Lower Ordovician carbon isotope excursion in the eastern Yangtze Gorges area and its genetic analysis
-
摘要:
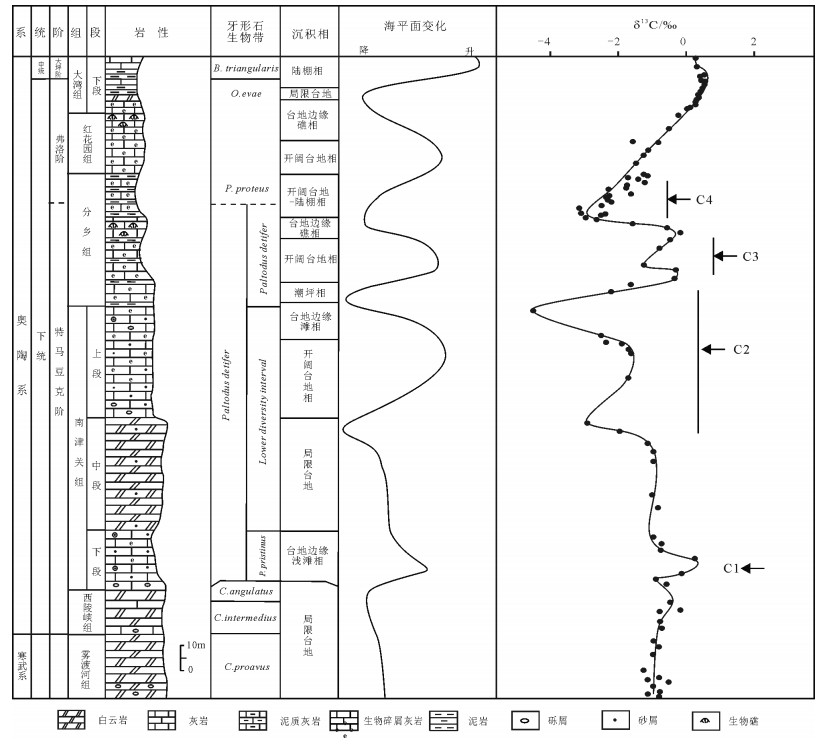
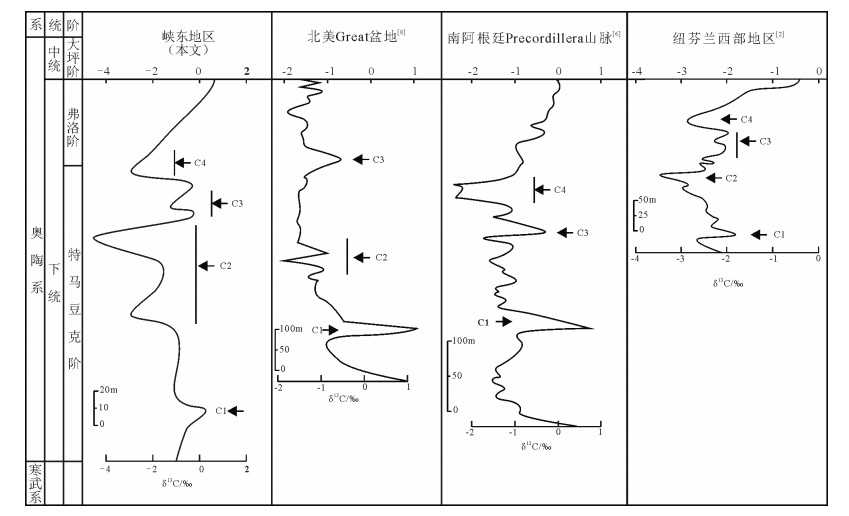
以宜昌黄花场奥陶系剖面为研究对象,开展峡东地区早奥陶世C同位素研究,建立了峡东地区早奥陶世C同位素曲线,并识别出可全球对比的2次正漂移(C1,C3)和2次负漂移(C2,C4)。通过分析峡东地区沉积相序列及海平面变化特征,发现峡东地区C同位素变化曲线与海平面波动曲线一致,表明峡东地区C同位素的变化主要受控于海平面的波动。
Abstract:The carbon stable isotope curve was constructed in this paper from the Huanghuachang sections of Lower Ordovician in the eastern Yangtze Gorges area.δ13C data demonstrate that there existed two δ13C positive excursions (C1, C3) and two negative excursions (C2, C4), all of which are comparable in the global scale.Based on the sedimentary sequence characteristics of Lower Or-dovician in the eastern Yangtze Gorges area, the authors observed that the curve of δ13C is coincident with the curve of the regional sea-level fluctuations.This study indicates that the geochemistry as well as the sequences was well controlled by the sea level changes.
-
多龙矿集区位于青藏高原改则县西北约100km处,大地构造位置处于班公湖-怒江缝合带北缘、南羌塘地块最南缘、日土-多不杂岩浆弧东段,主要由多不杂、波龙、拿顿、拿若、铁格龙、尕尔勤、地堡那木岗等矿体组成,是新近探明具有超大型远景的、典型的富金斑岩型铜矿区,同时也是班公湖-怒江成矿带最大的斑岩型铜金矿区[1-2]。目前,关于多龙矿集区的成岩成矿地质背景依然存在争议:①曲晓明等[3]认为,其形成于大陆碰撞地壳隆升阶段;②佘宏全等[4]暗示,其成岩成矿作用与洋脊俯冲有关;③大多数学者均赞同,多龙矿集区是典型的岛弧型斑岩型铜金矿区,其成岩成矿作用与班公湖-怒江新特提斯洋的北向俯冲密切相关[5-13];④段志明等[14-15]和符家骏等[16]进一步强调,多龙斑岩型铜矿是发育在增生楔体系之上的岛弧型斑岩型铜金矿床。本文基于区域地质调查研究,在多龙矿集区新厘定出岩墙岭蛇绿岩残片,对揭示班公湖-怒江缝合带西段构造格架、班公湖-怒江洋的演化历史及多龙矿集区成岩成矿地质背景具有重要的地质意义。
1. 地质背景
班公湖-怒江缝合带横亘于青藏高原中部,向西延伸到克什米尔,向东南沿怒江河谷延伸出西藏,在中国境内延伸2500km 以上,是班公湖-怒江洋消亡闭合后的遗迹,是分割北拉萨地块和南羌塘地块的重要地质界线,同时也是青藏高原一条重要的多金属成矿带[2, 17]。班公湖-怒江洋的构造演化一直是地学界争论的焦点之一,主流观点认为其闭合时间为晚侏罗世—早白垩世[18-22],但越来越多的资料指示,班公湖-怒江洋在早白垩世仍具有一定规模[23-28]。
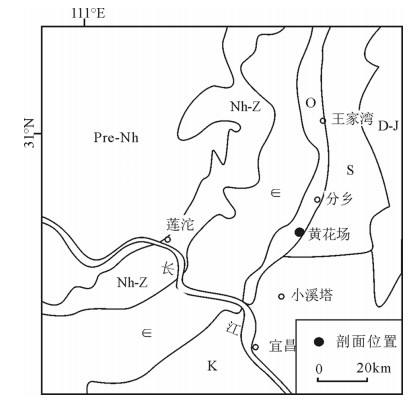
多龙矿集区位于班公湖-怒江缝合带西段,南羌塘地块最南缘日土-多不扎岩浆弧东段,受控于班公湖-怒江洋北向俯冲、消减、碰撞等动力学过程,构造地质特征极其复杂,同时具有良好的成矿条件(图 1-a)。矿集区出露的主体地层为下侏罗统曲色组和中侏罗统色哇组(图 1-b),岩性组成包括石英砂岩、长石岩屑杂砂岩、粉砂岩、页岩、泥岩、灰岩等,砂页岩韵律互层现象明显,砂岩的矿物成熟度和结构成熟度均较差,并发育底面印模构造和完整的鲍玛序列,是一套深水-半深水环境的复理石沉积①②(①吉林大学地质调查院.中华人民共和国1∶5 万多不扎幅区域地质调查报告.2015.②四川省地质调查院.中华人名共和国1∶25 万物玛幅区域地质调查报告.2004.)(待发表)。下白垩统美日切错组火山岩沉积地层角度不整合于下伏地层之上(图 1-b),岩石组合以杂色安山岩和安山质角砾岩为主,次为流纹岩、流纹质凝灰岩、玄武岩等,表现出多期次旋回性喷发的特点(待发表)。上白垩统阿布山组大面积分布于矿集区西北部,不整合于下伏地层之上(图 1-b),岩性主要为中厚-巨厚层状红褐色细砾岩、细-粗角砾岩与中厚层状含砾粗砂岩及中细砂岩,其中砾石成分包括橄榄岩、辉长岩、灰岩、砂岩、火山岩等,为班公湖-怒江洋闭合后的一套山间磨拉石沉积①(①吉林大学地质调查院.中华人民共和国1∶5 万多不扎幅区域地质调查报告.2015.)。
![]() 图 1 青藏高原构造简图(a)及班公湖-怒江缝合带西段多龙矿集区地质简图①(①吉林大学地质调查院.中华人民共和国1∶5 万多不扎幅区域地质调查报告.2015.)(b)KMKSZ—康西瓦-玛沁-昆仑山构造带;JSSZ—金沙江构造带;LSSZ—龙木错-双湖缝合带;BNSZ—班公湖-怒江缝合带;SNMZ—狮泉河-纳木错蛇绿混杂岩带;LMF—洛巴堆-米拉山断裂带;IYZSZ—印度河-雅鲁藏布缝合带;ATF—阿尔金断裂Figure 1. Tectonic framework of the Tibetan Plateau (a) and simplified geologicalmap of the Duolong ore concentration area in the westernsegment of Bangong-Nujiang River suture zone
图 1 青藏高原构造简图(a)及班公湖-怒江缝合带西段多龙矿集区地质简图①(①吉林大学地质调查院.中华人民共和国1∶5 万多不扎幅区域地质调查报告.2015.)(b)KMKSZ—康西瓦-玛沁-昆仑山构造带;JSSZ—金沙江构造带;LSSZ—龙木错-双湖缝合带;BNSZ—班公湖-怒江缝合带;SNMZ—狮泉河-纳木错蛇绿混杂岩带;LMF—洛巴堆-米拉山断裂带;IYZSZ—印度河-雅鲁藏布缝合带;ATF—阿尔金断裂Figure 1. Tectonic framework of the Tibetan Plateau (a) and simplified geologicalmap of the Duolong ore concentration area in the westernsegment of Bangong-Nujiang River suture zone岩浆岩在矿集区分布广泛,岩石类型复杂多样,包括中酸性侵入体、基性岩墙群等,均侵入于侏罗系内(图 1-b)。酸性岩浆活动最为强烈,主要岩性为花岗闪长斑岩、花岗斑岩、二长花岗岩、石英斑岩等;中性岩浆活动较弱,主要岩性为闪长岩、闪长玢岩等,侵入体规模较小,均为小型岩株及岩瘤,成群、成带分布,在横截面上多呈近圆形、椭圆形或纺锤状;基性岩浆活动较强,表现为近东西向展布的基性岩墙群,主要岩性为辉长岩。多项矿产普查和专题研究工作表明,区内优势矿种为铜和金,铜资源量超过1300×104t,金资源量超过400t[29],花岗闪长斑岩和花岗斑岩是区内斑岩型铜金矿主要的成矿岩体。大量的年代学资料表明,中酸性侵入体的形成时代集中在116~128Ma 之间[1, 3-13],矿体的成矿时代为118~119Ma[4, 6-7],侵入于侏罗纪增生楔体系内的基性岩墙群的形成时代为126~127Ma(图 1-b),表明多龙矿集区的成岩-成矿时代基本一致,同时指示多龙矿集区在早白垩世应处于伸展拉张的构造环境[30]。近年来的区域地质调查研究表明,多龙矿集区南侧出露一套岩石组合特征鲜明的岩墙岭蛇绿岩残片。
2. 蛇绿岩残片基本地质特征
蛇绿岩残片整体呈近东西向分布于矿集区岩墙岭地区(图 1-b),组成端元包括席状岩墙群、玄武岩及硅质岩,因后期构造肢解而缺失堆晶杂岩和地幔橄榄岩端元。岩墙岭蛇绿岩残片的各端元呈棱形或透镜体状断续分布于侏罗系,构成典型的网结状构造。糜棱岩普遍发育在岩墙岭蛇绿岩残片各端元和围岩的接触部位,为岩墙岭蛇绿岩属性的进一步确定提供了重要证据。各个岩性端元详细描述如下。
(1)席状岩墙群是岩墙岭蛇绿岩残片的重要组成端元,主体岩性为辉长岩,在一个露头上可见上百条岩墙呈平行的席状产出,部分岩墙呈直立状(图版Ⅰ-A),部分岩墙因后期构造作用呈斜坡状,单个岩墙的宽度一般在0.5~1m 之间,个体独立产出,且个体之间可见冷凝边和烘烤边。岩石风化面呈灰褐色、红褐色,新鲜面呈灰绿色、灰黑色,发育典型的辉长结构,由针柱状、板状斜长石和半自形辉石构成(图版Ⅰ-B),块状构造。
(2)玄武岩是岩墙岭蛇绿岩残片的另一组成端元,其中枕状玄武岩出露最为广泛,次为杏仁状玄武岩、气孔状玄武岩,枕状玄武岩的枕状构造保存完整(图版Ⅰ-C),单个岩枕呈椭圆形,长轴一般在0.2~0.5m 之间,部分不与岩墙群直接接触,部分直接覆盖于岩墙群之上(图版Ⅰ-D)。岩石风化面呈灰黑、红褐色,新鲜面为灰绿色、灰黑色。气孔状玄武岩构造破碎严重,多呈小岩块混杂在片理化砂岩内(图版Ⅰ-E)。杏仁状玄武岩发育斑状结构,由0.5~1.5mm 的椭圆状-圆状杏仁体和基质组成(图版Ⅰ-F)。
(3)硅质岩作为岩墙岭蛇绿岩残片的上覆岩系,代表着远洋深海沉积物,在矿集区内呈一系列构造块体分布于侏罗系内,天然露头较好,风化面呈黄白色、灰白色,新鲜面呈灰白色、灰色,条带状构造明显(图版Ⅰ-G)。
(4)糜棱岩主要发育在硅质岩、玄武岩与围岩的接触部位,由韧性基质(40%)和变斑晶(60%)组成,发育典型的眼球状构造(图版Ⅰ-H),这既明确了岩墙岭蛇绿岩与侏罗系间的构造接触关系,也为岩墙岭蛇绿岩构造属性的确定提供了重要依据。
3. 意义及结论
岩墙岭蛇绿岩残片主要由席状岩墙群、玄武岩及硅质岩组成,整体呈棱形或透镜体状断续分布于侏罗系中,两者共同组成多龙矿集区的增生楔体系。结合前人研究成果,笔者支持多龙矿集区是发育在增生楔体系之上的观点,早白垩世基性岩墙群的确定进一步指示,多龙矿集区早白垩世成岩成矿作用形成于增生楔之上伸展拉张的地质背景。岩墙岭蛇绿岩残片位于班公湖-怒江缝合带的北缘,应该是班公湖-怒江蛇绿岩带的重要组成部分,因此,它的发现为班公湖-怒江缝合带的延伸及其构造演化的研究提供了新的线索。
-
图 3 峡东地区早奥陶世δ13C变化及其对海平面变化的响应
(C1~C4—代表 4次δ13C源移,大湾组下部数据据参考文献[11])
Figure 3. δ13C variations and responses to the sea-leval changes during the Lower Ordovician in the east of Yangtze Gorges area
表 1 峡东地区早奥陶世C-O同位素测试结果
Table 1 δ13C and δ18O data of samples from the Lower Ordovician strata in the east of Yangtze Gorges area
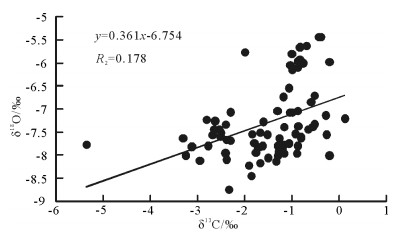
样品号 层位 δ13C/‰ δ18O/‰ YYHH-77T 红花园组 -0.28 -7.14 YYHH-76T 红花园组 -0.52 -6.71 YYHH-75T 红花园组 -0.89 -7.97 YYHH-74T 红花园组 -1.62 -7.8 YYHH-73T 红花园组 -1.16 -7.97 YYHH-72T 红花园组 -1.28 -7.93 YYHH-71T 红花园组 -1.51 -7.56 YYHH-70T 红花园组 -1.29 -7.8 YYHH-69T 分乡组 -1.2 -7.86 YYHH-68T 分乡组 -1.29 -8.02 YYHH-67T 分乡组 -1.79 -7.74 YYHH-66T 分乡组 -1.5 -8.06 YYHH-65T 分乡组 -1.33 -8.14 YYHH-64T 分乡组 -1.85 -8.46 YYHH-63T 分乡组 -1.83 -7.55 YYHH-62T 分乡组 -2.4 -7.96 YYHH-61T 分乡组 -1.66 -8.18 YYHH-60T 分乡组 -2.37 -7.67 YYHH-59T 分乡组 -2.5 -7.6 YYHH-58T 分乡组 -2.39 -7.34 YYHH-57T 分乡组 -2.29 -7.07 YYHH-56T 分乡组 -2.62 -7.26 YYHH-55T 分乡组 -3.3 -7.64 YYHH-54T 分乡组 -3.24 -8.01 YYHH-53T 分乡组 -2.49 -7.52 YYHH-52T 分乡组 -2.64 -7.45 YYHH-51T 分乡组 -3.11 -7.82 YYHH-50T 分乡组 -2.8 -7.24 YYHH-49T 分乡组 -2.76 -7.8 YYHH-48T 分乡组 -1.6 -7.28 YYHH-47T 分乡组 -0.65 -7.45 YYHH-46T 分乡组 -0.26 -7.56 YYHH-45T 分乡组 -0.56 -7.39 YYHH-44T 分乡组 -0.86 -7.37 YYHH-43T 分乡组 -1.26 -7.64 YYHH-42T 分乡组 -0.38 -5.44 YYHH-41T 分乡组 -0.42 -5.45 YYHH-40T 分乡组 -1.66 -7.52 YYHH-39T 分乡组 -2.29 -7.69 YYHH-38T 南津关组 -5.33 -7.78 YYHH-37T 南津关组 -2.67 -7.57 YYHH-36T 南津关组 -2.53 -7.45 YYHH-35T 南津关组 -2.37 -8.1 YYHH-34T 南津关组 -1.9 -8.23 YYHH-33T 南津关组 -1.76 -7.95 YYHH-32T 南津关组 -1.68 -7.83 YYHH-31T 南津关组 -1.72 -7.84 YYHH-30T 南津关组 -2.94 -8.12 YYHH-29T 南津关组 -1.99 -5.77 YYHH-28T 南津关组 -1.17 -6.74 YYHH-27T 南津关组 -0.99 -6.16 YYHH-26T 南津关组 -0.99 -7.08 YYHH-25T 南津关组 -0.87 -5.97 YYHH-24T 南津关组 -1.03 -6.05 YYHH-23T 南津关组 -1.06 -7.75 YYHH-22T 南津关组 -0.8 -7.64 YYHH-21T 南津关组 -0.8 -7.61 YYHH-20T 南津关组 0.13 -7.21 YYHH-19T 南津关组 -0.2 -8.01 YYHH-18T 南津关组 -0.92 -7.54 YYHH-17T 南津关组 -0.69 -5.63 YYHH-16T 西陵峡组 -0.51 -7.33 YYHH-15T 西陵峡组 -0.2 -5.98 YYHH-14T 西陵峡组 -0.82 -5.66 YYHH-13T 西陵峡组 -0.83 -5.67 YYHH-12T 西陵峡组 -0.76 -6.01 YYHH-11T 雾渡河组 -1 -5.81 YYHH-10T 雾渡河组 -0.87 -6.1 YYHH-9T 雾渡河组 -1.06 -6.55 YYHH-8T 雾渡河组 -1.3 -7.04 YYHH-7T 雾渡河组 -0.87 -7.05 YYHH-6T 雾渡河组 -1.16 -7.78 YYHH-5T 雾渡河组 -0.59 -6.85 YYHH-4T 雾渡河组 -1.04 -7.08 YYHH-3T 雾渡河组 -0.83 -5.93 YYHH-2T 雾渡河组 -1.16 -7.39 YYHH-1T 雾渡河组 -0.87 -7.8 -
Ainsaar L, Meidla T, Martma T. The middle Caradoc facies and fau-nal turnover in the Late Ordovician Baltoscandian palaeobasin[J]. Pa-laeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2004, 210:119-133. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2004.02.046
Azmy K, Lavoie D. High-resolution isotope strtigraphy of the Or-dovician St. George Group of western Newfoundland, Canada:impli-cations to carbonate for global correlation[J]. Can. J. Earth Sci., 2009, 46:403-423. doi: 10.1139/E09-032
Barta N C, Bergstroem S M, Saltzman M R, et al. First record of the Ordovician Guttenberg δ13C excursion (GICE) in New York State and Ontario:Local and regional chronostratigraphic implications[J]. Northeastern Geology and Environmental Sciences, 2007, 29:276-298. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279891268_First_record_of_the_Ordovician_Guttenberg_d13C_excursion_GICE_in_New_York_State_and_Ontario_Local_and_regional_chronostratigraphic_implications
Bergstroem S M, Chen X, Gutiérrez-Marco J C, et al. The new chronostratigraphic classification of the Ordovician System and its re-lations to major regional series and stages and to δ13C chemostratig-raphy[J]. Lethaia, 2009, 42:97-107. doi: 10.1111/let.2009.42.issue-1
Bergstroem S M, Saltzman M R, Schmitz B. First record of the Hirnantian (Upper Ordovician) δ13C excursion in the North Amer-ican Midcontinent and its regional implications[J]. Geological Maga-zine, 2006, 143:657-678. doi: 10.1017/S0016756806002469
Buggisch W, Keller M, Lehnert O. Carbon isotope record of late Cambrian to Early Ordovician carbonates of the Argentine Precordil-lera[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2003, 195:357-373. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(03)00365-1
Munnecke A, Zhang Y D, Liu X, et al. Stable carbon isotope stratig-raphy in the Ordovician of South China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeo-climatology, Palaeoecology, 2011, 307:17-43. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2011.04.015
Edwards C T, Saltzman M R. Carbon isotope (δ13Ccarb) stratigraphy of the Lower Ordovician (Tremadocian-Darriwilian) in the Great Basin, western United States:Implications for global correlation[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2014, 399:1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2014.02.005
Kaufman A J, Knoll A H. Neoproterozoic variations in the C-isoto-pic composition of seawater:Stratigraphic and biogeochemical impli-cations[J]. Precambrian Research, 1995, 73(1/4):27-29. http://www.oalib.com/references/15775635
Melchin M J, Holmden C. Carbon isotope chemostratigraphy in Arctic Canada:Sea-level forcing of carbonate platform weathering and implications for Hirnantian global correlation[J]. Palaeogeogra-phy, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2006, 234:186-200. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2005.10.009
Wang X F, Stouge S, Erdmann B D, et al. A proposed GSSP for the base of the Middle Ordovician Series:the Huanghuachang sec-tion, Yichang, China[J]. Episodes, 2005, 28:105-117. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Svend_Stouge/publication/242661737_A_proposed_GSSP_for_the_base_of_the_Middle_Ordovician_Series_The_Huanghuachang_section_Yichang_China/links/0c960535e40f14c7fa000000.pdf
Young S, Saltzman M R, Bergstroem S M. Upper Ordovician (Mo-hawkian) carbon isotope (δ13C) stratigraphy in eastern and central North America:Regional expression of a perturbation of the global carbon cycle[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecolo-gy, 2005, 222:53-76. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2005.03.008
涂珅, 王舟, 王家生.宜昌王家湾奥陶系-志留系界线地层高分辨率碳、氧同位素记录及其成因[J].地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 2012, 37(2):165-174. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX2012S2023.htm 冯洪真, 刘家润, 施贵军.湖北宜昌地区寒武系-下奥陶统的碳氧同位素记录[J].高校地质学报, 2000, 6(1):106-115. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200001011.htm Fang J X, Peng P A, Melchin M J. Carbon isotopes and event stra-tigraphy near the Ordovician-Silurian boundary, Yichang, South China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2009, 276:160-169. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2009.03.007
Gorjan P, Kaiho K, Fike D A, et al. Carbon-and sulfur-isotope geochemistry of the Hirnantian (Late Ordovician) Wangjiawan (Riverside) section, South China:global correlation and environ-mental event interpretation[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2012, 337/338:14-22. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2012.03.021
王传尚, 汪啸风, 陈孝红, 等.峡东地区奥陶系庙坡组地球化学异常与海平面变化研究[J].地质地球化学, 2003, 31(2):57-64. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ200302008.htm Chen X, Rong J Y, Fang J X, et al. The global boundary stratotype section and point (GSSP) for the base of the Hirnantian stage (the uppermost of the Ordovician system)[J]. Episodes, 2006, 29(3):183-196. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/262923312_The_Global_Boundary_Stratotype_Section_and_Point_GSSP_for_the_base_of_the_Hirnantian_Stage_the_uppermost_of_the_Ordovician_System
Wang X F, Stouge S, Chen X H, et al. The global stratotype sec-tion and point for the base of the middle Ordovician series and the third stage (Daping)[J]. Episodes, 2009, 32:96-113. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/287619805_The_Global_Stratotype_Section_and_Point_for_the_base_of_the_Middle_Ordovician_Series_and_the_Third_Stage_Dapingian
穆恩之, 朱兆玲, 陈均远, 等. 中国西南的奥陶系[C]//中国科学院南京地质古生物研究所编. 西南地区碳酸盐生物地层. 1979: 108-154. 曾庆銮, 赖才根, 徐光洪, 等.长江三峡地区生物地层学(早古生代分册)[M].北京:地质出版社, 1987:43-142. 曾庆銮.峡东地区奥陶纪腕足类群落与海平面升降变化[J].中国地质科学院宜昌地质矿产研究所所刊, 1991, 16:19-39. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ199101001003.htm 陈孝红, 汪啸风, 李志宏, 等.湖北宜昌黄花场中/下奥陶统界线附近几丁虫组合及其地层学意义[J].地层学杂志, 2002, 26(4):241-252. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ200204000.htm 汪啸风, Stouge S, 陈孝红, 等.全球下奥陶统-中奥陶统界线层型候选剖面-宜昌黄花场剖面研究新进展[J].地层学杂志, 2005, 29:467-489. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ2005S1011.htm 曾庆銮, 赖长根, 徐光洪, 等.长江三峡地区生物地层学(2), 早古生代分册:奥陶系[M].北京:地质出版社, 1987:43-142. Kaufman A J, Knoll A H. Neoproterozoic variations in the C-iso-topic composition of seawater:Stratigraphic and biogeochemical implications[J]. Precambrian Research, 1995, 73(1/4):27-29. http://www.oalib.com/references/19238429
Erdtmann B D, Paalits I. The Early Ordovician"Ceratopyge Re-gressiv Event" (CRE):its correlation and biotic dynamic across the East European Platform[J]. Lithuanian Geological Society, Geologi-ja, 1994, 17:36-57. http://www.academia.edu/1447683/Stable_carbon_isotope_stratigraphy_in_the_Ordovician_of_South_China
苏文博.上扬子地台东南缘奥陶纪层序地层及海平面变化研究[M].北京:地质出版社, 2001:24-59. 陈孝红, 张淼, 王传尚.华南地区奥陶纪几丁虫[M].北京:地质出版社, 2008:71-97. Bergstroem S M, Lofgren A, Maletz J. The GSSP of the Second (upper) Stage of the Lower Ordovician Series:Diabasbrottet at Hunneberg, Province of Vastergotland, southwestern Sweden[J]. Episodes, 2004, 27(4):265-272. http://portal.research.lu.se/portal/en/publications/the-gssp-of-the-second-upper-stage-of-the-lower-ordovician-series-diabasbrottet-at-hunneberg-province-of-vastergotland-southwestern-sweden(760b5da2-39ae-43eb-8076-ceff6c6b3aba).html
陈旭, 丘金玉.宜昌奥陶纪的古环境演变[J].地层学杂志, 1986, 10(1):1-15. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ198601000.htm




 下载:
下载: