The genesis of epigenetic alteration and its relationship with uranium mineralization in the Nalinggou uranium deposit, Ordos Basin
-
摘要:
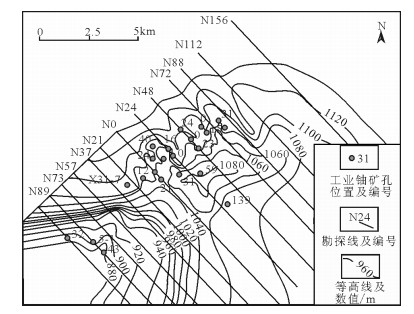
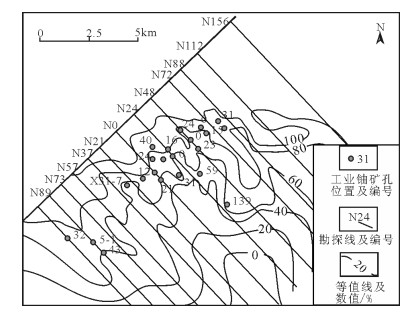
鄂尔多斯盆地纳岭沟铀矿床是中国近期落实的又一特大型铀矿床,为古层间氧化带砂岩型铀矿床。根据蚀变作用与成矿作用的关系,建立了新的古层间氧化带砂岩型铀矿床后生蚀变分类方法,即将其划分为控矿蚀变、成矿蚀变和保矿蚀变3类。分别从垂向上和平面上分析了后生蚀变的空间分布规律,剖面自下而上整体表现为保矿蚀变-成矿蚀变-控矿蚀变的垂向序列;平面上重点分析了氧化砂体厚度、氧化砂体百分率、氧化砂体底埋深、氧化砂体底标高等参数特征。
Abstract:The Nalinggou sandstone-hosted uranium deposit is a large-sized paleo-interlayer oxidation zone sandstone type uranium deposit. According to the study of the relationship between alteration and uranium mineralization, a new classification method for epigenetic alteration in paleo-interlayer oxidation zone sandstone type uranium deposits was established. There are three categories, i.e., ore control alteration, mineralization alteration, and ore-protecting alteration. The spatial distribution of epigenetic alteration was analyzed vertically and horizontally. On cross sections, from the bottom to top, there exists a vertical alteration sequence of ore-protecting alternation, mineralization alteration, and ore control alteration. This paper also discussed distribution characteristics of the thickness of oxidized sandstone, the percentage of oxidized sandstone, the bottom depth of oxidized sandstone, and the elevation of oxidized sandstone bottom.
-
华南地区是中国重要的有色、稀有和贵金属矿产资源产地,也是中国乃至全球大密度成矿区[1],目前研究程度较高[2-15]。粤东地区位于华南东南部(图 1),为东南沿海锡、钨、铜、铅锌矿产的重要产地,沿莲花山深大断裂带发育大量的锡、钨、铜、银、金多金属矿床(点),构成著名的莲花山锡多金属成矿带(图 1)。新寮岽铜多金属矿是近年来在粤东地区新发现的一个矿床,目前研究程度较低,尚未见相关报道,仅笔者对矿床中的绿泥石进行了相关研究[17]。新寮岽铜矿成因类型为斑岩型,本次选择与成矿关系密切的石英闪长岩为研究对象,利用高精度的分析测试手段,深入研究该岩体的岩相学、年代学、同位素地质学和岩石地球化学特征,并探讨其岩石成因。这不仅为进一步阐明成岩与成矿关系提供了依据,也有助于粤东地区区域成岩成矿规律理论研究,更为重要的是,对于研究矿床成因和下一步找矿勘探具有重要的理论和现实意义。
![]() 图 1 粤东地区地质略图(据参考文献[16]修改)Figure 1. Schematic geological map of eastern Guangdong Province
图 1 粤东地区地质略图(据参考文献[16]修改)Figure 1. Schematic geological map of eastern Guangdong Province1. 地质背景
粤东地区位于南岭东西向构造-岩浆带和中国东南沿海火山岩带的交会部位[18-19],整体上属于华南褶皱系,是环太平洋构造域的一个重要组成部分。粤东地区出露的地层比较简单,主要为上三叠统小坪组和下侏罗统金鸡组砂页岩及第四系沉积物。区内岩浆活动强烈,侵入岩多为燕山期花岗闪长岩、花岗岩和喜马拉雅期基性橄榄岩、玄武岩,喷出岩主要为晚侏罗世火山熔岩、次火山岩,其中尤以中生代岩浆活动最为频繁,徐晓春等[19]称之为I-S过渡型花岗质火山-侵入杂岩。区内断裂构造发育,主要由北东向海丰-丰顺断裂、普宁-潮州断裂及惠来-饶平断裂构成莲花山深大断裂带的主体,其次还有一些次级断裂,这些断裂系统控制着粤东地区岩浆活动及其矿床(点)的空间分布(图 1)。
新寮岽铜多金属矿区位于揭阳市揭东县与梅州市丰顺县交界处,区域上位于粤东隆起区西缘北东向新华夏系莲花山断裂挤压带的南东侧(图 1)。矿区出露地层比较简单(图 2),主要为侏罗系和第四系,其中下侏罗统长埔组为矿床的赋矿围岩。下侏罗统长埔组下段岩性为粉砂岩和泥质粉砂岩,长埔组上段岩性为泥质粉砂岩,偶夹长石石英砂岩;第四系出露全新统莲下组洪、冲积层。
区内岩浆活动强烈,主要出露燕山期花岗岩类。燕山三期中粗粒黑云母花岗岩主要出露于矿区东北部和西南部,燕山四期石英闪长岩出露于矿区中部及东南部,该岩体与成矿关系密切。此外,在矿区的中部和南部见有几条时代不明的辉绿岩脉和英安玢岩脉。
矿区构造以断裂构造为主。由于处于区域性莲花山断裂构造带的南东侧,在区域构造运动的影响下,矿区发育规模大小不等的、以北东向和近东西向为主的断裂。
新寮岽铜多金属矿床矿体主要赋存于石英闪长岩体与围岩的接触带或围岩裂隙中,局部产在石英闪长岩体内。因此,在空间上,石英闪长岩与成矿关系密切,是新寮岽矿床的成矿母岩。矿石呈浸染状、细脉浸染状、细网脉状产出,主要金属矿物有黄铜矿、黄铁矿、毒砂、辉银矿、辉钼矿等,非金属矿物主要为石英、方解石、绿泥石、绢云母、高岭石等。矿床围岩蚀变主要有硅化、绢云母化、绿泥石化、黑云母化、碳酸盐化、高岭石化等,尤以硅化和绿泥石化最为普遍,并与矿化关系密切。一般绿泥石化较强的地段,矿化亦强,反之矿化较弱。
2. 样品特征及分析方法
2.1 样品特征
用于锆石U-Pb同位素测定的石英闪长岩样品(XLDY-005)采自新寮岽铜多金属矿区,地理坐标为北纬23°37′43.2″、东经116°07′57.9″。岩石新鲜面呈灰白色,自形-半自形中细粒花岗结构、块状构造(图 3-a),野外定名为灰白色中细粒石英闪长岩。组成岩石的主要矿物为斜长石、钾长石、石英、普通角闪石和黑云母。副矿物主要有榍石、锆石、磷灰石、磁铁矿等,尤其是磁铁矿含量较多,此外还可见少量次生矿物,如方解石、绢云母、绿泥石等,局部可见星点状分布的硫化物。其中斜长石自形程度较好,呈半自形板状,聚片双晶发育(图 3-c),粒径多集中在1~2mm之间,含量约55%,部分斜长石可见环带构造(图 3-d),少量斜长石发生高岭石化。石英呈他形粒状充填在斜长石颗粒间或交代溶蚀斜长石(图 3-d),粒径多为0.1~0.5mm,含量约15%。普通角闪石呈他形,解理不清晰,粒径多为1~2mm,含量较少,约占15%。黑云母多呈自形片状,粒径0.3~1mm,含量约10%。其他矿物约占5%。
2.2 分析方法
石英闪长岩中锆石的挑选及岩石探针片磨制在北京大学碎样室和磨片室完成。其中,锆石分选采用常规方法,即将石英闪长岩原岩粉碎至300μm左右,经淘洗去除轻矿物、富集重矿物,再经磁选和重液分选后,在双目镜下进一步挑选出晶形、透明度和色泽较好的锆石颗粒。用环氧树脂将选得的锆石晶体制作成样品靶,待靶固结后打磨并抛光至锆石中心暴露。然后拍摄阴极发光(CL)、透射光和反射光照片,其中锆石CL照片在北京锆年领航科技有限公司实验室拍摄。实验中,根据3种图像选择合适的锆石晶体位置进行U-Pb定年和Hf同位素分析。
LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素测定在南京大学内生金属矿床成矿机制研究国家重点实验室完成。激光剥蚀系统为New Wave公司生产的UP213型,ICP-MS型号的Agilent 7500a型,采用氦作为剥蚀物质的载气,通过直径3mm的PVC管将剥蚀物质传送到ICP-MS,并在进入ICP-MS之前与氩气混合,形成混合气。实验中采用剥蚀直径为25μm的激光束斑,激光脉冲频率为5Hz,剥蚀时间50s,背景扫描时间40s。详细的分析方法和流程见黄卉等[20]。年龄计算及U-Pb谐和图的绘制用Isoplot程序3.0版完成[21]。
锆石Hf同位素分析在中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所MC-ICP-MS实验室完成,所用仪器为Finnigan Neptune型MC-ICP-MS及与之配套的Newwave UP 213激光剥蚀系统。激光剥蚀直径为55μm,测定时使用锆石标样GJ1和Plesovice作为参考物质,分析点与U-Pb同位素分析点位置相同或相近。相关仪器运行条件及详细分析流程见侯可军等[22]。分析过程中,锆石标准GJ1的176Hf/177Hf测试加权平均值为0.282007±0.000007(2σ,n=36),与文献报道值[22-23]在误差范围内完全一致。
单矿物斜长石微区剖面成分分析及黑云母化学成分分析在中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所电子探针室完成。测试仪器为JEOL-JXA-8230型电子探针,加速电压为15kV,加速电流10nA,束斑直径5μm,分析精度为0.001%。具体方法为:选取典型岩石样品磨制成抛光探针片,在光学显微镜下观察并圈定待测矿物,然后对探针片进行喷碳处理,利用电子探针显微分析仪选取矿物晶形完整、表面干净处进行测试分析。
全岩主量、微量和稀土元素均在长安大学成矿作用与动力学实验室测定。主量元素采用XRF分析完成,分析误差小于5%。微量和稀土元素(REE)分析采用HF+HNO3密封溶解,加入Rh内标溶液后转化为1% HNO3介质,以ICP-MS(USA ThermoElectron Co.X7型)测定,详细操作方法及原理参考Qi等[24]。REE含量测试误差小于7%,其余微量元素的分析误差一般小于10%。
3. 分析结果
3.1 锆石U-Th-Pb同位素
锆石均为无色,自形-半自形,近等轴状或长柱状,长宽比多介于1.5~1之间,个别可达3。从阴极发光图像(图 4)看,锆石内部结构清晰,多数锆石具有较明显的振荡环带,部分锆石具有扇形分带结构,可能是锆石结晶时外部环境的变化导致各晶面的生长速率不一致造成的[25]。从所测锆石的同位素比值和年龄数据(表 1)可以看出,25个分析测点的Th含量变化范围为534×10-6~5470×10-6,平均值为2448×10-6,U含量变化范围为670×10-6~2603×10-6,平均值为1720×10-6,在Th-U图解(图 5-a)上,两者呈正相关,锆石Th/U值介于0.66~2.17之间(一般岩浆锆石Th/U>0.4,变质锆石Th/U<0.1)。以上特征表明,锆石属典型的岩浆锆石。
表 1 新寮岽铜多金属矿区石英闪长岩(XLDY-005)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素测定结果Table 1. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb isotopic data of the quartz-diorite (XLDY-005)from the Xinliaodong Cu polymetallic ore district测点号 含量/10-6 Th/U 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 208Pb/232Th 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 208Pb/232Th Th U 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 1 1122 880 1.3 0.0491 0.0016 0.1749 0.0056 0.0258 0.0004 0.0077 0.0018 153 75 164 5 164 2 155 35 2 1112 1677 0.7 0.0508 0.0017 0.1737 0.0056 0.0248 0.0004 0.0130 0.0069 230 75 163 5 158 2 260 137 4 3523 2535 1.4 0.0494 0.0014 0.1727 0.0049 0.0253 0.0004 0.0126 0.0060 168 65 162 4 161 2 253 120 6 2730 2603 1.1 0.0495 0.0011 0.1726 0.0038 0.0253 0.0004 0.0110 0.0042 173 51 162 3 161 2 222 83 7 2810 1771 1.6 0.0491 0.0012 0.1746 0.0042 0.0258 0.0004 0.0092 0.0029 154 56 163 4 164 2 185 58 8 2918 1687 1.7 0.0496 0.0023 0.1719 0.0079 0.0251 0.0005 0.0110 0.0067 177 106 161 7 160 3 220 134 9 2231 1398 1.6 0.0492 0.0014 0.1680 0.0047 0.0248 0.0004 0.0093 0.0032 156 64 158 4 158 2 186 65 11 2717 2085 1.3 0.0496 0.0013 0.1713 0.0045 0.0251 0.0004 0.0078 0.0023 174 60 161 4 160 2 157 46 12 1756 1545 1.1 0.0494 0.0014 0.1742 0.0050 0.0256 0.0004 0.0080 0.0025 168 66 163 4 163 2 162 51 13 1502 1130 1.3 0.0499 0.0015 0.1726 0.0052 0.0251 0.0004 0.0077 0.0023 188 70 162 5 160 2 155 47 14 3708 2048 1.8 0.0497 0.0021 0.1707 0.0070 0.0249 0.0004 0.0078 0.0039 180 95 160 6 159 3 157 79 15 2575 1924 1.3 0.0512 0.0016 0.1799 0.0056 0.0255 0.0004 0.0114 0.0059 248 71 168 5 162 2 229 118 17 2354 1978 1.2 0.0499 0.0016 0.1721 0.0055 0.0250 0.0004 0.0099 0.0053 192 74 161 5 159 2 199 107 18 5470 2521 2.2 0.0501 0.0012 0.1741 0.0042 0.0252 0.0004 0.0080 0.0013 201 56 163 4 160 2 160 27 20 4248 2491 1.7 0.0501 0.0011 0.1740 0.0038 0.0252 0.0004 0.0089 0.0015 198 51 163 3 160 2 180 30 21 2369 1513 1.6 0.0512 0.0011 0.1785 0.0038 0.0253 0.0004 0.0089 0.0015 248 48 167 3 161 2 178 30 22 534 725 0.7 0.0487 0.0020 0.1725 0.0071 0.0257 0.0004 0.0084 0.0014 132 94 162 6 164 3 168 29 23 2953 1737 1.7 0.0507 0.0013 0.1772 0.0044 0.0253 0.0004 0.0087 0.0015 229 56 166 4 161 2 176 29 24 2223 2341 1.0 0.0503 0.0009 0.1777 0.0032 0.0256 0.0004 0.0089 0.0015 207 41 166 3 163 2 180 30 26 1512 1187 1.3 0.0509 0.0027 0.1790 0.0092 0.0255 0.0005 0.0095 0.0016 237 117 167 8 162 3 192 33 27 919 670 1.4 0.0501 0.0031 0.1741 0.0106 0.0252 0.0005 0.0087 0.0015 201 138 163 9 160 3 174 30 28 2931 1592 1.8 0.0521 0.0013 0.1793 0.0043 0.0249 0.0004 0.0087 0.0015 291 54 168 4 159 2 175 29 29 958 1096 0.9 0.0499 0.0014 0.1747 0.0049 0.0254 0.0004 0.0092 0.0016 188 65 163 4 162 2 184 31 30 4156 2260 1.8 0.0492 0.0010 0.1709 0.0035 0.0252 0.0004 0.0086 0.0014 158 48 160 3 160 2 172 29 31 1860 1615 1.2 0.0508 0.0011 0.1751 0.0039 0.0250 0.0004 0.0086 0.0015 232 50 164 3 159 2 173 29 因本次的样品较年轻,故锆石的年龄采用206Pb/238U年龄[26]。在石英闪长岩样品中的31个分析点有6个分析点(XLDY-005-3、XLDY-005-5、XLDY-005-10、XLDY-005-16、XLDY-005-19、XLDY-005-25)谐和度较低,可能测点在残留锆石上年龄较老或所测区域跨越不同世代的晶域或跨越了颗粒边缘,因此在年龄统计时舍去这6个点的分析结果,剩余25个数据点的分析结果在谐和图上组成密集的一簇(图 5-b),206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值为161±1Ma(MSWD=0.57),代表了石英闪长岩的形成年龄。
3.2 地球化学特征
新寮岽铜多金属矿区石英闪长岩全岩地球化学分析结果及相关参数见表 2。
表 2 新寮岽铜多金属矿区石英闪长岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果及锆石饱和温度Table 2. Major, trace and rare earth elements data of the quartz-diorite from the Xinliaodong Cu polymetallic ore district and zircon saturation temperatures样品号 XLD05001 XLD05002 XLD05003 XLD05004 XLD05005 XLD05006 XLD05007 SiO2 57.63 58.07 57.32 57.56 57.57 57.46 58.14 TiO2 0.88 0.95 0.99 0.92 0.98 0.92 0.94 Al2O3 16.30 16.53 15.88 16.21 16.40 16.06 16.23 TFe2O3 7.12 7.67 7.81 7.39 7.48 7.55 7.33 MnO 0.12 0.13 0.18 0.12 0.22 0.15 0.34 MgO 4.56 4.91 4.63 4.58 4.55 4.64 4.53 CaO 6.76 6.68 6.12 6.43 6.17 6.64 6.02 Na2O 2.52 2.61 2.36 2.56 2.56 2.39 2.40 K2O 2.01 1.38 2.69 2.29 1.62 2.35 2.45 P2O5 0.18 0.18 0.18 0.18 0.19 0.18 0.18 烧失量 1.19 1.82 1.23 0.99 1.73 0.89 0.92 总量 99.27 100.93 99.39 99.23 99.47 99.23 99.48 σ 1.40 1.06 1.78 1.62 1.20 1.55 1.55 A/CNK 0.88 0.92 0.89 0.88 0.95 0.87 0.93 A/NK 2.58 2.86 2.34 2.42 2.75 2.48 2.46 DI 45.13 43.39 46.72 45.45 45.28 46.11 47.20 Na 2O+K2O 4.53 3.99 5.05 4.85 4.18 4.74 4.85 K2O/Na2O 0.80 0.53 1.14 0.89 0.63 0.98 1.02 Li 17.49 27.38 20.19 19.87 22.01 17.91 25.99 Be 1.56 1.56 1.57 1.58 1.82 1.56 1.76 Sc 21.05 22.77 21.52 20.91 20.85 20.70 19.78 V 151.0 152.1 147.8 148.8 160.6 148.4 144.3 Cr 150.6 155.1 140.3 135.7 133.7 138.3 127.4 Co 24.06 26.02 22.25 22.70 26.46 23.51 19.62 Ni 45.27 41.05 37.90 36.77 41.77 40.95 33.57 Cu 17.53 21.80 22.81 22.84 40.28 20.89 9.30 Zn 112.0 99.63 164.5 106.7 196.6 125.6 171.3 Ga 20.18 21.06 20.25 20.31 21.70 19.71 19.43 Rb 78.85 56.33 122.6 112.8 63.67 96.68 89.78 Sr 361.6 374.8 349.1 336.0 398.5 300.0 298.9 Y 19.72 20.62 20.29 20.58 21.41 20.98 19.90 Zr 180.2 22.98 53.97 205.4 214.4 162.8 160.7 Nb 9.16 9.42 9.84 9.68 11.20 9.24 9.20 Cd 0.29 0.17 0.53 0.79 1.22 0.51 0.60 In 0.23 0.14 1.27 0.27 0.12 0.11 0.14 Cs 7.25 3.89 5.84 15.13 5.69 11.90 10.63 Ba 457.8 392.8 590.3 416.6 670.0 412.6 502.9 Hf 4.24 0.68 1.57 4.91 5.21 3.92 3.98 Ta 0.64 0.67 0.71 0.71 0.78 0.65 0.67 Pb 12.44 11.31 18.03 52.45 111.1 17.66 114.3 Bi 0.74 0.23 4.66 2.60 1.80 0.30 0.26 Th 8.61 10.31 8.86 9.95 9.76 9.43 9.53 U 2.56 2.78 2.78 3.20 3.00 2.68 3.16 La 23.59 26.73 24.49 26.56 27.15 25.03 21.34 Ce 50.13 54.87 51.94 56.28 56.92 53.19 45.80 Pr 5.89 6.62 6.16 6.59 6.75 6.28 5.49 Nd 23.45 25.93 24.76 25.92 26.82 25.04 22.65 Sm 4.58 5.04 4.90 4.93 5.13 4.84 4.56 Eu 1.16 1.17 1.25 1.14 1.20 1.14 1.14 Gd 4.83 5.25 5.13 5.17 5.42 5.14 4.83 Tb 0.67 0.73 0.72 0.71 0.75 0.72 0.68 Dy 3.78 4.05 3.98 3.99 4.16 4.02 3.83 Ho 0.75 0.79 0.78 0.79 0.82 0.80 0.76 Er 2.15 2.24 2.20 2.26 2.35 2.29 2.17 Tm 0.29 0.30 0.30 0.31 0.32 0.31 0.29 Yb 1.91 1.92 1.91 2.02 2.08 2.03 1.93 Lu 0.28 0.29 0.28 0.30 0.31 0.31 0.29 ΣREE 123.5 135.9 128.8 137.0 140.2 131.1 115.8 LREE 108.8 120.4 113.5 121.4 124.0 115.5 101.0 HREE 14.68 15.57 15.29 15.56 16.21 15.62 14.79 LREE/HREE 7.41 7.73 7.42 7.80 7.65 7.39 6.83 (La/Yb)N 8.84 9.98 9.21 9.43 9.38 8.84 7.93 δEu 0.75 0.69 0.76 0.68 0.69 0.69 0.74 δCe 1.01 0.98 1.01 1.01 1.00 1.01 1.01 T/℃ 748 610 660 759 775 738 747 3.2.1 主量元素
新寮岽铜多金属矿区石英闪长岩主量元素分析结果(表 2)显示:岩石SiO2含量变化于57.32%~58.14%之间,平均为57.68%,属于中性岩范畴;Al2O3含量为15.88%~16.53%,TFe2O3含量较高,介于7.12%~7.81%之间,平均为7.48%,碱含量中等(Na2O+K2O=3.99%~5.05%,平均为4.60%)且相对富钠(K2O/Na2O=0.53~1.14,平均为0.86), 分异指数DI=43.39~47.20,平均为45.61;岩石高镁(MgO=4.53%~4.91%),铝饱和指数A/CNK=0.87~0.95,A/NK=2.34~2.86,为准铝质,在岩石A/CNK-A/NK图解(图 6-a)上亦投入准铝质范围,里特曼指数(σ)为1.06~1.78,属钙碱性系列,在SiO2-K2O图解(图 6-b)上落入高钾钙碱性系列和钙碱性系列区域,且落在钙碱性系列区域的投点靠近分界线。总之,岩石主量元素特征表明,石英闪长岩为镁质、碱含量中等、准铝质、钙碱性系列。
3.2.2 稀土及微量元素
新寮岽铜多金属矿区石英闪长岩的稀土元素测试结果见表 2。样品的稀土元素总量较低,介于115.8×10-6~140.2×10-6之间,平均为130.3×10-6。轻稀土元素(LREE)含量为101.0×10-6~124.0×10-6,平均值为114.9×10-6,重稀土元素(HREE)含量为14.68×10-6~16.21×10-6,平均值为15.39×10-6,轻、重稀土元素分馏明显,LREE/HREE值为6.83~7.80,平均为7.46,(La/Yb)N变化范围为7.93~9.98,平均为9.09,整体显示轻稀土元素富集、重稀土元素亏损的特征。所有样品不存在Ce异常(δCe平均为1.01),δEu范围为0.68~0.76,平均值为0.72,出现弱负Eu异常,表明岩体在成岩过程中发生过斜长石和富轻稀土矿物(磷灰石、独居石)的分离结晶作用。在稀土元素球粒陨石标准化图解(图 7-a)上,7件样品的稀土元素配分曲线极为相似,总体表现为轻稀土元素富集的右倾特征,其中重稀土元素Ho-Lu表现为平坦型。
![]() 图 7 新寮岽铜多金属矿区石英闪长岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化图解(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)(标准化值据参考文献[29])Figure 7. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns(a)and primitive mantlenormalized trace-element spider diagram(b)of quartz-diorite in the Xinliaodong Cu polymetallic ore district
图 7 新寮岽铜多金属矿区石英闪长岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化图解(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)(标准化值据参考文献[29])Figure 7. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns(a)and primitive mantlenormalized trace-element spider diagram(b)of quartz-diorite in the Xinliaodong Cu polymetallic ore district在微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(图 7-b)上,石英闪长岩的微量元素分布较一致,表现为相对富集K、Rb、Ba、Th、U等大离子亲石元素,相对亏损Ta、Nb、Ti、P等高场强元素,其中P、Ti轻度亏损,说明磷灰石和钛铁矿已开始从岩浆中分离。此外,有2个样品(XLD05002和XLD05003)较其他5个样品Zr、Hf明显异常,可能是测试误差所致。
3.3 矿物化学特征
3.3.1 黑云母矿物化学
黑云母作为岩体中一种常见的暗色矿物,其成分特征反映了成岩时的地质环境和物理化学条件。因此,本次对石英闪长岩中的黑云母进行了电子探针分析(表 3),数据处理采用郑巧荣[30]电价差值法计算得出(以11个氧原子为基准)。由表 3可知,石英闪长岩中黑云母的MgO含量介于11.64%~16.85%之间,MF值介于0.56~0.79之间,均显示高镁、低铁的特点。马昌前等[31]对国内外文献中120个不同产状的黑云母成分特征进行研究后发现:退变质和固相线下交代作用成因的黑云母具有低Ti特征(Ti<0.20);进变质成因的黑云母Ti的变化范围较大,且Mg/(Mg+Fe2++Fe3+)值多大于0.55;而岩浆成因的黑云母具有中等的Ti含量(0.20<Ti<0.55),且Mg/(Mg+Fe2++Fe3+)值变化于0.30~0.55之间。本文中的黑云母Ti含量(表 3)介于0.23~0.30之间,Mg/(Mg+Fe2++Fe3+)值介于0.52~0.71之间,类似岩浆成因黑云母的成分特征,表明所测黑云母均为岩浆成因的原生黑云母,而非变质或固相线下交代成因的黑云母。在Foster[32]黑云母成分分类图解(图 8)中,所有样品点均落入镁质黑云母区域。
表 3 石英闪长岩黑云母电子探针分析结果及相关参数(以11个氧原子为基准)Table 3. Electron microprobe analyses of biotite from quartze-diorite(based on 11 oxygen atoms)测点号 XLD XLD XLD XLD XLD 测点号 XLD XLD XLD XLD XLD 05001-4-1 05001-4-2 05007-1-1 05007-1-2 05007-1-3 05001-4-1 05001-4-2 05007-1-1 05007-1-2 05007-1-3 SiO2 38.57 37.48 37.81 38.23 38.52 ArⅣ 1.14 1.15 1.20 1.12 1.12 TiO2 4.08 3.98 5.44 4.62 4.88 AlⅣ 0.10 0.06 0.00 0.04 0.03 Al2O3 14.24 13.49 13.20 13.09 12.96 Ti 0.23 0.23 0.30 0.26 0.27 FeOT 17.28 18.48 11.80 18.51 16.32 Fe3+ 0.20 0.27 0.29 0.20 0.17 MnO 0.17 0.14 0.32 0.53 0.51 Fe2+ 0.91 0.95 0.46 1.01 0.89 MgO 12.90 12.36 16.85 11.64 13.01 Mn 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.03 CaO 0.02 0.00 0.06 0.05 0.03 Mg 1.43 1.40 1.86 1.31 1.45 Na2O 0.12 0.05 0.09 0.17 0.20 Ca 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 K2O 9.01 8.78 9.06 9.04 8.99 Na 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.03 Cr2O3 0.22 0.20 0.25 0.24 0.20 K 0.85 0.85 0.86 0.87 0.86 总量 96.61 94.97 94.87 96.11 95.62 Cr 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 Si 2.86 2.85 2.80 2.88 2.88 MF 0.61 0.59 0.79 0.56 0.61 注: TFeO为全铁;FeO3+和Fe2+采用郑巧荣[30]的方法校正;MF=n(Mg)/n(Mg+Fe2++Mn) ![]() 图 8 黑云母成分分类(底图据参考文献[32])Figure 8. Classification of biotites
图 8 黑云母成分分类(底图据参考文献[32])Figure 8. Classification of biotites3.3.2 斜长石矿物化学
一般认为,斜长石的环带记录了岩浆熔体在结晶过程中物理、化学条件的变化,斜长石的环带模式与其形成的地质环境和地质过程密切相关;有学者还认为,斜长石环带的形貌反映了岩浆的冷却速率和晶体生长的其他物性[33-34]。因此,本次对石英闪长岩中发育环带结构的斜长石进行了电子探针分析(表 4)。由表 4可知,具环带结构的斜长石牌号An介于53.08~60.40之间,为拉长石(图 9)。斜长石环带成分从核部到边部依次为An(60.40)-An(60.12)-An(53.08)-An(56.16)-An(56.21)-An(55.91),说明此环带为一韵律环带。总体来看,An%从中心到边缘呈下降趋势,且在环带的核部与幔部交界处,An%突然降低,至边部又突然升高。据此推测,岩浆结晶早期为正常结晶,形成正环带,到中晚期出现异常结晶,导致斜长石成分发生突变,说明环带斜长石在中晚期处于不稳定的岩浆环境,可能受构造活动等的影响使压力反复变化及晶体上下运动[36]。
表 4 石英闪长岩中环带结构斜长石电子探针成分分析结果Table 4. Electron microprobe analyses of zoned plagioclase from quartz-diorite% 测点 XLD0500 XLD0500 XLD0500 XLD0500 XLD0500 XLD0500 6-2-1-1 6-2-1-2 6-2-1-3 6-2-1-4 6-2-1-5 6-2-1-6 边部→核部 SiO2 51.78 52.35 51.45 51.51 51.27 51.72 TiO2 0.06 0.11 0.10 0.05 0.07 0.02 Al2O3 32.12 31.02 30.31 30.62 30.93 29.83 FeO 0.14 0.30 0.24 0.32 0.36 0.35 MgO 0.03 0.01 0.02 0.00 0.01 0.00 Cr2O3 0.00 0.00 0.04 0.01 0.03 0.02 MnO 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.02 CaO 11.45 11.64 11.31 10.94 12.29 12.32 Na2O 4.84 4.81 4.70 5.12 4.32 4.32 K2O 0.22 0.30 0.27 0.35 0.28 0.21 P2O5 0.03 0.02 0.03 0.01 0.00 0.04 总量 100.72 100.59 98.48 98.96 99.57 98.92 Si 2.33 2.37 2.37 2.37 2.35 2.38 Al 1.71 1.65 1.65 1.66 1.67 1.62 Ca 0.55 0.56 0.56 0.54 0.60 0.61 Na 0.42 0.42 0.42 0.46 0.38 0.39 K 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.01 Ba 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 An 55.91 56.21 56.16 53.08 60.12 60.40 Ab 42.80 42.05 42.24 44.92 38.25 38.35 Or 1.29 1.74 1.60 2.00 1.64 1.25 注:数据处理采用Geokit软件计算得出 ![]() 图 9 斜长石分类图解及环带状斜长石成分剖面(底图据参考文献[35])Qtz—石英;Pl—斜长石Figure 9. Classification of feldspar and electron microprobe analyses of zoned plagioclase
图 9 斜长石分类图解及环带状斜长石成分剖面(底图据参考文献[35])Qtz—石英;Pl—斜长石Figure 9. Classification of feldspar and electron microprobe analyses of zoned plagioclase3.4 Hf同位素特征
在锆石U-Th-Pb测年的基础上,在锆石年龄分析点或附近进行了Hf同位素分析,分析结果见表 5。从表 5可以看出,除少数几个分析点外(11、20、30),大部分测点的176Lu/177Hf值均低于0.002,表明石英闪长岩中绝大多数锆石形成后放射性成因Hf积累较少,因此,本次测定的锆石176Lu/177Hf值能较好地反映其形成过程中Hf同位素的组成特征[38-39]。考虑到石英闪长岩fLu/Hf值介于-0.93~-0.98之间,明显小于硅铝质地壳的fLu/Hf值(-0.72)[40]和镁铁质地壳的fLu/Hf值(-0.34)[41],因此二阶段模式年龄更能反映其源区物质从亏损地幔被抽取的时间(或其源区物质在地壳的平均存留年龄)。
表 5 新寮岽铜多金属矿区石英闪长岩的锆石Hf同位素分析结果Table 5. Lu-Hf isotopic data of zircon from quartz-diorite in the Xinliaodong Cu polymetallic ore district测点号 t/Ma 176Yb/177Hf 176Lu/177Hf 176Hf/177Hf 2σ (176Hf/177Hf)i εHf(0) εHf(t) tDM1/Ma tDM2/Ma fLu/Hf 2 158 0.067067 0.001030 0.282631 0.000014 0.282627 -5.0 -1.6 881 1312 -0.97 6 161 0.075668 0.001280 0.282660 0.000013 0.282656 -4.0 -0.6 845 1245 -0.96 8 160 0.098102 0.001804 0.282678 0.000018 0.282672 -3.3 0.0 831 1210 -0.95 11 160 0.131231 0.002008 0.282756 0.000018 0.282750 -0.6 2.7 722 1033 -0.94 12 163 0.086784 0.001220 0.282664 0.000016 0.282660 -3.8 -0.4 838 1235 -0.96 13 160 0.050521 0.000718 0.282640 0.000017 0.282638 -4.7 -1.2 860 1288 -0.98 15 162 0.137709 0.001854 0.282669 0.000018 0.282664 -3.6 -0.3 844 1228 -0.94 17 159 0.114314 0.001635 0.282722 0.000018 0.282717 -1.8 1.5 764 1110 -0.95 20 160 0.116023 0.002127 0.282689 0.000021 0.282683 -2.9 0.4 822 1186 -0.94 21 161 0.096930 0.001492 0.282681 0.000015 0.282677 -3.2 0.2 819 1199 -0.96 22 164 0.034677 0.000682 0.282509 0.000033 0.282507 -9.3 -5.8 1042 1579 -0.98 23 161 0.125353 0.001983 0.282653 0.000014 0.282647 -4.2 -0.9 871 1266 -0.94 27 160 0.066417 0.001374 0.282672 0.000016 0.282668 -3.5 -0.2 829 1219 -0.96 29 162 0.119899 0.001741 0.282729 0.000016 0.282724 -1.5 1.9 755 1091 -0.95 30 160 0.161227 0.002218 0.282736 0.000019 0.282729 -1.3 2.0 756 1082 -0.93 31 159 0.061143 0.001105 0.282683 0.000015 0.282680 -3.1 0.2 808 1193 -0.97 注:εHf(t)={[(176Hf/177Hf)s-(176Lu/177Hf)s×(eλt-1)]/[(176Hf/177Hf)CHUR, 0-(176Lu/177Hf)CHUR×(et-1)]-1}×10000;TDM1=1/ λ×ln {1+[(176Hf/177Hf)s-(176Hf/177Hf)DM]/[(176Lu/177Hf)s-(176Lu/177Hf)DM]};TDM2=1/λ×ln{1+[(176Hf/177Hf)s, t-(176Hf/177Hf)DM, t]/[(176Lu/177Hf)C-(176Lu/177Hf)DM]}+t;s=sample, (176Hf/177Hf)CHUR, 0=0.282772, (176Lu/177Hf)CHUR=0.0332, (176Hf/177Hf)DM=0.28325, t为锆石结晶年龄,λ=1.867×10-11a-1, (176Lu/177Hf)C=0.015 本次所测石英闪长岩样品中锆石176Hf/177Hf值范围为0.282509~0.282756,由对应的测点年龄计算得到的Hf同位素初始比值(176Hf/177Hf)i为0.282507~0.282750,Hf同位素变化范围较宽,εHf(t)变化于-5.8~2.7之间,对应的两阶段模式年龄tDM2=1.03~1.58Ga,由二阶段Hf模式年龄(tDM2)和εHf(t)频率分布直方图(图 10)可以看出,εHf(t)主体在-1.0~0.0范围内,tDM2主体在1.2~1.3Ga范围内。
4. 讨论
4.1 岩体形成时代
本次获得的石英闪长岩锆石U-Pb年龄为161±1Ma(MSWD=0.57),与矿区花岗斑岩(锆石U-Pb年龄160±1Ma,另文发表)、黑云母花岗岩(锆石U-Pb年龄157±1Ma,另文发表)的锆石U-Pb年龄较一致,矿区在晚侏罗世发生过一次较明显的岩浆活动,但需要岩石地球化学及相关同位素分析等证据进一步确认。杨进辉(2014,个人报告)统计了粤东地区中生代花岗岩类的成岩时代,认为粤东地区中生代花岗岩类的形成时代主要集中在165~155Ma和142~135Ma两个阶段。本次获得的石英闪长岩的成岩年龄(161±1Ma)正好与165~155Ma这一阶段相吻合,应同属粤东地区该阶段岩浆侵入活动的产物。
4.2 成岩条件
锆石是花岗岩中结晶较早的矿物,Zr的分配系数受温度控制较明显, 其锆石饱和温度可近似为岩浆结晶温度,因此锆石饱和温度计用于岩浆温度的计算是一个有效的方法[42-43]。根据Watson等[37]提供的锆石溶解度-饱和温度的计算方法,用岩石主要元素及其Zr含量计算得出矿区石英闪长岩的锆石饱和温度平均为720℃。花岗质岩石中黑云母的化学成分受控于岩浆冷却结晶时的物理化学条件,因此,黑云母可以近似地指示岩浆冷却结晶时的物理化学状态。从黑云母Mg/(Mg+Fe)-Ti温度图解(图 11)中,可以估算本区石英闪长岩中新鲜黑云母的结晶温度范围大致为620~720℃,与计算的锆石饱和温度接近。
黑云母是花岗岩类岩石中常见的暗色造岩矿物之一,保存了岩石结晶时大量的地球化学信息。氧逸度可以反映氧化还原条件。前人研究指出,可以利用与磁铁矿、钾长石共生的黑云母的成分特征估算黑云母结晶时的氧逸度[45]。通过镜下观察可知,石英闪长岩中可见黑云母-磁铁矿-钾长石-石英共生组合,满足氧逸度使用条件,故在黑云母Fe3+-Fe2+-Mg图解(图 12)中,所有样品点均落在Fe3O4-Fe2O3缓冲线与Ni-NiO缓冲线之间,实验证明[47],在相同温度下,从Fe2SiO4-SiO2-Fe3O4缓冲线经Ni-NiO缓冲线,到Fe2O3-Fe3O4缓冲线,氧逸度系统升高,说明黑云母结晶时氧逸度较高。此外,由图 8可知,岩石中黑云母均为镁质黑云母,而黑云母富镁是岩浆高氧逸度的标志之一[46]。另外,根据前人研究[46, 48],氧逸度的变化受岩浆结晶时水逸度的控制,随着水逸度的升高氧逸度逐渐下降,可进一步得出本次研究的黑云母结晶时水逸度较低。云母的镁质率[MF=n(Mg)/n(Mg+Fe2++Mn)]可以作为区分长江深源系列和南岭浅源系列岩石的重要指标[49],MF>0.45表明岩体形成于深源环境。石英闪长岩中黑云母镁质率介于0.56~0.79之间,表明石英闪长岩形成于深源环境。
![]() 图 11 黑云母Mg/(Mg+Fe)-Ti图解(底图据参考文献[44])Figure 11. Mg/(Mg+Fe)-Ti diagram of biotites
图 11 黑云母Mg/(Mg+Fe)-Ti图解(底图据参考文献[44])Figure 11. Mg/(Mg+Fe)-Ti diagram of biotites![]() 图 12 黑云母Fe3+-Fe2+-Mg图解(底图据参考文献[46])Figure 12. Fe3+-Fe2+-Mg diagram of biotites
图 12 黑云母Fe3+-Fe2+-Mg图解(底图据参考文献[46])Figure 12. Fe3+-Fe2+-Mg diagram of biotites4.3 成岩物质来源
石英闪长岩主量元素显示富镁的特征(MgO=4.53%~4.91%),稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线表现为轻稀土元素富集的右倾型(LREE/HREE=6.83~7.80,(La/Yb)N=7.93~9.98),原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图显示,该岩体相对富集大离子亲石元素(K、Rb、Ba、Th、U等),亏损高场强元素(Ta、Nb、Ti、P等),岩石地球化学特征表明,岩体具有俯冲带岩浆岩的特征[50-51]。Nb、Ta、Ti等高场强元素的亏损,反映可能有富钛矿物的分离结晶,P的亏损则表明可能有磷灰石的分离结晶[52]。Ti的贫化表示岩浆物质有地壳物质的参与,因为Ti不易进入熔体而残留在源区。亏损P反映岩浆幔源的特点。Nb/Ta值对源区具有一定指示作用[53],本文7个石英闪长岩样品Nb/Ta值介于13.6~14.4之间,即介于下地壳(Nb/Ta=8.3)与亏损地幔(Nb/Ta>17.0)之间[29],暗示幔源组分的贡献。综上,岩石地球化学特征表明,石英闪长岩的源区既有幔源物质,又有壳源物质,推测其可能与俯冲洋壳部分熔融有关。
黑云母作为花岗质岩体中重要的暗色矿物,其化学成分是区分壳型、幔型、壳幔混源型花岗质岩体的有效手段[54]。通常情况下,典型壳源黑云母中MgO小于6%,幔源黑云母的中MgO大于15%[55],石英闪长岩黑云母中MgO介于11.64%~16.85%之间,表现为壳幔过渡性质。同样在黑云母物质来源判别图解(图 13)中,所有样品点均落入壳幔混源区域,并靠近壳源分界线。
![]() 图 13 黑云母物质来源判别图(底图据参考文献[56])Figure 13. Diagram for discrimination of material source of biotite
图 13 黑云母物质来源判别图(底图据参考文献[56])Figure 13. Diagram for discrimination of material source of biotite锆石化学性质稳定,抗风化能力强,Lu/Hf值低,不受部分熔融作用和分离结晶作用的影响,这使得锆石Hf同位素组成可以记录岩浆源区不同性质的原岩特征,成为讨论岩浆甚至是地壳演化及壳幔相互作用过程的重要工具。研究表明,不同地球化学储库具有明显不同的176Hf/177Hf同位素组成:亏损地幔和球粒陨石的176Hf/177Hf值较大(大于0.282772),εHf(t)值为零或正值;地壳及富集地幔的εHf(t)值则较小,且εHf(t)为负值[39-40]。本文所测石英闪长岩锆石176Hf/177Hf值介于0.282507~0.282750之间,平均值为0.282669,εHf(t)值变化于-5.8~2.7,二阶段模式年龄(tDM2)为1.03~1.58Ga,平均为1.2Ga,在Hf同位素演化图解(图 14)上,样品εHf(t)值落在球粒陨石演化线附近及下地壳区域,样品锆石Hf同位素组成的不均一性,指示石英闪长岩成岩源区为壳幔混源,岩体的形成可能与俯冲板片局部熔融并与楔形地幔橄榄岩相互作用有关,且岩浆上升侵位过程中混染了部分陆壳物质。
![]() 图 14 石英闪长岩的Hf同位素演化图解(底图据参考文献[57])(地壳派生物的谐和线为通过假定的平均大陆地壳176Lu/177Hf值为0.015计算得到)Figure 14. Hf isotope evolution diagram of quartz-dioriteⅠ—小于0.83Ga; Ⅱ—0.83~1.1Ga; Ⅲ—1.1~1.4Ga; Ⅳ—1.4~1.6Ga; Ⅴ—1.6~1.9Ga
图 14 石英闪长岩的Hf同位素演化图解(底图据参考文献[57])(地壳派生物的谐和线为通过假定的平均大陆地壳176Lu/177Hf值为0.015计算得到)Figure 14. Hf isotope evolution diagram of quartz-dioriteⅠ—小于0.83Ga; Ⅱ—0.83~1.1Ga; Ⅲ—1.1~1.4Ga; Ⅳ—1.4~1.6Ga; Ⅴ—1.6~1.9Ga由以上岩石地球化学特征、黑云母矿物化学特征及其锆石Hf同位素组成特征综合分析推断,矿区石英闪长岩成岩物质具有壳幔混合的特征,其可能为俯冲板片局部撕裂熔融,并与楔形地幔相互作用而成,岩浆上侵过程中有部分古老地壳物质混染。
4.4 成岩构造环境
中国华南地区分布大面积的中生代花岗岩类,这些花岗岩类的构造环境及其动力学背景,长期以来是众多学者研究的焦点[1, 4-5, 12]。虽然不同学者通过对华南花岗岩类地球化学、年代学、同位素的研究提出不同的构造模型,但大多数学者认为其与太平洋板块的俯冲有关。邓晋福等[58]认为,中国东部在燕山期发生了岩石圈-软流圈系统(LAS)大灾变事件,并识别出被扰动的LAS的2种类型,即在挤压造山环境下的岩石圈巨大减薄与巨大增厚作用。中生代晚期,古太平洋板块向欧亚板块的俯冲消减导致中国东部发生了大规模的中酸性岩浆侵位和火山喷发[59]。近年来, 岩浆岩、构造、矿床等多方面的证据表明, 华南在180~170Ma已经完成由特提斯构造域向滨太平洋构造域的转换[60-64],燕山期华南成岩成矿的构造背景可能与太平洋板块向西俯冲挤压碰撞有关[65-70]。中晚侏罗世(170~150Ma),南岭及其邻区大陆岩石圈以伸展背景为主,由于Izanagi板块向欧亚大陆持续低角度俯冲,于170~160Ma期间发生俯冲板片多处撕裂,形成I同熔型斑岩铜矿,160~150Ma期间由于俯冲板块开天窗,软流圈物质上涌到下地壳形成壳幔源型高分异花岗质岩石[1]。粤东地区作为太平洋板块与华南板块作用的前缘,不同于南岭地区的板内环境,其发生的岩浆活动应早于华南板块内部。刘鹏等[17]研究认为,粤东地区不仅发现190Ma左右太平洋板块开始俯冲时的岩浆活动,又有160Ma左右俯冲板片撕裂形成的火山-侵入岩和140Ma之后太平洋板块俯冲方向调整形成的火山-侵入岩。作为华南板块大陆边缘,粤东地区岩浆活动记录了从太平洋板块开始俯冲到俯冲板片撕裂,再到俯冲方向调整的整个事件过程。
因此,笔者认为,矿区晚侏罗世的石英闪长岩岩体形成于受太平洋板块俯冲作用控制的活动大陆边缘环境,其可能为俯冲板片局部撕裂熔融,并与楔形地幔相互作用而成。
Abdel-Rahman[71]认为,非造山带碱性花岗岩形成于高温、缺水环境,该环境不利于早期富铁矿物(磁铁矿、钛铁矿)结晶,所以晚期结晶的黑云母表现出高铁的特征;而造山带钙碱性花岗岩产于富水环境下,有利于早期富铁矿物的结晶,因此晚期结晶的黑云母表现出相对高镁、低铁的特点;因而利用黑云母的化学成分可以判断花岗质岩体的构造背景。在黑云母MgO-TFeO-Al2O3及Al2O3-MgO图解(图 15)中,石英闪长岩落入造山带钙碱性花岗岩区域,这与全岩地球化学数据得出的结论一致(石英闪长岩成分富集LILE,亏损Nb、Ta、Ti等特征,说明其具有典型俯冲带岩浆岩特征[50-51])。
![]() 图 15 黑云母构造环境判别图(底图据参考文献[71])A—非造山的碱性岩系;C—造山带钙碱性岩系;P—过铝质岩系Figure 15. Discrimination diagram of tectonic settings for biotite
图 15 黑云母构造环境判别图(底图据参考文献[71])A—非造山的碱性岩系;C—造山带钙碱性岩系;P—过铝质岩系Figure 15. Discrimination diagram of tectonic settings for biotite花岗岩类的微量元素组成明显受其成岩构造环境制约,在Batchelor[72]提出的R1-R2多阳离子图解(图 16)上,样品点落入活动板块边缘花岗岩区域。在Pearce等[73]提出的花岗岩构造环境判别图(图 17)上,样品点全部投影于火山弧花岗岩区域。通过以上岩石地球化学特征及岩石矿物化学特征,结合本区区域位置及其演化历史,推测石英闪长岩岩体可能形成于俯冲背景下的活动大陆边缘环境,是俯冲板片局部撕裂熔融,并与楔形地幔相互作用的结果。
![]() 图 16 石英闪长岩R1-R2多阳离子图解(底图据参考文献[72])1—地幔分异花岗岩;2—活动板块边缘花岗岩;3—碰撞后隆起花岗岩;4—造山晚期花岗岩;5—非造山花岗岩;6—同碰撞花岗岩;7—造山后的A型花岗岩Figure 16. R1 versus R2 multicationic diagram for quartz diorites
图 16 石英闪长岩R1-R2多阳离子图解(底图据参考文献[72])1—地幔分异花岗岩;2—活动板块边缘花岗岩;3—碰撞后隆起花岗岩;4—造山晚期花岗岩;5—非造山花岗岩;6—同碰撞花岗岩;7—造山后的A型花岗岩Figure 16. R1 versus R2 multicationic diagram for quartz diorites![]() 图 17 石英闪长岩构造环境判别图解(底图据参考文献[73])syn-COLG—同碰撞花岗岩;VAG—火山弧花岗岩;WPG—板内花岗岩;ORG—洋脊花岗岩Figure 17. Discrimination diagram for tectonic settings of quartz diorates
图 17 石英闪长岩构造环境判别图解(底图据参考文献[73])syn-COLG—同碰撞花岗岩;VAG—火山弧花岗岩;WPG—板内花岗岩;ORG—洋脊花岗岩Figure 17. Discrimination diagram for tectonic settings of quartz diorates5. 结论
(1)矿区石英闪长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-ThPb年龄为161±1Ma,与矿区出露的黑云母花岗岩、花岗斑岩及花岗闪长斑岩的成岩年龄较一致,为矿区晚侏罗世岩浆活动的产物。
(2)石英闪长岩在地球化学特征上显示,碱含量中等(Na2O+K2O=3.99%~5.05%,平均4.60%),岩石高镁(MgO=4.53%~4.91%),轻、重稀土元素分馏较明显,富集轻稀土元素及大离子亲石元素(K、Rb、Ba、Th、U),亏损重稀土元素和高场强元素(Nb、Ta、Ti、P),为准铝质、钙碱性系列岩石。
(3)石英闪长岩中黑云母属镁质黑云母,黑云母矿物化学特征表明岩体形成于深源环境,形成时氧逸度较高,水逸度较低,岩体成岩物质来源为壳幔混合源。
(4)石英闪长岩的Hf同位素组成变化范围较窄,εHf(t)变化于-5.8~2.7(主体在-1.0~0.0范围内)之间,tDM2=1.03~1.58Ga(主体在1.2~1.3Ga范围内),岩石地球化学、矿物化学及锆石Hf同位素特征综合分析推断,岩体的形成可能与俯冲板片局部撕裂熔融并与楔形地幔橄榄岩相互作用有关,且岩浆上侵过程中有部分陆壳物质混染,岩体可能形成于俯冲背景下的活动大陆边缘环境。
致谢: 核工业北京地质研究院、核工业208大队在项目研究过程中给予了大力支持和帮助,审稿专家提出宝贵的修改意见和建议,在此深表谢意。 -
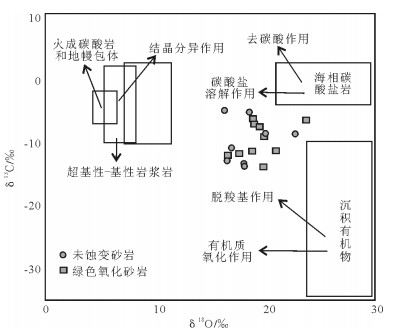
图 2 纳岭沟铀矿床C、O同位素组成判别图[17]
Figure 2. Carbon and oxygen isotope composition of the Nalinggou uranium deposit
-
张金带, 徐高中, 陈安平, 等.我国可地浸砂岩型铀矿成矿模式初步探讨[J].铀矿地质, 2005, 21(3):139-145. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ200503002.htm 潘蔚.伊犁盆地铀成矿时空分布特征与层间氧化带砂岩型铀矿找矿思路分析[J].铀矿地质, 2000, 16(1):19-25. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ200001003.htm 吴柏林, 刘池阳, 张复新, 等.东胜砂岩型岩矿后生蚀变地球化学性质及其成矿意义[J].地质学报, 2006, 80(5):740-747. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200605017.htm 彭云彪, 陈安平, 方锡衍, 等.东胜砂岩型铀矿床中烃类流体与成矿关系[J].地球化学, 2007, 36(3):267-274. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200703005.htm 李子颖, 方锡衍, 陈安平, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地北部砂岩型铀矿目标层灰绿色砂岩成因[J].中国科学 (D辑), 2007, 37(增刊1):139-146. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2007S1015.htm 戴明建, 彭云彪, 苗爱生.纳岭沟铀矿床铀成矿主要控制因素与找矿标志[J].矿物学报, 2013, 33(2):201-202. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB2013S2112.htm 杨建新, 陈安平.鄂尔多斯盆地呼斯梁地区可地浸砂岩型铀矿地质特征及找矿前景[J].铀矿地质, 2008, 24(2):96-100. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ200802008.htm 苗爱生, 焦养泉, 常宝成, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地东北部东胜铀矿床古层间氧化带精细解剖[J].地质科技情报, 2010, 29(3):55-61. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201003009.htm 侯惠群, 韩绍阳, 柯丹.砂岩型铀矿弱信息提取方法应用研究[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(7):1344-1349. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20150712&journal_id=gbc 别列里曼А И主编. 熊福清等译. 水成铀矿床[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 1995: 7. 庞雅庆. 东胜铀矿床和钱家店铀矿床后生蚀变特征及其与铀成矿关系[D]. 核工业北京地质研究院硕士学位论文, 2007. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-82806-2009061147.htm 丁万烈, 申科峰.水成铀矿沉积岩的后生蚀变[J].铀矿地质, 2001, 17(2):83-89. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ200102003.htm 肖新建. 东胜地区砂岩铀矿体低温流体成矿作用地球化学研究[D]. 核工业北京地质研究院博士学位论文, 2004. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis_Y1011696.aspx 丁万烈.绿色蚀变带的地球化学性质及其找矿意义探讨[J].铀矿地质, 2003, 19(5):277-282. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ200305003.htm 韩效忠, 张字龙, 姚春玲, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地东北部构造特征及其对铀矿化的控制作[J].铀矿地质, 2009, 25(5):277-283. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ200905003.htm 冯乔, 张小莉, 王云鹏, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地北部上古生界油气运聚特征及其铀成矿意义[J]. 2006, 80(5): 749-753. 刘建明, 刘家军, 顾雪祥.沉积盆地中的流体活动及其成矿作用[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 1997, 16(4):341-352. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW704.006.htm 吴柏林, 刘池阳, 张复新, 等.东胜砂岩型铀矿后生蚀变地球化学性质及其成矿意义[J].地质学报, 2006, 80(5):740-747. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200605017.htm




 下载:
下载: