Sedimentary rocks and geochemical characteristics as well as detrital zircon of Abushan Formation in Woruobale and Bailong area, Tibet, and their indicating significance for provenance information
-
摘要:
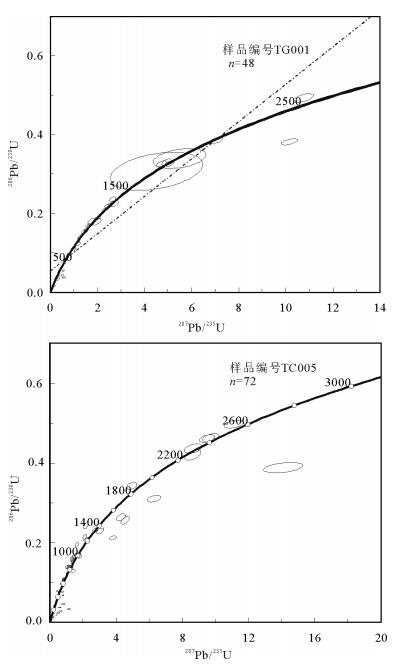
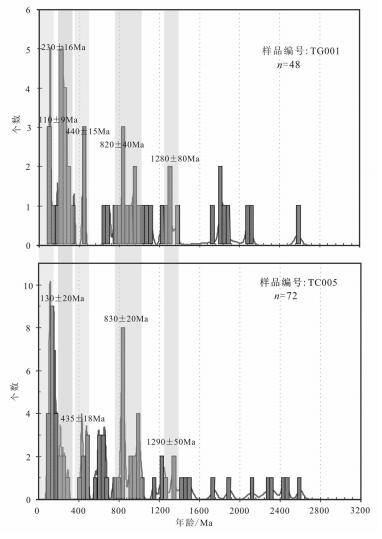
在白龙地区和窝若巴勒地区1:5万区域地质矿产调查中,根据阿布山组的野外岩石及沉积特征,将阿布山组分为上、下2段,分别为山前河流和湖泊相沉积。该组上段砂岩的地球化学特征显示,物源主要来自上地壳,且主要为长英质岩石。对阿布山组上段的砂岩层进行碎屑锆石采样,从该组的2个样品中得到的最年轻的碎屑锆石年龄分别为85.9Ma和100.39Ma,为该组的时代归属提供了依据。同时,2组样品存在110Ma、440Ma、820Ma、1280Ma四期年龄峰值,结合该组的岩石地球化学特征及物源信息,对羌塘地体的构造演化做了一定的探讨。
Abstract:From the 1:50000 regional geological and mineral survey of Bailong and Woruobale area, and on the basis of the field rock and sendimentary characteristics, the authors divided the Abushan Formation into two sections, i.e., piedmont alluvial and lacustrine facies clastic sediments. Geochemical characteristics of the sandstone samples from the upper Abushan Formation show that the provenance was mainly from the upper crust, and was mainly felsic rocks. The authors obtained for the first time two detrital zircon samples from Upper Abushan Formation, and the analytical results show that the youngest detrital zircon ages are 85.9Ma and 100.39Ma. The results provide a basis for determining the ages of Abushan Formation. In addition, there exist four peak ages for the two samples, i.e., 10Ma, 440Ma, 820Ma and 1280Ma. Combined with the geochemical characteristics and provenance information of this group, the authors made a discussion on the tectonic evolution of Qiangtang terrane.
-
致谢: 感谢西藏地质调查院刘鸿飞院长、黄玮主任,西藏区调队曾庆高总工程师在野外给予的指导,感谢南京大学周国庆老师、中山大学殷征欣和钟云博士在室内研究给予的帮助,以及审稿专家给予的辛苦帮助,在此一并表示衷心的感谢。
-
图 1 工作区区域构造图[15]及采样位置
Qhapl—第四系;K2ab—阿布山组;T3t—亭共错组;P1q—曲地组;J1-2M—木嘎岗日岩群;J1q—曲色岩组;J2s—色哇岩组;J3K1s—沙木罗组;δμK1—闪长玢岩;1—蛇绿岩带;2—断裂;3—缝合带北界;4—碎屑锆石样;5—地球化学样
Figure 1. Regional tectonic map of the study area, showing sampling sites
表 1 阿布山组砂岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析数据
Table 1 Major, trace and rare earth elements compositions of sandstone from Abushan Formation
送样编号 TG001 TG002 TG004 TG005 TC005 样品岩性 紫红色长石石英砂岩 紫红色细粒长石石英砂岩 深紫色粗粒含岩屑长石砂岩 紫红色细粒岩屑石英砂岩 紫红色中粒含岩屑长石砂岩 Bi 2.53 1.38 0.55 0.40 0.09 Sb 20.26 10.26 3.50 2.18 1.46 Y 8.39 14.71 13.46 19.21 6.04 La 15.65 22.09 23.02 15.26 33.53 Ce 23.96 37.84 39.29 23.54 51.80 Pr 3.36 4.91 5.28 3.61 6.55 Nd 13.34 19.42 20.25 15.38 24.25 Sm 2.46 3.73 3.90 3.51 4.10 Eu 0.42 0.80 0.67 0.70 0.98 Gd 3.41 3.69 3.72 3.74 3.77 Tb 0.43 0.58 0.58 0.65 0.52 Dy 1.83 3.18 3.00 3.95 1.91 Ho 0.39 0.57 0.52 0.66 0.34 Er 0.63 1.37 1.04 1.37 0.35 Tm 0.22 0.29 0.25 0.27 0.17 Yb 1.13 1.56 1.27 1.33 0.88 Ba 140.05 593.28 116.91 93.10 145.25 Co 14.20 11.60 10.70 7.10 12.00 Cr 31.40 35.60 46.70 33.00 40.90 Cu 81.24 49.31 17.14 9.04 25.67 Nb 5.40 7.60 5.70 3.70 12.30 Ni 45.30 25.80 22.83 12.20 23.20 Pb 877.62 426.75 153.34 120.94 23.17 Rb 41.20 46.10 27.60 21.10 19.10 Sr 171.11 144.35 101.33 157.58 295.00 Th 3.01 3.02 3.04 3.01 3.01 V 49.14 41.70 42.70 40.30 77.30 Zn 106.30 63.00 43.70 31.70 62.30 Zr 194.88 194.69 212.26 116.35 167.00 W 49.42 10.92 77.06 26.96 6.94 Mo 1.81 1.07 1.32 0.61 0.42 Au 0.52 0.20 0.06 0.06 0.0006 Ag 1.88 0.53 0.19 0.13 0.05 Hf 4.30 6.20 6.50 3.10 8.00 Sn 2.34 1.73 1.98 1.54 1.64 Al2O3 4.69 5.73 3.25 2.54 15.26 CaO 10.58 12.97 15.94 16.82 4.26 K2O 0.87 1.10 0.54 0.36 0.33 MgO 1.02 1.30 0.37 0.52 1.35 MnO 0.06 0.12 0.24 0.29 0.05 Na2O 0.02 1.31 0.21 0.04 0.83 P2O5 0.06 0.08 0.10 0.09 0.26 SiO2 67.68 61.65 61.80 62.16 63.17 TiO2 0.31 0.43 0.29 0.22 0.61 TFe2O3 2.58 2.31 3.27 2.60 3.40 Li 70.08 29.21 32.21 22.83 73.95 Be 0.76 0.89 0.69 0.48 1.21 In 0.03 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.05 Cs 3.49 4.42 1.45 1.21 1.23 Ce 28.32 42.65 44.04 23.15 48.13 Ta 0.84 0.89 0.63 0.44 1.30 Sc \ \ \ \ \ U 0.89 1.27 0.85 0.84 1.13 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量为10-6 表 2 西藏窝若巴勒—白龙地区阿布山组砂岩与不同构造环境砂岩地球化学特征
Table 2 Geochemical parameter compartion between the sandstone from Abushan Formation in Woruobale and Bailong area, Tibet and that from various tectonic settings
参数 研究区 被动大陆边缘 活动大陆边缘 大陆岛弧 大洋岛弧 上地壳 SiO2 63.29 81.95 73.86 70.69 58.83 66 TiO2 0.37 0.49 0.46 0.64 1.06 0.5 Al2O3 6.29 8.41 12.89 14.04 17.11 15.2 TFeO+MgO 2.99 2.89 4.63 6.79 11.73 6.7 Al2O3/SiO2 0.1 0.1 0.18 0.2 0.29 7.15 K2O/Na2O 10.08 1.6 0.99 0.61 0.39 0.23 Al2O3/(CaO+Na2O) 0.84 4.15 2.56 2.42 1.72 0.87 La 35.29 39 37 27 8.2 30 Ce 4.74 85 78 59 19.4 64 ∑REE 94.63 210 186 146 58 146 LREE/HREE 9.91 8.5 9.1 7.7 3.8 9.47 (La/Yb)N 12.92 15.9 12.3 11 4.2 9.2 Th/U 3.12 5.6 4.8 4.6 2.1 3.8 Ti/Zr 1.28 6.74 15.3 19.7 56.8 15.8 Rb/Sr 0.21 1.19 0.89 0.65 0.05 0.32 Ba/Sr 1.43 4.7 3.8 3.55 0.95 1.57 注:主量元素含量单位为%,稀土元素含量为10-6;构造环境特征参数据参考文献[16];上地壳值据参考文献[17] 表 3 阿布山组砂岩碎屑锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb定年数据
Table 3 Detrital zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb dating results of Abushan Formation sandstone
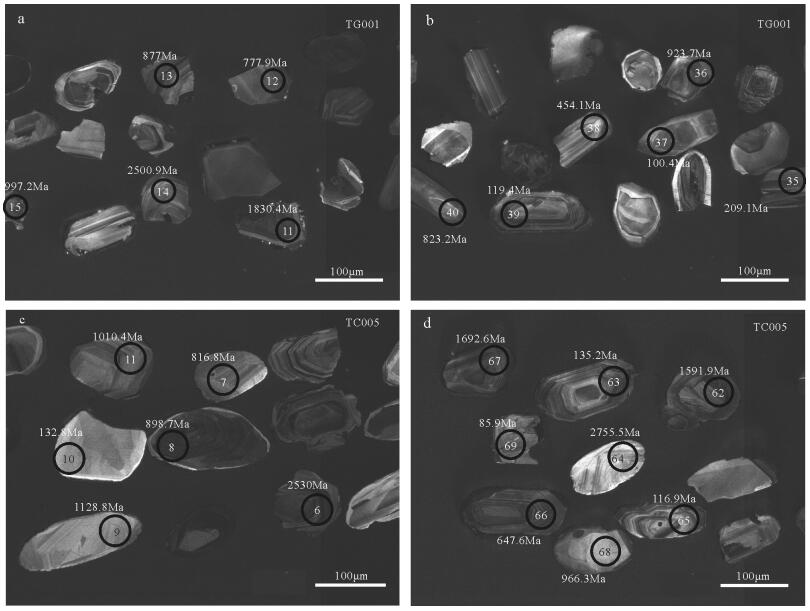
样品号 元素含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 同位素年龄/Ma Pb Th U 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 谐和度 TG001-1 27.37 62.40 65.89 0.95 4.51 0.31 1732.53 1726.76 99% TG001-2 6.24 289.71 243.36 1.19 0.15 0.02 145.76 107.16 69% TG001-3 5.21 59.48 125.18 0.48 0.28 0.03 254.39 214.61 83% TG001-4 20.84 195.40 478.09 0.41 0.25 0.04 224.77 224.21 99% TG001-5 96.02 43.95 234.44 0.19 5.49 0.34 1899.22 1883.93 99% TG001-6 47.52 69.50 214.57 0.32 1.88 0.18 1073.00 1064.42 99% TG001-7 19.89 180.09 378.76 0.48 0.35 0.04 306.04 271.70 88% TG001-8 146.96 52.07 316.88 0.16 7.06 0.39 2118.83 2102.89 99% TG001-9 49.92 182.40 277.11 0.66 1.26 0.14 829.55 835.75 99% TG001-10 52.47 155.63 181.19 0.86 2.27 0.21 1204.06 1221.15 98% TG001-11 66.20 148.34 139.96 1.06 5.07 0.33 1830.38 1818.16 99% TG001-12 33.95 122.78 204.76 0.60 1.19 0.13 794.84 777.99 97% TG001-13 34.74 118.63 180.19 0.66 1.34 0.15 864.31 877.06 98% TG001-14 42.29 41.89 62.13 0.67 10.74 0.49 2500.89 2582.20 96% TG001-15 51.26 262.75 203.97 1.29 1.58 0.17 961.99 997.24 96% TG001-16 9.28 255.71 141.25 1.81 0.57 0.04 457.10 236.29 36% TG001-17 35.18 79.48 176.49 0.45 1.52 0.16 937.67 948.11 98% TG001-18 130.46 67.68 493.31 0.14 2.57 0.22 1293.01 1300.93 99% TG001-19 21.13 316.70 431.38 0.73 0.24 0.04 218.35 231.20 94% TG001-20 15.08 241.55 239.42 1.01 0.33 0.05 293.26 305.23 96% TG001-21 13.38 119.78 288.04 0.42 0.24 0.04 214.97 240.65 88% TG001-22 337.22 223.05 643.89 0.35 10.16 0.38 2449.58 2084.27 83% TG001-23 13.35 86.42 188.74 0.46 0.54 0.06 440.74 346.79 76% TG001-24 35.38 232.15 369.12 0.63 0.56 0.07 454.30 450.28 99% TG001-25 106.12 38.64 269.91 0.14 4.93 0.33 1807.39 1838.35 98% TG001-26 45.27 73.85 342.78 0.22 1.06 0.11 735.81 656.25 88% TG001-27 23.82 117.30 569.26 0.21 0.24 0.04 221.49 225.77 98% TG001-28 13.28 258.65 381.34 0.68 0.21 0.03 196.31 177.94 90% TG001-29 126.24 314.91 506.61 0.62 2.02 0.19 1120.95 1113.64 99% TG001-30 36.58 206.94 736.28 0.28 0.30 0.04 262.51 258.85 98% TG001-31 69.81 179.66 227.66 0.79 2.45 0.22 1256.84 1276.79 98% TG001-32 80.62 136.18 260.66 0.52 2.64 0.24 1312.31 1365.53 96% TG001-33 54.34 185.36 231.06 0.80 1.64 0.17 985.50 1012.97 97% TG001-34 154.59 83.50 380.16 0.22 4.72 0.33 1771.38 1820.36 97% TG001-35 27.66 297.67 646.32 0.46 0.25 0.03 222.72 209.13 93% TG001-36 42.06 134.79 203.09 0.66 1.41 0.15 891.25 923.74 96% TG001-37 8.60 168.87 434.59 0.39 0.10 0.02 98.94 100.39 98% TG001-38 12.99 68.99 134.66 0.51 0.59 0.07 469.61 454.11 96% TG001-39 11.12 247.02 474.35 0.52 0.11 0.02 110.18 119.38 91% TG001-40 47.17 43.76 286.50 0.15 1.24 0.14 816.75 823.18 99% TG001-41 60.73 175.37 329.20 0.53 1.22 0.14 810.16 839.53 96% TG001-42 6.93 45.78 36.57 1.25 1.16 0.12 781.36 748.68 95% TG001-43 92.40 168.06 320.13 0.52 2.72 0.22 1333.15 1306.19 97% TG001-44 17.04 521.08 752.23 0.69 0.12 0.02 112.51 106.76 94% TG001-45 95.63 171.92 670.39 0.26 1.03 0.11 718.16 699.23 97% TG001-46 4.27 44.42 69.24 0.64 0.50 0.04 414.97 272.29 58% TG001-47 41.01 457.37 367.29 1.25 0.54 0.07 441.42 428.21 96% TG001-48 81.01 172.40 406.60 0.42 1.52 0.16 937.67 934.35 99% TC005-1 5.15 91.23 200.35 0.46 0.18 0.02 172.26 123.32 66% TC005-2 28.84 92.49 227.64 0.41 0.77 0.11 582.61 657.93 87% TC005-3 10.24 156.06 221.20 0.71 0.66 0.03 517.29 181.43 93% TC005-4 4.56 194.44 211.24 0.92 0.15 0.02 142.43 106.53 71% TC005-5 178.61 169.96 295.38 0.58 9.50 0.46 2387.42 2445.26 97% TC005-6 187.76 182.38 280.21 0.65 11.09 0.50 2530.45 2601.67 97% TC005-7 10.68 86.36 53.23 1.62 1.40 0.13 887.61 783.57 87% TC005-8 80.99 288.87 448.85 0.64 1.33 0.14 857.17 852.79 99% TC005-9 19.22 36.95 94.46 0.39 1.78 0.17 1039.43 988.67 94% TC005-10 3.80 81.25 132.04 0.62 0.25 0.02 226.60 145.03 56% TC005-11 25.75 83.81 117.15 0.72 1.71 0.17 1010.62 993.07 98% TC005-12 130.05 115.20 228.21 0.50 8.63 0.42 2299.56 2259.77 98% TC005-13 185.36 118.19 612.99 0.19 4.54 0.26 1738.21 1469.92 83% TC005-14 126.06 139.24 194.60 0.72 9.72 0.46 2408.65 2453.59 98% TC005-15 50.07 82.82 104.11 0.80 6.28 0.31 2016.08 1743.07 85% TC005-16 32.60 391.34 522.96 0.75 1.15 0.03 775.07 212.12 85% TC005-17 59.61 200.05 338.79 0.59 1.24 0.14 817.69 833.94 98% TC005-18 32.13 389.48 188.60 2.07 0.78 0.10 587.91 597.07 98% TC005-19 27.44 192.39 289.58 0.66 0.55 0.07 447.93 442.91 98% TC005-20 85.79 55.61 314.32 0.18 2.71 0.23 1331.69 1335.93 99% TC005-21 78.92 141.96 315.06 0.45 2.19 0.21 1177.89 1217.23 96% TC005-22 23.80 122.12 254.82 0.48 0.79 0.07 589.08 425.65 67% TC005-23 25.30 184.15 195.28 0.94 0.79 0.09 592.99 565.00 95% TC005-24 17.31 153.83 394.76 0.39 0.29 0.03 261.09 219.31 82% TC005-25 13.21 64.05 103.87 0.62 0.70 0.10 536.88 601.28 88% TC005-26 12.67 247.30 355.64 0.70 0.18 0.03 171.58 166.43 96% TC005-27 15.61 303.54 505.85 0.60 0.14 0.02 131.20 150.83 86% TC005-28 165.74 295.91 842.74 0.35 1.36 0.16 870.97 950.56 91% TC005-29 3.88 77.85 151.40 0.51 0.19 0.02 173.27 127.82 69% TC005-30 81.45 162.08 159.74 1.01 4.93 0.34 1808.13 1898.06 95% TC005-31 36.42 97.26 202.08 0.48 1.15 0.14 778.60 826.65 94% TC005-32 11.63 242.93 490.77 0.50 0.13 0.02 121.19 114.65 94% TC005-33 19.82 81.71 162.13 0.50 0.76 0.10 575.01 594.60 96% TC005-34 85.75 9.01 547.89 0.02 1.32 0.14 855.76 820.02 95% TC005-35 172.06 211.22 1057.13 0.20 1.29 0.14 842.48 830.33 98% TC005-36 33.48 169.20 128.61 1.32 1.74 0.17 1024.16 1010.62 98% TC005-37 99.54 105.00 580.68 0.18 1.36 0.15 874.02 905.98 96% TC005-38 9.33 41.34 67.28 0.61 0.85 0.11 623.73 652.77 95% TC005-39 138.68 325.35 662.65 0.49 1.41 0.16 891.33 982.18 90% TC005-40 19.25 67.68 106.27 0.64 1.03 0.14 717.39 842.65 83% TC005-41 8.14 47.95 55.80 0.86 0.87 0.11 635.78 663.23 95% TC005-42 138.76 109.76 539.09 0.20 2.11 0.21 1153.05 1254.52 91% TC005-43 24.71 222.05 413.84 0.54 0.60 0.04 474.94 237.44 93% TC005-44 51.47 139.59 188.15 0.74 1.62 0.20 979.27 1149.20 84% TC005-45 47.42 537.73 359.14 1.50 0.74 0.08 564.49 474.69 82% TC005-46 47.77 82.47 535.55 0.15 0.42 0.08 355.18 489.34 68% TC005-47 18.50 206.13 225.19 0.92 0.80 0.05 596.07 292.28 91% TC005-48 8.15 147.61 207.00 0.71 0.51 0.02 415.89 153.83 98% TC005-49 14.63 105.93 288.51 0.37 0.23 0.04 208.89 263.60 76% TC005-50 150.62 212.45 502.07 0.42 2.40 0.25 1242.76 1446.87 84% TC005-51 130.73 160.37 844.45 0.19 1.23 0.15 813.42 880.19 92% TC005-52 31.70 159.03 126.26 1.26 1.49 0.17 928.28 1002.73 92% TC005-53 6.41 101.77 165.20 0.62 0.27 0.03 242.99 185.99 73% TC005-54 6.36 105.15 188.55 0.56 0.24 0.02 216.81 157.65 68% TC005-55 7.78 116.18 337.87 0.34 0.15 0.02 144.69 118.73 80% TC005-56 20.18 48.05 98.32 0.49 1.62 0.16 977.29 976.44 99% TC005-57 43.18 98.64 125.66 0.79 3.42 0.24 1508.45 1396.85 92% TC005-58 41.56 176.43 245.52 0.72 1.15 0.13 779.18 780.20 99% TC005-59 61.37 68.06 745.56 0.09 0.59 0.07 470.37 444.88 94% TC005-60 14.85 198.70 600.47 0.33 0.14 0.02 132.54 131.83 99% TC005-61 8.70 207.49 248.61 0.83 0.21 0.03 194.32 162.82 82% TC005-62 165.19 78.64 599.11 0.13 3.80 0.21 1591.92 1241.09 75% TC005-63 27.60 418.36 1023.06 0.41 0.16 0.02 148.96 135.19 90% TC005-64 51.51 36.24 71.00 0.51 14.09 0.39 2755.50 2114.90 73% TC005-65 19.62 331.88 625.64 0.53 0.39 0.02 334.79 116.88 93% TC005-66 35.44 90.40 270.36 0.33 0.82 0.11 610.22 647.60 94% TC005-67 98.53 190.78 264.91 0.72 4.30 0.26 1692.58 1509.20 88% TC005-68 183.28 350.55 844.60 0.42 1.59 0.17 966.30 1013.43 95% TC005-69 3.59 140.97 193.21 0.73 0.21 0.01 192.07 85.91 93% TC005-70 25.73 135.39 123.65 1.09 1.19 0.14 793.79 840.05 94% TC005-71 205.31 343.42 296.34 1.16 8.64 0.44 2300.71 2332.78 98% TC005-72 48.59 561.26 409.48 1.37 0.51 0.08 421.41 474.96 88% 表 4 羌塘盆地工作区部分前人碎屑锆石年龄及地质事件解释表
Table 4 The explanation table about previous work of detrital zircon ages and geological events of study area in Qiangtang Basin workplace
资料来源 样品类型 年龄组/Ma 地质解释 [13] 绢云母石英糜棱片岩 509~548 羌塘地块与拉萨地块碰撞事件 929~1126 新元古代超大陆碰撞拼合事件年龄 1300~1372 羌塘结晶基底主期变质作用年龄 2056~2432 羌塘变质结晶基底原岩年龄 [24] 黑云母片麻岩 198~223 班-怒洋的打开与岩浆活动 233~402 古特提斯洋的演化岩浆活动 420~465 加里东造山运动 522~645 羌塘地块与拉萨地块碰撞事件年龄 1666~1780 羌塘结晶基底主期变质作用年龄 2374~2498 太古代末全球超大陆拼合事件年龄 [25] 石英岩 520~700 泛非构造岩浆热事件 800~1100 格林威尔-晋宁构造岩浆热事件 > 1200 变质基底早期年龄纪录 [26] 石英砂岩 470~520 泛非运动晚期的岩浆热事件 580~800 格林威尔-晋宁构造岩浆热事件 950~1100 变质基底早期年龄记录 本文 石英岩屑砂岩 90~230(120) 班-怒洋演化岩浆活动 240~330 古特提斯洋演化岩浆活动 410~430 加里东造山运动 510~630 泛非构造岩浆热事件 720~1200(830) 新元古代超大陆碰撞拼合事件年龄 > 1200 变质基底早期年龄纪录(主变质年龄期在1280±60Ma左右) -
Wang C S, Li X H, Liu Z F, et al. Revision of the Cretaceous-Paleogene stratigraphic framework, facies architecture and provenance of the Xigaze forearc basin along the Yarlung Zangbo suture zone[J]. Gondwana Research, 2011, 22(2): 415-433. http://www.deepdyve.com/lp/elsevier/revision-of-the-cretaceous-paleogene-stratigraphic-framework-facies-skWgy2U8TZ
常承法, 郑锡澜, 潘裕生.喜马拉雅的地质发展历史构造带的划分和隆起原因探讨[M].北京:地质出版社, 1978: 108-175. Kapp P, Decelles P G, Gehrels G E, et al. Geological records of the Lhasa-Qiangtang and Indo-Asian collisions in the Nima area of central Tibet[J]. Geologic Society of American, 2007, 119(7/8): 917-932. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/234118793_Geological_records_of_the_Cretaceous_Lhasa-Qiangtang_and_Indo-Asian_collisions_in_the_Nima_basin_area_central_Tibet?ev=auth_pub
Kapp P, Yin A, Harrison T M, et al. Cretaceous-Tertiary shortening, basin development, and volcanism in central Tibet[J]. Geologic Society of American Bulletin, 2005, 117(7): 865-878. doi: 10.1130/B25595.1
王立成, 魏玉帅.西藏羌塘盆地白垩纪中期构造事件的磷灰石裂变径迹证据[J].岩石学报, 2013, (3): 1039-1047. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201303025.htm 夏军, 钟华明, 童劲松, 等.藏北龙木错东部三岔口地区下奥陶统与泥盆系的不整合界面[J].地质通报, 2006, 25(1/2): 113-117. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2006Z1017.htm 黄继均.藏北羌塘盆地构造特征及演化[J].中国区域地质, 2001, 20(2): 178-186. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10697-2003097227.htm 李才.羌塘基底质疑[J].地质论评, 2003, 49(1): 5-9. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200301001.htm 黄继均.羌塘盆地基底构造特征[J].地质学报, 2001, 75(3): 333-337. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200103009.htm Yue Y, Graham S A, Ritts B D, et al. Detrital zircon provenance evidence for large scale extrusion along the Altyn tagh fault[J]. Tectonophysics. 2005, 406(3/4): 165-178. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229416181_Detrital_zircon_provenance_evidence_for_large-scale_extrusion_along_the_Altyn_Tagh_Fault
Rainbird R H, Mcnicoll V J, Thériault R J, et al. Pan-contineral river system dranning Grenville Oregen record by U-Pb and SmNd geochronology of Neoproterozoic quartzarenites and mudrocks, northwestern Canada[J]. Journal of Geology, 1997, 105(1): 1-17. doi: 10.1086/606144
Fedo C M, Eriksson K A. Stratigraphie framework of the-3.0Ga Buhwa Greenstone Belt:a unique stable-shelf sueeession in the Zimbabwe Archean Craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 1996, 77(3): 161-178. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0301926895000534
王成善, 伊海生, 林金辉.西藏羌塘盆地地质演化与油气远景评价[M].北京:地质出版社, 2001: 1-215. 谭富文, 王剑, 丁俊, 等.青藏高原油气资源战略选区调查与评价[M].北京:地质出版社, 2009: 1-645. 李金祥, 李光明, 秦克章, 等.班公湖带多不杂富金斑岩铜矿床斑岩-火山岩的地球化学特征与时代:对成矿构造背景的制约[J].岩石学报, 2008, (3): 531-543 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200803013.htm Bhatia M R. Plate tectonics and geochemical composition of sandstones[J]. Geology, 1983, 91(6): 611-627. doi: 10.1086/628815
Taylor S R, McLennan S M. The continenetal crust: Its composition and evolution[M]. Oxford: Balcwell Scientific, 1985.
McLennan S M. Rare earth element in sedimentary rocks:Influence of provenance and sedimentary processes[C]//Linpin B R, Mckay G A. Geochemistry and Mineralogy of Rare Earth Elements. Review Mineralogy, 1989, 21: 169-200. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/303145235_Rare_earth_elements_and_sedimentary_rocks_influence_of_provenance_and_sedimentary_processes
Boynton W V. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: metcoritestudies[C]//Henderson P. Rare earth element geochemistry. Elservier, 1984: 63-114.
Girty G H, Ridge D L, Knaack C, et al. Provenance and depositional setting of paleozoic chert and argillite, Sierra Nevada, California[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1996, 66(1): 107-118. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279710026_Provenance_and_depositional_setting_of_Paleozoic_chert_and_argillite_Sierra_Nevada_California
Wronkiewicz D J, Condie K C. Geochemistry and provenance of sediments from the Pongola Supergroup, South africa:Evidence for a 3.0Ga old Continental craton[J]. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 1989, 53: 1537-1549. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(89)90236-6
Roser B P, Korsch R J. Provenance signatures of sandstone-mudstone suites determined using discrimiant function analysis of major-element data[J]. Chemical Geology, 1988, 67: 119-139. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(88)90010-1
Floyd P A, Leveridge B E. Tectonic environment of the Devonian Gramscatho basin, south Cornwall: framework mode and geochemical evidence from turbiditic sandstones[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of London, 1987, 144: 531-542. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.144.4.0531
谭富文, 王剑, 付修根, 等.藏北羌塘盆地基底变质岩的错石SHRIMP年龄[J].岩石学报, 2009, 25(1): 139-146. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200901012.htm 董春艳, 李才, 万渝生, 等.西藏羌塘龙木错-双湖缝合带南侧奥陶纪温泉石英岩碎屑锆石年龄分布模式:构造归属及物源区制约[J].中国科学(D辑), 2011, (3): 299-308. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201103003.htm 杨耀, 赵中宝, 苑婷媛, 等.藏北羌塘奥陶纪平行不整合面的厘定及其构造意义[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(8): 2381-2392. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201408019.htm 王国芝, 王成善.西藏羌塘基底变质岩系的解体和时代厘定[J].中国科学(D辑), 2001, 31(增刊): 77-82. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2001S1011.htm 多吉, 温存齐, 郭建慈, 等.西藏4.1Ga碎屑锆石年龄的发现[J].科学通报, 2007, 52(1): 19-22. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200701002.htm Kapp P, Yin A, Manning C E, et al. Tectonic evolution of the early Mesozoic buleschist-bearing Qiangtang lmetamorphic belt, central Tibet[J]. Tectonic, 2003, 22: 1043-1068. doi: 10.1029/2002TC001383/citedby
Pullen A, Kapp A, Gehrels G E, et al. Triassic continental subduction in central Tibet and Mediterranean-style closure of the PaleoTethys Ocean[J]. Geology, 2008, 36: 351-354. doi: 10.1130/G24435A.1
Leier A, Kppa P, Gehrels G E, et al. Detrital zircon geochronology of Carboniferous-Cretaceous strata in the Lhasa terrane, Southern Tibet[J]. Basin Res., 2007, 19: 361-378. doi: 10.1111/bre.2007.19.issue-3
Gehrels G E, Kapp P, Pullen A, et al. U-Pb basement and detrital zircon geochronology of the southern Tibetan Plateau and Tethyan Himalaya[J]. Geol. Soc. Amer. Abstract Programs. 2008, 40: 329. https://gsa.confex.com/gsa/2008AM/finalprogram/abstract_146790.htm
李才.青藏高原龙木错-双湖-澜沧江板块缝合带研究二十年[J].地质论评, 2008, 54(1): 105-119. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200801013.htm 李才, 翟刚毅, 王立全, 等.认识青藏高原的重要窗口——羌塘地区近年来研究进展评述(代序)[J].地质通报, 2009, 28(9): 1169-1177. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200909002.htm 吉林大学地质调查研究院. 1: 25万玛依岗日幅地质调查成果与进展[J].沉积与特提斯地质, 2005, 25(Z1): 51-56. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD2005Z1008.htm 李才, 王天武.西藏羌塘中部都古尔花岗质片麻岩同位素年代学研究[J].长春科技大学学报, 2000, 30(2): 1236-1243. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200002000.htm 施建荣, 董永胜, 王云生.藏北羌塘中部果干加年山斜长花岗岩定年及其构造意义[J].地质通报, 2009, 28(9): 1236-1243. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200909012.htm 王剑, 汪正江, 陈文西, 等.藏北北羌塘盆地那底岗日组时代归属的新证据[J].地质通报, 2007, 26(4): 32-37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200704004.htm 翟庆国, 李才.藏北羌塘菊花山那底岗日组火山岩锆石SHRIMP定年及其意义[J].地质学报, 2007, 81(6): 795-800. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200706006.htm 李才, 翟庆国, 陈文, 等.青藏高原羌塘中部榴辉岩Ar-Ar定年[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22: 2843-2849. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2006.12.003 邱瑞照, 周肃, 邓晋福, 等.西藏班公湖-怒江西段舍马拉沟蛇绿岩中辉长岩年龄测定——兼论班公湖-怒江蛇绿岩带形成时代[J].中国地质, 2004, 31(3): 262-268. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200403003.htm 史仁灯.班公湖SSZ型蛇绿岩年龄对班-怒洋时限的制约[J].科学通报, 2007, 52(2): 223-227. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200702016.htm Kapp P, Murphy M A, Yin A, et al. Mesozoic and Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Shiquanhe area of western Tibet[J]. Tectonics, 2003, 22(4): 1029. doi: 10.1029/2001TC001332/full
曲晓明, 辛洪波, 杜德道, 等.西藏班公湖-怒江缝合带中段碰撞后A型花岗岩的时代及其对洋盆闭合时间的约束[J].地球化学, 2012, 41(1): 1-14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201201002.htm 翟庆国, 李才, 王军, 等. 青藏高原羌塘中部中奥陶世片麻状花岗岩及其地质意义(内部资料). 2009.




 下载:
下载: