A study of geochronology, geochemistry and genesis of Maqigang beschtauite pluton, south-eastern Guangxi
-
摘要:
马其岗石英二长斑岩体出露于桂东南博白-梧州断裂带南东侧,对其开展了锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学、Sr-Nd-Hf同位素及成因研究。结果表明,岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为90.2±1.5Ma(MSWD=1.7)。岩体富碱(ALK=7.38%~8.14%)、富钾(K2O=4.41%~4.78%),稀土元素特征为轻稀土元素富集型,微量元素特征为富集大离子亲石元素(Rb、Th、U、K、Pb、LREE),亏损高场强元素(Nb、Ta、P、Ti、HREE),符合钾玄岩系列的岩石特点。岩体有较高的Mg#值(42.82~50.35),较低的Sr含量(268.00×10-6~304.00×10-6),以及较高的锆石饱和温度(860~883℃),同时Nb/Ta(平均值为11.24)、Zr/Hf(平均值为38.20),Th/La值(平均值为0.17)明显不同于大陆地壳特征,表明岩浆主要来自下部地壳或地幔,在上升侵位过程中受到地壳大规模混染程度较小,具有EMⅡ富集地幔端元的Sr-Nd同位素特征。二阶段Nd模式年龄(tDM2)变化于1.33~1.36Ga之间,二阶段Hf模式年龄(tDM2)主体为1.20~1.50Ga,两者模式年龄较一致,显示马其岗岩体可能是中元古代中期镁铁质岩石部分熔融的产物。石英二长斑岩形成于板内伸展环境,整个华南在90Ma左右存在一次大规模的伸展事件,其动力学机制与古太平洋板块低角度俯冲有关。
Abstract:Maqigang beschtauite pluton is located in the southeast of the Bobai-Wuzhou fault, southeastern Guangxi.The zircon UPb geochronology, elemental geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic components as well as petrogenesis of Maqigang beschtauite were investigated in this paper.The LA-ICPMS zircon U-Pb age is 90.2±1.5Ma (MSWD=1.7).The beschtauite is characterized by rich alkalis (ALK=7.38%~8.14%) and K (K2O=4.41%~4.78%).The rare earth elements exhibit the light REE enrichment type, with trace elements characterized by enrichment of LILE (e.g., Rb, Th, U, K, Pb, LREE) and depletion of HFSE elements (e.g., Nb, Ta, P, Ti, HREE).The geochemical characteristics of Maqigang beschtauite show shoshonitic features.The beschtauite has relatively high Mg# values (42.82~50.35) and zircon saturation temperatures (860~883℃) and low Sr values (268.00×10-6~304.00×10-6).The Nb/Ta ratios (11.24 on average), Zr/Hf ratios (38.20 on average) and Th/La ratios (0.17 on average) of the beschtauite are remarkably different from those of upper crustal rocks, indicating that the beschtauite originated from lower crustal or mantle source.In addition, the beschtauitic magma was less contaminated by the upper crust substance in the process of emplacement.The Sr-Nd isotopic com-positions show that they have the characteristics of the EMⅡ source.Nd isotopic two-phase model age (tDM2=1.33~1.36Ga) is similar to the Hf isotopic two-phase model principal age (tDM2=1.20~1.50Ga), inmplying that the beschtauite was derived dominantly from mafic rocks in the middle Proterozoic.The Maqigang beschtauite was formed in an intra-plate extensional environment.There was a huge stretching event throughout South China at 90Ma±.The dynamic mechanism of the event was connected with low angle sub-duction of the ancient Pacific plate.
-
Keywords:
- geochronology /
- geochemistry /
- genesis /
- Maqigang beschtauite pluton /
- southeastern Guangxi
-
桂东南地处特提斯构造域和环太平洋构造域的交汇部,同时处在扬子与华夏二大块体接合部,其形成是扬子、华夏和印支三大板块联合作用的结果,因此具有复杂的构造演化与岩浆作用特点。该区中生代岩浆活动强烈,并呈北东向大面积分布,长期以来受到广泛关注,尤其是该区发育的一套中生代钾玄质系列火成岩的研究取得了丰富成果[1-2]。钾玄质(Shoshonitic)系列火山岩的发现命名源于美国黄石公园Shoshone河地区中基性火山岩研究[3],此后发展为将岩石化学成分上与钾玄质系列火山岩相当的侵入岩也归于钾玄质系列,使其成为独立完整的岩浆岩系列,对新生代钾玄质系列岩石的研究表明,其对于探讨地幔性质、壳幔相互作用、构造背景等具有重要的科学意义。马其岗岩体属于钾玄质系列岩石,前人曾将其归为桂东南钾玄质侵入岩带的一部分[1],但缺乏系统的研究,其精确年代也未见公开报道。本文通过桂东南马其岗石英二长岩锆石U-Pb精确年龄的测定,结合地球化学及Sr-Nd-Hf同位素资料,探讨其成因和形成的构造背景,为华南腹地晚白垩世的动力学背景研究提供依据。
1. 地质背景和岩石学特征
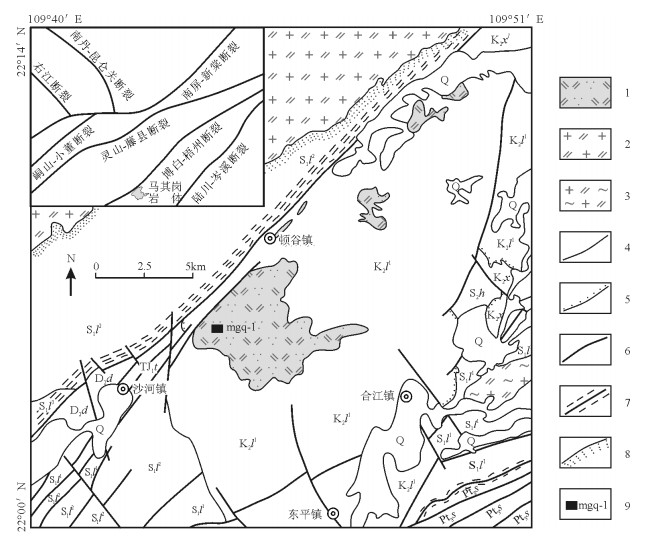
马其岗石英二长斑岩出露于博白-梧州断裂带南东侧,由马其岗、三贝岭等6个岩体组成,出露总面积28.76km2,岩体总体呈不规则状、长条状,展布方向与博白-梧州断裂带平行(图 1)。其中,马其岗岩体出露面积最大,为24.79km2。岩体侵入于上白垩统罗文组一段,岩体的岩石类型基本相同,岩性为石英二长斑岩。本次样品采自出露新鲜的马其岗岩体内,具斑状结构、块状构造,斑晶由斜长石、钾长石、辉石、石英组成,粒度0.2~8mm,其中斜长石(30%)呈半自形板状,杂乱分布或聚斑状产出,具轻粘土化,透长石(1%~5%)呈半自形板状-他形粒状,分布零星;辉石以斜方辉石为主(10%)、单斜辉石次之(1%~5%),半自形粒状,常见皂石沿其粒内裂隙及边缘交代;石英(1%~5%)呈自形-半自形粒状,零星分布。基质由长石、石英、黑云母、辉石组成,粒度小于0.2mm,其中长石(45%)呈微晶状嵌布在石英(10%)基底上构成包含嵌晶结构;黑云母(1%~5%)以微晶产出,相对集合呈堆状嵌布在石英上;辉石(<1%)微粒状,零星分布。副矿物主要由磁铁矿及磷灰石组成。
![]() 图 1 马其岗岩体地质图(据参考文献①修改)Q—第四系;K2l1—罗文组第一段;K2x1—西垌组第一段;K2x—西垌组(未分段);TJ1t—天堂组;D2d—东岗岭组;S2l2—连滩组第二段;S2l1—连滩组第一段;Pt3s—射广组;1—石英二长斑岩;2—二长花岗岩;3—片麻状二长花岗岩;4—地质界线;5—角度不整合界线;6—断层;7—韧性断层;8—角岩化;9—采样点Figure 1. Geological map of Maqigang beschtauite pluton
图 1 马其岗岩体地质图(据参考文献①修改)Q—第四系;K2l1—罗文组第一段;K2x1—西垌组第一段;K2x—西垌组(未分段);TJ1t—天堂组;D2d—东岗岭组;S2l2—连滩组第二段;S2l1—连滩组第一段;Pt3s—射广组;1—石英二长斑岩;2—二长花岗岩;3—片麻状二长花岗岩;4—地质界线;5—角度不整合界线;6—断层;7—韧性断层;8—角岩化;9—采样点Figure 1. Geological map of Maqigang beschtauite pluton2. 锆石同位素测年
锆石测年选择石英二长斑岩(Mgq-1)为测试对象,年龄样品采自广西博白县沙河镇山桥村(地理坐标为北纬22°05′32.99″、东经109°45′49.62″)。锆石样品挑选由国土资源部河北省地质矿产局廊坊实验室完成,锆石阴极发光(CL)照相在中国地质大学JXA-8100电子探针仪上完成。LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb年龄测定在西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室的Agilent7500型ICPMS和德国Lambda Physik公司的Compex102ArF准分子激光器(工作物质ArF,波长193nm)及MicroLas公司的GeoLas200M光学系统的联机上进行。仪器分析步骤及分析结果数据处理参照ICPMS-DataCal程序[4]完成。
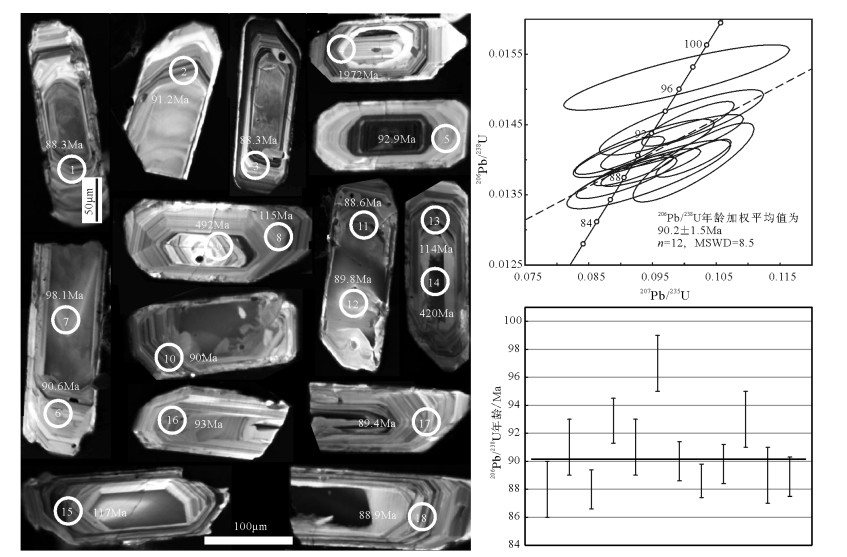
样品锆石呈长柱状,晶形完好,颗粒较大,一般为(60×150)~(80×250)mm,韵律环带发育。CL图像显示,大部分核部和边部无明显差异,少数可见明显的继承锆石核。所测锆石的18个分析点的Th含量为184×10-6~1357×10-6,U含量为376×10-6~ 3490×10-6,Th/U值为0.33~1.04。其中12个分析点的206Pb/238U年龄变化于88.3~98.1Ma之间,数据点在U-Pb谐和图上落在谐和线上及附近,206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值为90.2.±1.5Ma(MSWD=1.7),代表了侵入岩的形成时代(图 2;表 1)。此外,8、13、15号点的206Pb/238U年龄分别为115Ma、114Ma、117Ma,其时代相近,与侵入岩的形成时代相差25Ma,代表该岩体在114~117Ma时可能存在一期岩浆活动事件;4、9、14号测试点落在继承锆石核部,分别得到1972Ma、492Ma、420Ma三个206Pb/238U年龄,代表了捕获老锆石的年龄信息。
表 1 马其岗石英二长斑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析数据Table 1. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb data of Maqigang beschtauite点号 含量/10-6 同位素比值(经普通铅校正) 年龄(经普通铅校正)/Ma Pb Th U 207Pb/206Pb ±1σ 207Pb/235U ±1σ 206Pb/238U ±1σ 207Pb/206Pb ±1σ 207Pb/235U ±1σ 206Pb/238U ±1σ 1 11.09 379 654 0.0495 0.0028 0.0944 0.0052 0.0138 0.0002 172 131 91.6 4.9 88.3 1.3 2 12.26 333 737 0.0501 0.0024 0.0981 0.0046 0.0142 0.0002 211 111 95.0 4.2 91.2 1.0 3 38.28 1059 2383 0.0505 0.0013 0.0965 0.0026 0.0138 0.0001 217 61 93.6 2.4 88.3 0.7 4 198.7 391 376 0.1447 0.0020 7.188 0.123 0.3579 0.0041 2284 23 2135 15 1972 19 5 40.82 1076 2504 0.0500 0.0014 0.1006 0.0030 0.0145 0.0001 195 67 97.3 2.7 92.9 0.8 6 14.83 543 869 0.0482 0.0024 0.0936 0.0045 0.0142 0.0002 109 124 90.9 4.2 90.6 1.1 7 11.98 580 579 0.0558 0.0030 0.1181 0.0065 0.0153 0.0002 456 122 113 6 98.1 1.1 8 18.94 277 943 0.0515 0.0016 0.1269 0.0041 0.0179 0.0003 261 72 121 4 115 2 9 54.1 184 604 0.0558 0.0012 0.6149 0.0134 0.0794 0.0007 456 51 487 8 492 4 10 18.58 587 1123 0.0462 0.0015 0.0899 0.0029 0.0141 0.0001 9.36 74.1 87.4 2.7 90.0 0.7 11 41.4 1204 2552 0.0481 0.0014 0.0921 0.0025 0.0138 0.0001 106 69 89.4 2.4 88.6 0.6 12 50.8 1357 3102 0.0523 0.0012 0.1015 0.0024 0.0140 0.0001 298 54 98.1 2.2 89.8 0.7 13 27.94 575 1388 0.0487 0.0014 0.1182 0.0034 0.0178 0.0003 132 67 113 3 114 2 14 267.5 1135 3490 0.0530 0.0007 0.4946 0.0067 0.0674 0.0004 328 36 408 5 420 3 15 12.10 328 526 0.0644 0.0033 0.1593 0.0075 0.0182 0.0003 754 107 150 7 117 2 16 13.55 545 740 0.0505 0.0028 0.0995 0.0053 0.0145 0.0002 217 128 96.4 4.9 93.0 1.2 17 10.84 348 643 0.0536 0.0022 0.1014 0.0039 0.0140 0.0002 354 97 98.1 3.6 89.4 1.5 18 20.10 686 1124 0.0497 0.0018 0.0947 0.0032 0.0139 0.0001 189 81 91.9 3.0 88.9 0.7 3. 岩石地球化学特征
石英二长斑岩的主量元素分析在中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心完成(表 2)。分析方法为:Si和烧失量采用重量法,Al和Fe2+采用容量法,Fe3+、Ti和P采用分光光度法,K、Na、Ca、Mg和Mn采用原子吸收光谱法。微量元素分析在核工业北京地质研究院分析测试研究中心完成,微量元素采用HR-ICP-MS(Element Ⅰ)分析完成(表 2)。Sr、Nd同位素分析在中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心MAT261及Triton质谱仪上分析完成(表 3),实验流程及标准样品测定按照SmNd同位素实验方法[5]完成。Hf同位素测定在西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室多接收器等离子质谱仪(LA-MC-ICP-MS)上完成(表 4)。
表 2 马其岗石英二长斑岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果及参数Table 2. Compositions and parameters of major, trace and rare earth elements in Maqigang beschtauite样品 mqg-1 mqg-2 mqg-3 D3015-1 样品 mqg-1 mqg-2 mqg-3 D3015-1 D3013-1 样品 mqg-1 mqg-2 mqg-3 D3015-1 D3013-1 SiO2 64.76 64.04 64.26 64.00 La 70.30 68.70 69.20 71.31 67.58 Ba 1173.00 1049.00 1031.00 935.00 945.00 TiO2 0.94 1.07 1.08 1.06 Ce 128.00 127.00 128.00 138.60 135.40 Rb 176.00 170.00 155.00 160.00 164.00 Al2O3 14.66 14.69 14.68 14.68 Pr 14.20 14.30 14.30 15.93 15.55 Sr 268.00 280.00 304.00 283.00 268.00 Fe2O3 2.76 3.71 3.04 3.31 Nd 54.30 55.00 54.60 59.02 56.10 Y 47.50 56.20 47.80 39.22 39.35 FeO 3.38 2.80 2.99 2.25 Sm 10.30 9.98 9.96 10.87 10.77 Zr 265.00 207.00 386.00 429.00 457.00 MnO 0.09 0.10 0.09 0.07 Eu 2.45 2.30 2.32 2.45 2.52 Nb 37.80 37.20 37.80 31.40 32.00 MgO 1.42 1.49 1.45 1.28 Gd 9.19 9.27 9.20 9.62 9.73 Th 18.30 18.20 17.10 20.20 19.90 CaO 2.50 2.88 3.33 3.33 Tb 1.51 1.60 1.54 1.45 1.43 Pb 27.10 25.20 24.30 24.50 26.50 Na2O 3.36 3.27 3.08 2.95 Dy 8.80 9.48 8.94 8.19 8.17 Ga 23.80 23.10 22.50 17.50 17.60 K2O 4.78 4.52 4.41 4.43 Ho 1.60 1.75 1.56 1.57 1.60 Zn 101.00 139.00 102.00 87.00 97.00 P2O5 0.28 0.28 0.33 0.35 Er 4.68 5.56 4.92 4.26 4.25 Cu 17.30 15.70 15.70 14.90 15.90 H2O+ 0.42 0.81 0.81 1.58 Tm 0.77 0.84 0.70 0.68 0.66 Ni 10.10 10.30 8.73 12.00 14.90 CO2 0.17 0.15 0.15 0.09 Yb 4.53 5.18 4.53 4.24 4.19 V 55.80 52.90 60.00 87.60 82.90 灼失 0.78 0.84 0.90 Lu 0.68 0.82 0.67 0.62 0.63 Cr 14.50 13.10 13.50 7.10 13.30 总量 100.30 100.65 100.60 99.38 ∑REE 311.31 311.78 310.44 328.81 318.58 Hf 7.40 6.07 9.61 10.70 11.20 ALK 8.14 7.79 7.49 7.38 LREE 279.55 277.28 278.38 298.18 287.92 Cs 9.37 8.47 10.60 11.20 10.70 K2O/Na2O 1.42 1.38 1.43 1.50 HREE 31.76 34.50 32.06 30.63 30.66 Sc 8.20 8.29 9.40 2.40 2.10 ACNK 0.94 0.94 0.93 0.94 ∑L/∑H 8.80 8.04 8.68 9.73 9.39 Ta 2.15 2.16 2.15 15.90 17.20 σ 3.05 2.88 2.64 2.59 (La/Yb)n 11.13 9.51 10.96 12.06 11.57 Co 11.50 12.10 11.80 30.90 17.20 Mg# 42.82 48.68 46.36 50.35 δEu 0.25 0.24 0.24 0.24 0.25 U 3.63 3.44 3.29 74.30 60.60 注:石英二长斑岩样品D3015-1、D3013-1据参考文献①;主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素为10-6 表 3 马其岗石英二长斑岩Sr-Nd同位素组成分析结果Table 3. Sr-Nd isotope data of Maqigang beschtauite样号 Sm/10-6 Nd/10-6 147Sm/144Nd 143Nd/144Nd 2σ εNd(t) t/Ma Rb/10-6 Sr/10-6 87Rb/86Sr 87Sr/86Sr 2σ (87Sr/86Sr)i tDM2/Ga mqg-1 9.359 51.17 0.1113 0.512320 0.000002 -5.22 90.2 168.8 253.1 1.880 0.71158 0.00001 0.70916 1.33 mqg-2 9.419 51.36 0.1116 0.512312 0.000003 -5.38 90.2 165.0 274.6 1.694 0.71133 0.00003 0.70915 1.34 mqg-3 9.941 53.80 0.1124 0.512302 0.000004 -5.59 90.2 154.8 301.9 1.446 0.71097 0.00003 0.70911 1.36 表 4 马其岗石英二长斑岩锆石原位Hf同位素组成Table 4. LA-MC-ICP-MS zircon Hf isotope data of Maqigang beschtauite点号 176Yb/177Hf 176Lu/177Hf 176Hf/177Hf 2σ t/Ma εHf(t) 2σ tDM1/Ga tDM2/Ga 1 0.031335 0.000883 0.282641 0.000014 88 -2.7 0.5 0.86 1.33 2 0.024523 0.000692 0.282593 0.000013 91 -4.4 0.5 0.93 1.44 3 0.038007 0.001082 0.282694 0.000010 88 -0.9 0.3 0.79 1.21 4 0.028841 0.000795 0.281523 0.000014 1911 -2.5 0.5 2.40 2.70 5 0.037295 0.001070 0.282638 0.000019 92.9 -2.8 0.7 0.87 1.33 6 0.027701 0.000782 0.282609 0.000014 91 -3.8 0.5 0.90 1.40 7 0.044030 0.001216 0.282678 0.000019 97 -1.3 0.7 0.82 1.24 8 0.025466 0.000742 0.282573 0.000012 115 -4.6 0.4 0.95 1.47 9 0.057336 0.001613 0.282495 0.000015 492 0.5 0.5 1.09 1.43 10 0.026640 0.000762 0.282606 0.000012 90 -3.9 0.4 0.91 1.41 11 0.031684 0.000962 0.282626 0.000012 88.6 -3.3 0.4 0.89 1.36 12 0.045690 0.001275 0.282681 0.000011 89.8 -1.3 0.4 0.81 1.24 13 0.022608 0.000672 0.282619 0.000012 114 -3.0 0.4 0.89 1.36 14 0.036568 0.001099 0.282274 0.000010 420 -8.7 0.4 1.38 1.96 15 0.025953 0.000755 0.282707 0.000012 117 0.2 0.4 0.77 1.16 16 0.036549 0.001034 0.282666 0.000016 93 -1.8 0.6 0.83 1.27 17 0.022785 0.000658 0.282656 0.000011 89 -2.2 0.4 0.84 1.30 18 0.028315 0.000830 0.282663 0.000012 88.9 -1.9 0.4 0.83 1.28 3.1 主量元素
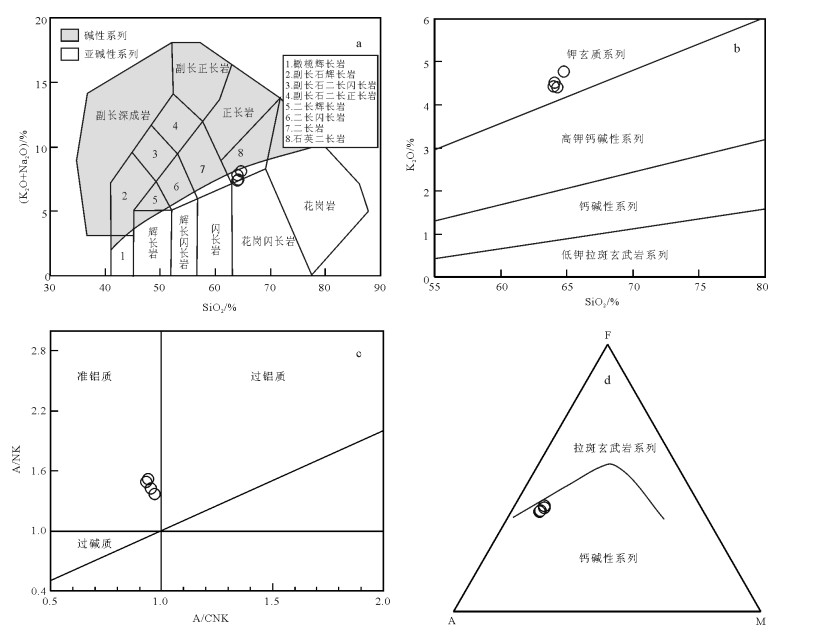
样品化学成分较均一,呈中性(SiO2=64.00%~ 64.76%),总体富碱(ALK=7.38% ~8.14%)、富钾(K2O=4.41%~4.78%)、钾大于钠(K2O/Na2O=1.38~ 1.50)、准铝质(A/CNK=0.93~0.94)、Mg#值高(42.82~50.35)。在侵入岩TAS图解(图 3-a)中样品点落入石英二长岩区,在SiO2-K2O图解(图 3-b)中落在钾玄质系列岩石范围内,在A/CNK-A/NK图解(图 3-c)中落入准铝质区,在AMF图解(图 3-d)上显示无明显的Fe富集,落入钙碱性系列范围,符合钾玄岩系列的特点。
3.2 稀土元素
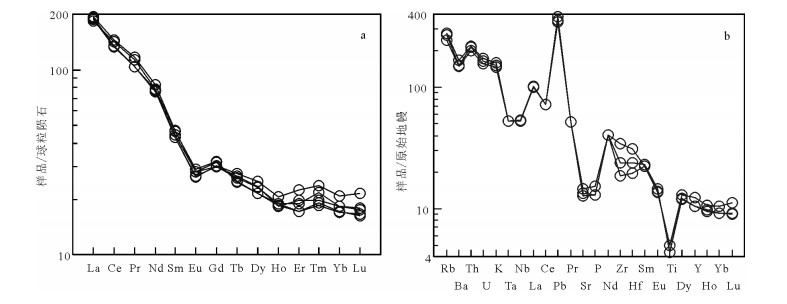
石英二长斑岩稀土元素(REE)配分模式总体相似(图 4-a),稀土元素总量变化不大(∑REE= 310.44×10-6~320.81×10-6),为轻稀土元素富集型,(∑ LREE/∑ HREE)=8.04~9.73,(La/Yb)N=9.51~ 12.06,负Eu异常明显(δEu=0.24~0.25)。
![]() 图 4 马其岗石英二长斑岩稀土元素配分曲线(a)及微量元素蛛网图(b)(球粒陨石标准化数值据参考文献[10])Figure 4. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns(a)and primitive mantle-normalized trace elements patterns(b)of Maqigang beschtauite
图 4 马其岗石英二长斑岩稀土元素配分曲线(a)及微量元素蛛网图(b)(球粒陨石标准化数值据参考文献[10])Figure 4. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns(a)and primitive mantle-normalized trace elements patterns(b)of Maqigang beschtauite3.3 微量元素
在微量元素蛛网图(图 4-b)上,石英二长斑岩均表现为富集大离子亲石元素(LILE)(如Rb、Th、U、K、Pb、LREE),亏损高场强元素(HFSE)(如Nb、Ta、P、Ti、HREE),而无明显的Zr亏损。
3.4 Sr-Nd-Hf同位素
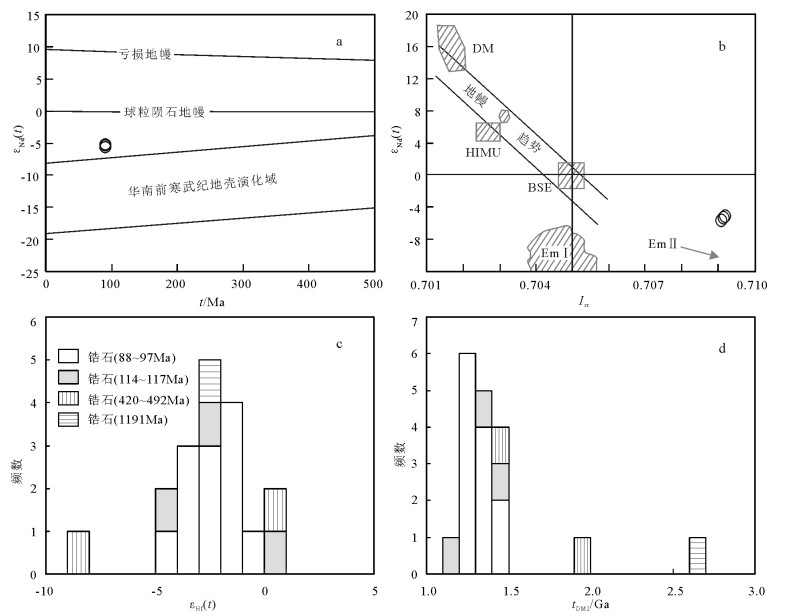
全岩Sr-Nd同位素组成变化小(表 3),Sr同位素组成较高(ISr=0.709117~0.709169),Nd同位素均一,εNd(t)=-5.22-~-5.59,相应的二阶段Nd模式年龄(tDM2)变化于1.33~1.36Ga之间。εNd(t)落在球粒陨石地幔与寒武纪地壳演化区域之间[11],反映源区以壳幔源为特征(图 5-a),在ISr-εNd(t)关系图解(图 5-b)中,样品点主要落在亏损地幔(DM)与富集地幔(EMⅡ)之间且靠近EMⅡ区域,与EMⅡ地幔具有亲源性[12]。锆石的原位Hf同位素组成变化较大(表 4),(176Hf/177Hf)i=0.281523~0.282707,εHf(t) =-8.7~0.5,二阶段Hf模式年龄(tDM2)为1.16~ 2.70Ga,主体为1.20~1.50Ga(图 5-c、d)。其中年龄为1191Ma及420Ma分析点的(176Hf/177Hf)i值分别为0.281523和0.282274,模式年龄(tDM2)分别为2.70Ga和1.96Ga,与主体锆石差别较大;年龄分别为492Ma、117Ma、115Ma、114Ma的4个分析点的(176Hf/177Hf)i值及模式年龄与主体锆石相近。
4. 讨论
4.1 岩体形成时代及起源
1:25万玉林市幅区域地质调查研究中,通过锆石蒸发法获得马其岗岩体的锆石U-Pb年龄为92Ma ①。本次获得的马其岗石英二长斑岩LAICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为90.2.±1.5Ma,与前人研究结果一致,属于晚白垩世岩浆活动的产物。
前人对华南燕山晚期花岗岩的研究表明,晚白垩世花岗岩岩体除少数零星分布外,主要集中分布于浙闽沿海地区和广西南丹—昆仑关一带,浙闽沿海地区该期花岗岩形成时代集中于86~ 101Ma[13-16]之间,沿政和-大埔断裂以东分布,并在北东向与其他方向(以北西向为主)断裂的交会处产出,为一套铝质A型花岗岩或碱性岩[15-16];其成因为太平洋板块俯冲角度变大,岛弧岩浆作用变弱的弧后伸展环境;南丹-昆仑关该期花岗岩的形成时代为91~93Ma,受北西向丹池断裂控制,为一套铝质A型花岗岩带,与该时期印度板块北移引起的古太平洋板块高角度俯冲所导致的弧后拉张有关[17]。尽管马其岗岩体与上述地区岩体形成时代一致,但在空间上远离政和-大埔,即丹池断裂带,明显受控于北东向的博白-梧州断裂带,同时岩体地球化学特征也与铝质A型花岗岩或碱性岩有一定差异。马其岗石英二长斑岩属于钾玄质系列岩石,前人将其归为桂东南钾玄质侵入岩带的一部分[1]。目前数据显示,桂东南钾玄质侵入岩带的时代主要集中在燕山早期,可能是亏损的软流圈地幔和富集的岩石圈地幔岩浆混合的产物,有较高的εNd(t)值,无明显Nb、Ta负异常,这与马其岗岩体时代及较低的εNd(t)值和明显Nb、Ta负异常不同。因此,其成因与上述地区可能存在差异。
马其岗石英二长斑岩的Mg#值较高,为42.82~50.35,略低于洋中脊拉斑玄武岩的Mg#值(60左右)[18],其Nb/Ta平均值为11.24,Zr/Hf平均值为38.20,总体介于原始地幔值(Nb/Ta=17.5、Zr/Hf=36.27)与大陆地壳平均值(Nb/Ta=11、Zr/Hf=33)之间[19-20]。Th/La平均值为0.17,明显低于大陆地壳的平均值(Th/La=0.28),稍高于下地壳的Th/La值(Th/La=0.15)[21],说明在岩浆上升侵位过程中受到地壳大规模混染程度较小,同时有低的Sr含量,其平均值为280.60×10-6,也显示岩浆上侵定位过程发生地壳混染程度小。石英二长斑岩地球化学特征以富集大离子亲石元素(Rb、Th、U、K、Pb、LREE)、亏损Nb、Ta和HREE为特征,同位素显示具有EMⅡ富集地幔端元的特征(图 5-b),EMⅡ地幔端元与上部陆壳有亲缘关系。一般认为,EMⅡ型地幔是俯冲带陆源物质进入上地幔再循环的结果,因为大陆沉积物的同位素特征对于EMⅡ的形成最理想[12]。尽管马其岗岩体处在扬子与华夏板块的结合带上,但扬子板块与华夏板块至少是在中-晚志留世沿现今的钦杭结合带发生碰撞,形成加里东期碰撞带[22]。“印支造山运动”Sibumasu地块向印支-华南地块斜向汇聚的主碰撞期为258~ 243Ma[23],但其碰撞缝合带远离桂东南,迄今为止,桂东南地区没有发现印支期的蛇绿岩及洋中脊-大洋盆地硅质岩。因此,其源区可能与早期俯冲作用带入部分上地壳物质进入地幔后,释放流体交代的富集大陆岩石圈地幔有关。石英二长斑岩的锆石饱和温度为860~883℃[24],远高于S型花岗岩和I型花岗岩,说明其形成时有地幔组分参与。元素地球化学和Sr-Nd-Hf同位素结果表明,石英二长斑岩可能源自基性岩浆与酸性岩浆的混合或由镁铁质下地壳部分熔融形成,附近并无同期基性岩石的记录,可以排除基性岩浆与酸性岩浆混合的可能,石英二长斑岩更可能是中元古代中期镁铁质下地壳部分熔融的产物,记录了富集地幔的信息。
4.2 构造意义
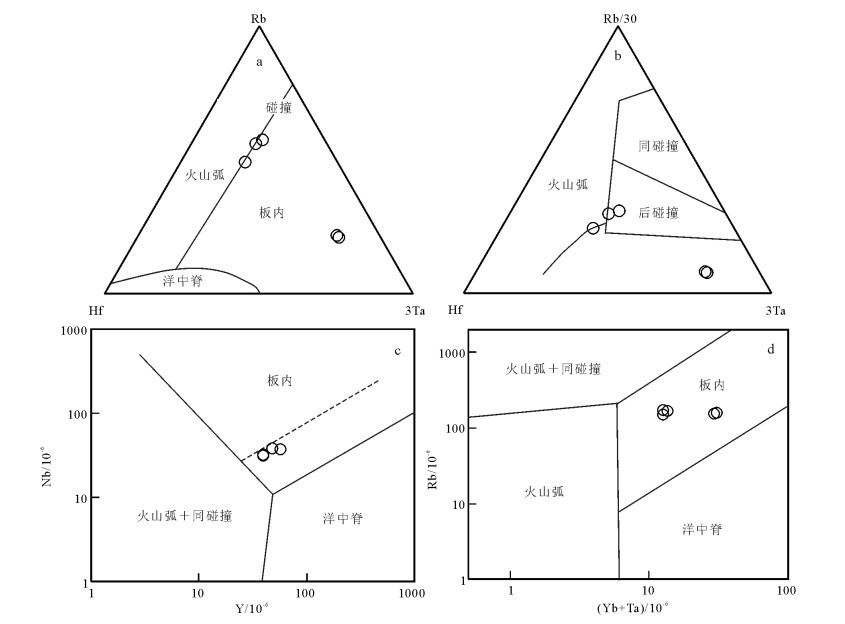
马其岗石英二长斑岩样品在Harris等[25]的花岗岩类微量元素Rb/10-Hf-3Ta、Rb/30-Hf-3Ta构造判别图解(图 6-a、b)上主要落在板内花岗岩区,少数落在板内及火山弧花岗岩交界处;在Pearce等[26]的花岗岩类微量元素Y-Nb、(Yb+Ta)-Rb判断图解(图 6-c、d)上,落在板内花岗岩区。对新生代钾玄质系列岩石研究也表明,其可以产于板内环境[27-28]。广西晚白垩世出现的断陷盆地及与下伏地层的角度不整合关系,也反映张性环境。
华南中生代构造演化是地学界长期关注的问题。随着晚白垩世A型花岗岩、基性岩脉、红盆研究的深入,晚白垩世处于拉张伸展的构造背景已成为不争的事实,但拉张伸展的年代学框架尚未精确厘定,同时伸展背景的动力学机制也长期存在争议。马其岗石英二长斑岩属产于板内环境的钾玄岩,浙闽沿海地区的铝质A型花岗岩或碱性岩形成时代集中在86~101Ma之间;南丹-昆仑关铝质A型花岗岩带时代集中在91~93Ma之间;同时东南沿海及海南岛存在大量90Ma左右的基性岩脉及岩墙群[29-32],说明整个华南在90Ma左右存在一次大规模的伸展事件。但这一时期的岩石分布特点表明,伸展事件的强度及规模为华南内陆略弱于东南沿海,其原因也可能与伸展背景的动力学机制差异有关。华南晚白垩世的动力学背景有多种观点,如浙闽沿海地区,该期花岗岩形成于古太平洋板块俯冲所导致的弧后伸展环境[33];南丹-昆仑关该期花岗岩形成与印度板块在该时期北移引起的古太平洋板块高角度俯冲导致的弧后拉张有关[17];华南晚白垩世A型花岗岩类或碱性侵入岩及板内基性岩脉与岩石圈伸展有关[34];华南腹地晚白垩世花岗岩类或碱性侵入岩与大陆边缘弧的塌陷或俯冲洋壳反转后的岩石圈伸展有关[16]。马其岗石英二长斑岩的地理位置远离东南沿海,相邻的南丹-昆仑关带花岗岩明显受丹池断裂控制,而马其岗石英二长斑岩严格受控于北东向的博白-梧州断裂带,这与北东向西太平洋构造域的体制匹配。已有西太平洋地震层析成像资料显示,古太平洋的俯冲洋壳存在且连续无间断,在1200~2000km处古俯冲洋壳明显偏西,暗示古太平洋板块是低角度的连续俯冲[35],这也解释了伸展事件的强度及规模为华南内陆略弱于东南沿海这一现象。
5. 结论
(1)马其岗石英二长斑岩符合钾玄岩系列的岩石特点,岩体富碱、富钾、稀土元素特征表现为轻稀土元素富集型,负Eu异常明显,微量元素特征为富集大离子亲石元素(Rb、Th、U、K、Pb、LREE),亏损高场强元素(Nb、Ta、P、Ti、HREE)。
(2)岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为90.2± 1.5Ma(MSWD=1.7),具有EMⅡ富集地幔端元的Sr-Nd同位素特征。二阶段Nd模式年龄(tDM2)变化于1.33~1.36Ga之间,二阶段Hf模式年龄(tDM2)主体为1.20~1.50Ga,两者的模式年龄较一致,显示岩体可能是中元古代中期镁铁质岩石部分熔融的产物。其岩浆主要来自下部地壳或地幔,在上升侵位过程中受地壳大规模混染程度较小。
(3)岩体构造判断图解显示板内特征,其形成于板内伸展环境,整个华南在90Ma左右存在一次大规模的伸展事件,其动力学机制与古太平洋板块低角度俯冲有关。
致谢: 成稿过程中得到中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心徐德明研究员的帮助指导,在此予以感谢。 -
图 1 马其岗岩体地质图(据参考文献①修改)
Q—第四系;K2l1—罗文组第一段;K2x1—西垌组第一段;K2x—西垌组(未分段);TJ1t—天堂组;D2d—东岗岭组;S2l2—连滩组第二段;S2l1—连滩组第一段;Pt3s—射广组;1—石英二长斑岩;2—二长花岗岩;3—片麻状二长花岗岩;4—地质界线;5—角度不整合界线;6—断层;7—韧性断层;8—角岩化;9—采样点
Figure 1. Geological map of Maqigang beschtauite pluton
图 4 马其岗石英二长斑岩稀土元素配分曲线(a)及微量元素蛛网图(b)(球粒陨石标准化数值据参考文献[10])
Figure 4. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns(a)and primitive mantle-normalized trace elements patterns(b)of Maqigang beschtauite
表 1 马其岗石英二长斑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析数据
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb data of Maqigang beschtauite
点号 含量/10-6 同位素比值(经普通铅校正) 年龄(经普通铅校正)/Ma Pb Th U 207Pb/206Pb ±1σ 207Pb/235U ±1σ 206Pb/238U ±1σ 207Pb/206Pb ±1σ 207Pb/235U ±1σ 206Pb/238U ±1σ 1 11.09 379 654 0.0495 0.0028 0.0944 0.0052 0.0138 0.0002 172 131 91.6 4.9 88.3 1.3 2 12.26 333 737 0.0501 0.0024 0.0981 0.0046 0.0142 0.0002 211 111 95.0 4.2 91.2 1.0 3 38.28 1059 2383 0.0505 0.0013 0.0965 0.0026 0.0138 0.0001 217 61 93.6 2.4 88.3 0.7 4 198.7 391 376 0.1447 0.0020 7.188 0.123 0.3579 0.0041 2284 23 2135 15 1972 19 5 40.82 1076 2504 0.0500 0.0014 0.1006 0.0030 0.0145 0.0001 195 67 97.3 2.7 92.9 0.8 6 14.83 543 869 0.0482 0.0024 0.0936 0.0045 0.0142 0.0002 109 124 90.9 4.2 90.6 1.1 7 11.98 580 579 0.0558 0.0030 0.1181 0.0065 0.0153 0.0002 456 122 113 6 98.1 1.1 8 18.94 277 943 0.0515 0.0016 0.1269 0.0041 0.0179 0.0003 261 72 121 4 115 2 9 54.1 184 604 0.0558 0.0012 0.6149 0.0134 0.0794 0.0007 456 51 487 8 492 4 10 18.58 587 1123 0.0462 0.0015 0.0899 0.0029 0.0141 0.0001 9.36 74.1 87.4 2.7 90.0 0.7 11 41.4 1204 2552 0.0481 0.0014 0.0921 0.0025 0.0138 0.0001 106 69 89.4 2.4 88.6 0.6 12 50.8 1357 3102 0.0523 0.0012 0.1015 0.0024 0.0140 0.0001 298 54 98.1 2.2 89.8 0.7 13 27.94 575 1388 0.0487 0.0014 0.1182 0.0034 0.0178 0.0003 132 67 113 3 114 2 14 267.5 1135 3490 0.0530 0.0007 0.4946 0.0067 0.0674 0.0004 328 36 408 5 420 3 15 12.10 328 526 0.0644 0.0033 0.1593 0.0075 0.0182 0.0003 754 107 150 7 117 2 16 13.55 545 740 0.0505 0.0028 0.0995 0.0053 0.0145 0.0002 217 128 96.4 4.9 93.0 1.2 17 10.84 348 643 0.0536 0.0022 0.1014 0.0039 0.0140 0.0002 354 97 98.1 3.6 89.4 1.5 18 20.10 686 1124 0.0497 0.0018 0.0947 0.0032 0.0139 0.0001 189 81 91.9 3.0 88.9 0.7 表 2 马其岗石英二长斑岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果及参数
Table 2 Compositions and parameters of major, trace and rare earth elements in Maqigang beschtauite
样品 mqg-1 mqg-2 mqg-3 D3015-1 样品 mqg-1 mqg-2 mqg-3 D3015-1 D3013-1 样品 mqg-1 mqg-2 mqg-3 D3015-1 D3013-1 SiO2 64.76 64.04 64.26 64.00 La 70.30 68.70 69.20 71.31 67.58 Ba 1173.00 1049.00 1031.00 935.00 945.00 TiO2 0.94 1.07 1.08 1.06 Ce 128.00 127.00 128.00 138.60 135.40 Rb 176.00 170.00 155.00 160.00 164.00 Al2O3 14.66 14.69 14.68 14.68 Pr 14.20 14.30 14.30 15.93 15.55 Sr 268.00 280.00 304.00 283.00 268.00 Fe2O3 2.76 3.71 3.04 3.31 Nd 54.30 55.00 54.60 59.02 56.10 Y 47.50 56.20 47.80 39.22 39.35 FeO 3.38 2.80 2.99 2.25 Sm 10.30 9.98 9.96 10.87 10.77 Zr 265.00 207.00 386.00 429.00 457.00 MnO 0.09 0.10 0.09 0.07 Eu 2.45 2.30 2.32 2.45 2.52 Nb 37.80 37.20 37.80 31.40 32.00 MgO 1.42 1.49 1.45 1.28 Gd 9.19 9.27 9.20 9.62 9.73 Th 18.30 18.20 17.10 20.20 19.90 CaO 2.50 2.88 3.33 3.33 Tb 1.51 1.60 1.54 1.45 1.43 Pb 27.10 25.20 24.30 24.50 26.50 Na2O 3.36 3.27 3.08 2.95 Dy 8.80 9.48 8.94 8.19 8.17 Ga 23.80 23.10 22.50 17.50 17.60 K2O 4.78 4.52 4.41 4.43 Ho 1.60 1.75 1.56 1.57 1.60 Zn 101.00 139.00 102.00 87.00 97.00 P2O5 0.28 0.28 0.33 0.35 Er 4.68 5.56 4.92 4.26 4.25 Cu 17.30 15.70 15.70 14.90 15.90 H2O+ 0.42 0.81 0.81 1.58 Tm 0.77 0.84 0.70 0.68 0.66 Ni 10.10 10.30 8.73 12.00 14.90 CO2 0.17 0.15 0.15 0.09 Yb 4.53 5.18 4.53 4.24 4.19 V 55.80 52.90 60.00 87.60 82.90 灼失 0.78 0.84 0.90 Lu 0.68 0.82 0.67 0.62 0.63 Cr 14.50 13.10 13.50 7.10 13.30 总量 100.30 100.65 100.60 99.38 ∑REE 311.31 311.78 310.44 328.81 318.58 Hf 7.40 6.07 9.61 10.70 11.20 ALK 8.14 7.79 7.49 7.38 LREE 279.55 277.28 278.38 298.18 287.92 Cs 9.37 8.47 10.60 11.20 10.70 K2O/Na2O 1.42 1.38 1.43 1.50 HREE 31.76 34.50 32.06 30.63 30.66 Sc 8.20 8.29 9.40 2.40 2.10 ACNK 0.94 0.94 0.93 0.94 ∑L/∑H 8.80 8.04 8.68 9.73 9.39 Ta 2.15 2.16 2.15 15.90 17.20 σ 3.05 2.88 2.64 2.59 (La/Yb)n 11.13 9.51 10.96 12.06 11.57 Co 11.50 12.10 11.80 30.90 17.20 Mg# 42.82 48.68 46.36 50.35 δEu 0.25 0.24 0.24 0.24 0.25 U 3.63 3.44 3.29 74.30 60.60 注:石英二长斑岩样品D3015-1、D3013-1据参考文献①;主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素为10-6 表 3 马其岗石英二长斑岩Sr-Nd同位素组成分析结果
Table 3 Sr-Nd isotope data of Maqigang beschtauite
样号 Sm/10-6 Nd/10-6 147Sm/144Nd 143Nd/144Nd 2σ εNd(t) t/Ma Rb/10-6 Sr/10-6 87Rb/86Sr 87Sr/86Sr 2σ (87Sr/86Sr)i tDM2/Ga mqg-1 9.359 51.17 0.1113 0.512320 0.000002 -5.22 90.2 168.8 253.1 1.880 0.71158 0.00001 0.70916 1.33 mqg-2 9.419 51.36 0.1116 0.512312 0.000003 -5.38 90.2 165.0 274.6 1.694 0.71133 0.00003 0.70915 1.34 mqg-3 9.941 53.80 0.1124 0.512302 0.000004 -5.59 90.2 154.8 301.9 1.446 0.71097 0.00003 0.70911 1.36 表 4 马其岗石英二长斑岩锆石原位Hf同位素组成
Table 4 LA-MC-ICP-MS zircon Hf isotope data of Maqigang beschtauite
点号 176Yb/177Hf 176Lu/177Hf 176Hf/177Hf 2σ t/Ma εHf(t) 2σ tDM1/Ga tDM2/Ga 1 0.031335 0.000883 0.282641 0.000014 88 -2.7 0.5 0.86 1.33 2 0.024523 0.000692 0.282593 0.000013 91 -4.4 0.5 0.93 1.44 3 0.038007 0.001082 0.282694 0.000010 88 -0.9 0.3 0.79 1.21 4 0.028841 0.000795 0.281523 0.000014 1911 -2.5 0.5 2.40 2.70 5 0.037295 0.001070 0.282638 0.000019 92.9 -2.8 0.7 0.87 1.33 6 0.027701 0.000782 0.282609 0.000014 91 -3.8 0.5 0.90 1.40 7 0.044030 0.001216 0.282678 0.000019 97 -1.3 0.7 0.82 1.24 8 0.025466 0.000742 0.282573 0.000012 115 -4.6 0.4 0.95 1.47 9 0.057336 0.001613 0.282495 0.000015 492 0.5 0.5 1.09 1.43 10 0.026640 0.000762 0.282606 0.000012 90 -3.9 0.4 0.91 1.41 11 0.031684 0.000962 0.282626 0.000012 88.6 -3.3 0.4 0.89 1.36 12 0.045690 0.001275 0.282681 0.000011 89.8 -1.3 0.4 0.81 1.24 13 0.022608 0.000672 0.282619 0.000012 114 -3.0 0.4 0.89 1.36 14 0.036568 0.001099 0.282274 0.000010 420 -8.7 0.4 1.38 1.96 15 0.025953 0.000755 0.282707 0.000012 117 0.2 0.4 0.77 1.16 16 0.036549 0.001034 0.282666 0.000016 93 -1.8 0.6 0.83 1.27 17 0.022785 0.000658 0.282656 0.000011 89 -2.2 0.4 0.84 1.30 18 0.028315 0.000830 0.282663 0.000012 88.9 -1.9 0.4 0.83 1.28 -
Li X H, Zhou H W, Liu Y, et al. Shoshonitic intrusive suite in SE Guangxi:Petrology and geochemistry[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 2000, 45(7):653-659. doi: 10.1007/BF02886045
郭新生, 陈江峰, 张巽, 等.桂东南富钾岩浆杂岩的Nd同位素组成:华南中生代地幔物质上涌事件[J].岩石学报, 2001, 17(1):19-27. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200101003.htm Iddings J P. Absarokite-shoshonite-banakite series[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1895, 3(8):935-959. doi: 10.1086/607398
袁洪林, 吴福元, 高山, 等.东北地区新生代侵入体的锆石激光探针U-Pb年龄测定与稀土元素成分分析[J].科学通报, 2001, 48(14):1511-1520. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200314007.htm 王银喜, 杨杰东, 陶仙聪, 等.化石、矿物和岩石样品的Sm-Nd同位素实验方法研究及其应用[J].南京大学学报(自然科学版), 1988, 21(2):297-308. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJDZ198802017.htm Middlemost E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994, 37(3):215-224. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/223901164_Naming_materials_in_the_magmaigneous_rock_system
Peccerillo A, Taylor S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline vol-canic rocks from the Kastamonu area, northern Turkey[J]. Contribu-tions to mineralogy and petrology, 1976, 58(1):63-81. doi: 10.1007/BF00384745
Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. Tectonic Discrimination of Granitoids[J]. Geological society of America bulletin, 1989, 101(5):635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
Irvine T N, Baragar W R A. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks[J].Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 1971, 8(5):523-548. doi: 10.1139/e71-055
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oce-anic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1):313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
孙涛, 周新民, 陈培荣, 等.南岭东段中生代强过铝花岗岩成因及其大地构造意义[J].中国科学(D辑), 2003, 48(2):165-174. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200312009.htm Zinder A, Hart S R. Chemical geodynamics[J]. Annual Reviews of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1986, 14:493-573. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ea.14.050186.002425
吴才来, 周洵若, 黄许陈, 等.安徽茅坦A型花岗岩研究[J].地质学报, 1998, 72(3):237-248. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE199803004.htm 邱检生, 王德滋, McInnes B I A.浙闽沿海地区I型-A型复合花岗岩体的地球化学及成因学及成因[J].岩石学报, 1999, 15(2):237-246. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB902.009.htm 邱检生, 王德滋, 蟹泽聪史, 等.福建沿海铝质A型花岗岩的地球化学及岩石成因[J].地球化学, 2000, 29(4):313-321. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200004000.htm 王强, 赵振华, 简平, 等.华南腹地白垩纪A型花岗岩类或碱性侵入岩年代学及其对华南晚中生代构造演化的制约[J].岩石学报, 2005, 21(3):795-808. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200503020.htm 谭俊, 魏俊浩, 李水如, 等.广西昆仑关A型花岗岩地球化学特征及构造意义[J].地球科学, 2008, 33(6):743-754. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200806001.htm Beard J S, Lofgren G E. Dehydration melting and water-saturated melting of basaltic and andesitic greenstones and amphibolites at 1, 3, and 6.9 kb[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1991, 32(2):365-401. doi: 10.1093/petrology/32.2.365
Taylor S R, McLennan S M. The Continental Crust:Its Composi-tion and Evolution[M]. Oxford:Blackwell, 1985:1-312.
Stolz A J, Jochum K P, Spettel B, et al. Fluid-and melt-related en-richment in the subarc mantle:Evidence from Nb/Ta variations in island-arc besalts[J].Geology, 1996, 24(7):587-590. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1996)024<0587:FAMREI>2.3.CO;2
Rudnick R L, Barth M, Horn I, et al. Rutile-bearing refractory eclogites:Missing link between continents and depleted mantle[J]. Science, 2000, 287(5451):278-281. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5451.278
殷鸿福, 吴顺宝, 杜远生, 等.华南是特提斯多岛洋体系的一部分[J].地球科学, 1999, 24(1):1-12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX901.000.htm Carter A, Roques D, Bristow C, et al. Understanding Mesozoic ac-cretion southeast Asia:Significance of Triassic thermotectonism(in-dosinian orogeny) in Vietnam[J]. Geology, 2001, 29(3):211-214. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0211:UMAISA>2.0.CO;2
Watson E B, Harrison T M. Zircon saturation revisited:tempera-ture and composition effects in a variety of crustal magmatypes[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983, 64(2):295-304. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(83)90211-X
Harris N B W, Marzouki F M H, Ali S. The Jabel Sayid Complex, Arabian Shield:geochemical constraints on the origin of peralka-line and related granites[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1986, 143(2):287-295. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.143.2.0287
Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. Trace element discrimina-tion diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of petrology, 1984, 25(4):956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
吴少波, 白玉宝, 杨友运.银根盆地早白垩世火山岩特征及形成的大地构造环境[J].矿物岩石, 1999, 19(1):24-28. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS901.004.htm Scarrow J H, Molina J F, Bea F, et al. Within-plate calc-alkaline rocks:insights from alkaline mafic magma peraluminous crustal melt hybrid appinites of the Central Iberian Variscan continental collision[J]. Lithos, 2009, 110(1):50-64. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229224401_Within-plate_calc-alkaline_rocks_Insights_from_alkaline_mafic_magma-peraluminous_crustal_melt_hybrid_appinites_of_the_Central_Iberian_Variscan_continental_collision
李献华, 胡瑞忠, 饶冰.粤北白垩纪基性岩脉的年代学和地球化学[J].地球化学, 1997, (2):14-31. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX702.003.htm 董传万, 张登荣, 徐夕生, 等.福建晋江中-基性岩墙群的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年和岩石地球化学[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(6):1696-1702. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200606026.htm 唐立梅, 陈汉林, 董传万, 等.中国东南部晚中生代构造伸展作用——来自海南岛基性岩墙群的证据[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(4):1204-1216. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201004019.htm 朱捌, 凌洪飞, 沈渭洲, 等.粤北下庄矿田晚白垩世辉绿玢岩的地球化学特征及其构造意义[J].地质论评, 2012, 54(1):26-36. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200801005.htm Geng H T, Xu X S, O' Reilly S Y, et al. Cretaceous volcanic-in-trusive magmatism in western Guangdong and its geological signifi-cance[J]. Science in China (Series D), 2006, 49(7):696-713. doi: 10.1007/s11430-006-0696-7
Li X H. Cretaceous magmatism and lithospheric extension in Southeast China[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2000, 18(3):293-305. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(99)00060-7
李武显, 周新民.古太平洋岩石圈消减与中国东南部晚中生代火成岩成因——岩石圈消减与玄武岩底侵相结合模式的补充证据[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2001, 25(1):55-63. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200101005.htm 广西区域地质调查研究院. 广西1: 25万玉林市幅区域地质调查报告. 2006.



 下载:
下载: