LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age and petrochemistry of the Samalong diorite in the Duolong metallogenic area of Tibet and its constraint on the metallogenic setting of the porphyry deposits
-
摘要:
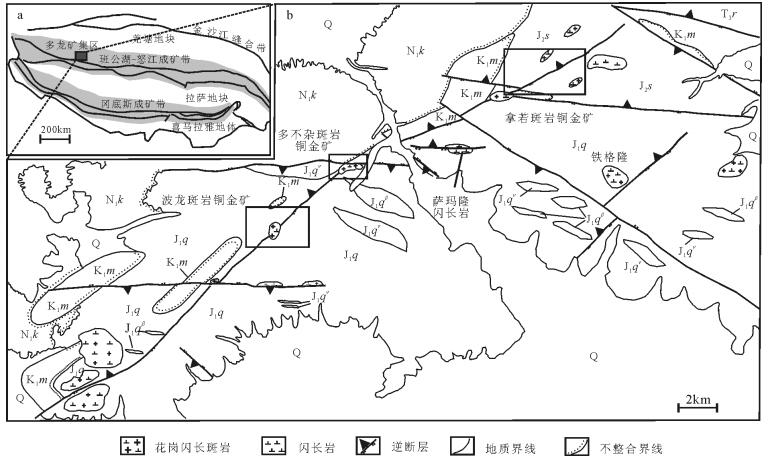
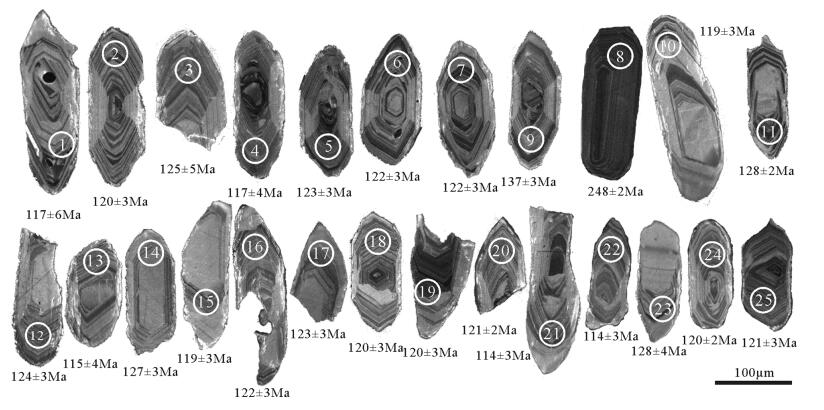
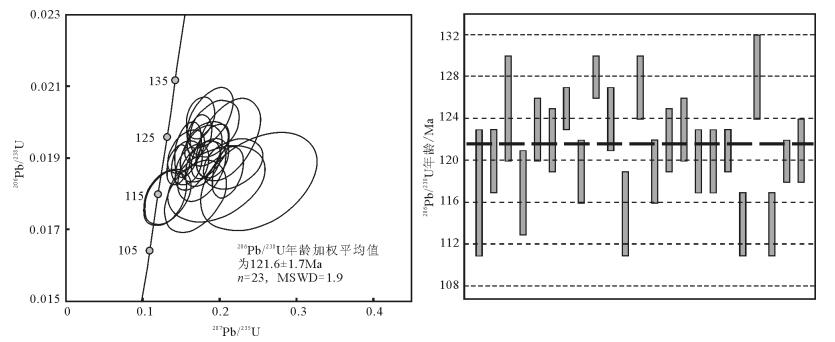
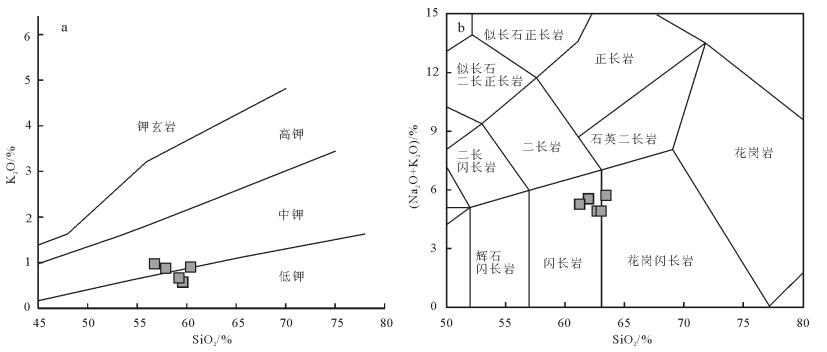
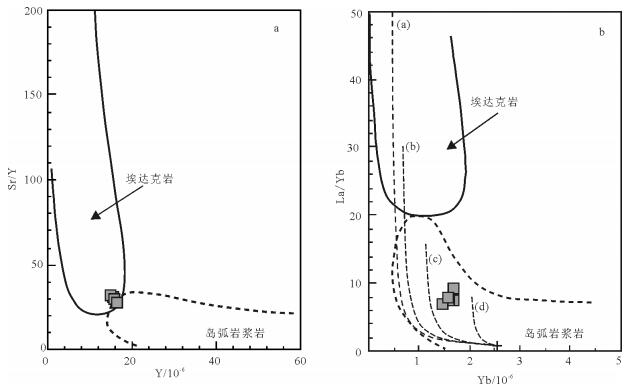
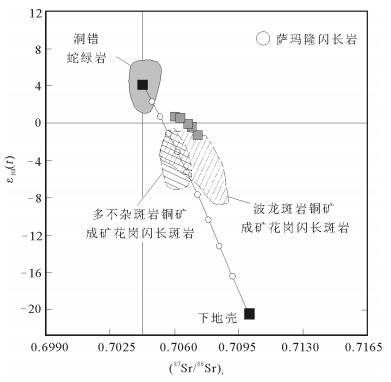
西藏多龙矿集区是目前班公湖-怒江成矿带内最具潜力的找矿远景区,矿集区内已发现4处大型斑岩铜矿,但其成矿背景尚有争议。通过开展成矿前的萨玛隆闪长岩锆石U-Pb测年、岩石化学分析,结合区域内构造发育序次,对系列斑岩铜矿的成矿背景进行探讨。对萨玛隆闪长岩中进行LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年,获得23颗锆石的206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值为121.6±1.7 Ma(MSWD=1.9),代表了闪长岩的成岩年龄。萨玛隆闪长岩的全岩岩石化学分析结果显示,该岩石属于中钾富钠岩石,富集轻稀土元素和大离子亲石元素,亏损重稀土元素和高场强元素,具有高Sr、低Y特征,相对富集Cr、Ni等不相容元素,有埃达克岩的亲和性。闪长岩具相对较高的(87Sr/86Sr)i值和较低的(143Nd/144Nd)i值、εNd(t)。全岩岩石化学特征显示,萨玛隆闪长岩起源于下地壳角闪岩相,可能有幔源物质混入。矿区内早期走滑断层切穿萨玛隆闪长岩,指示多龙矿集区内主要控岩-控矿走滑断层可能形成于116~121 Ma,多龙矿集区内系列斑岩铜矿形成于班公湖-怒江洋向北俯冲末期的构造转换阶段。
Abstract:The Duolong ore concentration area is the most favorable potential prospecting area in the Bangong Co-Nujiang metallo-genic belt.Four porphyry Cu-Au deposits have been discovered in the Duolong area, but their metallogenic setting is still in contro-versy.The Samalong diorite is located in the central part of the Duolong area.Combined with the tectono-magmatic activation, the authors studied geochronology and bulk geochemistry of the Samalong diorite so as to constrain the metallogenic setting of the por-phyry deposits.25 zircon samples selected form the Samalong diorite intrusion were analyzed by LA-ICP-MS, which yielded a weighted 206Pb/238U age of 121.6±1.7 Ma (MSWD=1.9, n=23), which represents its intrusive age.According to the bulk petrochemi-cal results, the Samalong diorite intrusion belongs to the middle potassium and sodium-rich magmatic series.The Samalong diorite is also enriched in light rare earth elements and large ion lithophile elements and depleted in heavy rare earth elements and high fieldstrength elements, with high Sr and low Y concentrations, suggesting adakite-like affinity.The high initial 87Sr/86Sr values (0.7056~0.7073) and low initial 143Nd/144Nd (0.5124~0.5125) and εNd(t)(-1.3~0.7) suggest that the Samlong diorite was generated from the lower crust, and its relative high MgO content and incompatible elements (Cr, Ni, etc.) concentrations indicate that there might have been some melt derived from the peridotitic mantle wedge mixed in the source region.The Samalong diorite was cut by the former strike-slip faults, which probably suggests that these later strike-slip faults controlled the formation of the porphyry deposits within 116~121 Ma, and the porphyry deposits in the Duolong ore concentration area were formed within the structural transferring period at the last stage of the northward subduction of Bangong Co-Nujiang Neo-Tethys Ocean.
-
渤海海域是渤海湾盆地的一部分,由北部下辽河坳陷、西南部黄骅坳陷和南部济阳坳陷的延伸部分和渤中坳陷组成,是盆地自古近纪以来由水域变陆域演化过程中仅存的水域部分[1-3]。新生代盆地为中生代末以来叠置在华北中—古生界基底上发育的克拉通裂谷断陷盆地,对海域内中生代火山岩的研究,能深入地揭示盆地发育前的大地构造动力学背景。海域内中生代火成岩从基性、中性到酸性均有,以中、酸性为主,为碱性或亚碱性的钙碱性系列,普遍富K和Al[4],受西伯利亚板块和扬子板块碰撞、西太平洋依泽奈崎-库拉板块向亚洲大陆的俯冲作用及郯庐断裂的影响,整个中生代火山活动频繁[5-9]。区域研究认为,火山岩分布主要受郯庐断裂、秦皇岛-老铁山断裂、塘沽-埕北断裂的控制,火山岩类型主要为安山岩、玄武岩、火山凝灰岩等[1, 4, 10]。
然而,受限于海域内的钻井数量,有关中生代火山岩整体研究程度偏低,缺乏系统的地球化学研究,对岩体形成时代的认识也不同。以研究区庙西北凸起蓬莱9-1构造花岗岩为例,前人研究认为,该花岗岩为一套元古宙或太古宙混合花岗岩[11-12],与锦州25-1南变质花岗岩具有相似的构造演化,但后期钻井揭示,该区花岗岩并未发生变质作用,重力、磁力资料也将其解释为中生代火山岩[4]。因此利用锆石U-Pb同位素测定技术,重新测定构造区花岗岩的年龄十分必要。在前人工作的基础上,本次对渤海海域庙西北凸起蓬莱9-1构造潜山花岗岩进行了锆石U-Th-Pb同位素测定,以及主量、微量和稀土元素分析,解释其侵入时代、源区性质及成岩背景,为进一步认识庙西北凸起花岗岩岩浆活动、构造演化及油气成藏提供重要资料。
1. 区域地质背景
庙西北凸起位于渤海海域东部,是海域内唯一的独立构造单元渤中坳陷的一部分。该凸起夹持于渤东凹陷和庙西凹陷之间,是受东南侧北东向边界大断裂(庙西1号断裂)控制的半背斜构造,长条状,走向为NNE向,面积约242km2(图 1),总体显示为北西较深,向南东逐渐变浅过渡为斜坡的不对称碟状坳陷[1, 12-14]。凸起位于郯庐断裂渤海段渤中段东部,作为NE走向的辽东湾段和NNE走向的莱州湾段之间的转折地带,始新世时被北京-蓬莱断裂带错切,因此研究区受郯庐断裂带和张家口-蓬莱断裂带的双重影响[15]。多期断裂活动使研究区潜山长期遭受风化剥蚀,新近系直接超覆或披覆于潜山之上,同时受庙西北凸起东界大断层控制,研究区次生断层发育。
钻井揭示,庙西北凸起地层自上而下划分为平原组、明化镇组、馆陶组、中生界和元古宇。新近系岩性以砂泥岩互层为主,中生界为花岗岩,元古宇则以石英片岩为主。
通过对庙西北凸起A井及B井(井点位置见图 1-C)174块中生界岩心样品镜下鉴定,结合粉晶X衍射分析及主量元素成分分析结果进行CIPW计算,在剔出蚀变样品后,QAP图解投点显示,中生代花岗岩主要为花岗闪长岩,少量二长花岗岩。其中A井主要为二长花岗岩,呈灰白色,具花岗结构和二长结构(图 2-b),块状构造。岩石主要矿物组成为石英、钾长石、斜长石、黑云母或角闪石。B井则为花岗闪长岩,呈灰白色,局部钾化区域显示红色斑块,具半自形粒状结构,块状构造(图 2-a)。主要矿物组成为石英、钾长石、斜长石、角闪石、黑云母。斜长石含量占长石总量的65%~90%,多为更长石、中长石,聚片双晶发育,蚀变严重,暗色矿物以角闪石为主,多发生绿泥石化。此外,在B井酸性侵入岩中还发现少量基性岩脉,主要为辉绿岩(图 2-c)。
2. 分析方法
本文对4块庙西北凸起花岗岩进行了LAICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年,样品采自A井1400m、1500m深度及B井1387.6m、1555m深度(井位见图 1)。锆石分选在河北省地质调查局廊坊实验室完成,将样品粉碎至200目,依次用磁力和重力进行分选,最后在双目镜下挑选出用于定年的锆石。锆石制靶及反射光、透射光、阴极发光(CL)图像照相在北京锆年领航科技公司完成。LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb同位素测定在南京大学内生金属矿床成矿机制国家重点实验室测定,采用Agilent7500型ICP-MS和德国Lambda Physik公司的Com Pex102 ArF准分子激光器(工作物质ArF,波长193nm),以及MicroLas公司的GeoLas 200M光学系统联机进行。激光束斑直径为30μm,激光剥蚀样品的深度为20~40μm,利用氦气作为剥蚀物质的载气,采样方式为单点剥蚀,数据采集选用一个质量峰一点的跳峰方式,每完成4~5个测点的样品测定,加测标样1次。在所测锆石样品分析15~ 20个点前后各测2次NISTSRM 610,锆石年龄采用标准锆石91500作为外标标准物质,用NISTSRM 610校正微量元素含量。每个锆石测试点的U-Pb年龄由Glitter4.4.1[16]程序计算,获得的同位素比值、年龄及误差值、普通铅校正用Excel和ComPbCorr#_151程序计算,年龄计算及U-Pb谐和图的绘制由Isoplot程序完成[17]。
元素分析样品采自A、B、C、D四口井不同深度岩心及岩屑(井位见图 1),样品的主量、微量和稀土元素分析在核工业北京地质研究院分析测试研究中心完成。其中, 主量元素分析采用X射线荧光光谱法分析,使用仪器为AB104-L, PW2404X射线荧光光谱仪;微量及稀土元素分析采用ICP-MS方法,利用酸溶法将样品溶液制备好后,用Element等离子体质谱分析仪分析,分析误差小于10%。
3. 测定结果
3.1 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素测定
研究区测定2件二长花岗岩样品(A井1405m,1500m)及花岗闪长岩样品(B井1387.6m,1555m),年龄数据舍弃了测试过程中受老核或后期裂隙影响的偏年轻和偏老的数据。对A井1405m样品测定了22颗锆石、22个分析点。U-Pb分析结果表明(表 1)),校正后的锆石有效数据点为16个,其所测锆石的阴极发光图像、测定点位和相应的206Pb/238U视年龄如图 3-a所示。锆石阴极发光图像显示,锆石为双锥柱状晶形,自形程度较高,具有明显的岩浆振荡环带,个别颗粒中心存在明显的核部,为继承性锆石的残留。所测锆石颗粒的Th、U含量变化不大,分别为49.93×10-6~801.83×10-6和61.77× 10-6~1497.96×10-6,Th/U值为0.08~1.85,锆石颗粒阴极发光特征及Th/U值均反映出岩浆锆石特征[18]。所测LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果见表 1、图 4-a。16个分析数据点在206Pb/238U-207Pb/ 235U谐和图上均落在谐和线上或其附近,获得的16个206Pb/238U年龄数据集中于159±2~178±3Ma之间,给出的年龄加权平均值为164.2 ± 1.9Ma(n=16,MSWD=0.60)。
表 1 渤海海域庙西北凸起中生代花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb测年数据Table 1. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb dating data for Mesozoic granite of Miaoxibei uplift in Bohai Sea area测试点号 含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Th U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 208Pb/232Th 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 208Pb/232Th 1σ A-1405-2 155 402 0.39 0.0489 0.0011 0.1786 0.0041 0.0266 0.0004 0.0014 0.0000 141 54 167 3 169 3 27.3 0.8 A-1405-3 132 170 0.77 0.0486 0.0024 0.1818 0.0089 0.0273 0.0005 0.0032 0.0002 127 114 170 8 173 3 65 3 A-1405-4 239 387 0.62 0.0498 0.0016 0.1735 0.0055 0.0253 0.0004 0.0047 0.0002 188 77 162 5 161 2 95 5 A-1405-7 128 353 0.36 0.0497 0.0015 0.1734 0.0051 0.0254 0.0004 0.0044 0.0002 179 71 162 4 162 2 89 4 A-1405-8 320 615 0.52 0.0475 0.0012 0.1665 0.0042 0.0255 0.0004 0.0031 0.0001 74 57 156 4 162 2 62 3 A-1405-9 192 342 0.56 0.0485 0.0011 0.1771 0.0040 0.0266 0.0004 0.0039 0.0001 123 54 166 3 169 2 79 2 A-1405-10 341 569 0.60 0.0509 0.0012 0.1747 0.0041 0.0250 0.0004 0.0025 0.0001 234 54 163 4 159 2 50 1 A-1405-11 114 62 1.85 0.0499 0.0033 0.1775 0.0115 0.0258 0.0005 0.0065 0.0003 188 150 166 10 164 3 132 7 A-1405-14 142 157 0.90 0.0486 0.0029 0.1727 0.0100 0.0258 0.0005 0.0062 0.0005 128 134 162 9 164 3 125 10 A-1405-15 135 310 0.44 0.0482 0.0014 0.1768 0.0053 0.0266 0.0004 0.0024 0.0001 107 69 165 5 169 3 49 2 A-1405-16 366 282 1.30 0.0509 0.0016 0.1781 0.0054 0.0254 0.0004 0.0074 0.0005 236 73 166 5 162 2 148 10 A-1405-17 98 411 0.24 0.0478 0.0013 0.1744 0.0048 0.0264 0.0004 0.0069 0.0006 91 65 163 4 168 2 139 11 A-1405-18 802 1498 0.54 0.0500 0.0007 0.1770 0.0029 0.0257 0.0004 0.0031 0.0001 196 35 166 3 163 2 63 2 A-1405-20 550 755 0.73 0.0495 0.0012 0.1759 0.0043 0.0258 0.0004 0.0013 0.0001 172 57 165 4 164 3 26 1 A-1405-21 134 328 0.41 0.0502 0.0013 0.1784 0.0045 0.0258 0.0004 0.0063 0.0004 203 59 167 4 164 2 128 8 A-1405-22 50 650 0.08 0.0485 0.0010 0.1718 0.0037 0.0257 0.0004 0.0059 0.0005 123 51 161 3 164 2 119 9 A-1500-1 180 417 0.43 0.0501 0.0017 0.2041 0.0068 0.0294 0.0005 0.0013 0.0001 201 82 189 6 187 3 25 1 A-1500-2 188 484 0.39 0.0488 0.0017 0.1701 0.0057 0.0253 0.0004 0.0062 0.0006 138 81 159 5 161 2 124 12 A-1500-4 432 1108 0.39 0.0492 0.0008 0.2288 0.0036 0.0337 0.0005 0.0009 0.0000 158 37 209 3 214 3 17.4 0.4 A-1500-6 146 268 0.55 0.0496 0.0016 0.2110 0.0065 0.0310 0.0006 0.0007 0.0000 175 79 194 5 197 4 13.1 0.6 A-1500-7 155 78 1.98 0.0501 0.0039 0.1712 0.0132 0.0248 0.0005 0.0027 0.0002 199 179 160 11 158 3 55 3 A-1500-9 246 457 0.54 0.0489 0.0015 0.1694 0.0051 0.0251 0.0004 0.0061 0.0006 143 72 159 4 160 2 123 12 A-1500-10 60 169 0.36 0.0499 0.0024 0.1874 0.0088 0.0273 0.0005 0.0038 0.0004 190 111 174 8 173 3 77 7 A-1500-11 284 780 0.36 0.0503 0.0011 0.1892 0.0044 0.0273 0.0004 0.0015 0.0001 208 53 176 4 174 3 31 2 A-1500-12 153 383 0.40 0.0485 0.0011 0.1667 0.0040 0.0249 0.0003 0.0039 0.0002 124 57 157 3 159 2 79 3 A-1500-14 74 56 1.32 0.0509 0.0027 0.2155 0.0110 0.0307 0.0006 0.0009 0.0000 235 121 198 9 195 3 18.6 0.6 A-1500-16 139 278 0.50 0.0484 0.0017 0.1700 0.0060 0.0255 0.0004 0.0044 0.0003 117 83 159 5 162 2 88 6 A-1500-17 270 164 1.65 0.0477 0.0012 0.1678 0.0043 0.0255 0.0004 0.0011 0.0000 82 59 157 4 162 2 23 0.4 A-1500-20 189 391 0.48 0.0512 0.0012 0.2408 0.0055 0.0341 0.0006 0.0007 0.0000 252 56 219 5 216 3 14.5 0.4 B-1387.6-2 122 384 0.32 0.0487 0.0012 0.1788 0.0045 0.0267 0.0004 0.1788 0.0045 133 59 167 4 170 3 3324 76 B-1387.6-3 267 555 0.48 0.0491 0.0009 0.1744 0.0033 0.0258 0.0003 0.1744 0.0033 153 43 163 3 164 2 3248 56 B-1387.6-4 292 474 0.62 0.0514 0.0009 0.1815 0.0032 0.0256 0.0003 0.1815 0.0032 261 39 169 3 163 2 3371 55 B-1387.6-5 90 304 0.30 0.0490 0.0017 0.1706 0.0058 0.0253 0.0004 0.1706 0.0058 147 82 160 5 161 3 3183 100 B-1387.6-6 107 182 0.59 0.0502 0.0019 0.1797 0.0068 0.0260 0.0004 0.1797 0.0068 202 92 168 6 165 3 3340 117 B-1387.6-8 48 128 0.38 0.0486 0.0019 0.1746 0.0065 0.0260 0.0005 0.1746 0.0065 128 90 163 6 166 3 3252 112 B-1387.6-13 275 691 0.40 0.0481 0.0010 0.1713 0.0035 0.0258 0.0004 0.1713 0.0035 104 48 161 3 164 2 3196 61 B-1387.6-14 76 269 0.28 0.0492 0.0014 0.1744 0.0048 0.0257 0.0004 0.0079 0.0005 155 67 163 4 164 2 158 9 B-1387.6-16 212 149 1.43 0.0500 0.0025 0.1801 0.0088 0.0261 0.0005 0.0018 0.0001 196 116 168 8 166 3 36 2 B-1387.6-19 96 272 0.35 0.0487 0.0021 0.1781 0.0074 0.0265 0.0005 0.0007 0.0001 135 99 166 6 169 3 14 1 B-1387.6-20 72 269 0.27 0.0507 0.0014 0.1814 0.0050 0.0260 0.0004 0.0037 0.0002 225 64 169 4 165 2 75 4 B-1387.6-21 78 160 0.49 0.0485 0.0022 0.1760 0.0078 0.0263 0.0005 0.0020 0.0001 125 103 165 7 167 3 40 2 B-1387.6-22 143 331 0.43 0.0499 0.0011 0.1790 0.0041 0.0260 0.0004 0.0066 0.0003 188 54 167 4 166 2 133 7 B-1555-1 293 737 0.40 0.0488 0.0010 0.1650 0.0034 0.0245 0.0003 0.0066 0.0003 139 49 155 3 156 2 133 7 B-1555-2 127 364 0.35 0.0481 0.0017 0.1704 0.0058 0.0257 0.0004 0.0013 0.0001 104 80 160 5 164 3 26 1 B-1555-3 100 429 0.23 0.0465 0.0017 0.1638 0.0060 0.0255 0.0004 0.0034 0.0002 25 78 154 5 163 3 69 4 B-1555-4 136 336 0.40 0.0491 0.0014 0.1682 0.0048 0.0249 0.0004 0.0068 0.0004 152 69 158 4 158 2 137 8 B-1555-5 112 329 0.34 0.0500 0.0017 0.1733 0.0059 0.0252 0.0004 0.0068 0.0006 193 82 162 5 160 2 138 11 B-1555-7 595 908 0.66 0.0518 0.0013 0.1705 0.0041 0.0239 0.0003 0.0074 0.0006 274 58 160 4 152 2 148 12 B-1555-8 374 655 0.57 0.0485 0.0010 0.1694 0.0035 0.0254 0.0003 0.0059 0.0003 123 49 159 3 161 2 118 6 B-1555-9 380 714 0.53 0.0483 0.0010 0.1666 0.0033 0.0250 0.0003 0.0057 0.0003 113 48 156 3 159 2 116 7 B-1555-11 358 577 0.62 0.0494 0.0010 0.1688 0.0034 0.0248 0.0003 0.0048 0.0003 167 47 158 3 158 2 96 5 B-1555-14 171 191 0.90 0.0488 0.0016 0.1739 0.0057 0.0258 0.0004 0.0064 0.0004 139 78 163 5 164 2 128 8 B-1555-15 225 514 0.44 0.0503 0.0014 0.1800 0.0051 0.0259 0.0004 0.0078 0.0007 210 67 168 4 165 2 157 13 B-1555-16 102 457 0.22 0.0487 0.0012 0.1743 0.0042 0.0259 0.0004 0.0064 0.0004 135 57 163 4 165 2 129 9 B-1555-21 40 152 0.27 0.0511 0.0027 0.1816 0.0094 0.0258 0.0005 0.0025 0.0002 244 124 169 8 164 3 51 4 B-1555-22 227 474 0.48 0.0479 0.0017 0.1773 0.0062 0.0268 0.0004 0.0076 0.0009 95 80 166 5 171 3 152 19 B-1555-23 122 294 0.42 0.0489 0.0014 0.1781 0.0050 0.0264 0.0004 0.0042 0.0003 141 67 166 4 168 3 85 5 对A井1500m样品测定了20颗锆石、20个分析点。U-Pb分析结果表明(表 1),校正后的锆石有效数据点为13个,其所测锆石的阴极发光图像、测定点位和相应的206Pb/238U视年龄如图 3-b所示。1405m样品的锆石颗粒阴极发光特征及Th/U值也反映出岩浆锆石的特征。所测LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果见表 1、图 4-b。13个数据点在206Pb/238U-207Pb/235U谐和图上均落在谐和线上或其附近,13个206Pb/238U年龄值变化较大,在159±2~216±3Ma之间,其年龄集中段(150~170Ma)给出的年龄加权平均值为160.6 ± 1.7Ma(n=6,MSWD=0.5)。
对B井1387.6m样品测定了24颗锆石、24个分析点。U-Pb分析结果表明(表 1),校正后的锆石有效数据点为16个,锆石的阴极发光图像、测定点位和相应的206Pb/238U视年龄如图 3-c所示。与二长花岗岩相似的锆石阴极发光图像显示,锆石为双锥柱状晶形,自形程度较高,所测锆石颗粒的Th、U含量分别为48.34×10-6~292.25× 10-6和127.86×10-6~690.52×10-6,Th/U值为0.27~ 1.43,为岩浆锆石特征。所测LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果见表 1、图 4-c。16个数据点在206Pb/238U-207Pb/235U谐和图上均落在谐和线上或其附近,16个206Pb/238U年龄集中于155±3~ 170 ± 3Ma之间,给出的年龄加权平均值分别为155.4 ± 2.5Ma(n=3,MSWD=0.07)和165.0 ± 1.3Ma(n=13,MSWD=0.75)。
B井1555m样品测定了23颗锆石、23个分析点,U-Pb分析结果表明(表 1),校正后的锆石有效数据点为15个,其所测锆石的阴极发光图像、测定点位和相应的206Pb/238U视年龄如图 3-d所示。所测样品的Th/U值为0.22~0.9,同样为岩浆锆石特征。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果见表 1、图 4-d。15个数据点在206Pb/238U-207Pb/235U谐和图上均落在谐和线上或其附近,15个206Pb/238U年龄集中于152±2~171±3Ma之间,给出的年龄加权平均值为160.9±2.6Ma(n=15,MSWD=0.93)。
3.2 地球化学特征
表 2列出了庙西北凸起所测花岗岩样品的主量、微量、稀土元素测定结果及计算所得的有关参数,其中花岗闪长岩样品采自B井、C井、D井(具体深度见表 2,C、D井井位坐标见图 1),二长花岗岩样品采自A井(具体深度见表 2)。
表 2 庙西北凸起中生代花岗岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析数据Table 2. Major, trace and rare earth element data for Mesozoic granite of Miaoxibei uplift元素 B井/m C井/m D井/m 1387.4 1492.5 1493.6 1498 1499.4 1502 1503.95 1505.6 1511.9 1514.85 1518.37 1518.6 1602.85 1603.77 1604 1605.5 1605.79 1640.76 SiO2 68.20 68.55 68.91 68.59 68.51 68.74 68.80 69.05 66.57 69.48 70.41 71.77 67.65 68.34 68.64 67.73 67.81 68.19 Al2O3 15.00 17.19 16.28 16.19 15.72 16.36 16.58 16.31 14.84 15.69 15.80 14.93 16.32 16.51 16.74 16.45 16.25 15.79 TFe2O3 2.44 2.06 2.62 3.23 3.86 3.31 2.74 2.71 2.83 2.51 2.29 2.12 3.64 3.15 2.96 3.31 3.42 3.35 MgO 0.65 0.37 0.48 0.52 0.53 0.51 0.48 0.54 0.48 0.48 0.37 0.43 0.51 0.59 0.55 0.62 0.57 0.83 CaO 3.10 1.78 2.13 2.42 2.35 2.70 2.58 2.50 3.05 1.23 2.19 2.30 0.65 0.89 0.64 0.75 0.74 3.06 Na2O 4.99 5.51 4.53 4.92 4.68 4.86 4.78 4.89 4.12 4.61 4.68 4.41 5.10 4.52 4.60 4.51 4.94 4.44 K2O 2.89 2.94 3.41 2.52 2.44 2.89 3.31 2.98 2.89 3.17 2.79 2.76 3.27 3.33 3.48 3.85 3.54 2.72 MnO 0.07 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.23 0.08 0.07 0.07 0.27 0.06 0.05 0.06 0.09 0.13 0.05 0.15 0.07 0.08 TiO2 0.19 0.22 0.23 0.23 0.23 0.22 0.19 0.23 0.10 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.26 0.28 0.28 0.27 0.24 0.30 P2O5 0.09 0.10 0.09 0.10 0.09 0.10 0.08 0.10 0.09 0.15 0.09 0.09 0.12 0.14 0.13 0.13 0.13 0.13 FeO 1.15 1.00 0.95 1.45 1.30 0.90 1.45 1.45 1.50 0.90 0.95 0.95 2.55 1.90 1.95 1.65 1.75 1.70 烧失量 2.30 1.24 1.25 1.19 1.34 0.20 0.37 0.59 4.71 2.39 1.12 0.91 2.35 2.11 1.91 2.22 2.27 1.09 总量 97.63 98.76 98.73 98.79 98.64 99.77 99.62 99.37 95.24 97.57 98.87 99.07 97.62 97.87 98.07 97.76 97.71 98.88 ALK 7.88 8.45 7.94 7.44 7.12 7.75 8.09 7.87 7.01 7.78 7.47 7.17 8.37 7.85 8.08 8.36 8.48 7.16 AKI 0.53 0.49 0.49 0.46 0.45 0.47 0.49 0.48 0.47 0.50 0.47 0.48 0.51 0.48 0.48 0.51 0.52 0.45 K/Na 0.58 0.53 0.75 0.51 0.52 0.59 0.69 0.61 0.70 0.69 0.60 0.63 0.64 0.74 0.76 0.85 0.72 0.61 A/NKC 1.37 1.68 1.62 1.64 1.66 1.57 1.55 1.57 1.48 1.74 1.64 1.58 1.81 1.89 1.92 1.81 1.76 1.55 δ 2.46 2.79 2.43 2.16 1.99 2.33 2.54 2.38 2.08 2.29 2.04 1.79 2.84 2.43 2.55 2.83 2.90 2.04 La 33.40 27.20 25.40 30.50 23.70 29.30 29.60 45.90 35.20 36.80 33.80 25.50 26.30 28.90 39.80 40.70 44.80 27.20 Ce 60.50 50.00 46.70 54.90 43.10 52.70 52.90 79.40 62.70 62.20 63.30 44.70 49.90 51.70 71.00 71.20 76.00 50.10 Pr 6.89 5.45 5.48 6.10 4.76 6.20 5.83 8.74 6.68 7.12 7.45 4.92 5.34 5.74 7.86 7.96 8.88 6.12 Nd 24.30 20.50 21.20 23.50 18.90 24.60 21.40 33.00 24.60 27.70 29.30 19.00 20.80 21.80 31.20 31.60 35.50 25.60 Sm 3.35 3.39 3.56 3.19 2.71 3.74 2.98 4.21 3.42 3.96 4.50 2.75 2.85 2.82 4.44 3.99 4.63 3.80 Eu 1.17 1.25 1.68 1.22 0.97 1.33 1.22 1.44 4.68 2.63 1.45 1.10 1.22 1.02 1.25 1.84 1.65 1.43 Gd 2.60 2.55 3.11 2.74 2.37 2.89 2.69 3.25 5.25 3.73 3.44 2.91 2.53 2.16 3.52 3.72 3.76 3.73 Tb 0.32 0.31 0.42 0.35 0.28 0.38 0.31 0.40 0.36 0.39 0.48 0.37 0.26 0.26 0.42 0.41 0.40 0.49 Dy 1.70 1.69 2.20 1.87 1.70 2.18 1.62 2.20 1.77 2.01 2.56 1.86 1.26 1.45 1.79 1.88 1.77 2.45 Ho 0.31 0.29 0.43 0.31 0.30 0.34 0.26 0.32 0.29 0.33 0.42 0.32 0.25 0.26 0.33 0.33 0.30 0.46 Er 0.81 0.77 1.20 0.92 0.86 1.07 0.73 1.03 1.01 1.02 1.20 0.96 0.70 0.70 0.92 0.90 0.86 1.20 Tm 0.13 0.12 0.19 0.17 0.15 0.17 0.13 0.18 0.13 0.17 0.22 0.15 0.12 0.12 0.15 0.16 0.13 0.19 Yb 0.84 0.98 1.41 1.00 0.92 1.39 0.73 0.98 0.99 1.00 1.18 0.97 0.66 0.80 1.07 0.99 0.85 1.16 Lu 0.13 0.13 0.18 0.18 0.14 0.19 0.11 0.14 0.13 0.14 0.18 0.12 0.11 0.13 0.15 0.15 0.13 0.15 Li 9.94 18.70 19.90 25.80 19.30 24.60 21.40 22.30 16.40 16.00 17.30 13.20 10.30 11.20 9.15 12.00 14.90 20.30 Be 0.76 1.80 1.42 1.61 1.69 1.84 1.40 1.36 1.44 1.47 1.41 1.20 1.17 1.55 1.89 1.45 1.58 1.44 Sc 2.52 2.70 3.04 2.79 2.66 2.79 2.64 2.96 3.03 2.99 3.17 2.55 3.06 3.01 3.27 3.24 3.33 3.37 V 30.60 23.90 27.10 27.90 26.20 31.70 25.60 27.30 35.10 23.80 27.90 25.00 34.70 37.80 38.40 40.70 39.90 44.80 Cr 6.20 128.00 11.20 11.80 11.80 11.60 9.37 10.10 12.00 12.40 10.10 10.40 11.50 11.00 10.90 12.70 14.90 12.80 Co 3.01 3.49 3.69 3.56 9.03 3.89 3.39 3.77 3.57 2.81 3.44 2.80 4.09 3.41 3.83 4.43 4.54 4.83 Ni 4.49 5.70 5.81 4.46 5.24 5.15 4.24 4.28 5.35 4.26 3.84 4.10 3.17 2.54 3.03 3.94 4.38 4.71 Cu 8.29 11.00 13.20 12.00 15.30 15.40 10.10 9.37 20.20 16.30 10.50 9.60 13.50 13.30 9.59 14.20 18.80 13.90 Zn 40.90 59.00 53.10 54.90 49.40 82.80 43.80 58.20 120.00 70.20 53.90 45.80 50.00 45.20 47.50 55.90 55.30 57.60 Ga 16.00 20.50 17.70 20.10 17.60 21.10 18.00 20.80 19.10 20.00 20.50 17.70 18.30 19.00 19.20 21.30 21.30 19.60 Rb 71.70 81.80 84.70 73.80 61.90 82.70 75.30 79.40 94.60 115.00 75.10 69.10 83.90 89.30 104.00 103.00 98.30 68.00 Sr 843 797 783 783 679 909 808 846 820 649 845 751 539 489 485 642 740 904 Y 9.03 8.86 12.90 9.97 9.00 11.50 7.96 10.30 9.27 10.50 13.40 10.40 7.29 7.19 9.72 9.72 8.80 13.50 Nb 6.22 11.40 8.47 6.92 6.46 8.09 5.62 6.68 5.67 7.64 8.86 7.06 6.22 6.07 8.14 6.74 7.69 8.49 Mo 0.34 0.72 0.75 0.87 1.87 0.77 0.40 0.46 1.03 0.87 0.26 0.43 0.45 0.19 0.23 0.84 1.06 0.43 Cd 0.49 0.06 0.08 0.02 0.04 0.07 0.09 0.08 0.37 0.10 0.05 0.06 0.04 0.04 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.03 In 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.02 0.01 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.03 元素 B井/m C井/m D井/m 1387.4 1492.5 1493.6 1498 1499.4 1502 1503.95 1505.6 1511.9 1514.85 1518.37 1518.6 1602.85 1603.77 1604 1605.5 1605.79 1640.76 Sb 0.19 0.12 0.34 0.28 0.37 0.29 0.13 0.15 7.59 2.99 0.12 0.12 0.44 0.21 0.31 0.59 0.34 0.14 Cs 0.77 1.43 1.34 1.16 1.14 1.11 0.95 1.19 1.55 1.91 0.93 0.75 1.69 1.40 2.12 1.53 1.62 1.70 Ba 1265 841 1498 706 723 861 1021 1002 6392 3087 888 816 1347 1018 1076 2142 1728 1174 Ta 0.42 0.55 0.63 0.47 0.44 0.58 0.38 0.46 0.41 0.53 0.52 0.48 0.44 0.45 0.61 0.53 0.59 0.72 W 0.35 8.04 0.36 0.31 0.26 0.15 0.10 0.10 0.84 1.39 0.16 0.09 0.34 0.56 2.05 0.78 0.60 0.13 Tl 0.46 0.49 0.52 0.47 0.62 0.45 0.41 0.43 1.59 1.10 0.38 0.39 0.52 0.47 0.61 0.63 0.56 0.35 Pb 18.80 19.50 24.70 21.40 326.00 24.20 20.60 23.50 177.00 63.40 28.20 21.40 24.00 15.50 16.10 28.10 21.60 19.90 Bi 0.06 0.09 0.13 0.05 0.05 0.04 0.03 0.03 0.04 0.06 0.03 0.03 0.11 0.06 0.05 0.05 0.04 0.02 Th 4.02 3.57 3.97 6.34 3.22 3.95 3.31 7.97 3.50 4.06 4.41 2.80 3.99 3.60 4.35 4.66 5.50 3.13 U 2.77 5.67 7.40 3.53 3.95 8.14 3.68 1.90 1.42 2.23 0.80 0.51 1.38 1.12 1.00 1.14 1.37 0.80 Zr 43.90 70.10 53.60 62.70 58.00 67.20 46.90 52.60 36.50 46.30 43.00 36.50 35.90 32.70 31.40 26.70 26.60 31.70 Hf 1.34 2.37 1.95 2.01 1.88 2.27 1.54 1.80 1.09 1.39 1.56 1.18 1.39 1.15 1.24 0.89 1.13 1.18 δEu 1.21 1.30 1.54 1.26 1.17 1.24 1.32 1.19 3.38 2.09 1.13 1.19 1.39 1.26 0.97 1.46 1.21 1.16 ∑REE 145.48 123.50 126.05 136.91 109.86 137.98 128.47 191.49 156.48 159.69 162.88 116.04 119.59 125.04 173.62 175.54 188.45 137.57 LREE 129.61 107.79 104.02 119.41 94.14 117.87 113.93 172.69 137.28 140.41 139.80 97.97 106.41 111.98 155.55 157.29 171.46 114.25 HREE 6.84 6.85 9.13 7.53 6.72 8.61 6.58 8.50 9.93 8.78 9.68 7.67 5.89 5.87 8.35 8.53 8.19 9.82 LREE/HREE 18.94 15.74 11.39 15.86 14.00 13.69 17.31 20.33 13.82 15.98 14.44 12.78 18.06 19.08 18.63 18.43 20.93 11.63 元素 A井/m 1300 1320 1330 1340 1350 1360 1370 1380 1390 1410 1420 1435 1450 1460 1470 1475 1485 1500 SiO2 71.73 70.54 69.92 72.12 71.91 70.86 70.93 71.08 71.40 68.86 69.10 67.36 66.99 69.24 69.69 67.37 68.68 69.21 Al2O3 13.27 14.56 14.25 14.18 13.85 14.13 14.58 14.30 14.63 16.01 15.47 15.32 14.95 14.83 15.26 16.28 15.85 15.60 Fe2O3T 4.14 3.78 4.02 2.41 3.11 3.35 2.92 3.11 2.11 2.30 2.59 3.87 4.38 3.71 2.38 2.12 1.91 2.19 MgO 0.38 0.44 0.52 0.49 0.53 0.54 0.46 0.45 0.46 0.45 0.52 0.50 0.67 0.57 0.51 0.46 0.39 0.44 CaO 1.56 1.77 1.96 1.76 1.52 1.47 1.72 1.30 1.25 2.19 2.14 2.02 2.41 2.26 2.14 2.49 2.30 1.97 Na2O 3.51 3.91 4.02 3.86 3.91 3.60 3.98 4.03 4.16 4.38 4.13 4.08 4.39 3.84 4.18 4.42 4.44 4.41 K2O 3.76 3.91 3.79 3.85 3.69 4.31 4.08 4.06 4.24 4.29 4.24 4.13 4.11 3.93 4.12 4.55 4.06 4.50 MnO 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.07 0.09 0.09 0.06 0.06 0.05 0.07 TiO2 0.10 0.11 0.12 0.12 0.13 0.11 0.11 0.14 0.12 0.13 0.14 0.15 0.16 0.14 0.14 0.13 0.13 0.11 P2O5 0.05 0.06 0.08 0.05 0.05 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.04 0.07 0.06 0.07 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.06 0.06 0.05 FeO 3.55 3.00 3.10 1.60 2.20 2.50 2.50 2.60 1.35 1.15 1.75 2.75 3.45 2.70 1.70 1.30 1.00 1.30 烧失量 1.44 0.85 1.22 1.06 1.20 1.47 1.07 1.38 1.50 1.22 1.49 2.36 1.62 1.27 1.42 2.00 2.06 1.42 总量 98.55 99.15 98.74 98.91 98.75 98.49 98.90 98.59 98.46 98.74 98.45 97.56 98.20 98.67 98.53 97.95 97.88 98.55 ALK 7.27 7.82 7.81 7.71 7.60 7.91 8.06 8.09 8.40 8.67 8.37 8.21 8.50 7.77 8.30 8.97 8.50 8.91 AKI 0.55 0.54 0.55 0.54 0.55 0.56 0.55 0.57 0.57 0.54 0.54 0.54 0.57 0.52 0.54 0.55 0.54 0.57 K/Na 1.07 1.00 0.94 1.00 0.94 1.20 1.03 1.01 1.02 0.98 1.03 1.01 0.94 1.02 0.99 1.03 0.91 1.02 A/NKC 1.50 1.52 1.46 1.50 1.52 1.51 1.49 1.52 1.52 1.47 1.47 1.50 1.37 1.48 1.46 1.42 1.47 1.43 δ 1.84 2.22 2.27 2.04 2.00 2.25 2.33 2.33 2.48 2.91 2.68 2.77 3.01 2.30 2.58 3.30 2.81 3.03 La 13.90 12.60 12.40 14.20 17.50 16.40 18.80 13.40 21.90 25.10 17.10 20.40 18.60 19.70 27.60 27.00 28.50 24.70 Ce 26.30 23.90 23.10 25.90 32.60 30.50 35.00 24.50 38.30 46.20 32.30 37.40 33.90 36.70 49.90 50.30 52.00 45.10 Pr 2.90 2.83 2.67 2.92 3.71 3.37 3.83 2.71 3.82 5.16 3.72 4.16 3.90 4.13 5.52 5.64 5.69 5.12 Nd 11.20 9.83 9.12 10.50 12.80 11.50 13.30 10.30 13.50 18.10 13.10 15.40 14.30 14.90 19.30 19.80 20.00 17.70 Sm 1.76 1.50 1.27 1.71 2.05 1.86 1.97 1.40 1.91 2.62 1.99 2.18 1.98 2.28 2.39 2.84 2.70 2.69 Eu 0.78 0.77 0.82 0.82 0.84 0.85 0.85 0.70 0.76 0.93 0.68 0.83 0.71 0.84 0.90 0.99 1.09 0.96 Gd 1.21 1.25 0.91 1.17 1.33 1.16 1.20 1.03 1.44 1.78 1.44 1.53 1.60 1.61 1.83 2.07 1.97 1.93 Tb 0.20 0.17 0.16 0.19 0.20 0.19 0.16 0.12 0.15 0.24 0.21 0.19 0.20 0.22 0.20 0.21 0.24 0.25 Dy 1.09 0.65 0.79 0.99 0.95 0.82 1.04 0.64 0.99 1.19 1.14 1.13 1.09 1.19 1.23 1.12 1.40 1.24 Ho 0.19 0.15 0.13 0.16 0.19 0.18 0.16 0.15 0.18 0.20 0.17 0.22 0.23 0.20 0.22 0.26 0.24 0.25 Er 0.62 0.47 0.47 0.47 0.46 0.49 0.45 0.44 0.48 0.60 0.56 0.59 0.54 0.71 0.65 0.67 0.73 0.74 Tm 0.10 0.07 0.07 0.08 0.09 0.08 0.09 0.06 0.07 0.12 0.11 0.10 0.12 0.10 0.11 0.13 0.12 0.12 Yb 0.59 0.48 0.47 0.57 0.69 0.52 0.65 0.44 0.50 0.63 0.73 0.63 0.76 0.70 0.81 0.89 1.05 0.92 Lu 0.08 0.08 0.08 0.09 0.12 0.11 0.08 0.10 0.07 0.10 0.13 0.09 0.10 0.10 0.14 0.13 0.16 0.15 Li 17.00 20.90 23.20 18.00 19.90 23.90 21.40 20.30 25.50 20.90 22.70 22.00 26.10 22.80 19.00 16.00 24.80 23.60 元素 A井/m 1300 1320 1330 1340 1350 1360 1370 1380 1390 1410 1420 1435 1450 1460 1470 1475 1485 1500 Be 1.42 1.18 1.44 1.18 1.82 1.57 1.05 1.59 1.31 1.50 1.63 1.47 1.82 1.60 2.36 1.86 2.07 2.24 Sc 2.26 2.28 2.06 2.25 2.20 2.30 2.23 2.26 2.12 2.08 2.49 2.48 2.71 2.60 1.97 2.23 2.40 2.46 V 34.30 19.00 23.40 25.60 23.30 22.60 25.40 20.20 15.90 18.80 18.30 20.60 21.00 18.10 18.10 18.90 18.10 22.40 Cr 12.60 8.64 6.78 10.90 10.00 11.60 15.20 9.91 14.80 9.12 22.50 20.50 16.00 13.10 8.32 6.74 14.00 8.14 Co 4.29 3.52 3.10 3.65 9.46 3.00 3.06 2.56 2.71 3.09 5.02 6.12 4.45 3.45 2.43 2.41 3.10 3.47 Ni 5.03 4.71 3.60 4.53 8.84 4.54 5.31 3.14 4.57 3.68 6.25 5.52 4.62 3.77 3.23 2.78 3.82 4.04 Cu 8.67 9.02 6.07 9.42 7.85 6.84 8.60 5.45 7.25 7.60 12.00 11.50 8.68 6.51 8.55 6.71 6.12 6.71 Zn 39.50 42.40 40.40 45.00 40.30 66.90 61.50 43.30 48.10 48.80 51.70 60.10 48.70 45.30 41.70 38.70 42.30 51.90 Ga 15.50 17.10 16.70 17.20 16.80 15.60 18.10 18.00 17.70 19.40 18.60 19.20 18.90 20.10 21.40 21.20 21.70 20.50 Rb 88.50 89.20 93.50 97.70 103.00 105.00 99.30 108.00 97.80 97.80 112.00 97.00 110.00 117.00 122.00 112.00 117.00 116.00 Sr 617 646 665 634 615 766 627 575 746 818 678 724 758 780 746 713 850 733 Y 5.64 5.12 4.71 5.03 5.95 5.67 5.26 4.26 5.21 6.19 6.41 6.18 6.49 6.67 7.39 7.36 7.52 7.78 Nb 4.68 4.60 4.65 5.41 5.66 5.57 6.12 5.25 4.89 5.41 6.37 5.17 5.70 6.27 7.18 7.27 6.47 6.84 Mo 0.87 0.76 0.61 1.25 1.25 1.64 3.01 1.01 0.78 1.16 2.78 2.28 1.89 1.14 1.15 0.93 1.44 0.54 Cd 0.08 0.04 0.03 0.01 0.04 0.11 0.04 0.06 0.04 0.07 0.05 0.05 0.07 0.04 0.03 0.08 0.04 0.17 In 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.03 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.02 Sb 0.39 0.17 0.15 0.33 0.14 0.27 0.30 0.23 0.24 0.18 0.51 0.44 0.33 0.29 0.23 0.20 0.31 0.92 Cs 1.05 0.89 0.97 1.05 1.15 1.31 1.16 1.29 1.13 1.16 1.33 1.33 1.61 1.50 1.30 1.12 1.19 1.46 Ba 1384 1258 1317 1261 1424 1703 1270 1271 1658 1682 1332 1446 1447 1500 1536 1447 1813 1516 Ta 0.31 0.29 0.29 0.34 0.53 0.37 0.38 0.29 0.38 0.39 0.46 0.38 0.35 0.40 0.60 0.55 0.53 0.50 W 5.85 2.35 5.54 4.46 86.10 2.79 2.89 2.29 2.26 3.30 7.36 18.10 5.90 2.93 2.49 1.72 3.13 3.48 Tl 0.52 0.50 0.49 0.57 0.54 0.56 0.54 0.64 0.57 0.53 0.70 0.61 0.68 0.64 0.76 0.64 0.73 0.63 Pb 22.90 18.80 18.50 20.50 22.10 23.50 20.90 19.00 20.10 21.60 28.10 23.60 25.70 24.60 28.90 23.10 30.00 30.80 Bi 0.03 0.03 0.01 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.03 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.04 0.02 0.03 0.03 Th 2.23 2.40 1.66 2.01 2.55 2.33 2.62 2.17 3.24 3.69 3.29 3.71 2.82 3.17 4.06 4.64 4.06 3.61 U 0.63 0.67 0.49 0.85 0.74 1.19 0.68 0.56 0.61 0.74 1.37 1.41 0.72 0.80 1.18 0.76 1.04 0.72 Zr 35.50 22.00 22.50 24.00 33.60 27.90 32.30 26.30 37.30 40.70 43.30 34.60 39.10 42.70 43.80 41.00 50.60 45.90 Hf 1.35 0.94 1.27 1.23 1.53 1.20 1.42 1.27 1.78 1.80 1.92 1.27 1.44 1.67 1.92 1.90 2.10 2.26 δEu 1.63 1.71 2.33 1.77 1.56 1.78 1.69 1.78 1.41 1.31 1.23 1.40 1.22 1.33 1.32 1.25 1.45 1.29 ∑REE 66.56 59.86 57.16 64.79 79.48 73.69 82.85 60.25 89.27 109.15 79.78 91.03 84.51 90.05 118.19 119.41 123.40 109.64 LREE 56.84 51.43 49.38 56.05 69.50 64.48 73.75 53.01 80.19 98.11 68.89 80.37 73.39 78.55 105.61 106.57 109.98 96.27 HREE 4.08 3.31 3.07 3.71 4.02 3.54 3.84 2.98 3.87 4.86 4.48 4.48 4.63 4.83 5.19 5.48 5.90 5.59 LREE/HREE 13.93 15.53 16.07 15.09 17.28 18.24 19.23 17.81 20.72 20.20 15.39 17.95 15.84 16.26 20.37 19.45 18.63 17.21 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素为10-6 3.2.1 主量元素
花岗闪长岩与二长花岗岩主量元素具有相似性,其平均SiO2含量分别为68.60%和69.67%;ALK(K2O+Na2O)含量分别为7.79%和8.19%;两者A/NCK值分别为1.62和1.47,说明样品均为铝过饱和;SiO2-(Na2O+ K2O)图解(图 5-a)中[19],样品点均落于亚碱性区域内;SiO2-FeO*/MgO图解(图略)中[20],样品点落于钙碱性区域内,花岗闪长岩和二长花岗岩里特曼指数(σ)分别为1.79~2.90和1.84~3.30,均为钙碱性系列;A/CNK-A/NK图解(图 5-b)显示,样品均为(强)过铝质。此外,蓬莱9-1构造花岗闪长岩的烧失量为0.2%~4.7%,二长花岗岩烧失量为0.9%~2.7%,说明样品经历了强烈的剥蚀作用。
在Harker图解上,花岗闪长岩与二长花岗岩表现出不同的演化特征(图略)。花岗闪长岩中MgO、TFeO含量与SiO2含量呈负相关,而二长花岗岩中MgO、TFeO含量与SiO2含量呈弱的正相关或相关性差,说明花岗闪长岩形成过程中,铁镁质矿物对其有一定的贡献。
3.2.2 微量及稀土元素
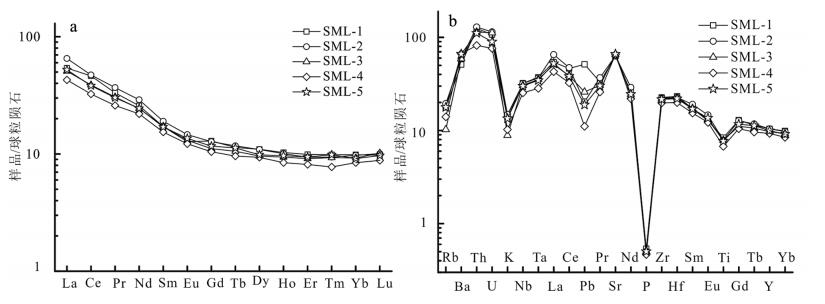
花岗闪长岩样品稀土元素总量(ΣREE)介于110×10-6~191×10-6之间,平均值为145×10-6;轻稀土元素(LREE)含量介于94×10-6~172×10-6之间,平均值为127×10-6;重稀土元素(HREE)含量介于6×10-6~ 10×10-6之间,平均值为8×10-6;LREE/HREE值介于11.39~20.93之间,平均值为16.17,说明轻、重稀土元素分异明显。二长花岗岩样品稀土元素总量介于57×10-6~123×10-6之间,平均值为87×10-6;LREE含量变化范围介于49×10-6~110×10-6之间,平均值为76×10-6;HREE含量变化范围介于3×10-6~ 6×10-6之间,平均值为4%;LREE/HREE值介于13.93~20.72之间,平均值为17.64,同样说明轻、重稀土元素分异明显。2种岩性样品(Ce/Yb)N值显示,两者整体具有重稀土元素亏损、轻稀土元素富集的特征,且δEu均大于1,说明Eu具有正异常。
2种样品在球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式图(图 6)和原始地幔标准化蛛网图(图 7)中分布规律一致,所有样品的稀土元素配分曲线整体形态一致,表现出轻稀土元素富集、重稀土元素亏损的右倾平滑曲线,Eu明显正异常。从原始地幔标准化蛛网图可以看出,大离子亲石元素(LILE)富集程度较强,在蛛网图中表现为明显的峰,如Pb、Sr;而高场强元素(HFSE)则表现出一定的亏损,在蛛网图中为明显的谷,如Th、Nb、Zr等。
![]() 图 6 庙西北凸起中生代花岗岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式图解(球粒陨石标准化值据参考文献[20])Figure 6. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns for Mesozoic granite of Miaoxibei uplift
图 6 庙西北凸起中生代花岗岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式图解(球粒陨石标准化值据参考文献[20])Figure 6. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns for Mesozoic granite of Miaoxibei uplift![]() 图 7 庙西北凸起中生代花岗岩微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(原始地幔标准化值据参考文献[20])Figure 7. Primitive-mantle-normalized trace element patterns for Mesozoic granite of Miaoxibei uplift
图 7 庙西北凸起中生代花岗岩微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(原始地幔标准化值据参考文献[20])Figure 7. Primitive-mantle-normalized trace element patterns for Mesozoic granite of Miaoxibei uplift4. 讨论
4.1 花岗岩形成年代
受限于海域内钻井数量和年代分析数据不足,火山岩中缺乏古生物证据,海域内火山岩年代学一直存在争议。前人认为,研究区花岗岩年代为太古宙,但本文采用精确度较高的LA-ICP-MS锆石UPb测年,对构造区花岗岩进行系统的年代学测定,得到的二长花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄加权平均值为164.2±1.9Ma(样品A-1405)和160.6± 1.7Ma(样品A-1500),花岗闪长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄加权平均值为155.4±2.5Ma、165.0± 1.3Ma(样品B-1387.6)、160.9 ± 2.6Ma(样品B-1555)。根据本次锆石阴极发光图像,锆石具有明显的韵律环带,反映锆石是在岩浆房形成的。对于这类锆石有学者认为,最年轻颗粒的年龄最接近火山喷发的年龄,可以用最年轻锆石的年龄代表火山的喷发年龄[21]。本次研究获得的最年轻锆石U-Pb年龄为155.4±2.5Ma,该年龄被解释为岩浆结晶年龄,故潜山花岗岩形成时期为早、中侏罗世,为海域内首个中生界花岗岩潜山油藏。
受印支运动和燕山运动影响,华北板块在中生代发生广泛的火山活动,与之有关的火山岩许多学者进行了研究[22-26],认为晚印支运动形成的碱性岩局限地分散在华北板块,早燕山期的高Sr、低Y火山岩广泛分布于华北板块,晚燕山期火山岩则受控于郯庐断裂及大兴安岭-太行山脉。但对于渤海湾盆地,尤其是渤海海域之前对于火山岩的研究大多限于新生代火山岩[27-29],有学者对济阳坳陷中生界火山岩做了系统研究,将凹陷内中生界火山岩划分为6个时期[30]。本次研究所确定的花岗岩形成时期与华北地区早—中侏罗世(燕山早期)侵入岩形成时代中的第二个集中时段(155~175Ma,SHRIMP)吻合,意味着渤海海域中生代盆地演化与华北地区中生代火山活动有着密切关系。
4.2 源岩特征及花岗岩类型
原始地幔标准化蛛网图上,重稀土元素富集、轻稀土元素亏损,Sm/Nd值为0.15,正Eu异常,表明岩浆主要来源于上地壳物质的部分熔融,低稀土元素含量及高LREE/HREE值显示,源岩可能为角闪岩或榴辉岩,高Sr/Y值显示,在岩浆源区斜长石已经不稳定并开始熔融,残留相不存在或很少存在斜长石。区域地质研究也证实,花岗岩可能为下地壳来源。基于该认识,笔者认为,本区花岗岩是在早—中侏罗世地壳物质发生熔融上升侵入形成的。
花岗岩成因分类目前使用最广的是MISA型(即M、I、S和A型),对于不同成因类型花岗岩的划分前人给出大量的文献[31-33]。根据这些划分原则,研究区两类花岗岩均为过铝质S型花岗岩,主要表现为:① 铝饱和指数(A/CNK)介于1.13~1.92之间,均大于1.1,这与高分异I型花岗岩及铝质A型花岗岩存在差异[34];② 研究区花岗岩SiO2含量较小,K/ Na值较高,相对富钾与I型花岗岩相区分,同时TiO2和P2O5含量均大于0.1,碱铝指数(AKI)平均值(0.58)低于A型花岗岩下限值;③ 右倾球粒陨石标准化曲线配分样式,低Zr、Nb、Zn含量及低于350× 10-6的Zr+Nb+Ce+Y含量值,说明构造区花岗岩不同于A型花岗岩[31];④ P2O5含量随SO2含量增加基本保持不变,符合S型花岗岩特征[35]。
4.3 构造意义
华北板块经历了印支运动的改造后,在燕山期进入新的构造演化时期,其形成的南北成带、东西分块的区域构造格局发生了明显改变[30]。早、中侏罗世由于受扬子板块碰撞后持续效应的影响及构造应力的改变,使整个区域内火山岩发育。其侵入岩主要分布在燕山带的两侧,岩石类型以花岗岩、花岗闪长岩为主;喷出岩主要见于燕山、阴山、山东、辽西等地,以安山岩和玄武岩为主,火山作用主要集中在东部隆起区的断陷盆地内。研究区所获得的锆石U-Pb年龄证实,海域内在燕山期同样有明显的火山活动迹象,花岗岩(Y+Nb)-Rb判别图解[36](图 8-a)显示,构造区花岗岩均位于火山弧花岗岩(VAG)区;R1-R2因子判别图解[37](图 8-b)显示,研究区花岗岩形成于造山晚期和同碰撞的形成环境。基于这些图解推断,早—中侏罗世(燕山期早期)大洋板壳俯冲导致地幔橄榄岩发生熔融形成玄武质岩浆,岩浆底侵到下地壳,使下地壳增厚发生部分重融,最终形成花岗岩,正Eu异常也证实地壳增厚[38],晚期下地壳分离导致软流圈物质上涌,花岗质岩浆侵入形成。
这同整个华北地区区域背景吻合,侏罗纪前后扬子地块及佳蒙地块的影响,导致华北地台发育一套高Sr、低Y的钙碱性火山岩,目前大多数学者认为,这是由于地壳增厚导致下地壳熔融形成的[25, 39-41]。越来越多的学者开始将中国东部燕山期这套火山岩认定为埃达克质岩或C型埃达克质岩[25, 30, 39, 42-43]。研究区花岗岩在地球化学特征上与这套埃达克质岩具有很好的可对比性,实验岩石学资料证实,埃达克岩是在适当的温度(850~1150℃)和压力(1.0~4.0GPa)条件下由玄武质岩石部分熔融形成的[44-45]。张旗等[25]认为,晚侏罗世—早白垩世中国东部的埃达克岩呈面型分布,推测同样是大范围地壳加厚事件的产物。
综合研究认为,渤海海域在燕山期由于受扬子板块及佳蒙地块挤压,形成一套背景为同碰撞时期的火山弧环境的花岗岩,碰撞作用导致地壳快速缩短增厚,致使下地壳物质由于升温发生熔融上涌侵入,从而形成正Eu异常,重稀土元素亏损、轻稀土元素富集的过铝质S型花岗岩的形成,首次证实海域内燕山期同样存在东部高原现象。
5. 结论
(1)蓬莱9-1构造花岗岩分花岗闪长岩及二长花岗岩2类,测得的锆石U-Pb年龄表明花岗岩形成年代为早、中侏罗世,为渤海海域首个证实的中生代花岗岩油藏。
(2)地球化学分析认为,构造区花岗岩均具有高钾、富碱、强过铝质,重稀土元素亏损、轻稀土元素富集特征,正Eu异常,源岩为角闪岩或榴辉岩,是下地壳基性岩部分熔融形成的。
(3)渤海海域在燕山期同样受扬子板块及佳蒙地块挤压,发育一套与渤海湾盆地全区可对比的S型花岗岩或埃达克岩,首次证实海域内燕山期存在东部高原现象。
致谢: 西藏地质五队李玉彬、李彦波工程师在野外工作中给予帮助,中国地质大学(武汉)地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室刘勇胜、周炼、陈海红等老师进行了岩石样品的微量元素和Sr-Nd同位素测试;审稿专家提出了许多宝贵的意见和建议,在此一并表示感谢。 -
图 6 萨玛隆闪长岩的稀土元素配分模式(a)和微量元素蛛网图(b)
(球粒陨石标准化数据据参考文献[29])
Figure 6. Chondrite-normalized REE (a) and chondrite -normalized trace element patterns (b) for the Samalong diorite
图 7 萨玛隆闪长岩的Y-Sr/Y图解(a)和Yb-La/Yb图解[30](b)
(a)—榴辉岩(辉石:石榴子石=50: 50)部分熔融演化曲线;(b)—角闪岩含25%石榴子石的部分熔融(c)—角闪岩含10%石榴子石的部分熔融演化曲线;(d)—角闪岩部分熔融演化曲线
Figure 7. Plots of Sr/Y versus Y (a) and La/Yb versus Yb (b) for the Samalong diorite
表 1 萨玛隆闪长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素测试结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircons U-Th-Pb isotopic analyses of the Samalong diorite
测点号 Pb/10-6 Th/10-6 U/10-6 Th/U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb/Ma 年龄1σ 207Pb/235U/Ma 年龄1σ 206Pb/238U/Ma 年龄1σ 1 1.50 23.4 64.8 0.36 0.0990 0.0204 0.2506 0.0501 0.0184 0.0009 1606 427 227 41 117 6 2 4.64 122 191 0.64 0.0837 0.0101 0.2173 0.0257 0.0188 0.0005 1284 247 200 21 120 3 3 2.26 27.2 91.1 0.30 0.0784 0.0106 0.2109 0.0274 0.0195 0.0008 1157 284 194 23 125 5 4 4.01 69.8 167 0.42 0.0777 0.0168 0.1960 0.0416 0.0183 0.0007 1140 474 182 35 117 4 5 4.44 83.3 187 0.45 0.0633 0.0052 0.1587 0.0114 0.0192 0.0005 718 147 150 10 123 3 6 6.69 136 252 0.54 0.0591 0.0061 0.1562 0.0157 0.0192 0.0004 570 233 147 14 122 3 7 5.87 122 238 0.51 0.0648 0.0043 0.1736 0.0107 0.0196 0.0004 766 126 163 9 125 2 8 51.2 568 1043 0.54 0.0499 0.0015 0.2739 0.0082 0.0392 0.0004 190 67 246 7 248 2 9 4.99 89.0 185 0.48 0.0463 0.0037 0.1367 0.0106 0.0214 0.0004 13 175 130 9 137 3 10 3.87 89.2 166 0.54 0.0687 0.0083 0.1765 0.0207 0.0186 0.0006 889 262 165 18 119 3 11 6.09 155 241 0.64 0.0652 0.0047 0.1750 0.0121 0.0201 0.0004 779 144 164 10 128 2 12 4.17 93.3 172 0.54 0.0685 0.0072 0.1831 0.0188 0.0194 0.0004 883 226 171 16 124 3 13 2.15 26.6 98.5 0.27 0.0681 0.0111 0.1684 0.0268 0.0179 0.0007 872 363 158 23 115 4 14 2.65 42.5 109 0.39 0.0707 0.0080 0.1932 0.0213 0.0198 0.0005 948 243 179 18 127 3 15 3.75 92.0 163 0.56 0.0853 0.0057 0.2109 0.0134 0.0186 0.0005 1323 116 194 11 119 3 16 3.30 57.5 144 0.40 0.0667 0.0070 0.1760 0.0178 0.0191 0.0005 830 228 165 15 122 3 17 3.78 81.2 157 0.52 0.0709 0.0065 0.1876 0.0164 0.0192 0.0005 955 193 175 14 123 3 18 3.79 75.3 162 0.46 0.0687 0.0060 0.1784 0.0152 0.0188 0.0004 890 188 167 13 120 3 19 4.12 65.1 178 0.37 0.0635 0.0058 0.1643 0.0146 0.0188 0.0004 726 201 154 13 120 3 20 4.59 87.4 194 0.45 0.0755 0.0058 0.1906 0.0138 0.0190 0.0004 1082 144 177 12 121 2 21 2.65 51.6 114 0.45 0.0524 0.0076 0.1294 0.0185 0.0179 0.0005 303 313 124 17 114 3 22 4.22 99.0 153 0.65 0.0674 0.0074 0.1872 0.0200 0.0201 0.0006 851 240 174 17 128 4 23 3.03 58.3 135 0.43 0.0537 0.0082 0.1326 0.0198 0.0179 0.0005 357 327 126 18 114 3 24 6.71 103 293 0.35 0.0594 0.0045 0.1465 0.0097 0.0188 0.0004 583 141 139 9 120 2 25 6.32 92.7 274 0.34 0.0643 0.0066 0.1573 0.0133 0.0189 0.0004 751 179 148 12 121 3 表 2 萨玛隆闪长岩全岩主量、微量元素和Sr-Nd同位素测试结果
Table 2 Whole-rock major, trace element and Sr-Nd isotopic data of the Samlong diorite
样品号 SML-1 SML-2 SML-3 SML-4 SML-5 样品号 SML-1 SML-2 SML-3 SML-4 SML-5 主量元素 微量元素 SiO2 60.42 56.76 59.59 59.22 57.90 Ba 123 141 141 160 159 Al2O3 17.87 16.71 17.09 17.17 16.74 La 12.8 15.4 12.0 10.1 12.3 Fe2O3 1.63 1.07 1.46 1.19 1.50 Ce 28.3 28.8 23.7 19.8 23.3 FeO 3.89 4.17 4.17 4.13 3.90 Pr 3.14 3.49 2.90 2.45 2.86 MnO 0.18 0.19 0.19 0.16 0.18 Nd 12.0 13.5 11.4 10.2 11.4 CaO 1.82 5.15 3.64 4.5 4.34 Sm 2.61 2.90 2.63 2.35 2.59 MgO 3.20 3.10 3.05 2.81 3.02 Eu 0.74 0.85 0.76 0.71 0.79 K2O 0.90 0.97 0.58 0.67 0.88 Gd 2.65 2.61 2.28 2.14 2.39 Na2O 4.54 3.91 4.05 3.96 4.30 Tb 0.42 0.44 0.39 0.36 0.42 TiO2 0.62 0.58 0.58 0.50 0.57 Dy 2.78 2.76 2.43 2.37 2.49 P2O5 0.15 0.14 0.14 0.13 0.14 Ho 0.58 0.57 0.53 0.48 0.55 LOI 3.98 6.34 4.54 5.02 5.54 Er 1.64 1.56 1.52 1.35 1.56 总计 99.2 99.09 99.08 99.46 99.01 Tm 0.25 0.24 0.24 0.20 0.25 K2O/Na2O 0.20 0.25 0.14 0.17 0.20 Yb 1.67 1.65 1.57 1.43 1.55 Mg# 48 48 50 51 49 Lu 0.25 0.26 0.26 0.22 0.25 微量元素 Hf 2.47 2.40 2.38 2.12 2.34 Li 110 84.4 119 109 82.1 Ta 0.52 0.51 0.49 0.40 0.48 Be 0.82 1.05 0.77 0.66 0.76 Tl 0.29 0.28 0.17 0.21 0.25 Sc 16.8 16.6 15.1 13.7 15.5 Pb 126 49.9 63.7 27.3 46.3 V 140 135 134 118 134 Th 3.61 3.73 3.29 2.37 3.21 Cr 38.0 38.3 35.0 24.5 34.7 U 0.86 0.91 0.89 0.61 0.71 Co 14.8 13.0 13.7 12.1 12.6 Sr-Nd同位素 Ni 17.3 16.9 16.6 12.9 17.3 (87Rb/86Sr)m 0.27 0.29 0.15 0.20 0.26 Cu 96.4 49.6 120 70.9 52.2 (87Sr/86Sr)m 0.707728 0.707455 0.706577 0.70637 0.707183 Zn 263 239 250 149 202 (2σ) 0.000004 0.000005 0.000004 0.00000 0.000004 Ga 16.9 16.5 16.5 16.0 16.5 (147Sm/144Nd)m 0.1315 0.1299 0.1396 0.1387 0.1375 Rb 40.9 45.0 23.7 32.4 41.0 (143Nd/144Nd)m 0.512521 0.512566 0.512623 0.51262 0.512587 Sr 456 457 475 475 479 (2σ) 0.000015 0.000007 0.00001 0.00000 0.000008 Y 16.3 16.3 15.2 14.6 15.6 (87Sr/86Sr)i 0.7073 0.7069 0.7063 0.7060 0.7067 Zr 87.2 85.9 84.4 76.3 83.2 (143Nd/144Nd)i 0.5124 0.5125 0.5125 0.5125 0.5125 Nb 7.87 7.81 7.46 6.23 7.36 εNd(0) -2.3 -1.4 -0.3 -0.1 -1.0 Mo 0.23 0.14 0.22 0.19 0.18 εNd(t) -1.3 -0.4 0.6 0.7 -0.1 Sn 1.26 1.13 1.97 1.91 1.75 TDM(Ga) 1.2 1.1 1.1 1.1 1.1 Cs 4.25 4.56 4.59 5.77 5.12 注:LOI=烧失量,Mg#=100×Mg2+/(Mg2++TFe2+)(87Sr/86Sr)i=(87Sr/86Sr)sample-87Rb/86Sr (eλt-1),87Rb/86Sr=Rb/Sr×2.981, λRb-Sr=1.42 × 10-11a-1;(143Nd/144Nd)i=(143Nd/144Nd)sample-(147Sm/144Nd)sample × (eλt-1),(143Nd/144Nd)CHUR(t) =0.512638-0.1967×(eλt-1),εNd(t)=[(143Nd/144Nd)sample/(143Nd/144Nd)CHUR(t)-1]×104,TDM=1/λ×ln{1+[((143Nd/144Nd)sample-0.51315)/ ((147Sm/144Nd)sample-0.21317)]}, λSm-Nd=6.54×10-12 a-1, t=121Ma。主量元素含量单位为%,微量元素为10-6 -
李光明, 段志明, 刘波, 等.西藏班公湖-怒江结合带北缘多龙地区侏罗纪增生杂岩的识别及意义[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(8):1256-1260. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20110812&journal_id=gbc 李光明, 李金祥, 秦克章, 等.西藏班公湖带多不杂超大型富金斑岩铜矿的高温高盐度高氧化成矿流体:流体包裹体证据[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(5):935-952. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200705009.htm 李金祥, 李光明, 秦克章, 等.班公湖带多不杂富金斑岩铜矿床斑岩-火山岩的地球化学特征与时代:对成矿构造背景的制约[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(3):531-543. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200803013.htm 佘宏全, 李进文, 马东方, 等.西藏多不杂斑岩铜矿床辉钼矿ReOs和锆石U-Pb SHRIMP测年及地质意义[J].矿床地质, 2009, 28(6):737-746. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200906002.htm 祝向平, 陈华安, 马东方, 等.西藏波龙斑岩铜金矿床的Re-Os同位素年龄及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2011, 27(7):2159-2164. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201107024.htm 祝向平, 陈华安, 马东方, 等.西藏多不杂斑岩铜金矿床地质与蚀变[J].地质与勘探, 2012, 48(2):199-206. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201202002.htm Li J X, Qin K Z, Li G M, et al. Magmatic-hydrothermal evolution of the Cretaceous Duolong gold-rich porphyry copper deposit in the Bangongco metallogenic belt, Tibet:Evidence from U-Pb and 40Ar/39Ar geochronology[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 41:525-536. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.03.008
Li J X, Li G M, Qin K Z, et al. High-temperature magmatic fluid exsolved from magma at the Duobuza porphyry copper-gold deposit, Northern[J]. Geofluids, 2011, 11:134-143. doi: 10.1111/gfl.2011.11.issue-2
Li J X, Li G M, Qin K Z, et al. Mineralogy and Mineral Chemistry of the Cretaceous Duolong Gold-Rich Porphyry Copper Deposit in the Bangongco Arc, Northern Tibet[J]. Resource Geology, 2011, 62(1):19-41. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-DZDQ201301005012.htm
潘桂棠, 朱弟成, 王立全, 等.班公湖-怒江缝合带作为冈瓦纳大陆北界的地质地球物理证据[J].地学前缘, 2004, 11(4):371-382. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200404005.htm 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 侯增谦, 等.冈底斯造山带的时空结构及演化[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(3):521-533. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200603001.htm 邱瑞照, 周肃, 邓晋福, 等.西藏班公湖-怒江西段舍马拉沟蛇绿岩中辉长岩年龄测定——兼论班公湖-怒江蛇绿岩带形成时代[J].中国地质, 2004, 31(3):262-268. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200403003.htm Zhu D C, Mo X X, Niu Y L, et al. Geochemical investigation of Early Cretaceous igneous rocks along an east-west traverse throughout the central Lhasa Terrane, Tibet[J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 268:298-312. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.09.008
Shi R D. SHRIMP dating of the Bangong Lake SSZ-type ophiolite:Constraints on the closure time of the ocean in the Bangong Lake-Nujiang River, northwestern Tibet[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2007, 52(7):936-941. doi: 10.1007/s11434-007-0134-z
Shi R D, Yang J S, Xu Z Q, et al. The Bangong Lake ophiolite (NW Tibet) and its bearing on the tectonic evolution of the Bangong-Nujiang suture zone[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2008, 32:438-457. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2007.11.011
曲晓明, 辛洪波.藏西班公湖斑岩铜矿带的形成时代与成矿构造环境[J].地质通报, 2006, 25(7):792-799. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=200607144&journal_id=gbc Li J X, Qin K Z, Li G M, et al. Petrogenesis of ore-bearing porphyries from the Duolong porphyry Cu-Au deposit, central Tibet:Evidence from U-Pb geochronology, petrochemistry and Sr-NdHf-O isotope characteristics[J]. Lithos, 2013, 160/161:216-227. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.12.015
李金祥. 班公湖带多不杂超大型富金斑岩铜矿床的成岩成矿年代学、岩石学及高氧化岩浆-流体-成矿作用[D]. 中国科学院研究生院博士学位论文, 2008: 1-225. 祝向平, 陈华安, 刘鸿飞, 等.西藏拿若斑岩铜金矿床成矿斑岩年代学、岩石化学特征及其成矿意义[J].地质学报, 2015, 89(1):109-128. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201501009.htm Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Gao S, et al. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 257:34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004
Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen:U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons of mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51:537-571. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egp082
Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Zong K Q, et al. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LAICPMS[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55:1535-1546. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4
Andersen T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192:59-79. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00195-X
Gao S, Liu X M, Yuan H L, et al. Determination of forty-two major and trace elements in USGS and NIST SRM glasses by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Geostandards Newsletter-Journal of Geostandards and Geoanalysis, 2002, 26:191-196. http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/database/awb6519e10103
Zhang H F, Gao S, Zhong Z Q, et al. Geochemical and Sr-NdPb isotopic compositions of Cretaceous granitoids:constraints on tectonic framework and crustal structure of the Dabieshan ultrahigh pressure metamorphic belt, China[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 186:281-299. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00006-2
Hoskin P W O, Schaltegger U. The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2003, 53:27-62. doi: 10.2113/0530027
Peccerillo A, Taylor S R. Geochemistry of eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58:63-81. doi: 10.1007/BF00384745
Middlemost E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994, 37:215-224. doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(94)90029-9
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society of London Special Publication, 1989, 42:313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Castillo P R. Adakite petrogenesis[J]. Lithos, 2012, 134-135:304-316. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2011.09.013
Wang B D, Chen J L, Xu J F, et al. Chronology and geochemistry of the Nadingcuo Volcanic rocks in the southern Qiangtang Region of the Tibet Plateau:Partial melting of the remnant Ocean crust along the Bangong-Nujiang suture[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2010, 84(6):1461-1473. doi: 10.1111/acgs.2010.84.issue-6
辛洪波, 曲晓明, 王瑞江, 等.藏西班公湖斑岩铜矿带成矿斑岩地球化学及Pb、Sr、Nd同位素特征[J].矿床地质, 2009, 28(6):785-792. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200906006.htm Kapp P, DeCelles P G, Gehrels G E, et al. Geological records of the Lhasa-Qiangtang and Indo-Asian collisions in the Nima area of central Tibet[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2007, 119:917-933. doi: 10.1130/B26033.1
Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, Niu Y L, et al. The Lhasa Terrane:record of a microcontinent and its histories of drift and growth[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2011, 301:241-255 doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2010.11.005
Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, Niu Y L, et al. The origin and pre-Cenozoic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 23(4):1429-1454 doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.02.002
曲晓明, 辛洪波, 杜德道, 等.西藏班公湖-怒江缝合带中段碰撞后A型花岗岩的时代及其对洋盆闭合时间的约束[J].地球化学, 2012, 41(1):1-14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201201002.htm Tatsumi Y, Hamilton D L, Nesbitt R W. Chemical characteristics of fluid phase released from a subducted lithosphere and the origin of arc magmas:Evidence from high pressure experiments and natural rocks[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 1986, 29:293-309. doi: 10.1016/0377-0273(86)90049-1
Foley S F, Barth M G, Jenner G A. Rutile/melt partition coefficients for trace elements and an assessment of the influence of rutile on the trace element characteristics of subduction zone magmas[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64:933-938. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00355-5
Richards J P. Postsubduction porphyry Cu-Au and epithermal Au deposits:Products of remelting of subduction-modified lithosphere[J]. Geology, 2009, 37:247-250. doi: 10.1130/G25451A.1
Defant M J, Drummond M S. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere[J]. Nature, 1990, 347:662-665. doi: 10.1038/347662a0
Richards J, Kerrich R. Special paper:Adakite-like rocks:their diverse origins and questionable role in metallogenesis[J]. Economic Geology, 2007, 102:1-40. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.102.1.1
张旗, 王焰, 刘伟, 等.埃达克岩的特征及其意义[J].地质通报, 2002, 21(7):431-435. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=200207108&journal_id=gbc Macpherson C G, Dreher S T, Thirwall M F. Adakites without slab melting:high pressure processing of basaltic island arc magma, Mindanao, the Philippines[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 243:581-593. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2005.12.034
Castillo P R. The origin of the adakite-high-Nb basalt association and its implications for post-subduction magmatism in Baja California, Mexico[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2008, 120:451-462. doi: 10.1130/B26166.1
Kay S M, Godoy E, Kurtz A. Episodic arc migration, crustal thickening, subduction erosion, and magmatism in the south-central Andes[J]. Geological Society A Bulletin, 2005, 117:67-88. doi: 10.1130/B25431.1
Goss A R, Kay S M. Extreme high field strength element (HFSE) depletion and nearchondritic Nb/Ta ratios in Central Andean ada-kite-like lavas (~28°S, 68°W)[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2009, 279:97-109. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2008.12.035
四川省地质调查院. 1: 250000物玛幅区域地质调查报告. 2006.




 下载:
下载: