Research progress of the Rammelsberg Cu-Zn-Pb-Ba deposit, Germany
-
摘要:
拉梅尔斯贝格矿床是中欧华力西期最重要的SHMS(以沉积岩为容矿围岩的块状硫化物)类矿床之一,位于莱茵海西期地体的上哈茨地块。该矿床形成于泥盆纪,矿体赋存于艾菲尔阶的威森巴赫页岩中,经华力西造山运动发生了强烈的变形。主要有新矿体、老矿体和富含重晶石的灰色矿体,主要硫化物矿物为黄铁矿、闪锌矿、方铅矿和黄铜矿。硫同位素数据显示,拉梅尔斯贝格矿床有2个硫源,一个是热液成因;一个是生物成因,来自细菌还原的海水中的硫酸盐。铅同位素说明,它的铅主要来自均匀的地壳。与其他SHMS类矿床相比,拉梅尔斯贝格矿床明显富铜。
Abstract:Located in the Upper Harz of Rhenohercynian terrane, the Rammelsberg deposit is one of the most important SHMS (sediment-hosted massive sulfide) deposits of the Variscan period in Central Europe. The deposit is hosted by the Devonian Eifelian Wissenbach shale, and the orebodies were intensely deformed by the Variscan oregeny. The main orebodies are composed of the old orebody, new orebody and the barite-rich gray orebody. The principal sulfide minerals are pyrite, sphalerite, galena and chalcopyrite. The data of the sulfur isotopes show two sulfur sources for the Rammelsberg deposit, one was from the hydrothermal component, and the other was from the biogenic compontent bacterial reduction of sea water sulfate. The Pb isotopes show that the lead was de-rived from a homogeneous crustal source. Compared with the other SHMS deposits, the Rammelsberg deposit is relatively copperenriched.
-
Keywords:
- SHMS deposit /
- Rheno Hercynian terrane /
- Wissenbach shale /
- Rammelsberg /
- Germany
-
SHMS(sediment-hosted massive sulphide, 以沉积岩为容矿围岩的块状硫化物)类矿床是一种极其重要的矿床类型。该类矿床是锌和铅的主要来源,分别超过世界储量的50%和60%[1]。SHMS类矿床在世界上主要分布在澳大利亚Mt.Isa-McArthur盆地、澳大利亚Curnamona克拉通、加拿大Selwyn山岭、南非Namaqualand盆地、印度Rajasthan、BeltPurcell盆地、爱尔兰Irish Midlands、德国Rhenish盆地等[2]。SHMS类矿床具有明显的时控性,多形成于古—中元古代(19~14亿年)和早—中古生代(5.3~3亿年) [3]。SHMS类矿床还具有明显的层控性,矿体均赋存在一定的地层层位中[3-4]。近年来对于该类矿床的研究又有新的进展,如黄志伟[4]认为,该类矿床既可以出现在离散板块动力学背景下的陆内裂谷、拗拉槽或被动大陆边缘裂谷,又可以出现在汇聚板块动力学背景下远离弧后的拉张断陷盆地,同生断层为其主要的控矿构造;成矿流体具有高fo2特征[5]。
德国拉梅尔斯贝格矿床是中欧华力西期最重要的SHMS类矿床之一。它的发现出于偶然,相传是在一次狩猎活动中,被一匹名为拉梅利乌斯的马刨开地面发现的,而后以这匹马的名字将该矿命名为拉梅尔斯贝格[6]。矿床的开采记录最早可以追溯到公元968年,直到1988年6月矿山才最终闭坑。矿石储量估计有2700×104~3000×104t, 平均品位为:Zn 14%、Pb 6%、Cu 2%、Au 1g/t、Ag 140g/t和重晶石20%[7]。这座矿山创造的财富是哥斯拉尔(Goslar)市发展的基础,同时也是中世纪德意志帝国的重要经济来源。现今,包括很多具有重要历史意义的地下采矿设施,以及地表的矿石处理厂在内,整个拉梅尔斯贝格矿区成为了一个博物馆,并且被联合国教科文组织(UNESCO)列入了世界文化遗产。
本文将拉梅尔斯贝格矿床作为一个SHMS类矿床的典型实例,介绍其基本地质概况、矿化特征及研究进展,以了解SHMS类矿床的主要特征,为中国开展该类型矿床的找矿勘查提供参考。
1. 区域地质背景
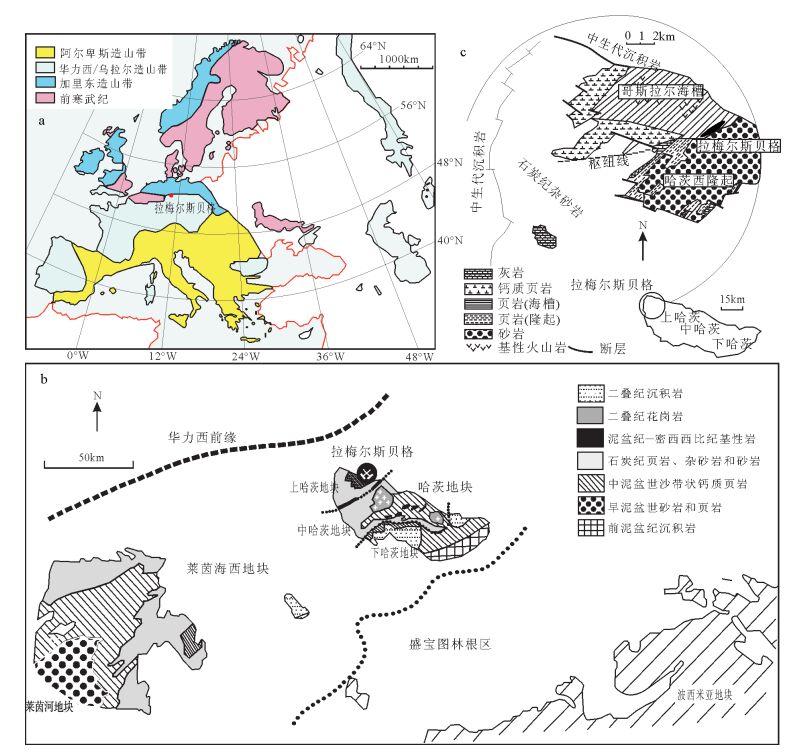
拉梅尔斯贝格矿床位于欧洲华力西造山带的莱茵海西期地体(Rhenohercynian terrane)(图 1)。该地体地处欧洲华力西复合拼贴地体的最北端,其北部推覆到劳亚古陆基底之上,南部与萨克森图林根(Saxothuringian)地块缝合接触。Berthelsen[9]认为,莱茵海西期地块向西延伸穿过阿登高地(Ar-dennes)一直到英格兰西南部,向东延伸到捷克共和国东北部的西里西亚—摩拉维亚一带。
哈茨地块是莱茵海西期内几个华力西地体中的一个隆起地块,由古生代沉积岩、火山岩和侵入岩构成[10],面积约90×30km2。其北部和西部以断层为界,南部和东部被二叠纪沉积岩和局部的火山岩覆盖。哈茨地块传统上被分为三大地质单元[11],即上哈茨、中哈茨和下哈茨。其中,上哈茨地块的沉积序列是连续的,虽然厚度和岩相在侧向上有很大的变化,但是并没有角度不整合或沉积不整合。拉梅尔斯贝格矿床位于上哈茨地块的西北角(图 1)。
上哈茨地块中的地层包括下泥盆统埃姆斯阶(Emsian)、中泥盆统艾菲尔阶(Eifelian)、中泥盆统吉维特阶(Givetian)、上泥盆统和下石炭统。埃姆斯阶总体上称为科尔贝格砂岩,由一系列中厚层状云母粉砂岩、砂岩和石英岩构成;艾菲尔阶的威森巴赫页岩(Wissenbach Shale)可以分为2个单元,下部单元由一系列薄-中厚层状细粒砂岩、粉砂岩和页岩构成,上部单元主要为深灰色页岩[7];吉维特阶由瘤状灰岩的压缩层序构成,深海光壳节石也越来越普遍;上泥盆统由厚约20m的深灰色微晶灰岩组成,之后逐渐沉积了泥质岩,反映了当时平静的沉积环境;下石炭统底部发育一套含大量黄铁矿的黑色页岩(明矾板岩或明矾页岩),在其之上沉积有燧石序列。
哈茨地块的泥盆纪—石炭纪沉积岩在华力西造山运动期间发生了变形,泥盆纪建造呈现一北西向褶皱,在晚石炭世变形达到最高峰,同时伴有低级变质作用(葡萄石-绿纤石[12])。同时,以辉绿岩为代表的区域火山活动发生在中泥盆世和晚泥盆世,在沉积岩中出现了部分层状凝灰岩,也反映了当时的火山活动。在页岩当中还普遍发育轴面劈理,劈理的产状相对一致,走向北东40°~60°,倾向南东38°~48°。在上哈茨地块,断层近垂直,主要走向为北西西—南东东向,并且有一个明显的侧向右旋及垂直方向的移动[7]。
在中欧华力西期的古生代火山沉积岩系中,赋存许多具有重要经济价值的层控贱金属块状硫化物和重晶石矿床、兰迪尔(Lahn-Dill)型层状铁矿化,以及众多的脉状贱金属、重晶石和萤石矿床[7]。在哈茨地块,除拉梅尔斯贝格铜-锌-铅-钡矿床外,还有许多其他的矿床,主要是脉状矿床,包括贱金属、重晶石、萤石等[7]。
2. 矿床地质特征
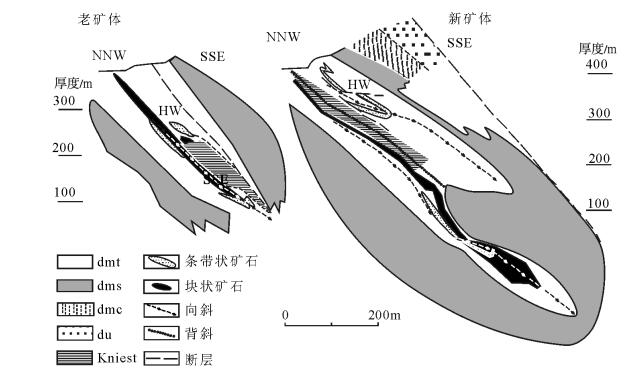
拉梅尔斯贝格矿床赋存于威森巴赫页岩中[8]。矿化层位于西哈茨隆起和哥斯拉尔海槽之间的转折端(图 2)。含矿地层以亮灰色和暗灰色纹层为特征,产于威森巴赫页岩沉积序列中的深灰色页岩中。与威森巴赫地层层序中的其他地层相比,含矿层中的碳酸盐含量明显更高,Walcher[13]认为,这些碳酸盐可能是热液成因。含矿层中含有大量的赋存在浅白色白云质纹层中的黄铁矿,这些黄铁矿以自形的颗粒状和细粒草莓状集合体产出。含矿层中Zn和Pb含量较高,但很少发现闪锌矿和方铅矿[7]。位于上哈茨地块的拉梅尔斯贝格矿床因华力西造山运动,矿化层发生褶皱,形成等斜向斜,使矿体厚度增加了一倍(图 2、图 3)。
![]() 图 2 拉梅尔斯贝格隆起到哥斯拉尔海槽横切面(据参考文献[7]修改)dmt1+2—中下威森巴赫页岩;dms—Sandband页岩;dmc—Calceola页岩;du—卡勒贝格砂岩;NL—新矿体;HW—上盘矿点Figure 2. Cross section through the Rammelsberg extending into the Goslar Through
图 2 拉梅尔斯贝格隆起到哥斯拉尔海槽横切面(据参考文献[7]修改)dmt1+2—中下威森巴赫页岩;dms—Sandband页岩;dmc—Calceola页岩;du—卡勒贝格砂岩;NL—新矿体;HW—上盘矿点Figure 2. Cross section through the Rammelsberg extending into the Goslar Through2.1 矿体特征
拉梅尔斯贝格矿床中经济价值最大的是老矿体(Old Orebody)、新矿体(New Orebody)和富含重晶石的灰色矿体(Grey Orebody)(图 3)。其他经济价值较小的矿体包括老矿体西、上盘矿点和Kniest[7]。
老矿体(包括老矿体西,是构造错断的老矿体的延伸)在走向上长约600m, 向深部延伸约300m, 厚约12m;新矿体垂深约500m, 真厚度约8m, 但由于褶皱作用使其厚度增加到约40m。新矿体是矿床中最大的矿体,铅锌储量为1930×104t, 估计品位为Pb 6%、Zn 14%和Cu 1%。该层状矿体向南东倾斜,倾角50°~60°。灰色矿体被硫化物矿体所叠覆,横向上与页岩相互穿插[14];Kniest矿体呈筒状矿化,受层控作用控制,呈菱形,长约1000m, 宽300m, 厚35m。其矿化位于老矿体的层状底板中及新矿体主要硫化物堆积往东南延伸的部分,是底板沉积物中的硅化部分,品位为Pb 1.5%、Zn 3%和Cu 1.3%。Muchez等[15]研究表明,Kniest为矿液补给带,热液流体沿Kniest向上运移并最终导致矿床的形成。Hannak[16]认为,Kniest是在华力西造山运动期间构造变形形成的与逆冲断层有关的不规则网脉。
2.2 矿物特征
拉梅尔斯贝格矿床的主要矿石矿物为黄铁矿、闪锌矿、方铅矿、黄铜矿和重晶石,其次为磁黄铁矿、毒砂、白铁矿、磁铁矿、辉铅铋矿、黝铜矿、自然金等;脉石矿物为铁白云石、萤石、方解石、石英和绿泥石[12]。由于重结晶作用和强烈的变形,硫化物的原生结构没有很好地保存下来。
黄铁矿和闪锌矿呈草莓状产出。在块状和条带状矿石中还可见结核状的成岩期黄铁矿,以及粒级层理、滑塌构造、重荷模等沉积构造[14-16]。Sperling[14]还展示了黄铜矿沿着闪锌矿内的特殊层理方向的结晶,这种结构可以与“黄铜矿病毒”结构进行对比[17],可能标志着黄铜矿开始交代闪锌矿[18]。
2.3 矿石类型
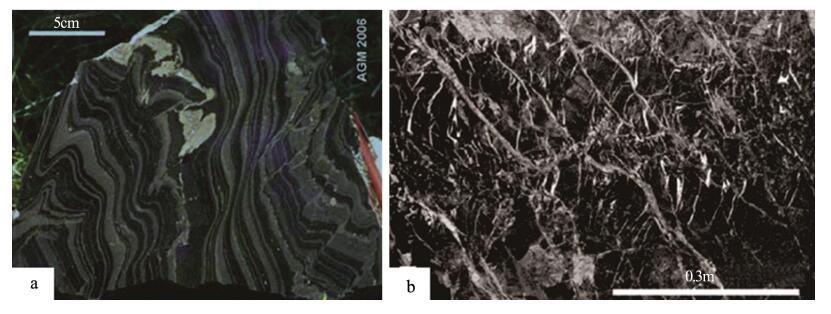
新、老矿体中的矿石分为块状矿石(LE)和条带状矿石(BE) 2类。其中块状矿石由黄铁矿、黄铜矿、闪锌矿、方铅矿及重晶石组成,在块状矿石内部还会出现清晰的侧向不连续的纹层;条带状矿石是一种有韵律的毫米级铁质白云石纹层(图 4-a),含细粒黄铁矿、闪锌矿和方铅矿,夹含黄铁矿的页岩。灰色矿体主要由细粒纹层状重晶石及共生的闪锌矿和方铅矿薄互层组成。Kniest矿化层由黄铜矿、黄铁矿、方铅矿和闪锌矿组成,矿石呈横切细脉状、透镜状和浸染状(图 4-b),常伴生石英、铁白云质方解石和绿泥石。
![]() 图 4 页岩中的条带状矿石(a)和Kniest矿石(b) (据参考文献[19])Figure 4. Banded ore in the shale(a)and Kniest ore(b)
图 4 页岩中的条带状矿石(a)和Kniest矿石(b) (据参考文献[19])Figure 4. Banded ore in the shale(a)and Kniest ore(b)2.4 蚀变
在拉梅尔斯贝格矿床中,容矿围岩的热液蚀变只表现为硅质和碳酸盐的少量增加,以及绿泥石矿物成分的轻微变化[7]。虽然细粒的电气石也出现在下盘岩石中,但被认为是沉积形成的[20]。含矿层与赋矿页岩中的绿泥石铁含量约为26%,但是矿体中的绿泥石铁含量会增加到37%~46%。绿泥石中的Fe/Mg值变化可能是接近热液活动中心的一个敏感指标[21]。
2.5 成矿阶段
根据详细的地质填图(图 1-c),矿体中的不同矿化类型与3个旋回有关,呈层状分布的块状矿石和条带状矿石组成了其中的2个旋回,条带状矿石和重晶石组成了另一个旋回(图 5)。Sperling[14]描述了Cu在核部和LE1及LE2底部富集的垂向分带特征。一些透镜状的重晶石矿产在LE1和上覆的BE2层之间的接触带上。同时,在老矿体的西缘和新矿体的东缘,发育一条富含重晶石的矿带。上覆BE3层在横向上的发育很局限,标志着新矿体中金属硫化物沉淀的结束。富含重晶石的层状灰色矿体在BE3层上方约6m产出,是该地区最后一期热液事件的产物[7]。位于新、老矿体东南边缘下盘的Kniest带富集石英,同时有锌铜矿化,标志着这种分带模型一直延伸到下盘[7]。此外,少量细脉状和浸染状硫化物产在块状硫化物下方300m处的Calceola页岩中。
![]() 图 5 拉梅尔斯贝格矿床中不同矿石类型旋回(据参考文献[7]修改)Figure 5. Different ore types in the Rammelsberg deposit
图 5 拉梅尔斯贝格矿床中不同矿石类型旋回(据参考文献[7]修改)Figure 5. Different ore types in the Rammelsberg deposit2.6 成矿年龄
拉梅尔斯贝格矿床的矿化年龄可以通过对威森巴赫页岩中古生物的研究推算出来。Reinaldo[8]对威森巴赫页岩中大量的动植物化石(包括腕足类、头足类、双壳类、海百合、珊瑚等)进行研究后发现,拉梅尔斯贝格矿床的矿化应该发生在艾菲尔期—吉维特期,这与Large and Walcher[7]的研究结论一致。
3. 矿床地球化学
3.1 硫同位素
Anger等[22]和Nielsen[23]发表了拉梅尔斯贝格矿床不同矿化类型中黄铁矿、闪锌矿、方铅矿、黄铜矿和重晶石的硫同位素数据。
黄铁矿的δ34S值变化范围为-15‰~+20‰,具有典型的成岩黄铁矿的特征。黄铜矿、闪锌矿和方铅矿中的δ34S值则较均一(5‰~10‰),块状矿石中硫化物的δ34S值为+5‰~+20‰ [7]。Nielsen[23]提供的数据表明,从Kniest到新矿体中的硫化物矿化,黄铜矿、闪锌矿、方铅矿的δ34S值逐渐变大。大部分重晶石的δ34S值为+20‰~+30‰,但Kniest中的重晶石及灰色矿体中的部分重晶石的δ34S值则较低(图 6)。
![]() 图 6 拉梅尔斯贝格矿床硫同位素数据图(据参考文献[7]修改)Figure 6. Sulfur isotope data for the Rammelsberg deposit
图 6 拉梅尔斯贝格矿床硫同位素数据图(据参考文献[7]修改)Figure 6. Sulfur isotope data for the Rammelsberg depositNielsen[23]用2个硫源来解释这些硫化物中的硫同位素数据,一个是热液成因,具有均一的δ34S值;另一个是生物成因,在矿化发生的地方细菌对海水中硫酸盐的还原作用。黄铜矿、闪锌矿和方铅矿中的硫来源于热液[23],成岩黄铁矿中的硫和重晶石中的SO42-来源于细菌对海水中硫酸盐的还原作用[14]。此外,Kniest中的重晶石是通过硫化物的氧化和溶解形成的[14],可能是其δ34S值较低的原因。
3.2 铅同位素
Doe等[24]指出,SHMS类矿床中铅同位素的形成经历了复杂的过程,包括地壳岩石在造山过程中发生熔融、沉积岩的改造、热液循环造成的沉积物的淋滤作用,以及在流体作用下发生的铅元素向矿化场所运移,是这些不同来源的铅同位素混合和均一作用的结果。
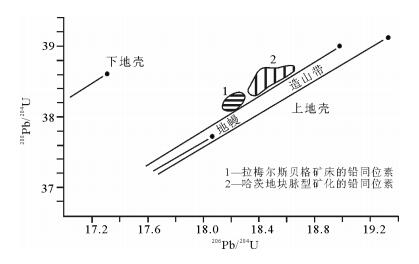
Tischendorf等[25]和Lévèque等[26]对哈茨地块的铅同位素进行了研究。由图 7可以看出,相比于哈茨地块的脉状矿化,拉梅尔斯贝格矿床中的铅同位素特征明显不同,方铅矿具有独特的铅同位素组成。此外,拉梅尔斯贝格矿床的方铅矿的铅模式年龄为340 ± 9Ma, 而地层的形成年龄约为400Ma。Tischendorf等[25]认为,华力西造山运动期间矿化岩石的变质重结晶作用造成了年龄的不同。
![]() 图 7 哈茨地块矿化层中矿石铅同位素的206Pb/204Pb和208Pb/204Pb值(据参考文献[7]修改)Figure 7. 206Pb/204Pb versus 208Pb/204Pb diagram of ore leads from mineralization bed in the Harz massif
图 7 哈茨地块矿化层中矿石铅同位素的206Pb/204Pb和208Pb/204Pb值(据参考文献[7]修改)Figure 7. 206Pb/204Pb versus 208Pb/204Pb diagram of ore leads from mineralization bed in the Harz massif拉梅尔斯贝格矿床中的铅同位素具有均匀一致的特征[12],其中206Pb/204Pb变化范围为18.242~18.311,208Pb/204Pb变化范围为38.087~38.312[27],Doe等[24]提出,这种特征和略异常的模式年龄可以用铅构造模式来解释。由此可见,拉梅尔斯贝格矿床中的铅应该来源于均匀的地壳。
4. 综合性成矿模式
4.1 拉梅尔斯贝格矿床与SHMS类矿床的对比
将拉梅尔斯贝格矿床的地质特征与SHMS类矿床的典型特征进行对比(表 1),可见拉梅尔斯贝格拥有SHMS类矿床的大部分特征。
表 1 拉梅尔斯贝格矿床与沉积型块状硫化物矿床特征对比(据参考文献[7]修改)Table 1. Attributes of the sediments-hosted massive sulfide(SHMS)deposits compared with the observations at Rammelsberg对比内容 沉积块状硫化物矿床 拉梅尔斯贝格矿床 形成环境 受断层控制的盆地内的沉积岩容矿。岩相和厚度横向上的变化反映了垂直构造运动和不同的沉降速率 哥斯拉尔海槽是以断层为边界的盆地,它与西哈茨隆起之间的沉积相和厚度有明显的变化。拉梅尔斯贝格位于西哈茨隆起和哥斯拉尔海槽之间的转折端附近 与盆地演化关系 矿化发生在盆地发展的后裂谷“热沉降”阶段 中泥盆统页岩序列是在后裂谷热沉降阶段沉积形成的 与岩浆活动关系 与岩浆活动在时间和空间上都有密切联系 哥斯拉尔海槽内的艾菲尔阶页岩序列中的辉绿岩岩床,含矿地层中见凝灰岩层 容矿围岩特征 容矿沉积岩:原地沉积岩是细碎屑岩和碳酸盐岩,它们都沉积在低能量环境中;异地沉积岩是在高能量环境中迅速沉积的粗碎屑岩、泥石流和砾岩,可能与同生沉积断裂活动有关 威森巴赫页岩序列中的页岩和粉砂岩反映了当时的低能量环境。局部的泥石流和松软沉积物变形 时代分布 沉积型块状硫化物矿床主要集中在中元古代和古生代 形成于泥盆纪 产出特征 块状硫化物矿化受层控产出,走向长达6km,厚度变化大。层状构造很常见 2个具有层状结构的块状硫化物矿体,一个层控重晶石矿体 筒状矿化特征 产出在块状硫化物下面的筒状矿化(脉、细脉和交代作用),可能为热液通道或者喷口 筒状矿化的Kniest带可能是层控块状硫化物的热液供给通道 品位和吨位 具有经济价值的矿体达到上千万吨的矿石量(一些元古宙矿床甚至有上亿吨矿石量),Zn+Pb品位大于10%,Cu通常并不重要 典型的具有经济价值的沉积型块状硫化物矿床,矿石储量27~30Mt,品位高,14%Zn+6%Pb,1%的Cu含量使其在沉积型块状硫化物矿床中也很少见 金属分带特征 Cu+Fe核靠近喷口,Pb和Zn分散在周围,在周边和/或者上覆有重晶石化 在块状硫化物中发现了Cu-Pn-Zn垂直分带,重晶石到处都有,但只在上覆的“灰矿”中富集 原生硫化物特征 原生硫化物主要为细粒闪锌矿-黄铜矿,并伴有磁黄铁矿和/或者黄铁矿,少量毒砂和黝铜矿 主要硫化物为黄铁矿、闪锌矿、方铅矿和黄铜矿,还有少量磁黄铁矿、毒砂、磁铁矿和黝铜矿 蚀变 常见硅化和碳酸盐化(主要为铁碳酸盐)。偶见电气石化、钠长石化、绿泥石化和绢云母化 Kniest微富集二氧化硅、绿泥石和钠长石。铁白云石是块状矿石的主要成分之一,菱铁矿脉也产在Kniest中 铅同位素特征 每个矿床中的铅同位素组成均一 拉梅尔斯贝格矿床的铅同位素组成均一 硫同位素特征 硫一般有2个来源:一个是热液来源,具有均一的δ34S值;另一个是生物还原海水硫,其δ34S值变化范围大。重晶石中的硫反映的是海水硫酸盐中的硫 拉梅尔斯贝格矿床中的硫有2种来源,一种是热液来源;另一种是生物成因,是细菌还原海水中硫 与大多数显生宙SHMS类矿床相比,拉梅尔斯贝格矿床相对富铜,原因目前还不清楚。富铜的源岩(如基性火山岩)和高温的矿化热液可能是主要原因,这可能与中泥盆世局部地壳破裂导致上哈茨地区产生的高地热梯度有关[28]。黄铜矿在温度低于300℃时具有可溶性[29],而高地热梯度可能会导致黄铜矿的溶解度降低,使拉梅尔斯贝格矿床的铜局部富集。
4.2 成矿物质来源
SHMS类矿床成矿流体的典型特征是成矿温度260℃,盐度8%~10%NaCl, 非常低的O2活性,非常高的CO2活性,低的H2S活性和弱酸-中性pH值[7]。尽管没有收集到拉梅尔斯贝格矿床的流体包裹体数据,但是矿物组合和硫同位素数据表明,成矿热液流体的化学特征可能与上述典型的SHMS类矿床相差不大。
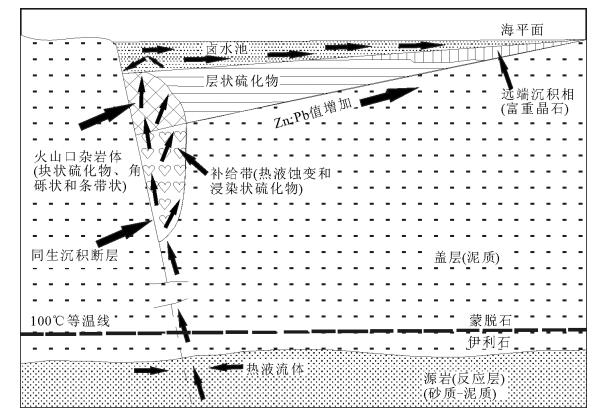
SHMS类矿床热液流体的来源可以用盆地排烃模式来解释。在这个模式中,流体来源于下伏的沉积岩。对发育在封闭的孔隙中的含金属卤水来说,下泥盆统同裂谷期沉积的碎屑岩是合适的可渗透储集层。在中泥盆世,该含水层被上覆的后裂谷期沉积的页岩(威森巴赫页岩)封闭。深穿透的断层和在后裂谷伸展构造期间地热梯度的增加,使这些含金属的热液卤水被集中到喷口处沉积成矿[7]。
与盆地排烃模式不同,Russell[30]通过对一些典型SHMS类矿床的研究,认为SHMS类矿床形成于海底热液对流系统中。他把该系统分为3个阶段:早期低温阶段,流体和地壳矿物之间未达到平衡,只有Fe、Ca、Mn、Zn和部分Si被溶解;中期阶段,对流核下渗,温度升高,流体和黄铁矿达到平衡;晚期阶段,在最理想的条件下,对流核渗透到底部为止,流体温度继续升高,体积继续增大,这时Pb、Zn、H2S,甚至是Cu的溶解度都会提高。这种情况下形成的矿体会随着地层层序的上升,Cu含量逐渐增加。
Goodfellow等[31]提出了SHMS类矿床成矿流体的3种来源:① 来源于含有蒸发岩的泥质沉积物的埋藏作用和压实作用;② 来源于含有高盐度含水层的沉积序列;③ 来源于达到海侵点的裂谷沉降。
4.3 SHMS类矿床的成矿模型
大多数人认为,SHMS类矿床是同生沉积的[12,28,31],形成于喷流沉积的环境中(图 8)。此类矿床模型有以下特征[32]。
(1) 闪锌矿-方铅矿-黄铁矿-重晶石矿化呈层状分布,细层状硫化物在单一地层中横向延伸,同时含有沉积构造,例如粒级层理、交错层理、硫化物碎屑等。
(2) 硫化物层全部由热液矿物组成,夹层由少量同源的热液矿物组成,硫化物层和夹层之间接触界线截然。
(3) 硫化物层发生不协调褶皱,上覆未发生变形的地层。横向和纵向上的金属分带与交代作用无关。此外,一些矿床中的不整合接触的底板矿化和蚀变可能为流体卸载的通道。
5. 结论
(1) 拉梅尔斯贝格矿床的铜-锌-铅-钡矿体赋存于威森巴赫页岩中,具有明显的层控特点,是典型的以沉积岩为容矿围岩的块状硫化物(SHMS)矿床。矿床形成于泥盆纪,与同生断裂活动有关。
(2) 硫同位素组成显示,拉梅尔斯贝格铜-锌-铅-钡矿床有2个硫源,一个来自热液;另一个来自细菌还原的海水中的硫酸盐。与其他SHMS类矿床相比,拉梅尔斯贝格矿床明显富铜。
-
图 2 拉梅尔斯贝格隆起到哥斯拉尔海槽横切面(据参考文献[7]修改)
dmt1+2—中下威森巴赫页岩;dms—Sandband页岩;dmc—Calceola页岩;du—卡勒贝格砂岩;NL—新矿体;HW—上盘矿点
Figure 2. Cross section through the Rammelsberg extending into the Goslar Through
图 4 页岩中的条带状矿石(a)和Kniest矿石(b) (据参考文献[19])
Figure 4. Banded ore in the shale(a)and Kniest ore(b)
图 5 拉梅尔斯贝格矿床中不同矿石类型旋回(据参考文献[7]修改)
Figure 5. Different ore types in the Rammelsberg deposit
图 6 拉梅尔斯贝格矿床硫同位素数据图(据参考文献[7]修改)
Figure 6. Sulfur isotope data for the Rammelsberg deposit
图 7 哈茨地块矿化层中矿石铅同位素的206Pb/204Pb和208Pb/204Pb值(据参考文献[7]修改)
Figure 7. 206Pb/204Pb versus 208Pb/204Pb diagram of ore leads from mineralization bed in the Harz massif
表 1 拉梅尔斯贝格矿床与沉积型块状硫化物矿床特征对比(据参考文献[7]修改)
Table 1 Attributes of the sediments-hosted massive sulfide(SHMS)deposits compared with the observations at Rammelsberg
对比内容 沉积块状硫化物矿床 拉梅尔斯贝格矿床 形成环境 受断层控制的盆地内的沉积岩容矿。岩相和厚度横向上的变化反映了垂直构造运动和不同的沉降速率 哥斯拉尔海槽是以断层为边界的盆地,它与西哈茨隆起之间的沉积相和厚度有明显的变化。拉梅尔斯贝格位于西哈茨隆起和哥斯拉尔海槽之间的转折端附近 与盆地演化关系 矿化发生在盆地发展的后裂谷“热沉降”阶段 中泥盆统页岩序列是在后裂谷热沉降阶段沉积形成的 与岩浆活动关系 与岩浆活动在时间和空间上都有密切联系 哥斯拉尔海槽内的艾菲尔阶页岩序列中的辉绿岩岩床,含矿地层中见凝灰岩层 容矿围岩特征 容矿沉积岩:原地沉积岩是细碎屑岩和碳酸盐岩,它们都沉积在低能量环境中;异地沉积岩是在高能量环境中迅速沉积的粗碎屑岩、泥石流和砾岩,可能与同生沉积断裂活动有关 威森巴赫页岩序列中的页岩和粉砂岩反映了当时的低能量环境。局部的泥石流和松软沉积物变形 时代分布 沉积型块状硫化物矿床主要集中在中元古代和古生代 形成于泥盆纪 产出特征 块状硫化物矿化受层控产出,走向长达6km,厚度变化大。层状构造很常见 2个具有层状结构的块状硫化物矿体,一个层控重晶石矿体 筒状矿化特征 产出在块状硫化物下面的筒状矿化(脉、细脉和交代作用),可能为热液通道或者喷口 筒状矿化的Kniest带可能是层控块状硫化物的热液供给通道 品位和吨位 具有经济价值的矿体达到上千万吨的矿石量(一些元古宙矿床甚至有上亿吨矿石量),Zn+Pb品位大于10%,Cu通常并不重要 典型的具有经济价值的沉积型块状硫化物矿床,矿石储量27~30Mt,品位高,14%Zn+6%Pb,1%的Cu含量使其在沉积型块状硫化物矿床中也很少见 金属分带特征 Cu+Fe核靠近喷口,Pb和Zn分散在周围,在周边和/或者上覆有重晶石化 在块状硫化物中发现了Cu-Pn-Zn垂直分带,重晶石到处都有,但只在上覆的“灰矿”中富集 原生硫化物特征 原生硫化物主要为细粒闪锌矿-黄铜矿,并伴有磁黄铁矿和/或者黄铁矿,少量毒砂和黝铜矿 主要硫化物为黄铁矿、闪锌矿、方铅矿和黄铜矿,还有少量磁黄铁矿、毒砂、磁铁矿和黝铜矿 蚀变 常见硅化和碳酸盐化(主要为铁碳酸盐)。偶见电气石化、钠长石化、绿泥石化和绢云母化 Kniest微富集二氧化硅、绿泥石和钠长石。铁白云石是块状矿石的主要成分之一,菱铁矿脉也产在Kniest中 铅同位素特征 每个矿床中的铅同位素组成均一 拉梅尔斯贝格矿床的铅同位素组成均一 硫同位素特征 硫一般有2个来源:一个是热液来源,具有均一的δ34S值;另一个是生物还原海水硫,其δ34S值变化范围大。重晶石中的硫反映的是海水硫酸盐中的硫 拉梅尔斯贝格矿床中的硫有2种来源,一种是热液来源;另一种是生物成因,是细菌还原海水中硫 -
王炜, 鲍征宇, 李璇, 等. SEDEX型矿床地质地球化学特征及研究趋势[J].物探与化探, 2010, 34(4):415-434. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201004000.htm 毛景文, 张作衡, 王义天, 等.国外主要矿床类型、特点及找矿勘查[M].北京:地质出版社, 2012. 王玉奇. Sedex型矿床和VMS型矿床对比研究[J].资源环境与工程, 2009, 23(3):259-262. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK200903010.htm 黄志伟.喷流沉积型铅锌矿床的主要控矿构造[J].西部探矿工程, 2013, 10:154-157. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2013.06.051 Cooke D R, BullS W, Large R, et al. The importance of oxidized brines for the formation of Australian Proterozoic stratiform sedi-ment-hosted Pb-Zn(Sedex) deposits[J]. Economic Geology, 2000, 95:1-18. http://econgeol.geoscienceworld.org/content/95/1/1
关东杰.拉梅尔斯贝格——近代欧洲矿冶业的摇篮[J].金属世界, 1995, 3:26. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSSJ199503017.htm Large D, Walcher E. The Rammelsberg massive sulphide Cu-ZnPb-Ba-Deposit, Germany:an example of sediment-hosted, massive sulphide mineralisation[J].Miner. Deposita, 1999, 34:522-538. doi: 10.1007/s001260050218
Reinaldo S. Black shales and massive sulfide deposits:causal or casual relationships? Insights from Rammelsberg, Tharsis, and Draa Sfar[J]. Miner. Deposita, 2011, 46:584-614. doi: 10.1007/s00126-010-0311-x
Berthelsen A. Mobile Europe[C]//Blundell D, Freeman R, Mueller S. A continent revealed the European geotraverse. Cambridge:Cam-bridge University Press, 1992:11-32.
Wachendorf H. Der Harz-variszischer Bau und geodynamische Entwicklung[J]. Geol. Jahrb. A, 1986, 91:3-67.
Albrecht A. Isotopic age determinations of crystalline rocks of the Upper Harz Mountains, Germany[J]. Geologische Rundschau, 1991, 80(3):669-690. doi: 10.1007/BF01803694
Müller G, Strauss W B. Beitrag zur Regionalmetamorphose des Harzes[J]. Geologische Rundschau, 1985, 74:87-94. doi: 10.1007/BF01764572
Walcher E H. Geologisch-lagerstättenkundliche Untersuchungen am Zeitäquivalent (Lagerhorizont) der Lagerstätte Rammelsberg[D]. Germany:TU Clausthal phD Thesis, 1986.
Sperling H. Das Neue Lager der Blei-Zink-Erzlagerstätte Ram-melsberg[J]. Geol. Jahrb D, 1986, 85:5-177.
Muchez P, Stassen P. Multiple origin of the'Kniest feeder zone' of the stratiform Zn-Pb-Cu ore deposit of Rammelsberg, Germa-ny[J]. Miner. Deposita, 2006, 41(1):46-51. doi: 10.1007/s00126-005-0039-1
Hannak W W. Genesis of the Rammelsberg ore deposit near Gos-lar/Upper Harz, Federal Republic of Germany[C]//Wolf K H. Handbook of stratabound and stratiform ore deposits. Elsevier, Am-sterdam, 1981, 9:551-642.
Craig J R, Vaughan D J. Ore microscopy and ore petrology[M]. New York:Wiley-Interscience, 1981.
Eldridge C S, Barton P B, Ohmoto H. Mineral textures and their bearing on formation of the Kuroko orebodies[J]. Econ. Geol. Monogr., 1983, 5:241-281.
Mueller A G. The Rammelsberg shale-hosted Cu-Zn-Pb sulfidebarite deposit, Germany:Linking SEDEX and Kuroko-type mas-sive sulfides. Slide presentation and explanatory notes[EB/OL] (2008-03-21)[2015-06-05] https://www.e-sga.org/index.php?id=199.
Paul D J. Sedimentologische und geologische Untersuchungenzur Rekonstruktion des Ablagerungsraumesvor and nach der Bildung der Rammelsberger Blei-Zink-Lager im Oberharz[J]. Geol. Jahrb D, 1975, 12:3-93.
Renner T. Schichtsilikate und Karbonateals Faziesindikatoren in den synsedimentär-exhalativen Lagerstätten Rammelsberg, Meg-gen und Eisen[J]. Z Dtsch Geol Ges, 1986, 137:253-285. http://www.schweizerbart.de/papers/zdgg_alt/detail/137/53840
Anger G, Nielsen H, Puchelt H, et al. Sulfur isotopes in the Ram-melsberg ore deposit (Germany)[J]. Econ. Geol., 1966, 61:511-536. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.61.3.511
Nielsen H. Sulfur isotope ratios in strata-bound mineralizations in Central Europe[J]. Geol. Jahrb D, 1985, 70:225-262.
Doe B, Zartman R E. Plumbotectonics. The Phanerozoic[C]//Barnes H L.Geochemistry of hydrothermal ore deposits. New York:Wiley-Interscience, 1979:22-70.
Tischendorf G, Bielicki K H, Franzke H J. On the genesis of Perm-ian and post-Permian mineralizations in the Harz Mountains ac-cording to new Pb-isotope measurements[C]//Möller P, Lüders V. Formation of hydrothermal vein deposits. A case study of the Pb-Zn, barite and fluorite deposits of the Harz Mountains. Monogr Ser on Mineral Deposits, 1993, 30:65-76.
Lévèque J, Haack U. Pb isotopes of hydrothermal ores in the Harz[C]//Möller P, Lüders V. Formation of hydrothermal vein de-posits. A case study of the Pb-Zn, barite and fluorite deposits of the Harz Mountains. Monogr Ser on Mineral Deposits, 1993, 30:197-210.
Monna F, Hamer K, Lévêque J, et al. Pb isotopes as a reliable mark-er of early mining and smelting in the Northern Harz province (Lower Saxony, Germany)[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1999, 68(3):201-210.
Large D E. Sediment-hosted massive sulphide lead-zinc deposits:an empirical model[C]//Sangster D F. Sediment-hosted, stratiform lead-zinc deposits. Miin Assoc Can Short Course Handbook, 1983, 8:1-29.
Lydon J W. Chemical parameters controlling the origin and deposi-tion of sediment-hosted stratiform lead-zinc deposits[C]//Sangster D F. Sediment-hosted, stratiform lead-zinc deposits.Miin Assoc. Can Short Course Handbook, 1983, 8:175-250.
Russel M J. Major sediment-hosted exhalative zinc-lead deposits:formation from hydrothermal convection cells that deepen during crustal extension[C]//Sangster D F. Short Course in SedimentHosted Stratiform Lead-Zinc Deposits. Victoria:Mineralogical As-sociation of Canada, 1983:251-282.
Goodfellow W D, Lydon J W, Turner R. Geology and genesis of stratiform sediment-hosted (SEDEX) zinc-lead-silver sulphidede-posits[J]. Geol. Assoc. Can. Spec. Pub., 1994, 40:201-251.
Misra K C. Understanding Mineral Deposits[M]. Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1999.



 下载:
下载: