Characteristics of the Paleozoic metabasite in Baoshan Terrane:Implications for the tectonic evolution
-
摘要:
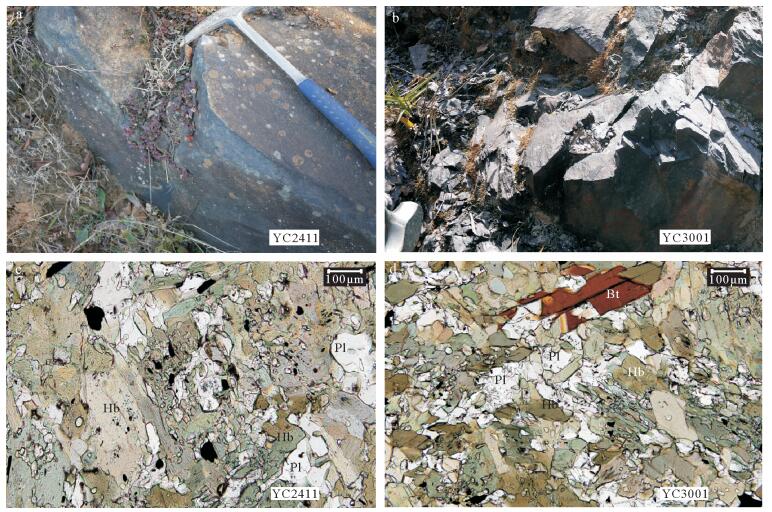
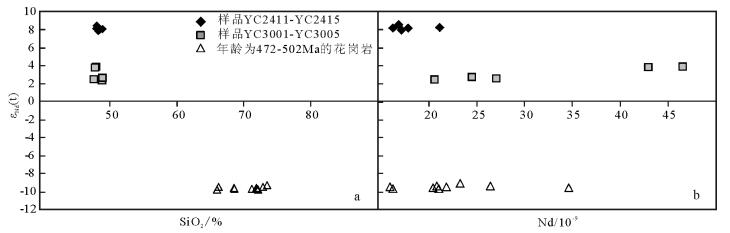
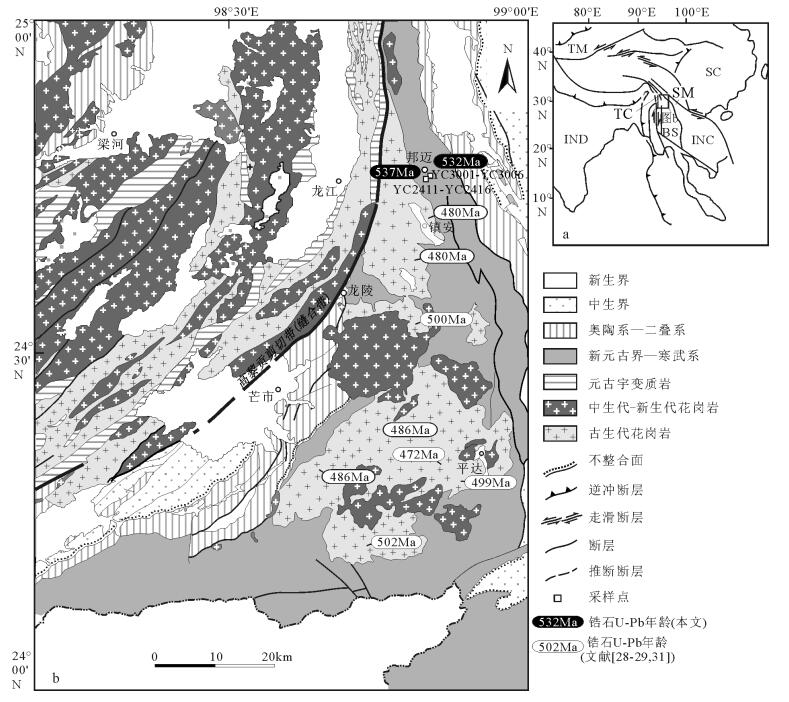
保山地体位于青藏高原东南缘。有关保山地体的岩浆作用研究大多集中在中生代及新生代,针对古生代岩浆作用的讨论较少。对云南省保山邦迈地区蒲满哨群中变质基性岩的锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及Sm-Nd同位素组成进行了研究。这些变质基性岩可分为2组:一组为斜长角闪岩,另一组为黑云斜长角闪岩。锆石U-Pb测年结果表明,斜长角闪岩的形成时代为536.7Ma,黑云斜长角闪岩的形成时代为532.0Ma。地球化学特征显示,斜长角闪岩的原岩为玄武安山岩,黑云斜长角闪岩的原岩为碱性玄武岩。稀土和微量元素配分曲线及多种构造环境判别图解显示,二者分别具有富集型大洋中脊玄武岩和洋岛玄武岩的地球化学特征。结合区域大地构造背景认为,保山地体邦迈变质基性岩为洋脊俯冲的产物。在新元古末期-早古生代,保山地体与拉萨地体、喜马拉雅地体等类似,皆位于冈瓦纳大陆边缘,且共同经历了增生造山过程。
Abstract:The Baoshan Terrane is located on the southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Previous studies of the magmatism of the Baoshan Terrane were mainly focused on the Mesozoic and Cenozoic periods, whereas the study of the Paleozoic magmatism was relatively insufficient. In this paper, zircon U-Pb geochronology, geochemistry and Sm-Nd isotopes are presented for metabasite of Pumanshao Group in Bangmai area, Baoshan, Yunnan Province. The metabasites can be divided into two groups:amphibolite and biotite-plagioclase amphibolite. Zircon U-Pb geochronologic study shows that the two groups were formed at 536.7Ma and 532.0Ma, respectively. Geochemical characteristics indicate that the protolith of amphibolite was basaltic andesites and that of biotite-plagioclase amphibolite was alkaline basalt. REE and trace element distribution and diagrams for discriminating the tectonic settings reveal that the two groups have geochemical features of E-MORB and OIB, respectively. Combined with the regional tectonic setting, the authors hold that metabasites are products of Proto-Tethyan ridge subduction. During Late Neoproterozoic-Early Paleozoic, like things in the Lasha and Himalaya terranes, the Baoshan Terrane was situated on the margin of Gondwana too and experienced accre-tionary orogeny.
-
Keywords:
- southeastern Tibetan Plateau /
- Baoshan Terrane /
- Early Paleozoic /
- metabasite /
- accretion /
- Gondwana
-
致谢: 感谢中国地质科学院地质研究所李源、杨红博士的宝贵意见。
-
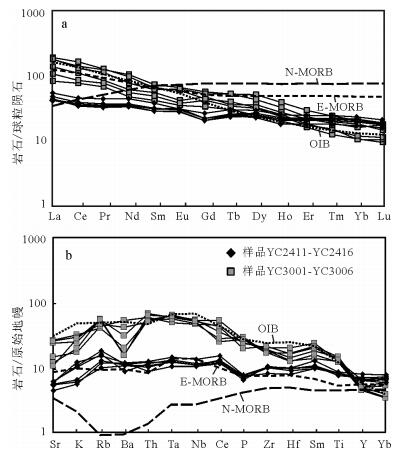
图 4 变质基性岩的稀土元素配分曲线(a)和微量元素蛛网图(b)(原始地幔和球粒陨石标准值据参考文献[50])
E-MORB—富集型大洋中脊玄武岩;N-MORB—正常大洋中脊玄武岩;OIB—洋岛玄武岩
Figure 4. REE abundance patterns(a) and trace element spider diagram (b) of the metabasites
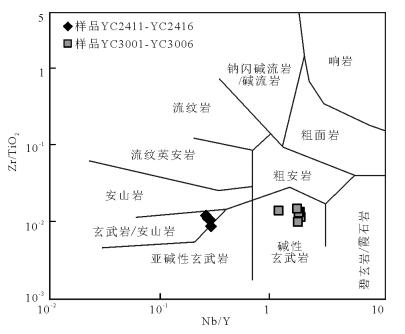
图 5 变质基性岩的Nb/Y-Zr/TiO2图解[53]
Figure 5. Nb/Y-Zr/TiO2 diagram for the metabasites
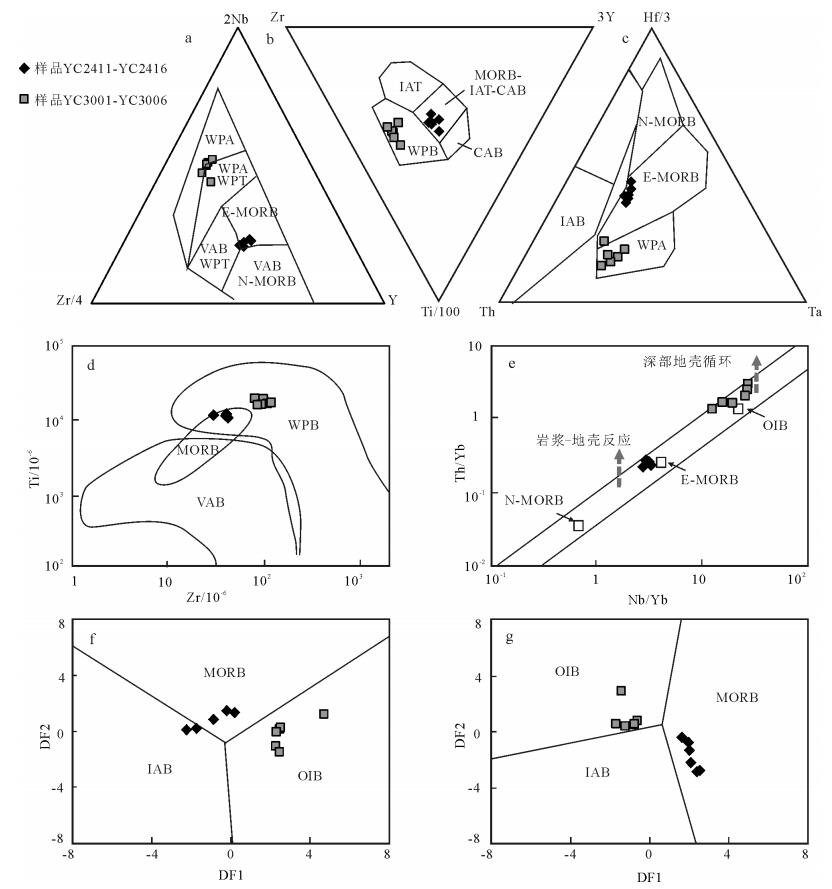
图 6 变质基性岩构造环境判别图解
a—Nb-Zr-Y图解[54];b—Ti-Zr-Y图解[52];c—Hf-Th-Ta图解[55];d—Zr-Ti图解[56];e—Nb/Yb-Th/Yb图解[57];f、g—不活动元素对数图解[58]。CAB—陆缘弧玄武岩;IAB—岛弧玄武岩;IAT—岛弧拉斑玄武岩;MORB—洋中脊玄武岩;VAB—火山岛弧玄武岩;WPA—板内碱性玄武岩;WPB—板内玄武岩;WPT—板内拉斑玄武岩。f图中的DF1=0.3518ln(La/Th)+0.6013ln(Sm/Th)-1.3450ln(Yb/Th)+2.1056ln(Nb/Th)-5.4763,DF2=-0.3050ln(La/Th)-1.1801ln(Sm/Th)+1.6189ln(Yb/Th)+1.2260ln(Nb/Th)-0.9944;g图中的DF1=-0.5558ln(La/Th)-1.4260ln(Sm/Th)+2.2935ln(Yb/Th)-0.6890ln(Nb/Th)+4.1422,DF2=-0.9207ln(La/Th)+3.6520ln(Sm/Th)-1.9866ln(Yb/Th)+1.0574ln(Nb/Th)-4.4283
Figure 6. Tectonic discrimination diagrams of the metabasites
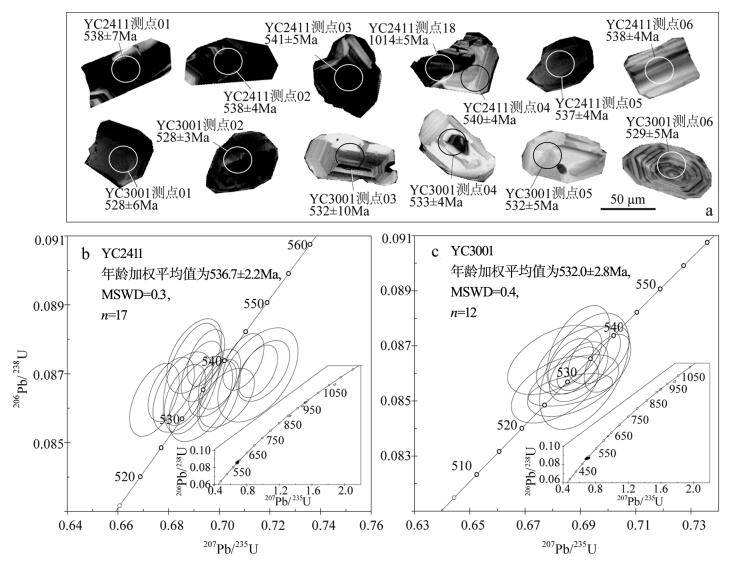
表 1 保山邦迈变质基性岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb测年分析结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb dating results of the metabasites of Bangmai area, Baoshan
样品 U/10-6 Th/10-6 Th/U 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 比值 误差 比值 误差 年龄/Ma 误差/Ma 年龄/Ma 误差/Ma 样品YC241 测点01 293 324 1.10 0.7153 0.0129 0.08696 0.00112 547.9 7.7 537.6 6.6 测点02 1561 659 0.42 0.6931 0.0067 0.08706 0.00072 534.7 4.0 538.1 4.3 测点03 812 227 0.28 0.6901 0.0089 0.08751 0.00089 532.9 5.3 540.8 5.2 测点04 1537 648 0.42 0.6948 0.0061 0.08746 0.00067 535.7 3.6 540.5 4.0 测点05 804 217 0.27 0.7001 0.0068 0.08684 0.00071 538.8 4.1 536.8 4.2 测点06 834 226 0.27 0.7153 0.0063 0.08707 0.00062 547.9 3.7 538.2 3.7 测点07 819 222 0.27 0.7096 0.0066 0.08734 0.00067 544.5 3.9 539.8 4.0 测点08 1768 829 0.47 0.6998 0.0069 0.08637 0.00086 538.7 4.1 534.0 5.1 测点09 1176 489 0.42 0.6893 0.0093 0.08686 0.00131 532.4 5.6 536.9 7.8 测点10 1465 618 0.42 0.6865 0.0067 0.08639 0.00072 530.7 4.0 534.1 4.3 测点11 751 202 0.27 0.7174 0.0085 0.08708 0.00072 549.1 5.0 538.2 4.3 测点12 509 260 0.51 0.6974 0.0077 0.08658 0.00067 537.2 4.6 535.3 4.0 测点13 628 558 0.89 0.6855 0.0096 0.08647 0.00095 530.1 5.8 534.6 5.7 测点14 605 479 0.79 0.6744 0.0080 0.08624 0.00087 523.4 4.9 533.3 5.2 测点15 645 508 0.79 0.6811 0.0075 0.08654 0.00076 527.4 4.5 535.1 4.5 测点16 477 246 0.52 0.7030 0.0089 0.0863 0.0007 540.6 5.3 533.6 4.2 测点17 675 600 0.89 0.6927 0.0103 0.08627 0.00101 534.4 6.2 533.4 6.0 测点18 851 381 0.45 1.7693 0.0122 0.1704 0.0009 1034.3 4.5 1014.1 4.9 测点19 336 28 0.08 0.9493 0.0068 0.1108 0.0006 677.7 3.5 677.6 3.3 测点20 352 60 0.17 1.5980 0.0128 0.1621 0.001 969.4 5.0 968.3 5.6 样品YC3001 测点01 1106 926 0.84 0.6808 0.0129 0.08541 0.00099 527.0 8.0 528.0 6.0 测点02 1012 879 0.87 0.6864 0.0125 0.0854 0.00048 531.0 7.0 528.0 3.0 测点03 429 133 0.31 0.6914 0.0132 0.08608 0.00173 533.6 7.9 532.3 10.2 测点04 1774 834 0.47 0.6894 0.0064 0.08617 0.00065 532.4 3.8 532.9 3.8 测点05 1701 806 0.47 0.6894 0.0086 0.08606 0.00089 532.4 5.2 532.2 5.3 测点06 158 166 1.05 0.6873 0.0135 0.08556 0.00092 531.2 8.1 529.2 5.5 测点07 1465 618 0.42 0.6865 0.0067 0.08639 0.00072 530.7 4.0 534.1 4.3 测点08 1768 829 0.47 0.6998 0.0069 0.08637 0.00086 538.7 4.1 534.0 5.1 测点09 1861 1453 0.78 0.6893 0.0124 0.08648 0.00101 532.0 7.0 535.0 6.0 测点10 915 782 0.85 0.6807 0.0139 0.08649 0.00103 527.0 8.0 535.0 6.0 测点11 1861 877 0.47 0.6967 0.0090 0.08667 0.00086 536.8 5.4 535.8 5.1 测点12 1176 489 0.42 0.6893 0.0093 0.08686 0.00131 532.4 5.6 536.9 7.8 测点13 151 72 0.48 1.3325 0.0108 0.1407 0.0008 860.0 4.7 848.8 4.3 测点14 217 95 0.44 1.4870 0.0122 0.1520 0.0007 925.1 5.0 912.1 4.0 测点15 908 94 0.10 1.5191 0.0086 0.1563 0.0006 938.1 3.5 936.0 3.4 测点16 90 70 0.78 1.5196 0.0152 0.1564 0.0009 938.3 6.1 936.8 4.9 测点17 847 397 0.47 1.8812 0.0123 0.1775 0.0009 1074.5 4.3 1053.3 4.9 表 2 保山邦迈地区变质基性岩的主量、微量和稀土元素测试结果
Table 2 Major, trace and rare earth element concentrations of the metabasites in Bangmai area, Baoshan
样品号 YC2411 YC2412 YC2413 YC2414 YC2415 YC2416 YC3001 YC3002 YC3003 YC3004 YC3005 YC3006 SiO2 47.96 48.18 47.90 48.40 48.80 49.23 47.94 48.25 49.06 49.14 48.04 49.03 TiO2 1.71 1.88 1.94 1.86 1.87 1.83 3.03 2.73 2.66 2.57 3.12 2.81 Al2O3 13.81 14.03 13.85 13.82 13.80 13.73 12.94 14.23 13.04 13.08 12.49 12.51 Fe2O3 2.22 2.15 1.86 2.56 2.21 2.79 2.98 3.90 4.24 4.13 2.68 2.21 FeO 13.65 12.84 13.44 12.56 12.74 12.20 11.97 11.93 11.99 11.67 12.78 12.33 MnO 0.45 0.34 0.35 0.35 0.35 0.34 0.55 0.47 0.51 0.54 0.42 0.57 MgO 6.81 6.82 6.82 6.83 6.79 6.62 5.97 4.28 4.55 4.48 5.78 4.51 CaO 11.48 11.50 11.04 11.35 11.67 11.14 9.93 8.95 8.96 9.12 11.05 10.92 Na2O 0.54 0.56 0.54 0.59 0.54 0.50 2.13 2.54 2.24 2.29 1.07 2.24 K2O 0.19 0.32 0.38 0.34 0.21 0.18 0.94 0.51 0.74 0.59 0.87 0.84 P2O5 0.15 0.18 0.18 0.17 0.17 0.16 0.52 0.51 0.58 0.63 0.58 0.42 烧失量 1.08 1.27 1.61 1.26 0.92 1.39 1.22 1.07 1.06 1.58 1.03 1.37 总量 99.90 99.91 99.76 99.90 99.90 99.90 100.12 99.37 99.63 99.82 99.91 99.76 Mg# 45.56 47.01 46.57 46.76 46.95 46.16 43.63 34.27 35.05 35.31 42.08 37.67 La 10.10 10.60 13.30 11.50 10.20 10.80 30.82 40.01 18.72 24.15 42.7 40.71 Ce 22.30 23.00 28.60 24.40 22.20 21.50 62.68 80.78 44.32 49.51 94.86 75.15 Pr 3.36 3.46 4.27 3.62 3.27 3.16 7.72 11.15 6.11 6.89 11.49 10.18 Nd 16.80 17.10 21.10 17.80 16.20 15.90 27.21 46.42 20.85 24.68 42.87 34.09 Sm 4.89 4.80 5.95 4.95 4.51 4.46 8.01 10.57 6.14 7.04 9.37 8.85 Eu 1.80 1.88 1.84 1.80 1.71 1.65 2.29 3.61 1.91 2.06 3.26 3.47 Gd 4.68 4.63 5.57 4.64 4.35 4.28 9.17 11.14 6.45 8.16 8.55 10.11 Tb 0.98 0.95 1.14 0.95 0.89 0.93 1.29 1.87 1.08 1.21 1.42 1.85 Dy 6.88 6.56 7.68 6.54 6.24 5.86 8.73 12.36 5.96 7.56 7.89 10.46 Ho 1.30 1.25 1.46 1.24 1.18 1.04 1.45 2.06 1.07 1.26 1.34 1.73 Er 3.77 3.65 4.20 3.61 3.47 3.05 3.44 4.56 2.55 2.74 2.85 3.64 Tm 0.58 0.56 0.64 0.56 0.53 0.47 0.45 0.58 0.3 0.37 0.35 0.47 Yb 3.70 3.56 4.01 3.53 3.39 3.01 2.58 3.32 1.71 1.67 1.89 2.92 Lu 0.50 0.49 0.54 0.47 0.45 0.41 0.43 0.42 0.23 0.25 0.27 0.35 Sr 121.00 137.00 133.00 132.00 125.00 98.60 559.54 307.09 500.58 246.31 532.92 221.18 K 1586 2665 3146 2814 1718 1478 7803 4234 6143 4898 7222 6973 Rb 6.65 10.60 10.10 12.10 8.57 7.88 25.64 27.08 34.15 35.12 29.46 34.54 Ba 77.80 65.10 86.00 82.30 79.80 86.30 140.42 365.01 214.03 108.42 292.25 105.94 Th 0.91 1.04 1.11 1.08 0.96 0.79 4.64 5.02 5.78 4.65 4.25 5.46 Ta 0.53 0.56 0.61 0.52 0.52 0.45 2.55 1.98 2.43 2.27 2.63 2.45 Nb 8.30 8.57 9.99 8.23 8.24 7.85 38.74 33.03 36.19 34.13 37.76 36.18 Ce 22.30 23.00 28.60 24.40 22.20 21.50 62.68 80.78 44.32 49.51 94.86 75.15 P 655 764 781 746 729 698 2270 2226 2531 2750 2531 1833 Zr 122.50 116.30 118.40 117.00 96.60 117.80 210.64 225.34 205.32 192.07 186.85 237.32 Hf 3.13 3.13 3.22 3.12 2.60 2.94 4.36 6.17 3.91 3.75 5.07 4.95 Sm 4.89 4.80 5.95 4.95 4.51 4.46 8.01 10.57 6.14 7.04 9.37 8.85 Ti 10251 11271 11630 11151 11211 10971 18143 16378 15923 15389 18686 16846 Y 33.80 32.20 38.00 31.60 30.20 30.40 22.09 29.21 21.13 20.13 22.58 22.12 Yb 3.70 3.56 4.01 3.53 3.39 3.01 2.58 3.32 1.71 1.67 1.89 2.92 Sc 50.90 48.00 56.10 48.50 46.10 42.80 20.68 35.42 14.31 24.01 17.37 22.23 Cr 153.00 73.40 69.20 75.70 65.70 75.30 122.96 132.75 98.52 141.19 125.48 125.12 Nb/Yb 2.24 2.41 2.49 2.33 2.43 2.61 15.02 9.95 21.16 20.44 19.98 12.39 Th/Yb 0.25 0.29 0.28 0.31 0.28 0.26 1.80 1.51 3.38 2.78 2.25 1.87 Nb/Y 0.25 0.27 0.26 0.26 0.27 0.26 1.75 1.13 1.71 1.70 1.67 1.64 Zr/Ti2O 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 Nb/La 0.82 0.81 0.75 0.72 0.81 0.73 1.26 0.83 1.93 1.41 0.88 0.89 (Th/Ta)PM 0.83 0.90 0.87 0.99 0.90 0.85 0.88 1.22 1.15 0.99 0.78 1.07 (Th/Nb)PM 0.92 1.02 0.93 1.10 0.98 0.84 1.01 1.27 1.34 1.14 0.94 1.27 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量为10-6 表 3 保山邦迈变质基性岩的Sm-Nd同位素分析结果
Table 3 Sm-Nd isotope compositions of zircon in the metabasites of Bangmai area, Baoshan
样品 年龄/Ma Sm Nd 147Sm/144Nd 143Nd/144Nd 2σ Sm/Nd INd εNd(0) εNd(t) 2σ TDM/Ma TDMC/Ma YC2411 536.7 4.89 16.8 0.175867 0.513003 9 0.291 0.5123846 7.12 8.56 0.18 599 561 YC2412 536.7 4.8 17.1 0.169601 0.512951 5 0.281 0.5123547 6.11 7.98 0.10 693 609 YC2413 536.7 5.95 21.1 0.170380 0.512968 7 0.282 0.5123689 6.44 8.25 0.14 646 586 YC2414 536.7 4.95 17.8 0.168023 0.512956 8 0.278 0.5123652 6.20 8.18 0.16 653 592 YC2415 536.7 4.51 16.2 0.168208 0.512957 6 0.278 0.5123656 6.22 8.19 0.12 652 592 YC3001 532.0 8.01 27.2 0.177864 0.512697 17 0.29 0.512077 1.15 2.43 0.33 1930 1056 YC3002 532.0 10.57 46.4 0.137580 0.512625 12 0.23 0.512145 -0.25 3.77 0.23 1054 948 YC3003 532.0 6.14 20.9 0.177929 0.512692 11 0.29 0.512072 1.05 2.33 0.21 1955 1064 YC3004 532.0 7.04 24.7 0.172350 0.512686 22 0.29 0.512085 0.94 2.60 0.43 1714 1043 YC3005 532.0 9.37 42.9 0.132060 0.512601 10 0.22 0.512141 -0.72 3.68 0.20 1028 955 注:TDM为一阶段年龄;TDMC为二阶段年龄 -
Li C, Xie Y W, Sha S L, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of the Pan-African granite in Baxoi County, eastern Tibet, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2008, 4(1): 31-36. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/297269632_SHRIMP_U-Pb_zircon_dating_of_the_Pan-African_granite_in_Baxoi_County_eastern_Tibet_China
Hoffman P F. Did the breakout of Laurentia turn Gondwanaland insideout?[J]. Science, 1991, 252: 1409-1412. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5011.1409
Powell C M, Li Z X, Mcelhinny M W, et al. Paleomagnetic constraints on timing of the Neoproterozoic breakup of Rodinia and the Cambrian formation of Gondwana[J]. Geology, 1993, 21(10):889-892. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1993)021<0889:PCOTOT>2.3.CO;2
Grunow A. Were aspects of Pan-African deformation linked to Iapetus opening?[J]. Geology, 1996, 24(24): 228-233. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/geology/article/24/12/1063/189677/were-aspects-of-pan-african-deformation-linked-to
Rogers J J W. A History of Continents in the past Three Billion Years[J]. Journal of Geology, 1996, 104(1): 91-107. doi: 10.1086/629803
Parrish R R, Hodges V. Isotopic constraints on the age and provenance of the Lesser and Greater Himalayan sequences, Nepalese Himalaya[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1996, 108(7): 904-911. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1996)108<0904:ICOTAA>2.3.CO;2
Decelles P G, Gehrels G E, Quade J, et al. Tectonic implications of U-Pb zircon ages of the himalayan orogenic belt in nepal[J]. Science, 2000, 288(5465): 497-499. doi: 10.1126/science.288.5465.497
Miller C, Thöni M, Frank W, et al. The early Palaeozoic magmatic event in the Northwest, Himalaya, India: source, tectonic setting and age of, emplacement[J]. Geological Magazine, 2001, 138(3): 237-251. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/240464282_The_early_Palaeozoic_magmatic_event_in_the_Northwest_Himalaya_India_Source_tectonic_setting_and_age_of_emplacement
Meert J G. A synopsis of events related to the assembly of eastern Gondwana[J]. Tectonophysics, 2003, 362(1/4): 1-40. http://www.academia.edu/705376/A_synopsis_of_events_related_to_the_assembly_of_eastern_Gondwana
Cawood P A. Terra Australis Orogen: Rodinia breakup and development of the Pacific and Iapetus margins of Gondwana during the Neoproterozoic and Paleozoic[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2005, 69 (3/4): 249-279. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222512827_Terra_Australis_Orogen_Rodinia_breakup_and_development_of_the_Pacific_and_Iapetus_margins_of_Gondwana_during_the_Neoproterozoic_and_Paleozoic
Cawood P A, Johnson M R W, Nemchin A A. Early Palaeozoic orogenesis along the Indian margin of Gondwana: Tectonic response to Gondwana assembly[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 255(1): 70-84. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/223886945_Early_Palaeozoic_orogenesis_along_the_Indian_margin_of_Gondwana_Tectonic_response_to_Gondwana_assembly
Kumar R, Shah A N, Bingham D K. Positive evidence of a Precambrian tectonic phase in central Nepal, Himalaya[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 1978, 19: 519-522. http://www.geosocindia.org/index.php/jgsi/article/view/64357
Garzanti E, Casnedi R, Jadoul F. Sedimentary evidence of a Cambro-Ordovician orogenic event in the northwestern Himalaya[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1986, 48(3/4): 237-265. http://www.academia.edu/11018138/Sedimentary_evidence_of_a_Cambro-Ordovician_orogenic_event_in_the_northwestern_Himalaya
Hodges K V, Parrish R R, Searle M P. Tectonic evolution of the central Annapurna Range, Nepalese Himalayas[J]. Tectonics, 1996, 15(6): 1264-1291. doi: 10.1029/96TC01791
Jeffrey L, Hacker B R, Dinklage W S, et al. Evolution of the Kangmar Dome, southern Tibet: Structural, petrologic, and thermochronologic constraints[J]. Tectonics, 2000, 19(5): 872-895. doi: 10.1029/1999TC001147
Marquer D, Chawla H S, Challandes N. Pre-Alpine High grade metamorphism in High Himalaya Crystalline Sequences: Evidences from Lower Palaeozoic Kinnar Kailas granite and surrounding rocks in the Sutlej Valley (Himachal pradesch, India)[J]. Eclogae Geologicae Helvetiae, 2000, 93: 207-220. http://file.scirp.org/Html/7009.html
许志琴, 杨经绥, 梁凤华, 等.喜马拉雅地体的泛非—早古生代造山事件年龄记录[J].岩石学报, 2005, 21(1): 1-12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200501001.htm 张泽明, 王金丽, 沈昆, 等.环东冈瓦纳大陆周缘的古生代造山作用:东喜马拉雅构造结南迎巴瓦岩群的岩石学和年代学证据[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(7): 1627-1637. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200807020.htm Baig M S, Lawrence R D, Snee L W. Evidence for late Precambrian to early Cambrian orogeny in northwest Himalaya, Pakistan. Geological Magazine, 1988, 125: 83-86. doi: 10.1017/S0016756800009390
Gaetani M, Garzanti E. Multicyclic History of the Northern India Continental Margin (Northwestern Himalaya) (1)[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1991, 75(9): 1427-1446. http://archives.datapages.com/data/bulletns/1990-91/data/pg/0075/0009/0000/1427.htm?q=%2BtextStrip%3Aphanerozoic+textStrip%3Atethys+textStrip%3Aregion
Meert J G, Voo R V D. The assembly of Gondwana 800-550Ma[J]. Journal of Geodynamics, 1997, 23(3): 223-235. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264370796000464
Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, Niu Y, et al. Cambrian bimodal volcanism in the Lhasa Terrane, southern Tibet: Record of an early Paleozoic Andean-type magmatic arc in the Australian proto-Tethyan margin[J]. Chemical Geology, 2012, 328(11): 290-308. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254112000034
Wang X, Zhang J, Santosh M, et al. Andean-type orogeny in the Himalayas of south Tibet: Implications for early Paleozoic tectonics along the Indian margin of Gondwana[J]. Lithos, 2012, 154(4): 248-262. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S002449371200285X
李才, 吴彦旺, 王明, 等.青藏高原泛非—早古生代造山事件研究重大进展——冈底斯地区寒武系和泛非造山不整合的发现[J].地质通报, 2010, 29(12): 1733-1736. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.12.001 计文化, 陈守建, 赵振明, 等.西藏冈底斯构造带申扎带寒武系火山岩的发现及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2009, 28(9): 1350-1354. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200909028.htm 宋述光, 季建清, 魏春景, 等.滇西北怒江早古生代片麻状花岗岩的确定及其构造意义[J].科学通报, 2007, 52(8): 927-930. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200708012.htm 丛峰, 林仕良, 李再会, 等.滇西腾冲地块片麻状花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年龄[J].地质学报, 2009, 83(5): 651-658. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200905006.htm Chen F, Li X H, Wang X L, et al. Zircon age and Nd-Hf isotopic composition of the Yunnan Tethyan belt, southwestern China[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2007, 96(6): 1179-1194. doi: 10.1007/s00531-006-0146-y
Liu S, Hu R Z, Gao S, et al. U-Pb zircon, geochemical and SrNd-Hf isotopic constraints on the age and origin of Early Palaeozoic I-type granite from the Tengchong-Baoshan Block, Western Yunnan Province, SW China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2008, 36: 168-182. https://www.deepdyve.com/lp/elsevier/u-pb-zircon-geochemical-and-sr-nd-hf-isotopic-constraints-on-the-age-2MjFkmg01W
刘琦胜, 叶培盛, 吴中海.滇西高黎贡山南段奥陶纪花岗岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb测年和地球化学特征[J].地质通报, 2012, 31(2/3): 250-257. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2012Z1006.htm 董美玲, 董国臣, 莫宣学, 等.滇西保山地块早古生代花岗岩类的年代学、地球化学及意义[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(5): 1453-1464. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201205011.htm 蔡志慧, 许志琴, 段向东, 等.青藏高原东南缘滇西早古生代早期造山事件[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29 (6): 2123-2140. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201306020.htm 莫宣学, 路凤香, 沈上越, 等.三江特提斯火山作用与成矿[M].北京:地质出版社, 1993: 178-235. Wu H, Boulter C A, Ke B, et al. The Changning-Menglian suture zone; a segment of the major Cathaysian-Gondwana divide in Southeast Asia[J]. Tectonophysics, 1995, 242(3/4): 267-280. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/004019519400210Z
钟大赉.滇川西部古特提斯造山带[M].北京:科学出版社, 1998: 231. Sone M, Metcalfe I. Parallel Tethyan sutures in mainland Southeast Asia: New insights for Palaeo-Tethys closure and implications for the Indosinian orogeny[J]. Comptes Rendus Geosciences, 2008, 340 (2/3): 166-179. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S163107130700260X
Metcalfe I. Tectonic framework and Phanerozoic evolution of Sundaland[J]. Gondwana Research, 2011, 19(1): 3-21. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2010.02.016
Morley C K. Nested strike-slip duplexes, and other evidence for Late Cretaceous-Palaeogene transpressional tectonics before and during India-Eurasia collision, in Thailand, Myanmar and Malaysia[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2004, 161(5): 799-812. doi: 10.1144/0016-764903-124
Metcalfe I. Gondwana dispersion and Asian accretion: Tectonic and palaeogeographic evolution of eastern Tethys[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 66: 1-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.12.020
Wang J H, Yin A, Harrison T M, et al. A tectonic model for Cenozoic igneous activities in the eastern Indo-Asian collision zone[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2001, 188(1/2): 123-133. http://www.citeulike.org/group/102/article/235734
Metcalfe I. Paleozoic and Mesozoic geological evolution of the SE Asian region: multidisciplinary constraints and implications for biogeography[C]//Hall R, Halloway J D. Biogeography and geological evolution of SE Asian, 1998: 25-41. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/267796868_Palaeozoic_and_Mesozoic_geological_evolution_of_the_SE_Asian_region_multidisciplinary_constraints_and_implications_for_biogeography
Ueno K. The Permian fusulinoidean faunas of the Sibumasu and Baoshan blocks: their implications for the paleogeographic and paleoclimatologic reconstruction of the Cimmerian Continent[J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 2003, 193(1): 1-24. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(02)00708-3
陈福坤, 李秋立, 王秀丽, 等.滇西地区腾冲地块东侧混合岩锆石年龄和Sr-Nd-Hf同位素组成[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(2): 439-448. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-DZDQ200702001040.htm 侯可军, 李延河, 田有荣. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石微区原位UPb定年技术[J].矿床地质, 2009, 28(4): 481-492. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200904009.htm Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51(1/2): 537-571. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Keqing_Zong2/publication/268411794_Continental_and_Oceanic_Crust_Recycling-induced_MeltPeridotite_Interactions_in_the_Trans-North_China_Orogen_UPb_Dating_Hf_Isotopes_and_Trace_Elements_in_Zircons_from_Mantle_Xenoliths/links/551434ad0cf2eda0df306881.pdf
濮巍, 高剑峰, 赵葵东, 等.利用DCTA和HIBA快速有效分离Rb-Sr、Sm-Nd的方法[J].地球学报, 2005, 41(s1): 54-54. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGKD200510002020.htm Schilling J G, Thompson G, Kingsley R, et al. Hotspot-migrating ridge interaction in the South Atlantic[J]. Nature, 1985, 313(313): 187-191. http://www.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1985Natur.313..187S
Condie K C. Geochemical changes in baslts and andesites across the Archean-Proterozoic boundary: Identification and significance[J]. Lithos, 1989, 23(1/2): 1-18. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/223658712_Geochemical_changes_in_baslts_and_andesites_across_the_Archean-Proterozoic_boundary_Identification_and_significance
Melson W G, Vallier T L, Wright T L, et al. Chemical Diversity of Abyssal Volcanic Glass Erupted Along Pacific, Atlandtic, and Indian Ocean Sea-Floor Spreading Centers. Chapter 30 in Geophysics of the Pacific Ocean Basin and Its Margin[J]. Geophysical Monograph, 1976, (19): 351-368. http://www.bcin.ca/Interface/openbcin.cgi?submit=submit&Chinkey=29510
Sun S S, Mcdonough W F. Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts: Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Barnes S J, Naldrett A J, Gorton M P. The origin of the fractionation of platinum-group elements in terrestrial magmas[J]. Chemical Geology, 1985, 53(85): 303-323. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/223494290_The_origin_of_the_fractionation_of_Platinum-Group_elements_in_terrestrial_magmas
Pearce J A, Cann J R. Tectonic Setting of Basic Volcanic Rocks determined using Trace Element Analyses[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1973, 19(2): 290-300. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(73)90129-5
Winchester J A, Floyd P A. Geochemical magma type discrimination: application to altered and metamorphosed basic igneous rocks[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1976, 28(3): 459-469. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(76)90207-7
Meschede M. A method of discriminating between different types of mid-ocean ridge basalts and continental tholeiites with the NbZr-Y diagram[J]. Chemical Geology, 1986, 56(3): 207-218. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222365828_A_method_of_discriminating_between_different_types_of_Mid-Ocean_Ridge_Basalts_and_continental_tholeiites_with_the_Nb-Zr-Y_diagram
Wood D A. The application of a Th, Hf, Ta diagram to problems of tectonomagmatic classification and to establishing the nature of crustal contamination of basaltic lavas of the British Tertiary Volcanic Province[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 1980, 50(1): 11-30. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222024988_The_application_of_a_Th-Hf-Ta_diagram_to_problems_of_tectonomagmatic_classification_and_to_establishing_the_nature_of_crustal_contamination_of_basaltic_lavas_of_the_British_Tertiary_Volcanic_Province
Pearce J A. Trace element characteristics of lavas from destructive plate boundaries[C]//Thorpe R S. Andesites. Wiley, New York, 1982: 528-548. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10003358278
Pearce J A. Role of the sub-continental lithosphere in magma genesis at active continental margins[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1983, 147(6): 2162-2173. http://orca.cf.ac.uk/8626/
Agrawal S, Guevara M, Verma S P. Tectonic discrimination of basic and ultrabasic volcanic rocks through log-transformed ratios of immobile trace elements[J]. International Geology Review, 2008, 50(12): 1057-1079. doi: 10.2747/0020-6814.50.12.1057
Sisson V B, Poole A R, Harris N R, et al. Geochemical and geochronologic constraints for genesis of a tonalite-trondhjemite suite and associated mafic intrusive rocks in the eastern Chugach Mountains, Alaska: A record of ridge-transform subduction[J]. Geological Society of America, 2003, 10(11): 861-72. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/230983071_Geochemical_and_geochronologic_constraints_for_genesis_of_a_tonalite-_trondhjemite_suite_and_associated_mafi_c_intrusive_rocks_in_the_eastern_Chugach_Mountains_Alaska_A_record_of_ridge-transform_subdu
Cole R B, Nelson S W, Layer P W, et al. Eocene volcanism above a depleted mantle slab window in southern Alaska[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2006, 118(1): 140-158. http://bulletin.geoscienceworld.org/content/118/1-2/140
Zindler A, Hart S. Chemical Geodynamics[J]. Annual Review of Earth & Planetary Sciences, 2003, 14(1): 493-571. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0040195182901251
Niu Y, Batiza R. Trace element evidence from seamounts for recycled oceanic crust in the Eastern Pacific mantle[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1997, 148(3/4): 471-483. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.524.6636
Donnelly K E, Goldstein S L, Langmuir C H, et al. Origin of enriched ocean ridge basalts and implications for mantle dynamics[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 226(3/4): 347-366. http://www.ldeo.columbia.edu/node/10920
Hawkins J W. Geology of supra-subduction zones-Implications for the origin of ophiolites[J]. Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, 2003, 373: 227-268. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279974250_Geology_of_supra-subduction_zones-Implications_for_the_origin_of_ophiolites
杨学俊, 贾小川, 熊昌利, 等.滇西高黎贡山南段公养河群变质基性火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2012, 31(2/3): 264-276. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2012Z1008.htm 毛晓长, 尹福光, 唐渊, 等.保山地块西缘早古生代增生造山作用[J].地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 2014, 39 (8): 1129-1139. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201408014.htm Frey F A, Green D H, Roy S D. Integrated Models of Basalt Petrogenesis: A Study of Quartz Tholeiites to Olivine Melilitites from South Eastern Australia Utilizing Geochemical and Experimental Petrological Data[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1978, 19(3): 463-513. doi: 10.1093/petrology/19.3.463
Takazawa E, Frey F A, Shimizu N, et al. Geochemical evidence for melt migration and reaction in the upper mantle[J]. Nature, 1992, 359(6390): 55-58. doi: 10.1038/359055a0
Maury R C, Fourcade S, Coulon C, et al. Post-collisional Neogene magmatism of the Mediterranean Maghreb margin: a consequence ofslab breakoff[J]. Comptes Rendus de l'Academie des Sciences Series IIA Earth and Planetary Science, 2000, 331(3): 159-173. http://www.academia.edu/25042718/Post-collisional_Neogene_magmatism_of_the_Mediterranean_Maghreb_margin_a_consequence_of_slab_breakoff
Ayuso R A, Haeussler P J, Bradley D C, et al. The role of ridge subduction in determining the geochemistry and Nd-Sr-Pb isotopic evolution of the Kodiak batholith in southern Alaska[J]. Tectonophysics, 2009, 464(1/4): 137-163. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228899760_The_role_of_ridge_subduction_in_determining_the_geochemistry_and_Nd-Sr-Pb_isotopic_evolution_of_the_Kodiak_batholith_in_southern_Alaska
Cole R B, Stewart B W. Continental margin volcanism at sites of spreading ridge subduction: Examples from southern Alaska and western California[J]. Tectonics, 2009, 464 (1/4): 118-136. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222903554_Continental_margin_volcanism_at_sites_of_spreading_ridge_subduction_Examples_from_southern_Alaska_and_western_California
黄勇, 郝家栩, 白龙, 等.滇西施甸地区晚泛非运动的地层学和岩石学响应[J].地质通报, 2012, 26 (1): 1-6. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2012Z1012.htm Decelles P G, Gehrels G E, Quade J, et al. Neogene foreland basin deposits, erosional unroofing, and the kinematic history of the Himalayan fold-thrust belt, western Nepal[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1998, 110(1): 2-21. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1998)110<0002:NFBDEU>2.3.CO;2
Laurent G, Parrish R R, Brown R L, et al. Crustal thickening leading to exhumation of the Himalayan Metamorphic core of central Nepal: Insight from U-Pb Geochronology and 40Ar/39Ar Thermochronology[J]. Tectonics, 2001, 20(5): 729-747. doi: 10.1029/2000TC001204
刘文灿, 梁定益, 王克友, 等.藏南康马地区奥陶系的发现及其地质意义[J].地学前缘, 2002, 31(2/3): 306-313. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200204004.htm Gehrels G E, Decelles P G, Ojha T P, et al. Geologic and U-ThPb geochronologic evidence for early Paleozoic tectonism in the Kathmandu thrust sheet, central Nepal Himalaya[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2006, 118(1/2): 185-198. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/249527353_Geologic_and_U-Th-Pb_geochronologic_evidence_for_Early_Paleozoic_tectonism_in_the_Kathmandu_thrust_sheet_central_Nepal_Himalaya
Gehrels G, Kapp P, Decelles P, et al. Detrital zircon geochronology of pre-Tertiary strata in the Tibetan-Himalayan orogen[J]. Tectonics, 2011, 30: 1-27. doi: 10.1029/2011TC002868/full
李才, 董永胜, 翟庆国, 等.青藏高原羌塘早古生代蛇绿岩-堆晶辉长岩的锆石SHRIMP定年及其意义[J].岩石学报, 2008, 4(1): 31-36. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200801003.htm 戚学祥, 李化启, 李天福, 等.东喜马拉雅构造结南迦巴瓦群高压麻粒岩中含石榴石花岗岩脉锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其与折返作用[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(3):975-984. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201003026.htm 胡培远, 李才, 苏犁, 等.青藏高原羌塘中部蜈蚣山花岗片麻岩锆石U-Pb定年——泛非与印支事件的年代学记录[J].中国地质, 2010, 37(4): 1050-1061. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201004021.htm Pullen A, Kapp P, Gehrels G E, et al. Metamorphic rocks in central Tibet: Lateral variations and implications for crustal structure[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2011, 123(3/4): 585-600. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/234118475_Metamorphic_rocks_in_central_Tibet_Lateral_variations_and_implications_for_crustal_structure
Guynn J, Kapp P, Gehrels G E, et al. U-Pb geochronology of basement rocks in central Tibet and paleogeographic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 43(1): 23-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.09.003
Gehrels G E, Decelles P G, Martin A, et al. Initiation of the Himalayan Orogen as an Early Paleozoic Thin-skinned Thrust Belt[J]. GSA Today, 2003, 13(9): 75-85. https://arizona.pure.elsevier.com/en/publications/initiation-of-the-himalayan-orogen-as-an-early-paleozoic-thin-ski
Boger S D, Wilson C J L, Fanning C M. Early Paleozoic tectonism within the East Antarctic craton: The final suture between east and west Gondwana?[J]. Geology, 2001, 29(5): 463-466. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0463:EPTWTE>2.0.CO;2
云南地质调查局. 1: 25万潞西市幅区域地质报告. 2008.



 下载:
下载: