Constraints of geochemistry, geochronology and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopes on the Xinzhai peralu-minous granite in northern Guangxi:implications for petrogenesis and tectonic significance
-
摘要:
LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年结果显示,桂北新寨花岗岩形成于中奥陶世(465±2Ma)。该花岗岩的地球化学特征表现为化学成分较均一,具有高硅(SiO2=68.54%~74.57%)、富碱(K2O+Na2O=7.61%~8.31%)、更富钾(K2O/Na2O=1.77~2.35)、强过铝质(A/CNK=1.09~2.39)和富集大离子亲石元素而亏损高场强元素等特征,属于S型花岗岩。新寨花岗岩具有比较均一的Sr、Nd同位素组成(ISr=0.71137~0.71328,ε Nd(t)=-7.89~-7.26)。锆石Hf同位素组成为:(176Hf/177Hf)i=0.28232~0.28252,εHf(t)=-6.18~+0.61,Hf同位素两阶段模式年龄TDM2变化于1.67~2.11Ga之间。元素及Nd-Sr-Hf同位素分析结果显示,新寨花岗岩可能源自古元古代地壳变质泥岩的部分熔融,在成岩过程中有少量幔源组分的参与。新寨S型花岗岩可能是广西运动第二幕在桂北地区的岩石学响应,为早古生代构造-岩浆群事件的建立提供了新证据。
-
关键词:
- 中奥陶世 /
- S型花岗岩 /
- Sr-Nd-Hf同位素 /
- 广西运动 /
- 桂北
Abstract:LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating shows that the Xinzhai granites, emplaced in northern Guangxi, were generated in Mid-dle Ordovician (465±2Ma).These granites are characterized by uniform silicon content (SiO2=68.54%~4.57%), enrichment of alkali val-ues and considerable enrichment of K values (K2O+Na2O=7.61%~8.31%, K2O/Na2O=1.77~2.35), concentration of peraluminous (A/CNK=1.09~2.39) and high large ion lithophile elements (LILE)(e.g., Rb, K, Th) but relative depletion of high field-strength el-ements (HFSE)(e.g., Nb, Ta, P, Ti) and Sr.They belong to S-type granite.Granitic samples have homogeneous Sr-Nd isotope compositions (ISr=0.71137~0.71328, ε Nd (t)=-7.89~-7.26).Zircon Hf isotope compositions of the Xinzhai granites have relatively wide ranges (176Hf/177Hf=0.28232~0.28252, εHf(t)=-6.18~+0.61, TDM2=1.67~2.11Ga).The authors hold that the Xinzhai granites were likely generated by partial melting of Paleoproterozoic metapelite, with the addition of small amounts of mafic magma mantle-derived material.The Xinzhai S-type granites might have been the petrological response to the second activity of the Kwangsian orogen in northern Guangxi, which provided new evidence for the establishment of the Early Paleozoic tectonic-magma events in South China.
-
长期以来,华南早古生代的大地构造背景一直存在争议。有的学者认为存在“华南洋”,倡导用“洋-陆碰撞”的模式来解释[1-3]。然而,越来越多的证据表明,发生于华南早古生代的“广西运动”更可能是板内造山运动[4-14],是世界上为数不多的板内造山运动的实例之一[15]。近年来,对该板内造山运动(广西运动)的构造属性和动力机制研究已经取得了重大进展[4-8, 15],但广西运动在不同地区的表现形式仍未得到有效制约。
华南早古生代花岗岩分布广泛且数目较多(约100个),岩体规模悬殊,总面积约2.2×104km2[16]。其中,强过铝质的花岗质侵入体约占总数的58.7%(A/ CNK>1.10)[17],属于S型花岗岩,可能源自于加厚地壳状态下含水矿物的脱水熔融或加厚地壳垮塌产生的等温减压引发的部分熔融[7]。其中,约460Ma的过铝质花岗岩主要集中于武夷—云开、赣南—粤北等地区[4-6],对于限定板内造山运动的性质具有重要的指示意义,而南岭西段地区远离造山核部,鲜有相关报道。最近,笔者通过对桂北灵川县新寨花岗岩的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄研究发现,该岩体形成于465±2Ma,地球化学特征上属于强过铝质的S型花岗岩,本文重点报道该成果。同时,在岩体地质、元素地球化学和Sr-Nd-Hf同位素研究的基础上,结合华南其他地区早古生代花岗岩的研究资料,讨论其岩石成因和动力学意义。
1. 岩体地质特征
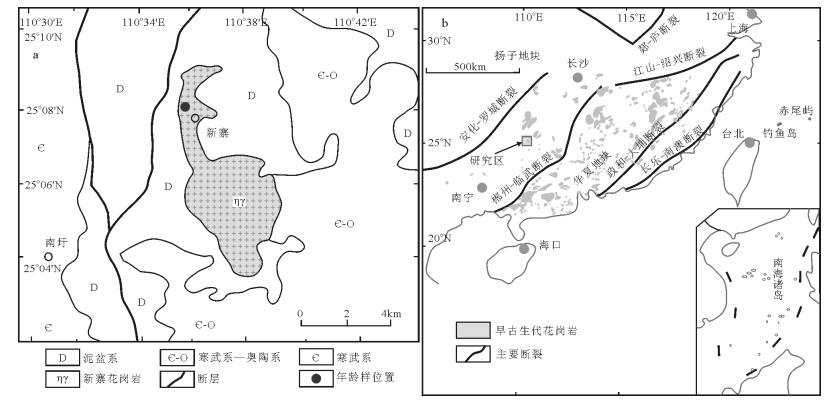
新寨花岗质侵入体位于湘中—桂中南北西向构造带和海洋山复式向斜的西南端,区域上受控于近南北向的大镜-沙子断裂(图 1-a)。侵入体侵入寒武系—奥陶系,为泥盆系沉积覆盖。大地构造位置上,侵入体位于扬子地块和华夏地块的结合部位,安化-罗城断裂和郴州-临武断裂之间(图 1-b)。相对于郴州-临武断裂以东地区,研究区及其附近早古生代花岗岩分布较少。侵入体出露面积16.7km2,侵入于老厂穹隆的轴部。广西壮族自治区地质局①据侵入关系将新寨花岗质侵入体年代定为加里东期,张相训等[18]获得其锆石207Pb/206Pb年龄为493±21Ma,归于早奥陶世。
新寨侵入体主要岩性为中细粒斑状角闪黑云二长花岗岩,少量中细粒花岗闪长岩和黑云母花岗岩。岩石普遍遭受蚀变,岩体内部发育暗色包体,多为闪长质和花岗闪长质。岩石主要造岩矿物为斜长石(35%)、钾长石(40%)、石英(20%)和少量黑云母、角闪石( < 5%)。其中斜长石呈半自形板状,绢云母化,黝帘石化,局部可见被钾长石交代的蚕蚀状、净边结构;钾长石为条纹长石,半自形板状-他形粒状,高岭土化;黑云母和角闪石多绿泥石化。副矿物组合为磁铁矿、锆石、磷灰石和电气石。
2. 分析方法
本次采集的锆石U-Pb同位素年龄测试样品为N38-1,样品坐标为北纬25°08′14.9″、东经110°34′ 55.2″。锆石样品挑选过程中,先将新鲜的岩石样品粉碎至120目以下,用常规的人工淘洗和电磁选方法富集锆石,再在双目镜下手工逐个精选锆石颗粒。本次锆石定年样品与主量和微量元素分析的样品相对应。锆石阴极发光(CL)图像拍摄在中国地质大学JXA-8100电子探针仪上完成。LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb年龄测定在西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室的Agilent7500型ICPMS和德国Lambda Physik公司的Compex102ArF准分子激光器(工作物质ArF,波长193nm)及MicroLas公司的GeoLas200M光学系统的联机上进行。激光束斑直径为44μm,剥蚀深度为20~40μm。实验中采用氦气作为剥蚀物质的载气,用美国国家标准技术研究院研制的人工合成硅酸盐玻璃标准参考物质NIST610进行最佳化,使仪器达到最高的灵敏度、最小的氧化物产率、最低的背景值和稳定的信号,采样方式为单点剥蚀,数据采集选用一个质量峰一点的跳峰方式(peak jumping)。锆石U-Pb年龄测定采用标准锆石91500作为外标标准物,外标校正方法为每隔6个样品分析点测1次标样,保证标准和样品的仪器条件尽可能一致。元素含量采用NIST SRM610作为外标,29Si作为内标。锆石U-Pb年龄测试仪器的运行条件、详细的分析流程参见袁洪林等[19]。样品的同位素比值采用软件ICPMSDataCal完成[20],相关结果按照Anderson的方法处理[21],年龄计算及谐和图的绘制采用Isoplot(ver2.49)[22]完成。分析数据列于表 1。在进行锆石U-Pb年龄测定的同时,在LA-MC-ICP-MS上获得锆石原位Hf同位素组成。测定时采用标样91500和GJ-1、MON-1作为外标。在ε Hf(t)值计算中,采用Blichert等[23]推荐的球粒陨石值。亏损地幔模式年龄(TMD)计算采用Griffin等[24]的推荐值。分析数据列于表 2。
表 1 新寨花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析数据Table 1. LA-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb isotopic data for zircons of the Xinzhai granites点号 Pb Th U 比值(经普通铅校正) 年龄(经普通铅校正)/Ma /10-6 207Pb/206Pb ±1σ 207Pb/235U ±1σ 206Pb/238U ±1σ 207Pb/206Pb ±1σ 207Pb/235U ±1σ 206Pb/238U ±1σ 1 340 1852 3872 0.05193 0.00073 0.5387 0.0073 0.07484 0.00055 282 27 438 5 465 3 2 314 1485 3695 0.04815 0.00062 0.5014 0.0067 0.07502 0.0005 107 28 413 5 466 3 3 279 1304 3243 0.05273 0.00101 0.5520 0.0138 0.07484 0.00067 317 54 446 9 465 4 4 218 983 2585 0.04956 0.00074 0.5187 0.0074 0.07546 0.00035 174 32 424 5 469 2 5 180 696 2182 0.04983 0.00081 0.5184 0.0084 0.07500 0.00038 187 37 424 6 466 2 6 251 1809 2752 0.05398 0.00097 0.5621 0.0099 0.07515 0.00054 370 37 453 6 467 3 7 367 1511 4445 0.05268 0.00074 0.5448 0.0077 0.07464 0.00051 315 29 442 5 464 3 8 307 1709 3336 0.05406 0.00077 0.5684 0.0087 0.07580 0.00054 373 31 457 6 471 3 9 506 3225 6517 0.05389 0.00064 0.5140 0.0064 0.06884 0.00052 366 23 421 4 429 3 10 254 1070 3089 0.05584 0.00083 0.5800 0.0078 0.07506 0.00057 446 25 464 5 467 3 11 431 2850 4939 0.05645 0.00074 0.5833 0.0073 0.07472 0.00062 470 21 467 5 465 4 12 335 1456 3850 0.05733 0.00095 0.6010 0.0099 0.07574 0.00065 504 32 478 6 471 4 13 448 2762 5309 0.05446 0.00078 0.5646 0.0081 0.07499 0.00067 390 26 455 5 466 4 14 397 3076 4596 0.05262 0.00066 0.5448 0.0068 0.07472 0.00035 313 27 442 4 465 2 15 436 3203 5232 0.05188 0.00063 0.5262 0.0064 0.07320 0.00037 280 26 429 4 455 2 16 317 2249 3757 0.05144 0.00064 0.5232 0.0068 0.07346 0.00051 261 26 427 5 457 3 17 438 2426 5146 0.05038 0.00057 0.5234 0.0062 0.07501 0.00045 213 24 427 4 466 3 18 268 1250 3182 0.05094 0.00066 0.5272 0.0077 0.07470 0.00055 238 30 430 5 464 3 表 2 新寨花岗岩锆石Lu-Hf同位素分析结果Table 2. Lu-Hf isotopic analyses for zircons of the Xinzhai granites点号 176Yb/177Hf 176Lu/177Hf 176Hf/177Hf 2σ T/Ma ε Hf(t) 2σ THf1/Ga THf2/Ga 01 0.025163 0.000830 0.282463 0.000011 465 -0.95 0.4 1.11 1.78 02 0.027225 0.000853 0.282346 0.000013 466 -5.06 0.5 1.27 2.04 03 0.029851 0.000952 0.282370 0.000012 465 -4.27 0.4 1.24 1.99 04 0.040693 0.001246 0.282317 0.000014 469 -6.18 0.5 1.33 2.11 05 0.029434 0.000908 0.282359 0.000009 466 -4.63 0.3 1.26 2.02 06 0.054760 0.001624 0.282430 0.000014 467 -2.32 0.5 1.18 1.86 07 0.030690 0.000943 0.282388 0.000009 464 -3.66 0.3 1.22 1.95 08 0.036582 0.001166 0.282469 0.000011 471 -0.73 0.4 1.11 1.77 09 0.051495 0.001635 0.282528 0.000019 429 0.35 0.7 1.04 1.64 10 0.047695 0.001418 0.282391 0.000012 467 -3.64 0.4 1.23 1.94 11 0.044739 0.001420 0.282480 0.000014 465 -0.51 0.5 1.10 1.74 12 0.032905 0.001018 0.282385 0.000014 471 -3.65 0.5 1.23 1.96 13 0.042287 0.001289 0.282477 0.000013 466 -0.55 0.5 1.10 1.75 14 0.051338 0.001555 0.282513 0.000018 465 0.61 0.6 1.06 1.67 15 0.034169 0.001069 0.282458 0.000012 455 -1.42 0.4 1.12 1.79 16 0.048987 0.001475 0.282427 0.000014 457 -2.59 0.5 1.18 1.86 17 0.038565 0.001186 0.282391 0.000012 466 -3.58 0.4 1.22 1.94 18 0.022362 0.000739 0.282463 0.000011 464 -0.95 0.4 1.11 1.78 主量元素分析在中国地质调查局宜昌地质矿产研究所中南检测中心完成。分析方法为Si和烧失量采用重量法,Al和Fe2+采用容量法,Fe3+、Ti和P采用分光光度法,K、Na、Ca、Mg和Mn采用原子吸收光谱法。分析数据列于表 3。
表 3 新寨花岗岩主量和微量元素分析结果Table 3. Chemical composition of the Xinzhai granites元素 N38-1 N38-2 N38-3 N38-4 N38-5 N38-6 SiO2 74.07 74.57 68.54 68.70 72.43 71.89 Al2O3 13.25 13.39 15.25 14.78 15.44 15.33 Fe2O3 0.30 0.50 1.18 1.49 1.02 2.11 FeO 1.57 1.49 2.55 2.29 1.30 0.97 CaO 0.95 0.17 0.42 0.97 0.18 0.07 MgO 0.62 0.41 1.63 1.52 0.88 0.87 k2O 5.37 5.83 5.24 5.12 5.59 5.56 Na2O 2.84 2.48 2.37 2.90 0.16 0.16 TiO2 0.16 0.12 0.39 0.37 0.46 0.46 P2O5 0.04 0.02 0.09 0.09 0.12 0.04 MnO 0.03 0.02 0.07 0.06 0.02 0.04 总计 99.19 99.00 97.73 98.28 97.60 97.50 烧失量 0.62 0.83 1.96 1.45 2.25 2.37 Sc 3.34 3.26 9.16 9.66 11.4 8.55 V 21.4 16.9 59.3 61.7 75.6 71.6 Cr 15.7 9.19 27.1 33.2 41.9 39.4 Co 3.27 3.25 8.56 9.15 4.85 7.58 Ni 6.62 6.58 16.8 17.6 13.8 14.9 Ga 13.1 13.2 17.1 17.9 18.5 17.9 Rb 304 309 300 247 292 268 Sr 58.3 32.7 73.3 146 7.51 6.05 Y 26.2 19.7 33.4 30.1 31.2 20.1 Nb 11.1 11.6 12.8 12.4 14.8 14.4 Cs 15.8 18.2 29.4 16.1 36.7 27.4 Ba 469 604 962 702 1110 1083 La 34.5 31.5 31.3 38.4 32.1 38.6 Ce 64.1 56.2 66.9 62.5 65.6 72.8 Pr 6.73 6.2 6.96 8.27 7.95 8.96 Nd 23.1 21.2 27.0 30.5 29.9 35.2 Sm 4.13 3.73 5.44 5.90 6.42 6.28 Eu 0.49 0.42 0.97 0.99 0.96 1.03 Gd 3.44 2.89 4.95 5.14 5.31 4.58 Tb 0.65 0.52 0.88 0.93 1.00 0.80 Dy 4.01 3.22 5.56 5.07 5.75 4.25 Ho 0.84 0.63 1.10 1.04 1.10 0.71 Er 2.51 1.97 3.28 2.91 3.18 2.22 Tm 0.53 0.40 0.60 0.51 0.58 0.39 Yb 3.55 2.93 3.66 3.40 3.32 2.51 Lu 0.63 0.53 0.60 0.50 0.52 0.33 Ta 3.20 3.20 1.88 1.77 1.95 2.01 Pb 55.8 53.3 29.4 46.4 20.5 16.1 Th 33.4 43.4 27.6 32.6 31.3 31.2 U 8.82 10.0 7.62 10.1 6.28 8.24 Zr 134 156 196 197 244 197 Hf 5.74 6.59 6.31 5.89 7.46 5.98 注:主量元素单位为%,微量和稀土元素为10-6 微量元素和Sr-Nd同位素分析在核工业北京地质研究院分析测试研究中心完成。微量元素采用酸溶法,制备好的样品溶液在ICP-MS上测试,所用仪器为HR-ICP-MS(Element I),德国Finnigan-MAT公司制造,工作温度、相对湿度分别为20℃和30%,微量元素含量大于10×10-6时的相对误差小于5%,小于10×10-6时的相对误差小于10%,详细的分析流程见参考文献[25]。主量、微量元素分析数据列于表 3。Sm和Nd的分离使用常规的两次离子交换技术,质谱分析使用7个接收器的Finnigan MAT-62(MAT-262?)质谱仪,Sr用静态模式,Nd用动态模式。Nd同位素比值测定以146Nd/144Nd = 0.7219进行标准化,对La Jolla测定的143Nd/144Nd = 0.511554±7(2σ,n=8);Sr同位素比值测定采用86Sr/88Sr=0.1194进行质量分馏校正,Sr同位素标准为NBS607,87Sr/86Sr = 1.20035±l(2σ,n=6)。实验室全流程本底:Rb、Sr为10-10~10-11g,Sm、Nd为10-11~ 10-12g。详细的实验流程及各类标准样品测定结果见王银喜等[26]。Sr-Nd同位素分析结果列于表 4。
表 4 新寨花岗岩Sr-Nd同位素分析结果样品号 Sm /10-6 Nd /10-6 147Sm/144Nd 143Nd/144Nd 2σ ε Nd(t) TDM2/Ga Rb /10-6 Sr /10-6 87Rb/86Sr 87Sr/86Sr 2σ (87Sr/86Sr)i N038-1 4.13 23.1 0.1088 0.511% 0.000004 -7.88 1.85 304 58.3 14.71 0.80984 0.000011 0.71137 N038-3 5.44 27 0.1226 0.51201 0.000007 -7.89 1.85 300 73.3 11.54 0.76544 0.000010 0.68815 N038-4 5.9 30.5 0.1177 0.51202 0.000006 -7.26 1.80 247 146 4.770 0.74523 0.000013 0.71328 3. 分析结果
3.1 锆石U-Pb测年
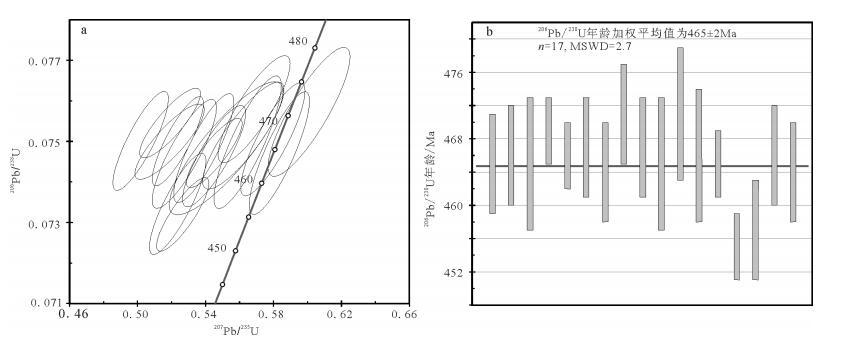
本次对新寨花岗岩进行LA-ICP-MS锆石UPb测年的样品N38-1中不含包体或捕虏体等,成分较均一,其锆石可代表岩体的主体锆石。
样品中锆石多呈长柱状,晶形较完好,颗粒较大,一般为80mm×200mm,韵律环带发育。在CL图像上大部分核部和边部无明显差异。所测锆石的18个分析点中,Th含量为696×10-6~3225×10-6,U含量为2182×10-6~6517×10-6,Th/U值为0.32~0.67。其中17个分析点206Pb/238U年龄变化于455~471Ma之间,在U-Pb谐和图上投于谐和线上及其附近(图 2),得到206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值为465 ± 2Ma(MSWD=2.7),代表了侵入岩的形成时代。09号点的206Pb/238U年龄偏低,为429±3Ma,结合该锆石颗粒CL图像具有较圆滑边部的特征,表明429±3Ma可能代表了后期变质年龄。
3.2 元素地球化学
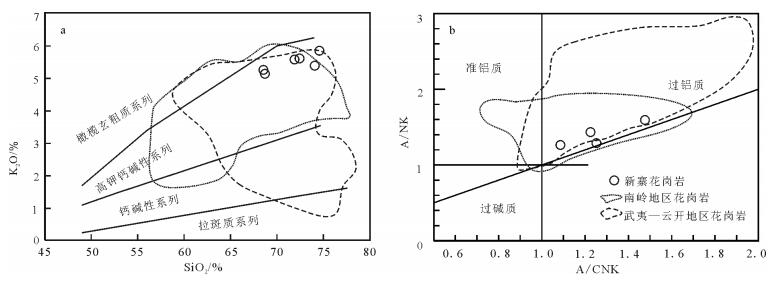
新寨花岗岩化学成分较均一,高硅(SiO2= 68.54%~74.57%)、富碱(Na2O+K2O=7.61%~8.31%)、更富钾(K2O/Na2O=1.77~2.35)、相对富铁而贫镁((Fe2O3+FeO)/MgO=2.29~4.85)。在TAS图解上,新寨花岗岩样品落入花岗岩图区(图略)[27]。新寨花岗岩为高钾钙碱性,与南岭地区的大部分花岗岩(如雪花顶、桂岭及宁冈等)相似(图 3-a)[28]。相对而言,武夷—云开地区加里东期花岗岩范围最广,从橄榄玄粗质-高钾钙碱性-钙碱性,反映了更宽广的元素变化范围。新寨花岗岩为强过铝质(A/ CNK=1.09~2.39),与大部分云开—武夷地区加里东期花岗岩相似,而南岭地区其他同期花岗岩则主要为准铝-弱过铝质(图 3-b)。
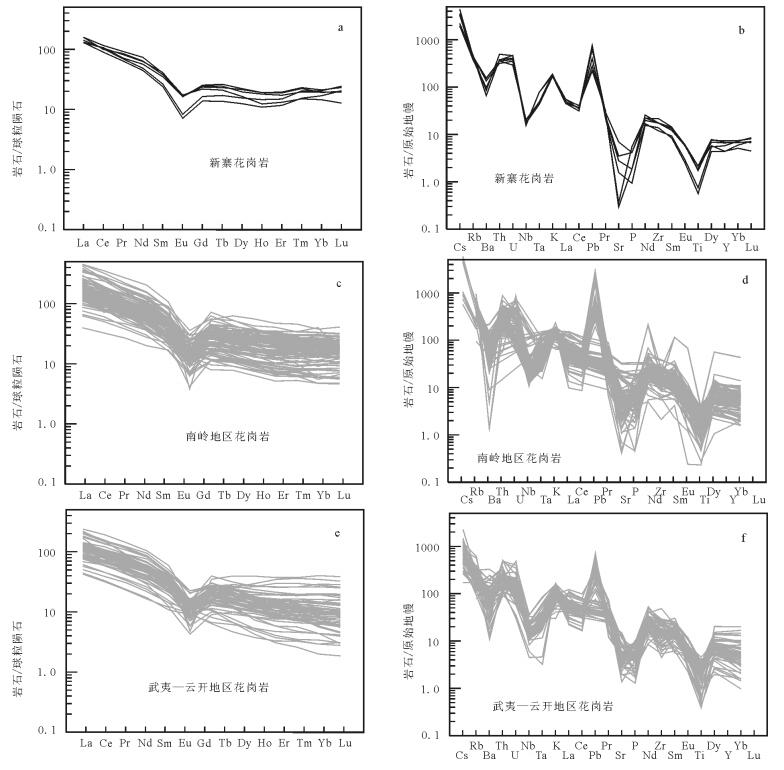
新寨花岗岩稀土元素总量为152×10-6~199×10-6,为轻稀土元素弱富集型((La/Yb)N=6.13~8.10)(图 4-a),轻、重稀土元素比值变化于2.92~4.09之间,中等负Eu异常(δEu=0.37~0.56)。新寨花岗岩稀土元素配分模式与南岭地区早古生代花岗岩总体上相似(图 4-c),但与赣南石雷石英二长闪长岩差别较大[41],与云开—武夷地区同期花岗岩也有所差别(后者表现为重稀土元素含量变化大,呈发散型)(图 4-e)。微量元素蛛网图上,新寨花岗岩均表现为富集大离子亲石元素(LILE)(如Rb、K、Th等),亏损高场强元素(HFSE)(如Nb、Ta、P、Ti)和Ba、Sr等元素(图 4-b)及过渡族元素(Sc、Cr、Co、Ni)(表 3),而无明显的Zr亏损。总体上,南岭和武夷—云开地区同期花岗岩表现出相似的微量元素特征,差别主要在于个别元素的更加亏损或更加富集(图 4-d、f)。
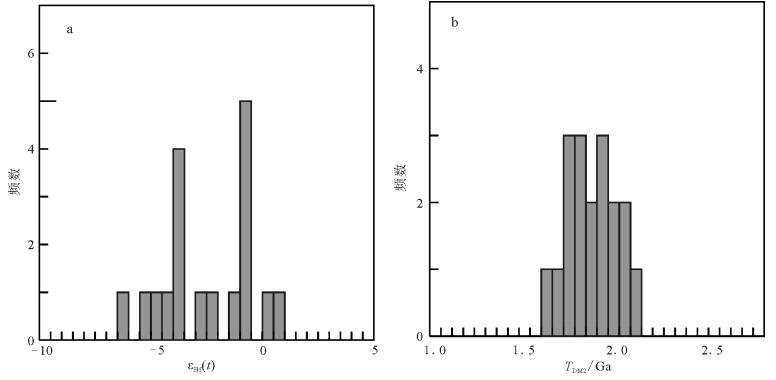
3.3 Sr-Nd-Hf同位素
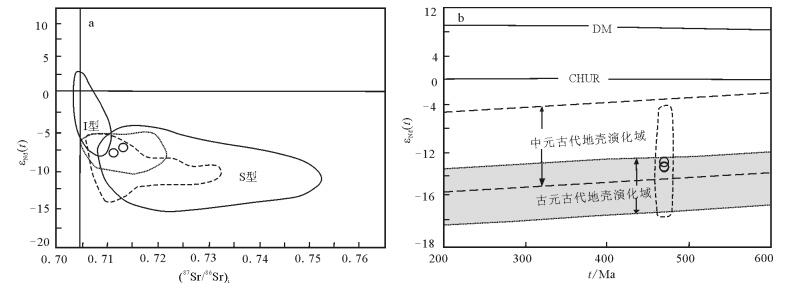
本次选择部分花岗岩样品进行全岩Sr-Nd同位素比值分析,分析结果见表 4。新寨花岗岩Sr同位素组成较高(ISr=0.71137~0.71328),样品N038-3获得了低于0.6900的Sr同位素初始值,可能由于该样品蚀变或风化严重,使得年龄对ISr值的校正十分敏感,在这种情况下,岩石的Sr同位素不具明确的成因意义,仅可作为参考因素[44]。相对而言,Nd同位素由于强的抗扰动性,能有效地示踪岩浆源区性质。新寨花岗岩的Nd同位素组成十分均一,ε Nd(t)=-7.89~-7.26(图 5-a),相应的两阶段Nd模式年龄(TDM2)变化于1.80~ 1.85Ga之间。Sr-Nd同位素资料显示,武夷—云开地区早古生代花岗岩的ISr=0.70726~0.73126,ε Nd(465Ma)=-13.1~-0.97,两阶段Nd模式年龄TDM2=1.29~2.28Ga;南岭东段地区(宁冈)花岗岩的ISr=0.71054~0.71681,ε Nd(465Ma)=-9.01~-8.30,两阶段Nd模式年龄TDM2=1.89~1.95Ga;代表幔源信息的石雷石英二长闪长岩的ISr=0.69923~ 0.71265,ε Nd(t)=-8.05~-5.57,两阶段Nd模式年龄TDM2=1.67~1.87Ga;南岭西段地区(包括雪花顶、诗洞、广平和板杉铺)花岗岩的ISr=0.70627~ 0.72045,ε Nd(t)=-9.65~-5.43,两阶段Nd模式年龄TDM2=1.65~2.00Ga。新寨花岗岩的Sr、Nd同位素组成与南岭西段岩体(如雪花顶)花岗岩较相似(图 5-b)。
![]() 图 5 新寨侵入岩(87Sr/86Sr)i-ε Nd(t)(a)和t-ε Nd(t))图解(b)(图例同图 3)DM—亏损地幔;CHUR—球粒陨石均一储存Figure 5. (87Sr/86Sr)i-ε Nd(t) and t-ε Nd(t) diagrams of the Xinzhai intrusive rocks
图 5 新寨侵入岩(87Sr/86Sr)i-ε Nd(t)(a)和t-ε Nd(t))图解(b)(图例同图 3)DM—亏损地幔;CHUR—球粒陨石均一储存Figure 5. (87Sr/86Sr)i-ε Nd(t) and t-ε Nd(t) diagrams of the Xinzhai intrusive rocks在岩浆演化过程中,锆石是最早结晶的矿物之一,保留了岩浆体系初始的同位素组成,因此可以示踪岩石成因[45]。新寨花岗岩主体锆石的Hf同位素组成为:(176Hf/177Hf)I=0.28232~0.28252,ε Hf(t)=-6.18~+0.61,两阶段Hf模式年龄(TDM2)为1.67~2.11Ga(图 6;表 2)。对于09分析点锆石(429Ma),其Hf同位素组成与主体锆石相近,(176Hf/177Hf)i值为0.28254,ε Hf(t)值为+0.35,TDM2为1.64Ga,暗示其可能亦为主体锆石。武夷—云开地区早古生代花岗岩的ε Hf(t)值变化于-19~+5之间,峰值为-4~-6,相应的Hf同位素两阶段模式年龄TDM2变化于1.1~2.6Ga之间,峰值为1.4Ga[7, 14, 46-50];南岭地区同期花岗岩的ε Hf(t)值变化于-17~+3之间,相应的Hf同位素两阶段模式年龄TDM2变化于1.4~ 2.5Ga之间[40-41, 50],新寨花岗岩的Hf同位素组成与其峰值相近。
4. 讨论
4.1 岩石成因
新寨花岗岩为强过铝质(A/CNK=1.26~ 2.45),具有S型花岗岩的特征(图 5-a),与大部分华南地区同期S型花岗岩具有相似的地球化学特征(图 3、图 4)及Sr-Nd同位素组成(图 5),暗示古老地壳物质是其主要的源区组成。在Al2O3/TiO2-CaO/Na2O,Rb/Sr-Rb/Ba和CaO/(MgO + TFeO)-Al2O3/(MgO+TFeO)花岗岩源区判别图解(图 7)上,新寨花岗岩样品点落入变质泥岩源区,暗示其可能由变泥质岩部分熔融所形成。结合Nd-Hf同位素两阶段模式年龄,认为新寨花岗岩可能源自古元古代变沉积岩的部分熔融(图 5-b)。
新寨花岗岩样品的Harker图解显示(图略),随SiO2含量的增加,Al2O3、CaO、K2O、Na2O、P2O5、MnO等未表现出相关的演化趋势,MgO和TFeO表现出微弱的负相关关系,结合样品弱的负Eu异常(0.37~0.56)和低Rb/Sr值(1.69~44.3)、Rb/Ba值(0.25~0.65),暗示分异结晶在花岗质岩浆演化过程中作用较弱。样品具有变化的TFeO(1.87%~ 3.78%)和MgO(0.41%~1.63%)含量,Mg#值(100× Mg/(Mg+Fe))变化范围大,且个别样品较高(27~ 45)。这些特征暗示,岩浆在形成过程中可能遭受一定程度的基性岩浆的混合作用。Hf同位素组成具有较大的变化范围(ε Hf(t)=-6.18~+0.61,TDM2=1.67~2.11Ga)也证明了这一点。此外,前人资料及本次工作在岩体中发现了一定量的镁铁质暗色微粒包体,也为岩浆混合作用的发生提供了证据。但新寨花岗岩具有均一的Nd-Sr同位素组成(ISr=0.71137~0.71328,ε Nd(t) =-7.89~-7.26,TDM2= 1.80~1.85Ga),暗示基性岩浆对于花岗质岩浆形成物源贡献有限,可能更多地表现在热源贡献上,具体体现在花岗岩样品具有较高的形成温度(796~ 909℃)。因此,新寨花岗岩可能源自古元古代变质泥岩的部分熔融,并在成岩过程中与幔源基性岩浆发生弱的岩浆混合。
4.2 对陆内造山作用的启示
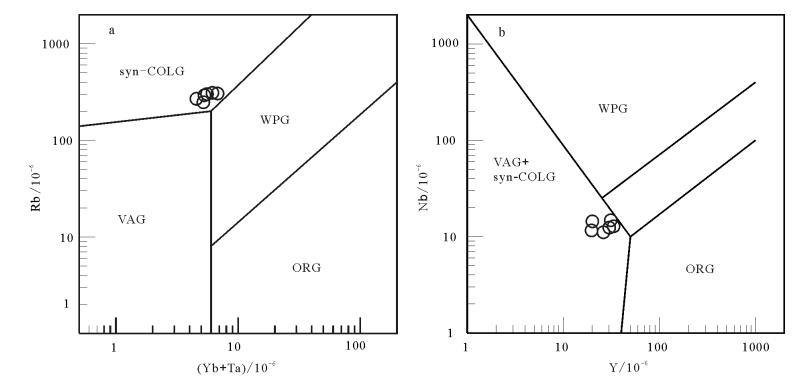
发生于华南早古生代的广西运动可能是世界上又一处典型的板内造山运动,然而该板内造山运动的性质(如启动时限、波及范围、变质程度、岩浆作用等)仍未得到有效制约[15],其构造应力机制亦众说纷纭[5-7, 11-12]。大量的研究结果表明[4-5, 7, 15, 51-52],约460Ma对限定广西运动的启动时限可能是一个关键时间点。武夷—云开地区的角闪岩相变质作用发生于460~445Ma之间,广西运动应早于460~415Ma发生[15],在粤北—赣南地区,晚奥陶世桑比阶—凯迪阶(460.9~455.3Ma)期间,沉积相由深水笔石相转变为浅水碎屑岩相,代表了沉积突变[51],且这种突变由粤南至湘赣表现为由早到晚的变化规律[52],暗示造山运动存在由南至北的过程。大体上由南东至北西,华南早古生代沉积地层之间的角度不整合时代逐渐变新(依次为后奥陶纪/前奥陶纪、中泥盆世/前泥盆纪、晚三叠世—早侏罗世/前三叠纪)[8],江南-雪峰山造山带内早古生代地层存在由角度不整合、微角度不整合至平行不整合的变化[53],也暗示广西运动具有北西向迁移的特征。张爱梅等[49]在桃溪岩群中获得2个花岗片麻岩的结晶年龄为494~496Ma,认为可能是广西运动首幕郁南运动的岩石学响应。新寨S型花岗岩形成于中奥陶世(465±2Ma),与赣南粤北地区沉积突变的时间一致,是广西运动在桂北地区的岩石学响应。在花岗岩构造判别图解(图 8)上,样品落入同碰撞环境图区,暗示新寨花岗岩为同碰撞花岗岩,可能是造山运动次幕的岩石学响应。上述研究成果表明,广西运动作为多幕式的板内造山运动,不同幕式可能具有不同的影响范围,即在不同地区的表现形式相同。首幕可能发生于496Ma左右,规模较小,桂北地区未受波及;次幕可能发生在465~460Ma,规模较大,且率先于赣南、粤北、桂北等地启动,之后向北西波及整个华南,表现在岩浆岩大爆发,分布面积广且持续时间长(465~410Ma),早古生代地层存在广泛的高角度不整合和微角度不整合;第三幕可能启动于约404Ma,可能主要发生于郴州-临武断裂以西的雪峰山地区,表现为岩浆岩分布面积小且持续时间短(404~381Ma)[55]、区域早古生代地层的平行不整合等。
![]() 图 8 新寨花岗岩(Yb+Ta)-Rb(a)和Y-Nb图解(b)[54]VAG—火山岛弧花岗岩;WPG—板内花岗岩;ORG—洋脊花岗岩;syn-COLG—同碰撞期花岗岩Figure 8. (Yb+Ta) -Rb(a)and Y-Nb(b)diagrams for the Xinzhai granites
图 8 新寨花岗岩(Yb+Ta)-Rb(a)和Y-Nb图解(b)[54]VAG—火山岛弧花岗岩;WPG—板内花岗岩;ORG—洋脊花岗岩;syn-COLG—同碰撞期花岗岩Figure 8. (Yb+Ta) -Rb(a)and Y-Nb(b)diagrams for the Xinzhai granites5. 结论
(1)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年结果显示,新寨花岗岩形成时代为465±2Ma,属中奥陶世。
(2)元素地球化学及Nd-Sr-Hf同位素分析结果显示,新寨花岗岩可能源自古元古代地壳变泥质岩的部分熔融,在成岩过程中有少量的幔源组分参与。新寨S型花岗岩可能是广西运动第二幕(启动于465~460Ma)在桂北地区的岩石学响应,为早古生代构造-岩浆事件群的建立提供了新证据。
致谢: 西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室袁洪林和魏君奇教授在锆石U-Pb测年方面给予了帮助和指导,审稿专家提出了建设性的意见,在此一并感谢。 -
图 4 新寨、南岭地区、武夷—云开地区早古生代花岗岩稀土元素分布模式(a、c、e)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b、d、f)
(标准化数据据参考文献[43], 引文数据据参考文献[7, 14, 29-34, 36-39, 41])
Figure 4. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a, c, e) and primitive mantle-normalized multi-element diagrams (b, d) of the Xinzhai granites and the Paleozoic granites in Nanling Mountains, as well as Wuyi-Yunkai area
图 5 新寨侵入岩(87Sr/86Sr)i-ε Nd(t)(a)和t-ε Nd(t))图解(b)(图例同图 3)
DM—亏损地幔;CHUR—球粒陨石均一储存
Figure 5. (87Sr/86Sr)i-ε Nd(t) and t-ε Nd(t) diagrams of the Xinzhai intrusive rocks
图 8 新寨花岗岩(Yb+Ta)-Rb(a)和Y-Nb图解(b)[54]
VAG—火山岛弧花岗岩;WPG—板内花岗岩;ORG—洋脊花岗岩;syn-COLG—同碰撞期花岗岩
Figure 8. (Yb+Ta) -Rb(a)and Y-Nb(b)diagrams for the Xinzhai granites
表 1 新寨花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析数据
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb isotopic data for zircons of the Xinzhai granites
点号 Pb Th U 比值(经普通铅校正) 年龄(经普通铅校正)/Ma /10-6 207Pb/206Pb ±1σ 207Pb/235U ±1σ 206Pb/238U ±1σ 207Pb/206Pb ±1σ 207Pb/235U ±1σ 206Pb/238U ±1σ 1 340 1852 3872 0.05193 0.00073 0.5387 0.0073 0.07484 0.00055 282 27 438 5 465 3 2 314 1485 3695 0.04815 0.00062 0.5014 0.0067 0.07502 0.0005 107 28 413 5 466 3 3 279 1304 3243 0.05273 0.00101 0.5520 0.0138 0.07484 0.00067 317 54 446 9 465 4 4 218 983 2585 0.04956 0.00074 0.5187 0.0074 0.07546 0.00035 174 32 424 5 469 2 5 180 696 2182 0.04983 0.00081 0.5184 0.0084 0.07500 0.00038 187 37 424 6 466 2 6 251 1809 2752 0.05398 0.00097 0.5621 0.0099 0.07515 0.00054 370 37 453 6 467 3 7 367 1511 4445 0.05268 0.00074 0.5448 0.0077 0.07464 0.00051 315 29 442 5 464 3 8 307 1709 3336 0.05406 0.00077 0.5684 0.0087 0.07580 0.00054 373 31 457 6 471 3 9 506 3225 6517 0.05389 0.00064 0.5140 0.0064 0.06884 0.00052 366 23 421 4 429 3 10 254 1070 3089 0.05584 0.00083 0.5800 0.0078 0.07506 0.00057 446 25 464 5 467 3 11 431 2850 4939 0.05645 0.00074 0.5833 0.0073 0.07472 0.00062 470 21 467 5 465 4 12 335 1456 3850 0.05733 0.00095 0.6010 0.0099 0.07574 0.00065 504 32 478 6 471 4 13 448 2762 5309 0.05446 0.00078 0.5646 0.0081 0.07499 0.00067 390 26 455 5 466 4 14 397 3076 4596 0.05262 0.00066 0.5448 0.0068 0.07472 0.00035 313 27 442 4 465 2 15 436 3203 5232 0.05188 0.00063 0.5262 0.0064 0.07320 0.00037 280 26 429 4 455 2 16 317 2249 3757 0.05144 0.00064 0.5232 0.0068 0.07346 0.00051 261 26 427 5 457 3 17 438 2426 5146 0.05038 0.00057 0.5234 0.0062 0.07501 0.00045 213 24 427 4 466 3 18 268 1250 3182 0.05094 0.00066 0.5272 0.0077 0.07470 0.00055 238 30 430 5 464 3 表 2 新寨花岗岩锆石Lu-Hf同位素分析结果
Table 2 Lu-Hf isotopic analyses for zircons of the Xinzhai granites
点号 176Yb/177Hf 176Lu/177Hf 176Hf/177Hf 2σ T/Ma ε Hf(t) 2σ THf1/Ga THf2/Ga 01 0.025163 0.000830 0.282463 0.000011 465 -0.95 0.4 1.11 1.78 02 0.027225 0.000853 0.282346 0.000013 466 -5.06 0.5 1.27 2.04 03 0.029851 0.000952 0.282370 0.000012 465 -4.27 0.4 1.24 1.99 04 0.040693 0.001246 0.282317 0.000014 469 -6.18 0.5 1.33 2.11 05 0.029434 0.000908 0.282359 0.000009 466 -4.63 0.3 1.26 2.02 06 0.054760 0.001624 0.282430 0.000014 467 -2.32 0.5 1.18 1.86 07 0.030690 0.000943 0.282388 0.000009 464 -3.66 0.3 1.22 1.95 08 0.036582 0.001166 0.282469 0.000011 471 -0.73 0.4 1.11 1.77 09 0.051495 0.001635 0.282528 0.000019 429 0.35 0.7 1.04 1.64 10 0.047695 0.001418 0.282391 0.000012 467 -3.64 0.4 1.23 1.94 11 0.044739 0.001420 0.282480 0.000014 465 -0.51 0.5 1.10 1.74 12 0.032905 0.001018 0.282385 0.000014 471 -3.65 0.5 1.23 1.96 13 0.042287 0.001289 0.282477 0.000013 466 -0.55 0.5 1.10 1.75 14 0.051338 0.001555 0.282513 0.000018 465 0.61 0.6 1.06 1.67 15 0.034169 0.001069 0.282458 0.000012 455 -1.42 0.4 1.12 1.79 16 0.048987 0.001475 0.282427 0.000014 457 -2.59 0.5 1.18 1.86 17 0.038565 0.001186 0.282391 0.000012 466 -3.58 0.4 1.22 1.94 18 0.022362 0.000739 0.282463 0.000011 464 -0.95 0.4 1.11 1.78 表 3 新寨花岗岩主量和微量元素分析结果
Table 3 Chemical composition of the Xinzhai granites
元素 N38-1 N38-2 N38-3 N38-4 N38-5 N38-6 SiO2 74.07 74.57 68.54 68.70 72.43 71.89 Al2O3 13.25 13.39 15.25 14.78 15.44 15.33 Fe2O3 0.30 0.50 1.18 1.49 1.02 2.11 FeO 1.57 1.49 2.55 2.29 1.30 0.97 CaO 0.95 0.17 0.42 0.97 0.18 0.07 MgO 0.62 0.41 1.63 1.52 0.88 0.87 k2O 5.37 5.83 5.24 5.12 5.59 5.56 Na2O 2.84 2.48 2.37 2.90 0.16 0.16 TiO2 0.16 0.12 0.39 0.37 0.46 0.46 P2O5 0.04 0.02 0.09 0.09 0.12 0.04 MnO 0.03 0.02 0.07 0.06 0.02 0.04 总计 99.19 99.00 97.73 98.28 97.60 97.50 烧失量 0.62 0.83 1.96 1.45 2.25 2.37 Sc 3.34 3.26 9.16 9.66 11.4 8.55 V 21.4 16.9 59.3 61.7 75.6 71.6 Cr 15.7 9.19 27.1 33.2 41.9 39.4 Co 3.27 3.25 8.56 9.15 4.85 7.58 Ni 6.62 6.58 16.8 17.6 13.8 14.9 Ga 13.1 13.2 17.1 17.9 18.5 17.9 Rb 304 309 300 247 292 268 Sr 58.3 32.7 73.3 146 7.51 6.05 Y 26.2 19.7 33.4 30.1 31.2 20.1 Nb 11.1 11.6 12.8 12.4 14.8 14.4 Cs 15.8 18.2 29.4 16.1 36.7 27.4 Ba 469 604 962 702 1110 1083 La 34.5 31.5 31.3 38.4 32.1 38.6 Ce 64.1 56.2 66.9 62.5 65.6 72.8 Pr 6.73 6.2 6.96 8.27 7.95 8.96 Nd 23.1 21.2 27.0 30.5 29.9 35.2 Sm 4.13 3.73 5.44 5.90 6.42 6.28 Eu 0.49 0.42 0.97 0.99 0.96 1.03 Gd 3.44 2.89 4.95 5.14 5.31 4.58 Tb 0.65 0.52 0.88 0.93 1.00 0.80 Dy 4.01 3.22 5.56 5.07 5.75 4.25 Ho 0.84 0.63 1.10 1.04 1.10 0.71 Er 2.51 1.97 3.28 2.91 3.18 2.22 Tm 0.53 0.40 0.60 0.51 0.58 0.39 Yb 3.55 2.93 3.66 3.40 3.32 2.51 Lu 0.63 0.53 0.60 0.50 0.52 0.33 Ta 3.20 3.20 1.88 1.77 1.95 2.01 Pb 55.8 53.3 29.4 46.4 20.5 16.1 Th 33.4 43.4 27.6 32.6 31.3 31.2 U 8.82 10.0 7.62 10.1 6.28 8.24 Zr 134 156 196 197 244 197 Hf 5.74 6.59 6.31 5.89 7.46 5.98 注:主量元素单位为%,微量和稀土元素为10-6 表 4 新寨花岗岩Sr-Nd同位素分析结果
样品号 Sm /10-6 Nd /10-6 147Sm/144Nd 143Nd/144Nd 2σ ε Nd(t) TDM2/Ga Rb /10-6 Sr /10-6 87Rb/86Sr 87Sr/86Sr 2σ (87Sr/86Sr)i N038-1 4.13 23.1 0.1088 0.511% 0.000004 -7.88 1.85 304 58.3 14.71 0.80984 0.000011 0.71137 N038-3 5.44 27 0.1226 0.51201 0.000007 -7.89 1.85 300 73.3 11.54 0.76544 0.000010 0.68815 N038-4 5.9 30.5 0.1177 0.51202 0.000006 -7.26 1.80 247 146 4.770 0.74523 0.000013 0.71328 -
陈洪德, 侯明才, 许效松, 等.加里东期华南的盆地演化与层序格架[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 33(1):1-8. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG200601000.htm Hs K J, Li J L, Chen H H, et al. Tectonics of South China:key to tectonics of South China:key to understanding west Pacific geology[J]. Tectonophysics, 1990, 193:9-39.
Ma L, Chen H J, Gan K W, et al. Geotectonics and petroleum geology of marine sedimentary rocks in southern China[M]. Geological Publishing House, Beijing, 2004.
舒良树, 于津海, 贾东, 等.华南东段早古生代造山带研究[J].地质通报, 2008, 27(10):1581-1593. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.10.001 Wang Y J, Fan W M, Zhao G C, et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronology of gneisses in Yunkai Mountains and its implications on the Caledonian event in South China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2007, 12(4):404-416. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2006.10.003
Wang Y J, Zhang F F, Fan W M, et al. Tectonic setting of the South China Block in the early Paleozoic:resolving intracontinental and ocean closure models from detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology[J]. Tectonics, 2010, 29(6):1-70. doi: 10.1029/2010TC002750/full
Wang Y J, Zhang A M, Fan W M, et al. Kwangsian crustal anatexis within the eastern South China Block:geochemical, zircon U-Pb geochronological and Hf isotopic fingerprints from the gneissoid granites of Wugong and Wuyi-Yunkai Domains[J]. Lithos, 2011, 127:239-260. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2011.07.027
Wang Y J, Wu C M, Zhang A M, et al. Kwangsian and Indosinian reworking of the eastern South China Block:constraints on zircon U-Pb geochronology and metamorphismof amphibolites and granu-lites[J]. Lithos, 2012, 150:227-242. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.04.022
Wang Y J, Fan W M, Zhang G W, et al. Phanerozoic tectonics of the South China Block:key observations and controversies[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 23:1273-1305. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.02.019
Wang Y J, Zhang A M, Fan W M, et al. Origin of paleosubduction-modified mantle for Silurian gabbro in the Cathaysia Block:geochronological and geochemical evidence[J]. Lithos, 2013, 160/161:37-54. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.11.004
Faure M, Shu L S, Wang B, et al. Intracontinental subduction:a possible mechanism for the Early Palaeozoic Orogen of SE China[J]. Terra Nova, 2009, 21:360-368. doi: 10.1111/ter.2009.21.issue-5
Charvet J, Shu L S, Faure M, et al. Structural development of the lower Paleozoic belt of South China:genesis of an intracontinental orogen[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2010, 39:309-330. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.03.006
Huang X L, Yu Y, Li J, et al. Geochronology and petrogenesis of the early Paleozoic I-type granite in the Taishan area, South Chi-na:middle-lower crustal melting during orogenic collapse[J]. Lith-os, 2013, 177:268-284. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2013.07.002
Wan Y S, Liu D Y, Wilde S M, et al. Evolution of the Yunkai terrane, South China:evidence from SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating, geochemistry and Nd isotope[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2010, 37:140-153. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2009.08.002
Li Z X, Li X H, Wartho J A, et al. Magmatic and metamorphic events during the Early Paleozoic Wuyi-Yunkai Orogeny, southeastern South China:new age constraints and pressure-temperature conditions[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2010, 122(5/6):772-793. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Jo_Anne_Wartho/publication/50875443_Magmatic_and_metamorphic_events_during_the_early_Paleozoic_Wuyi-Yunkai_orogeny_southeastern_South_China_New_age_constraints_and_pressure-temperature_conditions/links/00b4953556253e9f44000000.pdf?origin=publication_detail
孙涛.新编华南花岗岩分布图及其说明[J].地质通报, 2006, 25(3):3327. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20060355&journal_id=gbc 周新民.对华南花岗岩研究的思考[J].高校地质学报, 2003, 9:556-565 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2003.04.009 张相训, 陈扬浦.灵川县新寨花岗岩体形成时代研究[J].广西地质, 1993, 6(1):23-28. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDZ199301002.htm 袁洪林, 吴福元, 高山, 等.东北地区新生代侵入体的锆石激光探针U-Pb年龄测定与稀土元素成分分析[J].科学通报, 2003, 48(14):1511-1520. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.14.008 Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Gao S, et al. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 257(1/2):34-43. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Yongsheng_Liu5/publication/222034389_In_situ_analysis_of_major_and_trace_elements_of_anhydrous_minerals_by_LA-ICP-MSLA-ICP-MS_without_applying_an_internal_standard/links/54067d610cf2c48563b2536f/In-situ-analysis-of-major-and-trace-elements-of-anhydrous-minerals-by-LA-ICP-MSLA-ICP-MS-without-applying-an-internal-standard.pdf
Anderson T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical geology, 2002, 192:59-79. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00195-X
Ludwig K R. ISOPLOT 3.00:A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. California:Berkeley Geochronology Center, 2003.
Blichert T J, Albarede F. The Lu-Hf isotope geochemistry of chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1997, 148(1):243-258. http://www.academia.edu/5433105/The_Lu-Hf_isotope_geochemistry_of_chondrites_and_the_evolution_of_the_mantle-crust_system
Griffin W L, Pearson N J, Belousova E, et al. The Hf isotope composition of cratonic mantle:LA-MC-ICPMS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64(1):133-147. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00343-9
Qu X M, Hou Z Q, Li Y G. Melt components derived from a subducted slab in late orogenic ore-bearing porphyries in the Gungdese copper belt, southern Tibetan (Xizang) plateau[J].Lithos, 2004, 74(3/4):131-148. http://www.academia.edu/14455616/Melt_components_derived_from_a_subducted_slab_in_late_orogenic_ore-bearing_porphyries_in_the_Gangdese_copper_belt_southern_Tibetan_plateau
王银喜, 杨杰东, 陶仙聪, 等.化石、矿物和岩石样品的Sm-Nd同位素实验方法研究及其应用[J].南京大学学报(自然科学版), 1988, 21(2):297-308. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJDZ198802017.htm Middlemost E A K.Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J].Earth Science Review, 1994, 37:215-224. doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(94)90029-9
Peccerillo A, Taylor S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions of Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58(1):63-8l. doi: 10.1007/BF00384745
李献华.万洋山-诸广山花岗岩复式岩基的地球化学研究及地壳形成演化历史[J].地质地球化学, 1989, (3):4-5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ198903018.htm 柏道远, 黄建中, 马铁球, 等.湘东南志留纪彭公庙花岗岩体的地质地球化学特征及其构造环境[J].现代地质, 2006, 20(1):130-140. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ200601015.htm 许德如, 陈广浩, 夏斌, 等.湘东地区板杉铺加里东期埃达克质花岗闪长岩的成因及地质意义[J].高校地质学报, 2006, 12(4):507-521. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200604012.htm 耿红燕, 徐夕生, 赵明, 等.粤西白垩纪火山-侵入岩浆活动及其地质意义[J].中国科学(D辑), 2006, 36(7):601-617. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200607001.htm 彭松柏, 金振民, 刘云华, 等.云开造山带强过铝深熔花岗岩地球化学, 年代学及构造背景[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2006, 31(1):110-120. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200601015.htm 周新民, 孙涛, 沈渭洲, 等. 华南中生代花岗岩-火山岩时空格局与成因模式[C]//南岭地区晚中生代花岗岩成因与岩石圈动力学演化. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007: 179-195. 伍光英, 马铁球, 冯艳芳, 等.南岭万洋山加里东期花岗岩地质地球化学特征及其成因[J].中国地质, 2008, 35(4):608-617. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200804006.htm 沈渭洲, 张芳荣, 舒良树, 等.江西宁冈岩体的形成时代, 地球化学特征及其构造意义[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(10):2244-2254. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200810006.htm 刘锐, 张利, 周汉文, 等.闽西北加里东期混合岩及花岗岩的成因:同变形地壳深熔作用[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(6):1205-1222. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200806006.htm 程顺波, 付建明, 徐德明, 等.桂东北大宁岩体锆石SHRIMP年代学和地球化学研究[J].中国地质, 2009, 36(6):1278-1288. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200906011.htm 程顺波, 付建明, 徐德明, 等.湖南雪花顶花岗岩及其包体的地质地球化学特征和成因分析[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2009, 33(4):588-597. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200904014.htm 王彦斌, 王登红, 韩娟, 等.湖南益将稀土-钪矿的石英闪长岩锆石U-Pb定年和Hf同位素特征:湘南加里东期岩浆活动的年代学证据[J].中国地质, 2010, 37(4):1062-1070. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201004022.htm 李光来, 华仁民, 胡东泉, 等.赣南地区石雷石英闪长岩的成因:岩石化学, 副矿物微量元素, 锆石U-Pb年代学与Sr-Nd-Hf同位素制约[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(3):903-918. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201003021.htm 颜乾坤. 桂东北桂岭二长花岗岩地球化学特征及其成因[D]. 桂林理工大学硕士学位论文, 2010: 1-30. Sun S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society of London Special Publications, 1989, 42(1):313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
邱检生, Mcinnes B I A, 蒋少涌, 等.江西会昌密坑山岩体的地球化学及其成因类型的新认识[J].地球化学, 2005, 34(1):20-32. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200501002.htm Griffin W L, Wang X, Jackson S E. Zircon chemistry and magma genesis, SE China:in-situ analysis of Hf isotopes, Tonglu and Pingtan igneous complexes[J]. Lithos, 2002, 61:237-269. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(02)00082-8
Zeng W, Zhang L, Zhou H W, et al. Caledonian reworking of Paleoproterozoic basement in the Cathaysia Block:constraints from zircon U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements[J]. Chinese Sci-ence Bulletin, 2008, 53(6):895-904. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/226901120_Caledonian_reworking_of_Paleoproterozoic_basement_in_the_Cathaysia_Block_Constraints_from_zircon_U-Pb_dating_Hf_isotopes_and_trace_elements
Xia Y, Xu X S, Zou H B, et al. Early Paleozoic crust-mantle interaction and lithosphere delamination in South China Block:evidence from geochronology, geochemistry, and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopes of granites[J]. Lithos, 2014, 184/187:416-435. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2013.11.014
Zhang A M, Wang Y J, Fan W M, et al. LA-ICPMS zircons UPb geochronology and Hf isotopic composition of the Taoxi migmatite (Wuping):constrains on the formation age of the Taoxi complex and the Yu'nan event[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2011, 35(1):64-72. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/281122575_LA-ICPMS_zircons_U-Pb_geochronology_and_Hf_isotopic_composition_of_the_Taoxi_migmatite_Wuping_constrains_on_the_formation_age_of_the_Taoxi_complex_and_the_Yu'nan_event
张爱梅, 王岳军, 范蔚茗, 等.福建武平地区桃溪群混合岩U-Pb定年及其Hf同位素组成:对桃溪群时代及郁南运动的约束[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2011, 35(1):64-72. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201101007.htm Shu X J, Wang X L, Sun T, et al. Crustal formation in the Nanling Range, South China Block:Hf isotope evidence of zircons from Phanerozoic granitoids[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 74:210-224. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.01.016
陈旭, 张元动, 樊隽轩, 等.赣南奥陶纪笔石地层序列与广西运动[J].中国科学(D辑), 2010, 40:1621-1631. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201012002.htm 陈旭, 张元动, 樊隽轩, 等.广西运动的进程:来自生物相和岩相带的证据[J].中国科学(D辑), 2012, 42:1621-1631. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201211002.htm 陈世悦, 李聪, 张鹏飞, 等.江南-雪峰地区加里东期和印支期不整合分布规律[J].中国地质, 2011, 35(8):1212-1219. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201105009.htm Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G.Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rock[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4):956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
Zhao K D, Jiang S Y, Sun T, et al. Zircon U-Pb dating, trace element and Sr-Nd-Hf isotope geochemistry of Paleozoic granites in the Miao' ershan-Yuechengling batholith, South China:implication for petrogenesis and tectonic-magmatic evolution[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 74:244-264. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.12.026
广西壮族自治区地质局. 1: 200000桂林幅区域地质测量报告. 1969.



 下载:
下载: