Compositional variation of Cenozoic detritus in the Lulehe area, Qaidam Basin, and its implications for Tibetan Plateau tectonic uplift
-
摘要:
碎屑组分变化是反映盆地物源演化历程的重要物质表现。路乐河地区作为柴达木盆地的重要组成部分,沉积地层记载着印度-欧亚板块碰撞以来青藏高原北缘造山带的构造隆升过程。高长石组分含量、物源方向及毗邻山脉岩性对比揭示,路乐河物源主要受南祁连和赛什腾山控制,其碎屑组分变化对毗邻造山带构造活动具有很好的耦合性。新生代53.5~2.9 Ma期间,路乐河地区存在3次物源转换事件,发生时间依次同印度-欧亚板块碰撞及高原内部构造隆升事件相吻合。其中早期50.1~46.6 Ma,南祁连山的快速抬升是对大陆初始碰撞的远程响应;44.5 Ma,高原以垂向增生和推覆构造发育为特点,赛北断裂高速剥露,致使路乐河地区物源发生转变;渐新世末期(22.6 Ma),青藏高原准同时整体隆升,赛什腾山和南祁连山协同为路乐河地区供给沉积物。所获认识为深入了解高原隆升演化和板块碰撞远程效应提供新的沉积依据。
Abstract:The change of detrital composition is a typical manifestation of the evolutionary process of sedimentary sources.As an im-portant part of the Qaidam Basin, the sedimentary strata in Lulehe have recorded tectonic uplift evolution of northern Tibetan since the Indo-Asian collision.All signatures, along with high feldspar content, provenance and contrast with adjacent mountain rocks, re-veal that the source region for Lulehe mainly came from Qilian and Saibei thrust.And there existed a coupling relationship between the change of clastic composition content and surrounding orogen.Three significant depositing transformation events occurred in Lu-lehe area, corresponding to the Indo-Asian collision and plateau tectonic uplift from Cenozoic in 53.5~2.9 Ma.The rapid uplift of southern Qilian, which happened at ca.50.1~46.6 Ma, responded to the propagation of initial continental collision.The uplift of Ti-betan Plateau with crustal vertical growth and thrust structure caused top erosion of Saibei thrust and provenance transformation event in Lulehe in Eocene (44.5 Ma).Both of Saishiteng and Qilian Mountain supplied sediments at the end of Oligocene (22.6 Ma) when different regions in plateau were raised synchronously.The findings will provide new crucial sedimentary data for deep under-standing of evolutionary history of whole Tibetan Plateau and distant effect of the continental collision.
-
Keywords:
- Lulehe /
- detrital composition /
- provenance transformation /
- tectonic uplift
-
致谢: 参加野外和室内工作的有成都理工大学马雪、李盛俊、杜秋定等,审稿专家提出了建设性的意见,在此一并表示衷心的感谢。
-
图版Ⅰ
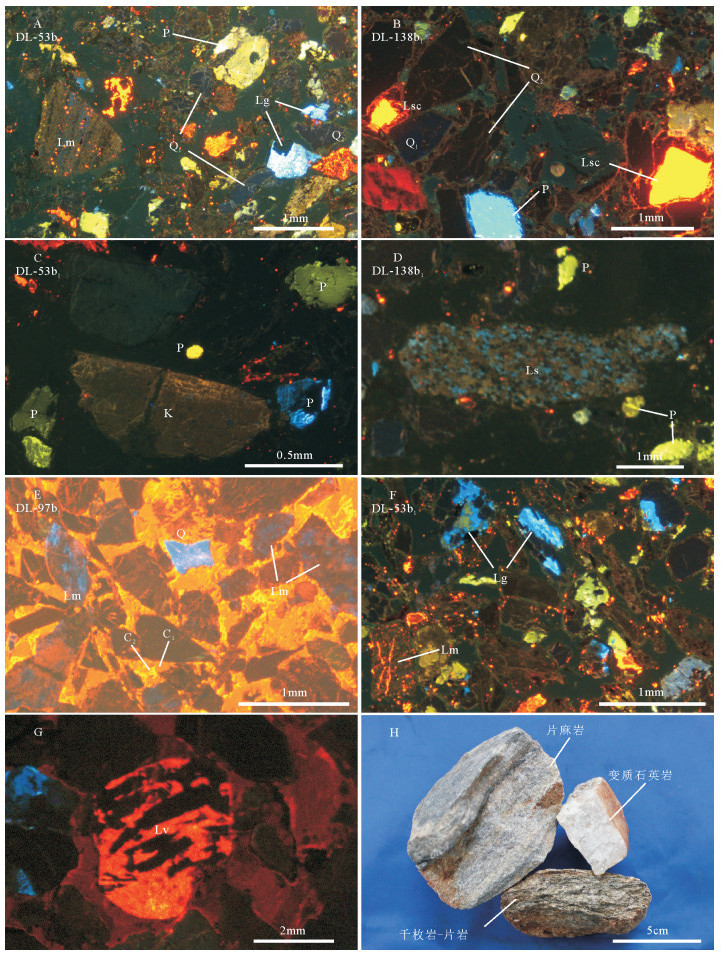
A.岩浆型石英(Q1)、变质型石英(Q2)阴极发光特征;B.碳酸盐岩(Lsc)阴极发光特征;C.不同类型长石(K为微斜长石,P为长石)阴极发光特征;D.泥岩(Ls)阴极发光特征;E.变质石英岩(Lm)及碳酸盐胶结世代(C1、2)阴极发光特征;F.千枚岩-片岩(Lm)、花岗岩(Lg)阴极发光特征;G.喷出岩(Lv)阴极发光特征(图片据参考文献[36]);H.路乐河砂岩砾石组分特征
图版Ⅰ.
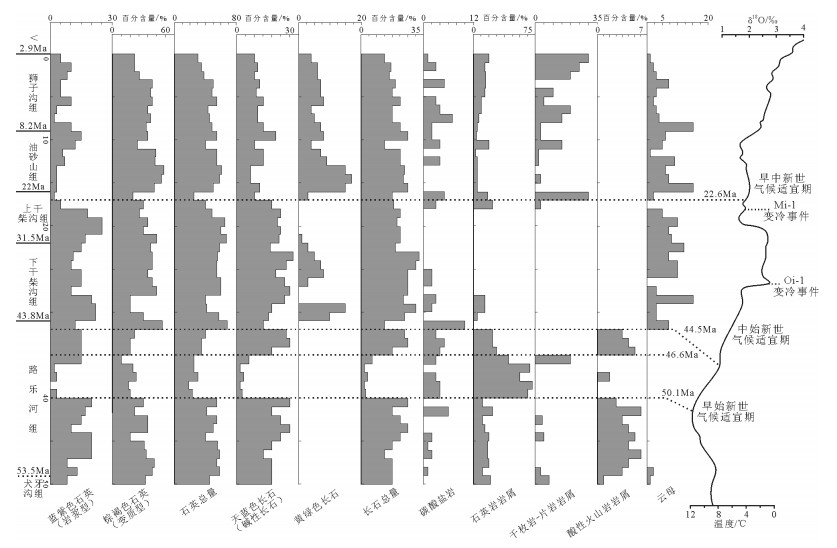
图 2 路乐河地区物源转换事件与全球气候变化图(δ18O据参考文献[40])
Figure 2. Transformation events in Lulehe and global climatic changes during the Cenezoic period
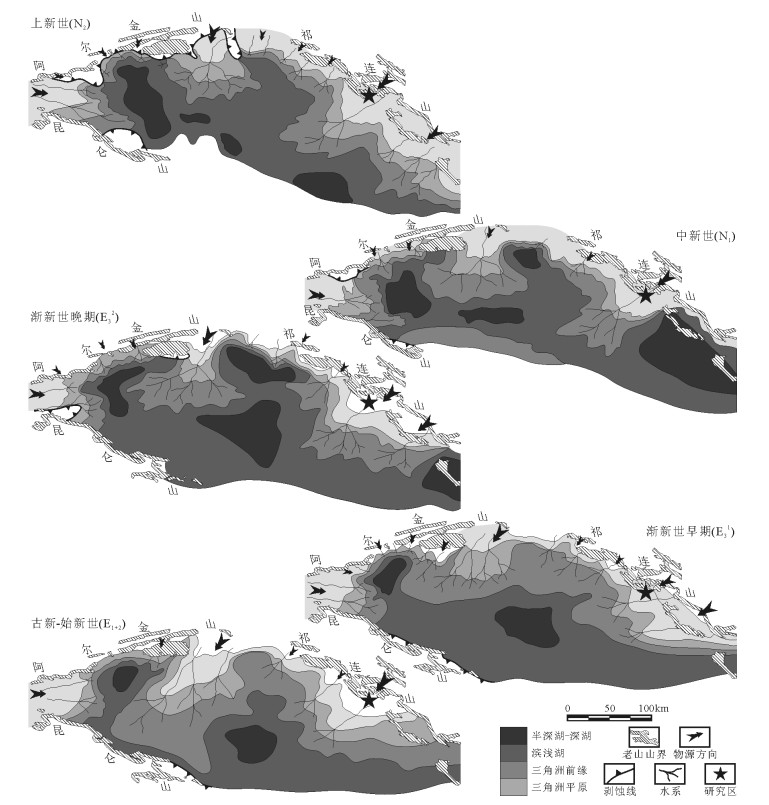
图 3 柴达木盆地新生代物源及古水流变化②
Figure 3. The change of provenance and paleocurrent in Qaidam basin during the Cenozoic period
-
Fang X, Zhang W, Meng Q, et al. High-resolution magnetostratig-raphy of the Neogene Huaitoutala section in the eastern Qaidam Ba-sin on the NE Tibetan Plateau, Qinghai Province, China and its im-plication on tectonic uplift of the NE Tibetan Plateau[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 258(1):293-306.
Yin A, Dang Y Q, Zhang M, et al. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Qaidam basin and its surrounding regions (Part 3):Structural ge-ology, sedimentation, and regional tectonic reconstruction[J]. Geo-logical Society of America Bulletin, 2008, 120(7/8):847-876.
Wang J, Wang Y J, Liu Z C, et al. Cenozoic environmental evolu-tion of the Qaidam Basin and its implications for the uplift of the Ti-betan Plateau and the drying of central Asia[J]. Palaeogeography, Pal-aeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1999, 152(1):37-47. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/301791261_Late_Cenozoic_pollen_concentration_in_the_western_Qaidam_Basin_northern_Tibetan_Plateau_and_its_significance_for_paleoclimate_and_tectonics
Zheng H B, Powell M C, An Z S, et al. Pliocene uplift of the north-ern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geology, 2000, 28(8):715-718. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<715:PUOTNT>2.0.CO;2
陈正乐, 宫红良, 李丽, 等.阿尔金山脉新生代隆升-剥露过程[J].地学前缘, 2006, 13(4):91-102. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200604007.htm Harrison T M, Copeland P, Kidd W S F, et al. Raising Tibet[J]. Sci-ence, 1992, 255(5052):1663-1670. doi: 10.1126/science.255.5052.1663
Yin A, Harrison T M. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibet-an orogen[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2000, 28(1):211-280. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.211
Royden L H, Burchfiel B C, van der Hilst R D. The geological evo-lution of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science, 2008, 321(5892):1054-1058. doi: 10.1126/science.1155371
尹安, 党玉琪, 陈宣华, 等.柴达木盆地新生代演化及其构造重建——基于地震剖而的解释[J].地质力学学报, 2007, 13(3):193-211. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX200703000.htm Yin A, Dang Y Q, Wang L C, et al. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of Qaidam basin and its surrounding regions (Part 1):The southern Qilian Shan-Nan Shan thrust belt and northern Qaidam basin[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2008, 120(7/8):813-846.
Cowgill E, Yin A, Feng W X, et al. Is the North Altyn fault part of a strike-slip duplex along the Altyn Tagh fault system?[J]. Geology, 2000, 28(3):255-258. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<255:ITNAFP>2.0.CO;2
Yin A, Rumelhart P E, Butler R, et al. Tectonic history of the Al-tyn Tagh fault system in northern Tibet inferred from Cenozoic sedimentation[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2002, 114(10):1257-1295. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(2002)114<1257:THOTAT>2.0.CO;2
Zhang K X, Wang G C, Cao K, et al. Cenozoic sedimentary re-cords and geochronological constraints of differential uplift of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Science in China Series D, 2008, 51(11):1658-1672. doi: 10.1007/s11430-008-0132-2
刘云田. 柴西第三系构造沉积演化与油气成藏[D]. 广州地球化学研究所博士学位论文, 2002: 7-14. 王成善, 戴紧根, 刘志飞, 等.西藏高原与喜马拉雅的隆升历史和研究方法:回顾与进展[J].地学前缘, 2009, 16(3):1-30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200903003.htm 张克信, 王国灿, 洪汉烈, 等.青藏高原新生代隆升研究现状[J].地质通报, 2013, 32(1):1-18. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20130101&journal_id=gbc 王二七.青藏高原大地构造演化——主要构造-热事件的制约及其成因探讨[J].地质科学, 2013, 48(2):334-353. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX201302004.htm 宋春晖. 青藏高原北缘新生代沉积演化与高原构造隆升过程[D]. 兰州大学博士学位论文, 2006: 113-126. 青海省地质矿产局.青海省区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社, 1991. 新疆维吾尔自治区地质矿产局.新疆维吾尔自治区区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社, 1993. Pagel M, Barbin V, Blanc P, et al. Cathodoluminescence in Geosci-ences[M]. Berlin:Springer Verlag, 2000:1-21.
Habermann D, Götze J, Neuser R D, et al. The phenomenon of in-trinsic cathodoluminescence:Case studies of quartz, calcite and apa-tite[J]. Zentralblatt für Geologie und Paläontologie Teil, 1999, 12:1275-1284.
Boggs S, Krinsley D H. Application of cathodoluminescence imag-ing to the study of sedimentary rocks[M]. Cambridge:Cambridge University Press, 2006:12-16.
Sippel R F. Sandstone petrology, evidence from luminescence pe-trography[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1968, 38(2):530-554. http://jsedres.geoscienceworld.org/content/38/2/530
Zinkernagel U. Cathodoluminescence of quartz and its application to sandstone petrology[M]. Stuttgart:Schweizerbart' sche Verlags-buchhandlung, 1978:1-69.
Götze J, Zimmerle W. Quartz and silica as guide to provenance in sediments and sedimentary rocks[M]. Stuttgart:Schweizerbart' sche Verlagsbuchhandlung, 2000:1-91.
Götze J, Plötze M, Habermann D. Origin, spectral characteristics and practical applications of the cathodoluminescence(CL) of quartz-a review[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2001, 71(3/4):225-250. doi: 10.1007/s007100170040
Richter D K, Götte T, Götze J, et al. Progress in application of cathodoluminescence (CL) in sedimentary petrology[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2003, 79(3/4):127-166. doi: 10.1007/s00710-003-0237-4
Götze J. Application of cathodoluminescence microscopy and spec-troscopy in geosciences[J]. Microscopy and Microanalysis, 2012, 18(6):1270-1284. doi: 10.1017/S1431927612001122
Matter A, Ramseyer K. Cathodoluminescence microscopy as a tool for provenance studies of sandstones[J]//Provenance of arenites. Springer Netherlands, 1985, 148:191-211.
Boggs S, Kwon Y I, Goles G G, et al. Is quartz cathodoluminescence color a reliable provenance tool? A quantitative examination[J]. Jour-nal of Sedimentary Research, 2002, 72(3):408-415. doi: 10.1306/102501720408
Smith J V, Stenstrom R C. Electron-excited luminescence as a pet-rologic tool[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1965, 73(4):627-635. doi: 10.1086/627098
Nickel E. Present status of cathode luminescence as a tool in sedi-mentology[J]. Minerals Science and Engineering, 1978, 10(2):73-100. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/286974421_PRESENT_STATUS_OF_CATHODE_LUMINESCENCE_AS_A_TOOL_IN_SEDIMENTOLOGY
Ingersoll R V. Actualistic sandstone petrofacies:discriminating mod-ern and ancient source rocks[J]. Geology, 1990, 18(8):733-736. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1990)018<0733:ASPDMA>2.3.CO;2
付玲, 关平, 赵为永, 等.柴达木盆地古近系路乐河组重矿物特征与物源分析[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(8):2867-2875. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201308022.htm 夏国清. 柴达木盆地西南缘新生代构造隆升的沉积记录[D]. 成都理工大学博士学位论文, 2012: 53. 邵磊, Stattegger K, 李文厚.从砂岩地球化学探讨盆地构造背景[J].科学通报, 1998, 43(9):985-988. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199809020.htm Armstrong F C, Oriel S S. Tectonic development of Idaho-Wyo-ming thrust belt[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1965, 49(11):1847-1866. http://aapgbull.geoscienceworld.org/content/49/11/1847
伊海生, 王成善.构造事件的沉积响应-建立青藏高原大陆碰撞、隆升过程时空坐标的设想和方法[J].沉积与特提斯地质, 2001, 21(2):1-15. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD200102000.htm Zachos J, Pagani M, Sloan L, et al. Trends, rhythms, and aberra-tions in global climate 65 Ma to present[J]. Science, 2001, 292(5517):686-693. doi: 10.1126/science.1059412
黄文杰, 汤懋苍.青藏高原隆升和夷平过程的数值模型研究[J].中国科学(D辑), 1997, 27(1):65-69. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199701010.htm Rust B R. Pebble orientation in fluvial sediments[J]. Journal of Sed-imentary Petrology, 1972, 42(2):384-388 doi: 10.1306/74d7255e-2b21-11d7-8648000102c1865d
马雪, 伊海生, 夏国清.柴达木盆地西部新生代砂岩碎屑组分变化记录的沉积转型事件[J].地质通报, 2010, 29(9):1294-1303. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20100905&journal_id=gbc 惠博, 伊海生, 夏国清, 等.柴达木盆地西部新生代沉积演化特征[J].中国地质, 2011, 38(5):1274-1281. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201105015.htm 曾允孚, 夏文杰.沉积岩石学[M].北京:地质出版社, 1986:116-117. 刘化清, 李相博, 完颜容, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地长8油层组古地理环境与沉积特征[J].沉积学报, 2011, 29(6):1086-1095. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201106009.htm Raymo M E, Ruddiman W F. Tectonic forcing of late Cenozoic climate[J]. Nature, 1992, 359(6391):117-122. doi: 10.1038/359117a0
Dupont-Nivet G, Krijgsman W, Langereis C G, et al. Tibetan pla-teau aridification linked to global cooling at the Eocene-Oligocene transition[J]. Nature, 2007, 445(7128):635-638. doi: 10.1038/nature05516
Duff P M. Holmes' principles of physical geology (4th edition)[M]. London:Chapman and Hall, 1993:1-73.
Lal D, Harris N B W, Sharma K K, et al. Erosion history of the Ti-betan Plateau since the last interglacial:constraints from the first studies of cosmogenic 10Be from Tibetan bedrock[J]. Earth and Plan-etary Science Letters, 2003, 217(1):33-42.
Kong P, Na C, Fink D, et al. Erosion in northwest Tibet from insitu-produced cosmogenic 10Be and 26Al in bedrock[J]. Earth Sur-face Processes and Landforms, 2007, 32(1):116-125. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1096-9837
Thiede R C, Ehlers T A, Bookhagen B, et al. Erosional variability along the northwest Himalaya[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2009, 114(F01015):1-19.
陈杰, Heermance R V, Burbank D W, 等.中国西南天山西域砾岩的磁性地层年代与地质意义[J].第四纪研究, 2007, 27(4):576-587. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200704013.htm 马钦忠, 李吉均.晚新生代青藏高原北缘构造变形和剥蚀变化及其与山脉隆升关系[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2003, 23(1):27-34. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200301005.htm Beck R A, Burbank D W, Sercombe W J, et al. Stratigraphic evi-dence for an early collision between northwest India and Asia[J]. Nature, 1995, 373(6509):55-58. doi: 10.1038/373055a0
Mo X, Niu Y, Dong G, et al. Contribution of syncollisional felsic magmatism to continental crust growth:a case study of the Paleo-gene Linzizong volcanic succession in southern Tibet[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 250(1):49-67.
丁林.西藏雅鲁藏布江缝合带古新世深水沉积和放射虫动物群的发现及对前陆盆地演化的制约[J].中国科学(D辑), 2003, 33(1):47-58. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200301005.htm Dewey J F, Cande S, Pitman W C. Tectonic evolution of the In-dia/Eurasia collision zone[J]. Eclogae Geologicae Helvetiae, 1989, 82(3):717-734.
戴霜, 方小敏, 宋春晖, 等.青藏高原北部的早期隆升[J].科学通报, 2005, 50(7):673-683. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200507011.htm 刘栋梁, 方小敏, 王亚东, 等.平衡剖面方法恢复柴达木盆地新生代地层缩短及其意义[J].地质科学, 2008, 43(4):637-647. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX200804001.htm 许志琴, 杨经绥, 李海兵, 等.印度-亚洲碰撞大地构造[J].地质学报, 2011, 85(1):1-33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201101001.htm Jolivet M, Brunel M, Seward D, et al. Mesozoic and Cenozoic tec-tonics of the northern edge of the Tibetan plateau:fission-track constraints[J]. Tectonophysics, 2001, 343(1):111-134.
张伟林. 柴达木盆地新生代高精度磁性地层与青藏高原隆升[D]. 兰州大学博士学位论文, 2006: 95-105. 梁涛, 罗照华, 李文韬, 等.托云火山群的火山地质特征及其构造意义[J].新疆地质, 2005, 23(2):105-110. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI200502002.htm 梁涛, 罗照华, 柯珊, 等.新疆托云火山群SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年代学及其动力学意义[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(6):1381-1391. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200706013.htm 李永安, 李强, 张慧, 等.塔里木盆地及其周边古地磁研究与盆地演化形成[J].新疆地质, 1995, 13(4):341-344. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-85402-1012006241.htm 钟大赉, 丁林.青藏高原的隆起过程及其机制探讨[J].中国科学, (D辑), 1996, 26(4):289-295. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199604000.htm 罗照华, 莫宣学, 侯增谦, 等.青藏高原新生代形成演化的整合模型-来自火成岩的约束[J].地学前缘, 2006, 13(4):196-211. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200604020.htm 吴珍汉, 孟宪刚, 胡道功, 等.当雄县幅地质调查新成果及主要进展[J].地质通报, 2004, 23(5/6):484-491. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20040587&journal_id=gbc Chung S L, Lo C H, Lee T Y, et al. Diachronous uplift of the Ti-betan plateau starting 40Myr ago[J]. Nature, 1998, 394(6695):769-773. doi: 10.1038/29511
Wang J H, Yin A, Harrison T M, et al. A tectonic model for Ceno-zoic igneous activities in the eastern Indo-Asian collision zone[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2001, 188(1):123-133.
李佑国, 莫宣学, 伊海生, 等.羌塘错尼地区新生代火山岩研究[J].矿物岩石, 2005, 25(2):27-34. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS200502006.htm 李忠雄, 陈智梁.青藏高原东部贡觉盆地新生代火山岩特征及其构造意义[J].地球学报, 2006, (4):297-302. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200604002.htm 邓万明, 孙宏娟, 张玉泉.青海囊谦盆地新生代火山岩的K-Ar年龄[J].科学通报, 1999, 44(23):2554-2558. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1999.23.018 Mo X X, Hou Z Q, Niu Y L, et al. Mantle contributions to crustal thickening during continental collision:evidence from Cenozoic ig-neous rocks in southern Tibet[J]. Lithos, 2007, 96(1):225-242. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493706002933
Wang Q, Wyman D A, Xu J F, et al. Eocene melting of subduct-ing continental crust and early uplifting of central Tibet:evidence from central-western Qiangtang high-K calc-alkaline andesites, dacites and rhyolites[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 272(1/2):158-171.
Dupont-Nivet G, Butler R F, Yin A, et al. Paleomagnetism indi-cates no Neogene rotation of the Qaidam Basin in northern Tibet during Indo-Asian collision[J]. Geology, 2002, 30(3):263-266. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0263:PINNRO>2.0.CO;2
Chen Y, Gilder S, Halim N, et al. New paleomagnetic constraints on central Asian kinematics:Displacement along the Altyn Tagh fault and rotation of the Qaidam Basin[J]. Tectonics, 2002, 21(5):1-19.
Liu Z, Zhao X, Wang C, et al. Magnetostratigraphy of Tertiary sed-iments from the Hoh Xil Basin:implications for the Cenozoic tec-tonic history of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geophysical Journal Interna-tional, 2003, 154(2):233-252. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246X.2003.01986.x
George A D, Marshallsea S J, Wyrwoll K H, et al. Miocene cooling in the northern Qilian Shan, northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau, revealed by apatite fission-track and vitrinite-reflectance analysis[J]. Geology, 2001, 29(10):939-942. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0939:MCITNQ>2.0.CO;2
Wang F, Lo C H, Li Q, et al. Onset timing of significant unroofing around Qaidam basin, northern Tibet, China:constraints from 40Ar/39Ar and FT thermochronology on granitoids[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2004, 24(1):59-69. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2003.07.004
王修喜, 李吉均, 宋春晖, 等.青藏高原东北缘西秦岭新生代抬升:天水盆地碎屑颗粒磷灰石裂变径迹记录[J].沉积学报, 2006, 24(6):783-789. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200606001.htm 喻学惠, 莫宣学, Flower M, 等.甘肃西秦岭新生代钾霞橄黄长岩火山作用及其构造含义[J].岩石学报, 2001, 17(3):366-377. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200103003.htm 喻学惠, 赵志丹, 莫宣学, 等.甘肃西秦岭新生代钾霞橄黄长岩的40Ar/39Ar同位素定年及其地质意义[J].科学通报, 2005, 50(23):2638-2643. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2005.23.013 Arnaud N O, Vidal Ph, Tapponnier P, et al. The high-K2O vol-canism of northwestern Tibet:Geochemistry and tectonic implica-tions[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1992, 111(2/4):351-367.
Turner S, Hawkesworth C, Liu J, et al. Timing of Tibetan uplift constrained by analysis of volcanic rocks[J]. Nature, 1993, 364(6432):50-54. doi: 10.1038/364050a0
Turner S, Arnaud N, Liu J, et al. Post-collision, shoshonitic volca-nism on the Tibetan Plateau:implications for convective thinning of the lithosphere and the source of ocean island basalts[J]. Journal of petrology, 1996, 37(1):45-71. doi: 10.1093/petrology/37.1.45
赖绍聪.青藏高原新生代三阶段造山隆升模式:火成岩岩石学约束[J].矿物学报, 2000, 20(2):182-190. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB200002013.htm 刘栋, 赵志丹, 朱弟成, 等.青藏高原拉萨地块西部雄巴盆地后碰撞钾质-超钾质火山岩年代学与地球化学[J].岩石学报, 2011, 27(7):2045-2059. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201107014.htm Jolivet M, Brunel M, Seward D, et al. Neogene extension and vol-canism in the Kunlun fault zone, northern Tibet:New constraints on the age of the Kunlun fault[J]. Tectonics, 2003, 22(5):1052. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/J_Malavieille/publication/233919828_Neogene_extension_and_volcanism_in_the_Kunlun_Fault_Zone_northern_Tibet_New_constraints_on_the_age_of_the_Kunlun_Fult/links/00b49514991a52c1a7000000/Neogene-extension-and-volcanism-in-the-Kunlun-Fault-Zone-northern-Tibet-New-constraints-on-the-age-of-the-Kunlun-Fult.pdf
Sun J, Zhu R, An Z. Tectonic uplift in the northern Tibetan Pla-teau since 13.7 Ma ago inferred from molasse deposits along the Al-tyn Tagh Fault[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 235(3):641-653. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Jimin_Sun/publication/222819757_Tectonic_uplift_in_the_northern_Tibetan_Plateau_since_137_Ma_ago_inferred_from_molasse_deposits_along_the_Altyn_Tagh_Fault/links/0c9605229ea3290709000000.pdf?origin=publication_detail
方小敏, 宋春晖, 戴霜, 等.青藏高原东北部阶段性变形隆升:西宁、贵德盆地高精度磁性地层和盆地演化记录[J].地学前缘, 2007, 14(1):230-242. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200701024.htm Sobel E R, Dumitru T A. Thrusting and exhumation around the mar-gins of the western Tarim basin during the India-Asia collision[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1997, 102(B3):5043-5063. doi: 10.1029/96JB03267
潘裕生.青藏高原的形成与隆升[J].地学前缘, 1999, 6(3):153-163. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY199903020.htm Wang G C, Cao K, Zhang K X, et al. Spatio-temporal framework of tectonic uplift stages of the Tibetan Plateau in Cenozoic[J]. Sci-ence China Earth Sciences, 2011, 54(1):29-44. doi: 10.1007/s11430-010-4110-0
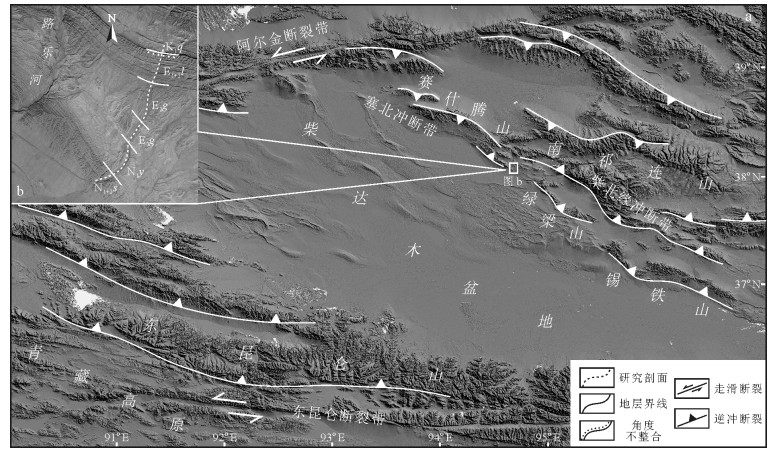
青海省地质局. 马海幅1: 20万区域地质调查报告. 1980. 中国石油勘探开发研究院. 柴达木盆地油气成藏主控因素及分布规律. 2009.




 下载:
下载: