Metallogenic model and prospecting direction of the Xiarihamu Ni-Cu sulfide deposit in East Kunlun area
-
摘要:
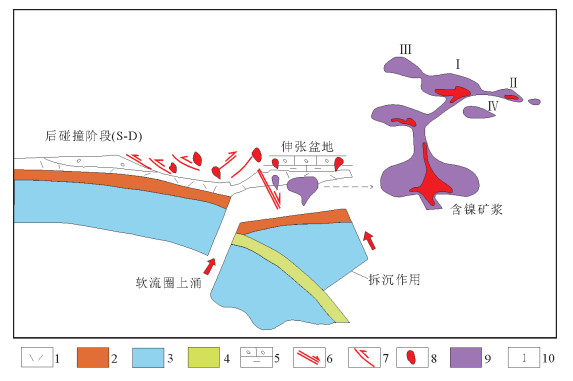
通过对夏日哈木铜镍矿成矿地质背景、矿床地质特征的研究,总结了夏日哈木铜镍矿床成矿模式。认为夏日哈木岩体群处于昆中岩浆弧带,晚志留世-早泥盆世处于陆-陆碰撞阶段伸展环境,是夏日哈木超大型镍-钴硫化物矿形成的先决条件;幔源岩浆深部熔离和向上贯入是成矿关键,熔离成矿过程中地壳混染也是一个必须条件,后期构造控制了矿体的定位以及形态。该区成矿经历了橄榄石和斜方辉石成矿期、黄铜矿和镍黄铁矿成矿期和镍华和孔雀石表生氧化期三期。据此提出下一步找矿方向,区域上昆中岩浆弧带是主要的成矿区带,矿区Ⅰ和Ⅲ号岩体中间是深部最有利的验证位置,外围拉宁灶火异常是验证的重要靶区。
Abstract:Based on a study of the metallogenic characteristics and condition as well as mechanism of the Xiarihamu Cu-Ni sulfide deposit, the authors summed up the metallogenic model of the Xiarihamu Ni-Cu sulfide deposit. The authors hold that Xiarihamu magma group was located in eastern Kunlun island arc magma zone, and that the collisional extension environment constituted the basic con-dition for the formation of the Xiarihamu superlarge Cu-Ni sulfide deposit during the Late Silurian-Early Devonian period. That constituted the prerequisite for the formation of the deposit and the key to the mineralization and the separation of sulfides as well as ore pulp injection. The crustal contamination of S played a very important role in forming Ni orebody. The orebodies are spatially controlled by faults. The metallogenic process of the Xiarihamu deposit can be divided into three stages, i.e., olivine and orthopyroxene metallogenic period, chalcopyrite and pentlandite metallogenic period, annabergite malachite and supergene oxidation stage. It is also pointed out that the regional key prospecting target is the central Kunlun magma arc zone, the area between Ⅰand Ⅲ rock bodies is the most favorable places for deep verification, and the Laningzaohuo anomaly in the periphery is an important target area for verification.
-
Keywords:
- Xiarihamu /
- Ni-Cu sulfide deposit /
- metallogenic model /
- prospecting direction
-
阶地指由于地壳上升,河流下切形成的阶梯状地貌。北京西山的隆升影响了大石河阶地的形成,阶地的研究对全面解析新构造运动的隆升意义重大。
北京西山从北向南依次分布永定河、大石河和拒马河3条河流,其中大石河形成时代最新,目前尚未见到公开发表的研究文献,对大石河阶地的研究对北京西山的新构造运动隆升有实际意义。
大石河属海河流域大清河水系北拒马河支流。发源于霞云岭乡堂上村西北,是唯一发源于房山境内的河流,《水经注》称“圣水”。大石河总流域面积为1280km2,河道全长129km,其中辛开口村以上山区河道长85km(平均比降为6.4‰),辛开口村至夏村长15km(平均比降为3‰),夏村至北京市界长21km(平均比降为0.3‰)[1]。流域内多年平均降水量600mm左右,多年平均天然径流量9570 × 104m3,枯水年天然径流量4785×104m3。建国后大石河下游发生过多次洪水灾害,1956年洪水流量为1860m3/s,是漫水河水文站实测最大洪峰流量[2]。
大石河是北京西山发育的一条未侵蚀至分水岭的河流,其阶地发育特征代表了北京西山隆升的发展过程,对北京地区现今地形地貌、新构造运动和平原区堆积物层序研究具有重要意义。
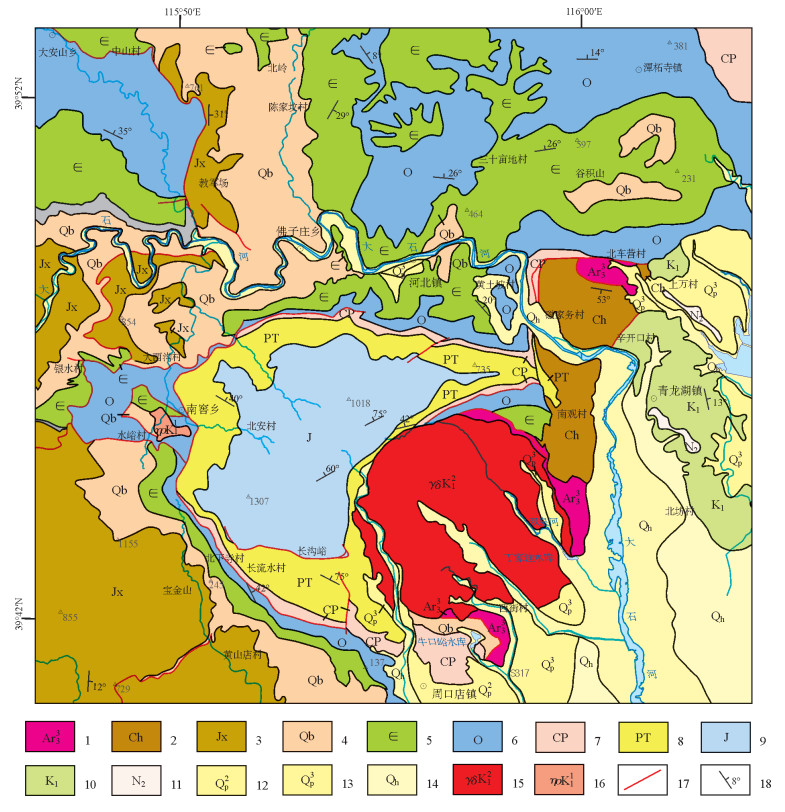
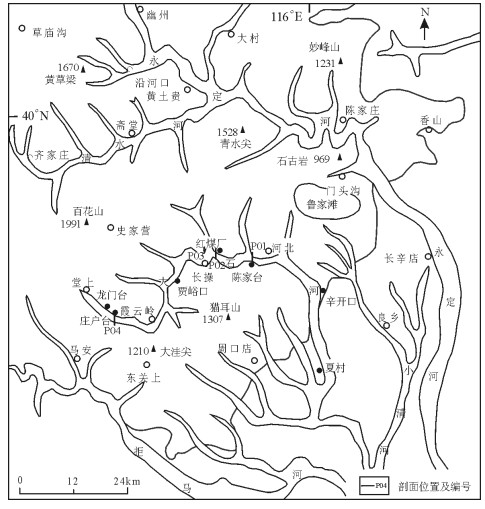
北京西山的基础地质[3]和新生代地质研究详细[4],也曾研究过永定河阶地[5],1:5万周口店幅曾测制陈家台河谷剖面[6],为大石河阶地的全面研究奠定了基础。本文对陈家台村—霞云岭乡堂上村河谷阶地进行了调查(图 1),对不同位置阶地发育特征进行了研究,结合沉积地层分析和阶地面高程测量,初步计算了大石河流域不同时代阶地的垂直落差,探讨了大石河流域山体中更新世以来隆升的速率。
1. 大石河阶地剖面特征
大石河流域陈家台村至霞云岭乡堂上村(山区)穿切的地层主要为长城系、蓟县系、青白口系和寒武系、奥陶系及少量二叠系,岩性主要为碳酸盐岩类的灰岩、白云岩类及陆相碎屑沉积岩(图 2)。河流阶地普遍发育,依序介绍如下。
1.1 陈家台河谷阶地特征(P01)
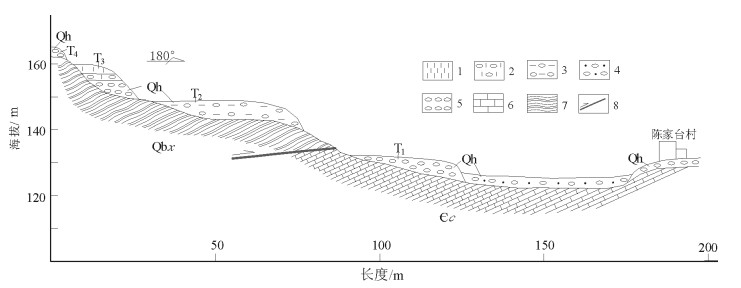
阶地地处房山区佛子庄乡陈家台村,阶地发育在河床左侧,共发育4级(图 3)。
河床宽56.6m,海拔125m,主要为砾石,含少量粗砂。砾石大小5~20cm,大者大于20cm,磨圆度较好,岩性以灰岩为主,含少量火山岩、砂岩砾石。
一级阶地(T1)为堆积型阶地,宽63.4m,主要为砾石,砾石特征与河床砾石相近。
二级阶地(T2)为基座型阶地,宽51.7m,阶高15.5m,基座为下马岭组千枚状板岩,向东追索,基座可见昌平组灰岩。二级阶地前缘上部为全新统河流洪积物,岩性为泥质砾石。泥质为土黄色,含量30%~40%,局部含量较高,砾石分选性中等,磨圆度中等,大小以小于5cm为主,10~20cm次之,成层性一般,砾石成分较复杂,灰岩砾石为主,见少量石英砂岩和火山岩砾石。底部见棕黄色粉砂质粘土透镜体,厚约60cm,长5.6m,走向320°,上覆泥质砾石,厚约3m。二级阶地后缘岩性为砾石层和土黄色粘土。砾石层含少量泥质,砾石大小约5cm,分选性、磨圆度中等,砾石成分同前缘一致,分选性、磨圆度中等。土黄色粘土粒度细,不含砾石,钙质含量较高,土质较硬,顶部20cm含少量砾石,砾石分选性、磨圆度均较差。
三级阶地(T3)为基座型阶地,阶宽15.3m,阶高2.8m,基座为下马岭组千枚状板岩。底部为砾石层,砾石大小约为5cm,分选性、磨圆度较好,为复成分砾石,主要为灰岩砾石;中部为土黄色含砾粘土,厚约80cm,砾石含量较少,均为千枚岩岩片,小于2cm,无磨圆;上部为土黄色粘土,厚约40cm,粒度细,手搓有滑感,湿时可搓成细条,不易断,为较典型的河流冲积、洪积产物。
四级阶地(T4)为基座型阶地,阶高9.5m,主要为砾石。砾石大小约为10cm,分选性、磨圆度中等,岩性以灰岩为主,含少量火山岩、砂岩砾石。基底为下马岭组千枚状板岩。
1.2 红煤厂河谷阶地特征
1.2.1 红煤厂公路边阶地特征(P02)
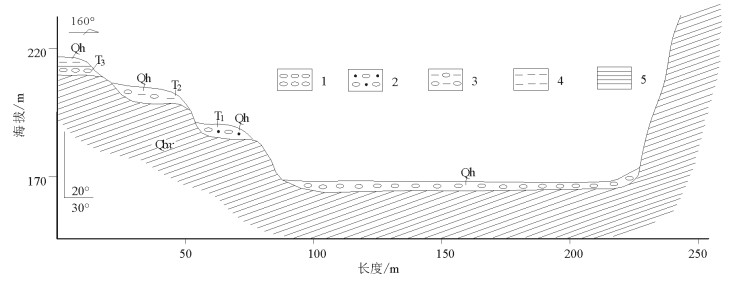
阶地地处房山区佛子庄乡红煤厂村,阶地发育在河床左侧,共发育3级。
河床宽135m,海拔167.1m,主要为砾石,大小不等,大者大于20cm,一般为5~10cm,磨圆度较好,岩性以灰岩、火山岩、砂岩砾石为主(图 4)。
一级阶地(T1)为基座型阶地,阶宽19.2m,阶高21.1m,基座为下马岭组灰黑色页岩,基座上主要为粗砂质砾石,砂含量20%~30%,砾石大小约10cm,分选性、磨圆度中等,成分主要为灰岩,见少量火山岩、砂岩砾石。为较典型的河流冲积、洪积物。
二级阶地(T2)为基座型阶地,阶宽10.8m,阶高3m,基座为下马岭组灰黑色页岩。基座之上覆盖较严重,零星可见砾石发育,含泥质成分,含量约15%,泥质为土黄色,手搓有滑感,粒度细。砾石砾径10cm左右,分选性、磨圆度一般,以灰岩砾石为主,含少量火山岩和砂岩。为河流洪积产物。
三级阶地(T3)为基座型阶地,阶宽大于10m,阶高7.1m,基座为下马岭组灰黑色页岩,产状20°∠30°。按岩性分为4层。
1层:土黄色粘土,粒度细,砾石含量少,层状,厚约1.5m,延伸稳定,为水平层。
2层:含泥质砾石,延走向厚度不稳定,最薄处厚约1.5m,最厚为3m。砾石未胶结或松散胶结,分选性、磨圆度中等,砾径以5~10cm为主,大者可达20cm,砾石岩性为灰岩、页岩和少量火山岩。
3层:土黄色粘土,岩性与1层一致。延伸不稳定,厚0.5~1.5m,透镜体状产出。
4层:含泥质砾石,沿走向厚度有变化,厚1.1~ 3.6m,砾石胶结差,分选性、磨圆度中等,砾径多小于5cm,成分为灰岩、火山岩和页岩。
三级阶地上发育较典型的河流冲积、洪积物。
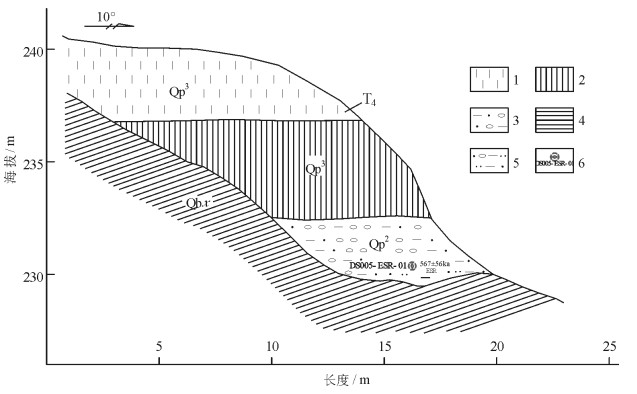
1.2.2 红煤厂西黄土台阶地特征(P03)
阶地地处房山区佛子庄乡红煤厂村西,阶地发育在河床右侧,为河流四级阶地,海拔230m(图 5)。
该阶地属基座型阶地,基座为下马岭组页岩,基座上为3套岩性,由上而下描述如下。
1层:土黄色粘土,粒度细,手搓有滑感,硬度较大,含钙质,未见砾石发育。厚约3m。
2层:棕红色黄土,粒度细,较硬,发育垂直节理,手搓有滑感,湿时可搓成条,不易断,未见砾石发育。厚3~4m。
3层:含砂泥质砾石,底部见薄层棕红色含砾泥质粉细砂。泥质为棕红色,粒度细,节理不发育,硬度较大。上部砂质含量相对较少,砾石磨圆度较好,分选性一般,砾径5cm左右,大者10~20cm,成分以灰岩、页岩为主。厚2~3m。
该阶地发育的岩石类型具有河流沉积和风积混合成因特点。
1.3 长操北岸二级阶地特征
阶地位于房山区佛子庄乡长操村西北,阶地发育在河床左侧,为二级阶地,海拔185m,河床海拔约175m。阶地属于基座型阶地,基座为下马岭组页岩,由上而下共分为5层。
1层:粉砂质粘土,土灰色、土黄色,粒度较细,手搓略有涩感,未见砾石,植物根系发育。
2层:含砾粗砂质细砂,土灰色,粒度不均匀,砂质含量约占80%,砾石大小约为2cm,分选性、磨圆度较好,以灰岩、页岩砾石为主,含少量泥质。
3层:土黄色粉砂质粘土,粒度均匀,较细,硬度大,手搓略有涩感,砾石很少。
4层:土灰色细砂,无胶结或松散胶结,硬度小,层状,分选性、磨圆度较好,砾石少见。
5层:砾石层,砾石大小2~10cm,分选性差。大砾石磨圆度中等,小砾石磨圆度较差,砂质充填。
该剖面岩石成层性较好,发育泥、砂二元结构,为较典型的河流冲积产物。
1.4 贾峪口村西三级阶地特征
阶地位于房山区佛子庄乡贾峪口村,阶地发育在河床左侧,为河流三级阶地,阶地属于基座型阶地,河床海拔282m。该剖面由上而下共分为16层,为土黄色粘土和砾石层互层状产出,其中8层砾石,8层土黄色粘土。上部砾石层和黄土层较厚,最厚处为1~1.5m,底部粘土层较厚,砾石层多为薄层,沿走向延伸较稳定。
粘土为土黄色,质地较硬,钙质含量较高,局部粉砂质含量略高,手搓较细,有砂感,局部含少量砾石。
砾石松散,砾径以5~10cm居多,大者可达20cm,分选性差,次棱角状磨圆,局部泥质充填。砾石成分较复杂,以白云岩为主,含少量火山岩和砂岩,为近源沉积的产物。
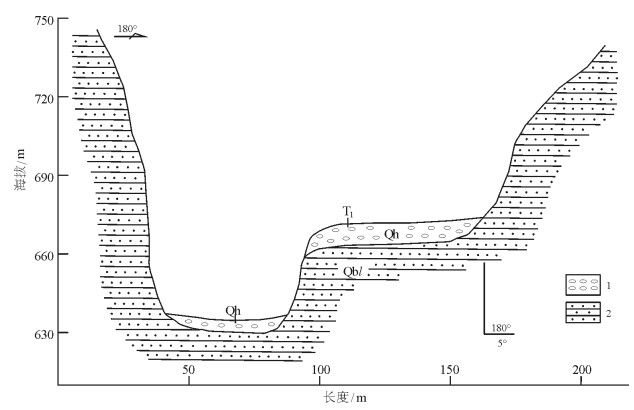
1.5 庄户台村一级阶地特征(P04)
阶地位于房山区霞云岭乡庄户台村,阶地发育在河床右侧,为河流一级阶地,阶地高30m,属基座阶地,基座为龙山组纹层状砂岩,产状平缓,倾角4°~5°,阶地海拔665m,河床海拔635m。
基座上为砾石层,泥砂质充填,松散胶结,砾石为次圆状-圆状磨圆,分选性差。大小以10~20cm为主,小者约5cm,大者50~80cm。砾石层厚3~4m,主要为河流洪积搬运的产物(图 6)。
1.6 龙门台村一级阶地特征
阶地位于房山区霞云岭乡龙门台村,发育在河床左侧,为河流一级阶地,阶地高约10m,属于基座型阶地,基座为龙山组砂岩,产状平缓,阶地海拔645m,河床海拔635m。
根据不同岩性,由上而下可分为4层。
1层:砾石层,泥砂充填,砾径以5~10cm居多,大者逾20cm,岩性以砂岩为主,分选性差,磨圆度中等,为流水搬运成因。
2层:土黄色粘土,粒度细,硬度中等,局部粉砂含量较高,见少量残积碎石,大小为5cm,岩性均为砂岩。
3层:残坡积物,由粘土、残积碎石及少量砂质组成。粘土为棕红色,砂质以中细砂为主,碎石无分选、无磨圆,砾径为5~20cm,大者达50cm,岩性单一,均为砂岩。
4层:棕红色粘土,粒度细,手搓较滑,硬度大,内部见少量残积碎石。
根据该剖面物质组成分析,龙门台村一级阶地早期为河流洪积粘土层,之后为近源的残坡堆积,晚期经历流水搬运沉积的粘土层和砾石层。
2. 样品采集与测试
2.1 样品采集
样品采自红煤厂西黄土台河流四级阶地之上(P03),样品号为DS005-ESR-01(图 5),位于剖面第3层底部,采样层厚度约20cm。采样处泥砂质成分较高,岩性为棕红色含砾泥质粉细砂。
2.2 样品测试
2.2.1 测年方法及原理
ESR是电子自旋共振(Electron Spin Reso⁃ nance)的简称,由德国科学家Zeller在1967年提出,是根据样品吸收自然辐照剂量来推导样品形成年代的测年方法[7]。ESR方法是一种非破坏性测量方法,其测年原理是用电子自旋共振方法直接测量晶体样品在自然环境中由于辐照损伤所产生的顺磁中心数目。测量谱仪为德国布鲁克公司生产的EMXBRUKERX-BandESR波谱仪。
2.2.2 实验过程
样品前处理流程如下:根据样品性状不同,取一定数量的原样品称重,放入干燥箱中烘干(温度40℃)。烘干前后记重量,并计算含水量。然后碎样,过筛分选出100~140μm粒径的样品约120g,放入1000ml烧杯中进行化学处理,获取石英矿物。① 用双氧水浸泡处理去除样品中的有机质;② 盐酸浸泡处理去除样品中的碳酸盐类;③ 氢氟酸浸泡处理(蚀刻)去除长石等矿物。
每一步处理完成后都要用清水反复清洗至中性再进行下一步处理。将处理好的样品放入(40℃)烘箱内烘干后待磁选。对该样品进行磁选(去除磁性矿物):每个样品称小样10份(每份称重0.25g),送北京大学分子化学院钴源实验室进行样品人工辐照;根据样品岩性、地质地貌信息及估计时代,辐照剂量为0、200、400、800、1400、2000、2800、3600、4600、6000(Gy);辐照后的样品需放置一段时间去除辐照后产生的不稳定信号。
2.2.3 古剂量和环境剂量测定
古剂量测定是在德国布鲁克公司生产的EMX1/6型ESR信号测量谱仪上对辐照后的样品进行信号测量。根据样品岩性、地质地貌信息及估计时代选择样品,测量功率为2.0MW(E`)和(Ge)`信号。根据ESR信号测量结果带入计算相应软件,计算古剂量。
环境剂量率测量是电子自旋共振测年的重要参数之一,样品所吸收的环境辐射剂量是其本身及周围物质中放射性核素(U238、Th232和K40)的α、β和γ衰变产生的电离辐射所提供的,同时也有宇宙射线的少量贡献。样品的环境剂量(铀、钍、钾)含量分析,委托核工业北京地质研究院分析测试中心完成,仪器型号为ELEMENT等离子体质谱分析仪。
样品埋藏层的水含量对样品所接收的剂量率有不可忽视的影响,水对α、β和γ辐射有一定的吸收作用。样品埋藏期间含水量的变化,对样品年龄结果有直接的影响。根据样品的铀、钍、钾含量和样品埋深宇宙射线的少量贡献、含水量等参数,计算样品年剂量。
2.2.4 计算结果
根据公式:A=P/D,计算样品的ESR年龄。其中,A表示年龄(ka);P表示古剂量(Gy);D表示年剂量(Gy/ka)。
样品测量信号总体较好,年龄结果为567±56ka(表 1),误差为10%~20%。
表 1 Diagram of the longitudinal river slope in Dashi River valleyTable 1. Analytical results of samples实验
室号野外号 样品
物质U
/10-6Th
/10-6K2O
/%含水量
/%古剂量
/Gy年剂量
/(Gy· ka-1)年龄
/ka15272 DS005-ESR-01 泥质含砂物质 2.46 12.3 2.68 4.90 2268±226 4.00 567±56 3. 讨论
红煤厂西黄土台四级阶地棕红色含砾粉砂经ESR测试年龄为567±56ka,推断大石河河谷在第四纪中更新世早期开始发育,由于新构造运动产生间歇性隆升,在高位宽谷之下发育4级阶地,形成了如今的地貌特征。
3.1 大石河阶地发育特征
通过本次调查发现,大石河流域河北镇陈家台村—霞云岭乡堂上村(山区)河谷阶地普遍发育,河北镇至贾峪口,河流一级至三级阶地保留较完整,而且在河北镇还保留清晰的四级阶地。至庄户台地区,河流下切较深,一级阶地阶高达30m,一级以上阶地保留不完整,庄户台-龙门台普遍发育砾石,至上游霞云岭乡堂上村,仅见巨砾发育。
3.2 河床纵比降特征
大石河流域地质构造为箱状背斜,上新世形成宽谷地貌,宽谷两侧发育放射性沟谷,形成现今的高位宽谷系统。
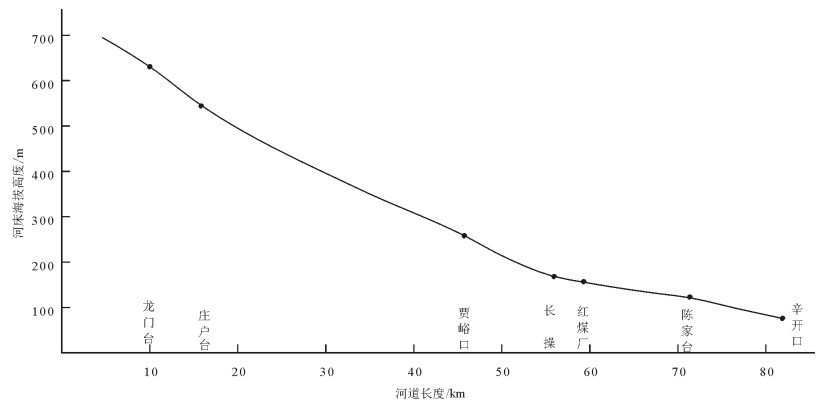
唐县期大石河高位宽谷系统是北京西山的特色地貌,从陈家台溯源而上至龙门台附近,明显发育宽谷地貌,如南窖、校军厂宽谷与大石河连通,组成宽谷系统。宽谷结束于下石堡,宽谷谷底高度从上游向下游,河床海拔高度依次为龙门台635m、庄户台535m、贾峪口282m、长操175m、红煤厂167m、陈家台125m、辛开口80m,至夏村以北田各庄一带,海拔降至40m。从龙门台至辛开口河流曲线长度约72km,高差555m,平均纵比降约为7.71‰(图 7)。
4. 结论
(1)大石河流域河北镇陈家台村—霞云岭乡堂上村(山区)河谷阶地普遍发育,且较完整,不同区段的各级阶地均可进行对比。
(2)通过阶地面的对比研究,得出大石河流域辛开口—龙门台(山区)平均比降为7.71‰。
(3)根据阶地发育和物质成分成因,以及ESR测年数据初步推断,大石河在中更新世早期初始发育,600ka以来,大石河流域山区隆升速率约为0.96mm/a。
致谢: 在成文过程中,青海省第五地质矿产勘查院夏日哈木项目组工程师杨启安、工程师张金玲在野外资料提供、采样方面给予帮助,青海省地质研究所高级工程师舒树兰完成图件制作,在此一并表示感谢。 -
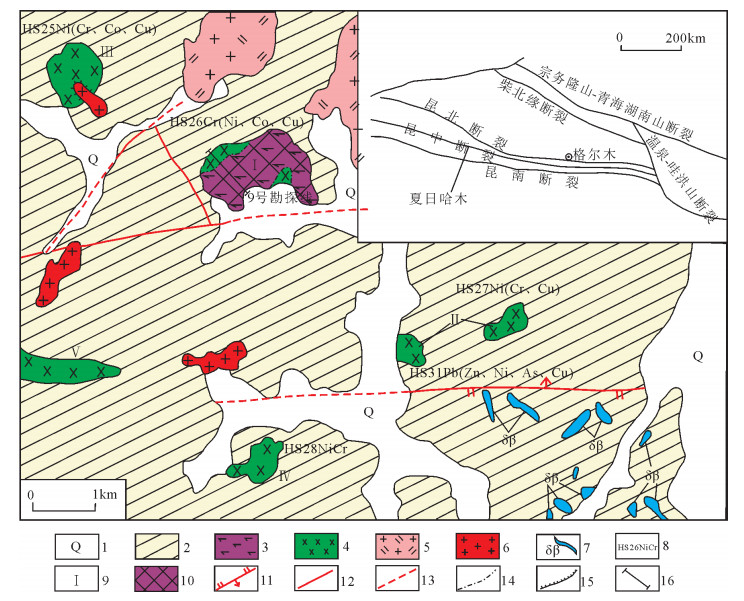
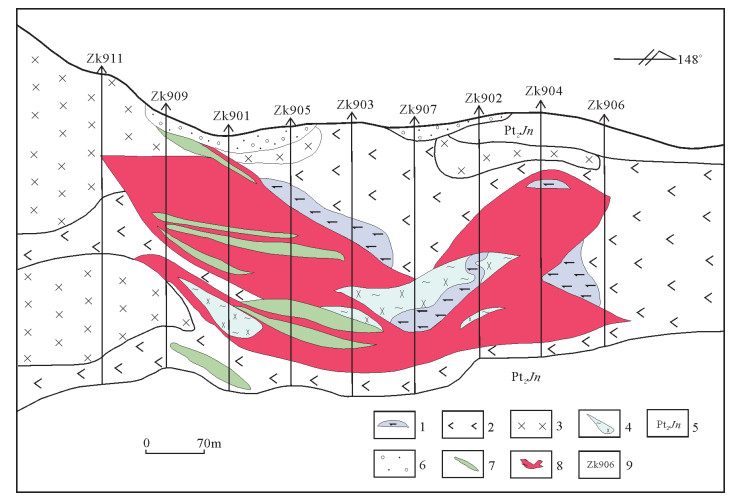
图 1 夏日哈木矿区地质略图③
1—第四系;2—下元古界金水口群白沙河岩组;3—辉石岩;4—辉长岩;5—似斑状二长花岗岩;6—花岗岩;7—黑云母闪长岩脉;8—1: 5水系异常位置;9—岩体编号;10—矿体;11—逆断层;12—性质不明断层;13—推测断层;14—脉动接触界线;15—超动接触界线;16—9号勘探线位置
Figure 1. Sketch geological map of the Xiarihamu ore district
图 3 夏日哈木矿区9号勘探线剖面图③
1—橄榄岩;2—辉石岩;3—辉长岩;4—苏长岩;5—金水口群片麻岩;6—第四系;7—铜矿体;8—镍矿体;9—钻孔编号
Figure 3. Geological section along No. 9 exploration line of the Xiarihamu ore district
表 1 夏日哈木矿区主要岩体特征
Table 1 Characteristics of main intrusions in the Xiarihamu ore district
岩体特征 Ⅰ号岩体 Ⅱ号岩体 Ⅲ号岩体 Ⅳ号岩体 岩体规模 1个岩体,控制长约1.76km,宽约700m,面积约1.23km2,长条状近东西向展布 2个岩体,长400~550m,宽50~350m,岩体出露面积约0.15km2;东岩体北东东向、西岩体东西向展布 1个岩体,出露面积约0.45km2,岩体形态呈椭圆形展布 1个岩体,长约0.7km,宽80~ 600m,面积约为0.3km2,呈长条状近东西向展布 岩石类型 橄榄岩、辉石岩和辉长岩 辉长岩,少量辉石岩 蛇纹岩、石榴子石辉石岩 蛇纹岩、辉长岩,局部为辉石岩 矿化蚀变 普遍具有绿泥石化、碳酸盐化、透闪石化、蛇纹石化 普遍具有碳酸盐化、褐铁矿化、蛇纹石化,局部孔雀石化、镍华、褐铁矿化 蛇纹岩普遍具有弱镍矿化,偶见辉石岩铜镍矿化 岩体偶见镍黄铁矿和黄铁矿 1:5万水系异常 HS26Cr(Ni、Co、Cu) HS27Ni(Cr、Cu) HS25Ni(Cr、pb、Zn、Sn) HS28Ni(Cr、Cu) 表 2 夏日哈木地区岩石主量、稀土和微量元素含量
Table 2 Major element, REE and trace element composition of rocks in Xiarihamu
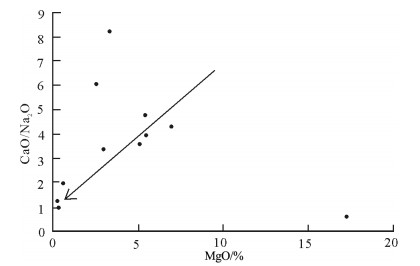
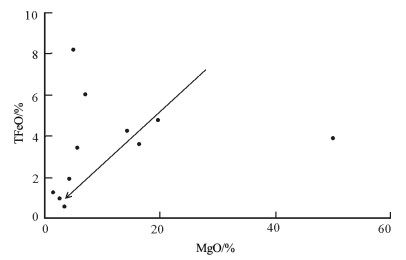
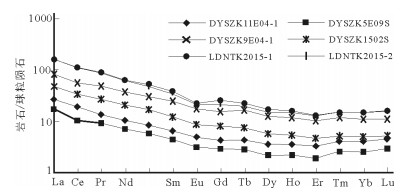
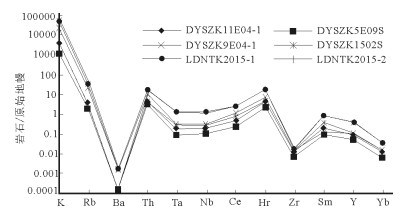
样品号 岩性 SiO2 TiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 FeO MnO MgO CaO Na2O K2O P2O5 H2O+ Total DYSZK11E04-1 镍黄铁矿化辉石岩 61.65 0.41 6.01 3.71 16.35 0.17 4.71 3.52 0.65 0.25 0.03 2.53 100.00 DYSZK5E09S 镍黄铁矿化辉石岩 38.35 0.18 3.10 5.58 45.06 0.13 3.92 2.05 0.38 0.07 0.02 1.16 100.00 DYSZK9E04-1 弱镍黄铁矿化辉石岩 55.90 0.49 15.93 1.47 5.97 0.12 5.99 7.18 2.80 1.43 0.11 2.63 100.00 DYSZK1502S 弱镍黄铁矿化辉石岩 59.74 0.38 5.74 8.33 8.88 0.14 3.57 3.70 0.73 0.26 0.06 8.48 100.00 LDNTK2015-1 弱镍黄铁矿化辉石岩 51.31 0.64 14.96 4.97 0.70 0.21 8.17 8.90 2.61 2.56 0.21 4.75 100.00 LDNTK2015-2 弱镍黄铁矿化辉石岩 53.04 0.70 22.16 3.68 2.56 0.07 3.41 3.69 1.23 4.21 0.12 5.14 100.00 样品号 La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Y DYSZK11E04-1 7.62 14.9 1.59 6.05 1.23 0.36 1.11 0.20 1.13 0.26 0.68 0.13 0.81 0.14 6.29 DYSZK5E09S 5.14 8.17 1.08 4.01 0.82 0.22 0.71 0.13 0.67 0.15 0.39 0.08 0.50 0.09 3.79 DYSZK9E04-1 25.3 44.8 5.82 21.8 4.67 1.23 4.03 0.76 4.08 0.87 2.12 0.37 2.26 0.35 22.9 DYSZK1502S 13.9 26.0 3.15 11.8 2.34 0.62 2.01 0.35 1.78 0.37 0.93 0.16 1.01 0.16 9.22 LDNTK2015-1 47.8 88.8 10.7 37.8 7.35 1.61 6.38 1.05 5.22 1.11 2.78 0.48 3.12 0.50 29.2 LDNTK2015-2 46.4 88.8 10.4 35.2 6.53 1.50 5.34 0.87 4.53 0.97 2.57 0.48 3.27 0.50 24.8 样品号 Rb Ba Th U K Ta Nb La Ce Pb Pr Sr P Nd Zr Hf Sm Eu Ti DYSZK11E04-1 14.6 0.0058 5.27 0.73 1576.6 0.09 0.89 7.62 14.9 11 1.59 28 85 6.05 31.9 3.10 1.23 0.36 2325 DYSZK5E09S 7.80 0.0062 2.58 0.33 423.191 0.06 0.99 5.14 8.17 19 1.08 17 59 4.01 19.2 2.40 0.82 0.22 1050 DYSZK9E04-1 76.1 0.051 7.54 1.46 10704.3 0.14 1.84 25.3 44.8 25 5.82 310 420 21.8 60.1 2.80 4.67 1.23 3300 DYSZK1502S 12.7 0.0067 5.45 0.82 1493.62 0.20 2.75 13.9 26.0 7 3.15 46 170 11.8 37.5 2.50 2.34 0.62 1950 LDNTK2015-1 120 0.090 15.7 5.41 21159.6 0.86 12.8 47.8 88.8 22 10.7 210 930 37.8 154 5.00 7.35 1.61 4800 LDNTK2015-2 188 0.089 15.4 4.10 35431.9 1.04 14.6 46.4 88.8 19 10.4 170 510 35.2 153 4.40 6.53 1.50 5325 注:主量元素含量单位为%,稀土和微量元素含量为10-6 -
杜玉良, 贾群子, 韩生福.青海东昆仑成矿带中生代构造-岩浆-成矿作用及铜金多金属找矿研究[J].西北地质, 2012, 45(4):69-76. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201204011.htm 王秉璋.祁漫塔格地质走廊域古生代-中生代火成岩岩石构造组合研究[M].北京:地质出版社, 2014:25-36. 杜玮, 凌锦兰, 周伟, 等.东昆仑夏日哈木镍矿床地质特征与成因[J].矿床地质, 2014, 33(4):713-726. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10183-1014281786.htm 张照伟, 李文渊, 钱兵, 等.东昆仑夏日哈木岩浆铜镍硫化物矿床成矿时代的厘定及其找矿意义[J].中国地质, 2015, 42(3):438-451. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201503004.htm 潘彤.青海省柴达木南北缘岩浆熔离型镍矿的找矿——以夏日哈木镍矿为例[J].中国地质, 2015, 42(3):713-723. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201503023.htm 李世金, 孙丰月, 高永旺, 等.小岩体成大矿理论指导与实践——青海东昆仑夏日哈木铜镍矿找矿突破的启示及意义[J].西北地质, 2012, 45(4):185-191. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201204021.htm 姜春发, 杨经绥, 冯秉贵, 等.昆仑开合构造[M].北京:地质出版社, 1992:1-217. 张雪亭, 杨生德.青海省板块构造研究——1:100万青海省大地构造图说明书[M].北京:地质出版社, 2007:1-178. 潘彤, 拜永山, 孙丰月, 等.青海省东昆仑有色、贵金属矿成矿系列研究[M].北京:地质出版社, 2011:1-250. 许长坤.青海成矿地质特征的特殊性及找矿布局探讨[J].地质与勘探, 2011, 47(5):783-793. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201105005.htm 秦克章, 汪东波, 王之田.中国东部铜矿床类型、成矿环境、成矿集中区与成矿系统[J].矿床地质, 1999, 18(4):359-371. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ199904009.htm 刘战庆, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等.东昆仑南缘布青山构造混杂岩带早古生代白日切特中酸性岩浆活动:来自锆石U-Pb测年及岩石地球化学证据[J].中国地质, 2011, 38(5):1150-1167. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201105004.htm 祁生胜, 宋述光, 史连昌, 等.东昆仑西段夏日哈木-苏海图早古生代榴辉岩的发现及意义[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(11):3345-3356. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201411018.htm 郝娜娜, 袁万明, 郑爱奎, 等.东昆仑祁漫塔格晚志留世-早泥盆世花岗岩:年代学、地球化学及形成环境[J].地质论评. 2014, 60(1):201-215. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201401021.htm 陈静, 谢智勇, 李彬, 等.东昆仑拉陵灶火钼多金属矿床含矿岩体地质地球化学特征及其成矿意义[J].地质与勘探, 2013, 49(5):813-824. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201305002.htm 刘彬, 马昌前, 郭盼, 等.东昆仑中泥盆世A型花岗岩的确定及其构造意义[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2013, 38(5):947-962. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201305005.htm 王冠, 孙丰月, 李碧乐, 等.东昆仑夏日哈木矿区早泥盆世正长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及其动力学意义[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2013, 37(4):685-697. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201304013.htm 姜常义, 凌锦兰, 周伟, 等.东昆仑夏日哈木镁铁质-超镁铁质岩体岩石成因与拉张型岛弧背景[J].岩石学报, 2015, 31(4):1117-1136. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201504019.htm Pearce J A, Cann J R.Tectonic setting of basic volcanic rocks determined using trace element analysis[J]. Earth Planet Sci. Lett., 1973, 19:290-300. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(73)90129-5
Adachi M, Yamamoto K, Sugisaki R.Hydrothermal chert and associated siliceous rocks from the Northern Pacific, their geological significance as indication of Ocean ridge activity[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1986, 47:125-148. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(86)90075-8
谌宏伟, 罗照华, 莫宣学, 等.东昆仑喀雅克登塔格杂岩体的SHRIMP年龄及其地质意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2006, 25(1):25-32. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200601002.htm 赵振明, 马华东, 王秉璋, 等.东昆仑早泥盆世碰撞造山的侵入岩证据[J].地质论评, 2008, 54(1):47-56. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200801007.htm 郭通珍, 刘荣, 陈发彬, 等.青海祁漫塔格山乌兰乌珠尔斑状正长花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及地质意义[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(8):1203-1211. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201108004.htm 宋谢炎, 易俊年, 陈列锰, 等.青海省中昆仑夏日哈木超大型镍-钴硫化物矿床发现的意义[J].矿床地质, 2014, 33(3):31-32. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2014S1018.htm 青海省地质调查院. 1: 5万拉陵灶火地区地质矿产调查(J46E020013, J46E020014, J46E021013, J46E021014, J46E022013 J46E022014) 报告. 2008—2010. 青海省地勘局区测队. 1: 20万开木棋陡里格区域地质调查报告. 1978—1991. 青海省第五地质矿产勘查院. 格尔木市夏日哈木镍钴矿勘查报告. 2012—2014.



 下载:
下载: