LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of the Late Triassic-Early Jurassic granites in the eastern part of Qimantag area and its geological significance
-
摘要:
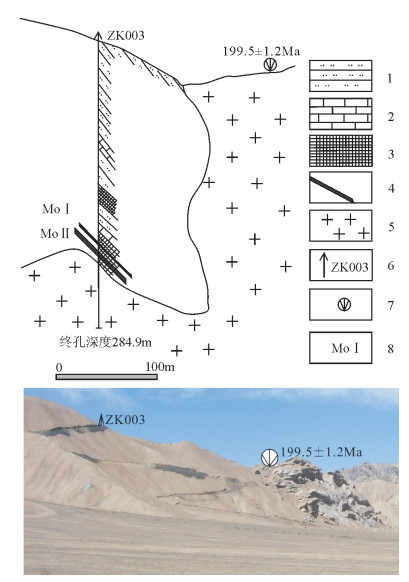
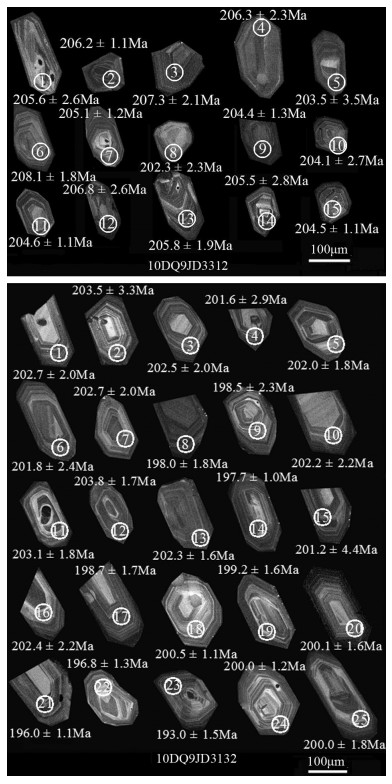
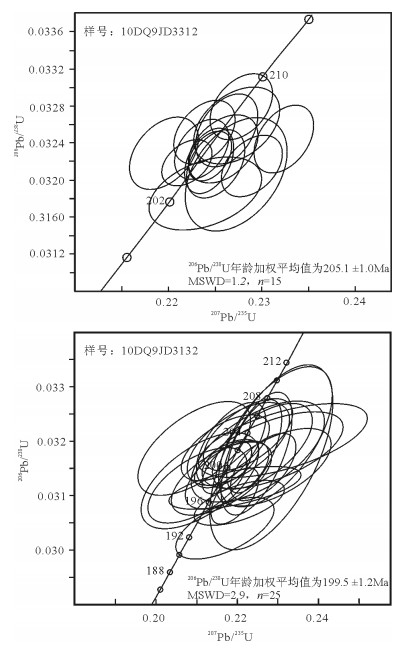
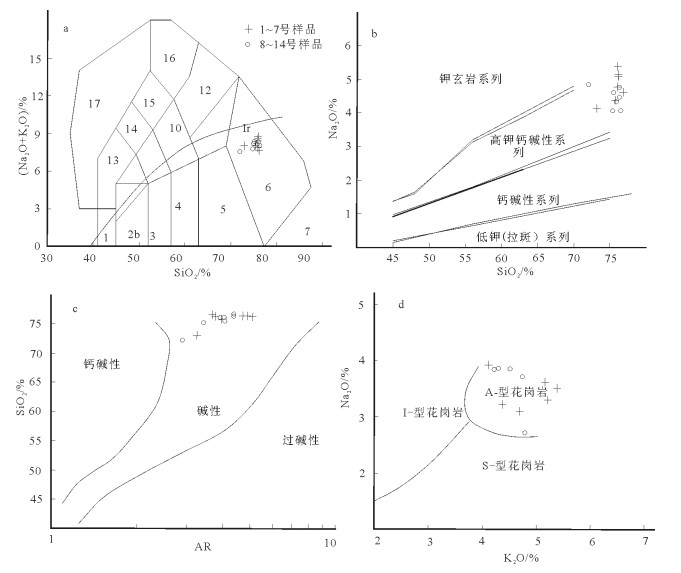
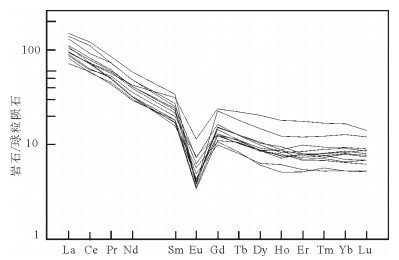
祁漫塔格东段拉陵高里河地区晚三叠世—早侏罗世花岗岩组合为高SiO(2 72.18%~76.55%)、高K2O(4.08%~5.32%)的碱性花岗岩组合,具有明显的负Eu异常(δEu平均值为0.28)。岩石组合为二长花岗岩+正长花岗岩,采用LA-ICP-MS技术测得二长花岗岩和正长花岗岩的年龄分别为205.1±1.0 Ma和199.5±1.2 Ma。该套花岗岩组合与拉陵高里河地区的矽卡岩型多金属矿关系密切,初步确定祁漫塔格地区晚三叠世—早侏罗世花岗岩组合也是一期重要的成矿岩浆建造。
-
关键词:
- 祁漫塔格 /
- 花岗岩 /
- 晚三叠世-早侏罗世 /
- LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄
Abstract:The Late Triassic-Early Jurassic granitic assemblage in the eastern part of Qimantag area has high SiO2 content (72.18%~76.55%), high K2O content (4.08%~5.32%) and obvious negative Eu anomaly (average σEu value being 0.28).The granitic assem-blage is composed of monzogranite and syenogranite, whose ages were precisely redefined by the LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb meth-od, being 205.1±1.0 Ma and 199.5±1.2 Ma respectively.This granitic assemblage has close relationship with skarn-type polymetallic deposits in Lalinggaoli area.Therefore, the authors preliminarily hold that the Late Triassic-Early Jurassic granitic assemblage is proba-bly an important ore-forming magmatic formation in the eastern part of Qimantag area.
-
Keywords:
- Qimantag /
- granite /
- Late Triassic-Early Jurassic /
- LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age
-
柴达木盆地为青藏高原北缘最大的山间盆地[1-2],随着高原的隆升,自新生代以来沉积了周缘造山带剥落的巨厚碎屑沉积物。长期以来,学者们对青藏高原的研究多围绕东部、南部和高原内部区域进行,关于其隆升历史的认识主要来自地层沉积速率变化和Ar-Ar定年、裂变径迹低温热年代学方法,对盆地尤其是柴达木盆地新生代沉积物与高原和毗邻山脉的制约关系涉及较少[3-5]。沉积物作为连接盆地和剥蚀源区的纽带,准确记录了印度和欧亚板块碰撞过程中周缘造山带的构造活动及隆升过程[6-9]。另一方面,沉积物在搬运、堆积过程中,成分受环境和气候影响小,且不受地域构造热事件的约束,可以作为洞悉盆山耦合过程及相互作用的理想载体。对柴达木盆地沉积物源追踪及特征的研究,是反演和认识高原北缘构造隆升历程的有效途径,有助于解决整个青藏高原的隆升问题。
本文以柴达木盆地北缘露头较好、年代精确、新生代地层连续的路乐河地区沉积剖面为研究对象,应用阴极发光技术,通过标志性碎屑组分变化的对比和系统的物源分析,识别路乐河地区对周缘造山带的响应沉积,有效界定青藏高原北缘构造运动和隆升事件的时限,为进一步科学认识高原演化、隆升历史及板块碰撞远程效应提供重要线索。
1. 地质概况
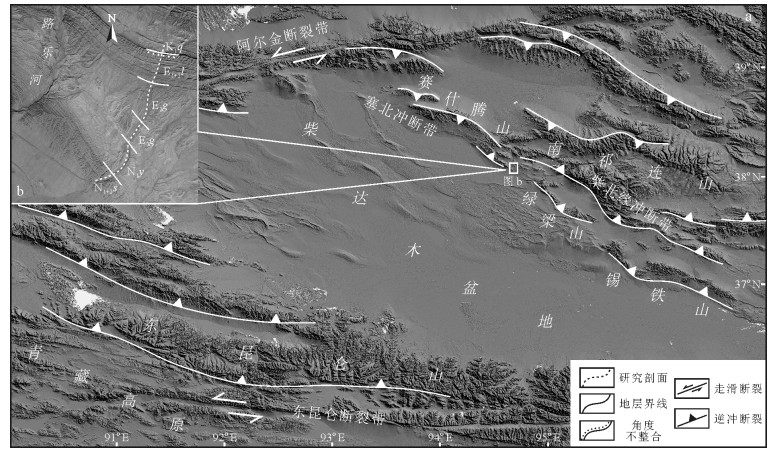
路乐河地区位于柴达木盆地的北缘,在大地构造位置上,东北毗邻祁连山-南山,西北靠近赛北逆冲断裂[10]和略远的阿尔金左行走滑断裂带[11-12],南端远离东昆仑山脉(图 1-a)。受南特提斯洋盆的俯冲消减及印度-欧亚碰撞远程效应的影响,柴达木盆地及邻接造山带经历了多期次的重大构造地质事件[13-17]。路乐河地区也沉积了巨厚的新生代岩层,记录着盆地接纳沉积物填充过程中山脉隆升与环境变化的演化信息,能够为研究青藏高原北缘造山带的隆升增添佐证。路乐河地区地层从底到顶依次为白垩系犬牙沟组(K1q)、古新统—始新统路乐河组(E1+2l)、始新统下干柴沟组(E2g)、渐新统上干柴沟组(E3g)、中新统下油砂山组(N1y1)和上油砂山组(N1y2),以及中新统—上新统狮子沟组(N1+2s)共7套地层(图 1-b)[18]。其中路乐河组与犬牙沟组呈角度不整合接触,下、上油砂山组界线不明显,文中并称为油砂山组。
据马海幅1:20万区域地质调查报告①,赛什腾山主要岩性有浅变质千枚岩和绢云母片岩、碎屑岩及大量花岗岩类,并含少量安山岩、玄武岩等中基性喷出岩。南祁连山以古元古界片麻岩和大理岩深变质岩系、石炭系和三叠系碎屑岩、碳酸盐岩及达肯大坂地区达肯大坂群的斜长片麻岩和变质石英岩为主,出露岩浆岩主要为加里东期和海西期花岗岩、奥陶纪和志留纪中酸性火山岩。阿尔金山脉主要出露中、新元古界及少量奥陶系[19-20],中元古界岩性为变质碎屑岩、碳酸盐岩,发育少量玄武岩-安山岩-流纹岩组合,蓟县系出露些许闪长岩、花岗岩等侵入岩;新元古界和奥陶系均由碎屑岩和碳酸盐岩组成,火山岩不发育;新元古界变质岩系分布较多,由变质砂岩、斜长变粒岩、角闪片岩及结晶灰岩构成。
2. 碎屑矿物阴极发光特征
2.1 阴极发光原理
在外部能量的激发下,多数绝缘矿物会发生光子辐射。当激发源为高能电子束时,矿物发射可见光波段的光子,即为阴极发光(Cathodolumines-cence)[21]。矿物阴极发光根本上是由晶格中的微量元素或固有缺陷激发引起的,这些元素和晶格缺陷统称为发光中心(Luminescence centers)[22]。晶格中发光中心含量越高、越密集,矿物阴极发光的强度越强[23]。碎屑岩中不同类型的矿物颗粒,像石英、长石等,以及不同成因的矿物晶体,如喷出型石英和侵入型石英,由于其内部结构、元素组成各不相同,其阴极发光的颜色和强度也有所差别,因此阴极发光可以很好地指示沉积岩碎屑成分,这已为多数学者认同[24-29]。
2.2 阴极发光特征
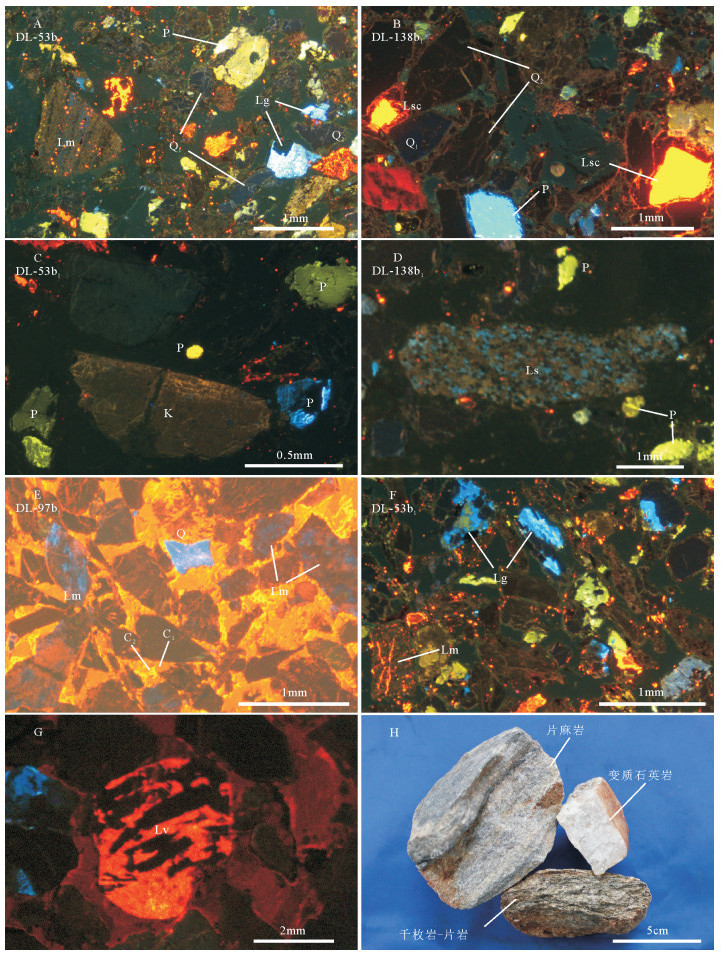
石英是碎屑岩中含量最高的造岩矿物,传统的碎屑组分统计方法将其简单地划分为单晶石英和多晶石英,忽略了石英不同成因及来源的深层次信息。一般而言,蓝紫色、深蓝色-蓝色为岩浆岩石英,棕色、深棕褐色阴极光为变质型来源(图版Ⅰ-A、B)。由于石英重结晶过程中微量元素和晶格缺陷重新调整,或变形强烈造成高密度的发光中心,能量激发时声子发射(能量热)代替光子发射,从而降低了发光强度[30-31]。长石也是碎屑岩中常见的造岩矿物,在长距离搬运过程中易发生破裂、溶解,故长石含量的高低可以作为岩石风化强度和搬运距离的量化指标。如图版Ⅰ-B、C所示,斜长石阴极发光显示天蓝色、灰蓝色、黄绿色和少量黄色,微斜长石发黄灰色阴极光,其中亮蓝色为碱性长石(钙长石、钾长石),钙长石因Fe2+的存在呈芥末黄色、灰蓝色,酸性更长石以黄绿色居多[24, 32-33]。
![]() 图版ⅠA.岩浆型石英(Q1)、变质型石英(Q2)阴极发光特征;B.碳酸盐岩(Lsc)阴极发光特征;C.不同类型长石(K为微斜长石,P为长石)阴极发光特征;D.泥岩(Ls)阴极发光特征;E.变质石英岩(Lm)及碳酸盐胶结世代(C1、2)阴极发光特征;F.千枚岩-片岩(Lm)、花岗岩(Lg)阴极发光特征;G.喷出岩(Lv)阴极发光特征(图片据参考文献[36]);H.路乐河砂岩砾石组分特征图版Ⅰ.
图版ⅠA.岩浆型石英(Q1)、变质型石英(Q2)阴极发光特征;B.碳酸盐岩(Lsc)阴极发光特征;C.不同类型长石(K为微斜长石,P为长石)阴极发光特征;D.泥岩(Ls)阴极发光特征;E.变质石英岩(Lm)及碳酸盐胶结世代(C1、2)阴极发光特征;F.千枚岩-片岩(Lm)、花岗岩(Lg)阴极发光特征;G.喷出岩(Lv)阴极发光特征(图片据参考文献[36]);H.路乐河砂岩砾石组分特征图版Ⅰ.岩屑是母岩机械破碎的产物,继承了母岩岩性和岩石的结构特征,可直接反映物源区的岩石类型及岩性组合[34-35]。常见的岩屑类型有沉积岩、变质岩和岩浆岩。沉积岩岩屑含泥岩、碳酸盐岩等;泥岩岩屑不具阴极发光,但内部显示大量无规则的蓝色石英斑点(图版Ⅰ-D),识别标志独特,碳酸盐岩阴极发光颜色主要为亮黄色和橙红色色调,且可观察到碎屑颗粒至少经历了2期世代的碳酸盐胶结作用(图版Ⅰ-B、E)。路乐河碎屑组分变质岩岩屑含量较高,主要为千枚岩-片岩和石英岩。千枚岩-片岩岩屑与泥岩相似,表面含蓝色和棕色阴极光斑点,但其微定向排列的特点及规则外形易于被甄别(图版Ⅰ-A、F)。石英岩由砂岩和硅质岩经区域变质或接触变质作用形成,由多个亚石英晶粒构成,颗粒之间呈镶嵌接触,阴极发光呈棕色和部分蓝色(图版Ⅰ-E),前者表示其经历了高级变质重结晶作用[26]。侵入岩岩屑以花岗岩岩屑最常见,阴极发光下,花岗岩岩屑亦可见典型的花岗结构(图版Ⅰ-A、F),矿物颗粒明显;酸性喷出岩基质阴极发光呈血红色,石英斑晶不发光,两者界线截然(图版Ⅰ-G)。
3. 分析结果及物源指示
盆地沉积物主要由周缘造山带基岩经抬升剥蚀、搬运堆积形成,碎屑成分变化可以间接反映母岩或物源区的改变[37]。另外,沉积序列中特征岩石组分的出现标志着毗邻造山带隆升活动的启动[38-39]。依据上述不同矿物及岩屑类型的阴极发光特征,共完成了50件碎屑岩薄片组分的统计。统计工作在中国石油华北油田勘探开发研究院生油实验室完成,样品分布于各个层组,并对特征矿物和岩屑含量垂向序列变化进行了比较。
3.1 碎屑组分变化
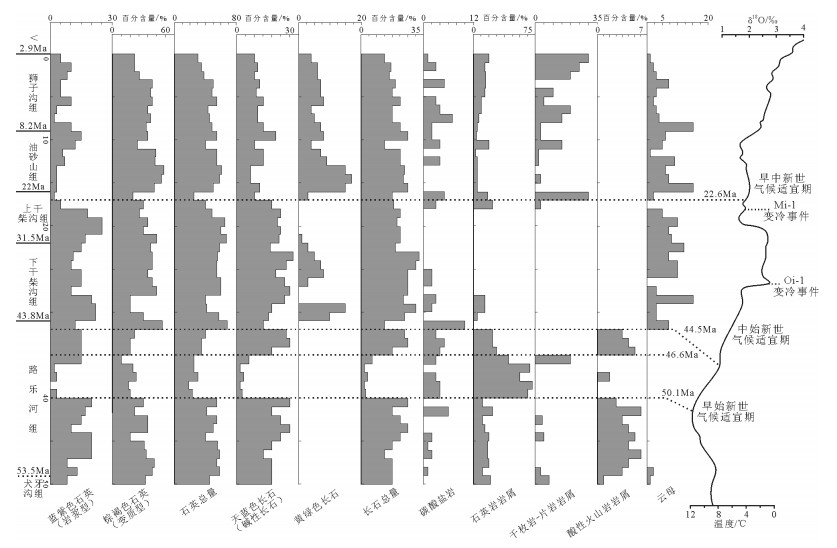
沉积碎屑组分变化是反映盆地物源演化历程的重要物质表现。值得注意的是,单种碎屑成分的突然出现或消失,可以解释为构造运动造成源区物质组成的改变,再者出露地层被剥蚀殆尽所致。通过对比发现(图 2),新生代53.5~2.9Ma期间,路乐河沉积碎屑组分垂向上有3次明显的阶段性波动。第一次急剧变化发生在路乐河组中部,时间为50.1~46.6Ma,石英、长石及火山岩岩屑含量均保持在最低水平,石英岩岩屑达到峰值。盆地沉积物的高速率堆积与高原造山带的隆升相对应[41],暗示路乐河源区山脉经历了相对短暂的快速隆升剥蚀事件。在路乐河组与下干柴沟组交界(约44.5Ma),以云母和黄绿色长石首次大量出现及火山岩岩屑消失为标志,为路乐河地区沉积物源的第二次转换事件,碳酸盐岩和变质岩岩屑含量也急剧降低。云母主要赋存于花岗岩类或低级变质岩中,故云母的出现表征了物源区上述岩石的大面积暴露。第三次显著变化位于上干柴沟组顶部,时间为22.6Ma左右,黄绿色长石、碳酸盐岩和变质岩岩屑突增,变质型石英也呈增加趋势。概略地说,在50.1~46.6Ma、44.5Ma和22.6Ma前后,路乐河物源区可能爆发了剧烈的构造活动,致使路乐河地区沉积物组分发生阶段性变化。
![]() 图 2 路乐河地区物源转换事件与全球气候变化图(δ18O据参考文献[40])Figure 2. Transformation events in Lulehe and global climatic changes during the Cenezoic period
图 2 路乐河地区物源转换事件与全球气候变化图(δ18O据参考文献[40])Figure 2. Transformation events in Lulehe and global climatic changes during the Cenezoic period3.2 物源分析
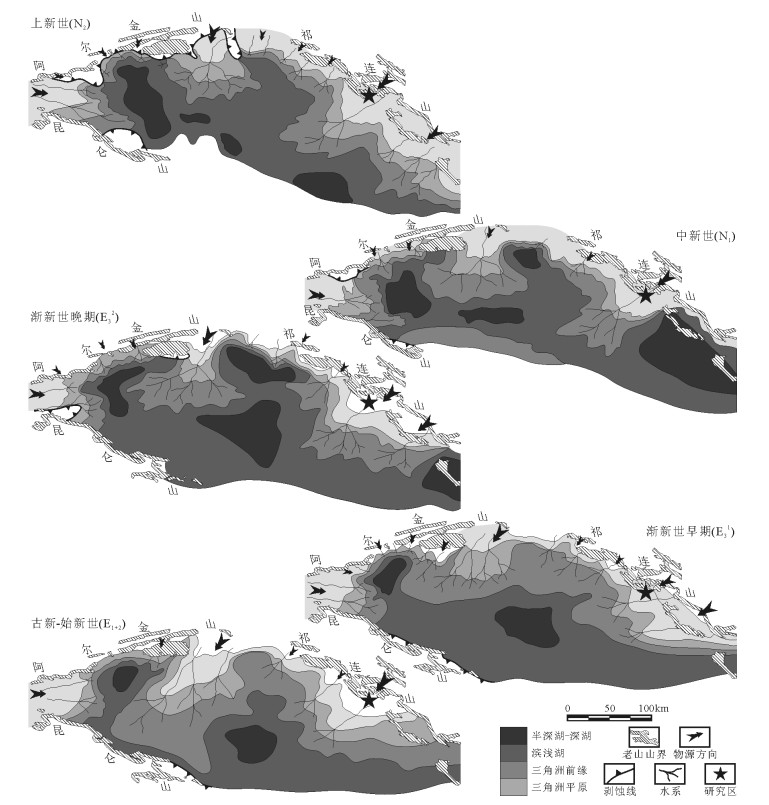
河流是沉积物搬运的主要载体,古水流流向或优势流向的识别,有助于判别物源方位、追溯源区[42]。自古新世以来,柴达木盆地一直是一个内流汇水盆地[43-44],古水系[10]和物源恢复显示(图 3),路乐河地区新生代水流方向变化稳定,主体方位为SW向。此外,在路乐河地区除50.1~46.6Ma整个新生代沉积期外,碎屑矿物长石含量较高,平均为24.3%,其母岩类型应以含长石丰富的花岗岩或花岗片麻岩类为主[45-46],这同野外见到大量花岗岩及片麻岩砾石成分的事实一致(图版Ⅰ-H)。高长石含量的特征反映碎屑岩成分成熟度低,地层为干旱气候条件近物源快速搬运堆积形成。结合古水流方向和沉积物源方向可知(图 3),路乐河沉积体系主要受NE向南祁连和赛什腾造山带的供给制约,其沉积碎屑组分的3次变化分别表征物源的3次转变事件。
![]() 图 3 柴达木盆地新生代物源及古水流变化②Figure 3. The change of provenance and paleocurrent in Qaidam basin during the Cenozoic period
图 3 柴达木盆地新生代物源及古水流变化②Figure 3. The change of provenance and paleocurrent in Qaidam basin during the Cenozoic period(1)从犬牙沟组顶部到50.1Ma,各造岩矿物(长石、石英)及岩屑组分(石英岩、火山岩等)稳定沉积。通过对比赛什腾和南祁连山的岩性发现,变质石英岩、酸性火山岩和碳酸盐岩仅在南祁连山发育,因此路乐河此阶段物源区主要为南祁连山。50.1~46.6Ma,石英岩含量急增,表明南祁连可能经历过加速隆升事件[41],隆升引起变质岩基高速剥蚀,进而石英岩岩屑含量增大,其余组分则大幅减少。46.6Ma之后,碎屑组分恢复至50.1Ma之前的状态,南祁连山构造趋于稳定。
(2)44.5Ma,云母的发育表征了花岗岩类或含云母低级变质岩的大面积暴露,这与赛什腾山岩性一致,表明南祁连山不再是路乐河物源的主要供给者;另一方面,酸性火山岩岩屑的消失也指示路乐河的主要物源区由南祁连山向赛什腾山转变,石英岩和碳酸盐岩岩屑含量逐渐减少至消失亦印证了这一观点。
(3)22.6Ma前后,路乐河物源区再次发生转变。云母的稳定沉积及千枚岩-片岩的出现,反映赛什腾山持续为路乐河供给物源,而石英岩和碳酸盐岩岩屑的重新发育,表明南祁连山也开始为路乐河地区提供大量碎屑物质。变质岩贡献比例的加强,使岩浆型和变质型石英分别呈缩减和增加趋势。
4. 物源转换对构造隆升的响应
造山带的隆升和盆地的沉积是一个耦合过程,气候变化和构造运动对青藏高原隆升均具有一定的影响,如构造隆升促进化学风化作用的增加[47-48],造成大量基岩的脱落和搬运堆积;气候异常引起的快速侵蚀卸载作用造成山体总质量的亏缺,进而发生重力均衡效应[49],迫使山体抬升。但在长时间和大空间尺度上,构造运动对地体抬升的制约更甚于气候变化的影响[50-53],且构造活动的强弱程度能够由山脉剥蚀量或物源区岩性的变化直接体现[54]。与此同时,始新世早—中期和中新世早期全球气候变化趋于稳定(图 2),因此气候条件对路乐河地区新生代物源变化的影响可不予考虑。
(1)50.1~46.6Ma构造隆升响应
早在65~55Ma,印度和欧亚板块就已发生拼贴碰撞[12, 55-57],并在55~45Ma达到高峰[58],陆内拉萨、羌塘等刚性块体远程传递两大板块汇聚的强劲应力,隆升活动也同步传达到了高原北部地区[59-61]。现有柴达木和河西走廊地层学资料显示,阿尔金断裂起始于古新世49Ma[12],柴盆北缘的赛北断裂带及柴北缘断裂带在54.8~49Ma开始形成[10]。Jo-livet等[62]通过片麻岩磷灰石热模拟研究发现,祁连山在50Ma左右发生了快速的剥露事件,在路乐河剖面也曾报道51Ma存在一期高速率沉积[63]。从更大空间尺度看,青藏高原早期阶段的隆升在其他地区也有响应,如距高原较远的西南天山托云盆地新生代48.1±1.6Ma的幔源岩浆活动[64-65]和白垩纪—古近纪期间的托云块体旋转运动[66],可见青藏高原北缘构造变形活动相比印度-欧亚板块碰撞,滞后了约10±5Ma。以上研究均与南祁连山开始为路乐河地区提供大量剥蚀物的时限一致,揭示南祁连山50.1~46.6Ma的急剧抬升是对印度-欧亚板块碰撞的远程响应,也是碰撞应力在高原北部远程传递的有力证据。
(2)44.5Ma构造隆升响应
此时,印度与欧亚板块已完成全面碰撞,汇聚产生的应力推挤陆内已拼合的块体,使之横向缩短并相互叠置,引起陆内严重形变和逆冲推覆构造[67-68]。经热年代学研究[69],在当雄地区新厘定的纳木错逆冲推覆构造于古近纪44Ma经历过一次变形抬升事件,在高原腹地不同位置还发现大规模挤压型钾质-超钾质火山岩的踪迹[70-73],且在45~40Ma岩浆活动异常活跃。岩浆是板块碰撞挤压最直观的表现,区域性的岩浆侵位必将造成岩石圈增厚,高原整体性抬升[68, 74-75],在羌塘多格错仁地区新发现的埃达克岩表明,地壳在45~38Ma经历了缩短加厚[76]。然而,古地磁数据揭示[77],中始新世—早渐新世阿尔金主断裂和柴北缘断裂带山前沉积未发生明显的旋转变形,换言之,青藏高原新生代第二阶段的隆升以地壳垂向增生为主,具体表现为陆内块体南北向缩短、岩浆侵位和块体边界逆冲构造的发育。从44.5Ma开始,路乐河物源区由南祁连山向赛什腾山快速转变,表明赛北逆冲断裂伴随显著的隆升卸载作用,对应于高原内部的构造隆升事件。
(3)22.6Ma构造隆升响应
印度板块在中新世持续向大陆俯冲,逆冲构造以前展式推覆方式向前陆迁移、消减,形成一系列走滑-逆冲断裂和地层形变[67, 78]。来自五道梁雅西措组的古地磁结果显示,可可西里盆地在渐新世末期有29.1°±8.5°的顺时针垂轴旋转[79],赛北断裂山前地层有14°左右的移位[78]。George等[80]基于酒西盆地磷灰石裂变径迹分析,揭示出祁连山23Ma的快速隆升事件,Wang等[81]也获得了相同的冷却年龄。同时,西秦岭发生与高原隆升响应的构造-热事件,剥蚀速率急增[82],此次运动得到岩浆活动(22~23Ma)的证实[83-84],在高原内部也广泛存在相近年龄的火山喷发活动[85-89]。另一方面,在东昆仑山和阿尔金山前盆地也保留了中新世22Ma前后的岩浆活动、磨拉石沉积、断层平移、物源转型等隆升事件的地质记录[43, 62, 90-92],遥远的喀拉昆仑和西天山地区[93]亦发生与印度-欧亚板块碰撞相关的山体快速剥露事件。不言而喻,青藏高原在渐新世—中新世之交发生了大规模的构造运动,几乎波及整个高原。青藏高原整体性准同时隆升,进一步肯定了22.6Ma南祁连山与赛什腾山协同为路乐河供应沉积物的合理性。路乐河地区物源3次阶段性变化的认识也间接反映了青藏高原为阶段式隆升的观点[13, 67, 94-95]。
5. 结论
(1)沉积碎屑组分变化是反映盆地物源演化过程的重要物质表现。路乐河地区新生代碎屑组分高长石含量的特点,指示其为近物源搬运沉积形成。同时沉积物来源方向和周缘山系岩性对比揭示,路乐河物源主要受南祁连山和赛什腾山供给的控制。
(2)路乐河地区物源在新生代53.5~2.9Ma期间至少存在3次转换,发生时间同印度-欧亚板块碰撞及高原构造隆升事件吻合,间接反映了青藏高原为阶段式隆升的观点,时间依次为50.1~46.6Ma、44.5Ma和22.6Ma,深入认识青藏高原隆升历史及板块碰撞远程效应具有重要意义。
(3)44.5Ma之前,路乐河物源区主要为南祁连山,而50.1~46.6Ma南祁连山的快速抬升是对印度-欧亚板块初始碰撞应力的传递响应;青藏高原第二阶段的隆升以地壳垂向增厚为主,逆冲推覆构造发育,赛北断裂于44.5Ma发生显著的剥露作用,路乐河物源区由南祁连向赛什腾山转变;渐新世—中新世之交(22.6Ma),青藏高原准同时整体性隆升,赛什腾山和南祁连山协同为路乐河地区供应沉积物。
致谢: 野外工作得到青海省地质调查院拉陵灶火地区矿产远景调查、矿产勘查项目组同志的帮助,天津地质矿产研究所同位素实验室、湖北省地质实验测试中心在测试和数据处理过程中给予帮助,审稿专家给予了有益指导,在此一并深表感谢。 -
图 7 稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线(标准化值据参考文献[11])
Figure 7. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns
表 1 二长花岗岩(10DQ9JD3312)和正长花岗岩(10DQ9JD3132)锆石U-Th-Pb同位素数据
Table 1 Zircon U-Th-Pb isotopic composition of the samples of monzogranite (10DQ9JD3312) and syenogranite (10DQ9JD3132) as measured by LA-ICP-MS technique
测点号 含量/10-6 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U Th U 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 10DQ9JD3312(二长花岗岩) 1 60.7 98.1 0.0515 0.0004 0.2259 0.0025 0.0323 0.0002 207.5 2.1 205.6 2.6 2 141.5 132.4 0.0507 0.0004 0.2238 0.0022 0.0325 0.0002 205.2 2.7 206.2 1.1 3 157.7 360.8 0.0513 0.0005 0.2273 0.003 0.0326 0.0003 208.1 3.4 207.3 2.1 4 152.8 396.2 0.0512 0.0003 0.2262 0.0022 0.0325 0.0003 207.3 2 206.3 2.3 5 110.5 281.5 0.0522 0.0005 0.2272 0.0036 0.0321 0.0004 208.3 3 203.5 3.5 6 88.5 204.7 0.0511 0.0003 0.2278 0.0022 0.0328 0.0002 208.6 2.1 208.1 1.8 7 123.2 290 0.0509 0.0003 0.2236 0.0019 0.0323 0.0002 205.1 2.9 205.1 1.2 8 21 23.8 0.0519 0.0009 0.2239 0.004 0.0319 0.0003 205.1 3.5 202.3 2.3 9 181.9 408.6 0.0513 0.0002 0.2244 0.0017 0.0322 0.0002 206.1 1.5 204.4 1.3 10 108.5 192.6 0.0516 0.0003 0.2251 0.0021 0.0322 0.0002 206.9 2.2 204.1 2.7 11 67.5 215.5 0.0525 0.0004 0.2289 0.0022 0.0321 0.0002 209.2 2.1 204.6 1.1 12 97.7 278.9 0.0527 0.0003 0.2324 0.0021 0.0324 0.0002 212.4 2.3 206.8 2.6 13 157.3 486 0.0512 0.0002 0.2244 0.0015 0.0323 0.0002 206.2 1.77 205.8 1.9 14 99.7 249.6 0.05 0.0003 0.2195 0.0024 0.0323 0.0003 201 2.1 205.5 2.8 15 169.4 210.4 0.0508 0.0003 0.222 0.0018 0.0322 0.0002 204.7 1.6 204.5 1.1 10DQ9JD3132(正长花岗岩) 1 158.9 374.4 0.0496 0.0006 0.2185 0.0035 0.0319 0.0003 200.6 3.2 202.7 2 2 68.6 188 0.0519 0.001 0.2294 0.0057 0.0321 0.0005 209.7 5.2 203.5 3.3 3 179.4 222 0.0514 0.0011 0.2262 0.005 0.0319 0.0003 207 4.6 202.5 2 4 187.5 514.6 0.0513 0.0004 0.2248 0.0036 0.0318 0.0005 205.9 3.3 201.6 2.9 5 118.3 154.6 0.0522 0.0016 0.2287 0.0071 0.0318 0.0003 209.1 6.5 202 1.8 6 299.1 571.2 0.0513 0.0015 0.2251 0.0067 0.0318 0.0004 206.1 6.1 201.8 2.4 7 134.9 227.6 0.05 0.0011 0.2203 0.0051 0.0319 0.0003 202.1 4.7 202.7 2 8 300.4 327.4 0.0489 0.0011 0.2102 0.005 0.0312 0.0003 193.7 4.6 198 1.8 9 149.9 270.4 0.0489 0.0014 0.2108 0.0059 0.0313 0.0004 194.2 5.4 198.5 2.3 10 327.8 257.8 0.0476 0.0012 0.2094 0.0057 0.0319 0.0004 193.1 5.2 202.2 2.2 11 163.5 149.7 0.0523 0.0018 0.2312 0.0085 0.032 0.0003 211.2 7.8 203.1 1.8 12 386.7 560.9 0.0503 0.0009 0.2227 0.0045 0.0321 0.0003 204.1 4.1 203.8 1.7 13 100.4 223.4 0.0494 0.001 0.2171 0.0044 0.0319 0.0002 199.5 4.1 202.3 1.6 14 387.1 461.2 0.0511 0.0014 0.2194 0.0066 0.0311 0.0002 201.5 6.1 197.7 1 15 46.3 121.3 0.0522 0.0007 0.2284 0.0062 0.0317 0.0007 208.9 5.7 201.2 4.4 16 85.9 330 0.051 0.0003 0.2242 0.0028 0.0319 0.0003 205.4 2.5 202.4 2.2 17 80.2 121.4 0.0501 0.0009 0.2161 0.005 0.0313 0.0003 198.7 4.6 198.7 1.7 18 131.7 249.1 0.0499 0.0007 0.2174 0.0032 0.0316 0.0002 199.7 3 200.5 1.1 19 216.6 249.7 0.0503 0.0009 0.2175 0.0042 0.0314 0.0003 199.8 3.9 199.2 1.6 20 85.3 166.8 0.0521 0.0006 0.2264 0.0033 0.0315 0.0003 207.2 3 200.1 1.6 21 146.6 381.4 0.0518 0.0009 0.2205 0.0045 0.0309 0.0002 202.3 4.2 196 1.1 22 105.5 294.8 0.0514 0.0004 0.2194 0.0024 0.031 0.0002 201.4 2.2 196.8 1.3 23 190.8 332.3 0.0518 0.0013 0.217 0.0049 0.0304 0.0002 199.4 4.5 193 1.5 24 103.6 232.3 0.05 0.0005 0.2174 0.0025 0.0315 0.0002 199.8 2.3 200 1.2 25 99.4 202.4 0.0528 0.0013 0.229 0.0058 0.0315 0.0003 209.4 5.3 200 1.8 表 2 拉陵高里河地区晚三叠世—早侏罗世花岗岩主量、微量和稀土元素含量
Table 2 Composition of major, trace and rare earth elements of Late Triassic -Early Jurassic granites in Lalinggaoli area
序号
岩性1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 正长花岗岩 二长花岗岩 正长花岗岩 样号 9GS 9GS 9GS 9GS 9GS 9GS Pm28 Pm25 Pm25 Pm25 10DQ9 10DQ9 PM21 PM2 6467 3400 3405 3605 Jan-85 3205 Gs5-1 GS3-3 GS3-4 GS3-5 GS3132 GS3603 GS1-1 1GS6-1 SiO2 76.2 75.93 76.02 76.55 75.37 75.09 72.18 76.09 76.17 76.15 76.16 76.43 75.77 73.13 TiO2 0.07 0.14 0.13 0.08 0.22 0.18 0.33 0.07 0.1 0.08 0.14 0.16 0.17 0.22 Al2O3 12.57 12.59 12.48 12.04 13.05 12.79 13.75 12.35 12.3 12.49 12.67 12.44 12.41 13.51 Fe2O3 0.42 0.85 0.5 0.61 0.01 0.72 0.3 0.58 0.94 0.8 0.26 0.4 0.94 0.75 FeO 0.67 0.5 0.82 1.1 1.15 0.87 1.82 0.5 0.42 0.33 1.13 1.03 0.68 1 MnO 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.03 0.04 0.06 0.02 0.03 0.03 0.04 0.04 0.03 0.04 MgO 0.06 0.23 0.23 0.13 0.34 0.37 0.85 0.2 0.17 0.15 0.29 0.33 0.37 0.56 CaO 0.76 0.92 0.95 0.67 0.64 1.37 1.73 0.64 0.65 0.65 0.74 0.8 0.99 1.52 Na2O 3.62 3.73 3.75 3.9 3.74 3.72 2.75 3.44 3.25 3.54 3.09 3.18 3.8 3.88 K2O 4.77 4.31 4.38 4.1 4.57 4.08 4.81 5.32 5.18 5.14 4.73 4.44 4.22 4.12 P2O5 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.05 0.03 0.12 0.02 0.03 0.03 0.07 0.07 0.05 0.06 H2O+ 0.61 0.52 0.4 0.55 0.58 0.5 1.03 0.43 0.45 0.32 0.44 0.45 0.38 0.54 CO2 0.13 0.08 0.13 0.06 0.04 0.06 0.07 0.21 0.16 0.16 0.09 0.09 0.06 0.51 总量 99.91 99.85 99.85 99.85 99.79 99.82 99.8 99.87 99.85 99.87 99.85 99.86 99.87 99.84 alk 8.39 8.04 8.13 8 8.31 7.8 7.56 8.76 8.43 8.68 7.82 7.62 8.02 8 La 12.94 27.9 40.73 25.62 27 33.66 29.7 29.5 29 22.3 34.6 32.4 46.5 43.4 Ce 37.8 50.93 74.11 46.38 49.68 59.06 58.2 57.8 58.6 47.7 66.5 63.5 98.4 90.3 Pr 5.95 6.22 8.96 5.54 6.5 7.16 6.91 6.01 6.07 5.29 7.55 7.36 10.4 8.88 Nd 31.61 19.37 29.01 18.07 21.38 23.6 25.5 19.1 19.1 17.6 24.8 24.7 35.2 29.1 Sm 12.15 3.55 5.33 3.37 3.87 4.22 6.12 3.32 3.08 3.54 4.51 4.71 6.64 4.93 Eu 0.38 0.36 0.3 0.25 0.55 0.46 0.838 0.319 0.418 0.262 0.304 0.279 0.284 0.531 Gd 16.26 2.58 3.98 2.86 3.25 3.36 6.17 3.27 2.77 3.19 3.74 3.93 5.9 4.24 Tb 3.07 0.38 0.6 0.5 0.53 0.52 1.05 0.486 0.395 0.491 0.529 0.599 0.858 0.594 Dy 20 2.04 3.32 2.74 2.95 2.8 6.57 2.76 1.95 2.83 2.78 3.43 4.75 3.18 Ho 4.17 0.44 0.68 0.57 0.62 0.62 1.29 0.551 0.367 0.542 0.515 0.632 0.879 0.59 Er 11.87 1.14 1.68 1.43 1.66 1.47 3.7 1.61 1.08 1.54 1.68 2.08 2.52 1.77 Tm 1.78 0.17 0.25 0.22 0.26 0.23 0.545 0.262 0.183 0.247 0.237 0.304 0.397 0.288 Yb 11.5 1.1 1.45 1.35 1.73 1.37 3.46 1.78 1.1 1.68 1.65 1.95 2.67 1.9 Lu 1.69 0.17 0.22 0.2 0.28 0.22 0.455 0.258 0.166 0.248 0.239 0.29 0.388 0.275 Y 104 11.34 17.37 15.55 16.24 14.46 16.8 11.4 15.6 24.3 33.9 28.3 17.9 Zr 61.9 59.2 66.1 112 135 Nb 8.8 1.89 6.75 14 12.3 Ba 278 370 258 227 492 Hf 3.3 2.66 3.4 4.84 5.12 Ta 1.55 1.13 1.43 1.82 1.4 Sc 2.55 2.15 2.43 4.19 3.78 Rb 128 112 140 187 171 Th 18.1 16 16.2 26.4 24 Sr 101 82.5 53.7 81.1 195 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量为10-6,8~14号样品据参考文献① -
莫宣学, 罗照华, 邓晋福, 等.东昆仑造山带花岗岩及地壳生长[J].高校地质学报, 2007, 13 (3): 403-414. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200703005.htm 王秉璋, 罗照华, 吴正寿, 等.祁漫塔格地质走廊域古生代—中生代火成岩岩石构造组合研究[M].北京:地质出版社, 2014:1-230. 丰成友, 王松, 李国臣, 等.青海祁漫塔格中晚三叠世花岗岩:年代学、地球化学及成矿意义[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(2): 665-678. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201202025.htm 张爱奎, 刘光莲, 莫宣学, 等.青海祁漫塔格晚古生代—早中生代侵入岩构造背景与成矿关系[J].西北地质, 2012, 45(1):9-19. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201201005.htm 丰成友, 李东生, 吴正寿, 等.东昆仑祁漫塔格成矿带矿床类型、时空分布及多金属成矿作用[J].西北地质, 2010, 43(4):10-17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201004004.htm 李怀坤, 耿建珍, 郝爽, 等.用激光烧蚀多接收器等离子体质谱仪(LA-MC-ICPMS)测定锆石U-Pb同位素年龄的研究[J].矿物学报, 2009, 28(增刊):600-601. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB2009S1311.htm Middlemost E A K. Naming Materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 1994, 37 (3/4): 215-224.
Rollison H R.Using geochemical data: Evalution, presentation, inter-pretation[M]. New York:Longman Scientific & Technical, 1993: 102-213.
Wright J B. A simple alkalinity ratio and its application to questions of non-orogenic granite genesis[J]. Geological Magazine, 1969, 106 (4): 370-384. doi: 10.1017/S0016756800058222
Collins W J, Beams S D, White A J R, et al. Nature and origin of A type granites with paticular reference to Southeastern Australia[J]. Contrib. Miner. Petro., 1982, 80:189-200. doi: 10.1007/BF00374895
Boynton W V. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: meteorit-estudies[C]//Henderson P. Rare earth element geochemistry. Elser-vier, 1984:63-114.
宋忠宝, 张雨莲, 贾群子, 等.青海祁漫塔格地区野马泉花岗闪长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2016, 35(12):2006-2013. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.12.008 刘云华, 莫宣学, 喻学惠, 等, 东昆仑野马泉地区景忍花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(10): 2457-2463. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2006.10.006 王秉璋, 王涛. 青海省东昆仑祁漫塔格火成岩类成矿作用及找矿靶区优选. 青海省地质调查院, 2011.




 下载:
下载: