Geological and geochemical characteristics and age of gran-ite porphyry in the Hongdoushan copper deposit, South Langcangjiang belt, western Yunnan Province
-
摘要:
南澜沧江火山弧带红豆山花岗斑岩属于过铝质钾玄岩性S型花岗岩,SiO2含量为71.1%~74.4%,全碱含量高(K2O+Na2O=8.4%~9.4%),富钾(K2O/Na2O=3.9~5.0),铝饱和指数(A/CNK)为1.06~1.21;具轻稀土元素富集特征,负Eu异常(δEu=0.53~0.74);相对富集大离子亲石元素(LILE,如Rb、Ba、Th、U等),但亏损Sr、P、Ti等元素。地球化学特征表明,红豆山花岗斑岩具火山弧花岗岩与同碰撞花岗岩的特征,为活动大陆边缘弧的产物。红豆山花岗斑岩的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为220.3±3.6Ma,形成于晚三叠世。红豆山花岗斑岩的地球化学特征和形成时代与小定西组基性火山岩非常相似,两者是同一期岩浆活动不同阶段的产物。
-
关键词:
- 南澜沧江带 /
- 花岗斑岩 /
- LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄 /
- 地球化学 /
- 小定西组
Abstract:The Hongdoushan granite porphyry in the South Langcangjiang volcanic arc zone is a peraluminous and shoshonite Stype granitoid. The granite porphyry contains 71.1%~74.4% of SiO2, high total alkalis (K2O+Na2O=8.4%~9.4%), high K and high A/CNK of 1.06~1.21, and is characterized by enrichment of light rare earth elements with negative europium anomalies (δEu=0.53~0.74), relative enrichment of large ion lithophile elements (LILE) such as Rb, Ba, Th and U, and relative depletion of Sr, P and Ti. Geochemical features indicate that the Hongdoushan granite porphyry has characteristics of volcanic arc granite and syn-collision granite, and is epicontinental arc-volcanic rock. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating age of the Hongdoushan granite porphyry is 220.3±3.6Ma, indicating that the rock was formed during Late Triassic. Geochemical features and formation age of the Hongdoushan granite porphyry is very similar to features of basic volcanic rock of Xiaodingxi Formation, which suggests that they are products of different stages of the same magmation.
-
三水盆地是南海北部陆缘唯一具有大规模新生代火山喷发记录的沉积盆地。盆地新生代火山喷发组合以粗面岩、玄武岩和流纹岩为代表,总体体现板内的大陆裂谷环境[1-10]。根据前人研究,三水盆地存在13期火山喷发[1-2, 5-6, 8, 11],其中大多数集中于古新世和始新世。时代最新的玄武岩年龄为38Ma[12],这也是南海北部大陆边缘地区迄今获得的南海扩张之前最晚的火山喷发年龄。本文报道的西樵山独岗流纹岩和石头村玄武岩样品是新近采得,应用K-Ar法经过严格的测试和检验,分别测得28.25Ma和29.27Ma的同位素地质年龄。这一新的结果将三水盆地的火山喷发序列推迟至渐新世中期,也改变了长期以来关于南海扩张期间(32~ 16Ma)无陆上火山喷发活动的传统认识,对于区域构造环境的解读和南海扩张过程的研究具有重要意义。
1. 地质背景
三水盆地位于广东省南部,是中国华南大陆最贴近南海的内陆盆地。盆地主要断裂带是吴川-四会断裂带、西江断裂带和三水-西樵山断裂带,新生代地层自下而上有莘庄村组、㘵心组、宝月组和华涌组。
三水盆地是南海北部唯一存在早新生代大规模火山喷发的陆缘盆地,前人总结的13期火山喷发活动中绝大部分(10~11期)发生在古新世—中始新世(60.5~38Ma),喷发岩的主要种类为玄武岩、粗面岩和流纹岩,地表出露地点主要有紫洞、王借岗、走马营、西樵山、狮岭、黎边山等地,基性岩与中酸性岩呈近南北向双列线性展布。本文分析样品是采自石头村的玄武岩和独岗的流纹岩(图 1)。
西樵山是三水盆地出露面积最大的火山喷发点,各类熔岩、集块岩、熔结凝灰岩、凝灰岩发育齐全。根据以往报道,该地粗面岩数量巨大,年龄一般为45Ma,是盆地火山活动最强烈的第10期喷发的主要代表。独岗贴近西樵山,可能是西樵山火山体系的一部分,也可能属于后期的独立喷发。独岗岩体呈灰黄色,柱状节理非常发育,化学分析结果表明其为典型的流纹岩。石头村位于三水盆地东北部,是盆地内玄武岩出露的主要地区之一,但随着当地经济建设的发展,露头已被挖掘殆尽,本文的分析样品来自某工程施工现场。
2. K-Ar年代测试
测试玄武岩选用剔除斑晶的基质,流纹岩选用透长石单矿物,测试在北京大学造山带与地壳演化教育部重点实验室完成,K含量测量采用锂内标钠缓冲火焰光度计法,火焰光度计型号为6400,所用标样为房山花岗闪长岩体黑云母(编号ZBH-25)和腾冲芒棒玄武岩(编号TC-18)。Ar含量测量采用VSS-RGA-10质谱计,稀释法静态测量,标样为房山花岗闪长岩体黑云母(编号ZBH-25)。计算过程中的标准值据桑海清等[17]。计算所用衰变常数λ= 5.543×10-10/a,40K/∑K=1.167×10-4。
玄武岩测试年龄为29.27±1.52Ma,流纹岩测试结果为28.25±1.14Ma,均属渐新世,具体测试结果见表 1。测试过程中所选标样房山花岗闪长岩体黑云母(编号ZBH-25)K含量标准值为7.60%,实测值7.04%,腾冲芒棒玄武岩(编号TC-18)K含量标准值1.04%,实测值1.01%。Ar含量测量标样ZBH-25标准值为132.9±1.3Ma,实测值为132.47Ma。测试方法合理,数据可靠,笔者认为测试年龄可为后续科学研究提供可靠的年代学依据。
表 1 三水盆地火山岩K-Ar测年数据结果Table 1. The K-Ar isotopic dating results of the volcanic rocks in Sanshui Basin岩性 玄武岩 流纹岩 K含量/% 1.70±2.56 4.92±2.92 称样量/g 0.0211 0.0101 40Ar*/(mol·g-1) 8.70E-11 2.43E-10 40Ar*% 48.8661 54.64888 38Ar/mol 7.12E-12 7.15E-12 40/38Ar 0.527478±2.51E-05 0.628125±0.000384 36/38Ar 0.000932±2.01E-05 0.000984±7.39E-06 40Ar*/40K 0.001715±8.97E-05 0.001654±6.71E-05 年龄值/Ma 29.27±1.52 28.25±1.14 注:40Ar*代表放射性成因40Ar 3. 岩石矿物和地球化学特征
3.1 岩石矿物学特征
石头村玄武岩呈黑色,少见气孔,具斑状结构(图 2-a),斑晶为斜长石(15%)、橄榄石(10%)和辉石(5%)。基质为拉斑玄武结构,包含斜长石微晶(20%)和火山玻璃(30%),橄榄石形状不规则,晶体较大,有不规则裂纹且个别橄榄石有蛇纹石化现象(图 2-b)。辉石形状较规则,呈八边形,有裂纹,发育较弱的环带,且裂纹穿过环带(图 2-c)。斜长石形状规则,发育大量环带,且环带清晰、完整,无裂纹、无蚀变现象。
流纹岩呈灰色,少见气孔,斑状结构,块状构造(图 3-a),矿物组成为长石、石英、黑云母。斑晶主要为碱性长石(10%),偶见长石斑晶中包裹小颗粒长石(图 3-b),碱性长石斑晶呈自形-半自形,有不规则裂纹,大小为1~1.5mm,基质为微晶结构,碱性长石微晶半定向排列,其间充填有玻璃质成分。副矿物为菱铁矿(1%~2%)(图 3-c)。以上岩石矿物特征与前人研究的时代较老的同类岩石一致[5, 11, 18]。
3.2 地球化学特征
石头村玄武岩和独岗流纹岩元素地球化学分析数据见表 2。石头村玄武岩(图 4)SiO2含量为47.57%,TiO2含量为2.78%(大于2%),K2O+Na2O含量为4.54%,且Na2O>K2O。该类岩石富集Nb、Ta、Zr、Hf等不相容元素,稀土元素总量为133.74×10-6,轻稀土元素富集,重稀土元素亏损,La/Yb值为12.12,Ce/Yb值为25.1。在微量元素蛛网图上具有与OIB(洋岛玄武岩)相似的地球化学特征(图 5- a)。La/Nb值为0.45,Nb/Zr值为0.28,Th/Nb值为0.05,与地幔热柱玄武岩特征相似[19-20]。构造环境投图判别为板内玄武岩(图 6-a)。以上特征均与盆地时代较老的玄武岩一致(图 5-a),指示伸展拉张的陆内裂谷环境。
表 2 三水盆地火山岩地球化学数据分析结果Table 2. The major, trace and rare earth elements analysis data of the volcanic rocks in Sanshui Basin地名 石头村 独岗 样品编号 14SS004 14SS013 岩性 玄武岩 流纹岩 SiO2 47.57 70.43 TiO2 2.78 0.24 Al2O3 17.34 14.24 Fe2O3 12.07 3.28 MnO 0.15 0.09 MgO 5.06 0.18 CaO 9.67 0.17 Na20 2.82 5.47 K20 1.7 4.99 P2O5 0.49 0.01 总计 99.65 99.1 Be 1.25 7.74 Sc 24.3 1.42 V 240 1.4 Cr 67.3 1.68 Co 42 9.06 Ni 40.7 1.07 Cu 45.6 7.08 Zn 100 211 Ga 22.6 44.3 Rb 32.4 325 Sr 768 8.22 Y 24.2 159 Zr 187 1504 Nb 53.1 460 Cs 0.32 2.54 Ba 318 19 La 24 175 Ce 49.7 324 Pr 6.48 36.8 Nd 27.4 125 Sm 6.19 24.1 Eu 2.16 0.21 Gd 5.96 23.3 Tb 0.92 4.21 Dy 5.01 26 Ho 0.91 5.43 Er 2.4 16.2 Tm 0.34 2.64 Yb 1.98 16.4 Lu 0.29 2.46 Hf 4.56 37.4 Ta 3.13 26.5 Pb 2.57 37.6 Th 2.55 58 U 0.73 14.7 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素为10-6 ![]() 图 6 玄武岩(a)和流纹岩(b)构造环境判别图(a底图据参考文献[25];数据据参考文献[6-7, 12, 15-16])和流纹岩构造环境判别图;b底图据参考文献[26];A型花岗岩数据据参考文献[27-28];其他对比数据据参考文献[5-7, 12, 15-16, 18])
图 6 玄武岩(a)和流纹岩(b)构造环境判别图(a底图据参考文献[25];数据据参考文献[6-7, 12, 15-16])和流纹岩构造环境判别图;b底图据参考文献[26];A型花岗岩数据据参考文献[27-28];其他对比数据据参考文献[5-7, 12, 15-16, 18])
A—岛弧拉斑玄武岩;B—MORB、岛弧拉斑玄武岩、钙碱玄武岩;C—钙碱性玄武岩;D—板内玄武岩;ORG—洋脊花岗岩;WPG—板内花岗岩;VAG—火山弧花岗岩;syn-COLG—同碰撞花岗岩Figure 6. The discrimination of tectonic setting of basalts (a) and rhyolites (b)独岗流纹岩(图 4)SiO2含量为70.43%,Na2O为5.47%,K2O为4.99%,Al2O3为14.24%,属高钾钙碱性;富集Nb、Ta、Zr、Hf、Th等不相容元素,亏损Ba、Sr、P、Ti、Eu等;稀土元素总量为781.75×10-6,轻稀土元素总量为708.41×10-6,La/Yb值为10.67,Ce/ Yb值为19.76,具有负Eu异常,构造环境判别图显示其产出于板内环境(图 6-b)。与A型花岗岩特征相似,在微量元素蛛网图上与红海Afar地幔柱流纹岩具有一致的分布曲线(图 5-b)。以上特征与盆地时代较老的流纹岩一致,属于板内拉张的陆内裂谷环境。
综上所述,石头村玄武岩和独岗流纹岩与三水盆地新生代基性岩和酸性岩的基本特征一致,均产自板内构造环境,表明它们与前人总结的研究区古、始新世双峰式火山喷发模式一脉相承[5-7, 15],仍属于陆内裂谷体系[1-6]。
4. 讨论
三水盆地古新世—始新世发生大规模的火山喷发活动,有“三水热点”之称[5-8]。这种多期次、多旋回的激烈火山活动在华南地区同时期构造盆地中“一枝独秀”,没有类似的地域可供比拟。盆地基性和中酸性喷出岩分别与OIB和Afar地区同类型火山岩具有相似的地球化学特征,可能受控于地幔柱上涌[5-6],代表大陆裂谷[1-6],是大陆边缘发生破裂的产物。结合南海演化过程及北部陆域的区域地质特征,推测盆地火山活动的性质和时间(38~ 60Ma),大体相当于Afar于红海开裂,属于威尔逊旋回中洋盆扩张前的陆内裂谷阶段。
大西洋、红海的演化路径是体现威尔逊旋回的典型范例,即它们在发生扩张的同时,邻近陆域伴有长期的裂谷型火山喷发活动。北大西洋扩张始于早侏罗世末期,北美大陆边缘保存有至新生代早期的火山记录,红海扩张发生在渐新世初,其阿拉伯一侧的火山喷发活动至今未绝。南海被认为是大西洋式张裂形成的海盆[29-32],但是根据以往资料,在南海扩张期间其周缘陆地鲜有岩浆活动记录,即使如三水盆地这类新生代早期具有陆内裂谷火山活动特征的火山喷发中心,也在南海扩张之前的始新世中晚期(38Ma)完全停止了岩浆活动。这一现象受到研究者的广泛关注[8-9, 33-38],但迄今尚没有合理的解释。
在南海海域自始新世中晚期至南海开裂期间基本没有火山记录,洋岛火山岩年龄多集中在3.69~ 18.61Ma[39-43],基本属于南海扩张停止以后的岩浆活动的产物,对理解南海早期开裂-扩张机制可能不具有太大意义。而本文火山岩喷发正值南海早期扩张阶段,玄武岩和流纹岩构成常见的双峰裂谷模式,与盆地之前的火山活动较一致,将伴随南海扩张的陆域火山活动记录拉长至渐新世中期,改变了南海扩张期间周边陆域无重要火山活动的传统认识。虽然仅从它们的发现还不足以构建南海早期的开裂-扩张模式,但是对传统认识已经形成突破,为正确理解南海早期演化提供了新的材料和视角。
5. 结论
三水盆地渐新世火山岩的发现修正了关于南海早期扩张过程中在其北部陆域缺乏火山喷发记录的传统认识,将双峰式陆内裂谷岩浆活动延续至渐新世中期,即南海早期扩张阶段。这一新的认识对于通过海陆对比进一步分析和总结南海的早期演化模式具有重要意义。
-
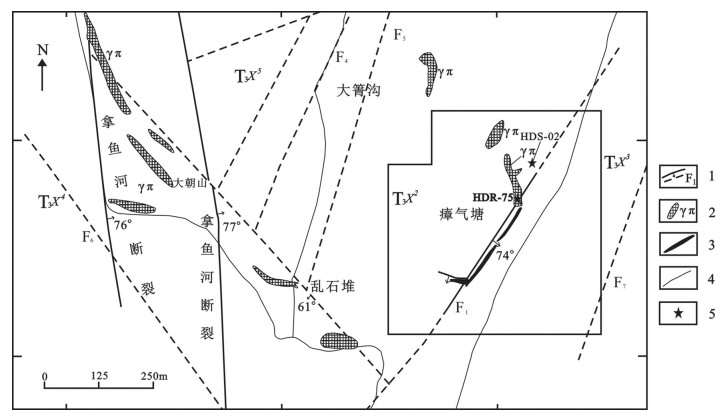
图 1 南澜沧江带区域地质简图[4]
①—甘孜-理塘板块结合带;②—金沙江-哀牢山板块结合带;③—澜沧江板块结合带;④—怒江板块结合带。1—洋脊/洋岛玄武岩;2—超镁铁岩;3—钾质/钙质弧火山岩;4—花岗岩;5—被动边缘半深水-深水相;6—主动边缘(浊积岩)弧前斜坡相;7—洋盆深水相;8—半深水-深水相;9—浅水碳酸盐台地;10—前泥盆系地层;11—前寒武系地层;12—上三叠统-第四系;13—铜矿床(点)
Figure 1. Geological sketch map of the South Langcangjiang belt
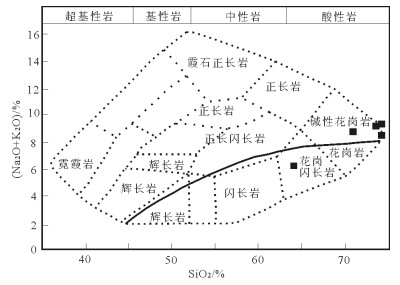
图 3 红豆山岩体岩石分类图解(底图据参考文献[9])
Figure 3. Rock classification diagram of the Houdoushan rock body
图 4 红豆山花岗斑岩SiO2-K2O图解(底图据参考文献[10])
Figure 4. SiO2-K2O diagram of the Hongdoushan granite porphyry
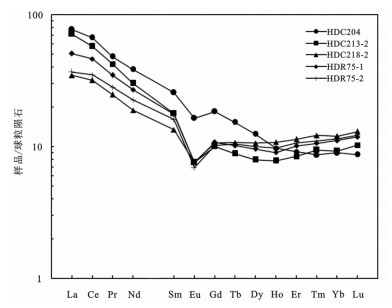
图 5 稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分模式图(球粒陨石数据据参考文献[10])
Figure 5. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns of the Hongdoushan granite porphyry
图 6 红豆山花岗斑岩微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(原始地幔数据据参考文献[12])
Figure 6. Primitive mantle-normalized trace element patterns of the Hongdoushan granite porphyry
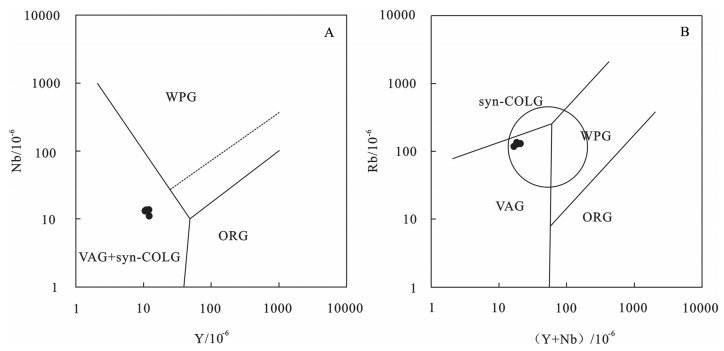
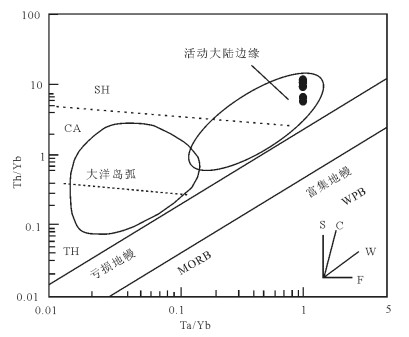
图 7 红豆山花岗斑岩Y-Nb(a)和(Y+Nb)-Rb(b)图解(底图据参考文献[13])
WPG—板内花岗岩;ORG—洋脊花岗岩;VAG—火山弧花岗岩;syn-COLG—同碰撞花岗岩
Figure 7. Y-Nb(a) and(Y+Nb) -Rb (b) discrimination diagrams of the Hongdoushan granite porphyry
表 1 红豆山花岗斑岩体主量元素含量及地球化学参数
Table 1 Major element content and geochemical parameters of the Hongdoushan granite porphyry
% 样品号
描述HDC204
长英岩化斑岩HDC213-2
紫红色斑岩HDC218-2
矿化斑岩HDR75-1
紫红色斑岩HDR75-2
紫红色斑岩SiO2 64.2 74.3 71.1 74.4 73.9 TiO2 0.17 0.18 0.25 0.19 0.18 Al2O3 7.64 11.85 11.95 12 11.8 Fe2O3 1.64 1.29 1.3 1.13 1.24 MnO 0.14 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.02 MgO 0.16 0.16 0.16 0.07 0.07 CaO 10.7 1.38 2.51 1.1 1.36 Na2O 0.08 1.72 1.46 1.86 1.84 K2O 6.12 6.7 7.27 7.49 7.39 P2O5 0.05 0.04 0.07 0.04 0.04 BaO 0.08 0.08 0.1 0.1 0.07 CuO 0.01 0.04 0.23 0.08 0.05 SO3 0.08 0.13 0.96 0.16 0.1 LOI 8.72 1.7 2.25 1.34 1.52 Total 99.84 99.67 99.71 99.99 99.61 K2O/Na2O 76.5 3.9 5 4 4 ALK 6.2 8.4 8.7 9.4 9.2 A/CNK 0.45 1.21 1.06 1.15 1.11 注:测试单位为中国地质大学(武汉)地质过程与矿产资源重点实验室,由熔片X射线荧光光谱法(XRF)测定,分析偏差优于5% 表 2 红豆山花岗斑岩微量和稀土元素含量
Table 2 Trace and rare earth element content of the Hongdoushan granite porphyry
10-6 样号 HDC204 HDC213-2 HDC218-2 HDR75-1 HDR75-2 La 18.3 16.9 8.2 12 8.7 Ce 41 35.2 19.5 28.2 21.4 Pr 4.57 4.01 2.35 3.3 2.68 Nd 17.9 14.1 8.8 12.6 10.5 Sm 3.93 2.72 2.05 2.7 2.45 Eu 0.95 0.44 0.44 0.44 0.4 Gd 3.78 2.06 2.19 2.21 2.09 Tb 0.57 0.33 0.4 0.38 0.39 Dy 3.15 2.01 2.69 2.43 2.53 Ho 0.55 0.44 0.61 0.51 0.55 Er 1.51 1.39 1.88 1.67 1.76 Tm 0.22 0.24 0.31 0.27 0.28 Yb 1.52 1.57 2.04 1.89 1.95 Lu 0.22 0.26 0.33 0.3 0.31 Y 32 26.6 31.2 27.1 27.7 ΣREE 98.17 81.67 51.79 68.9 55.99 LR/HR 7.52 8.84 3.96 6.13 4.68 (La/Yb)N 8.14 7.27 2.72 4.29 3.01 δEu 0.74 0.55 0.63 0.53 0.53 δCe 1.03 0.98 1.03 1.04 1.03 Cr 10 10 12 29 29 Ni 1.9 2.6 2.5 1.4 1.7 Co 1.1 1.4 11.4 0.9 0.9 Zn 8 15 21 10 Cu 103.5 263 1850 612 370 Rb 170 199.5 206 214 205 W 1.7 0.9 3 0.7 0.9 Sr 58.2 43.7 56.6 32.2 31.8 Ba 710 850 820 670 630 V 7 28 6 5 Nb 13.3 21.2 21.8 21.2 21.7 Ta 1.08 1.65 1.74 1.58 1.62 Zr 53.4 60.1 116 67.4 68.9 Hf 1.8 2.1 3.3 2.2 2.3 Sn 1.3 1.5 4.7 1.7 1.6 Pb 4.8 7.9 186.5 6 6.7 Ag 0.05 0.04 1.74 0.05 0.03 U 1.4 3.8 3.6 3.8 3.8 Th 12.3 18.5 16.2 22.5 21.8 P 230 150 290 160 150 注:微量、稀土元素分析在中国地质大学(武汉)地质过程与矿产资源重点实验室进行,使用方法为ICP-MS法,分析偏差优于10% 表 3 红豆山花岗斑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb测年结果
Table 3 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb results for Hongdoushan granite porphyry
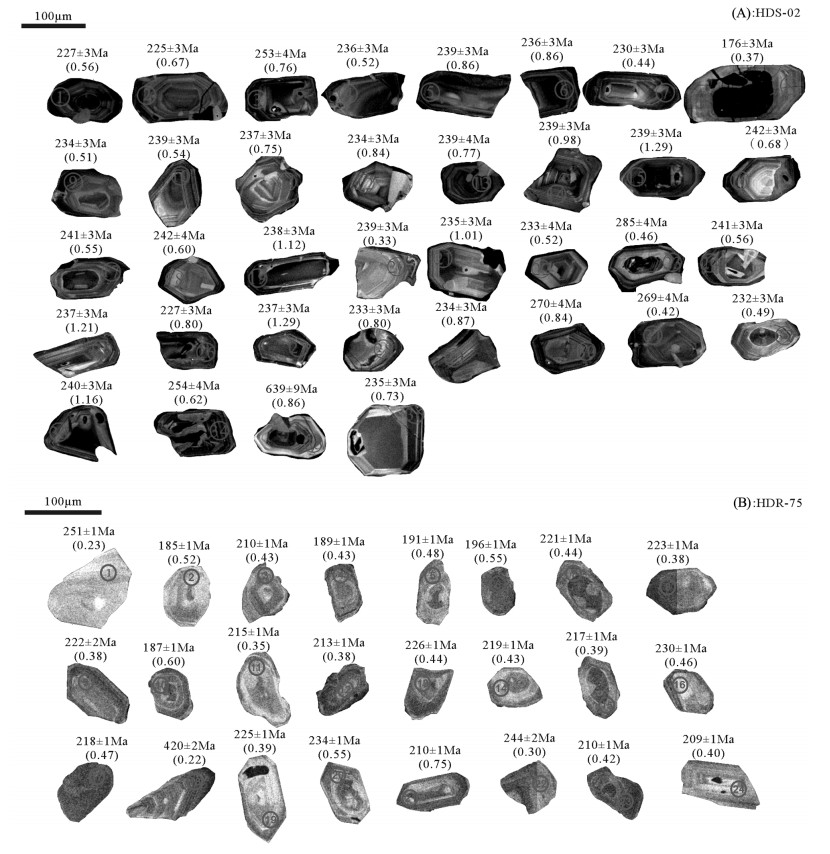
点号 Th/U Th/10-6 U/10-6 比值(经普通铅校正) 年龄(经普通铅校正)/Ma 207Pb/206Pb ±1σ 207Pb/235U ±1σ 206Pb/238U ±1σ 207Pb/206Pb ±1σ 207Pb/235U ±1σ 206Pb/238U ±1σ 1 0.56 305 550 0.0507 0.0017 0.2499 0.0053 0.0358 0.0005 226 77 227 4 227 3 2 0.67 194 291 0.0512 0.0017 0.2506 0.0048 0.0355 0.0005 251 73 227 4 225 3 3 0.76 323 423 0.0519 0.0016 0.2858 0.0047 0.0400 0.0006 280 70 255 4 253 4 4 0.52 111 214 0.0508 0.0017 0.2606 0.0051 0.0372 0.0005 232 74 235 4 236 3 5 0.86 294 343 0.0517 0.0016 0.2695 0.0046 0.0378 0.0005 270 71 242 4 239 3 6 0.86 658 768 0.0514 0.0016 0.2650 0.0043 0.0374 0.0005 260 69 239 3 236 3 7 0.44 308 702 0.0507 0.0016 0.2542 0.0044 0.0363 0.0005 229 71 230 4 230 3 8 0.37 326 875 0.0534 0.0018 0.2040 0.0043 0.0277 0.0004 347 75 189 4 176 3 9 0.51 162 319 0.0511 0.0018 0.2606 0.0059 0.0370 0.0005 246 78 235 5 234 3 10 0.54 182 336 0.0515 0.0017 0.2682 0.0050 0.0378 0.0005 261 72 241 4 239 3 11 0.75 260 346 0.0512 0.0017 0.2645 0.0051 0.0375 0.0005 248 73 238 4 237 3 12 0.84 240 287 0.0507 0.0016 0.2580 0.0046 0.0369 0.0005 225 72 233 4 234 3 13 0.77 49 63 0.0511 0.0021 0.2661 0.0084 0.0377 0.0006 247 92 240 7 239 4 14 0.98 532 541 0.0504 0.0016 0.2642 0.0043 0.0378 0.0005 229 70 238 3 239 3 15 1.29 688 533 0.0509 0.0016 0.2650 0.0043 0.0378 0.0005 236 69 239 3 239 3 16 0.68 172 252 0.0512 0.0017 0.2703 0.0056 0.0383 0.0006 250 75 243 5 242 3 17 0.55 246 448 0.0513 0.0017 0.2689 0.0054 0.0380 0.0006 253 74 242 4 241 3 18 0.60 136 227 0.0509 0.0019 0.2681 0.0071 0.0382 0.0006 234 84 241 6 242 4 19 1.12 632 566 0.0511 0.0017 0.2647 0.0051 0.0375 0.0005 247 73 239 4 238 3 20 0.33 95 290 0.0509 0.0017 0.2644 0.0055 0.0377 0.0006 234 75 238 4 239 3 21 1.01 628 619 0.0510 0.0016 0.2609 0.0041 0.0371 0.0005 241 69 235 3 235 3 22 0.52 78 148 0.0517 0.0032 0.2630 0.0147 0.0369 0.0007 274 137 237 12 233 4 23 0.46 98 214 0.0521 0.0021 0.3244 0.0094 0.0452 0.0007 288 87 285 7 285 4 24 0.56 238 427 0.0516 0.0017 0.2704 0.0050 0.0380 0.0006 267 72 243 4 241 3 25 1.21 584 483 0.0511 0.0016 0.2639 0.0048 0.0375 0.0005 245 71 238 4 237 3 26 0.80 398 498 0.0509 0.0018 0.2515 0.0060 0.0358 0.0005 236 80 228 5 227 3 27 1.29 816 633 0.0511 0.0016 0.2640 0.0043 0.0375 0.0005 245 69 238 3 237 3 28 0.80 399 501 0.0508 0.0016 0.2581 0.0045 0.0369 0.0005 230 71 233 4 233 3 29 0.87 422 486 0.0521 0.0017 0.2661 0.0051 0.0370 0.0005 291 72 240 4 234 3 30 0.84 239 286 0.0516 0.0017 0.3039 0.0061 0.0428 0.00063 266 74 270 5 270 4 31 0.42 88 209 0.0520 0.0017 0.3056 0.0059 0.0426 0.00062 284 72 271 5 269 4 32 0.49 265 545 0.0522 0.0016 0.2640 0.0047 0.0367 0.00053 295 70 238 4 232 3 33 1.16 646 556 0.0508 0.0016 0.2655 0.0046 0.0379 0.00055 230 70 239 4 240 3 34 0.62 483 784 0.0512 0.0017 0.2843 0.060 0.0403 0.0006 250 75 254 5 254 4 35 0.86 222 258 0.0609 0.0019 0.8746 0.0141 0.1042 0.00151 635 64 638 8 639 9 36 0.73 135 185 0.0508 0.0017 0.2593 0.0058 0.0371 0.00055 229 77 234 5 235 3 表 4 红豆山花岗斑岩HDR-75样品LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb测年结果
Table 4 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb results for sample HDR-75 from Hongdoushan granite porphyry
点号 Th/U Th/10-6 U/10-6 比值(经普通铅校正) 年龄(经普通铅校正)/Ma 207Pb/206Pb ±1σ 207Pb/235U ±1σ 206Pb/238U ±1σ 207Pb/206Pb ±1σ 207Pb/235U ±1σ 206Pb/238U ±1σ 1 0.23 55 234 0.0603 0.0031 0.2828 0.0144 0.0340 0.0004 616 114 253 11 215 3 2 0.52 212 409 0.0542 0.0009 0.2191 0.0036 0.0291 0.0004 380 27 201 3 185 3 3 0.43 166 389 0.0465 0.0008 0.2128 0.0033 0.0331 0.0006 23 26 196 3 210 4 4 0.43 212 489 0.0536 0.0008 0.2213 0.0033 0.0298 0.0001 354 25 203 3 189 1 5 0.48 213 442 0.0738 0.0033 0.3066 0.0134 0.0302 0.0004 1035 91 272 10 191 2 6 0.55 228 418 0.0681 0.0012 0.2903 0.0048 0.0310 0.0002 873 24 259 4 196 1 7 0.44 186 418 0.0494 0.0007 0.2390 0.0037 0.0349 0.0004 168 23 218 3 221 3 8 0.38 142 375 0.0479 0.0008 0.2334 0.0037 0.0352 0.0005 95 25 213 3 223 3 9 0.38 146 388 0.0500 0.0008 0.2422 0.0034 0.0350 0.0005 197 22 220 3 222 3 10 0.60 363 608 0.0651 0.0008 0.2652 0.0031 0.0294 0.0004 777 15 239 2 187 2 0.35 142 409 0.0499 0.0007 0.2350 0.0032 0.0340 0.0005 191 22 214 3 215 3 12 0.38 194 513 0.0578 0.0008 0.2692 0.0037 0.0336 0.0005 521 21 242 3 213 3 13 0.44 281 643 0.0524 0.0007 0.2600 0.0034 0.0357 0.0004 304 20 235 3 226 2 14 0.43 218 509 0.0542 0.0009 0.2593 0.0041 0.0345 0.0005 380 26 234 3 219 3 15 0.39 214 547 0.0518 0.0014 0.2451 0.0065 0.0343 0.0005 278 63 223 5 217 3 16 0.46 220 477 0.0626 0.0011 0.3144 0.0052 0.0364 0.0005 693 26 278 4 230 3 17 0.47 137 293 0.0536 0.0019 0.2547 0.0090 0.0345 0.0004 354 83 230 7 218 3 18 0.22 77 359 0.0555 0.0010 0.5144 0.0092 0.0673 0.0003 431 42 421 6 420 2 19 0.39 212 548 0.0544 0.0008 0.2684 0.0037 0.0356 0.0005 387 22 241 3 225 3 20 0.55 260 473 0.0519 0.0008 0.2660 0.0038 0.0370 0.0005 281 22 240 3 234 3 21 0.75 548 727 0.0676 0.0009 0.3098 0.0040 0.0331 0.0007 855 17 274 3 210 4 22 0.30 104 347 0.0508 0.0019 0.2702 0.0097 0.0386 0.0003 230 86 243 8 244 2 23 0.42 283 677 0.0579 0.0024 0.2644 0.0106 0.0331 0.0006 527 91 238 9 210 4 24 0.40 182 451 0.0518 0.0019 0.2353 0.0084 0.0330 0.0007 274 86 215 7 209 5 -
莫宣学, 沈上越, 朱勤文, 等.三江中南段火山岩-蛇绿岩与成矿[M].北京:地质出版社, 1998. 李兴振, 刘文均, 王义昭, 等.西南三江地区特提斯构造演化与成矿[M].北京:地质出版社, 1999:122-145. 李定谋, 王立全, 须同瑞, 等.金沙江构造带铜金矿成矿与找矿[M].北京:地质出版社, 2002. 张彩华, 刘继顺, 张洪培, 等.滇西南澜沧江带晚三叠世富钾火山岩地球化学特征及成因[J].中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(3):669-679. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201203008.htm 黎彤, 倪守斌. 中国大陆岩石圈的化学元素丰度[J]. 1997, (1): 31-37. 孔会磊, 董国臣, 莫宣学, 等.滇西三江地区临沧花岗岩的岩石成因:地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素约束[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(5):1438-1452. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201205010.htm 刘德利. 澜沧江火山岩带官房铜矿区矿床地球化学与成矿模式[D]. 中南大学博士学位论文, 2009. 张彩华. 澜沧江火山弧云县段铜矿床地质特征、成矿模式与找矿预测[D]. 中南大学博士学位论文, 2007. Middlemost E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock-system[J]. Earth-Science Review, 1994, 37(3/4):215-224.
Rickwood P C. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J]. Lithos, 1989, 22:247-263. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(89)90028-5
Taylor S R, Mclennan S M. The continental crust:Its composition and evolution[M]. Oxford:Blackwel Scientific Publications, 1985:1-312.
Sun S S, Mcdonough W F.Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalt:Implications for mantle composition and process[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Spc. Publ. Geol. Soc. Lond., 1989, 42:313-345.
Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. Trace element discrimina-tion diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granite rock[J]. J. Petrol., 1984, 25:956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
Wilson M. Igneous Petrogenesis:A Globe Tectonic Approach[M]. London:Unwin Hyman, 1989.
张彩华, 刘继顺, 刘德利.滇西南澜沧江带官房地区三叠纪火山岩地质地球化学特征及其构造环境[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2006, 25(5):377-386. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200605002.htm Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Gao S, et al. In situ analysis of major and trace el-ements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standary[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 257:34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004
Ludwing K R. ISOPLOT 3.00:A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publi-cation, 2003.
吴元宝, 郑永飞.锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J].科学通报, 2004, 49(16):1589-1604. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002 陈莉, 王立全, 王保弟, 等.滇西云县-景谷火山弧带官房铜矿床成因:流体包裹体及年代学证据[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(4):1279-1289. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201304014.htm -
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 王剑,张豪薇,张健,沈利军,张建勇,付修根. 论羌塘含油气盆地关键地层划分对比问题. 海相油气地质. 2024(01): 17-29 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘佳,宋艾,丁林,苏涛,周浙昆. 青藏高原及其周边古近纪综合地层、生物群与古地理演化. 中国科学:地球科学. 2024(04): 1308-1342 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 毕文军,张佳伟,李亚林,邓玉珍. 西藏中部羌塘地体白垩纪以来隆升剥露过程. 地学前缘. 2023(02): 18-34 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. Li-jun Shen,Jian-yong Zhang,Shao-yun Xiong,Jian Wang,Xiu-gen Fu,Bo Zheng,Zhong-wei Wang. Evaluation of the oil and gas preservation conditions, source rocks, and hydrocarbongenerating potential of the Qiangtang Basin: New evidence from the scientific drilling project. China Geology. 2023(02): 187-207 .  必应学术
必应学术
5. 王剑,王忠伟,付修根,宋春彦,谭富文,韦恒叶. 青藏高原羌塘盆地首口油气科探井(QK-1)新发现. 科学通报. 2022(03): 321-328 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 赵嘉峰,王剑,付修根,沈利军,郑波,韦恒叶,张豪薇,唐为. 西藏羌塘盆地古近纪康托组沉积物源及构造背景分析. 地质论评. 2022(01): 93-110 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 寇琳琳,李海龙,李振宏,董晓朋,崔加伟,黄婷. 青藏高原东北缘烟筒山构造带二叠系红泉组沉积时代及物源示踪. 地质通报. 2022(Z1): 315-326 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 王剑,付修根,沈利军,谭富文,宋春彦,陈文彬. 论羌塘盆地油气勘探前景. 地质论评. 2020(05): 1091-1113 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 赵珍,吴珍汉,杨易卓,季长军. 羌塘中部陆相红层时代的U-Pb年龄约束. 地质论评. 2020(05): 1155-1171 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 吴珍汉,季长军,赵珍,陈程. 羌塘盆地中部侏罗系埋藏史和生烃史. 地质学报. 2020(10): 2823-2833 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: