Characterization and evaluation on the source rock of gas hydrate in Muli permafrost area, Nanqilian Basin
-
摘要:
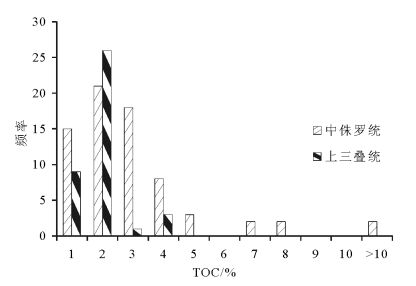
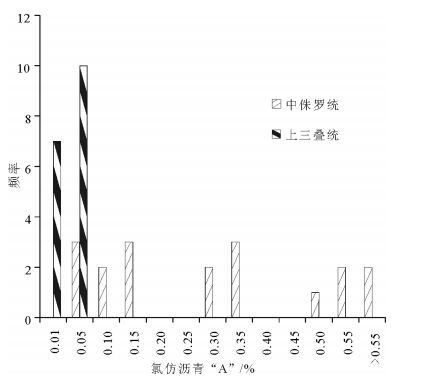
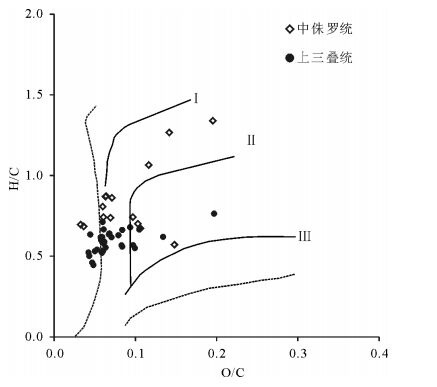
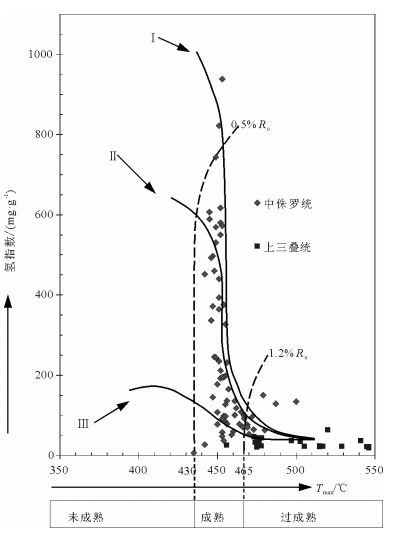
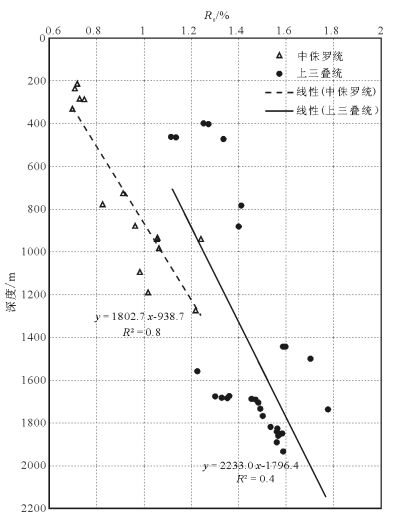
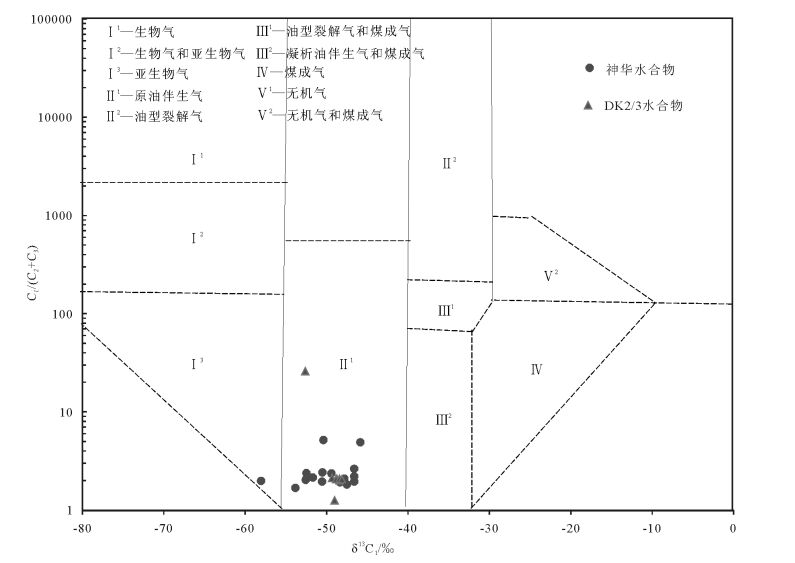
中国地质调查局2008年在南祁连盆地木里冻土区采集到了中国陆域第一例天然气水合物实物样品,对于天然气水合物的气体来源存在不同的认识。利用新完钻3口井样品的化验分析结果,分析了中侏罗统和上三叠统烃源岩有机地球化学特征。结果表明,中侏罗统江仓组、木里组煤系地层烃源岩有机质丰度较高,TOC(总有机碳含量)大于1%的样品占78.9%;氯仿沥青“A”含量大于0.1%的占总数的72.2%;有机质类型以Ⅱ2、Ⅱ1型为主;镜质体反射率Ro多介于0.7%~1.2%之间;71个样品生烃潜量平均值为8.8mg/g,总体处于生烃高峰期的生油阶段或凝析油阶段,属于好、很好烃源岩,为天然气水合物主力生烃层系。上三叠统尕勒得寺组亦为煤系地层烃源岩,TOC含量大于1%的样品占76.9%;氯仿沥青“A”含量小于0.05%;有机质类型以Ⅲ、Ⅱ1型为主;镜质体反射率Ro介于1.1%~1.77%之间;总体处于生湿气或干气阶段,但由于构造抬升影响其生烃潜量,平均值仅为0.35mg/g,当前整体生烃能力较差,为非烃源岩或较差烃源岩,对天然气水合物成藏贡献不大。
Abstract:China's first permafrost gas hydrate samples were collected by China Geological Survey in 2008 in Muli permafrost area, Nanqilian Basin. There exist different opinions concerning the genesis or origin of gases from gas hydrate. The organic geochemical indictors were systematically analyzed on the gas source rocks of the Middle Jurassic and the Upper Triassic from recently drilled 3 wells. The results show that the organic matter values are at high levels in source rocks of the Middle Jurassic strata (Jiangcang and Muli Formation) in the study area. 78.9% of TOC values are more than 1.0%, and 72.2% of chloroform bitumen 'A' are more than 0.1%. The main organic matter is of type Ⅱ2 and Ⅱ1. The vitrinite reflectances of most samples are between 0.7% to 1.2%. The average value of total hydrocarbon generation potential is 8.8mg/g rock in total 71 samples. So the organic matters in most samples are at mature levels, or at condensate levels, which are good and very good source rocks for the gases of gas hydrates. The organic matter values are also at high levels in source rocks of the Upper Triassic strata (Galedesi Formation). 76.9% of TOC values are more than 1.0%. The chloroform bitumen 'A' is less than 0.05%. The main organic matters are of type Ⅲ and Ⅱ1. The vitrinite reflectances of most samples are between 1.1% and 1.77%. Hence the organic matters in most samples are at post mature levels, or at dry gas levels, but the average value of total hydrocarbon generation potential is only 0.35 mg/g rock in total 39 samples, suggesting poor source rocks or barren rocks for the gases of gas hydrates.
-
Keywords:
- gas hydrate /
- Middle Jurassic /
- Upper Triassic /
- source rock characteristics /
- Muli permafrost /
- Nanqilian Basin
-
致谢: 成文过程中得到中国地质调查局油气资源调查中心翟刚毅教授级高工的指导,在此深表谢意。
-
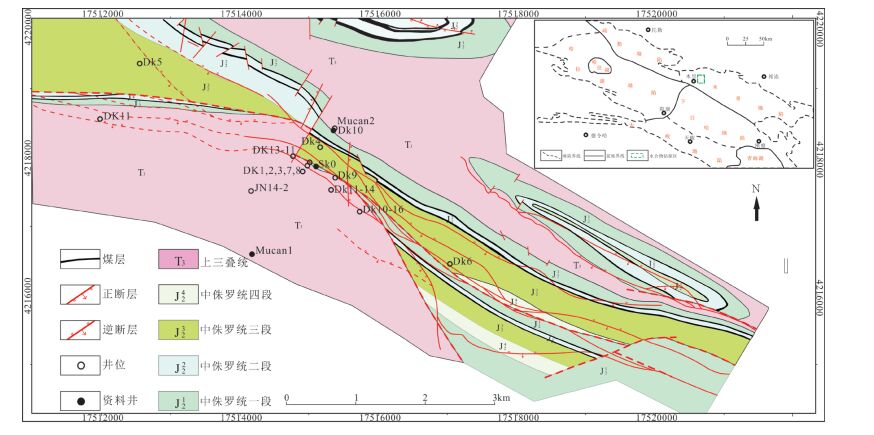
图 1 南祁连盆地构造单元划分及木里冻土区井位地质图[23]
Figure 1. Division of tectonic units in southern Qilian Basin and geological map of wells in Muli permafrost area
表 1 烃源岩有机质类型划分评价标准[31]
Table 1 Evaluation criteria for classification of organic matter in source rocks
类别 类型 热解参数 化学元素 族组分 显微组分 IO HI H/C O/C 饱/芳 指数(TI) Ⅰ 腐泥 <20 >600 >1.4 <0.1 >3 80~100 Ⅱ1 腐植腐泥 20~40 250~600 1.1~1.4 0.1~0.15 1.6~3 40~80 Ⅱ2 腐泥腐植 40~60 120~250 0.8~1.1 0.15~0.25 1~1.6 0~40 Ⅲ 腐植 >60 <120 <0.8 >0.25 0.5-1 -100 表 2 研究区烃源岩有机质类型综合评价
Table 2 Comprehensive evaluation of organic matter types of source rocks in the study area
井名 深度/m 层位 显微组分类型指数 (TI) 化学元素 热解参数氢指数
(HI)/(mg· g-1)综合
评价腐泥质/% 壳质组/% 镜质组/% 惰质组/% 类型指数 H/C O/C 木参1井 724~725 J 9.0 61.0 24.0 6.0 16.0 0.7 0.1 71.2 Ⅱ2 木参1井 776~777 J 9.0 52.0 32.0 7.0 4.0 0.6 0.1 77.9 Ⅱ2 木参1井 876~877 J 6.0 69.0 21.0 4.0 21.0 0.9 0.1 135.9 Ⅱ2 木参1井 931~932 J 3.0 70.0 26.0 1.0 18.0 0.6 0.2 33.0 Ⅱ2 木参1井 938~939 J 14.0 74.0 11.0 1.0 42.0 0.7 0.1 70.1 Ⅱ1 木参1井 981~982 J 16.0 76.0 8.0 48.0 0.8 0.1 91.7 Ⅱ1 木参1井 1092~1093 J 9.0 76.0 15.0 36.0 0.7 0.1 96.4 Ⅱ2 木参1井 1187~1188 J 3.0 54.0 41.0 2.0 ~3.0 0.7 0.0 150.2 Ⅲ 木参1井 1272~1273 J 4.0 72.0 22.0 2.0 22.0 0.7 0.0 128.8 Ⅱ2 SK~0井 212.39 J 0.0 79.0 20.5 0.6 25.4 0.9 0.1 194.8 Ⅱ2 SK~0井 234.4 J 11.3 70.6 17.6 0.5 41.6 1.1 0.1 375.5 Ⅱ1 SK~0井 282.16 J 23.9 64.8 11.0 0.3 47.7 1.3 0.1 530.5 Ⅱ1 SK~0井 285.48 J 14.8 68.1 17.0 0.0 43.1 1.3 0.2 569.1 Ⅱ1 SK~0井 330 J 2.2 63.3 33.3 1.2 12.7 0.9 0.1 211.6 Ⅱ2 木参1井 939.16 J 1.3 28.2 68.0 2.6 ~37.8 0.7 0.1 108.3 Ⅲ 木参2井 70 J 1.1 30.7 67.6 0.6 ~32.1 0.6 0.1 Ⅲ 木参1井 1566~1567 T3g 14.0 69.0 14.0 3.0 35.0 0.6 0.1 63.6 Ⅱ2 木参1井 1676~1677 T3g 27.0 67.0 6.0 56.0 0.5 0.1 36.1 Ⅱ1 木参1井 1678~1679 T3g 25.0 68.0 5.0 2.0 53.0 0.7 0.1 17.0 Ⅱ1 木参1井 1685 T3g 40.0 55.0 4.0 1.0 64.0 0.7 0.1 22.8 Ⅱ1 木参1井 1686~1687 T3g 41.0 55.0 4.0 66.0 0.6 0.1 23.0 Ⅱ1 木参1井 1689~1690 T3g 43.0 48.0 7.0 2.0 60.0 0.6 0.1 19.0 Ⅱ1 木参1井 1692~1693 T3g 37.0 56.0 6.0 1.0 60.0 0.6 0.1 21.4 Ⅱ1 木参1井 1705~1707 T3g 44.0 53.0 3.0 68.0 0.6 0.1 18.1 Ⅱ1 木参1井 1730~1734 T3g 39.0 59.0 2.0 67.0 0.6 0.1 13.9 Ⅱ1 木参1井 1765~1766 T3g 19.0 75.0 5.0 1.0 52.0 0.7 0.1 21.1 Ⅱ1 木参1井 1814~1815 T3g 7.0 63.0 25.0 5.0 15.0 0.5 0.0 17.1 Ⅱ2 木参1井 1821~1822 T3g 14.0 70.0 15.0 1.0 37.0 0.5 0.1 15.4 Ⅱ2 木参1井 1835~1836 T3g 8.0 65.0 25.0 2.0 20.0 0.7 0.1 22.7 Ⅱ2 木参1井 1843~1844 T3g 4.0 66.0 22.0 8.0 13.0 0.6 0.1 13.4 Ⅱ2 木参1井 1846~1847 T3g 15.0 76.0 7.0 2.0 46.0 0.6 0.1 15.2 Ⅱ1 木参1井 1854~1855 T3g 15.0 79.0 5.0 1.0 50.0 0.5 0.1 14.8 Ⅱ1 木参1井 1883~1884 T3g 19.0 74.0 5.0 2.0 50.0 0.6 0.0 14.2 Ⅱ1 木参1井 1923~1924 T3g 6.0 52.0 36.0 6.0 -1.0 0.6 0.1 11.9 Ⅲ 木参1井 1503.97 T3g 1.2 25.6 71.7 1.5 -41.2 0.5 0.0 21.9 Ⅲ 木参1井 2002.63 T3g 0.0 11.0 87.4 1.6 -61.4 0.5 0.0 4.5 Ⅲ 木参1井 2004.03 T3g 0.0 39.4 59.3 1.3 -26.1 0.4 0.0 25.1 Ⅲ 木参2井 399.94 T3g 0.6 32.8 66.7 0.0 -33.1 0.7 0.1 29.9 Ⅲ 木参2井 403.24 T3g 2.0 32.2 64.9 0.9 -31.5 0.6 0.1 34.5 Ⅲ 木参2井 878.6 T3g 10.1 27.0 62.0 0.9 -23.0 0.6 0.1 43.0 Ⅲ 木参2井 1450.02 T3g 0.3 37.6 61.8 0.3 -27.5 0.6 0.1 21.9 Ⅲ -
Kvenvolden K A. A review of the geochemistry of methane in natu-ral gas hydrate[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1995, 23(11/12):997-1008. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222491531_A_review_of_the_geochemistry_of_methane_in_natural_gas_hydrate
史斗, 郑军卫.世界天然气水合物研究开发现状和前景[J].地球科学进展, 1999, 14(4):330-339. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ904.003.htm 祝有海, 张永勤, 文怀军, 等.青海祁连山冻土区发现天然气水合物[J].地质学报, 2009, 83(11):1762-1771. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2009.11.018 张洪涛, 祝有海.中国冻土区天然气水合物调查研究[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(12):1809-1815. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.12.001 Collett T S. Energy resource potential of natural gas hydrates[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2002, 86(11):1971-1992. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/234149371_The_Potential_of_Natural_Gas_Hydrates_as_an_Energy_Resource
Makogon Y F, Holditch S A, Makogon T Y. Natural gashydrates:A potential energy source for 21st Century[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2007, 56:14-31. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2005.10.009
张立薪, 徐学祖, 马巍.青藏高原多年冻土与天然气水合物[J].天然气地球科学, 2001, 12(1):22-26. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYS201102015.htm 黄朋, 潘桂棠, 王立全, 等.青藏高原天然气水合物资源预测[J].地质通报, 2001, 21(11):794-798. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=2002011176&journal_id=gbc 伊海生, 时志强, 刘文均.青藏高原多年冻土区天然气水合物形成潜力及远景[J].西藏地质, 2002, 14(1):45-52. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200901020.htm 刘怀山, 韩晓丽.西藏羌塘盆地天然气水合物地球物理特征识别与预测[J].西北地质, 2004, 37(4):33-38. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI200404006.htm 陈多福, 王茂春, 夏斌.青藏高原冻土带天然气水合物的形成条件与分布预测[J].地球物理学报, 2005, 48(1):165-172. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200501022.htm 吴青柏, 蒋观利, 蒲毅彬, 等.青藏高原天然气水合物的形成与多年冻土的关系[J].地质通报, 2006, 25(1/2):29-33. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20060106&journal_id=gbc 坚润堂, 李峰, 王造成.青藏高原冻土区活动带天然气水合物异常特征[J].西南石油大学学报 (自然科学版), 2009, 31(2):13-17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNSY200902007.htm 祝有海, 赵省民, 卢振权.中国冻土区天然气水合物的找矿选区及其资源潜力[J].天然气工业, 2011, 31(1):13-19. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201101004.htm 祝有海, 张永勤, 文怀军.祁连山冻土区天然气水合物科学钻探工程概况[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(12):1816-1822. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.12.002 祝有海, 卢振权, 谢锡林.青藏高原天然气水合物潜在分布区预测[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(12):1918-1926. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.12.016 曹代勇, 王丹, 李靖, 等.青海祁连山冻土区木里煤田天然气水合物气源分析[J].煤炭学报, 2012, 37(8):1364-1368. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201208020.htm 王佟, 刘天绩, 邵龙义, 等.青海木里煤田天然气水合物特征与成因[J].煤田地质与勘探, 2009, 37(6):26-30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MDKT200906008.htm 卢振权, 祝有海, 张永勤, 等.青海祁连山冻土区天然气水合物的气体成因研究[J].现代地质, 2010, 24(3):581-588. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201003024.htm 黄霞, 祝有海, 王平康, 等.祁连山冻土区天然气水合物烃类气体组分的特征和成因[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(12):1851-1856. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.12.006 翟刚毅, 卢振权, 卢海龙, 等.祁连山冻土区天然气水合物成矿系统[J], 矿物岩石, 2014, 34(4):79-92. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ201310012067.htm 卢振权, 唐世琪, 王伟超, 等.青海木里三露天冻土天然气水合物气源性质研究[J], 现代地质, 2015, 29(5):995-1001. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201505002.htm 刘昌岭, 贺行良, 孟庆国, 等.祁连山冻土区天然气水合物分解气碳氢同位素组成特征[J].岩矿测试, 2012, 31(3):489-494. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS201203022.htm 贺行良, 刘昌岭, 孟庆国, 等.青海聚乎更钻探区含水合物岩心气体组成及其指示意义[J].现代地质, 2015, 29(5):1194-1200. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201505025.htm 谢其峰, 周立发, 马国福, 等.南祁连盆地三叠系烃源岩有机地球化学特征[J].北京大学学报 (自然科学版), 2011, 47(6):1034-1040. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ201106011.htm 潘语录, 田贵发, 栾安辉, 等.测井方法在青海木里煤田冻土研究中的应用[J].中国煤炭地质, 2008, 20(12):7-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2008.12.003 文怀军, 鲁静, 尚潞君, 等.青海聚乎更矿区侏罗纪含煤岩系层序地层研究[J].中国煤田地质, 2006, 18(5):19-21. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT200605006.htm 青海省地质矿产局.青海省区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社, 1991. 胡见义, 黄第藩, 徐树宝, 等.中国陆相石油地质理论基础[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 1991:1-322. 陈荣书.石油及天然气地质学[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1994:1-262. 黄第藩, 李晋超, 周翥虹, 等.陆相有机质演化和成烃机理[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 1984:1-196. 梁世友, 李凤丽, 付洁, 等.北黄海盆地中生界烃源岩评价[J].石油实验地质, 2009, 31(3):249-252. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200903249 龙华山, 王绪龙, 向才富, 等.准噶尔盆地南缘侏罗系烃源岩评价[J].现代地质, 2013, 27(5):1070-1080. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201305009.htm 戴金星.戴金星天然气地质和地球化学论文集 (卷二)[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2000.



 下载:
下载: