The discovery of the Changtuxili Mn-Ag-Pb-Zn polymetallic deposit in the middle-southern segment of Da Hinggan Mountains and its significance
-
摘要:
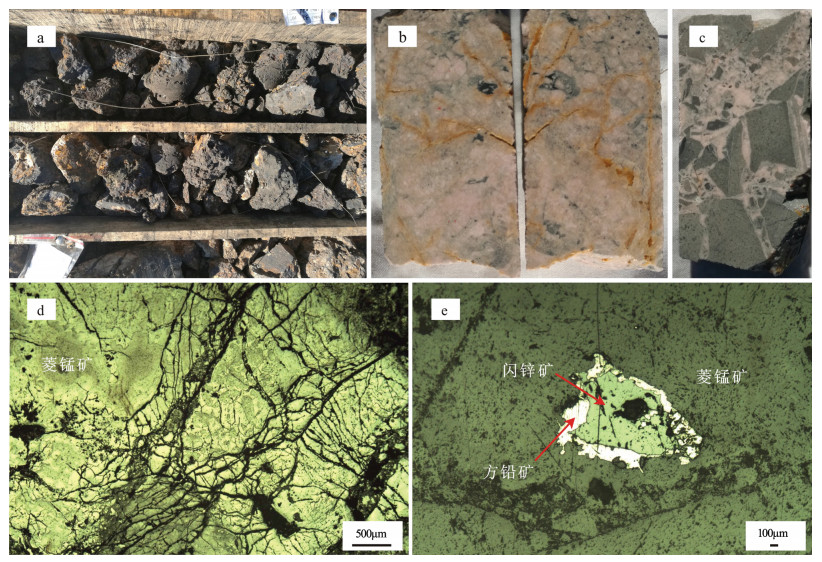
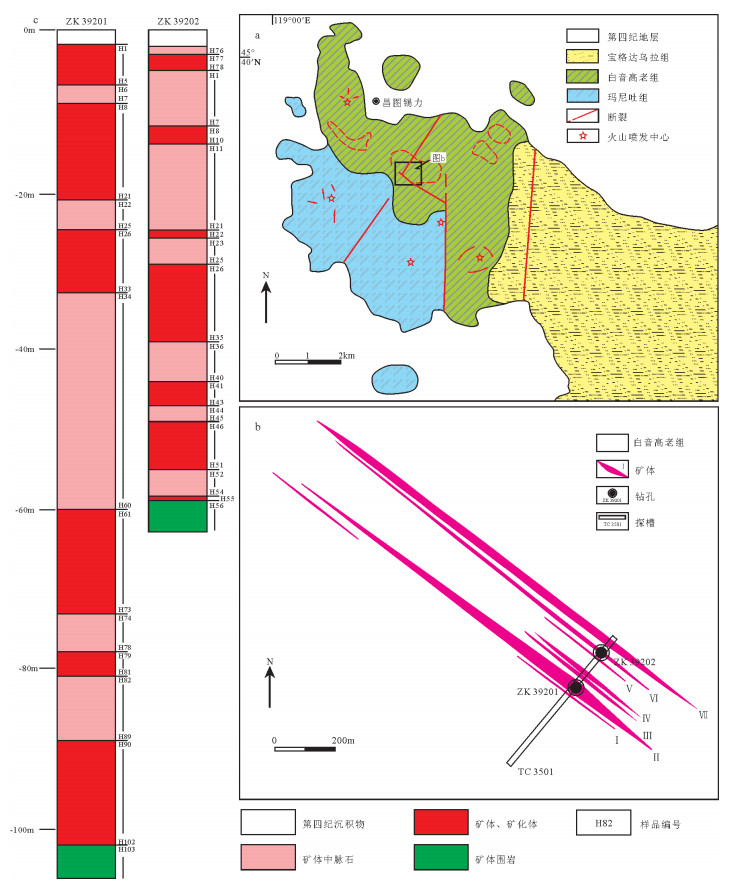
中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心与黑龙江省地质调查研究总院齐齐哈尔分院合作,在内蒙古霍林郭勒地区发现昌图锡力锰、银、铅、锌多金属矿床。矿床所在大地构造位置为中亚造山带东段,矿床产于中生代白音高老组中发育的北西向破碎蚀变带中。经地表槽探揭露可见7条矿脉沿北西向平行展布。矿体及围岩中仅发现低温蚀变,主要包括硅化、绢云母化、绿泥石化、褐铁矿化及碳酸盐化。根据蚀变矿物类型及矿体强烈受北西向构造控制等特征,初步判断矿床可能为浅成低温热液矿床。在大兴安岭中南段首次发现锰多金属热液矿床,暗示在太平洋构造域控制下,大兴安岭中南段北东向成矿带内部可能存在受北西向构造控制的次级成矿带。
Abstract:A Mn, Ag, Pb, Zn polymetallic deposit was discovered in Huolingol area of Inner Mongolia by Tianjin Center of China Geological Survey together with Qiqihar Branch of Heilongjiang Institute of Geological Survey and Research. The tectonic position of the deposit is in the eastern part of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. The deposit was formed by NW-striking cataclastic alteration in Baiyin-gaolao Formation. Seven parallel NW-striking ore veins are exposed by trenching. There are many kinds of low-temperature hydrothermal alteration in the orebody and wall rock, such as silicification, sericitization, chloritization, limonitization and carbonation. The deposit is probably an epithermal deposit, as shown by different kinds of alteration and the features of controlling role of the NW-striking structure. There probably exists a secondary metallogenic belt which is controlled by the NW-striking structure in the northeast metallogenic belt that is controlled by Pacific tectonic domain in the middle-southern segment of the Da Hinggan Mountains.
-
致谢: 对为本文提供帮助的中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心李怀坤研究员,以及黑龙江省地质调查研究总院齐齐哈尔分院昌图锡力项目组的野外工作人员表示衷心感谢。
-
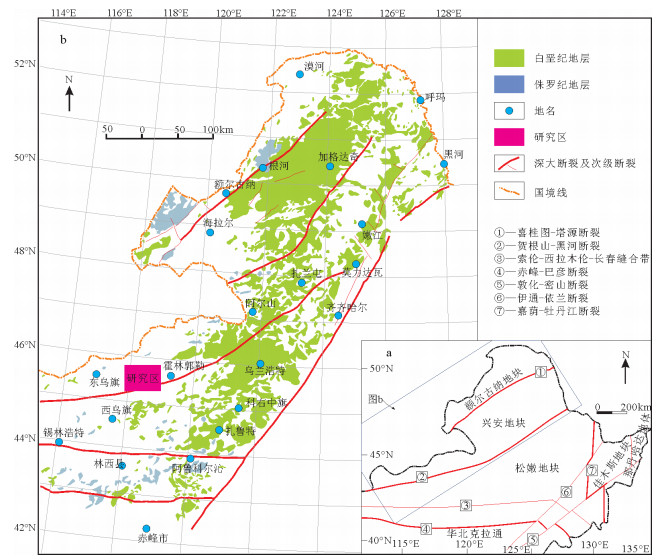
图 1 中国东北地区大地构造简图(a)和大兴安岭中生代火山岩分布(b)(据参考文献[15]修改)
Figure 1. Tectonic subdivisions of northeastern China (a) and distribution of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the Da Hinggan Mountains (b)
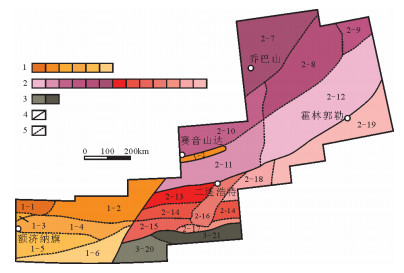
图 2 中蒙边境地区成矿分带(据参考文献[26]修改)
Figure 2. Distribution of metallogenic belts in Sino-Mongolian border area
表 1 昌图锡力矿床探槽TC3501化学分析结果
Table 1 Chemical analytical result of TC3501 of the Changtuxili deposit
样品号 Mn Ag Pb Zn 样品号 Mn Ag Pb Zn TC3501HX42 20.12 413.8 1.03 0.46 TC3501HX71 16.77 185.6 1.85 0.51 TC3501HX43 22.96 153.9 1.33 0.46 TC3501HX87 4.42 101.8 0.80 0.19 TC3501HX50 2.54 27.64 0.56 0.17 TC3501HX93 4.22 579.2 0.77 0.14 TC3501HX51 4.69 106.7 1.00 0.18 TC3501HX94 2.71 229.5 0.57 0.13 TC3501HX52 7.24 146.2 0.55 0.17 TC3501HX95 2.61 339.4 1.39 0.11 TC3501HX53 32.73 273.8 1.08 0.40 TC3501HX96 3.84 194.1 0.66 0.14 TC3501HX54 25.54 64.54 0.88 0.29 TC3501HX97 3.94 250.4 1.05 0.19 TC3501HX55 25.36 321.2 1.66 0.29 TC3501HX98 13.04 363.8 1.37 0.52 TC3501HX56 25.91 293.2 1.36 0.22 TC3501HX99 12.14 89.55 0.78 0.66 TC3501HX57 8.18 241.5 3.62 0.07 TC3501HX117 10.85 385.1 0.58 0.30 TC3501HX58 2.19 40.03 0.78 0.08 TC3501HX118 2.79 119.6 0.06 0.13 TC3501HX59 0.54 18.58 0.72 0.10 TC3501HX126 3.83 85.99 1.09 0.20 TC3501HX60 1.78 57.37 0.94 0.07 TC3501HX127 2.00 83.80 1.16 0.16 TC3501HX61 2.82 89.62 0.83 0.09 TC3501HX144 28.95 23.82 0.32 1.19 TC3501HX62 4.15 217.0 0.54 0.12 TC3501HX145 29.05 28.39 0.62 0.79 TC3501HX63 3.75 179.6 0.83 0.10 TC3501HX146 24.90 14.24 0.27 1.05 TC3501HX68 9.90 56.05 0.94 0.15 TC3501HX147 22.68 16.52 0.30 0.71 TC3501HX69 9.46 19.32 0.11 0.18 TC3501HX148 16.60 23.28 0.36 0.62 TC3501HX70 4.07 62.10 0.81 0.14 注:Ag元素含量单位为10-6,Mn、Pb和Zn元素含量单位为10-2 表 2 昌图锡力矿床钻孔ZK39201、ZK39202化学分析结果
Table 2 Chemical analytical result of drill hole ZK39201 and ZK39202 of the Changtuxili deposit
样品号 Mn Ag Pb Zn 样品号 Mn Ag Pb Zn ZK39201 H1 22.25 172.0 0.63 0.34 H62 34.07 9.16 0.33 0.89 H2 20.28 128.0 1.01 0.35 H63 7.52 63.61 0.94 1.74 H3 27.87 228.2 1.01 0.59 H64 8.10 294.9 1.24 1.11 H4 13.19 196.0 0.66 0.24 H65 6.82 15.56 0.21 0.65 H5 4.97 59.49 0.49 0.16 H66 3.59 27.02 0.41 0.95 H8 18.36 71.29 0.79 0.60 H67 7.18 35.47 0.47 1.07 H9 8.27 47.09 0.52 0.32 H68 7.72 43.34 0.70 1.83 H10 12.16 36.42 0.51 0.60 H69 18.65 14.07 0.29 1.01 H11 10.44 29.54 0.61 0.43 H70 12.57 102.7 0.45 0.94 H12 22.20 61.26 0.46 0.80 H71 12.73 87.69 0.45 1.02 H13 17.58 102.1 0.55 0.64 H72 14.29 87.03 1.46 1.2 H14 22.01 46.23 1.51 0.58 H73 9.60 30.74 0.82 1.54 H15 13.49 116.8 0.70 0.47 H79 17.36 18.16 0.52 1.19 H16 12.21 59.83 0.58 0.39 H80 18.12 11.27 0.33 1.61 H17 8.71 78.09 1.02 0.24 H81 13.12 5.79 0.10 0.60 H18 20.63 139.6 0.81 0.63 H90 7.53 83.54 1.75 1.25 H19 29.05 58.13 0.59 0.86 H91 6.55 71.17 1.89 0.97 H20 32.00 108.4 0.55 1.04 H92 8.65 65.10 1.78 1.10 H21 29.88 212.4 1.30 1.34 H93 16.41 67.89 2.49 0.24 H26 23.93 56.18 0.88 1.06 H94 7.26 110.8 2.24 0.51 H27 13.78 61.72 1.06 0.94 H95 4.38 100.4 1.71 0.76 H28 10.63 42.07 0.66 0.79 H96 5.15 103.9 1.87 0.57 H29 12.60 28.31 0.48 0.93 H97 4.90 165.23 3.88 0.39 H30 9.60 35.56 0.43 0.94 H98 4.34 400.5 2.78 1.65 H31 11.81 68.10 0.61 1.77 H99 3.75 114.6 1.31 1.41 H32 10.63 72.27 0.75 1.50 H100 3.06 485.5 6.92 1.96 H33 3.00 61.29 0.49 0.51 H101 4.49 400.7 2.92 1.15 H61 9.53 20.57 0.23 0.87 H102 4.40 45.47 0.37 0.32 ZK39202 H77 3.51 30.45 0.35 0.37 H33 23.14 31.11 0.90 0.71 H78 1.81 17.82 0.31 0.22 H34 15.83 125.3 0.95 0.56 H8 4.23 96.77 0.79 0.35 H35 18.32 34.24 0.81 0.75 H9 13.78 615.2 6.15 0.37 H41 10.50 39.77 0.61 0.54 H10 5.88 115.5 1.77 0.23 H42 3.52 22.38 0.52 0.31 H22 10.19 21.46 0.07 1.20 H43 23.66 31.56 0.41 0.80 H26 9.93 17.09 0.13 0.69 H46 12.39 31.25 0.94 0.24 H27 7.05 14.25 0.13 0.62 H47 12.01 43.02 1.72 0.19 H28 1.41 7.20 0.09 0.30 H48 13.36 36.43 0.77 0.23 H29 2.60 9.42 0.09 0.57 H49 17.00 36.50 0.77 0.48 H30 4.17 10.14 0.09 0.62 H50 11.26 28.89 0.80 0.33 H31 7.52 9.83 0.11 0.40 H51 10.84 22.80 0.62 0.25 H32 18.73 13.80 0.21 0.59 H55 27.73 5.73 0.31 0.35 注:Ag元素含量单位为10-6,Mn、Pb和Zn元素含量单位为10-2 -
任纪舜.论中国大陆岩石圈构造的基本特征[J].地质通报, 1991, (4):289-293. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD199104000.htm 张阔, 孙丰月, 赵小亮, 等.内蒙古贺根山北乌兰德勒花岗岩体锆石U-Pb测年、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J].世界地质, 2013, 32(2):244-254. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDZ201302005.htm 赵一鸣.内蒙古东南部铜多金属成矿地质条件及找矿模式[M].北京:地震出版社, 1994. 洪大卫, 王式光, 谢锡林, 等.试析地幔来源物质成矿域——以中亚造山带为例[J].矿床地质, 2003, 22(1):41-55. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200301006.htm 聂凤军, 江思宏, 张义, 等.中蒙边境及邻区斑岩型铜矿床地质特征及成因[J].矿床地质, 2004, 23(2):176-189. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200402005.htm 金岩, 刘玉堂, 谢玉玲.内蒙东乌旗地区岩浆活动与多金属成矿的关系[J].华南地质与矿产, 2005, (1):8-12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKC200501001.htm 盛继福.大兴安岭中段成矿环境与铜多金属矿床地质特征[M].北京:地震出版社, 1999. 聂凤军.中蒙边境中东段金属矿床成矿规律和找矿方向[M].北京:地质出版社, 2007. 王守光, 黄占起, 苏新旭, 等.一条值得重视的跨国境成矿带——南戈壁-东乌旗铜多金属成矿带[J].地学前缘, 2004, 11(1):249-255. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200401033.htm 田继勋.内蒙古东乌旗达赛脱铅锌矿的控矿构造[J].地质找矿论丛, 2005, 20(B08):102-105. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK2005S1025.htm 高群学, 钱明.内蒙古东乌旗阿尔哈达银铅锌矿区地质、物化探特征及其找矿意义[J].地质找矿论丛, 2005, 20(S1):95-99. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK2005S1023.htm 钱明, 高群学.内蒙古东乌旗阿尔哈达铅锌矿区矿床成因探讨[J].地质找矿论丛, 2006, 21(1):70-73. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK2006S1017.htm Miao L, Fan W, Liu D, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Hegenshan ophiolitic complex:Implications for late-stage tectonic evolution of the Inner Mongolia-Daxinganling Orogenic Belt, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2008, 32(5/6):348-370.
Wu F Y, Sun D Y, Ge W C, et al. Geochronology of the Phanero-zoic granitoids in northeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 41(1):1-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.11.014
Xu W L, Pei F P, Wang F, et al. Spatial-temporal relationships of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in NE China:Constraints on tectonic overprinting and transformations between multiple tectonic regimes[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 74(18):167-193.
Wu F Y, Sun D Y, Li H, et al. A-type granites in northeastern China:age and geochemical constraints on their petrogenesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 187(1/2):143-173.
石玉若, 刘翠, 邓晋福, 等.内蒙古中部花岗质岩类年代学格架及该区构造岩浆演化探讨[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(11):3155-3171. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201411005.htm 李文国.内蒙古自治区岩石地层[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1996. 张万益. 内蒙古东乌珠穆沁旗岩浆活动与金属成矿作用[D]. 中国地质科学院博士学位论文, 2008. 聂凤军.中蒙边境中东段金属矿床成矿规律和找矿方向[M].北京:地质出版社, 2007. 李俊建, 唐文龙, 付超, 等.中蒙边界地区成矿区带划分[J].地质通报, 2016, 35(4):461-487. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201604001.htm 徐志刚, 陈毓川, 王登红, 等.中国成矿区带划分方案[M].北京:地质出版社, 2008. 陈毓川.中国主要成矿区带矿产资源远景评价[M].北京:地质出版社, 1999. 陈毓川, 王登红, 朱裕生, 等.中国成矿体系与区域成矿评价[M].北京:地质出版社, 2007. 陈毓川.重要矿产和区域成矿规律研究技术要求[M].北京:地质出版社, 2010. 李俊建, 张锋, 任军平, 等.中蒙边界地区构造单元划分[J].地质通报, 2015, (4):636-662. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201504006.htm 潘桂棠, 肖庆辉, 陆松年, 等.中国大地构造单元划分[J].中国地质, 2009, 36(1):1-4. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200901004.htm 叶天竺, 张智勇, 肖庆辉, 等.成矿地质背景研究技术要求[M].北京:地质出版社, 2010:4-9. 许立权, 张彤, 张明, 等.内蒙古自治区重要矿种成矿规律综述[J].矿床地质, 2016, 35(5):966-980. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201605006.htm 曾庆栋, 刘建明, 褚少雄, 等.大兴安岭南段多金属矿成矿作用和找矿潜力[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2016, 46(4):1100-1123. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201604010.htm 郭利军, 葛昌宝, 冯贞, 等.内蒙古锡林浩特东部拜仁达坝银铅多金属矿勘查过程及远景评述[J].物探与化探, 2004, 28(5):394-397. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH200405004.htm 常勇, 赖勇.内蒙古银都银铅锌多金属矿床成矿流体特征及成矿年代学研究[J].北京大学学报自然科学版, 2010, 46(4):581-593. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ201004013.htm 王玉往.内蒙古大井矿床成矿作用[M].北京:科学出版社, 2014. 江思宏, 梁清玲, 刘翼飞, 等.内蒙古大井矿区及外围岩浆岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其对成矿时间的约束[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(2):495-513. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201202013.htm 廖震, 王玉往, 王京彬, 等.内蒙古大井锡多金属矿床岩脉LAICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(7):348-362. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201207029.htm 吕斌, 王涛, 童英, 等.中亚造山带东部岩浆岩浆热液矿床时空分布特征及其构造背景[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2017, 47(2):305-343. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201702001.htm 付勇, 徐志刚, 裴浩翔, 等.中国锰矿成矿规律初探——陈毓川院士八十华诞专辑[J].地质学报, 2014, 88(12):2192-2207. 吕志成, 张培萍, 段国正, 等.内蒙古额仁陶勒盖银矿床锰矿物的矿物学初步研究[J].矿物岩石, 2002, 22(1):1-5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS200201000.htm 郭光军, 王时麒.河北围场小扣花营锰银矿床稀土元素地球化学研究[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版), 1998, 34(4):510-518. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ804.014.htm



 下载:
下载: