Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen isotopes of the Huayuan Pb-Zn ore deposit in western Hu'nan Province and their implications for the source of ore-forming fluid
-
摘要:
湘西花垣地区铅锌矿床是铅锌矿资源储量超过千万吨的世界级超大型矿床之一。对该矿床主矿化期的方解石和闪锌矿进行了系统的C、H、O同位素研究。分析结果显示,花垣地区铅锌矿床主成矿期方解石样品的δ13CPDB值范围为-2.71‰~1.21‰,δ18OSMOW值范围为16.09‰~22.48‰,团结、李梅、土地坪、蜂塘和大石沟各铅锌矿床中主成矿期方解石的13C、18O同位素依次表现出逐渐降低的特征,在δ18OSMOW-δ13CPDB图上主要介于原生碳酸盐岩与海相碳酸盐岩之间,该地区铅锌矿床成矿流体中的碳主要来源于海相碳酸盐岩的溶解作用。花垣矿区围岩的δ13CPDB值范围为0.15‰~1.17‰,δ18OSMOW值范围为19.79‰~23.89‰,指示沉积成因海相碳酸盐岩的特征。方解石和闪锌矿样品中流体的δDSMOW变化于-91.1‰~-15‰之间,δ18Ofluid变化范围为-4.1‰~9.25‰,在矿区范围内流体的迁移方向是由北向南,δ18Ofluid-δDSMOW图显示,矿床成矿流体的主要来源是建造水和大气降水。成矿流体与围岩间的水-岩反应是导致湘西花垣地区铅锌矿床中方解石和闪锌矿矿物发生沉淀的主要机制。
Abstract:With more than ten million tons of lead and zinc resource reserves, the Huayuan lead-zinc deposit is expected to become the largest Pb-Zn deposit in China and one of the world-class superlarge ore deposits.In this paper, researches on carbon, hydrogen, oxygen isotope of calcite and sphalerite from the Huayuan lead-zinc deposit formed during the main mineralization period are report-ed.The analytical results show that δ13CPDB values of calcite samples display the range from 2.71‰ to 1.21‰, the δ18OSMOW values are in the range from 16.09‰ to 22.48‰.The δ13CPDB and δ18OSMOW isotope values of calcite minerals from the Tuanjie, Limei, Tu-diping, Fengtang and Dashigou lead-zinc deposits are gradually reduced in turn, falling between native carbonate rock and marine carbonate in the δ18OSMOW-δ13CPDB diagram.In the Huayuan lead-zinc deposit, the carbon in the ore-forming fluid was mainly de-rived from marine carbonate dissolution.The δ13CPDB values of surrounding rocks in the Huayuan lead-zinc deposit vary from 0.15‰ to 1.17‰, the δ18OSMOW values vary from 19.79‰ to 23.89‰, and the surrounding rock is sedimentary marine carbonate.The δDSMOW values of fluid in calcite and sphalerite vary from 91.1‰ to 15‰, the δ18O fluid vary from-4.1‰ to 9.25‰, and the migra-tion direction of fluid in the ore district was from north to south.The δ18Ofluid-δDSMOW diagram shows that the main source of oreforming fluid was formation water and atmospheric precipitation.Water-rock reaction between ore-forming fluid and wall rock was the main mechanism leading to the precipitation and crystallization of calcite and sphalerite in the Huayuan Pb-Zn deposit of western Hu'nan Province.
-
近年来,国家整装勘查项目在湘西花垣地区铅锌矿找矿工作取得重大突破,新发现了花垣超大型铅锌矿床(田)。矿床由7个矿段组成,矿体厚度达30m,钻孔见矿率在80%以上。其主矿区铅锌资源储量在1000×104t以上,预计远景储量超过2000×104t。将花垣矿田提升为千万吨级的世界资源基地,潜在价值达数千亿元。有望成为中国最大的铅锌矿基地,此项目将使中国增加一个世界级铅锌矿,有效地缓解资源瓶颈[1]。花垣地区铅锌矿床作为整个湘西地区铅锌矿床的典型代表,其矿床成因或成矿流体来源受到众多地质学者的广泛关注[2-11]。
C、H、O同位素组成是示踪成矿流体及其碳来源的有效手段[12-18],在认识碳酸盐成岩过程中的流体性质方面具有不可替代的作用[19]。热液成因方解石是花垣地区铅锌矿床原生矿石中最主要的脉石矿物,其形成贯穿整个成矿过程,因而研究花垣矿区方解石和闪锌矿的C、H、O同位素组成尤为重要,可提供成矿流体来源方面的重要信息。前人已对花垣铅锌矿床的C、H、O同位素组成进行过研究。夏新阶等[20]对花垣地区李梅锌矿床成矿流体来源进行研究,认为该区成矿溶液中的成矿物质来自寒武纪的海相碳酸盐岩围岩,即容矿层灰岩及其上、下层位的灰岩和白云岩,区内成矿溶液中的水应主要为地层水(包括一些油田水),还应有大量的当地地表水加入。刘文均等[10]对花垣铅锌矿床矿石及脉石矿物的液态包裹体进行成矿流体的H、O同位素组成测定,认为成矿流体来源于建造水,后期可能有雨水渗入。杨绍祥等[21]通过对湘西北铅锌矿床C、H、O同位素特征及成矿环境分析认为,矿床成矿流体是主要来源于深部的热卤水、大气降水和少量变质水的混合流体,成矿流体中的C和O主要来自围岩。蔡应雄等[22]对湘西—黔东下寒武统铅锌矿床的流体包裹体和C、O同位素地球化学特征进行分析,认为花垣铅锌矿床成矿流体可能为区域迁移流体与地层封存水构成的混合流体,成矿物质大部分来源于碳酸盐岩围岩地层。李堃等[23]通过对湘西黔东地区铅锌矿床C、O同位素地球化学特征的研究,认为成矿流体是一种高盐度的低温热卤水。有关成矿流体的来源众说纷纭,是该地区矿床系统研究的薄弱环节,前人在该区采集的用于C、H、O同位素组成研究的样品零散,各矿段系统研究的程度不足,数据少,分析结果统计意义不强,导致得出的结论无法达成一致,在一定程度上制约了对花垣铅锌矿床成因的认识。
在前人研究成果的基础上,本次补充测定了近年新开采地段或新发现矿体的代表性样品,根据矿床的纵向分带特征,整体上系统地分析了花垣地区由北向南分布的团结、李梅、土地坪、蜂塘、大石沟铅锌矿床中方解石的C、O同位素组成及方解石和闪锌矿的H、O同位素组成,探讨了成矿流体中碳的来源,以及区域内矿床成矿流体基本特征的变化趋势和成矿流体来源对矿物C、O同位素组成的影响,以期进一步认识并明确该地区铅锌矿床成矿流体中碳和成矿流体的来源。
1. 区域地质背景
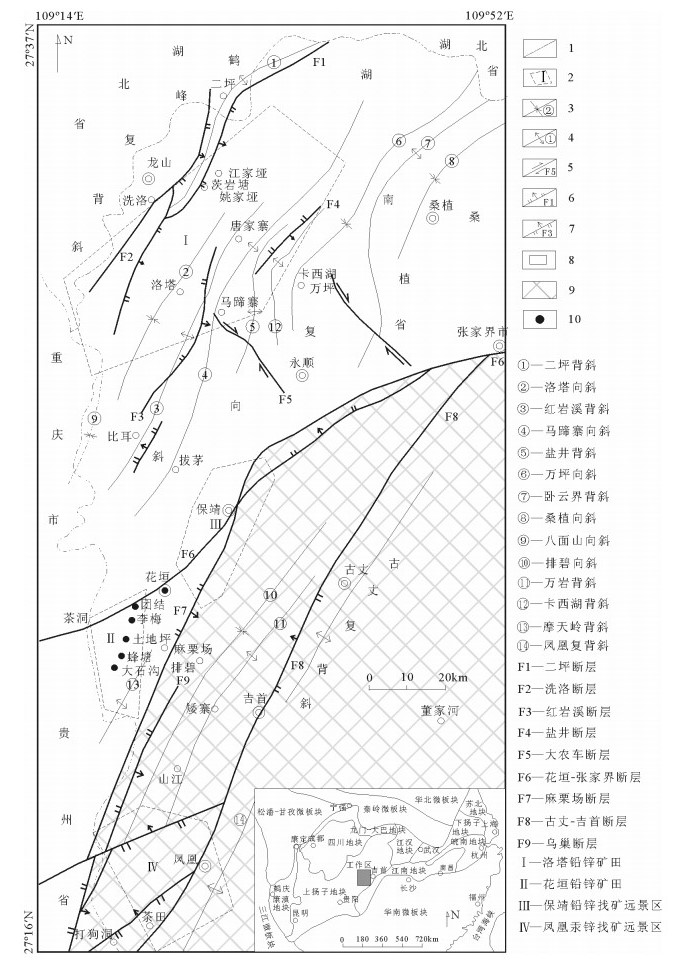
湘西位于上扬子地块东南缘,区内地层发育齐全,除缺失石炭系外,从中元古界冷家溪群,新元古界板溪群、震旦系至古—中生界及第四系均有出露。其中,主要赋矿层位为下寒武统上部、中寒武统下部及下奥陶统下部。储矿地层的岩性均为碳酸盐岩。寒武系—奥陶系碳酸盐岩台地相十分发育,厚约5000m,为铅锌主要含矿岩系[11, 24]。区内的地壳构造运动经历了武陵期、雪峰期—加里东期、海西期、印支期—喜马拉雅期4个发展阶段。总体以北东向褶皱变形和深大断裂为主,深大断裂则为以花垣-张家界断裂、吉首-古丈断裂、麻栗场断裂为主干所组成的断裂带,呈北北东—北东—北东东向弧形展布(图 1),并呈向南西方撒开,往北东方收敛的帚状[11]。这3条断裂为早期控相、后期控矿的深大断裂,花垣铅锌多金属矿集区即局限于这3条断裂及其所控制的下寒武统清虚洞组藻灰岩中[25]。区内大范围未见花岗岩出露,仅于古丈背斜龙鼻咀见基性超基性岩侵入板溪群地层。湘西北的铅锌矿总体呈北东向断续展布,省域内走向长230km,宽50~80km,面积万余平方千米[24]。
![]() 图 1 湘西北铅锌矿带区域构造略图(据参考文献[11]修改)1—省界;2—矿田界线;3—向斜及其编号;4—背斜及其编号;5—平移断层及其编号;6—正断层及其编号;7—逆断层及其编号;8—南区斜坡相;9—北区斜坡相;10—花垣地区铅锌矿床Figure 1. Regional tectonic sketch map of the lead-zinc deposits in northwest Hu'nan
图 1 湘西北铅锌矿带区域构造略图(据参考文献[11]修改)1—省界;2—矿田界线;3—向斜及其编号;4—背斜及其编号;5—平移断层及其编号;6—正断层及其编号;7—逆断层及其编号;8—南区斜坡相;9—北区斜坡相;10—花垣地区铅锌矿床Figure 1. Regional tectonic sketch map of the lead-zinc deposits in northwest Hu'nan2. 矿床地质特征
湘西花垣地区团结、李梅、土地坪、蜂塘和大石沟铅锌矿床均为层控矿床,含矿围岩岩性均为灰岩,矿化与热液作用形成的方解石化关系十分密切。铅锌矿体赋存于下寒武统清虚洞组,清虚洞组按岩性及岩相可分为5段,自上而下依次为:白云岩段(1q5)、鲕粒灰岩段(1q4)、藻灰岩段(1q3)、泥晶灰岩段(1q2)和条带灰岩段(1q1)。其中,清虚洞组藻灰岩段(1q3)为区内主要含矿层位,岩性为深灰色厚层状藻灰岩夹粉晶灰岩,藻屑灰岩及斑块状云化灰岩,灰色-浅灰色厚层细-中砂屑灰岩、含藻云质灰岩;鲕粒灰岩段(1q4)为区内次要含矿层位,岩性为藻球粒不等晶灰岩、亮晶含鲕粒碎屑灰岩等。含矿层位为下寒武统清虚洞组下段(藻)灰岩。
矿体形态以层状、似层状、透镜状为主,次为脉状、网脉状。矿体规模大小差异较大,层状、似层状矿体与围岩产状基本一致,偶尔有穿层现象[23]。
铅锌矿矿石的矿物组成较简单,以闪锌矿和方铅矿为主,次为黄铁矿,偶见微量白铁矿。脉石矿物主要为方解石和重晶石,次为少量萤石和沥青。矿化蚀变类型主要为方解石化,常伴有弱黄铁矿化、萤石化、重晶石化和不同程度的褪色重结晶等[11]。
矿石矿物以淡黄色和棕黄色闪锌矿为主,其次为方铅矿和黄铁矿。脉石矿物以方解石为主,次为重晶石、极少量的萤石和微量沥青。方解石常呈条带状或团块状,与铅锌矿石密切共生(图版Ⅰ)。矿石结构以自形-他形晶粒结构为主,此外还有充填或填隙结构、交代结构。闪锌矿以细中粒为主,方铅矿结晶粗大,而黄铁矿主要呈细粒及微细浸染状分布于闪锌矿与围岩接触面附近。矿石构造有浸染状、细粒斑点状、环带状、斑块状及网脉状。围岩蚀变以方解石化、白云石化、硅化为主,次为重晶石化、黄铁矿化、萤石化、沥青化及褪色化[23]。
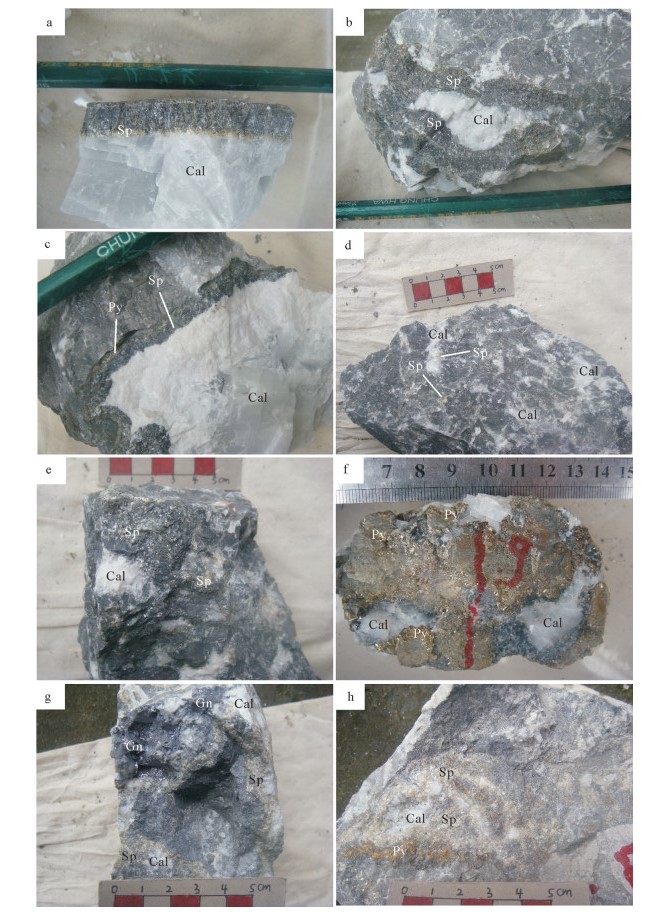
![]() 图版Ⅰa.团结铅锌矿床大脉状方解石化闪锌矿石,闪锌矿沿方解石脉与围岩接触带分布;b.团结铅锌矿床斑脉状方解石化闪锌矿石,闪锌矿沿方解石脉体边缘分布;c.李梅铅锌矿床粗脉状方解石化闪锌矿石,细粒黄铁矿与闪锌矿沿方解石脉与围岩接触带分布;d.蜂塘铅锌矿床斑脉状方解石化闪锌矿石,闪锌矿沿方解石脉边缘分布;e.蜂塘铅锌矿床斑脉状方解石化闪锌矿矿石,闪锌矿沿方解石脉边缘分布;f.土地坪铅锌矿床斑脉状方解石化黄铁矿矿石;g.大石沟铅锌矿床斑脉状方解石化闪锌矿石,闪锌矿和方铅矿沿方解石脉边缘分布;h.大石沟铅锌矿床斑脉状方解石化闪锌矿矿石,细粒黄铁矿与闪锌矿沿方解石脉与围岩接触带分布。Sp—闪锌矿;Gn—方铅矿;Cal—方解石;Py—黄铁矿图版Ⅰ.
图版Ⅰa.团结铅锌矿床大脉状方解石化闪锌矿石,闪锌矿沿方解石脉与围岩接触带分布;b.团结铅锌矿床斑脉状方解石化闪锌矿石,闪锌矿沿方解石脉体边缘分布;c.李梅铅锌矿床粗脉状方解石化闪锌矿石,细粒黄铁矿与闪锌矿沿方解石脉与围岩接触带分布;d.蜂塘铅锌矿床斑脉状方解石化闪锌矿石,闪锌矿沿方解石脉边缘分布;e.蜂塘铅锌矿床斑脉状方解石化闪锌矿矿石,闪锌矿沿方解石脉边缘分布;f.土地坪铅锌矿床斑脉状方解石化黄铁矿矿石;g.大石沟铅锌矿床斑脉状方解石化闪锌矿石,闪锌矿和方铅矿沿方解石脉边缘分布;h.大石沟铅锌矿床斑脉状方解石化闪锌矿矿石,细粒黄铁矿与闪锌矿沿方解石脉与围岩接触带分布。Sp—闪锌矿;Gn—方铅矿;Cal—方解石;Py—黄铁矿图版Ⅰ.3. 样品采集及测试方法
方解石和闪锌矿分别是花垣地区铅锌矿床中最重要的脉石矿物和矿石矿物。本次采集的方解石和闪锌矿样品分别来自花垣地区由北而南依次分布的团结、李梅、土地坪、蜂塘和大石沟铅锌矿床(图 1),方解石均形成于主成矿期,与闪锌矿和方铅矿紧密共生,呈块状、粗脉状或斑脉状,闪锌矿多沿方解石脉体边缘分布,或呈斑状、浸染粒状分布于方解石脉体中(图版Ⅰ)。
方解石样品的C、O同位素组成在武汉地质调查中心同位素地球化学实验室测定。首先将方解石样品粉碎至100目,在双目镜下挑选方解石单矿物,重复二次挑选,确保方解石纯度高于98%。挑选的单矿物在研钵中研磨成粉末,过200目筛后在烘箱中烘干2h备用。分析采用100%磷酸法,质谱仪型号为MAT-251,分析误差范围约为0.2‰。
称取30mg试样置于反应管中,并注入4ml 100%磷酸,抽真空2h并稳定在1.0Pa,待试样与磷酸充分混合后,将反应管置于恒温25℃的水中24h,再用液氮吸收CO2气体,纯化后的CO2气体在MAT-251质谱仪上测定C、O同位素组成。分析过程采用标准样品GBW04417和NBS19进行质量监控,分析结果以相对V-PDB的值给出。δ13C以PDB为标准,δ18O以SMOW为标准。计算δ18OSMOW时,采用Friedman等[26]的平衡方程:δ18OSMOW=1.03086×δ18OPDB+30.86。
方解石和闪锌矿样品的H、O同位素测试利用MAT-253完成,H同位素采用加热爆裂法从样品中提取原生流体包裹体中的H2O,将提取的包裹体中的H2O与Zn在400℃条件下反应30min制取H2,在MAT-253质谱仪上测定H2的δD,测试误差约为2‰。O同位素组成分析采用BrF5法,在MAT-253质谱计上测定δ18O值,测定精度为0.2‰。
4. 测试结果
4.1 C、O同位素
表 1为湘西花垣地区铅锌矿床热液方解石C、O同位素组成分析结果,表 2为湘西花垣地区铅锌矿床围岩的C、O同位素组成,可见以下特征。
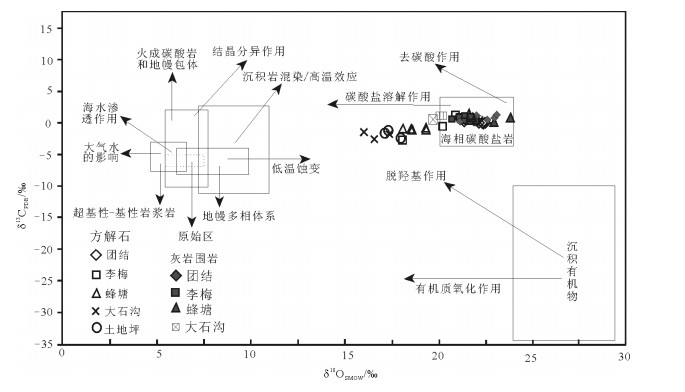
表 1 湘西花垣地区铅锌矿床主成矿期方解石C、O同位素组成Table 1. C and O isotopic compositions of calcites from the Huayuan Pb-Zn ore deposit in western Hu'nan矿区 原样品号 样品名称 δ13CPDB/‰ δ18OPDB/‰ δ18OSMOW/‰ 团结 11TJ-1B9 斑脉状方解石 0.04 -8.27 22.33 11TJ-1B9 斑脉状方解石 0.05 -8.23 22.38 11TJ-1B11 斑脉状方解石 0.13 -8.13 22.48 11TJ-1B12 斑脉状方解石 -0.24 -8.28 22.32 11TJ-1B14 斑脉状方解石 0.43 -8.75 21.84 13TJ-B1 大脉块状方解石 0.29 -8.54 22.06 13TJ-B10 斑脉状方解石 0.17 -9.18 21.40 13TJ-B13 桁脉状方解石 0.11 -8.46 22.14 13TJ-B18 桁脉状方解石 -0.61 -10.77 19.76 13TJ-B18 桁脉状方解石 -0.61 -10.76 19.77 李梅 13LM-B9 桁脉状方解石 0.88 -9.39 21.18 13LM-B11 大脉块状方解石 1.21 -9.66 20.90 13LM-B13-1 大脉块状方解石 1.12 -10.49 20.05 13LM-B31-1 大脉块状方解石 1.16 -10.28 20.26 13HYC-B5 斑脉状方解石 -2.71 -12.35 18.13 13HYC-B7 斑脉状方解石 -0.50 -10.32 20.22 土地坪 13TDP-B3 桁脉状方解石 -0.90 -12.35 18.13 13TDP-2B3 桁脉状方解石 -1.33 -13.15 17.30 13TDP-2B3 桁脉状方解石 -1.41 -13.23 17.22 蜂塘 13FT-B9 斑脉状方解石 -0.85 -11.17 19.35 13FT-B16 斑脉状方解石 -1.03 -11.93 18.56 13FT-B16 斑脉状方解石 -1.00 -11.85 18.64 13FT-B23 斑脉状方解石 -1.01 -11.18 19.33 13FT-B24 斑脉状方解石 -2.24 -12.47 18.01 大石沟 13DSG-B1 斑脉状方解石 -1.82 -13.05 17.41 13DSG-B3 斑脉状方解石 -1.55 -14.33 16.09 13DSG-B6 桁脉状方解石 -2.60 -13.81 16.62 13DSG-B7 斑脉状方解石 -1.29 -12.11 18.38 注:δ18OSMOW=1.03086×δ18OPDB+30.86[26] 表 2 湘西花垣地区铅锌矿床碳酸盐岩围岩的C、O同位素组成Table 2. C and O isotopic compositions of calcites from the Huayuan Pb-Zn ore deposit in western Hu'nan矿区 原样品号 样品名称 δ13CPDB/‰ δ18OPDB/‰ δ18OSMOW/‰ 数据来源 团结 13NZB-B17 灰岩 0.72 -8.52 22.08 本文 13NZB-B21-1 灰岩 0.92 -7.60 23.03 13NZB-B21-2 灰岩 0.97 -7.48 23.15 13HYC-B21 灰岩 0.15 -9.30 21.27 13HYC-B22 灰岩 0.57 -7.92 22.70 李梅 13LM-B23 灰岩 1.17 -8.83 21.76 本文 13LM-B28 灰岩 0.55 -9.44 21.13 13LM-B30 灰岩 0.62 -9.80 20.76 L16-4 无矿化藻灰岩 0.29 / 22.06 [20, 23] L16-6 无矿化藻灰岩 0.46 / 21.49 LM-11 灰岩 1.05 -9.11 21.47 [22] LM-16 灰岩 0.52 -9.24 21.33 蜂塘 SZS-14 灰岩 0.65 -8.95 21.63 SZS-21 灰岩 0.98 -8.99 21.59 [22] SZS-23 灰岩 0.97 -6.76 23.89 13FT-B30 灰岩 0.19 -7.60 23.03 13FT-B33-1 灰岩 0.69 -8.84 21.75 本文 13FT-B33-2 灰岩 0.65 -8.95 21.63 大石沟 13DSG-B20 灰岩 0.44 -8.47 22.13 13DSG-B21 灰岩 0.55 -10.74 19.79 本文 13DSG-B26 灰岩 0.77 -9.02 21.56 注:δ18OSMOW= 1.03086×δ18OPDB+30.86[26] (1)花垣地区铅锌矿床热液方解石的δ13CPDB值为-2.71‰~1.21‰,平均值为-0.58‰,δ18OSMOW值为16.09‰~22.48‰,平均值为19.72‰。其中,团结矿区方解石的δ13CPDB平均值为-0.024‰,δ18OSMOW平均值为21.648‰。李梅矿区方解石的δ13CPDB平均值为0.193‰,δ18OSMOW平均值为20.123‰。蜂塘矿区方解石的δ13CPDB平均值为-1.226‰,δ18OSMOW平均值为18.778‰。土地坪矿区方解石的δ13CPDB平均值为-1.213‰,δ18OSMOW平均值为17.55‰。大石沟矿区方解石的δ13CPDB平均值为-1.815‰,δ18OSMOW平均值为17.125‰。不同矿床的δ 13CPDB值和δ18OSMOW值较接近,变化范围也较小,组成非常集中,相对均一。花垣北东区域的团结、李梅矿区的δ 13CPDB值和δ18OSMOW值较西南区域的蜂塘、土地坪、大石沟矿区稍高。花垣地区铅锌矿床热液方解石的δ13CPDB值和δ18OSMOW值部分落入海相碳酸盐岩(δ13CPDB=0±4‰,δ18OSMOW=20‰~24‰)[27]范围内,部分介于原生碳酸盐岩和海相碳酸盐岩之间(图 2)。
![]() 图 2 湘西花垣地区铅锌矿床成矿期方解石C、O同位素图解(底图据参考文献[28])Figure 2. C-O isotope diagram of the calcite from Pb-Zn ore deposits in western Hu'nan
图 2 湘西花垣地区铅锌矿床成矿期方解石C、O同位素图解(底图据参考文献[28])Figure 2. C-O isotope diagram of the calcite from Pb-Zn ore deposits in western Hu'nan(2)花垣地区铅锌矿床的围岩(藻)灰岩的δ13CPDB值为0.15‰~1.17‰,平均值为0.66‰,δ18OSMOW值为19.79‰~23.89‰,平均值为21.87‰。其中,团结矿区灰岩的δ13CPDB值为0.15‰~0.97‰,平均值为0.67‰,δ18OSMOW值为21.27‰~23.15‰,平均值为22.45‰。李梅矿区(藻)灰岩的δ13CPDB值为0.29‰~ 1.17‰,平均值为0.67‰,δ18OSMOW值为20.76‰ ~ 22.06‰,平均值为21.43‰。花垣蜂塘矿区围岩灰岩的δ13CPDB值为0.19‰~0.98‰,平均值为0.69‰,δ18OSMOW值为21.63‰~23.89‰,平均值为22.25‰。花垣大石沟矿区围岩灰岩的δ13CPDB值为0.44‰~ 0.77‰,平均值为0.59‰,δ18OSMOW值为19.79‰ ~ 22.13‰,平均值为21.16‰。
(3)与热液成因方解石相比,围岩具有更高的δ 13CPDB值和δ 18OSMOW值,围岩的δ 13CPDB值和δ 18OSMOW值落入海相碳酸盐岩(δ 13CPDB=0±4‰,δ 18OSMOW=20‰~24‰)[27]范围内,与围岩为沉积碳酸盐岩的地质特征一致。
4.2 H、O同位素
本次研究选取了27件样品进行H、O同位素分析,包括23件方解石和4件闪锌矿,均与成矿密切相关。测试结果见表 3。
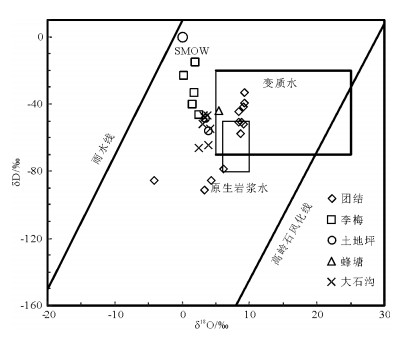
表 3 湘西花垣地区铅锌矿主成矿期成矿流体的D-O同位素组成Table 3. δO-δD composition of ore-forming fluid from typical lead-zinc deposits in Huayuan area, western Hu'nan矿区 样号 矿物 δ18OSMOW/‰ δDSMOW/‰ δOfluid/‰ 换算温度/℃ 团结 13TJ-B1 褐色脉状闪锌矿 / -85.50 4.30 150 13TJ-B2 褐色脉状闪锌矿 / -78.70 6.10 150 13TJ-B8 褐色脉状闪锌矿 / -85.30 -4.10 150 13TJ-B11 黄色脉状闪锌矿 / -91.10 3.30 150 13TJ-B1 方解石 21 -50.6 8.35 150 13TJ-B2 方解石 21.9 -39.4 9.25 150 13TJ-B3 方解石 21.9 -33.4 9.25 150 13TJ-B4 方解石 21.1 -44.3 8.45 150 13TJ-B7 方解石 21.3 -57.6 8.65 150 13TJ-B8 方解石 21.7 -51.6 9.05 150 13TJ-B10 斑脉状方解石 21.4 -50.7 8.75 150 13TJ-B11 方解石 21.8 -41.8 9.15 150 LM-1 斑脉状方解石 / -23 0.25 150 LM-2 斑脉状方解石 / -40 1.54 150 李梅 LM-3 斑脉状方解石 / -15 1.93 150 LM-4 斑脉状方解石 / -46 2.43 150 LM-5 斑脉状方解石 / -33 1.72 150 土地坪 13TDP-B3 粗脉状方解石 17.7 -55.8 3.89 135 13TDP-2B3 粗脉状方解石 17.3 -48.2 3.49 135 蜂塘 13FT-B26 斑脉状方解石 19.3 -44.2 5.49 135 13DSG-B10 块状方解石 17.7 -64.1 3.89 135 13DSG-B11 方解石 18 -54.7 4.19 135 13DSG-B12 方解石 17.1 -48.1 3.29 135 大石沟 13DSG-B13 方解石 16.3 -65.8 2.49 135 13DSG-B15 方解石 17.5 -46.5 3.69 135 13DSG-B16 方解石 16.8 -51.7 2.99 135 13DSG-B17 方解石 17 -46.8 3.19 135 注:δ18OSMOW=1.03086 ×δ18OPDB + 30.86[26];方解石与流体的转换公式采用1000lnα方解石-水=2.78×106T-2-2.89[29];换算温度采用测温结果的峰值,T为绝对温度 23件方解石样品的δDSMOW值介于-65.8‰~ -15‰之间,平均值为-45.75‰,流体中的δ18Ofluid值为0.25‰~9.25‰,平均值为5.02‰。4件闪锌矿样品的δDSMOW值为-91.1‰ ~-78.7‰,平均值为-85.15‰,流体中的δ18Ofluid值为-4.1‰~6.1‰,平均值为2.4‰。
将本次和前人测定的H、O同位素组成(表 3)投在δ18O-δD图解(图 3)上,可见与雨水线斜交的线性关系。李梅矿床的方解石H、O同位素组成更靠近雨水线,矿床成矿流体主要来源于建造水和大气降水,还有部分变质水的混入,而在后期可能有雨水渗入并造成流体盐度的稀释。这种特征也是许多与建造水有关的密西西比型矿床的共同特点[10]。
![]() 图 3 湘西花垣地区铅锌矿床成矿流体O-D同位素组成图解(底图据参考文献[30])Figure 3. O-D isotope diagram of the ore-forming fluid from Pb-Zn ore deposits in western Hu'nan
图 3 湘西花垣地区铅锌矿床成矿流体O-D同位素组成图解(底图据参考文献[30])Figure 3. O-D isotope diagram of the ore-forming fluid from Pb-Zn ore deposits in western Hu'nan5. 讨论
5.1 成矿流体中碳的来源
碳酸盐矿物的C同位素组成对于认识成岩过程中碳酸盐矿物碳的来源至关重要,O同位素组成在示踪碳酸盐成岩过程中流体性质和成岩温度方面具有不可替代的作用[19]。湘西花垣矿区碳酸盐类脉石矿物仅发现方解石,其他碳酸盐类脉石矿物少见,甚至未见,故方解石的δ13C基本代表成矿流体的C同位素组成,可以用方解石中C同位素的组成来指示成矿流体的碳来源。
花垣地区铅锌矿床的围岩及热液方解石样品的δ18O-δ13C同位素图解(图 2)上,热液方解石的δ13CPDB和δ18OSMOW值呈近水平分布,略低于同样呈近水平分布的围岩灰岩。由表 2和图 2可见,花垣地区铅锌矿床中远矿围岩的δ13CPDB值和δ18OSMOW值落入海相碳酸盐岩范围内,表明这些矿床的远矿围岩(灰岩)为沉积成因碳酸盐岩,与其地质特征吻合。不同矿床的热液成因方解石的C、O同位素组成范围较宽,但均处于地幔多相体系与海相碳酸盐岩间,且具有靠近海相碳酸盐岩C同位素组成缓慢升高的趋势(图 3)。表明花垣地区铅锌矿成矿流体中的碳可能来源于:① 沉积有机物的脱羟基作用;② 地幔多相体系的沉积岩混染或高温效应;③ 海相碳酸盐岩的溶解作用。如果碳来源于沉积物中有机质的脱羟基作用,则C同位素组成较有机质升高,O同位素组成较有机质降低(图 2)。花垣地区铅锌矿床热液方解石的C同位素组成明显高于沉积物有机质,O同位素组成明显低于沉积物有机质,沉积有机物的脱羟基作用很难形成如此大的C-O同位素分馏[31]。因此沉积有机物的脱羟基作用应该不是成矿流体中C来源的主要机制。地幔多相体系的沉积岩混染或高温效应会使从其中形成的矿物具有比其更高的δ13C和δ18O值,而花垣地区铅锌矿床中热液方解石的C同位素组成与地幔多相体系相近,但O同位素组成明显高于地幔多相体系(图 3)。另外,该地区铅锌矿床中热液方解石的δ13CPDB值和δ18OSMOW值投点呈近水平分布,如果C、O同位素组成的线性关系是由沉积岩混染作用或高温分异作用所致,则该作用对流体O同位素组成的影响并不明显,而对C同位素组成的影响显著,从而导致从该溶液中沉淀的方解石,其C同位素组成变化显著[12, 32-34]。这与测试结果显然不相符。因此,沉积岩混染或高温效应也不应是成矿流体中碳来源的主要因素。
海相碳酸盐岩的溶解作用是通过流体与围岩之间的水/岩反应,造成δ13CPDB与δ18OSMOW呈相关趋势[32-34],如果成矿流体中的碳形成于海相碳酸盐岩的溶解作用,则其C同位素组成与海相碳酸盐岩相似,但其O同位素组成较海相碳酸盐岩亏损[31]。因此,花垣地区铅锌矿床C、O同位素组成在δ18O-δ13C图解(图 2)中总体呈近水平展布,即因流体与围岩的水/岩反应,脉石矿物热液方解石的沉淀应该主要是由水/岩反应、温度降低耦合等作用所致[28]。因而花垣铅锌矿床成矿流体中的碳可能来源于围岩地层,碳酸盐岩溶解作用起关键作用(亏18O的成矿流体与地层海相碳酸盐岩围岩的水/岩反应)[12]。热液方解石与围岩碳酸盐岩相比,具有明显低的δ18OSMOW值,表明亏18O的成矿流体与围岩发生了同位素交换。
5.2 成矿流体的来源
刘文均等[10]对花垣铅锌矿床中大量流体包裹体进行了详细研究,结果显示,该区成矿流体为高盐度的低温CO2-H2O-NaCl型热卤水,流体密度为1.0~1.1g/cm3,成矿压力为35~40MPa,成矿深度为1.3~1.4km。杨邵祥等[11]通过花垣地区矿床流体包裹体测温,获得成矿流体温度为99~190℃。蔡应雄等[22]对花垣李梅铅锌矿床流体包裹体测温获得成矿流体温度为98~130℃,盐度范围为18.01%~19.95% NaCl eq.,成矿压力为22~40MPa。周云等[1]对花垣李梅、耐子堡、狮子山等典型矿床流体成矿作用的研究认为,该区成矿流体温度主要分布于80~230℃之间,盐度范围为9%~21%NaCl eq.,成矿压力为25~ 45MPa。综合湘西典型铅锌矿流体包裹体特征及数据,该区成矿流体温度主要为100~180℃,总盐度为10%~23%NaCl eq.,多数大于15%NaCl eq.,密度多数大于1g/cm3,流体气相成分以H2O为主,成矿流体体系为NaCl-CaCl2-H2O,CaCl2-H2O,NaClKCl-H2O,CaCl2-MgCl2-H2O-卤水,成分主要为Cl-、Na+、Ca2+、K+、Mg2+,是以钠和钙氯化物为主的高浓度溶液,属于具有中-高盐度、中-高密度、低温度的地下热卤水性质的含矿热水溶液,成矿压力平均值为34~48MPa,成矿深度平均值为1.20~ 1.66km,属浅成低温矿床[1]。前人对全球典型MVT铅锌矿床统计发现,此类矿床流体包裹体均一温度为50~250℃,但多在90~150℃之间(表 4)[35-37],成矿深度多为几百至千余米,包裹体的盐度在10%~30% NaCl eq.之间[38],与油田水组分相似,主要成分从多到少依次为Cl-、Na+、Ca2+、K+、Mg2+,成矿流体是高密度盆地卤水。通过比较发现,湘西地区铅锌矿床成矿流体与美国典型MVT铅锌矿床具有相似性,成矿流体均为低温、中高盐度、高密度性质的盆地卤水,但湘西地区铅锌矿床成矿流体温度整体比美国典型MVT铅锌矿床成矿流体温度稍高。
表 4 中美MVT铅锌矿床成矿温度对比Table 4. Metallogenic temperatures contrast between Chinese and American MVT lead-zinc deposits国家 矿床(区) 主矿物 Th/℃ 资料来源 中
国
湖
南花垣 闪锌矿
方解石120~160
90~180[1] 茶田 闪锌矿
方解石96~170
92~169闪锌矿 113~219 打狗洞 方解石 92~152 石英 85~195 闪锌矿 108~148 董家河 方解石 128~164 石英 100~343 闪锌矿 106~129 唐家寨 石英 100~220 方解石 115~139 美
国
中
部维伯纳姆和老铅带 闪锌矿 90~120 阿肯色北部 闪锌矿 95~170 三州交界地区 闪锌矿 80~120 上密西西比河谷地区 闪锌矿 75~160, 个别达220 [35-37] 田纳西中部 闪锌矿 90~150 田纳西东部 闪锌矿 70~170 肯塔基中部 闪锌矿 70~130 湘西花垣地区铅锌矿床成矿流体温度主要为100~180℃,花垣团结、李梅、土地坪、蜂塘、大石沟铅锌矿床的成矿流体温度依次下降,均一温度具有由北向南降低的趋势,反映了成矿流体的运移方向。刘文均等[10]通过研究也认为,在花垣矿区范围内,流体的温度、CO2、CH4、K+、Na+、Ca2+的含量,出现从矿区北段向南段、从矿区到外围同步下降的特点,表明在花垣矿区范围内流体的迁移方向为由北向南流动,且主要途径是沿清虚洞组三、四段间顺层流动。成矿流体在运移和沉淀过程中依次形成团结、李梅、土地坪、蜂塘、大石沟铅锌矿床。
花垣地区铅锌矿床的H、O同位素组成表明,成矿流体的主要来源是建造水和大气降水。自然界中天然水富集12C、16O等轻同位素而贫重同位素,尤其是18O的含量特别低,而沉积碳酸盐岩则富含13C、18O等重同位素[23]。因此,主要来源为建造水和大气降水的成矿流体相对集中较多的轻同位素,亏13C、18O的成矿流体与围岩地层的水-岩反应中,反复与碳酸盐围岩进行同位素交换,导致成矿期沉淀的方解石中13C、18O逐渐降低。花垣矿区范围内流体的迁移方向是由北向南,这也是团结、李梅、土地坪、蜂塘、大石沟铅锌矿床中成矿期方解石的13C、18O同位素逐渐降低的原因(表 1;图 2)。成矿流体与围岩的水-岩反应是导致湘西花垣地区铅锌矿床中方解石矿物沉淀的主要机制。
6. 结论
(1)湘西花垣地区铅锌矿床围岩为海相沉积成因碳酸盐岩,成矿期方解石中的碳主要来源于碳酸盐岩围岩,由围岩海相碳酸盐岩的溶解作用形成。该地区铅锌矿床脉石矿物热液方解石和矿石矿物闪锌矿的沉淀主要是成矿流体与围岩的水/岩反应、温度降低耦合等作用所致,亏18O的成矿流体与围岩发生了同位素交换。
(2)花垣地区铅锌矿床成矿流体的主要来源是建造水和大气降水,以及少量变质水。亏13C、18O的成矿流体与围岩地层发生水-岩反应,由北向南分布的铅锌矿床中成矿期方解石的13C、18O同位素表现出逐渐降低的特征,矿区范围内成矿流体的迁移方向是由北向南流动,可根据这一规律指导下一步找矿勘探。
致谢: 野外工作期间得到湖南省地质调查院405地质队刘健清队长、余沛然总工程师、曾健康高级工程师、张劲松工程师的大力支持,中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心同位素地球化学实验室叶荣工程师帮助测试样品,杨红梅研究员对样品处理和分析测试过程给予了悉心指导,审稿专家提出了诸多宝贵的意见,在此一并致以诚挚的谢意。 -
图 1 湘西北铅锌矿带区域构造略图(据参考文献[11]修改)
1—省界;2—矿田界线;3—向斜及其编号;4—背斜及其编号;5—平移断层及其编号;6—正断层及其编号;7—逆断层及其编号;8—南区斜坡相;9—北区斜坡相;10—花垣地区铅锌矿床
Figure 1. Regional tectonic sketch map of the lead-zinc deposits in northwest Hu'nan
图版Ⅰ
a.团结铅锌矿床大脉状方解石化闪锌矿石,闪锌矿沿方解石脉与围岩接触带分布;b.团结铅锌矿床斑脉状方解石化闪锌矿石,闪锌矿沿方解石脉体边缘分布;c.李梅铅锌矿床粗脉状方解石化闪锌矿石,细粒黄铁矿与闪锌矿沿方解石脉与围岩接触带分布;d.蜂塘铅锌矿床斑脉状方解石化闪锌矿石,闪锌矿沿方解石脉边缘分布;e.蜂塘铅锌矿床斑脉状方解石化闪锌矿矿石,闪锌矿沿方解石脉边缘分布;f.土地坪铅锌矿床斑脉状方解石化黄铁矿矿石;g.大石沟铅锌矿床斑脉状方解石化闪锌矿石,闪锌矿和方铅矿沿方解石脉边缘分布;h.大石沟铅锌矿床斑脉状方解石化闪锌矿矿石,细粒黄铁矿与闪锌矿沿方解石脉与围岩接触带分布。Sp—闪锌矿;Gn—方铅矿;Cal—方解石;Py—黄铁矿
图版Ⅰ.
图 2 湘西花垣地区铅锌矿床成矿期方解石C、O同位素图解(底图据参考文献[28])
Figure 2. C-O isotope diagram of the calcite from Pb-Zn ore deposits in western Hu'nan
图 3 湘西花垣地区铅锌矿床成矿流体O-D同位素组成图解(底图据参考文献[30])
Figure 3. O-D isotope diagram of the ore-forming fluid from Pb-Zn ore deposits in western Hu'nan
表 1 湘西花垣地区铅锌矿床主成矿期方解石C、O同位素组成
Table 1 C and O isotopic compositions of calcites from the Huayuan Pb-Zn ore deposit in western Hu'nan
矿区 原样品号 样品名称 δ13CPDB/‰ δ18OPDB/‰ δ18OSMOW/‰ 团结 11TJ-1B9 斑脉状方解石 0.04 -8.27 22.33 11TJ-1B9 斑脉状方解石 0.05 -8.23 22.38 11TJ-1B11 斑脉状方解石 0.13 -8.13 22.48 11TJ-1B12 斑脉状方解石 -0.24 -8.28 22.32 11TJ-1B14 斑脉状方解石 0.43 -8.75 21.84 13TJ-B1 大脉块状方解石 0.29 -8.54 22.06 13TJ-B10 斑脉状方解石 0.17 -9.18 21.40 13TJ-B13 桁脉状方解石 0.11 -8.46 22.14 13TJ-B18 桁脉状方解石 -0.61 -10.77 19.76 13TJ-B18 桁脉状方解石 -0.61 -10.76 19.77 李梅 13LM-B9 桁脉状方解石 0.88 -9.39 21.18 13LM-B11 大脉块状方解石 1.21 -9.66 20.90 13LM-B13-1 大脉块状方解石 1.12 -10.49 20.05 13LM-B31-1 大脉块状方解石 1.16 -10.28 20.26 13HYC-B5 斑脉状方解石 -2.71 -12.35 18.13 13HYC-B7 斑脉状方解石 -0.50 -10.32 20.22 土地坪 13TDP-B3 桁脉状方解石 -0.90 -12.35 18.13 13TDP-2B3 桁脉状方解石 -1.33 -13.15 17.30 13TDP-2B3 桁脉状方解石 -1.41 -13.23 17.22 蜂塘 13FT-B9 斑脉状方解石 -0.85 -11.17 19.35 13FT-B16 斑脉状方解石 -1.03 -11.93 18.56 13FT-B16 斑脉状方解石 -1.00 -11.85 18.64 13FT-B23 斑脉状方解石 -1.01 -11.18 19.33 13FT-B24 斑脉状方解石 -2.24 -12.47 18.01 大石沟 13DSG-B1 斑脉状方解石 -1.82 -13.05 17.41 13DSG-B3 斑脉状方解石 -1.55 -14.33 16.09 13DSG-B6 桁脉状方解石 -2.60 -13.81 16.62 13DSG-B7 斑脉状方解石 -1.29 -12.11 18.38 注:δ18OSMOW=1.03086×δ18OPDB+30.86[26] 表 2 湘西花垣地区铅锌矿床碳酸盐岩围岩的C、O同位素组成
Table 2 C and O isotopic compositions of calcites from the Huayuan Pb-Zn ore deposit in western Hu'nan
矿区 原样品号 样品名称 δ13CPDB/‰ δ18OPDB/‰ δ18OSMOW/‰ 数据来源 团结 13NZB-B17 灰岩 0.72 -8.52 22.08 本文 13NZB-B21-1 灰岩 0.92 -7.60 23.03 13NZB-B21-2 灰岩 0.97 -7.48 23.15 13HYC-B21 灰岩 0.15 -9.30 21.27 13HYC-B22 灰岩 0.57 -7.92 22.70 李梅 13LM-B23 灰岩 1.17 -8.83 21.76 本文 13LM-B28 灰岩 0.55 -9.44 21.13 13LM-B30 灰岩 0.62 -9.80 20.76 L16-4 无矿化藻灰岩 0.29 / 22.06 [20, 23] L16-6 无矿化藻灰岩 0.46 / 21.49 LM-11 灰岩 1.05 -9.11 21.47 [22] LM-16 灰岩 0.52 -9.24 21.33 蜂塘 SZS-14 灰岩 0.65 -8.95 21.63 SZS-21 灰岩 0.98 -8.99 21.59 [22] SZS-23 灰岩 0.97 -6.76 23.89 13FT-B30 灰岩 0.19 -7.60 23.03 13FT-B33-1 灰岩 0.69 -8.84 21.75 本文 13FT-B33-2 灰岩 0.65 -8.95 21.63 大石沟 13DSG-B20 灰岩 0.44 -8.47 22.13 13DSG-B21 灰岩 0.55 -10.74 19.79 本文 13DSG-B26 灰岩 0.77 -9.02 21.56 注:δ18OSMOW= 1.03086×δ18OPDB+30.86[26] 表 3 湘西花垣地区铅锌矿主成矿期成矿流体的D-O同位素组成
Table 3 δO-δD composition of ore-forming fluid from typical lead-zinc deposits in Huayuan area, western Hu'nan
矿区 样号 矿物 δ18OSMOW/‰ δDSMOW/‰ δOfluid/‰ 换算温度/℃ 团结 13TJ-B1 褐色脉状闪锌矿 / -85.50 4.30 150 13TJ-B2 褐色脉状闪锌矿 / -78.70 6.10 150 13TJ-B8 褐色脉状闪锌矿 / -85.30 -4.10 150 13TJ-B11 黄色脉状闪锌矿 / -91.10 3.30 150 13TJ-B1 方解石 21 -50.6 8.35 150 13TJ-B2 方解石 21.9 -39.4 9.25 150 13TJ-B3 方解石 21.9 -33.4 9.25 150 13TJ-B4 方解石 21.1 -44.3 8.45 150 13TJ-B7 方解石 21.3 -57.6 8.65 150 13TJ-B8 方解石 21.7 -51.6 9.05 150 13TJ-B10 斑脉状方解石 21.4 -50.7 8.75 150 13TJ-B11 方解石 21.8 -41.8 9.15 150 LM-1 斑脉状方解石 / -23 0.25 150 LM-2 斑脉状方解石 / -40 1.54 150 李梅 LM-3 斑脉状方解石 / -15 1.93 150 LM-4 斑脉状方解石 / -46 2.43 150 LM-5 斑脉状方解石 / -33 1.72 150 土地坪 13TDP-B3 粗脉状方解石 17.7 -55.8 3.89 135 13TDP-2B3 粗脉状方解石 17.3 -48.2 3.49 135 蜂塘 13FT-B26 斑脉状方解石 19.3 -44.2 5.49 135 13DSG-B10 块状方解石 17.7 -64.1 3.89 135 13DSG-B11 方解石 18 -54.7 4.19 135 13DSG-B12 方解石 17.1 -48.1 3.29 135 大石沟 13DSG-B13 方解石 16.3 -65.8 2.49 135 13DSG-B15 方解石 17.5 -46.5 3.69 135 13DSG-B16 方解石 16.8 -51.7 2.99 135 13DSG-B17 方解石 17 -46.8 3.19 135 注:δ18OSMOW=1.03086 ×δ18OPDB + 30.86[26];方解石与流体的转换公式采用1000lnα方解石-水=2.78×106T-2-2.89[29];换算温度采用测温结果的峰值,T为绝对温度 表 4 中美MVT铅锌矿床成矿温度对比
Table 4 Metallogenic temperatures contrast between Chinese and American MVT lead-zinc deposits
国家 矿床(区) 主矿物 Th/℃ 资料来源 中
国
湖
南花垣 闪锌矿
方解石120~160
90~180[1] 茶田 闪锌矿
方解石96~170
92~169闪锌矿 113~219 打狗洞 方解石 92~152 石英 85~195 闪锌矿 108~148 董家河 方解石 128~164 石英 100~343 闪锌矿 106~129 唐家寨 石英 100~220 方解石 115~139 美
国
中
部维伯纳姆和老铅带 闪锌矿 90~120 阿肯色北部 闪锌矿 95~170 三州交界地区 闪锌矿 80~120 上密西西比河谷地区 闪锌矿 75~160, 个别达220 [35-37] 田纳西中部 闪锌矿 90~150 田纳西东部 闪锌矿 70~170 肯塔基中部 闪锌矿 70~130 -
周云, 段其发, 唐菊兴, 等.湘西地区铅锌矿的大范围低温流体成矿作用——流体包裹体研究[J].地质与勘探, 2014, 50(3):515-532. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201403012.htm 刘文周, 徐新煌.论滇川黔铅锌成矿带矿床与构造的关系[J].成都理工学院学报, 1996, 23(l):71-77. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG601.009.htm 芮宗瑶, 叶锦华, 张立生, 等.扬子克拉通周边及其隆起边缘的铅锌矿床[J].中国地质, 2004, 31(4):337-346. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200404000.htm 张长青, 毛景文, 吴锁平, 等.川滇黔地区MVT铅锌矿床分布、特征及成因[J].矿床地质, 2005, 24(3):317-324. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200503012.htm 王奖臻, 李朝阳, 李泽琴, 等.川滇黔地区密西西比河谷型铅锌矿床成矿地质背景及成因探讨[J].地质地球化学, 2001, 29(2):41-45. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ200102006.htm 王奖臻, 李朝阳, 李泽琴, 等.川、滇、黔交界地区密西西比河谷型铅锌矿床与美国同类矿床的对比[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2002, 21(2):127-132. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200202011.htm 汤朝阳, 邓峰, 李堃, 等.湘西-黔东地区寒武系都匀阶清虚洞期岩相古地理与铅锌成矿关系研究[J].地质与勘探, 2013, 49(l):19-27. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201301004.htm 曾勇, 李成君.湘西董家河铅锌矿地质特征及成矿物质来源探讨[J].华南地质与矿产, 2007, 23(3):24-30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKC200703004.htm 林方成.扬子地台西缘大渡河谷超大型层状铅锌矿床地质地球化学特征及成因[J].地质学报, 2005, 79(4):540-556. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200504017.htm 刘文均, 郑荣才.花垣铅锌矿床成矿流体特征及动态[J].矿床地质, 2000, 19(2):173-181. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201705014.htm 杨绍祥, 劳可通.湘西北铅锌矿床的地质特征及找矿标志[J].地质通报, 2007, 26(7):899-908. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=200707147&journal_id=gbc 周家喜, 黄智龙, 周国富, 等.黔西北天桥铅锌矿床热液方解石C、O同位素和REE地球化学[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2012, 36(1):93-101. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201201016.htm 毛德明.贵州赫章天桥铅锌矿床围岩的氧-碳同位素研究[J].贵州工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2000, 29(2):8-11. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZGX200002001.htm 黄智龙, 陈进, 韩润生, 等.云南会泽超大型铅锌矿床地球化学及成因——兼论峨眉山玄武岩与铅锌成矿的关系[M].北京:地质出版社, 2004:28-58. 黄智龙, 李文博, 陈进, 等.云南会泽超大型铅锌矿床C、O同位素地球化学[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2004, 28(1):53-59. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200401007.htm Spangenberg J, Fontbote L, Sharp Z D. Carbon and oxygen isotope study of hydrothermal carbonates in the zinc lead deposits of the San Vicente district, central Peru:a quantitative modeling on mix-ing processes and CO2 degassing[J]. Chemical Geology, 1996, 133(1/4):289-315. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271528998_Rare_earth_element_patterns_in_the_host_and_gangue_carbonates_of_the_San_Vicente_zinc-lead_deposit_Peru
Huang Z L, Li W B, Chen J, et al. Carbon and oxygen isotope con-straints on mantle fluid involvement in the mineralization of the Huize super-large Pb-Zn deposits, Yunnan Province, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2003, 78/79:637-642. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/247864241_The_Source_of_Metals_in_the_Qilinchang_Zn-Pb_Deposit_Northeastern_Yunnan_China_Pb-Sr_Isotope_Constraints
Huang Z L, Li W B, Zhou MF, et al. REE and C-O isotopic geo-chemistry of calcites from the world-class Huize Pb-Zn deposits, Yunnan, China:Implications for the ore genesis[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2010, 84(3):597-613. doi: 10.1111/acgs.2010.84.issue-3
黄思静.碳酸盐岩的成岩作用[M].北京:地质出版社, 2000:1-288. 夏新阶, 舒见闻.李梅锌矿床地质特征及其成因[J].大地构造与成矿学, 1995, 19(3):197-204. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK503.001.htm 杨绍祥, 劳可通.湘西北铅锌矿床碳氢氧同位素特征及成矿环境分析[J].矿床地质, 2007, 26(3):330-340. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200703009.htm 蔡应雄, 杨红梅, 段瑞春, 等.湘西-黔东下寒武统铅锌矿床流体包裹体和硫、铅、碳同位素地球化学特征[J].现代地质, 2014, 28(1):29-41. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201401004.htm 李堃, 吴昌雄, 汤朝阳, 等.湘西黔东地区铅锌矿床C、O同位素地球化学特征及其对成矿过程的指示[J].中国地质, 2014, 41(5):1608-1619. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201405016.htm 钟九思, 毛昌明.湘西北密西西比河谷型铅锌矿床特征及成矿机制探讨[J].国土资源导刊, 2007, 4(6):52-56. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTDK200706041.htm 段其发, 曹亮, 曾健康, 等.湘西花垣矿集区狮子山铅锌矿床闪锌矿Rb-Sr定年及地质意义[J].地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 2014, 39(8):977-999. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201408004.htm Friedman I, O'Neil J R. Compilation of Stable Isotope Fraction-ation Factors of Geochemical[M]. Washington:United States Gov-ernment Printing Office, 1977:1-12.
Hoefs J. Stable isotope geochemistry[M]. Berlin:Spring Verlag, 1997:65-168.
刘家军, 何明勤, 李志明, 等.云南白秧坪银铜多金属矿集区碳氧同位素组成及其意义[J].矿床地质, 2004, 23(1):1-10. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200401000.htm O'Neil J R, Clayton R N, Mayeda T K. Oxygen isotope frac-tionation in divalent metal carbonates[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1969, 51(12):5547-5558. doi: 10.1063/1.1671982
路远发. GeoKit:一个用VBA构建的地球化学工具软件包[J].地球化学, 2004, 33(5):459-464. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200405003.htm 王林均, 包广萍, 崔银亮, 等.黔西北典型铅锌矿床碳-氧同位素地球化学研究[J].矿物学报, 2013, 33(4):709-712. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201304044.htm 郑永飞.稳定同位素体系理论模型及其矿床地球化学应用[J].矿床地质, 2001, 20(1):57-70. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200101008.htm Zheng Y F. Carbon-oxygen isotopic covariations in hydrothermal calcite during degassing of CO2:A quantitative evaluation and appli-cation to the Kushikino gold mining area in Japan[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 1990, 25:246-250. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/221953726_Geochemistry_and_stable_isotope_constraints_on_high-T_activity_from_sediment_cores_of_the_Saldanha_hydrothermal_field
Zheng Y F, Hoefs J. Carbon and oxygen isotopic covariations in hydrothermal calcites[J].Mineralium Deposita, 1993, 28:79-89. doi: 10.1007/bf00196332.pdf
Appold M S, Garven G. The hydrology of ore formation in the Southeast Missouri district:numerical models of topography-driv-en fluid flow during the Ouachit a orogen[J]. Economic Geology, 1999, 94:913-936. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.94.6.913
Leach D L, Sangster D F. Mississippi Valley-type lead-zinc deposits[C]//Kirkham R V, Sinclair W D, Thorpe R I. Mineral Deposit Modeling. Geological Association of Canada. Spec. Papers., 1993, 40:289-314.
Leach D L, Bradley D C, Lewchuk M, et al. Mississippi Valleytype lead-zinc deposits through geological time:implications from recent age-dating research[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2001, 36:711-740. doi: 10.1007/s001260100208
Leach D L, S angster D F, Kelley K D, et al. Sedement-hosted lead-zinc deposits:A global perspective[C]//Hedenquist J W, Thompson J F H, Goldfarb R J, et al. Economic Geology 100th Anniversary Volume, 2005:561-607.



 下载:
下载: