0.51 0.0516 10 0.174 1.7 0.0245 1.4 156 ±1 11 7 287 91 0.32 0.0488 15 0.166 1.1 0.0246 2.3 157 ±1 12 10 387 188 0.49 0.0486 9.9 0.164 1.7 0.0245 1.5 156 ±2 13 22 788 352 0.45 0.0567 13 0.198 1.6 0.0253 1.6 161 ±2 14 74 2737 869 0.32 0.0475 15 0.171 1.2 0.0260 2.3 166 ±2 15 68 2351 840 0.36 0.0496 14 0.175 1.3 0.0256 2.0 163 ±2 16 61 2393 1093 0.46 0.0514 11 0.181 1.6 0.0255 1.6 162 ±2 17 33 1225 693 0.57 0.0512 9.0 0.177 2.0 0.0251 1.3 160 ±1 18 82 3318 955 0.29 0.0499 17 0.173 1.0 0.0251 2.5 160 ±2 19 110 3074 1190 0.39 0.0547 14 0.186 1.3 0.0247 1.9 157 ±2 20 48 1872 985 0.53 0.0537 10 0.187 1.8 0.0252 1.4 160 ±2 TWS02 1 168 7124 3182 0.45 0.0492 1.0 0.157 1.2 0.0231 1.0 147 ±2 2 175 7534 3066 0.41 0.0503 1.1 0.157 1.0 0.0226 1.3 144 ±2 3 85 3403 2669 0.78 0.0511 4.8 0.160 3.7 0.0228 1.4 145 ±2 4 3 77 69 0.89 0.0497 8.8 0.157 3.3 0.0230 2.4 146 ±3 5 13 413 180 0.44 0.0523 9.1 0.163 3.4 0.0227 2.5 144 ±4 6 81 3208 1433 0.45 0.0509 2.1 0.154 2.8 0.0219 1.3 140 ±2 7 333 15004 3873 0.26 0.0482 1.1 0.152 1.2 0.0228 1.1 145 ±2 8 19 824 540 0.66 0.0484 1.1 0.149 1.1 0.0224 0.71 143 ±1 9 63 2518 1050 0.42 0.0497 0.99 0.153 1.4 0.0223 1.1 142 ±2 10 15 575 314 0.55 0.0475 5.2 0.151 6.1 0.0230 1.1 147 ±2 11 30 1296 720 0.56 0.0494 1.3 0.154 1.4 0.0227 1.4 144 ±2 12 271 11777 6196 0.53 0.0522 0.96 0.162 1.3 0.0225 1.3 144 ±2 13 101 4523 1167 0.26 0.0491 1.3 0.156 1.2 0.0231 2.6 147 ±4 14 83 3572 1454 0.41 0.0494 2.6 0.157 3.1 0.0231 1.3 147 ±2 15 82 3621 1869 0.52 0.0546 1.2 0.164 1.5 0.0217 0.83 139 ±1 16 46 367 215 0.59 0.0535 2.3 0.158 2.4 0.0215 0.83 137 ±2 17 65 2010 2793 1.39 0.0485 2.1 0.146 2.9 0.0218 1.7 139 ±2 18 16 2937 875 0.30 0.0479 1.0 0.148 1.3 0.0224 0.79 143 ±1 19 48 682 278 0.41 0.0544 1.7 0.167 2.0 0.0222 1.0 142 ±1 TWS03 1 66 3012 1346 0.45 0.0501 1.8 0.149 2.2 0.0215 1.0 137 ±1 2 45 2081 1322 0.64 0.0545 2.7 0.157 2.1 0.0209 1.0 134 ±1 3 59 2685 1333 0.50 0.0496 1.4 0.146 1.0 0.0214 1.3 137 ±2 4 47 2124 991 0.47 0.0489 0.97 0.146 1.1 0.0217 1.2 138 ±2 5 18 847 311 0.37 0.0499 1.9 0.148 2.1 0.0215 1.2 137 ±2 6 13 595 201 0.34 0.0498 4.1 0.147 4.6 0.0214 1.1 136 ±2 7 46 2115 819 0.39 0.0527 1.7 0.155 1.4 0.0214 1.2 136 ±2 8 66 2992 1247 0.42 0.0527 1.0 0.157 0.89 0.0217 1.2 138 ±2 9 8 397 300 0.75 0.0535 6.1 0.150 6.0 0.0204 0.94 130 ±1 10 59 2722 1216 0.45 0.0477 1.4 0.141 1.2 0.0215 1.1 137 ±1 11 50 2333 1181 0.51 0.0500 0.94 0.147 1.2 0.0213 1.1 136 ±1 12 60 2699 1474 0.55 0.0491 0.93 0.146 1.2 0.0215 1.2 137 ±2 13 29 1236 1227 0.99 0.0531 4.2 0.155 3.0 0.0212 1.1 135 ±1 14 134 6460 2309 0.36 0.0480 0.79 0.137 0.93 0.0207 1.2 132 ±2 15 74 3443 1230 0.36 0.0483 0.95 0.142 1.5 0.0214 1.3 136 ±2 16 70 3211 1403 0.44 0.0490 0.90 0.145 0.96 0.0215 0.93 137 ±1 17 52 2344 1233 0.53 0.0493 1.60 0.145 1.7 0.0213 1.1 136 ±2 18 63 2917 1390 0.48 0.0492 0.98 0.144 1.2 0.0212 1.2 135 ±2 19 64 2906 1385 0.48 0.0472 0.89 0.140 1.1 0.0215 1.3 137 ±2 20 68 3117 1269 0.41 0.0489 0.92 0.144 1.0 0.0214 1.2 137 ±2 注:误差为1σ;Pb*代表放射成因铅 表 2 石匠山A型花岗岩的主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 2 Major, trace element and REE analyses of the Shijiangshan A-type granite
样品号
(岩性)ST01
(zcπηγJ3)ST03
(xπηγβJ3)ST05
(zcπηγβJ3)ST07
(zcηγβK1)ST09
(zcηγK1)ST11
(zcηγK1)ST13
(zcηγK1)ST15
(zcηγK1)世界A型花岗岩平均(148) 中国A型花岗岩平均(197) SiO2 74.68 76.07 74.18 77.16 77.08 76.33 76.92 75.52 73.81 73.55 TiO2 0.182 0.080 0.120 0.051 0.049 0.062 0.040 0.081 0.26 0.23 Al2O3 13.3 12.99 13.69 12.54 12.4 12.42 12.65 12.72 12.40 12.81 Fe2O3 0.73 0.61 1.19 0.68 0.54 0.89 0.53 0.80 1.24 1.42 FeO 1.01 0.26 0.34 0.12 0.26 0.12 0.12 0.92 1.58 1.18 MnO 0.0300 0.0100 0.0170 0.0130 0.0061 0.0072 0.089 0.050 0.060 0.090 MgO 0.220 0.073 0.079 0.062 0.081 0.038 0.041 0.100 0.20 0.27 CaO 0.26 0.32 0.36 0.24 0.44 0.77 0.33 0.63 0.75 0.82 Na2O 4.15 3.93 4.09 4.13 3.93 3.90 4.20 4.05 4.07 3.76 K2O 4.32 4.85 5.07 4.31 4.54 4.75 4.57 4.51 4.65 4.69 P2O5 0.046 0.019 0.023 0.013 0.016 0.018 0.011 0.023 0.040 0.070 烧失量 1.01 0.74 0.83 0.66 0.64 0.67 0.55 0.52 总计 99.94 99.95 99.99 99.98 99.98 99.98 99.97 99.92 Ba 144.10 48.31 37.04 24.51 25.23 21.54 32.88 7.24 352 235.96 Rb 253.60 383.04 228.51 229.12 302.03 345.41 276.61 284.00 169 269.69 Sr 34.29 14.18 9.73 8.56 7.12 6.90 16.5 7.64 48 57.54 Zr 238.50 117.32 220.03 117.56 115.91 89.62 112.21 180.00 528 333.77 Pb 19.48 29.70 18.62 24.23 17.71 16.91 13.22 24 Zn 38.70 32.91 50.77 24.52 21.41 26.49 16.50 Cu 3.60 2.31 3.91 2.12 4.80 3.00 2.30 2 Ni 3.90 2.61 2.22 1.80 1.75 2.67 2.50 < 1 V 10.20 4.70 3.03 7.30 3.10 1.61 2.29 3.02 6 Cr 6.14 5.40 4.22 4.02 3.71 3.20 3.30 3.94 Hf 8.56 5.71 11.48 6.86 6.71 4.17 6.56 9.45 Sc 2.64 2.00 2.10 0.62 2.20 1.81 1.30 6.23 4.0 Ta 4.39 7.45 1.92 3.32 4.01 2.88 2.84 1.90 Nb 28.76 33.07 14.90 18.79 22.56 23.05 15.40 17.40 37 34.93 U 2.57 4.06 2.32 3.90 3.27 5.37 3.27 1.86 5.00 Th 14.68 14.33 10.58 12.97 15.43 29.98 31.31 27.60 23 Ga 32.21 29.81 28.80 30.90 34.22 34.70 27.90 41.01 24.6 18.54 Y 60.87 56.46 27.00 26.15 60.67 72.91 35.72 27.10 75 54.03 Rb/Sr 7.39 26.97 23.67 26.57 42.65 50.01 16.79 37.17 3.52 4.69 K/Rb 141.41 105.12 184.15 156.17 124.82 114.23 137.24 131.83 229 Ga/Al 4.57 4.34 3.98 4.66 5.21 5.29 4.16 6.09 3.75 La 24.49 20.08 46.83 8.75 8.78 21.80 24.99 17.00 Ce 104.80 48.99 148.20 28.91 26.66 56.82 40.29 26.90 Pr 6.57 5.44 10.02 2.50 4.66 8.47 9.41 6.36 Nd 22.81 18.02 34.26 9.33 21.61 36.52 39.21 25.8 Sm 5.79 3.57 5.16 2.42 7.84 10.64 10.18 6.3 Eu 0.37 0.15 0.12 0.050 0.060 0.061 0.11 0.016 Gd 6.37 3.06 4.75 2.46 6.46 8.82 6.84 5.38 Tb 1.55 0.64 0.68 0.66 1.51 1.85 1.31 0.96 Dy 10.75 4.24 3.71 4.77 9.64 10.94 7.08 5.21 Ho 2.31 0.94 0.77 1.08 2.00 2.20 1.26 0.94 Er 6.66 2.94 2.27 3.19 5.64 5.84 3.33 2.59 Tm 1.24 0.62 0.42 0.63 1.05 1.01 0.60 0.44 Yb 7.3 4.11 2.74 3.88 6.23 5.69 3.65 2.65 Lu 1.2 0.66 0.49 0.80 1.12 0.83 0.69 0.40 ΣREE 202.21 113.46 260.46 69.43 103.25 171.49 148.96 100.95 δEu 0.19 0.14 0.07 0.07 0.03 0.02 0.04 0.01 (La/Yb)N 2.26 3.29 11.53 1.52 0.95 2.58 4.62 4.33 注:主量元素含量单位为%,稀土、微量元素含量为10-6。zcπηγJ3—中粗粒似斑状二长花岗岩;xπηγβJ3—细粒似斑状黑云母二长花岗岩;zcηγβK1—中粗粒黑云母二长花岗岩;zcηγK1—中粗粒二长花岗岩 -
Loiselle M C, Wones D R. Characteristics and origin of anorogenic granites[J]. Geol. Soc. Am. Abstracts, 1979, 11: 468. http://www.oalib.com/references/19189721
Collins W J, Beams S D, White A J R, et al.Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to Southeastern Australia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1982, 80: 189-200. doi: 10.1007/BF00374895
Whalen J B, Currie K, Chappel B W. A-type granite: geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95: 407-419. doi: 10.1007/BF00402202
Eby G N. The A-type granitoids: a review of their occurrence and chemical characteristics and speculation on their petrogenesis[J]. Lithos, 1990, 26: 115-134. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(90)90043-Z
Eby G N. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids: Petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 1992, 20: 641-644. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0641:CSOTAT>2.3.CO;2
Pitcher W S. The Nature and Origin of Granite[M]. Blackie: Academic and Professional, 1993:1-316.
洪大卫, 王式洸, 韩宝福等.碱性花岗岩的构造环境分类及其鉴别标志[J].中国科学(B辑), 1995, 25(4):418-426. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/d03dc42558fb770bf78a5571-3.html King P L, White A J R, Chappe ll B W, et al. Characterization and origin of aluminous A-type granites from the Lachlan Fold Belt, Southeastern Australia[J]. J. Petrol., 1997, 38(3): 371-391. doi: 10.1093/petroj/38.3.371
许保良, 阎国翰, 张臣等. A型花岗岩的岩石学亚类及其物质来源[J].地学前缘, 1998, 5(3):113-124. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/a968ef05e87101f69e31952a-2.html 邱检生, 王德滋, 蟹泽聪等.福建沿海铝质A型花岗岩的地球化学及岩石成因[J].地球化学, 2000, 29(4):313-321. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/yj/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_dqhx200004001 Wu F Y, Sun D Y, Li H M, et al. A-type granites in northeastern China: Age and geochemical constraints on their petrogenesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 187: 143-173. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00018-9
刘红涛, 翟明国, 刘建明, 等.华北克拉通北缘中生代花岗岩:从碰撞后到非造山[J].岩石学报, 2002, 18(4):433-448. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/create_pdf.aspx?file_no=20020451&journal_id=ysxb&year_id=2002 张晓晖, 张宏福, 汤艳杰, 等.内蒙古中部锡林浩特-西乌旗早三叠世A型酸性火山岩的地球化学特征及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(11):2769-2780. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/create_pdf.aspx?file_no=2006011296&year_id=2006&quarter_id=11&falg=1 Bonin B. A-type granites and related rocks: Evolution of a concept, problems and prospects[J]. Lithos, 2007, 97: 1-29. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2006.12.007
吴锁平, 王梅英, 戚开静. A型花岗岩研究现状及其述评[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2007, 26(1):57-66. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/2faace9f680203d8ce2f2466.html 张旗, 冉白皋, 李承东. A型花岗岩的实质是什么?[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2012, 31(4):621-626. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=conference&id=7958130 石玉若, 刘敦一, 张旗, 等.内蒙古中部苏尼特左旗地区三叠纪A型花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其区域构造意义[J].地质通报, 2007, 26(2):183-189. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20070231&flag=1 石玉若, 刘翠, 邓晋福, 等.内蒙古中部花岗质岩类年代学格架及该区构造岩浆演化探讨[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(11):3155-3171. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB201411005.htm 薛富红, 张晓晖, 邓江夏, 等.内蒙古中部达来地区晚侏罗世A型花岗岩:地球化学特征、岩石成因与地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2015, 31(6):1774-1788. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201506020 Whalen J B, Jenner G A, Longstaffe F J, et al. Geochemical and isotopic (O, Nd, Pb and Sr) constraints on A-type granite:Petrogenesis based on the Topsails igneous suite, Newfoundland Appalachians[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1996, 37: 1463-1489. doi: 10.1093/petrology/37.6.1463
Barbarin B. Granitoids main petrogenetic classification in relation to origin and tectonic setting[J]. Geochemical Journal, 1990, 25: 227-238. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/227747123_Granitoids_Main_petrogenetic_classifications_in_relation_to_origin_and_tectonic_setting
Barbarin B. A review of the relationships between granitoid types, their origins and their geodynamic environments[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46: 605-626. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00085-1
Coleman D S, Frost T P, Glazner A F. Evidence from the Lamarck granodiorite for rapid Late Cretaceous crust formation in California[J]. Science, 1992, 258(5090): 1924-1926. doi: 10.1126/science.258.5090.1924
Bonin B, Azzouni S A, Bussy F, et al. Alkali calcic and alkaline post-orogenic (PO) granite magmatism: Petrologic constraints and geodynamic settings[J]. Lithos, 1998, 45(1/4): 45-70. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493798000255
Jahn B. M, Griffin W L, Windley B F. Continental growth in the Phanerozoic: Evidence from Central Asian[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000, 328: 1-227. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00175-X
陈志广, 张连昌, 吴华英, 等.内蒙古西拉木伦成矿带碾子沟钼矿区A型花岗岩地球化学和构造背景[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(4): 879-889. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/create_pdf.aspx?file_no=20080426&journal_id=ysxb&year_id=2008 孙金凤, 杨进辉.华北东部早白垩世A型花岗岩与克拉通破坏[J].地球科学, 2009, 34(1):137-147. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/270152614_huabeidongbuzaobaieshiAxinghuagangyanyukelatongpohuai 李竞妍, 郭锋, 李超文, 等.东北地区晚古生代—中生代I型和A型花岗岩Nd同位素变化趋势及其构造意义[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(7):1995-2008. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/create_pdf.aspx?file_no=20140713&journal_id=ysxb&year_id=2014 李英杰, 王金芳, 李红阳, 等.内蒙西乌旗白音布拉格蛇绿岩地球化学特征[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(8):2719-2730. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/create_pdf.aspx?file_no=20130809&journal_id=ysxb&year_id=2013 陈斌, 赵国春, Simon Wilde.内蒙古苏尼特左旗南两类花岗岩同位素年代学及其构造意义[J].地质论评, 2001, 47(4):361-367. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2001.04.005 Jian P, Liu DY, Kroner A, et al. Evolution of a Permian intraoceanic arc-trench system in the Solonker suture zone, Central Asian orogenic Belt, China and Mongolia[J]. Lithos, 2010, 118: 169-190. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2010.04.014
Miao L, Shi Y, Guo F, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Hegenshan ophiolitic complex: Implications for late-stage tectonic evolution of the Inner Mongolia-Daxinganling Orogenic Belt, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2008, 32(4): 404-415. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912007002222
王金芳, 李英杰, 李红阳, 等.内蒙古梅劳特乌拉蛇绿岩中埃达克岩的发现及其演化模式[J].地质学报, 2017, 91(8):1776-1795. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95080X/199604/2363561.html 李英杰, 王金芳, 李红阳, 等.内蒙古西乌旗梅劳特乌拉蛇绿岩的识别[J].岩石学报, 2015, 31(5):1461-1470. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/create_pdf.aspx?file_no=20150520&journal_id=ysxb&year_id=2015 李英杰, 王金芳, 李红阳, 等.内蒙古西乌旗迪彦庙蛇绿岩的识别[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(4):1282-1290. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_ysxb98201204024.aspx WANG Jinfang, LI Yingjie, LI Hongyang. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb Age and Island-Arc Origin of the Bayanhua Gabbro in the Hegenshan Suture Zone, Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2017, 91(6): 2316-2317. doi: 10.1111/acgs.2017.91.issue-6
王金芳, 李英杰, 李红阳, 等.内蒙古西乌旗努和特早白垩世A型花岗岩LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2017, 36(8):1343-1358. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170805&flag=1 程天赦, 杨文静, 王登红.内蒙古西乌旗阿鲁包格山A型花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及地质意义[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2014, 38(3):718-728. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4875936 Anderson T. Correction of commen lead U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192: 59-79. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00195-X
Claesson S, Vetrin V, Bayanova T, et al. U-Pb zircon age from a Devonian carbonatite dyke, Kola peninsula, Russia: A record of geological evolution from the Archaean to the Palaeozoic[J]. Lithos, 2000, 51: 95-108. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(99)00076-6
Corfu F, Hanchar J M, Hoskin P W O, et al. Atlas of Zircon Textures[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy & Geochemistry, 2003, 53(1): 469-500. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/238448416_Atlas_of_Zircon_Textures
Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society of America, 1989, 101: 635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
Peccerillo A, Taylor S R. Geochemistry of eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu Area, NorthernTurkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58: 63-81. doi: 10.1007/BF00384745
Boynton W V. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: meteorite studies[C]//Henderson P. Rare earth element geochemistry. Elsevier, 1984: 63-114.
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotope systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society of London, Special Publication, 1989, 42: 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
林强, 葛文春, 吴福元, 等.大兴安岭中生代花岗岩类的地球化学[J].岩石学报, 2004, 20(3):403-412. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/yj/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_ysxb98200403004 Liu W, Siebel W, Li XJ, et al.Petrogenesis of the Linxi granitoids, northern Inner Mongolia of China: Constraints on basaltic underplating[J]. Chem. Geol., 2005, 219(1/4): 5-35. https://homepages.uni-tuebingen.de/wolfgang.siebel/pdffiles/liu_wei.pdf
周振华, 吕林素, 杨永军, 等.内蒙古黄岗锡铁矿区早白垩世A型花岗岩成因:锆石U-Pb年代学和岩石地球化学制约[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(12):3521-3537. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_ysxb98201012006.aspx 解洪晶, 武广, 朱明田, 等.内蒙古道郎呼都格地区A型花岗岩年代学、地球化学及地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(2):483-494. http://www.ysxb.ac.cn/ysxb/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20120211 施光海, 苗来成, 张福勤, 等.内蒙古锡林浩特A型花岗岩的时代及区域构造意义[J].科学通报, 2004, 49(4):384-389. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_kxtb200404015.aspx Creaser R A, Price R C, Wormald R J. A-type granites revisited: Assessmentofaresidual-sourcemodel[J]. Geology, 1991, 19:163-166. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1991)019<0163:ATGRAO>2.3.CO;2
Patino Douce A E.Generation of metaluminous A-type granites by low-pressure melting of calc-alkaline granitoids[J]. Geology, 1997, 25: 743-746. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0743:GOMATG>2.3.CO;2
Hong D W, Wang S G, Han B F, et al. Post-orogenic alkaline granites from China and comparisons with anorogenic alkaline granites elsewhere[J]. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 1996, 13(1): 13-27. doi: 10.1016/0743-9547(96)00002-5
Rapp R P, Watson E B. Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8~32kbar: Implications for continental growth and crust-mantle recycling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36: 891-931. doi: 10.1093/petrology/36.4.891
Pearce J A, Lippard S J, Roberts S. Characteristics and tectonic significance of supra-subduction zone ophiolites[C]//Kokelaar B P, Howells M F. Marginal Basin Geology. Geological Society of London Special Publication, 1984, 16: 77-94. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/237966121_Characteristics_and_tectonic_significance_of_super-suduction_zone_ophilites
De La Roche H, Leteeeier J, Grande Claude P, et al. A classification of volcanic and plutonic rocks using R1-R2 diagrams and major element analyses—Its relationships and current nomemclature [J]. Chem. Geol. 1980, 29: 183-210. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(80)90020-0
辽宁省第二区域地质测量队. L-50-35(白塔子庙幅)1: 200000地质图说明书, 1972. 沈阳地质矿产研究所. L50C004003(西乌珠穆沁旗幅)1: 250000区域地质调查报告, 2004.




 下载:
下载: