The progress in the study of the Boroo gold deposit in Mongolia
-
摘要:
博洛(Boroo)金矿是蒙古国发现的首个岩金矿床,同时也是该国开采规模与黄金产量最大的金矿。该矿矿体主要产于博洛近水平断裂带内,整个矿化带(Au异常≥100×10-9) 长度超过2000m,宽度400m,局部厚度达100m,主要围岩为博洛花岗杂岩、变质沉积岩等。矿床主要矿化类型有金-硫化物、金-石英脉型矿化2种,与中国典型超大型造山型金山金矿具有较多相似点,判定其为造山型金矿。距博洛金矿35km处产出同类型且储量相近的大型金矿-盖特苏尔特(Gatsuurt)。在已有研究的基础上,从产出环境、地质特征、矿床成因等方面对其进行了介绍和总结,并在矿床邻区内划定3个找矿战略靶区,这对中国企业在蒙古寻找同类型金矿具有指导意义。
Abstract:The Boroo gold deposit, located in northern Khentei gold ore belt, is the first hard rock gold deposit discovered in Mongolia, and its scale of mining and the gold production are also the largest (averagely 3.52g/t gold, with total produced gold reaching 66t). The deposit is hosted in the Boroo fault, a nearly flat-lying fault zone. The total combined length of the mineralization zone (anomalous gold values≥100ppb) is more than 2500m, the width is at least 400m, and the thickness is locally as large as 100m. This area is underlain by granitoids of the Boroo Complex and metasedimentary rocks. Two main types of mineralization have been recognized in the Boroo gold deposit:the gold-sulfide type and the gold-quartz vein type. A comparison of the Boroo deposit with China's Jinshan gold deposit shows that there exist many similarities between these two deposits, and hence the authors consider that the Boroo gold deposit is an orogenic gold deposit. Meanwhile, there is another large-sized gold deposit called Gatsuurt gold deposit 35km away from the Boroo deposit, which shares the same deposit type and equal ore reserves. On the basis of previous researches, the authors have made a detailed summarization in the aspects of production environment, geological characteristics, and genesis of the deposit. This paper provides useful information for Chinese companies' prospecting for the same type gold deposits; in addition, three strategic targets in the adjacent areas of Boroo have been delineated.
-
Keywords:
- North Khentei gold ore belt /
- orogenic gold deposit /
- Boroo gold deposit /
- Mongolia
-
中亚造山带是世界上最大的古生代增生带和最大的显生宙大陆地壳生长带[1-7], 是一个持续俯冲增生造山带[8-10]。北山造山带作为中亚造山带的重要组成部分(图 1-a),是研究和支撑中亚造山带古生代构造格局的关键地区[12]。
![]() 图 1 北山造山带蛇绿岩时空分布(a)和中亚造山带构造简图(b)(据参考文献[11]修改)Figure 1. Temporal and spatial distribution of ophiolites in the Beishan orogenic belt(a) and structural sketch map of the Central Asian orogenic belt(b)
图 1 北山造山带蛇绿岩时空分布(a)和中亚造山带构造简图(b)(据参考文献[11]修改)Figure 1. Temporal and spatial distribution of ophiolites in the Beishan orogenic belt(a) and structural sketch map of the Central Asian orogenic belt(b)内蒙古北山地区位于中亚造山带南缘,西邻东天山,东接阿拉善,其大地构造位置较复杂[13-16]。经历了多阶段的俯冲拼贴过程,形成了从南向北依次出露的柳园-账房山、洗肠井-白云山-牛圈子-红柳河、小黄山-芨芨台子、红石山-百合山等多条蛇绿混杂岩带(图 1-b),前人对不同的蛇绿岩进行了研究,获得了丰富的资料[17-24]。近年的研究资料表明,北山造山带中部的洗肠井-白云山-牛圈子-红柳河蛇绿岩最早形成于寒武纪[13, 20, 25],奥陶纪向北强烈俯冲[10]。对于早泥盆世的构造属性,存在柳园蛇绿岩向北俯冲[26-28]、同碰撞或弧陆拼贴[29]、造山后伸展[30]等多种认识,泥盆纪岩浆岩成为研究古生代洋陆转化的重要载体之一。然而,前人的研究集中在花岗岩类,对火山岩的研究很少。李向民等[31]及Guo等[26]报道了在牛圈子地区的志留纪—泥盆纪三个井组火山岩,该火山岩地层的东西向延伸、区域对比亟需进一步研究。
鉴于此,本文以最新的1:5万填图资料及测试数据为基础,通过岩石学、岩石地球化学、锆石Lu-Hf同位素等特征的综合分析,对白云山南侧三个井组火山岩的时代归属进行重新厘定,研究其岩石成因及形成的大地构造环境,为探讨白云山洋盆的闭合时限提供重要的依据。
1. 区域地质
白云山东距额济纳旗约250 km,东临月牙山-洗肠井蛇绿构造混杂岩带,西部为牛圈子蛇绿岩带(图 1)。白云山蛇绿岩带呈北西西向带状展布,东西长约26 km,南北宽2~4.5 km。下部主要出露橄榄岩、辉橄岩、二辉橄榄岩等超基性杂岩,普遍蛇纹石化,构造混杂岩带强糜棱岩化,辉长岩和斜长花岗岩呈岩株状侵出地表;上部为红褐色-紫红色含放射虫硅质岩,构造作用强烈,多呈岩块分布于蛇绿构造混杂岩带中,表现出远洋沉积的特征并被后期辉绿岩脉侵入。蛇绿构造混杂岩带北部为晚奥陶世白云山组弧前盆地沉积建造及中志留世石英闪长岩,被认为是哈萨克斯坦板块与塔里木板块之间大洋俯冲的产物[13]。混杂岩带南部出露二叠纪、泥盆纪侵入体,地层主要为被动陆缘沉积的晚奥陶世锡林柯博组,主要岩性为灰绿色变质长石岩屑砂岩、灰绿色变质长石石英砂岩、灰褐色白云岩等,被敦煌地块中新元古界碳酸盐岩沉积盖层逆冲掩覆。研究区三个井组是从前人认为的横峦山群中新识别而来的,与北侧的锡林柯博组呈断层接触,岩石组合主要为一套凝灰质长石岩屑砂岩、凝灰质粉砂岩、硅质粘土岩夹基性-中基性火山岩。火山岩主要由玄武岩、玄武安山岩、流纹质凝灰岩等组成,玄武岩以层状构造为主,部分发育枕状构造及气孔杏仁状构造(图 2-a)。
![]() 图 2 月牙山幅地质简图(a)和三个井组PM06实测剖面(b)①a图:1—中、新元古界;2—寒武纪—奥陶纪西双鹰山组;3—晚奥陶世锡林克博组;4—晚奥陶世白云山组;5—早泥盆世三个井组二段;6—晚泥盆世墩墩山组;7—早白垩世赤金堡组;8—新近系;9—第四系;10—白云岩透镜体;11—蛇绿岩带;12—超基性岩块;13—花岗闪长岩;14—石英闪长岩脉;15—闪长岩脉;16—断层;17—PM06剖面位置;b图:1—安山质晶屑凝灰岩;2—长石岩屑砂岩;3—凝灰质长石岩屑砂岩;4—杏仁状安山岩;5—玄武岩;6—流纹斑岩;7—闪长岩;8—硅质白云岩;9—结晶灰岩;10—安山岩;11—断层破碎带;12—不整合界线;13—产状;14—采样位置Figure 2. Geological map of Yueyashan Sheet(a)and measured profile PM06 of Sangejing Formation(b)
图 2 月牙山幅地质简图(a)和三个井组PM06实测剖面(b)①a图:1—中、新元古界;2—寒武纪—奥陶纪西双鹰山组;3—晚奥陶世锡林克博组;4—晚奥陶世白云山组;5—早泥盆世三个井组二段;6—晚泥盆世墩墩山组;7—早白垩世赤金堡组;8—新近系;9—第四系;10—白云岩透镜体;11—蛇绿岩带;12—超基性岩块;13—花岗闪长岩;14—石英闪长岩脉;15—闪长岩脉;16—断层;17—PM06剖面位置;b图:1—安山质晶屑凝灰岩;2—长石岩屑砂岩;3—凝灰质长石岩屑砂岩;4—杏仁状安山岩;5—玄武岩;6—流纹斑岩;7—闪长岩;8—硅质白云岩;9—结晶灰岩;10—安山岩;11—断层破碎带;12—不整合界线;13—产状;14—采样位置Figure 2. Geological map of Yueyashan Sheet(a)and measured profile PM06 of Sangejing Formation(b)2. 岩石学特征
枕状玄武岩:中等风化程度,风化面呈灰色-灰绿色,新鲜面呈深灰色-灰色,局部枕状构造明显,表面常见小气孔。主要矿物组成为斜长石+辉石(75%),暗色矿物(25%),岩石由斑晶、基质组成。斑晶主要由矿物假象组成,粒径约1 mm,零星分布,后期被帘石交代呈假象产出,含量约为2%。基质由斜长石、暗色矿物组成,粒径小于0.2 m。斜长石呈板条状,长轴多显定向排列,略显残余间粒结构,后期具帘石化、粘土化、褐铁矿化、碳酸盐化、次闪石化;暗色矿物后期多具帘石化、褐铁矿化、次闪石化呈假象产出。岩内可见被硅质、褐铁矿、少量碳酸盐矿物充填的微裂纹。
气孔-杏仁状玄武岩:风化作用较强,风化面和新鲜面都为深灰色,岩内未见斑晶。岩石由斜长石、辉石和暗色矿物组成,斜长石含量约为65%,辉石含量约20%,暗色矿物约为15%。斜长石呈半自形板状、板条状,粒径为0.1~1 mm,长轴定向排列,显交织结构,后期具粘土化、绢云母化、碳酸盐化、褐铁矿化。暗色矿物后期具帘石化、褐铁矿化、碳酸盐化、绿泥石化,呈假象产出,杂乱分布于斜长石间。岩内多见被碳酸盐、硅质、帘石充填的杏仁体,呈云朵状、不规则状,大小为0.5~10 mm,长轴多显定向排列,岩内另见被碳酸盐矿物充填的裂隙。杏仁体占岩石体积的10%~15%。
3. 实验方法
用于岩石地球化学研究的玄武岩样品采自白云山一带锡林柯博组南部三个井组剖面(PM06)(图 2-b),样品采集过程中避开脉体发育地段。样品分别进行主量和微量元素测试。样品磨碎至200目后,在中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心实验室进行主量和微量元素分析测试。主量元素使用X-射线荧光光谱仪(XRF-1500)法测试,误差优于2%~3%。微量及稀土元素利用酸溶法制备样品,使用ICP-MS(ElementⅡ)测试,分析误差优于10%。化学分析测试流程见参考文献[32-33]。
本次选取(PM06)实测剖面中的气孔状玄武岩样品(4206-1),采样位置为北纬98°29′44″、东经41°32′36″。锆石分选由河北省廊坊诚信地质服务有限公司完成,首先进行粉碎分选,分选出的锆石在双目镜下挑选,选择透明度较高、晶形较完好且内部无裂隙具有代表性的锆石进行制靶,锆石阴极发光图像制备、制靶工作由北京锆年领航科技有限公司完成。通过反射光、透射光及阴极发光图像综合分析,选择晶形好、环带清晰的锆石样品进行测试。锆石LA-ICP-MS测试在天津地质调查中心实验室完成,利用激光剥蚀等离子体质谱仪(LA-ICP-MS)进行锆石U-Pb同位素测试。
激光剥蚀系统为New Wave UP213,ICP-MS为布鲁克M90。激光剥蚀过程中采用氦气作载气、氩气为补偿气以调节灵敏度,二者在进入ICP之前通过一个Y型接头混合。每个时间分辨分析数据包括20~30 s的空白信号和50 s的样品信号。对分析数据的离线处理(包括对样品和空白信号的选择、仪器灵敏度漂移校正、元素含量及U-Th-Pb同位素比值和年龄计算)采用软件ICPMSDataCal[34]完成。锆石样品的U-Pb谐和图绘制和年龄加权平均计算均采用Isoplot/Ex_ver3[35]完成。本次测试剥蚀直径根据实际情况选择25 μm。
锆石Hf同位素组成的分析是在阴极发光(CL)图像分析和锆石U-Pb定年的基础上进行的,分析前将锆石再次清洗干净并晾干。测试在天津地质调查中心实验室ThermoFinnigan Neptune型多接收电感耦合等离子质谱仪MC-ICP-MS上进行,各颗粒分析点的位置与锆石U-Pb分析的位置相同,激光频率为8 Hz,束斑直径为44 μm,信号采集时间26 s,详细分析流程见参考文献[36]。在计算初始176 Hf/177Hf值时,Lu的衰变常数采用1.867×10-11a-1[37],εHf值的计算采用[38]推荐的球粒陨石Hf同位素值,176 Lu/177Hf = 0.0336,176Hf/177Hf = 0.282785。在Hf单阶段模式年龄计算中,亏损地幔176Hf/177Hf现在值采用0.28325,176Lu/177Hf采用0.0384[39],两阶段模式年龄计算时采用平均地壳的176Lu/177Hf = 0.015[40]。
4. 分析结果
4.1 主量元素
白云山地区三个井组玄武岩的主量元素分析结果见表 1,SiO2含量为41.48%~48.36%,平均为46.03%,Na2O为2.93%~3.75%,平均为3.27%,K2O质量分数变化较大,为0.08%~2.06%,可能反映岩石后期变质较强。TiO2含量为1.76%~2.66%,平均为2.10%,Al2O3含量较高为14.55%~16.55%,平均为15.43%,FeO含量较高,为3.58%~6.13%,平均为5.22%。Fe2O3含量为2.74%~7.06%,平均为4.60%。Mg#值为43.19~67.93,平均为56.71,明显低于原生岩浆范围(Mg#=68~75)[41],同样低于典型的MORB的Mg#[42],表明岩浆经历了结晶分异作用。
表 1 三个井组玄武岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果Table 1. Geochemical data of major, trace elements and REE for Sangejing Formation basalt样号 P6YQ18-1 P6YQ25-1 P6YQ25-2 YQ4206-1 SiO2 41.48 48.36 46.87 47.41 Al2O3 16.55 14.92 14.55 15.68 Fe2O3 2.74 4.24 7.06 4.37 FeO 5.34 5.82 3.58 6.13 CaO 11.50 11.82 11.89 9.28 MgO 2.83 6.08 6.37 6.84 K2O 2.06 0.45 0.20 0.08 Na2O 3.75 2.93 3.12 3.28 TiO2 2.66 1.76 1.98 1.99 P2O5 0.47 0.21 0.22 0.24 MnO 0.13 0.16 0.19 0.15 灼失量 9.91 2.61 2.99 3.87 总计 99.42 99.36 99.02 99.32 Mg# 43.19 56.96 58.77 67.93 Hf 5.73 3.55 4.06 4.21 Zr 213 124 137 142 Cr 154 211 239 236 Ni 57.00 73.60 93.70 73.80 Ga 22.50 19.20 20.40 19.10 Rb 29.40 6.22 5.20 1.84 Sr 230 476 478 371 Y 282 267 32.2 392 Nb 18.50 8.05 9.61 9.39 Cs 2.29 0.13 0.24 0.15 Ba 173 554 237 94.4 Ta 1.35 0.63 0.74 0.68 Pb 1.94 1.83 2.12 2.18 Th 1.93 1.20 1.14 1.05 U 0.94 0.31 0.31 0.33 La 18.30 9.90 10.40 14.60 Ce 41.80 23.90 24.50 20.80 Pr 6.07 3.63 3.70 4.25 Nd 27.40 17.60 18.20 18.60 Sm 6.90 4.85 4.97 5.15 Eu 2.22 1.75 1.74 1.65 Gd 7.63 5.73 4.97 5.49 Tb 1.30 1.00 1.02 0.92 Dy 7.70 6.22 6.37 5.99 Ho 1.50 1.23 1.28 1.26 Er 3.88 3.31 3.39 3.46 Tm 0.56 0.48 0.51 0.52 Yb 3.61 3.30 3.35 3.39 Lu 0.54 0.50 0.51 0.50 ∑LREE 102.69 61.63 63.51 65.05 ∑HREE 26.72 21.77 21.4 21.53 LREE/HREE 3.84 2.83 2.97 3.02 (La/Yb)N 3.42 2.02 2.09 2.9 δEu 0.94 1.02 1.07 0.95 Nb/Y 0.50 0.26 0.30 0.54 ΔNb 0.79 0.86 0.01 0.97 注:Mg#=100×Mg/(Mg+Fe),△Nb=1.74+lg(Nb/Y)-1.92×lg(Zr/Y);主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 本次采集的4个三个井组火山岩样品,在火山岩TAS图解(图 4-a)上有3件落入玄武岩区域。Pearce提出的Nb/Y-Zr/TiO2×10-4图解被认为是划分蚀变、变质火山岩系列的有效图解[44]。由图 4-b可以看出,全部样品落入亚碱性玄武岩区域。进一步通过AFM图解(图 5)可知,亚碱性玄武岩基本为拉斑玄武岩系列。
![]() 图 4 火山岩TAS图解(a)[43]和玄武岩Nb/Y-TiO2×10-4图解(b)Pc—苦橄玄武岩;B—玄武岩;O1—玄武安山岩;O2—安山岩;O3—英安岩;R—流纹岩;S1—粗面玄武岩;S2—玄武质粗面安山岩;S3—粗面安山岩;T—粗面岩、粗面英安岩;F—副长石岩;U1—碱玄岩、碧玄岩;U2—响岩质碱玄岩;U3—碱玄质响岩;Ph—响岩;Ir—Irvine分界线,上方为碱性,下方为亚碱性Figure 4. TAS diagram for volcanic rock(a)and Nb/Y-TiO2×10-4 diagram for basalts(b)
图 4 火山岩TAS图解(a)[43]和玄武岩Nb/Y-TiO2×10-4图解(b)Pc—苦橄玄武岩;B—玄武岩;O1—玄武安山岩;O2—安山岩;O3—英安岩;R—流纹岩;S1—粗面玄武岩;S2—玄武质粗面安山岩;S3—粗面安山岩;T—粗面岩、粗面英安岩;F—副长石岩;U1—碱玄岩、碧玄岩;U2—响岩质碱玄岩;U3—碱玄质响岩;Ph—响岩;Ir—Irvine分界线,上方为碱性,下方为亚碱性Figure 4. TAS diagram for volcanic rock(a)and Nb/Y-TiO2×10-4 diagram for basalts(b)![]() 图 5 AFM图解[45]Figure 5. AFM diagram
图 5 AFM图解[45]Figure 5. AFM diagram4.2 稀土和微量元素
白云山地区蛇绿混杂岩带南侧三个井组玄武岩稀土元素分析结果见表 1。稀土元素总量(∑REE)为83.40×10-6~129.41×10-6, 平均为96.08×10-6,其中轻稀土元素(∑LREE)为67.36×10-6~110.32×10-6,平均为79.18×10-6,重稀土元素(∑HREE)为16.04×10-6~19.09×10-6,平均为16.90×10-6,轻、重稀土元素分馏明显,LREE/HREE值为4.17~5.78,平均为4.64,轻稀土元素较重稀土元素明显富集。(La/Yb)N值为2.15~3.64,稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线整体呈现轻稀土元素富集的右倾型(图 6-a),显示岛弧玄武岩的地球化学特征。δEu值为0.94~1.07,没有明显的Eu异常,表明没有发生斜长石结晶分异作用。
微量元素分析结果见表 1。Nb/Y值为0.26~0.54,主体小于1,是源区低压熔融的结果[33]。微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(图 6-b)显示,大离子亲石元素具有强烈的分异特征,Rb、Ba、Th、U、K等大离子亲石元素变化较大,可能与海相玄武岩形成时遭受海水热液蚀变及后期绿泥石、透闪石蚀变有关[48]。高场强元素整体含量变化不大,Nb等高场强元素呈亏损的特征。
4.3 锆石U-Pb年龄
本次分析获得32个测点的数据(表 2),由锆石阴极发光图像(图 7)可知,锆石颗粒多为暗黑,大部分锆石具有清晰的岩浆振荡环带。Th/U值介于0.06~1.62之间,绝大多数大于0.4,说明绝大多数锆石为岩浆成因[49-51]。玄武岩锆石通常为自形-半自形的板柱状或不具有韵律生长环带的浑圆状、不规则状。由CL图像可知,本次挑选的32颗锆石不完全属于玄武岩锆石,如15、16、19、25、30号等均属于花岗岩类的锆石,所以最终挑选出9颗玄武岩锆石进行研究(图 8-a)。
表 2 三个井组玄武岩样品(4206-1)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb数据Table 2. LA-ICP-MS zircons U-Th-Pb data of Sangejing Formation basalt(4206-1)测点号 Th/10-6 U/10-6 Pb/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 4206.1.01 86 105 7 0.82 0.057 0.002 0.494 0.014 0.057 0.002 484 58 408 11 394 4 4206.1.02 100 195 13 0.52 0.057 0.002 0.501 0.017 0.057 0.002 471 80 413 14 402 5 4206.1.03 105 998 34 0.11 0.053 0.001 0.266 0.006 0.053 0.001 329 30 240 5 231 4 4206.1.04 91 125 9 0.73 0.055 0.002 0.486 0.014 0.055 0.002 430 62 402 12 397 4 4206.1.05 19 62 4 0.31 0.053 0.003 0.469 0.026 0.053 0.003 326 120 390 21 401 5 4206.1.06 57 115 7 0.50 0.054 0.005 0.416 0.041 0.054 0.005 383 221 353 35 349 4 4206.1.07 147 116 6 1.26 0.052 0.002 0.304 0.012 0.052 0.002 270 86 270 10 270 3 4206.1.08 88 300 19 0.29 0.056 0.001 0.492 0.010 0.056 0.001 465 43 406 8 396 4 4206.1.09 140 182 13 0.77 0.055 0.002 0.487 0.018 0.055 0.002 397 84 403 15 404 4 4206.1.10 66 82 4 0.80 0.052 0.002 0.321 0.015 0.052 0.002 263 107 282 13 285 3 4206.1.11 90 172 12 0.52 0.055 0.001 0.496 0.012 0.055 0.001 424 51 409 10 406 4 4206.1.12 418 555 40 0.75 0.056 0.001 0.504 0.007 0.056 0.001 457 28 414 6 406 4 4206.1.13 51 246 115 0.21 0.163 0.002 0.109 0.156 0.163 0.002 2486 19 2445 38 2396 30 4206.1.14 383 294 23 1.30 0.057 0.001 0.495 0.009 0.057 0.001 485 37 409 7 395 4 4206.1.15 65 110 7 0.59 0.056 0.003 0.490 0.030 0.056 0.003 461 135 405 25 395 4 4206.1.16 133 162 10 0.82 0.054 0.001 0.398 0.010 0.054 0.001 387 52 340 8 333 4 4206.1.17 135 282 18 0.48 0.055 0.002 0.468 0.014 0.055 0.002 396 66 390 11 388 4 4206.1.18 538 332 206 1.62 0.166 0.002 0.910 0.144 0.166 0.002 2521 19 2515 33 2509 25 4206.1.19 223 587 38 0.38 0.056 0.001 0.493 0.009 0.056 0.001 449 39 407 8 399 4 4206.1.20 40 56 4 0.72 0.057 0.002 0.496 0.022 0.057 0.002 499 94 409 18 393 4 4206.1.21 44 58 4 0.76 0.056 0.003 0.483 0.027 0.056 0.003 460 119 400 22 390 4 4206.1.22 261 337 13 0.77 0.052 0.001 0.259 0.006 0.052 0.001 286 43 234 5 229 3 4206.1.23 122 226 75 0.54 0.110 0.001 4.704 0.062 0.110 0.001 1791 21 1768 23 1748 17 4206.1.24 257 710 46 0.36 0.056 0.001 0.486 0.008 0.056 0.001 431 34 402 7 397 4 4206.1.25 136 175 12 0.78 0.058 0.001 0.491 0.011 0.058 0.001 519 45 406 9 386 4 4206.1.26 176 623 38 0.28 0.056 0.001 0.488 0.007 0.056 0.001 464 27 403 6 393 4 4206.1.27 198 558 36 0.35 0.056 0.001 0.496 0.008 0.056 0.001 447 30 409 6 402 4 4206.1.28 87 215 14 0.41 0.058 0.001 0.502 0.011 0.058 0.001 518 41 413 9 395 4 4206.1.29 152 424 27 0.36 0.056 0.001 0.496 0.007 0.056 0.001 468 28 409 6 399 4 4206.1.30 249 399 31 0.62 0.056 0.001 0.496 0.012 0.056 0.001 448 44 409 9 402 4 4206.1.31 17 280 95 0.06 0.116 0.001 5.523 0.073 0.116 0.001 1900 21 1904 25 1908 19 4206.1.32 661 1208 137 0.55 0.068 0.001 1.029 0.016 0.068 0.001 882 24 718 11 667 8 4206-1样品中9颗玄武岩锆石的测试结果显示,9颗锆石的数据点都位于谐和线上或附近(图 8-b),其206Pb/238U年龄值明显分为2组,第一组7颗锆石的206Pb/238U年龄介于393~406 Ma之间,年龄加权平均值为396.6±3.3 Ma(MSWD=1.9)(图 8-b);第二组为270 Ma、285 Ma两个较年轻的锆石年龄。通过分析认为,数据较多且较集中的第一组年龄是玄武岩的岩浆结晶年龄,即早泥盆世,而第二组2个年轻的年龄可能是后期混入的岩浆碎屑锆石。
4.4 锆石Lu-Hf同位素
本次对白云山一带三个井组玄武岩U-Pb年龄测定的样品进行了锆石Lu-Hf同位素测试,测点尽量与U-Pb年龄测定位置相同或靠近,结果见表 3。通过5个点的测定,εHf(t)=+4.67~+8.02,176Hf/177Hf=0.282662~0.282762;一阶段锆石Hf模式年龄tDM1=692~826 Ma。
表 3 三个井组玄武岩锆石Lu-Hf同位素数据Table 3. Lu-Hf isotope data of Sangejing Formation basalt测点号 t/Ma 176Yb/177Hf 176Lu/177Hf 176Hf/177Hf 176Hf/177Hfi 2σ εHf(0) εHf(t) tDM1/Ma tDM2/Ma fLu/Hf 4206.01.11 406 0.020250 0.000876 0.282678 0.282672 0.000029 -3.31 5.40 811 1052 -0.97363 4206.01.14 395 0.017497 0.000782 0.282692 0.282686 0.000029 -2.82 5.67 789 1026 -0.97646 4206.01.20 393 0.013875 0.000589 0.282664 0.282660 0.000027 -3.82 4.68 825 1087 -0.98225 4206.01.21 390 0.019975 0.000787 0.282762 0.282756 0.000069 -0.36 8.02 692 873 -0.97630 4206.01.28 395 0.012072 0.000507 0.282662 0.282658 0.000022 -3.90 4.67 826 1090 -0.98474 5. 讨论
5.1 火山岩地层形成时代及归属讨论
白云山地区“横峦山群或咸水湖组”的时代及地层归属一直备受争议②[52]。甘肃省第二区测队1972年开展石板井幅1:20万区测时,依据岩石组合特征,将该套火山岩划分为横峦山群;甘肃地质力学测量队1977年、1979年开展五道明幅、黑鹰山幅、六驼山幅1:20万区测时,又将该套火山岩划分为咸水湖群。李文国等[52]通过对比研究,认为北山地区该套火山岩地层仍属于咸水湖组,同样缺乏确凿证据。尽管本次研究的该套火山岩与前人划分的横峦山群或咸水湖组火山岩的岩性组合、颜色具有相似性,然而,本次获得玄武岩锆石206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值为396.6±3.3 Ma(MSWD=1.9),属早泥盆世,并非前人划分的中奥陶世。前人在甘肃北山红柳园地区测得三个井组火山岩形成于420±15 Ma,所以将红柳园地区蛇绿岩带南侧的三个井组时代更新为晚志留世[31, 53],红柳园地区三个井组岩石组合为杏仁玄武岩、凝灰质砂岩夹粉砂岩及灰岩透镜体砾岩;白云山地区三个井组一段为灰黑色玄武岩、灰黑色细砂岩夹薄层灰白色-浅灰色灰岩、硅质岩等,二段为灰绿色长石岩屑细砂岩、中细砂岩夹复成分砾岩、灰岩透镜体、灰绿色枕状玄武岩、晶屑凝灰岩等。从年代学及岩石组合看,二者极相似,笔者认为,白云山一带所谓的横峦山群或咸水湖组应划分为下泥盆统三个井组。
5.2 构造环境
北山造山带是天山-兴蒙造山带的关键枢纽地带[20],该地区经历了南华纪前大陆地壳基底演化、超大陆裂解和洋壳演化、碰撞期后板内伸展-陆内叠覆造山4个演化阶段[54]。研究区蛇绿岩岩块仅出露于晚奥陶世锡林柯博组中,在三个井组未发现蛇绿岩岩块,因此蛇绿岩就位于早泥盆世之前,三个井组可能为洋盆闭合后伸展背景下形成。而且,本文厘定的三个井组拉斑玄武岩与区域大面积出露的泥盆纪S型、A型花岗岩[29]在空间上紧密伴生,在区域上并未发现同时代的安山岩等中性岩浆活动,即SiO2含量存在明显的Daly间断。由此可见,北山造山带中部早泥盆世为伸展构造背景。
地球化学特征是判别火山岩形成环境的重要标志之一。对于发生蚀变或弱变质作用的火山岩,使用在蚀变和变质作用过程中受影响最小、稳定性较好的Zr、Th、Nb、Ta、Y等高场强元素进行构造环境判别比较有效。玄武岩构造环境Nb/Zr-Th/Zr判别图解(图 9)显示,玄武岩具有裂谷背景的地球化学特征,TiO2/Al2O3-Zr/Al2O3及Zr/TiO2-Ce/P2O5构造环境判别图解(图 10)显示,玄武岩投点位于后碰撞弧范围,判别图解显示的弧岩浆岩地球化学特征与稀土元素配分曲线显示的岛弧玄武岩配分曲线特征吻合。综上所述,三个井组玄武岩形成于伸展的构造背景,源区具有岛弧玄武岩的部分特征。
![]() 图 9 玄武岩大地构造环境Nb/Zr-Th/Zr双对数判别图[55]Ⅰ—大洋板块发散边缘N-MORB区; Ⅱ—板块汇聚边缘(Ⅱ1—大洋岛弧玄武岩区; Ⅱ2—陆缘岛弧及陆缘火山弧玄武岩区); Ⅲ—大洋板内(洋岛、海山玄武岩区、T-MORB、E-MORB区); Ⅳ—大陆板内(Ⅳ1—陆内裂谷及陆缘裂谷拉斑玄武岩区; Ⅳ2—大陆拉张带(或初始裂谷)玄武岩区; Ⅳ3—陆-陆碰撞带玄武岩区); Ⅴ—地幔热柱玄武岩区Figure 9. Th /Zr and Nb /Zr double logarithmic plot for identification of tectonic settings for basalts
图 9 玄武岩大地构造环境Nb/Zr-Th/Zr双对数判别图[55]Ⅰ—大洋板块发散边缘N-MORB区; Ⅱ—板块汇聚边缘(Ⅱ1—大洋岛弧玄武岩区; Ⅱ2—陆缘岛弧及陆缘火山弧玄武岩区); Ⅲ—大洋板内(洋岛、海山玄武岩区、T-MORB、E-MORB区); Ⅳ—大陆板内(Ⅳ1—陆内裂谷及陆缘裂谷拉斑玄武岩区; Ⅳ2—大陆拉张带(或初始裂谷)玄武岩区; Ⅳ3—陆-陆碰撞带玄武岩区); Ⅴ—地幔热柱玄武岩区Figure 9. Th /Zr and Nb /Zr double logarithmic plot for identification of tectonic settings for basalts![]() 图 10 三个井组玄武岩TiO2/Al2O3-Zr/Al2O3图解(a)和Zr/TiO2-Ce/P2O5图解(b)[56]WIP—板内;CAP—陆弧;PAP—后碰撞弧;IOP—初始洋弧;LOP—晚期洋弧Figure 10. TiO2/Al2O3-Zr/Al2O3 (a)and Zr/TiO2-Ce/P2O5 (b)diagrams of Sangejing Formation basalts
图 10 三个井组玄武岩TiO2/Al2O3-Zr/Al2O3图解(a)和Zr/TiO2-Ce/P2O5图解(b)[56]WIP—板内;CAP—陆弧;PAP—后碰撞弧;IOP—初始洋弧;LOP—晚期洋弧Figure 10. TiO2/Al2O3-Zr/Al2O3 (a)and Zr/TiO2-Ce/P2O5 (b)diagrams of Sangejing Formation basalts5.3 岩石成因
锆石的Lu-Hf同位素体系有很高的封闭温度,且相对于U-Pb同位素体系更不易被后期流体、热事件改造[57],使得锆石可以记录岩浆源区的信息。因此,采用Hf同位素研究岩浆的来源。
三个井组玄武岩εHf(t)为较高的正值(+4.67~+8.02),为地幔物质部分熔融的产物。在t-176Hf/177Hf图解(图 11-a)上,数据点落入球粒陨石Hf同位素演化线和亏损地幔之间区域,相对集中,且tDM1=692~826 Ma,表明三个井组玄武岩源区主要为新元古代亏损地幔。其微量元素Ni(154.00×10-6~522.00×10-6)和Cr(57.00×10-6~453.00×10-6)含量主体低于原始岩浆的参考数值[58](Ni≈250.00×10-6、Cr≈300.00×10-6),仅有1个样品Ni、Cr含量高于该参考值,表明该玄武岩浆早期演化过程中可能发生过橄榄石、辉石的结晶分离作用,这与该区玄武岩较低的Mg#值吻合。研究表明,Dy/Yb值代表来源于不同矿物相源区、不同部分熔融程度的玄武岩浆[59]。一般认为,当Dy/Yb>2.50时,部分熔融发生在含石榴子石地幔源区,当Dy/Yb<1.50时,则为尖晶石地幔源区[60]。三个井组玄武岩的Dy/Yb值为1.77~2.13,在La/Yb-Dy/Yb图解(图 11-b)中,处于石榴子石二辉橄榄岩熔融趋势线以下,尖晶石二辉橄榄岩熔融趋势线以上,部分熔融程度接近20%。
6. 结论
(1) LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年结果表明,北山地区白云山蛇绿岩带南部玄武岩锆石的206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值为396.6±3.3 Ma,应为早泥盆世三个井组火山岩。
(2) 三个井组玄武岩岩浆来自新元古代亏损地幔的局部熔融,可能是亏损尖晶石相地幔橄榄岩向石榴子石相地幔橄榄岩过渡相较高程度部分熔融的产物,且在上升过程中可能受到一定程度的地壳物质混染。
(3) 三个井组玄武岩主要为拉斑玄武岩系列,与区域上同期的S型、A型花岗岩构成双峰式岩浆岩,结合地球化学研究认为其处于造山后伸展构造环境。
致谢: 成文过程中得到中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所聂凤军研究员与中国地质大学(北京)客座教授Richard J Goldfrab的指导并提供资料,中国地质大学(北京)李子羲博士研究生、缪广硕士研究生提供帮助,在此一并表示感谢。 -
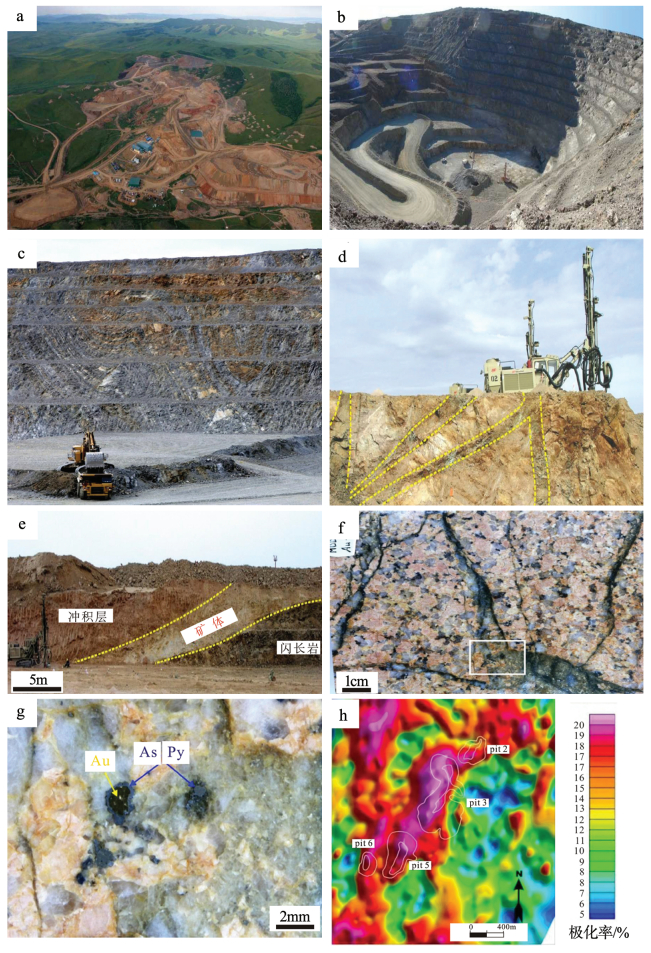
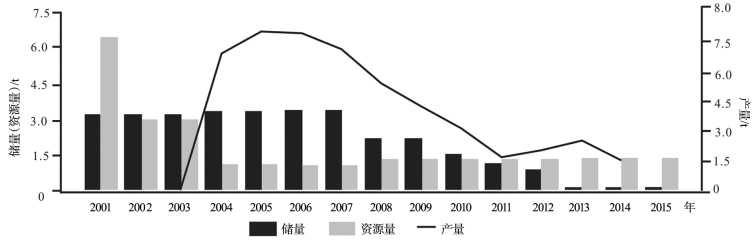
图 1 博洛金矿床金储量资源量和产量变化②
Figure 1. The variation of reserves/resources and production of the Boroo gold deposit
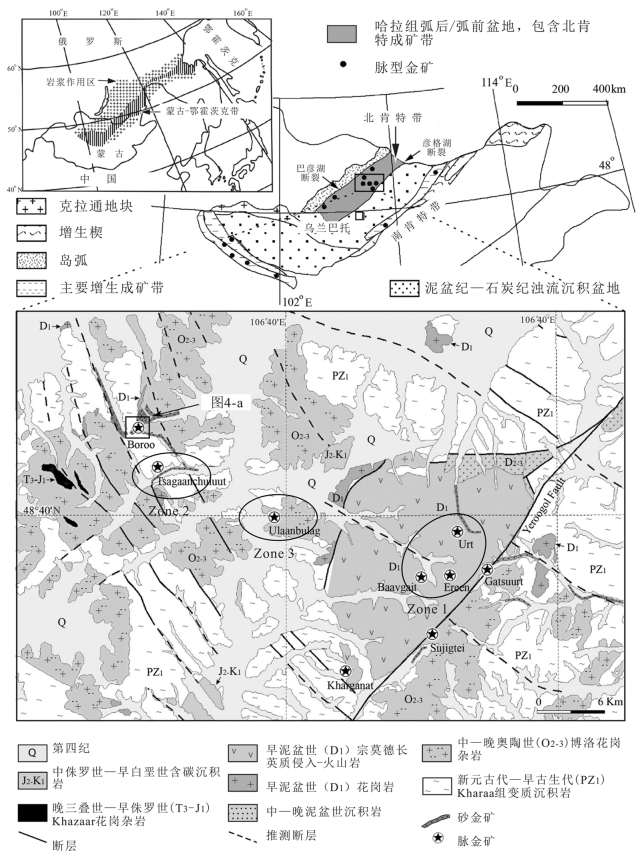
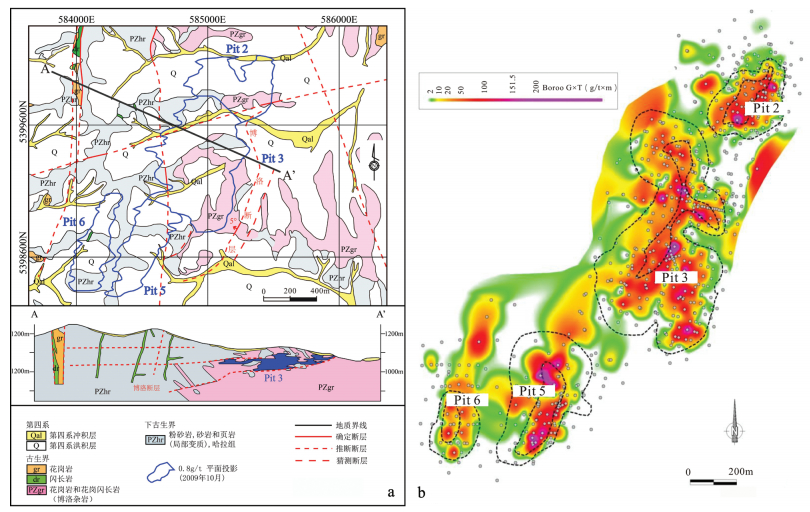
图 2 博洛金矿地理位置(据参考文献[8]修改,Zone1、Zone2、Zone3为圈定靶区,详见5.2节)
Figure 2. Geographical location of the Boroo gold deposit
图 4 蒙古国博洛金矿区地质简图(a)和博洛矿床金矿品位(G)×厚度(T)轮廓图①(b)
Figure 4. Geological map of the Boroo deposit with reserve pit footprints and interpretive section through Pit3 (a) and grade thickness, showing dominant northeast and northwest structural framework of the ore district (b)
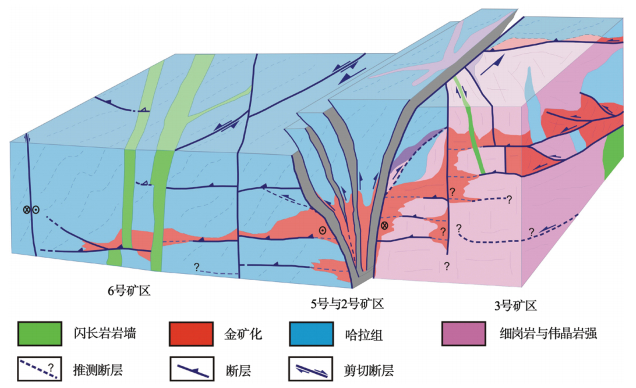
图 5 博洛金矿成矿模式②
Figure 5. Metallogenic model of the Boroo deposit
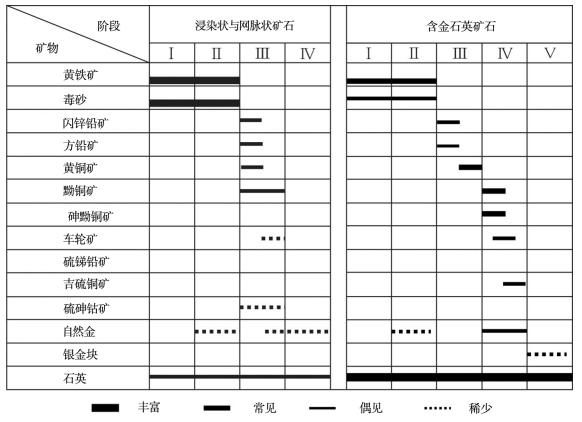
图 6 博洛矿床矿石矿物的共生序列[9]
Figure 6. Paragenetic sequence of ore minerals in the Boroo deposit
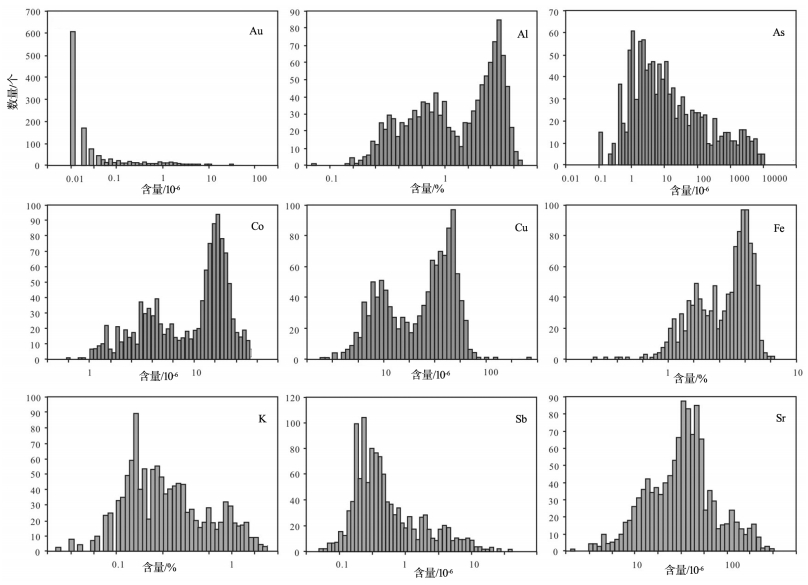
图 7 主量元素Al、Fe、K的双峰式分布与亲铁及微量元素Co、Cu的元素含量柱状图[1]
Figure 7. Histograms of selected elements (logs)
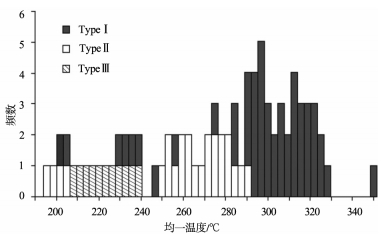
图 8 石英原生流体包裹体均一温度柱状图(样品为中央主矿区内浸染-网脉状矿石)[9]
Figure 8. Histogram of homogenization temperatures of the primary fluid inclusions in quartz of the disseminated and stockwork ores of the main and central zones
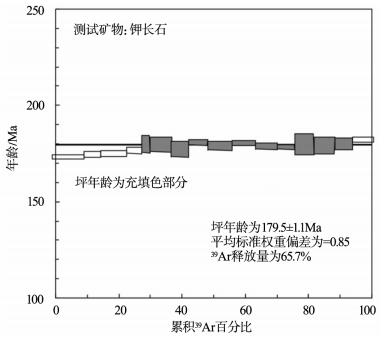
图 9 Ar-Ar坪年龄图[1]
Figure 9. The Plateau age data
序号 矿床名称 矿床外文名称 主要矿种 成因类型 品位与储量 1 博洛 Boroo 金 造山型脉状金矿床 平均品位3.52g/t
金储量约66t2 查干陶勒盖 Tsagaan tolgoi 金 热液型/石英脉型金矿 Au最高品位37g/t
预计储量1.5t3 苏开特 Sukhait 金 热液蚀变型/脉型 平均品位2.3g/t
最高品位20g/t4 库尔曼努尔 Khulman Nuur 金 热液蚀变/石英脉型 5 巴尔拉高尔 Barlag Gol 金 冲积型砂金矿 6 额仁 Ereen 金、银 岩金 Au品位1.0~11.6g/t
金储量6.91t7 依克通克罗尔 Ikh Tokhoirol 金 砂金 金储量3.77t 8 赫木尔 Humul 金 砂金 Au平均品位0.47g/m 3
储量41.3t9 达布金卡尔 Davkhyn khar 金 浅成热液型 Au品位2.03~22.13g/t
平均2.09g/t,资源量46t10 昆克尔 Khunkher 金 浅成热液角砾岩型 表 2 造山型金矿、蒙古国博洛金矿及江西金山金矿矿床特征对比
Table 2 Geological characteristic contrast between the orogenic-type gold deposit, the Boroo deposit and the Jinshan gold deposit
典型特征 造山型金矿 蒙古国博洛金矿 江西金山金矿 成矿跨度 从中太古代持续到古近纪,主要发生在晚太古代、古元古代与显生宙 中生代(185~210Ma) 未达成统一认识,成矿时间由161Ma至780Ma均有提出 构造背景 变形的大陆边缘,主要是外来地体(碰撞造山带、俯冲增生楔、陆内造山带) 增生到西伯利亚克拉通东南边缘的地体 经历多期造山作用的复合体 控矿构造 严格受挤压和转换拉伸构造的晚期阶段控制 近水平的大型逆冲断层-博洛断裂带,与区内主走滑断裂有关 地处赣东北深大断裂的金山韧性推覆变形带中,以低角度的韧性剪切变形为主 赋矿围岩 类型多样,主要是铁镁质火山岩、侵入岩或杂砂岩、板岩及浊积岩系列 主要是花岗杂岩侵入体(由浅色花岗岩和闪长岩脉组成),部分为浊积岩 杂砂岩、板岩、变凝灰岩,偶见闪长岩与辉绿岩 赋矿围岩变质相 从次绿片岩相到低麻粒岩相,主要为绿片岩相 绿片岩相 糜棱岩相与碎裂岩相 岩浆岩 一般为长英质到煌斑岩或大陆边缘岩基 主要有斜长花岗岩、黑云母花岗岩、钾长花岗岩、花岗闪长岩等浅色花岗岩 矿区岩浆活动微弱,仅见辉石闪长岩和辉绿岩 矿化类型 矿化类型多样,有细脉侵染状石英脉、大脉、鞍状矿脉,及富铁岩石的交代型 主要为脉状和侵染状 类型多样,星散侵染状、角砾状、脉状及网脉状均有出现 矿化构造特征 复杂多样,主要为脆-韧性区域 断层张性特征明显 复杂多样,主要为脆-韧性区域 矿床叠加程度 具有明显的多期次成矿事件叠加 ~ 叠加明显 金属元素组合 Au-Ag±As±B±Bi±Sb±Te±W Au-Ag±As±Sb±S Au-W±As±Sb±Bi 蚀变类型 绢云母化、碳酸盐化、硅化、硫化 硅化、绢云母化、青磐岩化、碳酸盐化 硅化、黄铁矿化、绢云母化、绿泥石化、碳酸盐化等 蚀变分带 具有潜在的侧向和垂向分带 具有明显蚀变分带 构造分带、蚀变分带及金矿化强度分带三者界限基本一致,具规律性 近矿围岩蚀变 随着变质程度的变化而变化,主要为云母-碳酸盐-Fe硫化物 位于剪切带的中心部位,主要是石英-黄铁矿化带 位于剪切带的中心部位,按金0.1g/t圈定矿化带基本框定金矿体的赋存空间,主要是石英-黄铁矿-铁白云石化带 温压条件 50~450MPa,220~600℃,一般为150±50MPa,350±50℃ 富Au矿区矿石流体包裹体均一温度194~355℃ 金矿流体包裹体均一温度在142~360℃、主要集中于260~290℃;含金石英脉的流体压力16.7Mpa,而含金糜棱岩流体压力98MPa 成矿流体 低盐度H2O-CO2±CH4±N2(盐度3%~10%),高CO2含量( > 5%) ~ 可变,NaCl-H2O流体包裹体盐度在1.2%~8.5%之间 热源 多源,软流圈的底辟作用,中地壳花岗岩类的侵入 ~ 区域大规模变质作用和构造-岩浆活动提供热量 成矿物质来源 俯冲地壳/上壳层岩石/深部花岗岩类 与岛弧有关的含金属侵入杂岩体 来源于壳源,与围岩关系密切,围岩双桥山群提供成矿物质 资料来源 [20-22] [①][1-2, 10] [21] -
Cluer J K, Kotlyar B, Gantsetseg O, et al. Geology of the Boroo gold deposit, northern Mongolia[J].SEG-IAGOD Guidbook Series 11:Cercams/NHM Longon, 2005:105-117.
李俊健.蒙古国地质矿产概况(第1版)[M].天津:天津科学技术出版社, 2013. 韩九曦, 连云长, 元春华.蒙古国地质矿产与矿业开发(第1版)[M].北京:地质出版社, 2013. 侯万荣, 聂凤军, 江思宏, 等.蒙古国博洛大型金矿区花岗岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb测年及地质意义[J].地球学报, 2010, (3):331-342. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201003009.htm Centerra Gold Inc.Centerra inches toward Mongolian investment agreement[J].The Northern Miner., 2008, 93(48):3.
聂凤军, 江思宏, 白大明, 等.蒙古矿产勘查与开发现状评述[J].地质论评, 2010, 56(1):105-113. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201001017.htm 莫申国, 韩美莲, 李锦轶, 等.蒙古-鄂霍茨克造山带的组成及造山过程[J].山东科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 3:50-52. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDKY200503013.htm Chinbat K, Masahide A. Mineralogy of the Boroo Gold Deposit in the North Khentei Gold Belt, Central Northern Mongolia[J].Resource Geology, 2015, 65(4):311-327. doi: 10.1111/rge.12073
Chinbat K, Masahide A, Hiroto O, et al.Gold Mineralization of the Gatsuurt Deposit in the North Khentei Gold Belt, Central Northern Mongolia[J].Resource Geology, 2014, 64(1):1-16. doi: 10.1111/rge.2014.64.issue-1
李俊健, 刘新秒.蒙古地质矿产研究进展[M].天津:天津科学技术出版社, 2013. 王鸿祯, 何国琦, 张世红, 等.中国与蒙古之地质[J].地学前缘, 2006, (6):1-13. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200606002.htm Badarch G, Cunningham W D, Windley B F.A new terrane subdivision for Mongolia:implications for the Phanerozoic crustal growth of Central Asia[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2002, 21(1):87-110. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(02)00017-2
Altanrio.com.Project:khavchuu, section 3[EB/OL](2011)[2015-09-20] www.altanrio.com/projects/khavchuu/(2011).
Dejidmaa G. Geochemical features of Boroo gold field in Mongolia[D]. Academy of Sciences (Novosibirsk):United Institute of Geology and Geophysics (U.S.S.R)(in Russian, PhD Thesis), 1985.
Dejidmaa G. Review of porphyry copper-molybdenum Erdenetiin-Ovoo deposit in Mongolia:Research on exploration and development of mineral resources in Mongolia[J]. Geological Survey of Japan Bulletin, 1995:69-102.
Goldfarb R J, Taylor R D, Collins G S, et al. Phanerozoic continental growth and gold metallogeny of Asia[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 25(1):48-102. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.03.002
Sillitoe R H. Intrusion-related gold deposits[C]//Foster R P. Gold metallogeny and exploration.Chapman & Hall, London, 1993:165-209.
Fan H R, Zhai M G, Xie Y H, et al. Oreforming fluids associated with granite-hosted gold mineralization at the Sanshandao deposit, Jiaodong gold province, China[J].Mineralium Deposita, 2003, 38(6):739-750. doi: 10.1007/s00126-003-0368-x
Qiu Y M, Groves D I, McNaughton N J, et al. Nature, age, and tectonic setting of granitoid-hosted orogenic gold deposits of the Jiadong Peninsula, eastern North China craton, China[J].Mineralium Deposita, 2002, 37(3/4):283-305. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/226394225_Nature_age_and_tectonic_setting_of_granitoid-hosted_orogenic_gold_deposits_of_the_Jiaodong_Peninsula_Eastern_North_China_craton_China?_sg=BDpEa5QsbT_DrYOlr7-W6tzMbiZcYwSufwBWgjAGjx8rCK7ug0wbXUZG5UGwSpgL5EN2w2SC2XsmlXBs3z1YQg
陈衍景.造山型矿床、成矿模式及找矿潜力[J].中国地质, 2006, 6:1181-1196. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200606002.htm 李晓峰, 华仁民, 韦星林, 等.江西德兴金山金矿[M].北京:地质出版社, 2011:1-165. Goldfarb R J, Groves D I, Gardoll S, et al.Orogenic gold and geologic time:a global synthesis[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2001, 18(1/2):1-75. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169136801000166
Tommaso R R, Daniel R. Technical report on the Boroo gold mine Mongolia. Centerra Gold Inc., 2009.
Ochir G. Mineral Deposits in Mongolia (PPT report). Geoscience Center Mongolian University of Science & Technology, 2015.
James W H, Willian E R, David A R, et al. Technical report on the Gatsuurt golod project, northern Mongolia. Roscoe Postle Associates Inc., 2006.
-
期刊类型引用(16)
1. 孟飞,张公. 基于数据采集技术的矿产资源监测评价研究. 粘接. 2024(06): 123-126 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 高伟. 临沂市资源环境承载力评价研究. 上海节能. 2024(11): 1785-1794 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王静,王焘,李梅. 生态文明视域下成都市资源环境承载力研究. 中国资源综合利用. 2024(12): 149-153 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 陈振宇,赵元艺,李小赛,刘冠男,张佳文,李瑞敏. 云南省威信县煤矿资源承载能力评价. 中国地质. 2023(02): 442-458 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王冲,张景,彭博,王继龙,于俊杰,吴佳瑜. 基于“双评价”的国土空间格局优化研究——以江西省安远县为例. 华北地质. 2023(02): 69-78 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 孙超,王昕洲,叶莹莹,刘琼,曹颐,韩冲,王轶. 河北省地下水资源承载能力评价及预警方法研究. 水文地质工程地质. 2022(06): 55-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 殷志强,郝爱兵,吴爱民,任金卫,周平,卫晓锋,彭令,李霞,邵海,庞菊梅. 承德自然资源综合调查主要进展与全国自然资源综合调查总体思路. 地质通报. 2022(12): 2087-2096 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 林燕,白秀佳,叶泽宇,张衡. 基于ArcGIS的南通市农业生产适宜性评价. 地质通报. 2021(06): 968-977 .  本站查看
本站查看
9. 宋立东,佟智强,刘浩,宋林旭,高博,韩佳宏. 牡丹江市资源环境承载能力评价. 华东地质. 2021(02): 185-192 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 宋漪. 新会区地质环境承载能力评价. 地下水. 2021(05): 160-162+197 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 倪欢,牛晓楠,李云峰,郝娇娇. 基于统计学习方法的安徽省安庆市自然资源自动化监测——以山体为例. 地质通报. 2021(10): 1656-1663 .  本站查看
本站查看
12. 宋漪. 新会区建筑用花岗岩矿资源承载能力评价. 地下水. 2021(06): 205-208 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 张定源,张景,牛晓楠,陈国光,吴佳瑜,周迅,王冲,张洁,侯振华,许美辉,郑志强,王斌,刘青帝. 双评价理论探索与福建实践. 华东地质. 2021(04): 419-428 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 高萌萌,李瑞敏,刘琼,王轶,李小磊. 基于GIS的地下水资源分区研究及承载本底评价. 水文地质工程地质. 2020(06): 184-190 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 王佳运,毕俊擘,杨旭东,李彦娥,马红娜,罗金. 山西吕梁山区城镇边坡风险分级与优化. 地质通报. 2020(12): 2004-2012 .  本站查看
本站查看
16. 李红梅,刘波,袁琴,梁晓艳. 长江沿线(宜昌—荆州段)资源环境承载力评价指标体系与实证研究. 资源环境与工程. 2020(S2): 78-82+117 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: