LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb ages of the granites from Mashan of Inner Mongolia and their geological significances
-
摘要:
对内蒙古北山南带东段的马山花岗岩体进行了LA-ICP-MS 锆石U-Pb 年代学和岩石地球化学研究,结果表明,马山花岗岩以花岗闪长岩为主,偏铝质-过铝质,中钾钙碱性特征,具有较高的SiO2(64.85%~79.17%)、Na2O+K2O(5.13%~6.62%),富钠(Na2O/K2O>1);在球粒陨石标准化配分模式图上,配分曲线相对平缓,富集轻稀土元素,重稀土元素分馏不明显且相对亏损,δEu=0.65~0.91,具有弱Eu 负异常;在微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图上,亏损Ba、Nb、Ta、P、Ti,富集Rb、Th、U、K。通过LA-ICP-MS 锆石U-Pb 测年,马山花岗岩体的侵位年龄为281.8±3.2Ma。结合区域地质背景,认为马山花岗岩体是壳幔混合成因的,形成于早二叠世后碰撞伸展体制之下,北山南带于早二叠世晚期进入后碰撞裂谷伸展发育阶段。
Abstract:This paper reports LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb ages and geochemistry of the granite in Mashan, east of the southern Beishan, Inner Mongolia, with the purpose of constraining its formation age and petrogenesis. The results show that the granitic body mainly consists of granodiorite which belongs to middle-K calc-alkaline series with metaluminous-peraluminous characteristics and high content of SiO2(64.85%~79.17%), Na2O+K2O (5.13%~6.62%) and Na2O/K2O>1. In addition, the granite invariably exhibits relatively gentle light rare earth elements (LREE) enrichment with flat heavy rare earth element (HREE) and weak negative Eu anomalies (δEu=0.65~0.91) in the chondrite-normalized REE patterns, depletion of Ba, Nb, Ta, P, Ti and enrichment of Rb, Th, U, K in the spidergram. The LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age of the granite is 281.8±3.2Ma. Based on regional geology, the above characteristics indicate that the Mashan granite was the mixing product of crustal and mantle derived magmas and was formed under the tectonic setting of post-collisional extension in Early Permian. This implies that the east of southern Beishan Mountain turned to the stage of rift in post-collisional extensional period during Early Permian.
-
北山地区花岗岩类岩石分布广泛,约占该区全部侵入岩的95%[1].虽然前人对本区的花岗岩类进行了大量的研究,积累了丰富的资料[2-19] ,但对北山同一时代花岗岩构造属性的认识却不相同,尤其是华力西期花岗岩,对其构造属性[20-21]和岩浆成因的认识存在分歧.对北山花岗岩地区构造属性、岩浆成因特点和与区域构造演化关系的认识影响了对区域动力学的进一步探讨.另外,花岗岩体的多集中在北山北带,而北山南带很少.目前仅有3 处石炭纪—二叠纪花岗岩的精确定年报道:桥湾北花岗岩303.7±2.4Ma[22]、音凹峡南花岗岩281.7±2.9Ma[23]、石板泉花岗岩280.5±5.5Ma[24].因此,对北山南带的花岗岩体形成时代、岩石成因的研究,对于研究其构造岩浆作用具有重要的意义.近年来,北山南带东段地区发现了一系列与花岗岩类侵入体密切相关的金属矿床,如白山堂铜矿[25]、玉山钨矿[26-28]等,对花岗岩类侵入体的认识在一定程度上制约了该地区的找矿勘探工作.基于此,本文针对北山南带东段梧桐沟马山花岗岩体,进行了详细的地球化学测试和锆石U-Pb 测年,对其形成时代和岩石成因进行约束,并结合区域资料,对其地球动力学意义进行探讨,以期为北山南带构造岩浆研究提供可靠的地质资料.
1. 区域地质背景
研究区梧桐沟—神螺山一带位于北山南带东段,内蒙古西南侧与甘肃省接壤位置.地质背景较复杂,左国朝等[3]、龚全胜等[29]、何世平等[30]认为其属于塔里木板块增生带北缘,并将其进一步划归为磁海-红柳园-白山堂晚古生代陆内裂谷带;刘雪亚等[31]、张新虎[32]、聂凤军等[1]认为其属于哈萨克斯坦板块的南缘.区内以晚古生代石炭纪—二叠纪火山-沉积地层为主,少量前震旦纪基底形成规模较小的推覆体,奥陶系浅变质碎屑岩发育;下石炭统红柳园组可分为上、下2 段,下段为正粒序的碎屑岩组合,底部为砾岩,向上变细,上段为火山熔岩及碎屑岩组合,熔岩包括安山岩和顶部的流纹岩,少量英安岩及流纹质熔结凝灰岩,局部为灰岩,上石炭统芨芨台子组为白云质灰岩;下二叠统双堡塘组为磨拉石组合,由砾岩、含砾砂岩、粗砂岩、杂砂岩组成正粒序层;双堡塘组与红柳园组为平行不整合接触或断层接触,与上覆中二叠统金塔组为整合接触,金塔组以大面积出露玄武岩、枕状玄武岩及少量安山岩、火山-沉积碎屑岩为主,上二叠统方山口组以凝灰质为主,夹少量沉凝灰岩,与金塔组无直接接触关系;差异性沉降地区为中新生界不整合覆盖.侵入岩以晚华力西期为主,主要岩石类型包括英云闪长岩、二长花岗岩、黑云母二长花岗岩、花岗闪长岩,多以岩株或小岩基产出,基性侵入岩十分发育,主要为辉长岩及辉绿岩,前者为小岩株,后者多为岩脉.
2. 岩体地质特征
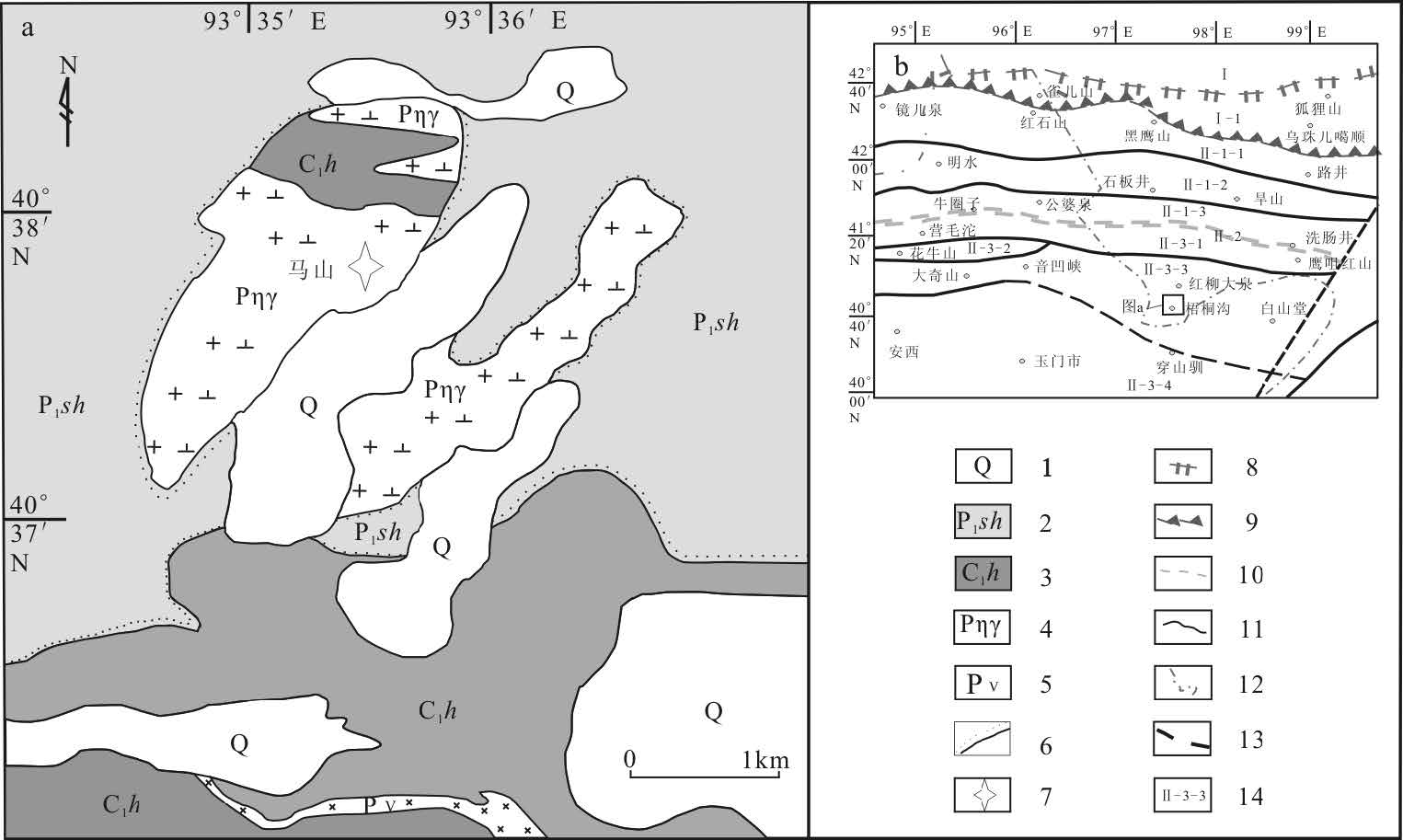
马山小岩体位于北山南带东段梧桐沟一带(图 1-a),岩体外表似椭球状,长约2.7km, 宽约1km, 出露面积约2.67km2,中心坐标为北纬40°37′45″、东经98°35′30″.侵入下石炭统红柳园组砂岩中,后被下二叠统双堡塘组砾岩、含砾砂岩覆盖.前人粗略地将其归入到华力西中晚期岩浆侵入活动①.
① 甘肃省地质局第二区域地质测量队. 红柳大泉幅1∶200000 区域地质测量报告. 1971.
![]() 图 1 马山二长花岗岩体地质简图及大地构造位置图(b 据参考文献[30]修改)1—第四系;2—下二叠统双堡塘组;3—下石炭统红柳园组;4—二叠纪花岗岩;5—二叠纪辉长岩;6—不整合界线;7—锆石U-Pb 采样位置;8—国界;9—板块缝合带;10—早古生代缝合带;11—主干断裂;12—省界;13—隐伏断裂;14—构造单元.Ⅰ—西伯利亚板块;Ⅰ-1—大南湖-雀儿山-狐狸山早古生代活动带陆缘带;Ⅱ—塔里木板块;Ⅱ-1-1 —黄山-红石山-路井晚古生代陆内裂谷带;Ⅱ-1-2— 星星峡-明水-旱山地块;Ⅱ-1-3 —白玉山南-公婆泉-东七一山早古生代晚期活动带陆缘带;Ⅱ-2 —红柳河-洗肠井构造混杂岩带;Ⅱ-3-1 —方山口-营毛沱-鹰咀红山早古生代中期活动陆缘带;Ⅱ-3-2 —花牛山早古生代陆缘裂谷带(裂陷槽);Ⅱ-3-3— 磁海-红柳园-白山堂晚古生代陆内裂谷带;Ⅱ-3-4 —敦煌地块Figure 1. Simplified geological map and tectonic location map of Mashan granite
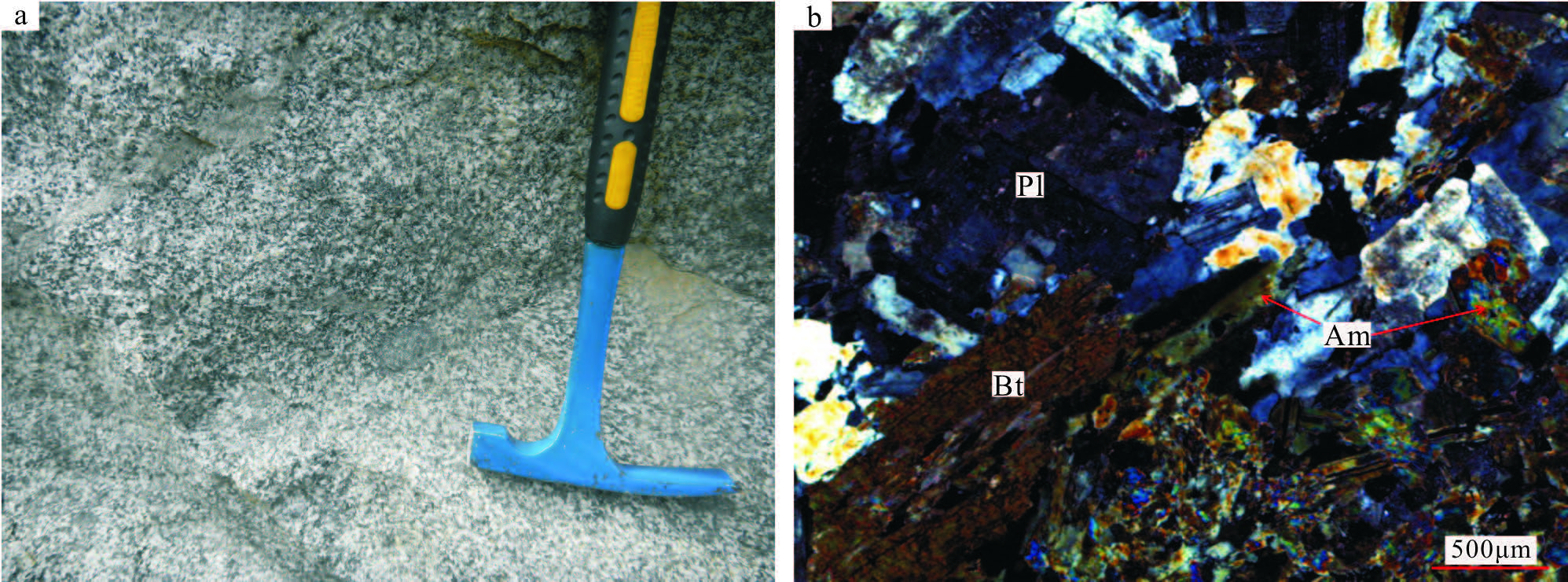
图 1 马山二长花岗岩体地质简图及大地构造位置图(b 据参考文献[30]修改)1—第四系;2—下二叠统双堡塘组;3—下石炭统红柳园组;4—二叠纪花岗岩;5—二叠纪辉长岩;6—不整合界线;7—锆石U-Pb 采样位置;8—国界;9—板块缝合带;10—早古生代缝合带;11—主干断裂;12—省界;13—隐伏断裂;14—构造单元.Ⅰ—西伯利亚板块;Ⅰ-1—大南湖-雀儿山-狐狸山早古生代活动带陆缘带;Ⅱ—塔里木板块;Ⅱ-1-1 —黄山-红石山-路井晚古生代陆内裂谷带;Ⅱ-1-2— 星星峡-明水-旱山地块;Ⅱ-1-3 —白玉山南-公婆泉-东七一山早古生代晚期活动带陆缘带;Ⅱ-2 —红柳河-洗肠井构造混杂岩带;Ⅱ-3-1 —方山口-营毛沱-鹰咀红山早古生代中期活动陆缘带;Ⅱ-3-2 —花牛山早古生代陆缘裂谷带(裂陷槽);Ⅱ-3-3— 磁海-红柳园-白山堂晚古生代陆内裂谷带;Ⅱ-3-4 —敦煌地块Figure 1. Simplified geological map and tectonic location map of Mashan granite该岩体由花岗闪长岩组成(图 2-a),其内部无明显结构分带和成分分带,为一次岩浆侵入活动的产物.岩石具有典型的花岗结构(图 2-b),矿物成分较简单,主要由斜长石、条纹长石和石英组成.长石0.4~3.8mm, 整体表面褐色粘土化显著,较石英脏,斜长石半自形-自形板状,双晶纹可见;石英呈他形粒状,表面干净透明,波状消光,粒径为0.3~2.7mm, 充填于其他矿物之间.
锆石U-Pb 年龄样品的采集位置为北纬40°37′46″、东经98°35′30″.
3. 分析方法
对采集的样品进行主量、稀土和微量元素及LA-ICP-MS 锆石U-Pb 年龄测定.在进行化学分析前,先在镜下观察薄片以确定样品的适应性.主量、微量元素由中国冶金地质总局西北地质勘查院测试中心测定,采用XRF 荧光光谱样分析方法,分析精度优于5%;微量和稀土元素采用ICP-MS 分析,利用国家一级标准物质进行质量监控(GB/T14506—1993),含量大于10×10-6的元素测试精度为5%,小于10×10-6的测试精度为10%.
用常规方法分选出锆石单矿物,然后在双目镜下根据锆石颜色、自形程度、形态、透明度等进行初步分类,挑选出具有代表性的锆石.将锆石样品用双面胶粘在载玻片上,放上PVC 杯,然后将环氧树脂和固化剂进行充分混合后注入PVC 杯中,待树脂充分固化后将其从载玻片上剥离,打磨和抛光至锆石中心部位暴露,然后拍摄透射光、反射光和阴极发光(CL)图像.最后用体积百分比为3%的HNO3清洗样品制成样品靶备用.
LA-ICP-MS 锆石U-Pb 同位素测定在西安地质矿产研究所实验测试中心完成.测定时根据可见光、CL 和BSE(背散射电子成像)图像选择合适的测点位置,如避免包裹体、裂隙位置等.详细的分析步骤和数据处理方法见参考文献[33-34],用Glit-ter(4.0 版)程序处理原始数据.普通铅扣除时,其组成由Stacey 等[35]的模式给出,年龄加权平均计算及U-Pb 谐和图的绘制采用Isoplot(3.0 版)[36]完成.
4. 锆石U-Pb 年龄
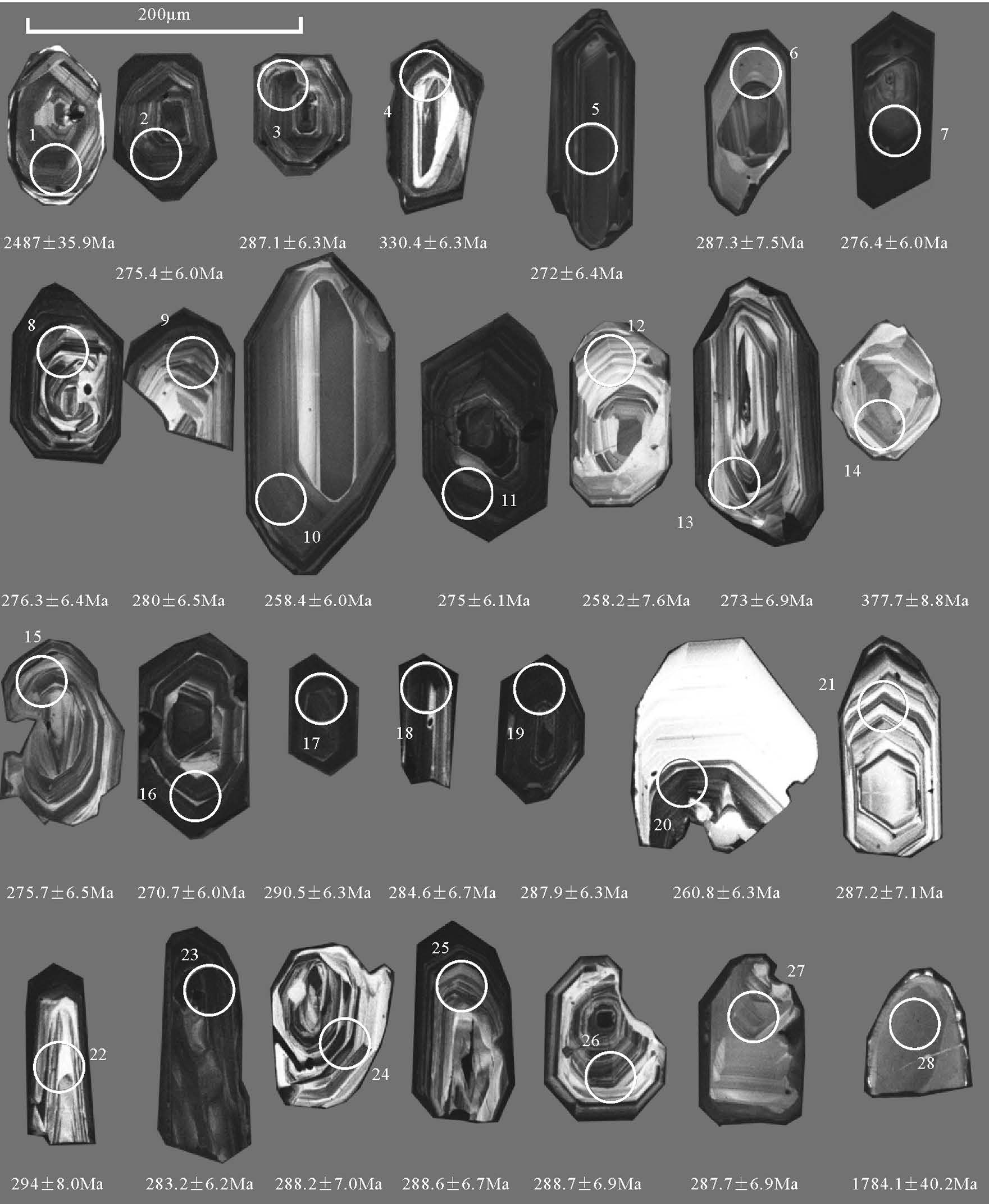
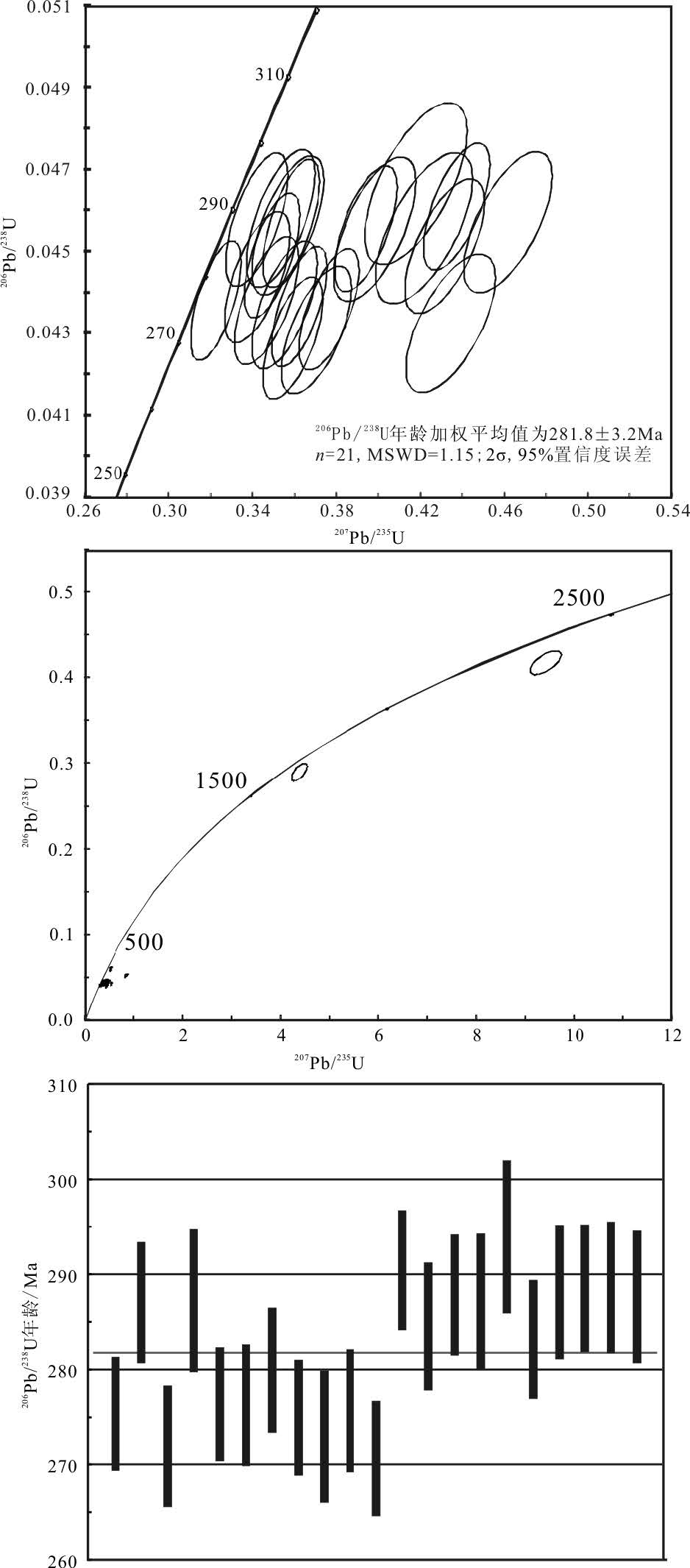
从样品中选取的锆石以浅黄色为主,个别颜色为浅玫瑰色和近于无色,玻璃-金刚光泽.按晶体形态可以分为2 类,一类呈自形双锥柱状,长60~160μm, 宽30~120μm, 长宽比多为2~3,透射光下可见锆石内部发育少量裂纹和包裹体,包裹体以长条形和椭圆形为主,多为小锆石包体,阴极发光图像显示,锆石具有典型的岩浆韵律环带和明暗相间的条带构造等,显示岩浆锆石的特征(图 3);另一类则有溶蚀现象,锆石长20~30μm, 宽100~120μm, 长宽比多为4~5.部分锆石具有残留的核部,为继承核或捕获核,部分锆石颗粒具有窄的浅色边,但核部仍显示出清晰的岩浆环带特征.测得的28 个颗粒的28 个数据中(表 1),21 个206Pb/238U 年龄(不包括1、4、10、12、14、20、28 点)介于270.7±6.0~294.0±8.0Ma 之间,给出的206Pb/238U 年龄加权平均值为281.8 ± 3.2Ma(MSWD=1.15,n=21,2σ)(图 4).U、Th 含量分别为155×10-6~1444×10-6和92×10-6~660×10-6.Th/U 值除2 个样品略低于0.4(0.39、0.31)外,其余的比值均介于0.42~0.99 之间,表现出典型岩浆锆石的特征.该年龄代表了岩体的结晶年龄.此外还获得了3 组年龄:①10、12、20 这3 个点的206Pb/238U 年龄分别为258.4±6.0Ma、258.2±7.6Ma、260.8±6.3Ma, 其年龄加权平均值为259.2±0.1Ma, 锆石具有较规则的外形,CL 图像较亮,具有弱分带特征,为热液变质锆石,可能代表一期热液蚀变活动;② 有2 个点获得了334.4Ma、369.9Ma 的年龄数据.这些锆石略磨圆,锆石环带特征不清楚,疑为继承性锆石;③1、28 这2 个点的年龄数据采用207Pb/206Pb 年龄,分别为2487±35.9Ma、1784.1±40.2Ma, 锆石外形不规则,具磨圆,环带特征不清楚,可能为老基底的捕获锆石.
表 1 马山花岗岩体LA-ICP-MS 锆石(TW01) U-Th-Pb 同位素数据Table 1. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb dating data of granite from Mashan(TW01)分析点 含量/10-6 232Th/238U 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 232Th 238U 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ TW01-1 280.96 449.94 0.62 9.3972 0.2158 0.4182 0.0092 2377.6 21.07 2252.3 41.73 TW01-2 523.95 1099.59 0.48 0.3621 0.0089 0.0437 0.0010 313.8 6.64 275.4 5.97 TW01-3 375.06 699.75 0.54 0.3941 0.0100 0.0456 0.0010 337.4 7.29 287.1 6.31 TW01-4 594.83 576.85 1.03 0.8243 0.0212 0.0526 0.0012 610.4 11.79 330.4 7.55 TW01-5 349.29 359.94 0.97 0.3703 0.0110 0.0431 0.0010 319.9 8.13 272 6.38 TW01-6 92.39 154.58 0.60 0.4218 0.0152 0.0456 0.0012 357.3 10.86 287.3 7.47 TW01-7 401.97 1310.93 0.31 0.3223 0.0078 0.0438 0.0010 283.7 6.01 276.4 5.96 TW01-8 191.06 372.5 0.51 0.3463 0.0101 0.0438 0.0010 301.9 7.58 276.3 6.38 TW01-9 292.29 294.14 0.99 0.3421 0.0102 0.0444 0.0011 298.8 7.73 280 6.53 TW01-10 99.79 354.71 0.28 0.3287 0.0093 0.0409 0.0010 288.5 7.14 258.4 5.96 TW01-11 408.08 804.03 0.51 0.3764 0.0095 0.0436 0.0010 324.4 7.02 275 6.06 TW01-12 49.69 106.02 0.47 0.4079 0.0170 0.0409 0.0012 347.4 12.27 258.2 7.6 TW01-13 133.16 156.37 0.85 0.4344 0.0141 0.0433 0.0011 366.3 10 273 6.93 TW01-14 81.57 213.17 0.38 0.5080 0.0149 0.0603 0.0015 417.1 10.03 377.7 8.81 TW01-15 291.58 308.2 0.95 0.3552 0.0104 0.0437 0.0010 308.6 7.79 275.7 6.45 TW01-16 252.32 605.27 0.42 0.3590 0.0094 0.0429 0.0010 311.5 7 270.7 6.04 TW01-17 660.33 1444.13 0.46 0.4373 0.0104 0.0461 0.0010 368.4 7.36 290.5 6.29 TW01-18 216.72 353.49 0.61 0.4315 0.0124 0.0451 0.0011 364.2 8.77 284.6 6.69 TW01-19 477.93 938.69 0.51 0.3581 0.0090 0.0457 0.0010 310.8 6.72 287.9 6.32 TW01-20 212.5 325.28 0.65 0.3001 0.0098 0.0413 0.0010 266.4 7.68 260.8 6.33 TW01-21 108.44 260.92 0.42 0.3980 0.0129 0.0456 0.0012 340.2 9.38 287.2 7.13 TW01-22 158.92 169.8 0.94 0.4177 0.0160 0.0467 0.0013 354.4 11.43 294 8.04 TW01-23 372.22 946.18 0.39 0.3493 0.0087 0.0449 0.0010 304.2 6.53 283.2 6.21 TW01-24 315.24 351.81 0.90 0.4617 0.0139 0.0457 0.0011 385.5 9.65 288.2 7.02 TW01-25 261.36 418.89 0.62 0.3418 0.0098 0.0458 0.0011 298.6 7.41 288.6 6.66 TW01-26 157.57 259.58 0.61 0.3533 0.0108 0.0458 0.0011 307.2 8.13 288.7 6.87 TW01-27 157.3 231.78 0.68 0.3569 0.0112 0.0456 0.0011 309.9 8.4 287.7 6.93 TW01-28 77.52 182.09 0.43 4.3637 0.1037 0.2902 0.0066 1705.5 19.64 1642.3 32.72 5. 岩石地球化学特征
5.1 主量元素
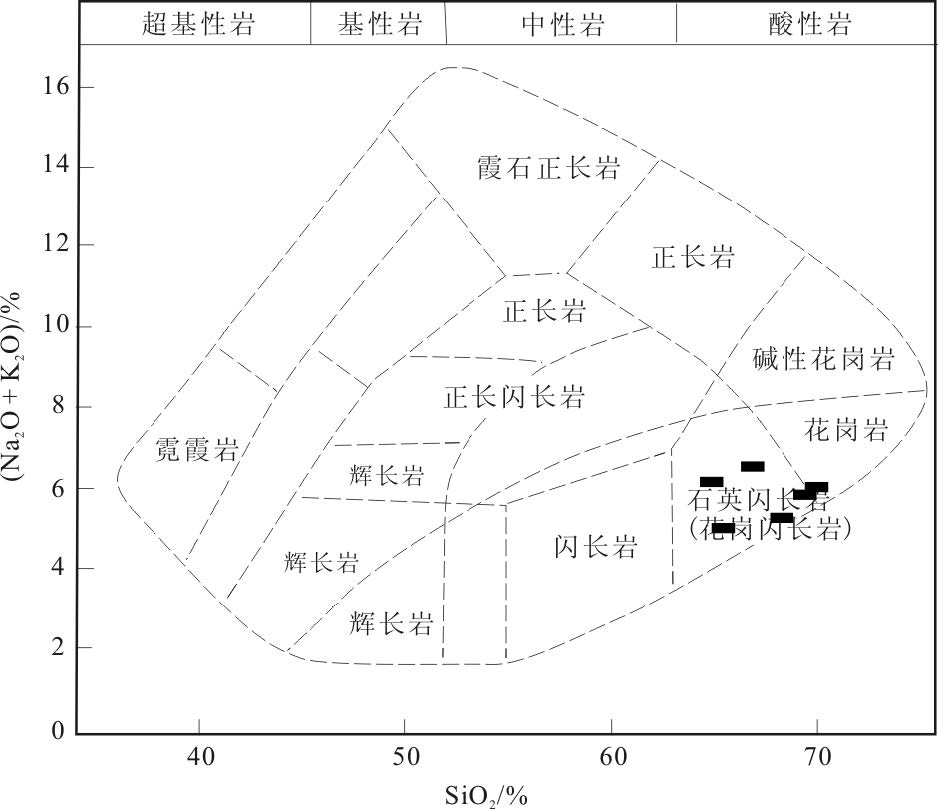
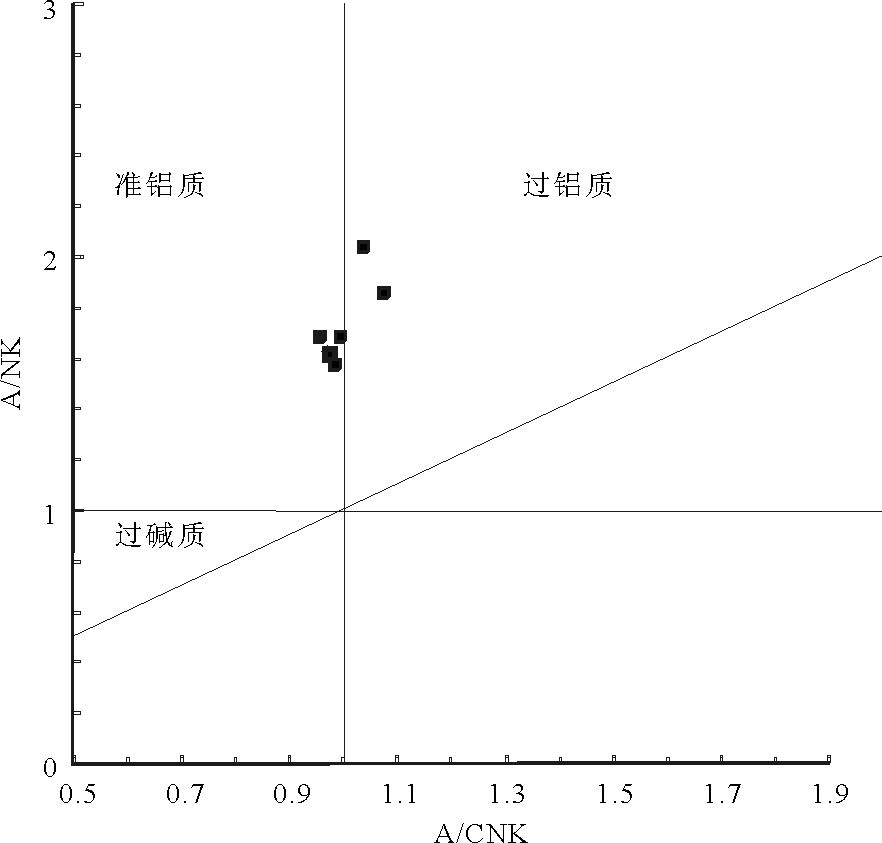
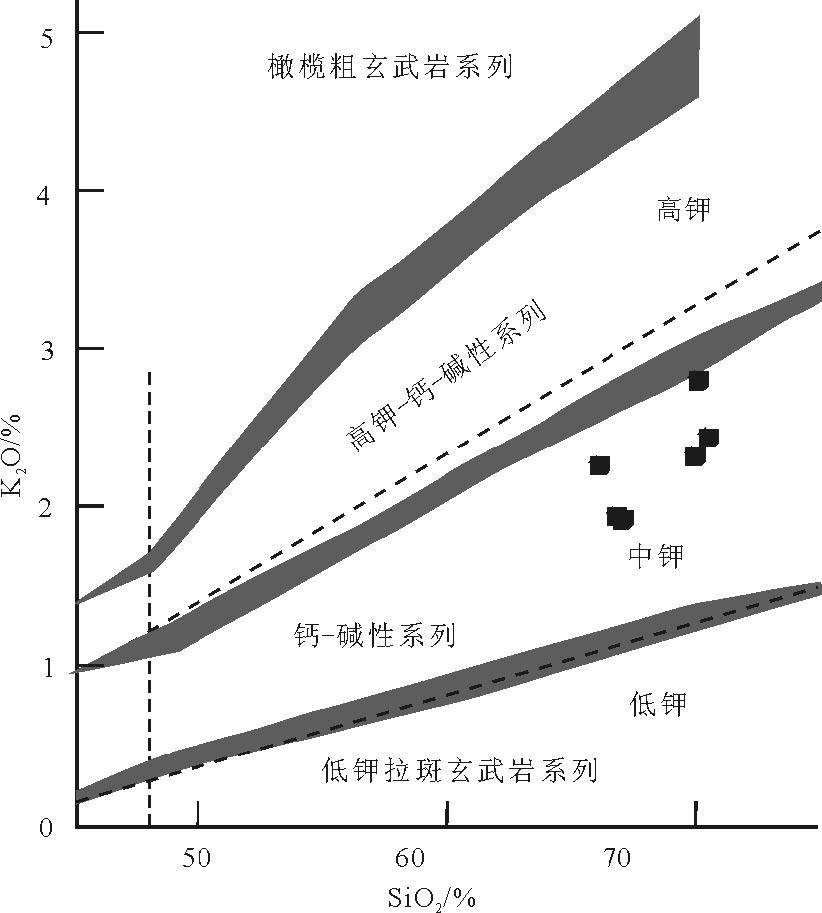
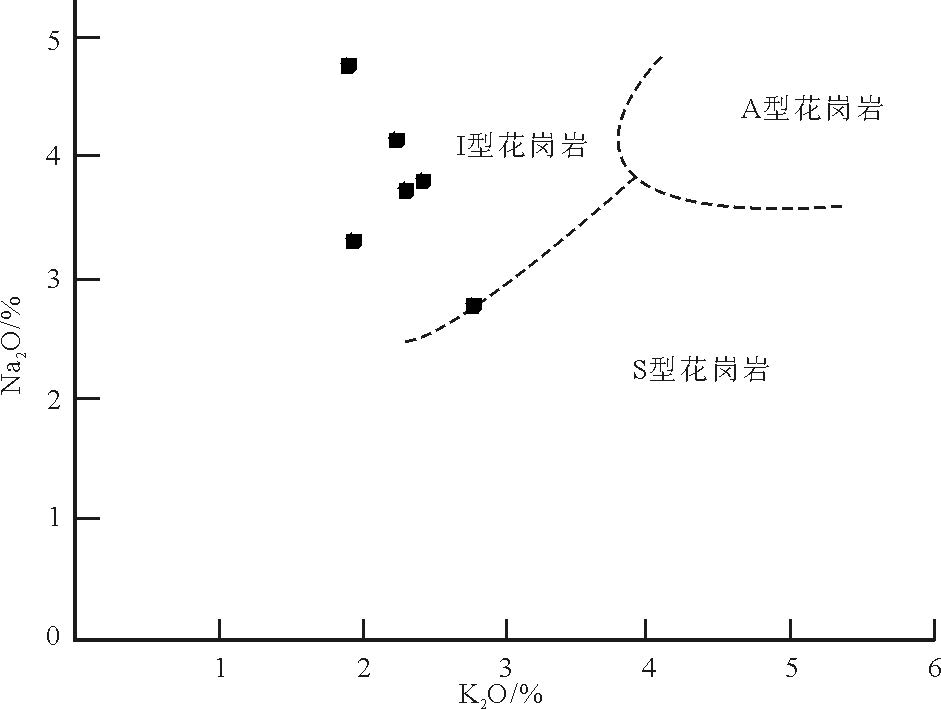
马山花岗岩类的岩石地球化学分析(表 2)表明,SiO2 含量为64.85%~69.75%,平均含量67.35%,属于酸性岩类,在SiO2-(Na2O+K2O)图解(图 5)上,大多数样品点投入花岗闪长岩区域;Na2O 含量为2.66%~4.72%,平均值3.68%,K2O含量为1.90%~2.71%, 平均值为2.23% ,Na2O + K2O 含量为5.13~6.62%,平均值为5.91%, Na2O/K2O 值为0.98~2.48,平均值为1.69;Al2O3含量为13.55%~15.49%,平均值为14.63% ;TiO2 含量为0.41% ~0.76% ,平均值为0.55% ;A/CNK 值为0.96~1.07,平均值为1.0,在A/CNK-A/NK 图解(图 6)中,样品点主要投入到偏铝质岩石范围内,2 个样品投入过铝质范围内;里特曼指数σ为1.15~1.84,为钙碱性系列岩石;在SiO2-K2O 图解(图 7)上,样品点全部投入中钾钙碱性系列;在K2O-Na2O 图解(图 8)上,样品点均投入I 型花岗岩区域.岩石的分异指数(DI)为65.74~76.80,表明原始岩浆的结晶分异程度一般.马山岩体主量元素特征显示,其具有钙碱性序列岩石的属性,属于中等分异程度的I 型花岗岩.
![]() 图 5 SiO2-(Na2O +K2O)图解(底图据参考文献[37])Figure 5. SiO2 versus Na2O +K2O diagram
图 5 SiO2-(Na2O +K2O)图解(底图据参考文献[37])Figure 5. SiO2 versus Na2O +K2O diagram![]() 图 6 A/CNK-A/NK 图解(底图据参考文献[38])Figure 6. A/CNK versus A/NK diagram
图 6 A/CNK-A/NK 图解(底图据参考文献[38])Figure 6. A/CNK versus A/NK diagram![]() 图 7 SiO2-K2O 图解(底图据参考文献[39])Figure 7. SiO2 versus K2O diagram
图 7 SiO2-K2O 图解(底图据参考文献[39])Figure 7. SiO2 versus K2O diagram![]() 图 8 K2O-Na2O 图解(底图据参考文献[40])Figure 8. K2O versus Na2O diagram
图 8 K2O-Na2O 图解(底图据参考文献[40])Figure 8. K2O versus Na2O diagram5.2 微量和稀土元素
(1) 稀土元素
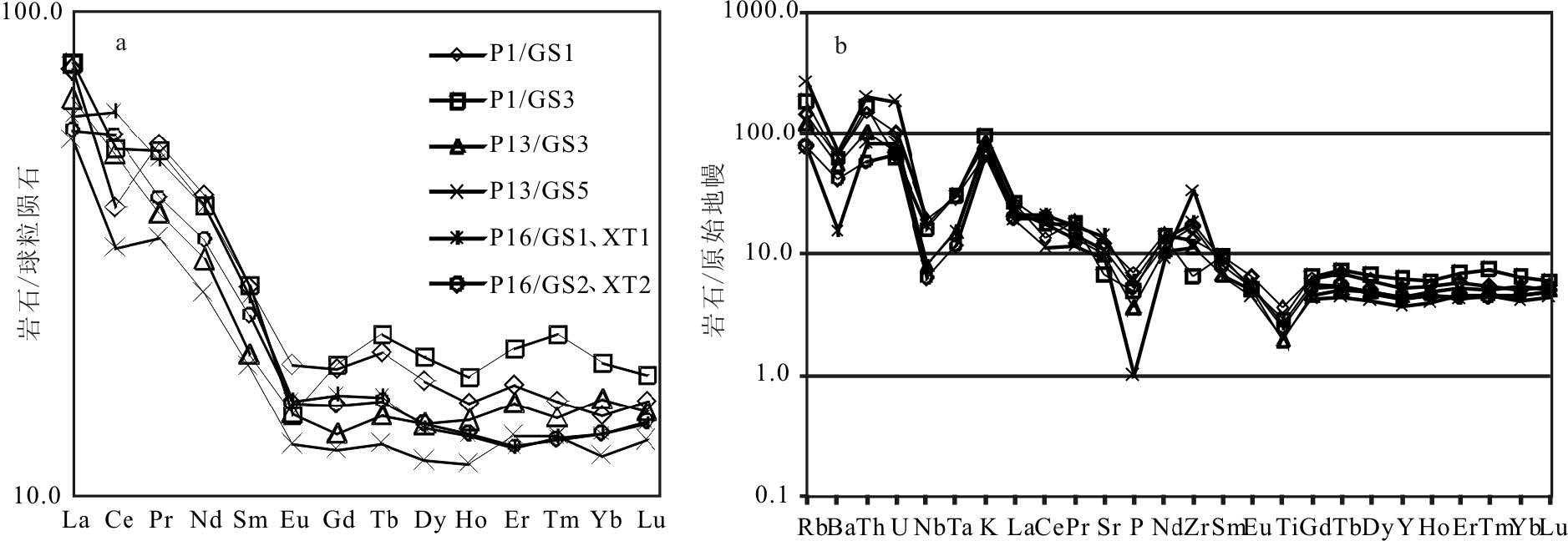
稀土元素分析结果如表 2 所示.样品的稀土元素总量为80.57 × 10-6~125.29 × 10-6,平均值为106.44×10-6,稀土元素总含量较低;在球粒陨石标准化配分模式图(图 9-a)上,具有相对平缓的富集轻稀土元素(LREE)的稀土元素配分模式,重稀土元素(HREE)分馏不明显且相对亏损,但都明显高于球粒陨石丰度10 倍.ΣLREE/ΣHREE 值为1.70~2.43, 平均值为1.99;轻稀土元素内部分异较明显,(La/Sm)N=2.37~3.37,平均值为2.80;La/Yb=5.81~7.23,平均值为6.23,(La/Yb)N=4.17~5.19,平均值为4.47;(Gd/Yb)N=0.85~1.25,δEu=0.65~0.91,平均值为0.80,具有弱负Eu 异常,可能与斜长石在源区残留有关.
表 2 马山花岗岩体主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果Table 2. Analytical data of major, trace, and rare earth elements of granite from Mashan样品号
岩石名称P1/GS1
花岗质碎裂岩P1/GS3
花岗质碎岩P13/GS3
中粗粒花岗闪长岩P13/GS5
中粗粒花岗闪长岩P16/GS1、XT1
黑云母花岗闪长岩P16/GS2、XT2
黑云母花岗闪长岩SiO2 65.48 68.06 69.75 69.21 64.85 66.77 Al2O3 15.00 13.55 14.09 14.33 15.30 15.49 Fe2O3 1.40 1.13 1.95 2.08 3.41 3.01 FeO 3.44 3.02 1.68 1.75 2.22 1.88 TiO2 0.76 0.62 0.41 0.43 0.56 0.53 MgO 2.55 2.05 1.36 1.20 1.78 1.62 CaO 3.92 2.93 3.15 3.57 3.48 3.25 P2O5 0.16 0.16 0.07 0.09 0.12 0.12 K2O 1.90 2.71 2.40 2.29 2.21 1.90 MnO 0.09 0.07 0.07 0.08 0.08 0.07 Na2O 3.23 2.66 3.74 3.67 4.05 4.72 烧失量 1.55 3.72 0.82 0.54 1.60 1.29 总量 99.46 100.69 99.49 99.23 99.66 100.65 A/CNK 1.04 1.07 0.97 0.96 0.99 0.99 NK/A 0.49 0.54 0.62 0.59 0.59 0.63 σ 1.17 1.15 1.41 1.35 1.79 1.84 Rb 88.84 114.35 75.02 170.00 47.34 48.32 Ba 430.78 435.03 370.10 481.29 109.25 283.55 Th 12.55 13.66 8.49 17.14 6.92 4.94 U 2.10 1.30 1.44 3.79 1.68 1.40 Nb 13.36 11.54 5.78 12.36 5.75 4.42 Ta 1.18 1.20 0.62 1.28 0.64 0.49 Sr 255.42 139.70 209.88 195.36 291.65 226.93 Zr 143.82 72.81 127.41 374.10 196.08 185.01 V 101.52 64.53 71.65 23.01 78.67 64.00 Cr 54.31 43.16 22.04 21.90 18.38 22.06 Co 13.38 6.74 6.29 1.34 10.11 7.72 Cu 15.99 16.80 7.21 3.16 22.49 17.54 Zn 76.13 53.91 33.03 41.80 47.13 39.88 Ga 18.83 16.43 15.27 16.56 14.36 13.37 La 18.00 18.59 15.70 12.85 14.47 13.48 Ce 24.17 31.86 31.06 19.91 37.94 34.31 Pr 5.07 4.90 3.65 3.23 4.69 3.94 Nd 19.47 18.51 14.39 12.23 18.34 15.69 Sm 4.14 4.16 3.01 2.83 3.94 3.60 Eu 1.08 0.85 0.86 0.74 0.91 0.90 Gd 3.76 3.84 2.77 2.56 3.31 3.16 Tb 0.74 0.81 0.55 0.48 0.60 0.59 Dy 4.40 4.95 3.57 3.00 3.52 3.57 Ho 0.88 1.00 0.81 0.66 0.75 0.76 Er 2.80 3.34 2.57 2.21 2.08 2.10 Tm 0.40 0.55 0.37 0.34 0.34 0.33 Yb 2.49 3.19 2.70 2.06 2.29 2.28 Lu 0.40 0.45 0.38 0.33 0.36 0.36 Y 23.71 28.29 20.30 17.14 19.75 20.25 REE 111.51 125.29 102.69 80.57 113.29 105.31 LREE 71.93 78.87 68.67 51.79 80.29 71.91 HREE 39.58 46.42 34.02 28.78 33.00 33.39 LREE/HREE 1.82 1.70 2.02 1.80 2.43 2.15 (La/Yb)N 5.19 4.18 4.17 4.47 4.54 4.25 (La/Sm)N 2.81 2.88 3.37 2.93 2.37 2.42 (Gd/Yb)N 1.25 1.00 0.85 1.03 1.20 1.15 δEu 0.84 0.65 0.91 0.84 0.77 0.82 注:元素由中国冶金地质总局西北地质勘查院测试中心测定;δEu=EuN/SQRT(SmN∗GdN);主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素为10-6 (2) 微量元素
在微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(图 9-b)上,所有样品的稀土元素配分模式和原始地幔标准化图基本平行,显示同源演化的特征;显著亏损Ba、Nb、Ta、P、Ti, Zr、Rb、Th、U、K,富集Zr 和亏损Nb、Ta、Ti, 表明岩浆源区岩石以陆壳组分为主.
岩石具有高Rb、低Sr(均小于400×10-6)、高Yb(大于2 × 10-6)的特征,Sr/Y 值很低(Sr/Y=4.94~14.77, 平均值为10.57),马山花岗岩微量元素Sr、Yb特征与华南低Sr、高Yb 型花岗岩相似.低Sr 、高Yb 型花岗岩为浙闽型花岗岩,与其平衡的是斜长石和角闪石残留相[38],说明形成的压力较低(小于0.8GPa 或1.0GPa),可能是地壳伸展变形减薄达正常地壳厚度(30km 左右)或低于正常地壳厚度的造山后阶段形成的[43].在大洋中脊标准化图解(图 10)上,样品与典型的后碰撞花岗岩显示出类似的趋势,说明马山花岗岩为典型的后碰撞花岗岩.
![]() 图 10 马山花岗岩体大洋中脊标准化图解(标准化值据参考文献[42])Figure 10. Ocean ridge granite (ORG) normalized geochemicalpatterns for samples of Mashan granite
图 10 马山花岗岩体大洋中脊标准化图解(标准化值据参考文献[42])Figure 10. Ocean ridge granite (ORG) normalized geochemicalpatterns for samples of Mashan granite6. 马山花岗岩体形成的构造背景及其成因
北山地区西邻东天山,东接阿拉善,以阿尔金和星星峡两大走滑断裂为界,位于一个巨大的构造楔形区内,构造过程复杂.其大地构造的归属一直存在争议,一是将北山地区划分为北部的哈萨克斯坦板块和南部的塔里木板块,左国朝等[3]以明水-石板井-小黄山缝合带(早古生代末)为界;龚全胜等[29]、何世平等[30]则以红石山-黑鹰山-六陀山蛇绿混杂岩带(晚古生代)为界;部分学者[31-32]以柳园-大奇山(晚古生代末)和红石山-黑鹰山-六陀山2 条深大断裂为界,将北山从南向北依次划分为塔里木板块、哈萨克斯坦板块和西伯利亚板块;李锦轶等[44]则以星星峡—白玉山—牛圈子—小黄山作为北山地区西伯利亚与中朝2 个古板块之间二叠系的分界线,认为北山南部柳园一带可能代表了二叠纪弧后盆地环境,柳园与白玉山—小黄山之间的区域为早古生代岛弧带.
对区域地质演化,前人有不同的观点,分歧的关键点在于洋盆的最终闭合时间.左国朝等[3]认为,在志留纪末—早泥盆世,北山地区的塔里木-中朝与哈萨克斯坦两大古板块最终拼合,并导致洋盆消失和碰撞造山;刘雪亚等[31]认为,在早二叠世之前,随着北山南带及南天山古洋盆的封闭,敦煌地块北缘的安北-旧寺墩构造带与北山造山带前缘的柳园-大奇山地体碰撞,导致塔里木板块、哈萨克斯坦板块和西伯利亚板块最终拼接;龚全胜等[45]认为,北山地区自泥盆纪开始转化为古亚洲洋构造域演化体系,晚石炭世末实现塔里木板块、哈萨克斯坦板块的最终碰撞对接;何世平等[46]认为,石炭纪末,哈萨克斯坦板块和塔里木板块之间的洋盆最终闭合,形成新的统一大陆,认为在早二叠世研究区洋盆已经闭合,经历了碰撞造山.而朱江[24]则认为,北山南带洋壳俯冲作用可能持续到早二叠世,并在早—中二叠世洋盆最终闭合,认为北山南带石炭纪—二叠纪的岩浆作用形成于俯冲环境,与毛启贵[47]、肖文交[48-49]、郭谦谦[50]等观点一致.
很多学者[3, 51-52]认为,北山地区在二叠纪是一种伸展拉伸的构造背景.左国朝等[3]认为,早二叠世北山南带在拉张背景下形成了峡东-俞井子裂陷槽,但并没有形成真正的大洋;刘明强等[53]指出,音凹峡晚古生代陆内裂谷带为一多旋回裂谷,主要裂谷作用发生于奥陶纪、志留纪、石炭纪和二叠纪,反映了多期次、多旋回性、继承性“开”、“合”演化的特征;龚全胜等[45]认为,北山地区晚石炭世—二叠纪为大陆板块碰撞时期;何世平等[46]认为,早石炭世沿石板山—大奇山—神螺山一带在前震旦纪古老基底上形成北山南部陆内裂谷带,该裂谷带一直发展演化到二叠纪末,并在早二叠世发展到鼎盛时期.
综上所述,结合野外地质特征,下石炭统红柳园组为火山-碎屑岩,火山岩组合为安山岩-英安岩-流纹岩组合;与红柳园组平行不整合接触的下二叠统双堡塘组为一套粗碎屑岩和细碎屑岩组合,中二叠统金塔组以出露海相枕状玄武岩为特征,并伴随大量的辉长岩、辉绿岩等幔源岩浆活动,其与双堡塘组为整合接触关系.多数学者[3, 46, 53]对区内北山南带存在晚古生代洋盆有异议,认为晚古生代为陆内裂谷环境,区内晚石炭世可能存在裂谷回返碰撞,导致石炭系与下二叠统之间的平行不整合接触,早二叠世裂谷进一步拉开,并在中二叠世达到鼎盛.结合地球化学特征,可进一步确定281.8±3.2Ma的马山花岗岩形成于后碰撞伸展环境.
吴泰然[54]将这类花岗岩归为拉张型过渡壳花岗岩(ECG),认为其形成是由于地壳的拉伸减薄,上地幔热物质上涌,使地壳形成一种高温低压的环境,并使地壳发生部分重熔,同时上地幔上涌的热物质沿拉张的裂隙与地壳的热物质发生混染作用,对陆壳的物质进行改造,使之向过渡类型转化,形成拉张型过渡壳的花岗岩.冯继承[22]、张文等[23]研究认为,北山南带音凹峡花岗岩也是该类型的花岗岩体.区域上,前人对北山南带不同地段的石炭纪—二叠纪代表性的中酸性侵入岩体进行了Sr、Nd、Hf 同位素研究,桥湾北花岗岩体[22, 24]的εNd(t)值在-0.40~-0.06 之间,εHf(t)值在-1.2~5.8 之间,是典型的壳幔混合型花岗岩,代表了兴蒙造山带广泛出现的晚古生代—中生代大陆地壳生长现象;音凹峡南花岗岩体也位于北山南带,张文[23]报道的该岩体的εHf(t)值在+4.4~+7.8 之间;石板泉花岗岩体的εNd(t)值在-0.1~-1.6 之间[24].一般认为,具有正εNd(t)和εHf(t)值的花岗质岩石来自于亏损地幔,或由亏损地幔中新增生的年轻地壳物质的部分熔融形成.结合研究区二叠纪大量基性岩浆活动(枕状玄武岩和辉长、辉绿岩的发现),认为北山南带石炭纪—二叠纪(305~280Ma)的花岗岩具有普遍的壳幔混合成因特征.
7. 结论
(1) 马山花岗岩体的LA-ICP-MS 锆石U-Pb年龄为281.8±3.2Ma, 为后碰撞花岗岩.
(2) 马山花岗岩体具有典型的壳幔混合特征,其机制可能是幔源基性岩浆底侵后遭受地壳物质混合或混染.北山南带305~280Ma 之间的花岗岩普遍具有壳幔混合成因的特征.
(3) 马山花岗岩体及北山南带众多壳幔混合成因的花岗岩体说明,北山南带在早二叠世总体为后碰撞伸展环境.
致谢: 西安地质矿产研究所实验测试中心的李艳广和汪双双工程师在LA-ICP-MS 实验操作及数据处理和解释方面给予了热情的帮助,审稿专家为本文提出了十分有益的修改意见和建议,在此一并表示衷心的感谢. -
图 1 马山二长花岗岩体地质简图及大地构造位置图(b 据参考文献[30]修改)
1—第四系;2—下二叠统双堡塘组;3—下石炭统红柳园组;4—二叠纪花岗岩;5—二叠纪辉长岩;6—不整合界线;7—锆石U-Pb 采样位置;8—国界;9—板块缝合带;10—早古生代缝合带;11—主干断裂;12—省界;13—隐伏断裂;14—构造单元.Ⅰ—西伯利亚板块;Ⅰ-1—大南湖-雀儿山-狐狸山早古生代活动带陆缘带;Ⅱ—塔里木板块;Ⅱ-1-1 —黄山-红石山-路井晚古生代陆内裂谷带;Ⅱ-1-2— 星星峡-明水-旱山地块;Ⅱ-1-3 —白玉山南-公婆泉-东七一山早古生代晚期活动带陆缘带;Ⅱ-2 —红柳河-洗肠井构造混杂岩带;Ⅱ-3-1 —方山口-营毛沱-鹰咀红山早古生代中期活动陆缘带;Ⅱ-3-2 —花牛山早古生代陆缘裂谷带(裂陷槽);Ⅱ-3-3— 磁海-红柳园-白山堂晚古生代陆内裂谷带;Ⅱ-3-4 —敦煌地块
Figure 1. Simplified geological map and tectonic location map of Mashan granite
图 5 SiO2-(Na2O +K2O)图解(底图据参考文献[37])
Figure 5. SiO2 versus Na2O +K2O diagram
图 6 A/CNK-A/NK 图解(底图据参考文献[38])
Figure 6. A/CNK versus A/NK diagram
图 7 SiO2-K2O 图解(底图据参考文献[39])
Figure 7. SiO2 versus K2O diagram
图 8 K2O-Na2O 图解(底图据参考文献[40])
Figure 8. K2O versus Na2O diagram
图 10 马山花岗岩体大洋中脊标准化图解(标准化值据参考文献[42])
Figure 10. Ocean ridge granite (ORG) normalized geochemicalpatterns for samples of Mashan granite
表 1 马山花岗岩体LA-ICP-MS 锆石(TW01) U-Th-Pb 同位素数据
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb dating data of granite from Mashan(TW01)
分析点 含量/10-6 232Th/238U 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 232Th 238U 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ TW01-1 280.96 449.94 0.62 9.3972 0.2158 0.4182 0.0092 2377.6 21.07 2252.3 41.73 TW01-2 523.95 1099.59 0.48 0.3621 0.0089 0.0437 0.0010 313.8 6.64 275.4 5.97 TW01-3 375.06 699.75 0.54 0.3941 0.0100 0.0456 0.0010 337.4 7.29 287.1 6.31 TW01-4 594.83 576.85 1.03 0.8243 0.0212 0.0526 0.0012 610.4 11.79 330.4 7.55 TW01-5 349.29 359.94 0.97 0.3703 0.0110 0.0431 0.0010 319.9 8.13 272 6.38 TW01-6 92.39 154.58 0.60 0.4218 0.0152 0.0456 0.0012 357.3 10.86 287.3 7.47 TW01-7 401.97 1310.93 0.31 0.3223 0.0078 0.0438 0.0010 283.7 6.01 276.4 5.96 TW01-8 191.06 372.5 0.51 0.3463 0.0101 0.0438 0.0010 301.9 7.58 276.3 6.38 TW01-9 292.29 294.14 0.99 0.3421 0.0102 0.0444 0.0011 298.8 7.73 280 6.53 TW01-10 99.79 354.71 0.28 0.3287 0.0093 0.0409 0.0010 288.5 7.14 258.4 5.96 TW01-11 408.08 804.03 0.51 0.3764 0.0095 0.0436 0.0010 324.4 7.02 275 6.06 TW01-12 49.69 106.02 0.47 0.4079 0.0170 0.0409 0.0012 347.4 12.27 258.2 7.6 TW01-13 133.16 156.37 0.85 0.4344 0.0141 0.0433 0.0011 366.3 10 273 6.93 TW01-14 81.57 213.17 0.38 0.5080 0.0149 0.0603 0.0015 417.1 10.03 377.7 8.81 TW01-15 291.58 308.2 0.95 0.3552 0.0104 0.0437 0.0010 308.6 7.79 275.7 6.45 TW01-16 252.32 605.27 0.42 0.3590 0.0094 0.0429 0.0010 311.5 7 270.7 6.04 TW01-17 660.33 1444.13 0.46 0.4373 0.0104 0.0461 0.0010 368.4 7.36 290.5 6.29 TW01-18 216.72 353.49 0.61 0.4315 0.0124 0.0451 0.0011 364.2 8.77 284.6 6.69 TW01-19 477.93 938.69 0.51 0.3581 0.0090 0.0457 0.0010 310.8 6.72 287.9 6.32 TW01-20 212.5 325.28 0.65 0.3001 0.0098 0.0413 0.0010 266.4 7.68 260.8 6.33 TW01-21 108.44 260.92 0.42 0.3980 0.0129 0.0456 0.0012 340.2 9.38 287.2 7.13 TW01-22 158.92 169.8 0.94 0.4177 0.0160 0.0467 0.0013 354.4 11.43 294 8.04 TW01-23 372.22 946.18 0.39 0.3493 0.0087 0.0449 0.0010 304.2 6.53 283.2 6.21 TW01-24 315.24 351.81 0.90 0.4617 0.0139 0.0457 0.0011 385.5 9.65 288.2 7.02 TW01-25 261.36 418.89 0.62 0.3418 0.0098 0.0458 0.0011 298.6 7.41 288.6 6.66 TW01-26 157.57 259.58 0.61 0.3533 0.0108 0.0458 0.0011 307.2 8.13 288.7 6.87 TW01-27 157.3 231.78 0.68 0.3569 0.0112 0.0456 0.0011 309.9 8.4 287.7 6.93 TW01-28 77.52 182.09 0.43 4.3637 0.1037 0.2902 0.0066 1705.5 19.64 1642.3 32.72 表 2 马山花岗岩体主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 2 Analytical data of major, trace, and rare earth elements of granite from Mashan
样品号
岩石名称P1/GS1
花岗质碎裂岩P1/GS3
花岗质碎岩P13/GS3
中粗粒花岗闪长岩P13/GS5
中粗粒花岗闪长岩P16/GS1、XT1
黑云母花岗闪长岩P16/GS2、XT2
黑云母花岗闪长岩SiO2 65.48 68.06 69.75 69.21 64.85 66.77 Al2O3 15.00 13.55 14.09 14.33 15.30 15.49 Fe2O3 1.40 1.13 1.95 2.08 3.41 3.01 FeO 3.44 3.02 1.68 1.75 2.22 1.88 TiO2 0.76 0.62 0.41 0.43 0.56 0.53 MgO 2.55 2.05 1.36 1.20 1.78 1.62 CaO 3.92 2.93 3.15 3.57 3.48 3.25 P2O5 0.16 0.16 0.07 0.09 0.12 0.12 K2O 1.90 2.71 2.40 2.29 2.21 1.90 MnO 0.09 0.07 0.07 0.08 0.08 0.07 Na2O 3.23 2.66 3.74 3.67 4.05 4.72 烧失量 1.55 3.72 0.82 0.54 1.60 1.29 总量 99.46 100.69 99.49 99.23 99.66 100.65 A/CNK 1.04 1.07 0.97 0.96 0.99 0.99 NK/A 0.49 0.54 0.62 0.59 0.59 0.63 σ 1.17 1.15 1.41 1.35 1.79 1.84 Rb 88.84 114.35 75.02 170.00 47.34 48.32 Ba 430.78 435.03 370.10 481.29 109.25 283.55 Th 12.55 13.66 8.49 17.14 6.92 4.94 U 2.10 1.30 1.44 3.79 1.68 1.40 Nb 13.36 11.54 5.78 12.36 5.75 4.42 Ta 1.18 1.20 0.62 1.28 0.64 0.49 Sr 255.42 139.70 209.88 195.36 291.65 226.93 Zr 143.82 72.81 127.41 374.10 196.08 185.01 V 101.52 64.53 71.65 23.01 78.67 64.00 Cr 54.31 43.16 22.04 21.90 18.38 22.06 Co 13.38 6.74 6.29 1.34 10.11 7.72 Cu 15.99 16.80 7.21 3.16 22.49 17.54 Zn 76.13 53.91 33.03 41.80 47.13 39.88 Ga 18.83 16.43 15.27 16.56 14.36 13.37 La 18.00 18.59 15.70 12.85 14.47 13.48 Ce 24.17 31.86 31.06 19.91 37.94 34.31 Pr 5.07 4.90 3.65 3.23 4.69 3.94 Nd 19.47 18.51 14.39 12.23 18.34 15.69 Sm 4.14 4.16 3.01 2.83 3.94 3.60 Eu 1.08 0.85 0.86 0.74 0.91 0.90 Gd 3.76 3.84 2.77 2.56 3.31 3.16 Tb 0.74 0.81 0.55 0.48 0.60 0.59 Dy 4.40 4.95 3.57 3.00 3.52 3.57 Ho 0.88 1.00 0.81 0.66 0.75 0.76 Er 2.80 3.34 2.57 2.21 2.08 2.10 Tm 0.40 0.55 0.37 0.34 0.34 0.33 Yb 2.49 3.19 2.70 2.06 2.29 2.28 Lu 0.40 0.45 0.38 0.33 0.36 0.36 Y 23.71 28.29 20.30 17.14 19.75 20.25 REE 111.51 125.29 102.69 80.57 113.29 105.31 LREE 71.93 78.87 68.67 51.79 80.29 71.91 HREE 39.58 46.42 34.02 28.78 33.00 33.39 LREE/HREE 1.82 1.70 2.02 1.80 2.43 2.15 (La/Yb)N 5.19 4.18 4.17 4.47 4.54 4.25 (La/Sm)N 2.81 2.88 3.37 2.93 2.37 2.42 (Gd/Yb)N 1.25 1.00 0.85 1.03 1.20 1.15 δEu 0.84 0.65 0.91 0.84 0.77 0.82 注:元素由中国冶金地质总局西北地质勘查院测试中心测定;δEu=EuN/SQRT(SmN∗GdN);主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素为10-6 -
聂凤军,江思宏,白大明, 等.北山地区金属矿床成矿规律及找矿方向[M].北京:地质出版社, 2002:1-408. 刘雪亚.甘肃北山区的钙碱系列岩浆活动及其与板块构造的关系[J].中国地质科学院院报, 1984,10:151-163. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB198403014.htm 左国朝,何国琦.北山板块构造及成矿规律[M].北京:北京大学出版社, 1990:1-226 穆志国,刘驰,黄宝玲,等.甘肃北山地区同位素定年与构造岩浆热事件[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版),1992,28(4):486-497. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ199204015.htm 穆志国,左国朝.甘肃北山古生代造山带地壳演化的同位素和稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 1994,30(2): 202-214. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ402.012.htm 孙桂英,张德全,徐洪林.格尔木-额济纳旗地学断面走廊域花岗岩类的地球化学特征与构造环境的判别[J].地球物理学报, 1995,38(s2):145-158. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX5S2.012.htm 于海峰, 陆松年, 梅华林, 等. 中国西部新元古代榴辉岩-花岗岩带和深层次韧性剪切带特征及其大陆再造意义[J].岩石学报, 1999,15(4): 532-328. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB199904004.htm 修勤业.甘肃北山地区花岗岩类地球化学特征及大地构造意义[J]. 前寒武纪研究进展, 1999,22(1):31-39. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ199901003.htm 梅华林,李惠民.甘肃柳园地区花岗质岩石时代及成因[J].岩石矿物学杂志,1999,18(1):14-17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW901.002.htm 徐保良,阎国翰, 陆凤香,等.北山-阿拉善地区二叠-三叠纪富碱侵入岩的岩石学特征[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2001,20(3):263-272. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200103007.htm 聂凤军,江思宏,刘妍,等.甘肃花牛山东钾长花岗岩40Ar/39Ar同位素年龄及其地质意义[J].地质科学, 2002,37(4):415-422. 聂凤军,江思宏,白大明,等.北山中南带海西-印支期岩浆活动与金的成矿作用[J].地球学报, 2003,24(5):415-422. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200305003.htm 江思宏,聂凤军,陈文,等.北山明水地区花岗岩时代的确定及其地质意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2003,22(2):107-111. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200302000.htm 江思宏,聂凤军,陈文,等.甘肃辉铜山铜矿床燕山期钾长花岗岩的发现及其地质意义[J].矿床地质, 2003,22(2):185-190. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200302009.htm 江思宏,聂凤军.北山地区花岗岩类成因的Nd同位素制约[J].地质学报, 2006,80(6):826-842. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200606005.htm 江思宏,聂凤军.北山地区花岗岩类的40Ar/39Ar同位素年代学研究[J].岩石学报, 2006,22(11):2719-2732. 戴霜,方小敏,张翔,等.北山中部地区闪长岩-花岗岩类成因及构造背景[J].兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2003,39(1):86-92. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDZK200301018.htm 赵泽辉,郭召杰,王毅.甘肃北山柳园地区花岗岩类的年代学、地球化学特征及构造意义[J].岩石学报, 2007,23(8):1847-1860. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200708006.htm 王立社,杨建国,谢春林,等.甘肃北山火石山哈儿根头口布花岗岩年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J].地质学报, 2009,83(3):377-387. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200903008.htm 江思宏.北山地区岩浆活动与金的成矿作用[D]. 中国地质科学院博士学位论文, 2004:1-175. 童英,王涛,洪大卫,等.北疆及邻区石炭-二叠纪花岗岩时空分布特征及其构造意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志,2010,29(6):619-641. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201006003.htm 冯继承,张文,吴泰然,等.甘肃北山桥湾北花岗岩体的年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版),2012,48(1): 61-70. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ201201011.htm 张文,冯继承,郑荣国,等.甘肃北山音凹峡南花岗岩体的LA-ICP MS定年及其构造意义[J].岩石学报,2011,27(6):1649-1661. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201106007.htm 朱江.北山造山带南带构造-岩浆建造与金多金属成矿[D]. 中国地质大学博士学位论文,2013:1-197. 陕亮,许荣科,郑有业,等.北山地区白山堂铜多金属矿区岩浆岩锆石LA-ICP MS U-Pb年代学及其地质意义[J].中国地质,2013,40(5):1600-1612. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201305023.htm 张新虎,苏犁,崔学军,等.甘肃北山造山带玉山钨矿成岩成矿时代及成矿机制[J].科学通报,2008,53(9):1077-1084. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200809017.htm 王银茹,黄满湘,赵亮,等.玉山钨矿岩石学特征及成矿关系[J].新疆地质,2011,29(2):217-221. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI201102021.htm 赵亮.甘肃金塔县玉山钨矿成矿规律及成矿预测研究[D]. 中南大学硕士学位论文,2010: 1-65. 龚全胜,刘明强,梁明宏,等.甘肃北山造山类型及基本特征[J]. 西北地质,2002,35(3):28-34. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI200203003.htm 何世平,任秉琛,姚文光,等.甘肃内蒙古北山地区构造单元划分[J]. 西北地质,2002,35(4):30-40. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI200204003.htm 刘雪亚,王荃.中国西部北山造山带的大地构造及其演化[J].地学研究, 1995,28:37-48. 张新虎.甘、青、蒙祁连山、北山造山带构造地层演化史[J],甘肃地质学报,1993,2(1): 80-86. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSDZ199301009.htm Horn L, Rudnick R L, Mcdonough W F. Precise elemental and isotope ratio determination by simultaneous solution nebulization and laser ablation-ICPMS: Application to U-Pb geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2000, 167:405-425. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(00)00229-1
Yuan H L, Gao S, Liu X M, et al. Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinations of zircon by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2004, 28(3):353-370. doi: 10.1111/ggr.2004.28.issue-3
Stacey J S, Kraners J D. Approximation of terrestrial lead isotope evolution by a two-stage model[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters.1975, 26(2):207-221. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(75)90088-6
Ludwig K R. User′s manual for Isoplot/Ex, version 3.00. A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J]. Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, 2003,4:1-70. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/284696948_User's_manual_for_a_geochronological_toolkit_for_Microsoft_Excel_IsoplotEx_version_30
Eric A K, Middelmost.Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J].Earth-Science Reviews,1994,37:215-224. doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(94)90029-9
Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. Tectionic discrimination in of granitoids[J]. Geological Society, Am. Bull.,1989, 1: 635-643.
Rickwood P C. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides for major and minor element[J]. Lithos, 1989,22: 246-263.
路远发.Geokit:一个用VBA构建的地球化学工具软件包[J].地球化学,2004,33(5):459-464. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200405003.htm Sun S S, Macdonough W F.Chemical and isotopic systematics of ocean basalts: Implations for mantle composition and processes[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society,London,Special Publications, 1989,42(1):313-345.
Pearce J A, Harris N B L, Tindle A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of the granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984,25: 956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
张旗,王焰,李承东,等.花岗岩按照压力的分类[J],地质通报,2006, 25(11):1274-1278. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=2006011236&journal_id=gbc 李锦轶,张进,杨天南,等.北亚造山区南部及其毗邻地区地壳构造分区与构造演化[J].吉林大学学报, 2009,39(4):584-605. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200904002.htm 龚全胜,刘明强,梁明宏,等.北山造山带大地构造相及构造演化[J]. 西北地质, 2003,36(1):11-17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI200301002.htm 何世平,周会武,任秉琛,等.甘肃内蒙古北山地区古生代地壳演化[J].西北地质, 2005,38(3):6-15. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI200503001.htm 毛启贵.北山及邻区古生代-早古生代增生与碰撞大地构造格架[D].中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所博士学位论文,2008. 肖文交,舒良树,高俊,等.中亚造山带大陆动力学过程与成矿作用[J].新疆地质,2008,23:599-603. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI200801005.htm Xiao W J, Windley B F, Huang B C, et al. Paleozoic multiple accretionary and collisional processes of the Beishan orogenic collage[J]. American Journal of Science, 2010, 310:1553-1594. doi: 10.2475/10.2010.12
Guo Q Q, Xiao W J, Brian F, et al. Provenance and tectonic settings of Permian turbidites from the Beishan mountains, NW China: Implications for the Late Paleozoic accretionary tectonics of the southern Altaids[J]. Journal of the Asian Earth Sciences,2012,49:54-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.03.013
姜常义,程松林,叶书锋,等.新疆北山地区中坡山北镁铁质岩体岩石地球化学与岩石成因[J].岩石学报, 2006,22(1):115-126 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200601012.htm 赵泽辉,郭召杰,韩宝福,等.新疆东部-甘肃北山地区二叠纪玄武岩对比研究及其构造意义[J].岩石学报, 2006,22(5):1279-1293. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200605019.htm 刘明强,龚全胜,梁明宏.甘肃北山地区音凹峡多旋回裂谷带[J].甘肃地质学报, 1999,8(2):15-22. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSDZ199902002.htm 吴泰然.花岗岩及其形成的大地构造环境[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版), 1995,31(3):358-365. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ503.012.htm



 下载:
下载: