Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of the albitite in the Boka gold ore district, Yunnan Province
-
摘要:
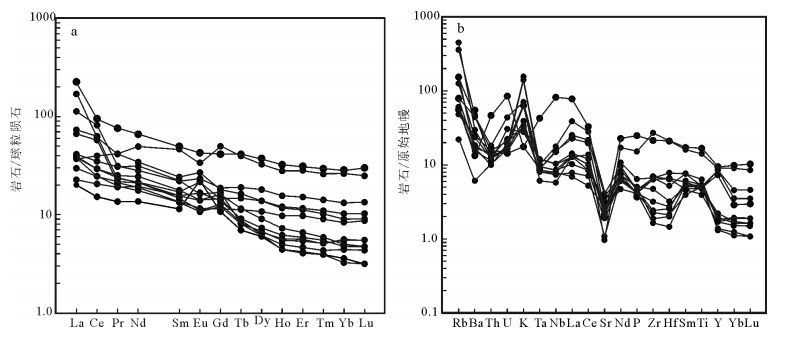
播卡金矿床位于滇中元古代铜金多金属成矿带之东川矿集区。重点报道了区内与成矿密切相关的钠长岩的岩相学、岩石地球化学及同位素特征。研究表明,播卡钠长岩的主要造岩矿物有钠长石、辉石、黑云母,主量元素特征显示其为富碱、高钠、偏铝质的碱性-过碱性岩石。岩石的稀土元素总量低,相对富集轻稀土元素,明显富集大离子亲石元素K、Rb、Nd及轻稀土元素La、Ce、Sm,相对亏损高场强元素Nb、Ta、U、Th等。岩石的Isr值、εNd(t)值显示,其可能为中元古代晚期会理-东川一带大陆裂谷岩浆作用的产物,来源于深部地幔,可能有部分陆壳物质的参与。
Abstract:The Boka gold deposit is located in the Dongchuan ore concentration area, and belongs to Yunnan Proterozoic copper polymetallic mineralization belt. This paper reports the petrography, geochemistry and isotope features of albitite that is closely related to mineralization. Studies show that the mineral compositions of albitite are albite, pyroxene, biotite, and the major element characteris-tics indicate a high Na, alkali-enriched, metaluminous, alkaline-peralkaline rock. This albitite is characterized by low ΣREE, strong enrichment of LILE(K, Rb, Nd)and LREE(La, Ce, Sm), and depletion of HFSE elements(Nb, Ta, U, Th). Based on Isr, εNd(t)isoto-pic geochemistry, it is suggested that Boka albitite was produced by magmatism of Middle Proterzoic continent rift in Huili-Dongch-uan area, and it was derived from the deep mantle with the addition of some crustal materials in the magma source region.
-
Keywords:
- Boka albitite /
- petrography /
- geochemistry /
- enriched mantle /
- Yunnan Province
-
江西省是中国重要的有色及贵金属产地,也是环太平洋成矿带的组成部分之一。长期以来,钦杭成矿带在铜、铅、锌、钨、锡、金、银、铁等矿种找矿勘查和科研方面均取得了重要进展。近年来在赣南—武夷地区,相继发现了园岭寨、铜坑嶂、葛廷坑、新安、熊家山、金竹坪等钼矿床,另外,在赣北地区又发现了大湖塘、石门寺、朱溪等钨矿床,使地质工作的中心向北部地区转移,提出“南钨北扩”的思想,使钨钼矿找矿勘查及成矿理论研究得到较大的进步。赣中地区的“新余式铁矿”,是中国重要的BIF型铁矿产地之一,在铁矿的勘查研究方面取得了较多的成果;对其他类型的金属矿床研究较少,且多以钨矿床及钨钼多金属矿床为主,如徐山钨矿、大王山钨矿、阳储岭钨钼矿床、浒坑钨钼矿床等。近年来,随着矿山开采深度的增加,在良山铁矿区发现了具有工业价值的钼矿体。现阶段工作证实,良山钼矿床具有良好的工业价值,钼资源储量达到中等规模,赣中地区具有钼矿床的找矿前景。
锆石是广泛存在于地质体中的一种副矿物。具有高U、Th值,却很少含Pb, 抗侵蚀能力很强,形成后不受外界因素的干扰。锆石是岩浆结晶年龄测定最理想的矿物,尤其适合酸性侵入岩测年[1]。本文选取矿区内与成矿关系密切的良山斑岩体进行LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄测定,获取准确的成岩年龄;同时,为确定该矿床的成矿时代,选取矿床的主要矿石矿物辉钼矿进行Re-Os同位素测定。以期查明成岩时代与成矿时代的世代关系,探讨成岩、成矿之间的关系,为深入研究该矿床的成因、深化区域成矿规律研究及指导同类矿床的进一步找矿提供科学依据。
1. 矿床地质特征
赣中良山钼矿主要分布于赣中地区中西部,钼矿床与新余良山铁矿产出位置相同,成矿区带为钦杭成矿区带(江西段);大地构造位置为钦杭结合带南侧边缘,南华造山带北缘武功山-北武夷隆起带西段。次一级区域构造为武功隆起带东段[2]的神山倒转背斜南翼北东、黄虎背形[3]向斜轴线以东的单斜构造[4-6](图 1),是铁矿田的区域性控矿构造,由东西向神山倒转背斜的南翼及其西部外倾转折端组成。神山复背斜由青白口系神山组构成核部,而南翼则由南华系上施组、下坊组和大砂江地层组成。
![]() 图 1 江西新余铁矿田区域地质简图(据参考文献[6]修改)Q—第四系;Z1l—乐昌群老虎塘组;Z1b—乐昌群坝里组;Nh2xf2—杨家桥群下坊组上段;Nh2xf1—杨家桥群下坊组下段;Nh2g—杨家桥群古家组;γ5—燕山期石英闪长岩;γ4—印支二云母花岗岩;γ3—加里东期花岗闪长岩;F—断层及推测断层图;★—良山钼矿所在地Figure 1. Geological map of the Xinyu iron orefield, Jiangxi Province
图 1 江西新余铁矿田区域地质简图(据参考文献[6]修改)Q—第四系;Z1l—乐昌群老虎塘组;Z1b—乐昌群坝里组;Nh2xf2—杨家桥群下坊组上段;Nh2xf1—杨家桥群下坊组下段;Nh2g—杨家桥群古家组;γ5—燕山期石英闪长岩;γ4—印支二云母花岗岩;γ3—加里东期花岗闪长岩;F—断层及推测断层图;★—良山钼矿所在地Figure 1. Geological map of the Xinyu iron orefield, Jiangxi Province区内构造活动非常强烈,褶皱构造与断裂构造均较发育。褶皱构造位于黄虎背形的倾伏端,轴线呈北西向展布,由倾向不同的倒转地层构成两翼,其次为同斜紧密褶皱构造。褶皱自地表向北西或北西西方向深部倾伏逐渐消失,具有浅繁深简的构造特点,并且在褶皱构造的基础上发育更次一级的断裂构造。断裂构造较发育,且有多期次活动的特点,主要有北东向、北西向、北北东向3组断裂构造。其中最主要的断裂构造是北东向,倾向南东,少数倾向北西,大多与褶皱轴平行或斜交,断层面倾角较陡,多属逆断层、复活断层,断层规模不大。
区内岩浆活动频繁,以侵入岩类为主。燕山期岩浆活动规模最大、最频繁、最强烈,岩石种类非常多。主要的岩浆岩有西部的山庄花岗闪长斑岩和东部的城上花岗岩体,两岩体皆呈岩基侵入于震旦系上部地层中,出露面积达120km2和164km2。张菲菲等[7]对山庄岩体测年,得到山庄花岗闪长岩年龄为424±3Ma(锆石U-Pb年龄)、楼法生等[8]测得的锆石U-Pb年龄为460.5±1.5Ma, 表明山庄岩体为加里东期复式岩体。城上岩体,李吉人[9]称其为金滩岩体,北部为加里东期斜长花岗岩,南部为华力西期(226±2Ma, 锆石U-Pb年龄)黑云母二长花岗岩,是一个多期次侵入的花岗岩体;其次为燕山期侵入酸性小岩体,在良山、北坑、粟木、城门北、武元、下桐岭、芳洲等地均有出露。
良山矿区出露的地层有南华系上施组、古家组、下坊组、松山组及第四系[10-11]。地层在矿区内总体倾向为北—北西向,倾角较平缓,多为20°~30°。南华系为一套浅变质相变火山岩-沉积岩组合。主要岩性有浅灰色、棕黄色变余砂岩、砂质千枚岩、石英砂岩、含砾绢云千枚岩、磁铁石英岩、变中酸性沉凝灰岩和含绿泥白云母石英片岩夹石英片岩薄层,以及褐灰色含炭质绢云石英片岩夹含锰白云质灰岩。石英粒晶普遍沿片理方向拉长,黑云母常退变质为绿泥石,本层自上而下黑云母减少,绿泥石增多。地层自井头矿区以东为向北倒转的层序,倾向北(北西)—北东,倾角20°~45°;以西为正常层序,倾向南西—西,倾角20°~70°。区内断裂构造发育,以北东—北北东向和北北西-北西向2组最发育。断裂构造是石英脉型钼矿体的赋矿部位,矿体及围岩蚀变主要沿断裂构造发育。区内岩浆岩主要为侵入岩,有东部的城上花岗岩体、西部的山庄花岗闪长岩和中部的良山石英闪长斑岩体。城上岩体(或称为金滩岩体)为多期复合岩体,呈岩基侵入震旦系上部地层中;北部为加里东期斜长花岗岩,南部为华力西期黑云母二长花岗岩,并有燕山早期花岗岩侵入[6](图 1)。良山岩体为燕山期小岩株,侵入含矿地层中,并且切割铁矿层,岩性主要为石英闪长斑岩、花岗闪长斑岩,近地表风化较严重,钼矿体主要产于岩体边缘外接触带(图 2)。区内变质岩系的变质程度不高,褶皱基底层为绿片岩相,局部的准盖层为亚绿片岩相,沉积盖层均未出现变质现象。由于经历了多期次的造山活动,变形及动力变质作用十分强烈。变质作用类型主要为区域变质作用,变质等级一般为绿片岩相,板岩、千枚岩发育,局部地段有云母片岩形成。在褶皱构造及其次级叠加构造之上发育的断裂构造为钼矿床的主要赋矿部位和控矿构造。
![]() 图 2 江西新余良山钼矿床地质简图(据参考文献[11]修改)Nh2xf2—杨家桥群下坊组上段;Nh2xf1—杨家桥群下坊组下段;Nh2s—潭头群上施组;γδπ52—燕山期石英闪长斑岩;γ4—印支期黑云母花岗岩;Fe—铁矿层;Mo—钼矿体;1—勘探线及编号;7802—钻孔及编号;F—正断层Figure 2. Geological map of the Liangshan molybdenum deposit in Xinyu County, Jiangxi Province
图 2 江西新余良山钼矿床地质简图(据参考文献[11]修改)Nh2xf2—杨家桥群下坊组上段;Nh2xf1—杨家桥群下坊组下段;Nh2s—潭头群上施组;γδπ52—燕山期石英闪长斑岩;γ4—印支期黑云母花岗岩;Fe—铁矿层;Mo—钼矿体;1—勘探线及编号;7802—钻孔及编号;F—正断层Figure 2. Geological map of the Liangshan molybdenum deposit in Xinyu County, Jiangxi Province良山钼矿床受勘查程度的影响,现阶段的主要矿体为良山斑岩体外接触带中产出的石英脉型钼矿,石英脉呈白色、乳白色块状,石英结晶较好、晶洞发育。矿石矿物为辉钼矿,金属矿物有黑钨矿、黄铁矿、黄铜矿、磁铁矿、闪锌矿等,脉石矿物主要为石英、绿泥石,次为方解石、绢云母、角闪石等。另外还含有极少量的副矿物,如磷灰石等。矿体的辉钼矿多呈灰黑色,颗粒较小,呈细小片状,一般为0.005~1.1mm, 少数粒度可达2mm。自形程度较差,有板片状、他形鳞片状、片状。但个别呈厚板状、带状分布,晶体常发生弯曲或挠曲,局部辉钼矿聚集呈玫瑰花状、束状或团块集合体,常发生弯曲,多色性也较明显。辉钼矿在石英脉中多以集合体形式产出,有脉状、团块状及薄膜状。
2. 锆石U-Pb测年
2.1 样品挑选及测试方法
用于锆石U-Pb定年的样品D011-01采于良山小岩体顶部,地理坐标为北纬27°38′55″、东经114°55′30″。锆石挑选在廊坊市地科勘探技术服务有限公司进行。野外采集2kg岩石样品,按照岩石中锆石的粒度,将样品按相应目数粉碎,反复淘洗,挑选出富集在重矿物组分中的锆石,随后进行电磁选分离,将样品按照不同磁性组分分选。在双目镜下对锆石样品进行挑选检查,除去其他残留矿物。按宋彪等[12]的锆石样品靶制作方法,将挑选好的无色透明、无裂隙、不含包裹体的锆石置于环氧树脂中,然后磨至约1/2,使锆石内部暴露,为防止击穿,磨掉的锆石部分均小于整体的1/2。待环氧树脂充分固化后,对样品进行抛光至最大面积露出锆石核部。之后在透射光与反射光下对锆石进行显微照相,并在阴极发光下对锆石进行图像观察与拍照,用以圈定测年用锆石颗粒的位置。锆石制靶及阴极发光(CL)照相由北京锆年领航科技有限公司完成。
锆石U-Pb同位素组成及微量元素组成分析在中国地质大学(武汉)地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室激光剥蚀等离子体质谱(LA-ICP-MS)仪器上完成,激光剥蚀孔径32μm, 脉冲8Hz, 以氦气作载气、氩气为补偿气以调节灵敏度。锆石年龄采用标准锆石91500作为外部标准物质,元素含量采用NIST610作为外标。样品分析流程为每测定5个样品点,测定2次锆石标准91500,在开始测量和测定结束后分别测定NIST610、91500和GJ-1等标样。每个样品点的数据采集时间共100s, 其中前20s为气体背景采集时间。由LA-ICP-MS获得的铅同位素数据采用Anderson的3D坐标法校正普通铅,离线数据采用软件ICP-MS DataCal完成后期处理。
2.2 测试结果
在进行锆石U-Pb测年分析前,在显微镜下对每个锆石的晶体形态进行观察并进行粒度统计,然后选择晶形好、包裹体和裂隙少的锆石颗粒制靶并进行阴极发光(CL)照相。测年锆石主要为半自形-自形晶,晶形完整,大多呈浅黄色-无色状,少量呈浅棕色,部分含有继承核,个别可见扇形分带结构。锆石颗粒粒径一般介于100~200μm之间,长宽比介于2:1~3:1之间;振荡环带生长边清晰,可见残留晶核(图 3)。锆石中振荡环带的形成受锆石结晶时岩浆温度的影响[13]。温度影响微量元素扩散的快慢,高温下微量元素扩散快,易形成较宽的结晶环带;低温下微量元素扩散慢,一般形成较窄的岩浆环带[14-15]。良山斑岩体主群锆石均具有较窄的结晶环带特征,暗示这些锆石可能形成于深部岩浆结晶过程的晚期,或岩浆浅成侵位时期[16]。
对良山钼矿区花岗岩岩株(D011-01)中的锆石进行了23个测试点的LA-ICP-MS分析,U-Pb同位素组成见表 1。
表 1 良山花岗岩体(DX011-01)锆石U-Pb同位素LA-ICP-MS分析结果Table 1. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb data of zircons from the Liangshang granites序号 同位素比值 同位素年龄/Ma 元素含量/10-6 Th/U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ Th U Pb 01 0.05048 0.000835 0.1814 0.00329 0.02598 0.000307 169.3 2.83 165.4 1.93 1680 7484 178 0.22 02 0.05152 0.000804 0.1817 0.00303 0.02551 0.000275 169.5 2.60 162.4 1.73 1792 6285 168 0.29 03 0.04964 0.000765 0.1794 0.00315 0.02614 0.000311 167.6 2.72 166.4 1.96 1885 6300 176 0.30 04 0.04841 0.000723 0.1782 0.00300 0.02660 0.000287 166.5 2.59 169.2 1.80 956 8452 158 0.11 05 0.05424 0.000871 0.2430 0.00456 0.03239 0.000411 220.9 3.73 205.5 2.57 1134 5801 162 0.20 06 0.05000 0.000834 0.1775 0.00321 0.02565 0.000273 165.9 2.77 163.3 1.72 2403 6830 200 0.35 07 0.05273 0.000879 0.1938 0.00385 0.02650 0.000321 179.9 3.28 168.6 2.02 2132 14208 307 0.15 08 0.04937 0.000924 0.1872 0.00372 0.02746 0.000346 174.3 3.19 174.7 2.17 1320 5389 139 0.24 09 0.04888 0.000812 0.1760 0.00319 0.02607 0.000315 164.6 2.76 165.9 1.98 1404 10589 205 0.13 10 0.04867 0.000795 0.1797 0.00342 0.02673 0.000354 167.8 2.95 170.1 2.22 1866 6410 175 0.29 11 0.05292 0.001050 0.3394 0.01086 0.04528 0.001236 296.7 8.24 285.5 7.62 712 2071 87 0.34 12 0.05306 0.001134 0.2000 0.00435 0.02726 0.000386 185.1 3.68 173.4 2.42 1689 5078 165 0.33 13 0.05420 0.000782 0.3503 0.00664 0.04665 0.000621 305.0 5.00 293.9 3.83 2454 4953 339 0.50 14 0.05248 0.000939 0.2692 0.00703 0.03689 0.000672 242.1 5.63 233.5 4.18 1480 4457 195 0.33 15 0.05785 0.000937 0.4196 0.00842 0.05259 0.000818 355.7 6.03 330.4 5.01 2339 4477 359 0.52 16 0.04913 0.000848 0.1749 0.00326 0.02581 0.000317 163.6 2.82 164.3 2.00 4040 7380 280 0.55 17 0.04966 0.000961 0.2105 0.00557 0.03067 0.000595 194.0 4.68 194.8 3.72 1507 4295 135 0.35 18 0.05360 0.000800 0.1968 0.00339 0.02661 0.000322 182.4 2.87 169.3 2.02 2163 8609 248 0.25 19 0.05798 0.001294 0.5659 0.01320 0.07096 0.000914 455.3 8.57 441.9 5.51 655 752 111 0.87 20 0.04693 0.000811 0.1751 0.00356 0.02707 0.000384 163.8 3.08 172.2 2.41 2022 4238 153 0.48 21 0.05059 0.000903 0.2060 0.00433 0.02949 0.000399 190.2 3.65 187.3 2.50 1767 3699 141 0.48 22 0.04956 0.000794 0.1813 0.00332 0.02654 0.000331 169.2 2.86 168.9 2.08 2282 6961 206 0.33 23 0.04849 0.000910 0.1846 0.00399 0.02759 0.000355 172.0 3.42 175.4 2.23 1497 4971 142 0.30 锆石中的Th/U值可以指示锆石的成因,一般情况下,岩浆锆石的Th、U含量较高,Th/U值较大(一般大于0.4);变质锆石的Th、U含量低,Th/U值小(一般小于0.1)[15,17]。U-Pb同位素分析结果表明,良山钼矿区花岗岩的U含量为800×10-6~15434×10-6,Th含量为656×10-6~4138×10-6,U、Th含量较高,Th/U值介于0.1~0.9之间,均大于0.1。典型的岩浆锆石晶体柱面平直发育,具有亮色的阴极发光,在阴极发光下具有明显的振荡环带结构[15,17-20]。锆石的阴极发光图像、自形程度及Th/U值表明,锆石为岩浆锆石,其主群锆石的U-Pb年龄代表岩体侵位年龄。
上述结果表明,锆石具有自形-半自形结构、典型的岩浆振荡环带、高Th/U值等特征,充分说明样品主群锆石的U-Pb谐和年龄可以代表岩体的侵位时代。样品D011-01共测试23个锆石数据,其中核部点位1个(11-19),中间环带5个分析点为11-05、11-11、11-13、11-14和11-15,剩下点位为边部环带。谐和年龄图(图 4)显示,良山岩体岩浆锆石年龄主要有3个阶段,分别为441.9±5.5Ma(继承核,加里东期)、203.2±2.6~293.9±3.8Ma(中间环带、海西期—印支期),以及168.2±2.3Ma(边部环带、燕山期),表明岩浆活动具有多期次、继承性的特征。在边部谐和年龄图中,11~17号的谐和性较差,偏离谐和线较远,其余16组分析点均投影在谐和线上或其附近,测试点的年龄值在162~187Ma之间,年龄加权平均值为168.2 ± 2.3Ma(MSWD=5.4,n=16,图 4)。数据变化范围小,数据点成群分布,锆石颗粒形成后的U-Pb同位素体系基本封闭[21]。这些锆石年龄具有较好的谐和度,个别锆石数据点落在谐和线附近,可能是铅丢失的原因[13],指示这些锆石在同一期岩浆事件中形成,代表了花岗岩最后的侵位年龄。
3. 辉钼矿Re-Os年龄测定
辉钼矿以含Re和放射性成因的187Os及极微量的普通Os为特征,且普通Os中的187Os更微量,测定N(187Os)/N(187Re)值可以获得准确的辉钼矿结晶年龄[22]。辉钼矿Re-Os同位素测定是目前有效的定年方法之一,广泛地应用于矿床年代学的研究。良山钼矿体中的辉钼矿含量较多,呈鳞片状集合体嵌布于石英和长石粒间,沿裂隙充填,少数呈浸染状分布。本文挑选了矿石样品中的辉钼矿进行ReOs年龄测定。
3.1 样品的采集与分析
用于Re-Os同位素测年的6件样品均采自良山钼矿床采坑的含钼石英脉中。辉钼矿单矿物的挑选在河北省廊坊市地科勘探技术服务有限公司进行,将样品粉碎至60~80目,经淘洗和磁选后,在双目镜下进一步分选,样品纯度达99%以上,然后用玛瑙钵研磨至200目。用于Re-Os同位素测试分析的辉钼矿质纯、无污染。
辉钼矿样品Re-Os同位素测试在国家地质实验测试中心Re-Os同位素实验室完成。采用美国TJA公司生产的电感耦合等离子体质谱仪TJA Xseries ICP-MS测定同位素比值。Re-Os同位素分析的化学分离过程与分析方法见参考文献[23],分析标样(HLP)的Re、187Os及模式年龄与标准值在误差范围内完全一致,表明所获辉钼矿的数据准确可靠(表 2)
表 2 良山钼矿床辉钼矿Re-Os同位素测年结果Table 2. Molybdenite Re-Os isotope test data sheet for the Liangshan deposit样名 样重/g Re/10-6 C普Os/10-9 187Re/10-6 187Os/10-9 模式年龄/Ma JX52-3A 0.00505 230.2±3.4 3.2538±0.8432 144.7±2.2 407.6±3.3 168.9±3.3 JX52-3C 0.00227 343.9±2.8 0.0073±0.3172 216.2±1.7 609.4±3.9 169.0±2.4 JX52-3E 0.00559 86.7±6.6 0.0024±0.1076 54.51±4.1 154.0±0.9 169.4±2.3 JX52-5B 0.00217 538.9±5.7 0.0078±0.4228 338.7±3.6 953.2±6.6 168.7±2.7 JX52-6A 0.00222 239.0±2.4 0.0074±0.1597 150.2±1.5 421.0±2.6 168.0±2.6 JX52-6B 0.00202 380.7±4.1 0.0083±0.4506 239.3±2.6 680.0±4.8 170.3±2.8 注:普Os是根据Nier值的Os同位素丰度,通过192Os/190Os测量比计算得出,Re、Os含量的不确定度包括样品和稀释剂的称量误差、稀释剂的标定误差、质谱测量的分馏校正误差、待分析样品同位素比值测量误差,置信水平95%,模式年龄的不确定度还包括衰变常数的不确定度(1.02%),置信水平95%;Re-Os模式年龄按下列公式计算:t=1/λ{ln[1+N(187Os)/N(187Re)]};λ为187Re的衰变常数1.666×10-11/a(±1.02%)[24];t表示矿物形成后的年龄,在公式中单位为年(a) 3.2 测年结果
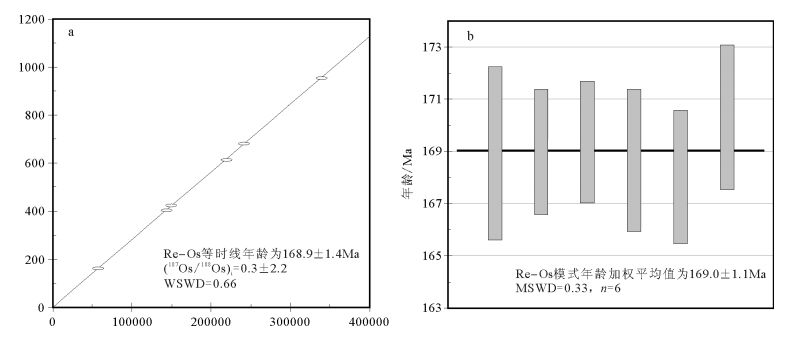
辉钼矿Re-Os年龄测试数据显示,6件辉钼矿样品的187Re含量为54.51×10-6~338.7×10-6,187Os含量为154.0×10-9~953.2×10-9。良山钼矿床6件样品的模式年龄分布在168.0±2.6~170.3±2.8Ma之间,模式年龄变化范围不大。测试结果显示,在Re-Os同位素比值等时线图(图 5-a)中,6件辉钼矿样品构成一条良好的等时线,等时线年龄为168.9±1.4Ma, MSWD=0.66;Re-Os模式年龄加权平均值为169.0±1.1Ma(图 5-b)。6件样品的初始Os值均近似于0,说明在辉钼矿形成时矿物内几乎不存在初始Os[14],同位素体系封闭后,Os完全由衰变而来。6件辉钼矿的Re-Os年龄无论是等时线年龄或单点模式年龄加权平均值,都有很好的一致性,表明辉钼矿的沉淀时间为168.9±1.4Ma。需要说明的是,辉钼矿的Re-Os体系可以在极强的区域变质或岩浆热事件(可达800℃)下依然保持封闭[25-26]。尽管良山矿区含矿斑岩遭受了一定程度的动力变形和后期风化剥蚀(前述石英的波状消光及黑云母的“膝折”),但是良山矿区的变质程度仅达到低级,变形则以脆性变形为主,其变质变形强度及温度均不足以干扰Re-Os同位素体系,故其测试数据可靠。
上述研究表明,良山钼矿床辉钼矿的沉淀年龄为168.9±1.4Ma, 其成矿时代为168.9±1.4Ma, 为中侏罗世。
4. 讨论
南华纪早期为强烈的火山-裂谷期,沿钦-杭结合带发生强烈伸展,形成了华南海盆及华南裂谷系,中性-中酸性-酸性火山喷发,中性-中酸性-酸性岩浆侵入;下扬子(皖浙)海槽属扬子陆块一部分,早古生代末海槽闭合。早古生代晚期的加里东运动,形成了华南加里东造山带,并有酸性岩浆侵入。本文获得的岩体继承锆石年龄为441.9 ±5.5Ma, 其代表的岩浆活动年龄与研究区内山庄花岗闪长岩岩体锆石U-Pb年龄460.5Ma[8]相当,表明其形成于华南早古生代晚期的一次重要构造-岩浆作用事件,与扬子地块与华夏地块在新元古代存在一次碰撞拼合作用的观点一致[28-30],至此完成了扬子、华夏古板块的拼合,表明良山地区经历此次岩浆-构造事件,形成了核部的继承锆石,这是该地区岩浆基底的形成阶段。二叠纪开始,大洋板片向西北方向水平俯冲,造成陆内迁移造山[9,31],古特提斯洋在早—中三叠世关闭,使华南地区发生强烈的构造-岩浆作用[32]。继承锆石中间环带的海西期—印支期岩浆活动痕迹表明,此次岩浆活动持续时间很久;至中三叠世末,印支期大规模造山运动,形成大型复式背向斜,出现了浅色花岗岩带,最后完成了区内由海到陆的变革事件,成为现代欧亚板块浅色花岗岩带的组成部分。中—晚三叠世,华北板块与扬子板块发生碰撞[33-34],均导致华南造山带重新活动,处于扬子板块东南侧的武功山也受到强烈挤压作用,导致岩石变形,拉开了武功山变质核杂岩形成的序幕。自晚三叠世起,本区进入滨太平洋构造域强烈陆(缘)内造山发展时期。侏罗纪爆发了具有变革意义的燕山运动,早侏罗世末陆内发生较强的挤压收缩,开始出现(向洋)隆、坳分异及北东向走滑冲断带。早侏罗世花岗岩体的存在,证明古太平洋(南部的库拉板块、北部的伊泽奈崎板块)向东亚陆缘低角度俯冲[32,35],导致大规模的中生代岩浆活动[36-38]。武功山地区经历了由挤压向拉张的转化,地壳伸展减薄,岩石圈厚度明显减薄,强烈的伸展为岩浆与成矿热液活动提供了有利的通道,导致大规模的岩浆活动,带来足够的热量,使中、下地壳部分熔融,大量酸性岩浆向上运移,向地壳减压处迅速扩张,促使周围岩石软化,软化或韧性的围岩环境有利于伸展构造的发展。
进入中生代后,区域构造环境由挤压向伸展环境转变[39],在中国东部大规模成矿作用下,晋宁期形成的大量花岗岩体被富含成矿物质的燕山期岩浆侵入。在岩浆作用过程中,钼在中酸性岩浆活动系列范围内以较强的运移能力富集,特别是花岗岩形成阶段。岩浆侵位过程中,上地壳岩石部分熔融,成矿热流体萃取早期花岗岩中的成矿物质,使得岩浆热液内成矿物质不断富集。富集成矿物质的岩浆热液沿断裂构造上涌的过程中,由于外部物理条件发生改变(特别是温度、压力等环境参数的改变),以及后期流体(地表渗水或地下水、大气降水)的加入,使成矿物质在运移中状态发生改变,并在通道内发生沉淀富集成矿。
良山矿区的岩浆岩主要为矿区内的良山石英闪长斑岩侵入体,在地表形似小岩株,侵入体与矿体的时空关系、矿体的成因存在明显的联系。侵入体锆石测年结果显示,石英闪长斑岩样品的206Pb/208U年龄为168.2±2.3Ma, 形成于燕山早期中侏罗世,应为碰撞造山期后伸展背景的产物。对矿石中辉钼矿样品进行Re-Os测年,获得的等时线年龄为168.9±1.4Ma。良山钼矿床矿石中硫的来源单一,主要来源于岩浆,其铅同位素组成变化较大,具有壳幔混源特点,以放射成因铅为主。氢、氧同位素研究结果表明,成矿流体具混合流体特征,因此推断,良山钼矿成矿流体早期以深源流体为主,随着成矿过程的演化,大气降水所占的比例越来越大。总体来说,良山钼矿床的成矿流体和成矿物质同位素地球化学特征,都指示矿床成因与岩浆热液成矿作用具有密切的联系[40]。矿脉主要沿北东向的构造侵入产出,自岩体向外,岩浆岩和矿体在空间上密切相关。良山钼矿床明显受岩浆作用控制,离斑岩越近,钼金属矿化越强;距离斑岩体越远矿化越弱,且矿化分散,矿体厚度和品位均逐渐减小。无论在走向或倾向上,发生矿化的距离都在岩浆活动的热力影响范围内,矿体分布也不超出岩浆岩热力影响范围。良山斑岩体和矿体具有明显的时空关系,表明它们之间具有密切的成因联系。强烈的岩浆活动,在提供矿质的同时,也为成矿作用提供了矿质、流体和热源,且岩浆岩本身就是矿体,带来了大量的成矿物质,同时也成为热流体与热液的主要供应者。本次研究获得的岩浆岩锆石U-Pb年龄和辉钼矿Re-Os年龄基本一致,成岩年龄接近成矿年龄,成岩作用与成矿作用同时发生,表明成矿与良山斑岩体产生的热液流体有密切关系。
5. 结论
良山钼矿床的成岩成矿年代学研究表明,矿床成矿时代为168.9 ± 1.4Ma, 成岩时代为168.2 ±2.3Ma, 表明良山钼矿床与赋矿岩体密切相关。综合硫、铅同位素地球化学特征,该矿床的成矿物质来源于下部花岗岩体,且成岩作用与成矿作用同时发生。良山钼矿床成矿地质体为石英闪长斑岩,岩浆活动具有多期次、多旋回的特点,钼矿化与矿区内岩浆活动关系密切,成岩作用与成矿作用同时发生于燕山早期挤压背景体制下的局部拉张环境,属于华南中生代成矿大爆发时期的产物。
致谢: 南京大学顾连兴教授参与并指导了该项研究工作,野外工作期间得到云南金山矿业公司总经理刘军等领导和同行的关心和支持,在此一并表示衷心的感谢。 -
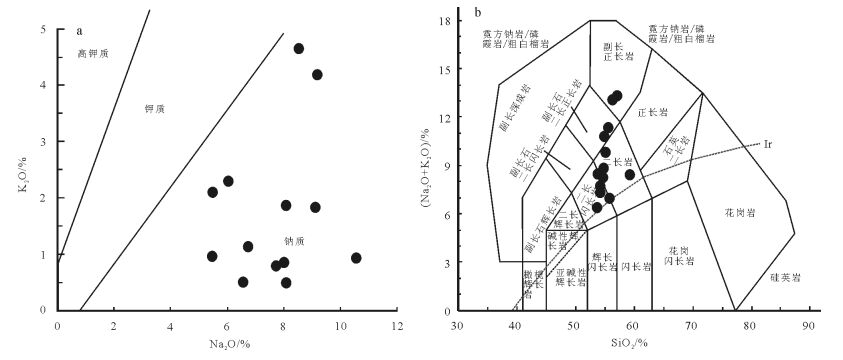
图 5 播卡钠长岩AR-SiO2判别图解[38]
Figure 5. AR-SiO2 discrimination diagram for albitite in the Boka gold ore district
表 1 碱性岩体中斜长石的电子探针分析结果
Table 1 Electron microprobe analyses of the plagioclase from alkali pluton
% 样品号
岩性
点号BK8
钠长岩BK88
钠长岩BK82
辉绿岩① ② ③ ① ② ③ ① ② ③ SiO2 65.92 65.93 70.27 65.87 67.26 67.44 64.88 66.06 65.05 TiO2 - - 0 0.01 - - 0.01 0.01 0.01 Al2O3 21.07 21.08 22.01 20.87 21.01 22.3 22.01 20.66 21.69 FeO 0.09 0.04 0.08 0.28 0.11 0.09 0.31 0.14 0.2 MnO - - - - 0 0.01 0.01 0.01 - MgO 0.02 - - 0.02 0.01 - 0.04 0.02 0.05 CaO 0.31 0.3 0.15 0.43 0.85 0.95 1.04 0.52 0.62 Na2O 11.74 12.06 7.01 11.79 11.4 9.22 11.12 11.94 11.61 K2O 0.05 0.07 0.04 0.21 0.12 0.13 0.23 0.04 0.05 F - - 0.05 - - - - - - Cl 0.01 0 0.01 - - - - - - 总计 99.21 99.48 99.62 99.48 100.76 100.14 99.65 99.4 99.28 An 1.43 1.35 1.16 1.95 3.93 5.34 4.85 2.35 2.86 Ab 98.29 98.27 98.47 96.91 95.41 93.79 93.87 97.44 96.87 Or 0.28 0.38 0.37 1.14 0.66 0.87 1.28 0.21 0.27 注:由东华理工大学重点实验室测试,“-”低于检出限 表 2 播卡金矿区钠长岩中LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb测试结果
Table 2 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb dating results of albitite in the Boka gold ore district
点号 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 208Pb/232Th 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ bk13-1 0.1059 0.0015 4.3136 0.0659 0.2954 0.0039 0.0584 0.0021 1696 13 1669 19 bk13-2 0.1088 0.0021 3.1197 0.0617 0.2080 0.0030 0.0414 0.0015 1438 15 1218 16 bk13-3 0.0870 0.0016 1.9981 0.0383 0.1666 0.0023 0.0360 0.0015 1115 13 993 13 bk13-4 0.1036 0.0018 2.6151 0.0480 0.1832 0.0026 0.0369 0.0014 1305 13 1084 14 bk13-5 0.1153 0.0024 3.5842 0.0743 0.2255 0.0034 0.0452 0.0017 1546 16 1311 18 bk13-6 0.1031 0.0024 2.8166 0.0658 0.1981 0.0031 0.0401 0.0015 1360 18 1165 17 bk13-7 0.1061 0.0014 3.1455 0.0463 0.2150 0.0028 0.0441 0.0016 1444 11 1255 15 bk13-8 0.1047 0.0014 2.7625 0.0401 0.1913 0.0025 0.0393 0.0014 1345 11 1128 13 bk13-9 0.1212 0.0016 3.1825 0.0469 0.1905 0.0025 0.0392 0.0014 1453 11 1124 13 bk13-10 0.1067 0.0018 3.0049 0.0520 0.2043 0.0028 0.0416 0.0015 1409 13 1198 15 bk13-11 0.1003 0.0017 3.4794 0.0609 0.2516 0.0035 0.0526 0.0019 1523 14 1447 18 bk13-12 0.1082 0.0021 3.3891 0.0658 0.2272 0.0033 0.0435 0.0016 1502 15 1320 17 bk13-13 0.0997 0.0013 3.1139 0.0453 0.2265 0.0029 0.0496 0.0018 1436 11 1316 15 表 3 播卡金矿区钠长岩主量元素组成
Table 3 The components of major elements for albitite in the Boka gold ore district
% 样品号 BK -8 BK -48 BK -85 BK -46 BK -88 BK52 BK56 BK57 BK59 BK74 BK78 BK80 BK81 SiO2 59.21 55.72 54.23 53.65 55.03 55.55 53.67 54.22 54.62 54.94 54.59 56.23 56.96 TiO2 3.63 1.06 1.12 1.03 0.95 1.08 3.07 1.06 1.38 1.1 0.87 1.17 1.15 Al2O3 15.54 17.54 16.89 16.39 17.62 15.3 14.41 17.17 16.84 14.32 15.18 15.09 15.31 TFe4O3 4.45 10.63 9.54 12.74 7.57 7.77 10.11 11.22 10.77 10.97 12.63 5.05 4.52 Fe2O3 1.27 3.04 2.73 3.64 2.16 2.22 2.89 3.21 3.08 3.13 3.61 1.44 1.29 FeO 3.18 7.59 6.81 9.1 5.41 5.55 7.22 8.01 7.69 7.84 9.02 3.61 3.23 MnO 0.14 0.05 0.12 0.04 0.03 0.13 0.21 0.05 0.05 0.06 0.14 0.03 0.05 MgO 5.22 5.47 4.6 6.47 6.58 6.62 7.95 7.25 5.18 5.72 6.6 7.55 6.39 CaO 1.33 0.68 2.92 1.57 0.99 0.96 0.86 0.52 1.06 0.92 0.75 0.79 1.05 Na2O 8.08 6.55 5.42 5.44 8.06 10.53 7.71 6.73 8.01 9.09 6.03 8.52 9.18 K2O 0.53 0.53 2.13 1.02 1.9 0.97 0.84 1.18 0.9 1.87 2.36 4.69 4.24 P2O5 0.54 0.09 0.1 0.09 0.08 0.11 0.33 0.09 0.14 0.09 0.09 0.1 0.11 烧失量 1.33 1.68 2.82 1.56 1.19 1.02 0.85 0.51 1.06 1.02 0.76 0.78 1.05 总计 103.12 108.95 106.61 111.18 106.38 106.79 109.27 110.71 109.72 110.05 111.87 104.27 103.48 K2O+Na2O 8.61 7.08 7.55 6.46 9.96 11.5 8.55 7.91 8.91 10.96 8.39 13.21 13.42 K2O/Na2O 0.07 0.08 0.39 0.19 0.24 0.09 0.11 0.18 0.11 0.21 0.39 0.55 0.46 TFe4O3/MgO 0.85 1.94 2.07 1.97 1.15 1.17 1.27 1.55 2.08 1.92 1.91 0.67 0.71 A/CNK 0.95 1.39 1.02 1.27 1.03 0.76 0.95 1.29 1.05 0.77 1.1 0.74 0.71 σ 4.48 3.79 4.7 3.74 8 10.3 6.68 5.5 6.65 9.83 5.95 12.97 12.63 AR 4.55 2.59 4.26 2.92 4.28 9.77 4.76 2.93 3.9 10.74 4.03 26.69 35.45 SI 28.56 23.6 21.21 25.2 27.29 25.57 29.88 27.48 20.84 20.69 23.9 29.25 26.26 表 4 播卡金矿区钠长岩微量和稀土元素组成
Table 4 The components of trace and rare earth elements for albitite in the Boka gold ore district
10-6 样品号 BK -8 BK -48 BK -85 BK -46 BK -88 BK52 BK56 BK57 BK59 BK74 BK78 BK80 BK81 Ba 93.05 117.95 317.01 309.39 383.89 129 108 42.6 174 165 117 208 327 Rb 35.4 49.76 96.04 51.29 97.47 38.5 34.4 14 30.6 79.9 97.6 285 227 Sr 45.42 41.49 86.52 79.19 59.49 48.2 20.4 22.9 41 58.3 40.1 53.5 67.9 Y 43.02 33.59 38.46 38.78 38.19 8.38 41.4 10.04 7.73 6.27 7.75 5.94 8.89 Zr 240.05 77.21 74.16 70.88 64.18 53 303 35.7 74.1 25.3 18.4 27.1 21.1 Nb 58.44 11.01 12.64 10.79 10.8 5.6 7.4 5.26 7.41 5.63 4.12 6.12 6.11 Th 3.96 1.2 1.55 1.31 1.42 1.12 0.97 0.87 1.33 1.03 0.85 1.06 1.04 U 1.78 0.3 0.92 0.32 0.41 0.47 0.64 0.34 0.44 0.35 1 0.37 0.36 Pb 1.34 2.48 4.94 10.78 7.2 4.9 7.44 3.83 4.65 10.8 6.82 5.25 5.2 Ni 12.37 78.25 60.13 52.46 86.32 25.1 28.8 39.8 44.2 31.5 180 33.7 31 V 138.29 58.6 84.59 67.58 80.52 193 164 168 285 144 240 253 233 Hf 6.49 2 2.41 2.02 1.93 0.99 6.55 0.84 1.61 0.66 0.45 0.79 0.62 Ta 1.75 0.36 0.41 0.36 0.35 0.33 0.49 0.33 0.49 0.35 0.25 0.39 0.39 Co 5.6 41.14 40.38 36.74 31.27 35.4 38.1 24.6 33.3 35.2 467 20.1 29.9 Cs 0.48 2.22 5.03 3.4 7.44 0.82 1.54 0.5 0.58 3.73 3.44 10.45 8.89 La 53.49 15.75 26.71 17.36 40.2 9.05 8.77 5.37 9.79 4.75 8.91 9.29 7.04 Ce 58.2 35.27 49.85 38.52 37.48 18 24.3 12.6 21.4 9.3 15.1 17.9 15 Pr 7.22 2.01 2.97 2.19 3.93 2.25 3.96 1.81 2.93 1.29 1.87 2.38 2.06 Nd 30.76 8.84 13.07 9.96 16.02 9.94 23.1 9.07 14.6 6.36 8.22 11.4 9.9 Sm 7.61 2.08 3.36 2.61 3.7 2.25 7.12 2.4 3.41 1.75 2.04 2.71 2.38 Eu 2.48 0.67 1.35 1.25 1.56 0.64 1.96 0.81 0.94 1.29 0.62 0.82 0.97 Gd 8.49 2.33 3.84 2.96 3.71 2.62 10.2 3.31 3.48 2.2 2.48 3.01 2.85 Tb 1.54 0.42 0.71 0.55 0.61 0.31 1.48 0.43 0.3 0.26 0.3 0.33 0.34 Dy 9.48 2.73 4.57 3.51 3.5 1.69 8.28 2.3 1.72 1.52 1.55 1.58 1.86 Ho 1.83 0.55 0.88 0.68 0.66 0.32 1.58 0.41 0.31 0.25 0.28 0.25 0.35 Er 5.15 1.61 2.5 1.92 1.85 0.93 4.67 1.09 0.89 0.69 0.77 0.67 0.97 Tm 0.75 0.23 0.36 0.28 0.26 0.13 0.66 0.15 0.13 0.1 0.11 0.1 0.14 Yb 4.85 1.42 2.24 1.74 1.53 0.95 4.44 0.85 0.93 0.61 0.75 0.55 0.81 Lu 0.76 0.22 0.34 0.26 0.23 0.14 0.63 0.12 0.14 0.08 0.11 0.08 0.12 ΣREE 192.61 74.13 112.75 83.79 115.24 49.22 101.15 40.72 60.97 30.45 43.11 51.07 44.79 LREE 159.76 64.62 97.31 71.89 102.89 42.13 69.21 32.06 53.07 24.74 36.76 44.5 37.35 HREE 32.85 9.51 15.44 11.9 12.35 7.09 31.94 8.66 7.9 5.71 6.35 6.57 7.44 LREE/HREE 4.86 6.79 6.30 6.04 8.33 5.94 2.17 3.70 6.72 4.33 5.79 6.77 5.02 LaN/YbN 7.91 7.96 8.55 7.16 18.85 6.83 1.42 4.53 7.55 5.59 8.52 12.12 6.23 Nb/Ta 33.39 30.58 30.83 29.97 30.86 16.97 15.10 15.94 15.12 16.09 16.48 15.69 15.67 Rb/Sr 0.78 1.20 1.11 0.65 1.64 0.80 1.69 0.61 0.75 1.37 2.43 5.33 3.34 δEu 0.94 0.93 1.15 1.37 1.27 0.80 0.70 0.88 0.83 2.01 0.84 0.87 1.14 δCe 0.63 1.32 1.13 1.31 0.58 0.95 1.01 0.99 0.97 0.90 0.86 0.91 0.95 表 5 钠长岩Rb-Sr和Sm-Nd同位素测试结果
Table 5 Rb-Sr and Sm-Nd isotopic analyses of albitite
样品编号 岩性 Rb/10-6 Sr/10-6 87Rb/86Sr 87Sr/86Sr 2σ Isr BK-8 钠长岩 35.4 45.42 2.26105 0.736645 5 0.71127 BK-88 钠长斑岩 97.47 59.49 4.76709 0.766728 4 0.71322 BK82 辉长辉绿岩 81.42 192.27 1.22633 0.718593 6 0.70106 样品编号 岩性 Sm/10-6 Nd/10-6 147Sm/144Nd 143Nd/144Nd 2σ εNd(t) BK-8 钠长岩 7.61 30.76 0.14948 0.512366 27 -0.56 BK-88 钠长斑岩 3.7 16.02 0.139548 0.511998 9 -6.75 BK82 辉长辉绿岩 3.73 15.63 0.14419 0.512113 5 -3.53 注:Isr在计算过程中,选择Rb的衰变常数λRb=1.42×10-11a-1,表中及TDM计算过程中选择衰变常数λSm=6.54×10-12a-1;表中采用标准值(147Sm/144Nd)CHUR=0.512638;tDMNd计算用(147Sm/144Nd)DM=0.21357,(143Nd/144Nd) DM=0.51315 -
龚琳, 王承尧.论"东川式铜矿"的成因[J].地质科学, 1981, (3):203-211. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX198103000.htm 何毅特.东川铜矿成矿系列、矿床类型及成矿模式[J].云南地质, 1996, 15(4):319-329. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNZD604.000.htm 何国朝, 杨成奎, 张祖圻.东川裂谷因民期火山-岩浆活动特征[J].矿产与地质, 1997, 11(4):236-242. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD704.003.htm 薛步高.东川式铜矿伴生组分地质特征[J].地质与勘探, 1995, 31(3):31-37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT503.006.htm 张学诚, 马丽华, 陈启良.东川稀矿山铜(铁)矿床火山-喷流沉积作用的初步研究[J].云南地质, 1994, 13(2):139-148. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNZD402.002.htm 冉崇英.东川式层状铜矿的成因模式[J].中国科学(B辑), 1983, 3:249-258. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ198902001.htm 华仁民.东川式层状铜矿的沉积-改造成因[J].矿床地质, 1989, 8(2):3-13. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ198902001.htm 李志伟.浅议"东川式"铜矿床成因[J].云南地质, 1992, 11(1):47-51. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNZD199201009.htm 龚琳, 何毅特, 陈天佑, 等.云南东川元古宙裂谷型铜矿[M].北京:冶金工业出版社, 1996:150-222. 薛步高.论东川脉状富铜矿的历史和现实意义[J].矿产与地质, 1997, 11(4):217-224. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD704.000.htm 常向阳, 朱炳泉, 孙大中, 等.东川铜矿床同位素地球化学研究:Ⅰ.地层年代与铅同位素化探应用[J].地球化学, 1997, 26(2):32-38. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX702.004.htm 蒋家申.东川矿区地质找矿研究问题[J].云南地质, 1998, 17(1):46-56. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNZD801.004.htm 陈和生.东川辉长岩型铜矿地质特征及其找矿意义[J].云南地质, 1998, 17(1):75-80. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNZD801.007.htm 曹德斌.滇中元江东昆阳群因民组-落雪组的厘定及其意义[J].云南地质, 1999, 18(2):196-200. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNZD199902009.htm 吴富强, 游廷安, 王伟华.云南东川地区播卡铜矿成矿规律研究[J].地质学刊, 2012, 36(1):17-22. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSDZ201201005.htm 李志伟, 钱祥贵, 田敏.东川拖布卡-布卡地区金矿地质特征及找矿意义[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2000, 24:37-43. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK2000S1004.htm 李志伟, 田敏, 刘和林, 等.东川拖布卡金矿地质及成矿年代学[J].云南地质, 2003, 22(4):371-381. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNZD200304002.htm 程辉明.昆明东川区播卡金矿地质[J].云南地质, 2005, 24(4):361-370. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNZD200504004.htm 薛步高.东川拖布卡金矿矿化层位与找金方向[J].云南地质, 2005, 24(3):243-253. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNZD200503000.htm 张建斌, 肖红.云南播卡金矿成因分析[J].地质找矿论丛, 2011, 26(4):399-405. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK201104008.htm 吴富强, 柳硕林, 赵培松, 等.云南东川地区播卡矿田沉积环境初探[J].地质学刊, 2010, 34(3):238-243. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSDZ201003002.htm 吴富强, 黄均权, 赵培松, 等.云南东川播卡金矿区以往地质勘查资料的分析与评价[J].地质找矿论丛, 2010, 25(1):30-35. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK201001006.htm 吴富强, 赵培松, 李朝旭.昆明东川区播卡金矿地球化学特征与成因[J].物探与化探, 2011, 35(1):28-32. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201101008.htm 吴富强, 梁胜跃.云南东川地区播卡金矿成矿规律研究[J].黄金科学技术, 2011, 19(1):1-5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ201101002.htm 张刚生, 李达明.云南东川铜矿田白锡腊铜矿床岩浆岩岩石地球化学特征[J].矿产与地质, 1996, 10(4):224-231. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD604.002.htm 张翼飞.云南东川地区含金剪切带型金矿[J].云南地质, 2003, 22(4):360-370. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNZD200304001.htm 张学诚, 高俊彩.昆明市东川拖布卡金矿矿石岩石学研究[J].云南地质, 2006, 25(3):276-285. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNZD200603001.htm 柳玉龙, 郑厚义.东川滥泥坪矿区辉长岩-闪长岩地质特征及找矿意义[J].中国矿业, 2011, 20(6):77-79. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA201106024.htm 肖晓牛, 张少云, 鞠昌荣, 等.云南东川人占石铜矿床地质特征及成因研究[J].地质与勘探, 2012, 48(2):237-249. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201202006.htm 应汉龙, 刘和林, 李志伟.云南东川播卡-拖布卡地区含金石英脉的40Ar/39Ar年龄及其地质意义[J].地质论评, 2004, 50(2):196-202. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200402015.htm Jackson S E, Pearson N J, Griffin W L, et al. The application of la-ser alblation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry to in situ U-Pb zircon geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 211:47-69. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.06.017
Anderson T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192:59-79. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00195-X
邱检生, 杨泽黎, 邢光福, 等.江西金溪熊家山钼矿床加里东期与燕山期花岗岩对比及其对成矿作用的启示[J].岩石学报, 2015, 31(3):656-674. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201503002.htm 濮巍, 赵葵东, 凌洪飞, 等.新一代高精度高灵敏度的表面热电离质谱仪(Triton TI)的Nd同位素测定[J].地球化学, 2004, 25(2):271-274. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200402032.htm 濮巍, 高剑峰, 赵葵东, 等.利用DCTA和HIBA快速有效分离Rb-Sr、Sm-Nd的方法[J].南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 41(4):445-450. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJDZ200504016.htm Middlemost E A K. A simple classification of volcanic rocks[J]. Bull. Volcanol., 1975, 36:282-397. http://www.scirp.org/journal/PaperInformation.aspx?paperID=16742
Rollinson H R. Using Trace Element Data. Using Geochemical Data:Education, Presentaion, Interpretation[M].New York:Pear-son Education Limited, 1993:1-315. https://static-content.springer.com/esm/art%3A10.1007%2Fs00531-015-1266-z/MediaObjects/531_2015_1266_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Wright J B. A simple alkalinity ratio and its application to questions of nonorogenic granite genesis[J]. Geol. Mag., 1969, 106:370-384. doi: 10.1017/S0016756800058222
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oce-anic basalts:implications for mantle composition and processes[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in ocean basins. Geological society, London, Special Publication, 1989, 42:313-345.
Mcdonough W F. Constraints on the composition of the continen-tal lithospheric mantle[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1990, 101(1):1-18. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(90)90119-I
Rudnick R L, Gao S. Composition of the continental crust[C]//Rudnick R L. Treatise on Geochemistry. Amsterdam:Elsevire, 2003, 3:1-6.
涂光炽.关于富碱侵入岩[J].矿产与地质, 1989, 3(13):1-4. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD198903000.htm Eby G N. The A-type granitoids:A review of their occurrence and chemical characteristics and speculations on their petrogeisis[J]. Lithos, 1990, 26:115-134. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(90)90043-Z
赵振华. 富碱侵入岩-窥视地幔成分的窗口[C]//欧阳自远. 中国矿物岩石地球化学研究进展[M]. 兰州: 兰州大学出版社, 1994: 113-114. Volkert R A, Feigenson M D, Patino L C. Sr and Nd isotopic com-positions age and petrogenesis of A-type granitoids of verson super-suite, New Jersey Highlands, USA[J]. Lithos, 2000, 50(4):325-347. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(99)00065-1
Fitton J G, Upton B G J. Alkaline igneous rocks[M]. Geol.Soc. Spec.Publ., 1987.
Taylor S R, Mclennan S M. The geochemical evolution of the con-tinental crust[J].Rev. Geophys., 1995, 33:165-241. doi: 10.1007/BF02842016
Green T H. Significance of Nb/Ta as an indicator of geochemical processes in the crust-mantle system[J].Chemical Geology, 1995, 120(3/4):347-359. doi: 10.1134/S001670291502007X
Weyer S, Munker C, Rehkamper M, et al. Determination of ultralow Nb, Ta, Zr and Hf concentrations and the chondritic Zr/Hf and Nb/Ta ratios by isotope dilution analyses with multiple collec-tor ICP-MS[J].Chemical Geology, 2002, 187(3):295-313. http://www.academia.edu/644809/Synthesis_and_preliminary_characterisation_of_new_silicate_phosphate_and_titanite_reference_glasses
朱华平, 范文玉, 周邦国, 等.论东川地区前震旦系地层层序:来自锆石SHRIMP及LA-ICP-MS测年的证据[J].高校地质学报, 2011, 17(3):452-461. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201103012.htm 张学诚.康滇裂谷带火山活动及其碱性(钠质)火山岩系列的岩石化学特征[J].云南地质, 1995, 14(2):81-98. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNZD502.000.htm 刘肇昌, 李凡友, 钟康惠, 等.扬子地台西缘及邻区裂谷(陷)构造与金属成矿[J].有色金属矿产与勘查, 1995, 4(2):70-76. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJS502.002.htm 赵彻终, 刘肇昌, 李凡友.会理-东川元古代海相火山岩带的特征与形成环境[J].矿物岩石, 1999, 19(2):17-74. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS902.004.htm




 下载:
下载: