Late Triassic magmatic activity in the Daqiao gold deposit of West Qinling belt: Zircon U-Pb chronology and Lu-Hf isotope evidence
-
摘要:
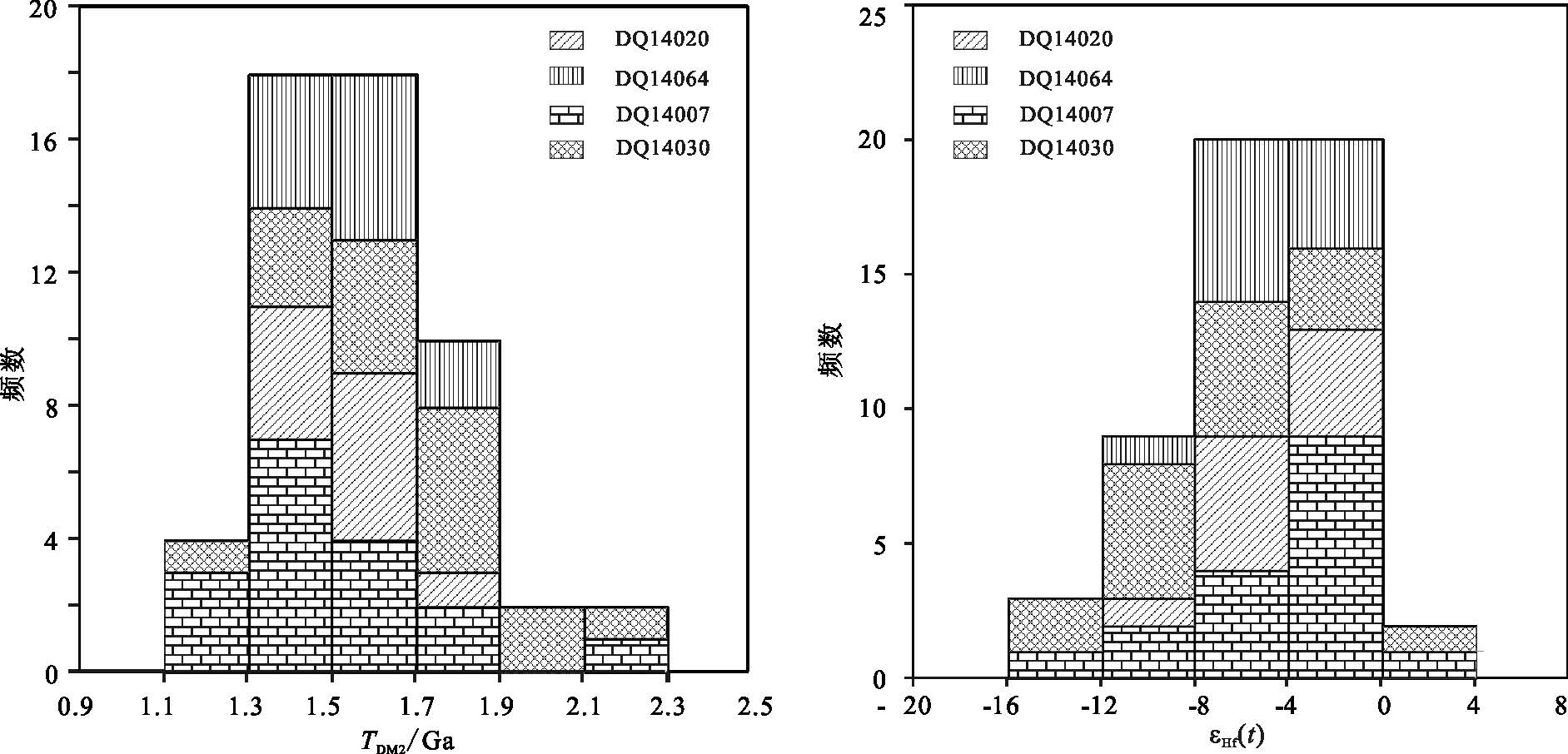
西秦岭是中国金矿的重要集中区之一。该区大桥金矿近年已达到超大型规模。最新矿床成因研究认为,成矿可能与矿区岩浆活动有关。矿区采集的4个花岗闪长岩样品LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄测试结果主要集中于228Ma、206Ma两组,对应于晚三叠世。相应的Hf同位素组成基本相似,也可分为2个单元。εHf(t)主体分布在-8~0之间,TDM2主体为1300~1900Ma,推测壳源源区为古-中元古代古老地壳岩石,岩浆主要来源于下地壳古老物质重熔,成岩过程可能有少量地幔组分的参与。结合稀土和微量元素研究结果,认为矿区存在2期印支晚期岩浆活动。大桥金矿可能为西秦岭地区印支晚期晚三叠世区域岩浆活动引发成矿作用的产物。
Abstract:The West Qinling area is one of the important gold ore concentration areas in China. The Daqiao gold deposit, located in the middle of the West Qinling area, has become a superlarge deposit with the growing Au reserves. Recent research reveals that the metallogenic process may be associated with magmatic activity in the area. The zircons LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating results of 4 granodiorite samples collected in the mining area are concentrated mainly at 228Ma and 206Ma, forming two groups obviously and corresponding to the Late Triassic. The corresponding Hf-isotopic compositions of zircons show similar phenomena and can also be divided into two units. The εHf(t) values are from -8 to 0, and the TDM2 values are from 1300Ma to 1900Ma. It is inferred that the source came from the old crustal rocks of the Paleoproterozoic-Proterozoic period, and most of the ancient lava was derived from remelting process of the old materials, which came from the lower crust, mixed probably with a small amount of mantle components which were involved in diagenetic process. In combination with REE and trace elements researches, the authors hold that there probably existed two phases of magmatic activity in late Indosinian period in the mining area. The Daqiao gold deposit is the product of metallogenic activity caused by regional magmatism in the late Indosinian epoch in West Qinling belt.
-
Keywords:
- West Qinling /
- Daqiao gold deposit /
- magmatic rock /
- zircon U-Pb dating /
- Lu-Hf isotope
-
随着地球科学家对地球系统研究的不断深入,人们发现新元古代时地球系统发生了一系列的剧烈变化。在地球地质历史的这一时期,地球从较稳定的古-中元古代(17~7.5亿年)[1],进入剧烈变动的中-晚新元古代时期(7.5~5.4亿年)。中-晚新元古代地球上出现多期极冷事件[2-7],条带状铁矿也在消失十多亿年后,在新元古代中期又重新出现[1, 8],大洋与大气圈的氧含量快速增加[9-11]。地球系统这一系列的剧变很可能发生在Rodinia超大陆裂解的背景下。因此,重建这一时期的古地理古板块位置对于理解这些剧变至关重要。然而,由于这一时期(7.5~5.4亿年)全球不同块体古地磁数据的缺乏和可靠性问题,其古地理重建一直存在较大的争议[12-20]。
影响这一时期古地磁数据可靠性的因素,除了考虑剩磁的获得时间外,近年来越来越多的学者注意到非偶极子场及磁倾角偏低对古地磁数据的影响[21-26],特别是红层中存在普遍的磁倾角偏低现象[27-28]。
最近,Jing等[29]报道了湖北宜昌三峡地区莲沱组红层可靠的古地磁极,并根据Lan等[30]最新的SIMS锆石U-Pb定年研究,确定这一古地磁极年龄应为720Ma。虽然这一古地磁极通过了Van der Voo[31]的6项Q检验,确保其剩磁获得的原生性,但这一结果是否受到后期压实作用的影响并产生磁倾角偏低,以及影响程度的大小等问题,都需要进一步研究。在长阳地区,由于古城冰碛岩覆盖在莲沱组之上,因此准确确定莲沱组的磁倾角,对确定华南这一时期的古纬度及“雪球地球”的研究都具有重要意义。另外,目前华南地块莲沱组古地磁极与南沱组古地磁极相似的问题,一直没有得到可信的解释,本文通过磁倾角偏低的研究,对这一问题进行探讨。
1. 区域地质概况及采样
采样区位于华南新元古代地层典型剖面区,湖北三峡地区(图 1)。研究区出露的新元古代沉积地层包括莲沱组、南沱组、陡山沱组、灯影组等。莲沱组一般不整合覆盖于黄陵花岗岩之上,主要为厚层的紫红色砂岩和砾岩,可分为2个大的沉积旋回(图 2),每个旋回底部为砾石或粗粒石英砂岩,向上逐渐变为粉砂岩、泥质砂岩,含多层凝灰岩或凝灰质碎屑岩。在区域上,西北部地层厚度较大,向西南变薄。本区南沱组与莲沱组平行不整合接触或低角度不整合接触,南沱组主要为暗绿色冰碛砾岩,部分为红色冰碛岩[32]。
![]() 图 2 本次研究获取的采点(下划线标注TLS编号)在地层上的分布(TL编号为Jing等[29]采点)Figure 2. Stratigraphic column of the Liantuo Formation and detailed sampling layer positions of three sub-sections at Yichang
图 2 本次研究获取的采点(下划线标注TLS编号)在地层上的分布(TL编号为Jing等[29]采点)Figure 2. Stratigraphic column of the Liantuo Formation and detailed sampling layer positions of three sub-sections at Yichang在三峡地区南部的长阳地区,莲沱组之上覆盖古城组冰碛岩和大塘坡组页岩,而不是直接与南沱组接触[33]。古城组冰碛岩应与扬子西南部广泛发育的长安组冰碛岩一致[33],属于Sturtian冰期的产物。古城组沉积时间应始于715Ma左右[33]。
三峡地区从埃迪卡拉纪开始长期沉积碳酸盐岩,早寒武世有一次沉积间断,直到志留纪宜昌地区大规模抬升,沉积间断接受剥蚀,随后沉陷到早三叠世再次抬升[34-35]。本地区经历了3次主要的构造运动:加里东期、印支期和燕山期构造运动。同时中扬子地区存在与这3次构造运动相关的3期油气生成和排烃过程[36]。区域内构造变形较弱。
本次在宜昌花鸡坡、头顶石及田家院子3个剖面共采集了17块手标本样品(TLS1-17),对莲沱组是否存在磁倾角偏低现象进行检验(图 2)。样品在野外用罗盘测量层面的走向和倾角,并标记在层面上。
2. 实验方法
在室内用台式钻机垂直手标本层面钻取2根以上岩心,并加工出1~2块高2.2cm、直径2.5cm的标准岩心样品。每根岩心选取1~2块,共31块标准样品进行系统热退磁实验。同时对应选择了30块样品进行Hodych等[23]磁倾角偏低校正实验。所有实验工作均在中国地质科学院地质力学研究所国土资源部古地磁与古构造重建重点实验室完成。使用美国ASC Scientific Inc.公司生产的IM-10-30脉冲充磁仪对样品进行充磁,样品系统热退磁由TD-48大型热退磁仪完成,样品剩磁测量在ARGICO-JR6A旋转磁力仪上完成。另外,对部分样品利用KLY-3 Kappabridges进行了氮气环境下磁化率随温度变化实验(K-T),获取连续加热-冷却曲线分析样品磁化率的变化。
3. 实验结果
3.1 逐步热退磁结果
宜昌三峡地区花鸡坡、头顶石及田家院子剖面莲沱组样品的岩石磁学实验结果显示,岩石的特征剩磁载磁矿物为赤铁矿[29]。因此,系统热退磁温度区间在低温段以50~100℃为间隔,高温段温度区间以20℃为间隔,热退磁温度达到680℃(图 3)。样品使用主向量分析法[37]进行剩磁组分分析。
逐步热退磁结果显示,样品中共可以分离出3个剩磁方向(图 3):低温分量一般在小于等于300℃的情况下分离出来, 共有15块样品分离出此分量,其在地理坐标系下的统计方向(Dg=5.9°,Ig=60.1°,kg=81.3, ɑ95=4.3°)与采样点现代地磁场方向接近,应为现代地磁场的热粘滞剩磁;中温分量的温度区间一般在300~600~640℃之间,共有6块样品分离出此分量,其平均方向在地理坐标系下为Dg=34.5°,Ig=78.1°,kg=244.2,ɑ95=4.3°,在地层坐标系下为Ds=78.9°,Is=78.4°,ks=243.5,ɑ95=4.3°。另外,从11块样品中分离出了与宜昌剖面得到的特征分量相似的高温分量(600~680℃),其平均方向在地理坐标系下为Dg=67.0°,Ig=71.6°,kg=124.7,ɑ95=3.9°,在地层坐标系下为Ds=95.3°,Is=67.8°,ks=196.0,ɑ95=3.1°。
3.2 等温剩磁各向异性实验结果
对12个样品,在与其层面呈45°方向,从低到高逐步增加等温直流磁场,获得平行于层面IRMx和垂直于层面IRMz的等温剩磁,直流磁场大小由20、40、60、100、225、315、415、510、510、710、810、950、1200mT依次递增。在每步施加直流场后使用JR6旋转磁力仪对样品进行剩磁测试。然后用TD48大型热退磁炉对所有样品进行系统热退磁,相关数据结果列于表 1中。
表 1 宜昌地区剖面莲沱组样品等温热剩磁各向异性及磁倾角偏低值Table 1. Anisotropy of isothermal remnant magnetization for Liantuo Formation red beds in Yichang areaID Iobs IRMz/IRMx
(610~1200mT)IF1 ΔI1(=IF1-Iobs) IRMz/IRMx
(600°C以上)IF2 ΔI2(=IF2-Iobs) 15 64.4 0.7796 69.518 5.118 0.8542 67.7425 3.3425 15-2c 71.5 0.8414 74.277 2.777 0.8513 74.1009 2.6009 15-5b 65 0.899 67.256 2.256 0.8757 67.7876 2.7876 17-1 72.1 0.831 74.976 2.876 0.8118 75.3075 3.2075 3-1 73 0.87 75.105 2.105 0.8859 74.8452 1.8452 4-2b 66.3 0.6147 74.899 8.599 0.901 68.4206 2.1206 5-2b 64.2 0.8472 67.728 3.528 0.9117 66.2153 2.0153 5-4b 66 0.7989 70.420 4.420 0.872 68.7818 2.7818 7-1 61.9 0.8579 65.389 3.489 0.8731 65.0054 3.1054 8-3 70 0.8737 72.359 2.359 0.856 72.6951 2.6951 8-4 66.8 0.8701 69.548 2.748 0.8977 68.9555 2.1555 平均值 67.8 0.8258 71.377 3.577 0.8719 70.4146 2.6146 注:ID为样品号,Iobs为热退磁实验所得样品磁倾角,IRMz/IRMx(610~1200mT)为610~1200mT之间垂直层面方向和平行层面方向等温剩磁大小的比值,IRMz/IRMx(600°C以上)为600 °C以上垂直层面方向和平行层面方向等温剩磁大小的比值,IF为校正后磁倾角,ΔI为校正值 考虑到实验过程中样品的等温剩磁方向可能受天然剩磁的影响,以及载磁矿物主要为赤铁矿,所以施加外部直流场在200~1200mT之间及系统热退磁温度在600~680℃之间的IRMz/IRMx拟合线反映了赤铁矿的剩磁各向异性特征。
由于垂直于层面的IRMz值大部分在500mT之后略小于平行于层面的IRMx值(图 4-a、d),所以从磁场强度方面考虑,选取在500mT之后的610~1200mT区间的IRMz/IRMx拟合线的斜率作为磁倾角偏低校正因子,其大小为0.8258,对应的沉积压实为18%。另外,从热退磁的方面考虑,选取600~680℃区间的IRMz/IRMx热退磁结果拟合线的斜率作为磁倾角偏低校正因子,其大小为0.8719,对应的沉积压实为13%。利用公式IRMz/ IRMx=tan (Iobs)/tan (IF)进行校正后得到莲沱组磁倾角分别为71.4°和70.4°,两者的磁倾角值差别不大。
![]() 图 4 45°方向加场后平行于层面方向(IRMx)和垂直于层面方向(IRMz)等温剩磁获得曲线图(a, d),IRMz/IRMx关系图(b, e)和IRMz/IRMx的热退磁结果(c, f)Figure 4. Plots of IRMx (parallel to bedding) and IRMz (perpendicular to bedding) acquisitions produced by applying magnetic field at 45° to bedding as function of increasing field (a, d), plots of IRMZ/IRMX(b, e), the thermal demagnetization results of IRMZ/IRMX(c, f)
图 4 45°方向加场后平行于层面方向(IRMx)和垂直于层面方向(IRMz)等温剩磁获得曲线图(a, d),IRMz/IRMx关系图(b, e)和IRMz/IRMx的热退磁结果(c, f)Figure 4. Plots of IRMx (parallel to bedding) and IRMz (perpendicular to bedding) acquisitions produced by applying magnetic field at 45° to bedding as function of increasing field (a, d), plots of IRMZ/IRMX(b, e), the thermal demagnetization results of IRMZ/IRMX(c, f)3.3 岩石磁学实验结果
为了排除样品在加热过程中可能存在的磁性矿物的变化,对几个代表性样品进行了磁化率随温度变化实验(K-T,图 5)。结果表明,部分样品在加热和冷却过程中样品磁化率明显不同(图 5,TLS11),可能是因为样品在加热过程中生成了一部分磁铁矿。但580~680℃之间的加热曲线与冷却曲线一致,表明加热过程中磁性矿物的变化并未影响到样品中赤铁矿的剩磁变化(图 5,TLS11),因此,不影响磁倾角偏低实验的结果。另一部分样品的K-T曲线显示,在加热与冷却过程中,样品的磁化率没有明显的差异,因此样品中不存在明显的磁性矿物的改变(图 5,TLS4)。
由于加热过程并未影响到高温分量载磁性矿物赤铁矿,再考虑到赤铁矿较大的矫顽力,因此,选用600~680℃区间的IRMz/IRMx值作为磁倾角偏低校正因子,利用公式IRMz/IRMx=tan (Iobs)/tan(IF)计算得到校正后的莲沱组磁倾角大小为70.4°,与热退磁实验所得莲沱组磁倾角67.8°比较,莲沱组的磁倾角偏低大小为2.6°。
4. 磁倾角偏低对莲沱组古纬度及古地磁极的影响
利用本研究得到的莲沱组磁倾角偏低校正因子,对Jing等[29]所得高温分量进行磁倾角偏低校正,利用校正后的高温分量求得的三峡地区莲沱组沉积古纬度为47.7°±5.1°,比校正前的43.7°±4.8°向高纬度地区运动了3.9°±6°。
校正后古地磁极(LT-corr)为14.7°N, 153.9°E, dp/dm=4.9/6.0,与未校正的莲沱组古地磁极(LT:12.7°N,157.4°E,dp/dm=4.5/5.8)相比更偏西北。虽然校正前后,莲沱组古地磁极在统计分析上不能显著区分,但校正后的莲沱组古地磁极与现有华南南沱组古地磁极(Nantuo)[38]明显不同(图 6)。
5. 讨论
由于Evans等[39]得到的莲沱组古地磁极与南沱组古地磁极重合,使得一些学者认为莲沱组古地磁结果可能比以前认为的更年轻[40],或是南沱期重磁化的结果。然而,Jing等[29]对宜昌莲沱组的古地磁研究表明,莲沱组中下部到顶部至少存在5个正负极性时,因此现有的莲沱组古地磁结果应该不是重磁化的结果。另外,Jing等[29]通过总结前人在三峡地区对莲沱组大量的定年结果[41-45],认为现有华南莲沱组古地磁极年龄应在720Ma左右,比之前认为的750Ma年轻,但仍老于635Ma的南沱组古地磁结果。
Jing等[29]得到的莲沱组古地磁极与南沱组古地磁极相差不大。Yang等[46]认为,莲沱组采样区可能发生过局部构造旋转作用;Zhang等[38]则认为,没有证据表明莲沱组采样区发生过局部旋转。
排除以上各方面的影响因素,笔者认为,造成莲沱组与南沱组古地磁极相似的原因应该与莲沱组岩石受压实作用影响、发生微弱的磁倾角偏低现象有关。由于目前未对南沱组取得高温分量的古地磁样品进行磁倾角偏低实验,两者真实的差别还不能确定,需要进一步研究。
经磁倾角偏低校正后的华南板块在720Ma时应位于中纬度地区(图 6)。这一时期扬子地块多处发育冰碛岩沉积,从该时期华南板块上发育的冰碛岩分布看[40],当时整个地球应处于较寒冷的气候阶段。但由于这一时期华南板块位于中纬度地区,对于地球这一时期是否处于“雪球地球”的环境,仅从莲沱组的古地磁结果不能做出明确的判定。
为此,笔者重建了华南板块及与华南关系较紧密的澳大利亚-东南极板块720Ma的古地理位置(图 6)。图 6中,将莲沱组古地磁极通过欧拉极(34.4°N、100°E,98.6°)旋转到地理北极。MDS、YF及EF分别为澳大利亚755Ma,640Ma和635Ma古地磁极[22, 47-48],位于同一大圆弧上(虚线),利用内插法求出其720Ma的古地磁极位置,通过欧拉极(-0.4°N、53.7°E,44.1°)旋转使其与莲沱组古地磁极重合。通过这一古地理重建,可以清楚地看到,这一时期有大量冰川从中纬度地区一直延续到赤道地区。这一证据直接证明,当时地球处于“雪球地球”的环境。
6. 结论
对华南三峡地区莲沱组的等温剩磁各向异性研究表明,通过磁倾角偏低校正后的莲沱组古地磁极与南沱组古地磁极存在明显差别,这表明造成莲沱组与南沱组古地磁极相似的一个重要原因是地层压实引起的磁倾角偏低。利用720Ma古地磁数据对华南和澳大利亚进行古地理重建,并对比这一时期冰碛岩的分布,结果表明,当时地球确实处于“雪球地球”的环境中。
-
图 5 大桥金矿岩浆岩微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(a)和稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线图(b)
(标准值据参考文献[24])
Figure 5. Primitive mantle-normalized trace element diagrams (a) and chondritenormalizedREE patterns (b) of plutons from Daqiao gold deposit
表 1 大桥金矿区岩浆岩锆石U-Th-Pb 同位素测试数据
Table 1 Magmatic zircon U-Th-Pb geochronologic data of the Daqiao gold deposit
测试点号 元素含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 表面年龄/Ma Pb Th U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 208Pb/232Th 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 208Pb/232Th 1σ DQ14007-1 39 241 1073 0.22 0.0528 0.0059 0.2325 0.0216 0.0326 0.001 0.0064 0.0007 320 249 212 18 207 6 129 15 DQ14007-2 18 143 491 0.29 0.0524 0.0051 0.2282 0.0207 0.0321 0.001 0.0065 0.0007 302 224 209 17 204 6 131 14 DQ14007-3 33 134 921 0.15 0.0515 0.0029 0.2337 0.0129 0.033 0.0007 0.0066 0.0005 265 131 213 11 209 4 134 10 DQ14007-4 70 407 1936 0.21 0.0526 0.0033 0.2391 0.0144 0.0328 0.0003 0.0061 0.0007 309 147 218 12 208 2 122 13 DQ14007-5 26 123 714 0.17 0.0535 0.0053 0.238 0.0215 0.033 0.0008 0.007 0.0005 350 231 217 18 209 5 140 11 DQ14007-7 25 109 715 0.15 0.0524 0.0028 0.2332 0.012 0.0324 0.0005 0.007 0.0005 302 129 213 10 205 3 140 9 DQ14007-8 56 632 1514 0.42 0.0508 0.0048 0.228 0.0193 0.0326 0.0015 0.0053 0.0004 232 204 209 16 207 10 108 8 DQ14007-9 14 78 389 0.2 0.0513 0.0057 0.2335 0.0261 0.0327 0.0008 0.0072 0.0007 254 246 213 21 208 5 146 13 DQ14007-10 27 119 774 0.15 0.0512 0.0039 0.2334 0.0178 0.0328 0.0006 0.0069 0.0006 250 169 213 15 208 4 140 12 DQ14007-12 33 95 741 0.13 0.052 0.0029 0.237 0.0128 0.033 0.0005 0.008 0.0006 287 126 216 10 209 3 160 12 DQ14007-13 55 243 1153 0.21 0.0505 0.0031 0.2324 0.0145 0.0331 0.0004 0.0057 0.0004 217 138 212 12 210 3 115 8 DQ14007-14 46 154 923 0.17 0.0521 0.0081 0.235 0.0346 0.033 0.0011 0.0081 0.001 300 313 214 28 209 7 162 21 DQ14007-15 64 209 1238 0.17 0.0515 0.0054 0.2309 0.0187 0.033 0.001 0.0065 0.0006 261 42 211 15 209 6 131 11 DQ14007-16 45 124 839 0.15 0.0506 0.005 0.2327 0.0257 0.0327 0.0011 0.0074 0.0008 220 211 212 21 207 7 149 15 DQ14007-17 37 81 662 0.12 0.052 0.0037 0.2316 0.016 0.0325 0.0005 0.0072 0.0005 287 160 212 13 206 3 146 10 DQ14007-18 33 91 573 0.16 0.0502 0.0038 0.2281 0.0184 0.0324 0.0005 0.0069 0.0005 206 178 209 15 206 3 138 9 DQ14007-20 57 321 909 0.35 0.0512 0.0021 0.2256 0.0092 0.0321 0.0004 0.006 0.0002 250 96 207 8 204 2 121 4 DQ14030-1 57 190 1471 0.13 0.0503 0.0028 0.2299 0.0134 0.033 0.0005 0.0066 0.0005 209 136 210 11 209 3 133 9 DQ14030-2 41 148 1057 0.14 0.0503 0.0065 0.231 0.035 0.0326 0.0013 0.0074 0.0007 209 278 211 29 207 8 149 14 DQ14030-3 47 340 1230 0.28 0.0514 0.0056 0.2305 0.0275 0.032 0.0011 0.0058 0.0006 257 243 211 23 203 7 117 13 DQ14030-4 46 124 1205 0.1 0.0523 0.0079 0.2368 0.036 0.0328 0.0009 0.01 0.0013 298 313 216 30 208 6 201 26 DQ14030-5 35 148 934 0.16 0.0525 0.0038 0.235 0.0145 0.0329 0.0006 0.0075 0.0005 309 132 214 12 209 4 151 11 DQ14030-6 53 192 1446 0.13 0.0526 0.0052 0.2345 0.0223 0.0325 0.0008 0.0081 0.0008 322 223 214 18 206 5 162 15 DQ14030-7 56 332 1488 0.22 0.0506 0.0037 0.2316 0.0168 0.0331 0.0006 0.0065 0.0005 220 170 212 14 210 4 130 10 DQ14030-9 24 63 680 0.09 0.0527 0.0064 0.2285 0.0273 0.0319 0.0015 0.0155 0.0024 317 278 209 23 203 9 310 48 DQ14030-10 50 299 1447 0.21 0.0504 0.0079 0.2228 0.0348 0.032 0.0011 0.0065 0.0014 213 326 204 29 203 7 131 28 DQ14030-11 52 358 1439 0.25 0.0515 0.007 0.2347 0.029 0.0333 0.0012 0.0059 0.0008 261 289 214 24 211 8 120 17 DQ14030-12 31 110 882 0.12 0.0511 0.0064 0.2292 0.0282 0.0325 0.0009 0.0093 0.001 256 267 210 23 206 5 187 19 DQ14030-13 38 206 1102 0.19 0.0524 0.0048 0.2348 0.0104 0.0326 0.0016 0.0055 0.0016 302 209 214 9 207 10 111 33 DQ14030-14 22 124 621 0.2 0.0509 0.0079 0.2283 0.0353 0.0328 0.001 0.0071 0.0009 239 322 209 29 208 6 144 18 DQ14030-16 54 728 1415 0.51 0.0505 0.0061 0.2288 0.0284 0.0326 0.0008 0.0056 0.0003 220 256 209 23 207 5 113 7 DQ14030-17 46 201 1358 0.15 0.0507 0.0069 0.2243 0.0324 0.0317 0.0004 0.0077 0.0006 233 289 205 27 201 3 155 12 DQ14030-18 47 302 1301 0.23 0.0516 0.0032 0.23 0.0133 0.0326 0.0006 0.0068 0.0004 265 173 210 11 207 4 137 8 DQ14030-19 45 278 1284 0.22 0.0505 0.0053 0.2191 0.0209 0.0317 0.0007 0.0067 0.0007 217 226 201 17 201 4 136 13 DQ14030-20 42 208 1200 0.17 0.0521 0.0056 0.2275 0.0225 0.0322 0.0007 0.0071 0.0006 300 242 208 19 204 5 144 12 DQ14020-1 20 139 506 0.28 0.0519 0.0058 0.2609 0.0283 0.0371 0.0011 0.0062 0.0007 280 58 235 23 235 7 124 15 DQ14020-2 32 110 823 0.13 0.0565 0.0124 0.2704 0.0529 0.0366 0.0013 0.0104 0.0012 472 422 243 42 232 8 208 23 DQ14020-3 23 97 615 0.16 0.0537 0.0052 0.2695 0.0267 0.0368 0.0009 0.0071 0.0007 367 220 242 21 233 6 143 15 DQ14020-4 35 471 854 0.55 0.0522 0.0029 0.2572 0.0138 0.0365 0.0005 0.0058 0.0003 295 126 232 11 231 3 116 7 DQ14020-5 42 179 1142 0.16 0.0523 0.0056 0.2571 0.0265 0.0361 0.001 0.0069 0.0006 302 246 232 21 228 6 139 12 DQ14020-7 49 213 1288 0.17 0.053 0.0036 0.2714 0.019 0.0371 0.0007 0.007 0.0006 332 154 244 15 235 4 141 12 DQ14020-9 42 120 1142 0.11 0.0513 0.0022 0.2633 0.0117 0.0371 0.0006 0.0069 0.0005 257 100 237 9 235 3 140 10 DQ14020-10 26 133 728 0.18 0.0506 0.0027 0.247 0.0131 0.0353 0.0006 0.0063 0.0005 233 122 224 11 224 4 127 9 DQ14020-15 39 140 1017 0.14 0.0536 0.0029 0.2665 0.0134 0.0365 0.0005 0.0066 0.0004 354 119 240 11 231 3 132 9 DQ14020-16 23 136 574 0.24 0.0535 0.0104 0.2624 0.0473 0.0363 0.0018 0.009 0.0009 350 394 237 38 230 11 181 18 DQ14020-17 45 280 1154 0.24 0.0527 0.0029 0.2581 0.0133 0.036 0.0005 0.0078 0.0006 322 126 233 11 228 3 157 12 DQ14020-18 13 113 294 0.38 0.0504 0.0049 0.2596 0.0381 0.0362 0.0025 0.0085 0.0014 213 220 234 31 229 16 171 28 DQ14020-19 26 266 619 0.43 0.0547 0.0057 0.2653 0.0221 0.0365 0.0014 0.0069 0.0008 467 234 239 18 231 9 140 15 DQ14020-20 46 146 1207 0.12 0.0533 0.0037 0.2589 0.0174 0.0356 0.0006 0.0068 0.0005 343 159 234 14 226 4 137 11 DQ14064-1 35 259 934 0.28 0.0518 0.0034 0.2619 0.017 0.0367 0.0006 0.0061 0.0006 280 156 236 14 232 4 122 13 DQ14064-2 28 148 791 0.19 0.0516 0.0032 0.2559 0.0161 0.0358 0.0006 0.0068 0.0007 333 144 231 13 227 4 136 13 DQ14064-3 27 271 737 0.37 0.0522 0.0029 0.2564 0.0145 0.0353 0.0006 0.0059 0.0005 300 125 232 12 224 4 119 10 DQ14064-4 26 235 714 0.33 0.0534 0.0034 0.2545 0.0152 0.0351 0.0006 0.0061 0.0005 343 144 230 12 222 4 123 10 DQ14064-5 62 702 1546 0.45 0.0504 0.002 0.2578 0.0102 0.0369 0.0005 0.0065 0.0004 213 93 233 8 234 3 132 9 DQ14064-6 26 116 728 0.16 0.0542 0.0034 0.265 0.017 0.0355 0.0007 0.0072 0.0006 376 145 239 14 225 4 145 12 DQ14064-7 56 489 1477 0.33 0.0469 0.0023 0.2315 0.0112 0.0357 0.0005 0.0068 0.0004 56 111 211 9 226 3 137 9 DQ14064-11 38 191 1065 0.18 0.0513 0.0031 0.2444 0.0151 0.0346 0.0008 0.0067 0.0005 254 141 222 12 219 5 135 11 DQ14064-13 59 741 1473 0.5 0.0522 0.0026 0.2574 0.0127 0.0356 0.0005 0.0065 0.0004 295 115 233 10 226 3 131 7 DQ14064-16 21 101 589 0.17 0.0506 0.0034 0.2465 0.0166 0.035 0.0006 0.0058 0.0004 233 156 224 14 222 4 116 9 DQ14064-18 26 106 724 0.15 0.0511 0.0028 0.2488 0.0132 0.0353 0.0006 0.0062 0.0005 243 121 226 11 224 4 125 9 表 2 大桥金矿岩浆岩锆石Hf 同位素分析结果
Table 2 Magmatic zircon Hf isotope data of the Daqiao gold deposit
测点号 176Yb/177Hf 76Lu/177Hf 76Hf/177Hf 2σ 176Hf/177Hfi εHf (0) εHf (t) TDM1/Ma TDM2/Ma fLu/Hf DQ1400701 0.038818 0.001595 0.282365 0.000021 0.282359 -14.39 -10.07 1273 1883 -0.95 DQ1400702 0.005274 0.000153 0.282643 0.000025 0.282642 -4.56 -0.03 843 1247 -1 DQ1400703 0.028993 0.001193 0.282535 0.000033 0.28253 -8.38 -4 1020 1499 -0.96 DQ1400704 0.030768 0.001169 0.28258 0.000028 0.282575 -6.79 -2.4 955 1398 -0.96 DQ1400705 0.018158 0.000788 0.282611 0.000027 0.282608 -5.69 -1.25 902 1325 -0.98 DQ1400707 0.014702 0.000621 0.282606 0.000021 0.282604 -5.87 -1.41 905 1334 -0.98 DQ1400708 0.083206 0.003148 0.282453 0.000028 0.282441 -11.28 -7.17 1197 1699 -0.91 DQ1400709 0.009044 0.000264 0.282631 0.000029 0.28263 -4.99 -0.47 862 1275 -0.99 DQ1400710 0.016075 0.000693 0.282562 0.00002 0.282559 -7.43 -2.97 968 1434 -0.98 DQ1400712 0.026939 0.001103 0.282266 0.000022 0.282262 -17.89 -13.5 1395 2100 -0.97 DQ1400713 0.021498 0.000892 0.282667 0.000027 0.282664 -3.71 0.72 826 1199 -0.97 DQ1400714 0.025965 0.001029 0.282486 0.000031 0.282482 -10.11 -5.71 1084 1607 -0.97 DQ1400715 0.0226 0.000944 0.282589 0.000023 0.282585 -6.47 -2.05 937 1375 -0.97 DQ1400716 0.029705 0.001197 0.282512 0.000036 0.282507 -9.19 -4.81 1052 1551 -0.96 DQ1400717 0.022308 0.000887 0.282557 0.00003 0.282554 -7.6 -3.18 980 1447 -0.97 DQ1400718 0.018454 0.000745 0.28237 0.00005 0.282367 -14.22 -9.77 1237 1865 -0.98 DQ1400720 0.026954 0.000942 0.282505 0.000031 0.282501 -9.44 -5.02 1055 1564 -0.97 DQ1402001 0.009214 0.0003 0.282557 0.000023 0.282556 -7.6 -2.59 965 1427 -0.99 DQ1402002 0.015858 0.000576 0.282508 0.000022 0.282506 -9.34 -4.37 1041 1540 -0.98 DQ1402003 0.03368 0.001336 0.28248 0.000033 0.282474 -10.33 -5.48 1101 1610 -0.96 DQ1402004 0.01521 0.000498 0.282585 0.000031 0.282583 -6.61 -1.63 932 1366 -0.99 DQ1402005 0.021747 0.000815 0.282511 0.000044 0.282507 -9.23 -4.3 1043 1536 -0.98 DQ1402007 0.03101 0.001206 0.28236 0.000036 0.282355 -14.57 -9.7 1267 1878 -0.96 DQ1402009 0.020929 0.000835 0.282481 0.000037 0.282477 -10.29 -5.36 1085 1603 -0.97 DQ1402010 0.020601 0.000824 0.282592 0.000033 0.282588 -6.37 -1.43 930 1354 -0.98 DQ1402015 0.024671 0.000995 0.282467 0.000031 0.282463 -10.79 -5.88 1110 1636 -0.97 DQ1402016 0.019972 0.00073 0.282569 0.00003 0.282566 -7.18 -2.23 960 1404 -0.98 DQ1403001 0.027844 0.001171 0.282222 0.000044 0.282217 -19.45 -15.09 1459 2200 -0.96 DQ1403002 0.029647 0.001223 0.282523 0.000034 0.282518 -8.81 -4.45 1037 1527 -0.96 DQ1403003 0.028701 0.001163 0.282393 0.000036 0.282389 -13.4 -9.04 1219 1818 -0.96 DQ1403004 0.024133 0.000902 0.282589 0.00004 0.282586 -6.47 -2.07 936 1376 -0.97 DQ1403005 0.023542 0.000925 0.282474 0.000024 0.28247 -10.54 -6.15 1098 1634 -0.97 DQ1403006 0.031068 0.001196 0.282577 0.000037 0.282572 -6.9 -2.54 960 1405 -0.96 DQ1403007 0.030971 0.001193 0.282465 0.000033 0.28246 -10.86 -6.5 1118 1657 -0.96 DQ1403009 0.023133 0.000953 0.282413 0.000043 0.282409 -12.7 -8.31 1184 1771 -0.97 DQ1403010 0.029299 0.001241 0.282428 0.000036 0.282423 -12.17 -7.82 1172 1740 -0.96 DQ1403011 0.030401 0.00125 0.2824 0.000028 0.282395 -13.16 -8.81 1212 1803 -0.96 DQ1403012 0.021183 0.000861 0.282295 0.000047 0.282292 -16.87 -12.47 1346 2034 -0.97 DQ1403013 0.016252 0.000701 0.282568 0.00002 0.282565 -7.21 -2.79 960 1421 -0.98 DQ1403014 0.039337 0.00154 0.2824 0.000031 0.282394 -13.16 -8.85 1221 1805 -0.95 DQ1403017 0.025256 0.001057 0.282652 0.000046 0.282648 -4.24 0.13 851 1235 -0.97 DQ1403018 0.028212 0.001168 0.282314 0.000056 0.28231 -16.2 -11.84 1330 1994 -0.96 DQ1403019 0.025577 0.001044 0.28246 0.000034 0.282456 -11.03 -6.66 1121 1667 -0.97 DQ1406401 0.031739 0.001188 0.282505 0.000037 0.2825 -9.44 -4.65 1062 1555 -0.96 DQ1406402 0.019135 0.000821 0.282499 0.000029 0.282496 -9.65 -4.81 1060 1565 -0.98 DQ1406403 0.00643 0.000198 0.282574 0.000032 0.282573 -7 -2.06 940 1391 -0.99 DQ1406404 0.010201 0.00033 0.282565 0.000026 0.282564 -7.32 -2.4 955 1412 -0.99 DQ1406405 0.040919 0.001402 0.282352 0.000035 0.282346 -14.85 -10.1 1285 1899 -0.96 DQ1406406 0.02757 0.001103 0.282487 0.000031 0.282482 -10.08 -5.28 1085 1594 -0.97 DQ1406407 0.021275 0.000854 0.28257 0.000035 0.282566 -7.14 -2.3 961 1406 -0.97 DQ1406411 0.020696 0.00088 0.282485 0.000028 0.282481 -10.15 -5.31 1081 1597 -0.97 DQ1406413 0.036264 0.001253 0.282463 0.000057 0.282458 -10.93 -6.15 1123 1650 -0.96 DQ1406416 0.017471 0.000744 0.282533 0.000024 0.28253 -8.45 -3.59 1010 1488 -0.98 DQ1406418 0.060024 0.00183 0.282431 0.000048 0.282423 -12.06 -7.37 1186 1727 -0.94 表 3 大桥金矿岩浆岩微量和稀土元素组成
Table 3 Magmatic trace element and rare earth element data of the Daqiao gold deposit
样品 DQ140201 DQ140202 DQ140203 DQ140641 DQ140642 DQ140643 DQ140061 DQ140062 DQ140063 DQ140301 DQ140302 DQ140303 Rb 61.4 60.5 57.8 67.4 58.6 60.9 105 97.3 106 95.9 108 103 Ba 242 235 226 543 466 488 625 548 632 1099 1158 1165 Th 4.63 4.59 4.25 3.76 3.3 3.25 5.17 4.97 5.45 6.57 7.51 7.39 U 1.35 1.37 1.28 1.57 1.32 1.37 1.78 1.77 1.94 3.01 3.3 3.56 K 15855 15855 15855 15772 15855 15855 27062 27311 27062 27145 27228 27560 Ta 0.483 0.434 0.435 0.426 0.405 0.384 0.793 0.605 0.649 0.617 0.695 0.67 Nb 5.55 5.31 5.09 5.17 4.44 4.7 7.46 6.91 7.51 6.75 7.5 7.63 Sr 32.5 32.9 30.9 26.7 23.6 23.6 34.3 33.1 35.4 157 177 172 P 87 87 87 44 44 44 131 175 175 480 480 436 Zr 58.7 64.5 61 63.4 54.5 52.8 97.4 75.1 84.2 77.1 81.1 75 Hf 2.1 2.08 2.16 2.17 1.87 1.77 2.89 2.79 3.01 2.85 2.94 3.12 Sm 1.54 1.51 1.43 1.29 1.15 1.1 2.79 2.55 2.87 2.53 3.05 2.92 Ti 1619 1619 1619 1259 1259 1199 1918 1918 1858 2038 2038 2038 La 12.1 12 11.8 11.8 9.97 10.6 19.8 18.3 20.8 19.5 20.5 20.5 Ce 22.3 22.8 22 21.9 17.6 19.3 38 34.6 38.8 35 37.5 37.8 Pr 2.59 2.6 2.44 2.46 1.97 2.07 4.41 4.08 4.6 3.98 4.41 4.34 Nd 9.47 9.33 9.24 8.64 7.11 7.31 16.5 15 16.9 14.7 16.5 15.6 Sm 1.54 1.51 1.43 1.29 1.15 1.1 2.79 2.55 2.87 2.53 3.05 2.92 Eu 0.268 0.284 0.269 0.214 0.186 0.195 0.585 0.507 0.534 0.712 0.869 0.849 Gd 1.08 0.919 0.977 0.834 0.832 0.699 2.07 1.98 2.16 2.39 2.49 2.31 Tb 0.1 0.097 0.095 0.109 0.086 0.091 0.268 0.215 0.288 0.286 0.289 0.316 Dy 0.443 0.426 0.437 0.422 0.409 0.456 1.42 1.45 1.42 1.39 1.75 1.67 Ho 0.06 0.074 0.067 0.079 0.067 0.072 0.232 0.232 0.242 0.232 0.262 0.272 Er 0.139 0.22 0.233 0.242 0.248 0.203 0.706 0.684 0.758 0.68 0.811 0.742 Tm 0.028 0.03 0.028 0.033 0.028 0.029 0.114 0.12 0.118 0.098 0.113 0.103 Yb 0.196 0.232 0.161 0.22 0.189 0.187 0.691 0.706 0.798 0.612 0.729 0.592 Lu 0.039 0.03 0.041 0.031 0.03 0.038 0.115 0.105 0.126 0.083 0.107 0.116 Y 1.89 1.91 1.77 2.47 2.17 2.07 7.41 6.67 7.33 7.28 8.4 7.94 ΣREE 50.35 50.55 49.22 48.27 39.88 42.35 87.7 80.53 90.41 82.19 89.38 88.13 LREE 48.27 48.52 47.18 46.3 37.99 40.58 82.09 75.04 84.5 76.42 82.83 82.01 HREE 2.09 2.03 2.04 1.97 1.89 1.78 5.62 5.49 5.91 5.77 6.55 6.12 LREE/HREE 23.15 23.93 23.14 23.5 20.11 22.86 14.62 13.66 14.3 13.24 12.64 13.4 (La/Yb)N 44.28 37.1 52.57 38.47 37.84 40.66 20.55 18.59 18.7 22.86 20.17 24.84 δEu 0.6 0.68 0.66 0.59 0.55 0.63 0.71 0.66 0.63 0.87 0.93 0.97 δCe 0.93 0.96 0.95 0.95 0.92 0.95 0.96 0.94 0.93 0.92 0.92 0.93 Zr/Hf 27.95 31.01 28.24 29.22 29.14 29.83 33.7 26.92 27.97 27.05 27.59 24.04 Th/U 3.43 3.35 3.32 2.39 2.5 2.37 2.9 2.81 2.81 2.18 2.28 2.08 Nb/Ta 11.49 12.24 11.7 12.14 10.96 12.24 9.41 11.42 11.57 10.94 10.79 11.39 -
刘家军, 郑明华, 刘建明, 等. 西秦岭大地构造演化与金成矿带的分布[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 1997, 21(4), 307-314. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK199704003.htm 陈衍景, 张静, 张复新, 等. 西秦岭地区卡林-类卡林型金矿床及其成矿时间、构造背景和模式[J]. 地质论评, 2004, 50(2): 134-152. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200402004.htm 毛景文. 西秦岭地区造山型与卡林型金矿床[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2001, 20(1): 11-13. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200101003.htm 朱赖民, 张国伟, 刘家军, 等. 西秦岭-松潘构造结中的卡林型-类卡林型金矿床:成矿构造背景、存在问题和研究趋势[J]. 矿物学报, 2009, 29(增): 201-204. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB2009S1104.htm 张作衡, 毛景文, 王勇. 西秦岭金山金矿床流体包裹体特征及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2002, 21(增): 1106-1109. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2002S1293.htm 杨涛. 西秦岭李子园造山型金矿床地质-地球化学特征与成矿动力学背景[D]. 西北大学硕士学位论文, 2012: 63-66. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10697-1012444401.htm 朱赖民, 郭波, 李犇, 等. 西秦岭马鞍桥金矿床成矿流体地球化学及矿床成因研究[J]. 矿物学报, 2011,31(s): 446-447. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB2011S1227.htm 张静, 陈衍景, 张复新, 等. 陕西金龙山卡林型金矿带成矿流体地球化学研究[J]. 矿床地质, 2002, 21(3): 283-291. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200203009.htm 张复新, 陈衍景, 李超, 等. 金龙山-丘岭金矿床地质地球化学特征及成因:秦岭式卡林型金矿成矿动力学机制[J]. 中国科学(D 辑), 2000, 30(增).73-81. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2000S1009.htm 杨涛, 朱赖民, 李犇, 等. 西秦岭金龙山卡林型金矿床地质-地球化学及矿床成因研究[J]. 矿物学报, 2012, 32(1): 115-130. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201201016.htm 李楠. 阳山金矿带成矿作用地球化学[D]. 中国地质大学博士学位论文, 2013: 122-128. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1014239403.htm 付于真, 方维萱, 刘家军, 等. 陕川丁家林-太阳坪-董家院金矿带的矿田构造-岩相学研究[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2014, 38(4): 787-801. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201404005.htm 张新虎, 任丰寿, 余超, 等. 甘肃成矿系列研究及矿产勘查新突破[J]. 矿床地质, 2015, 34(6): 1130-1142. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201506004.htm 徐克红. 大桥金矿床地质特征及找矿标志[J]. 资源环境, 2008, 37(6): 79-80. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LZKQ200806056.htm 尤关进, 张忠平. 甘肃大桥金矿地质特征及其发现意义[J]. 甘肃地质, 2009, 18(4): 1-8. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSDZ200904002.htm 刘月高, 吕新彪, 张振杰, 等. 甘肃西和县大桥金矿床的成因研究[J]. 矿床地质, 2011, 30(6): 1085-1099. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201106010.htm 孙则朋, 王自翔, 徐亮, 等. 甘肃大桥金矿硅质岩地球化学特征及其地质意义探讨[J]. 地球化学, 2016. 45(5): 499-509. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201605006.htm 徐亮, 吴保祥, 王永莉, 等. 甘肃大桥金矿的流体包裹体特征及其地质意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2015, 45(s1): 1-2. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-DZDQ201601009053.htm Ludwig K R. User's manual for Isoplot 3.00: Ageochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, 2003. http://www.oalib.com/references/19135527 Ludwig K R. User's manual for Isoplot 3.00: Ageochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, 2003. http://www.oalib.com/references/19135527
侯可军, 李延河, 田有荣. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石微区原位定年技术[J]. 矿床地质, 2009, 28(4): 481-492. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200904009.htm 侯可军, 李延河, 邹天人, 等. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石Hf同位素的分析方法及地质应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(10): 2595-2604. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200710026.htm 吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 等. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(2): 185-220. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200702002.htm 吴元保, 郑永飞. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(16): 1589-1604. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200416001.htm Sun S S, Mc Donough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematic of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[C]// Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society Special publications, London, 1989, 42: 313-346. Sun S S, Mc Donough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematic of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[C]// Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society Special publications, London, 1989, 42: 313-346.
Zeng Q T, Mccuaig T C, Tohver E, et al. Episodic Triassic magmatism in the western South Qinling Orogen, central China, and its implications[J]. Geological Journal, 2014, 49(4/5): 402-423. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1896330198&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Zeng Q T, Mccuaig T C, Tohver E, et al. Episodic Triassic magmatism in the western South Qinling Orogen, central China, and its implications[J]. Geological Journal, 2014, 49(4/5): 402-423. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1896330198&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
杨阳, 王晓霞, 柯昌辉, 等. 西秦岭碌础坝岩体的锆石U-Pb年龄、成因及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 89(10): 1735-1761. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201510003.htm 孔娟娟, 牛耀龄, 段梦, 等. 西秦岭碌础坝、吴茶坝花岗岩的成因: 年代学和地球化学证据[C]//中国地球科学联合学术年会, 2014, 46(1): 2041-2043. Qin J F, Lai S C, Grapes R, et al. Geochemical evidence for origin of magma mixing for the Triassic monzonitic granite and its enclaves at Mishuling in the Qinling orogen(central China)[J]. Lithos, 2009, 112(3/4): 259-276. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1973506361&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Qin J F, Lai S C, Grapes R, et al. Geochemical evidence for origin of magma mixing for the Triassic monzonitic granite and its enclaves at Mishuling in the Qinling orogen(central China)[J]. Lithos, 2009, 112(3/4): 259-276. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1973506361&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
李佐臣, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等. 西秦岭糜署岭花岗岩体年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(8): 2617-2634. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201308001.htm Cao X F, Lv X B, Yao S Z, et al. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb Zircon geochrongy, Geochemistry and kinetics of the Wenquan ore bearing granites from west Qinling, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2011, 43(1): 120-131. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2010.03.004 Cao X F, Lv X B, Yao S Z, et al. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb Zircon geochrongy, Geochemistry and kinetics of the Wenquan ore bearing granites from west Qinling, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2011, 43(1): 120-131. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2010.03.004
徐学义, 陈隽璐, 高婷, 等. 西秦岭北缘花岗质岩浆作用及构造演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(2): 371-389. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201402006.htm 王天刚, 倪培, 孙卫东, 等. 西秦岭勉略带北部黄渚关和厂坝花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄及源区性质[J]. 科学通报, 2010, 36(55): 3493-3505. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201036010.htm 刘明强. 甘肃西秦岭舟曲憨班花岗岩体的单颗粒锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 地质科学, 2012, 47(3): 899-907. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX201203025.htm 吴峰辉, 刘树文, 李秋根, 等. 西秦岭光头山花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学及其地质意义[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 45(5): 811-818. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BDXP200901006.htm 骆必继. 西秦岭造山带印支期岩浆作用及深部过程[D]. 中国地质大学博士学位论文, 2013: 62-96. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10491-1014158078.htm 陈衍景. 秦岭印支期构造背景、岩浆活动及成矿作用[J]. 中国地质, 2011, 37(4):854-865. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201004005.htm 朱赖民, 丁振举, 姚书振, 等. 西秦岭甘肃温泉钼矿床成矿地质事件及其成矿构造背景[J]. 科学通报, 2009, 16: 2337-2347. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200916014.htm 邱昆峰, 李楠, Taylor R D, 等. 西秦岭温泉钼矿床成矿作用时限及其对斑岩型钼矿床系统分类制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(9): 2631-2643. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201409014.htm 刘志鹏, 李建威. 西秦岭金厂石英闪长岩的岩浆混合成因:岩相学和锆石U-Pb年代学证据及其构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2012, 86(7): 1077-1090. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201207004.htm 闫海卿, 贺宝林, 刘巧峰, 等. 西秦岭大水金矿岩浆岩年代学、地球化学特征[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2014, 30(2): 371-389. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX201401010.htm Amelin Y, Lee D C, Halliday A N, et al. Nature of the Earth's earliest crust from hafnium isotopes in single detrital zircons[J]. Nature, 1999, 399: 252-255. doi: 10.1038/20426 Amelin Y, Lee D C, Halliday A N, et al. Nature of the Earth's earliest crust from hafnium isotopes in single detrital zircons[J]. Nature, 1999, 399: 252-255. doi: 10.1038/20426
Vervoort J D, Patchett P J, Albarède F, et al. Hf-Nd isotopic evolution of the low crust[J]. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2000, 181: 115-129. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(00)00170-9 Vervoort J D, Patchett P J, Albarède F, et al. Hf-Nd isotopic evolution of the low crust[J]. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2000, 181: 115-129. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(00)00170-9
Griffin W L, Belousova E A, Shee S R, et al. Archean crustal evolution in the northern Yilgarn Craton:U-Pb and Hf-isotope evi-dence from detrital zircons[J]. Precambrian Res., 2004, 131: 231-282 doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2003.12.011 Griffin W L, Belousova E A, Shee S R, et al. Archean crustal evolution in the northern Yilgarn Craton:U-Pb and Hf-isotope evi-dence from detrital zircons[J]. Precambrian Res., 2004, 131: 231-282 doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2003.12.011
Amelin, Y, Lee D C, Halliday A N. Early middle archaean crustal evolution deduced from Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotopic studies of single zircon grains[J]. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 2000, 64: 4205-4225. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00493-2 Amelin, Y, Lee D C, Halliday A N. Early middle archaean crustal evolution deduced from Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotopic studies of single zircon grains[J]. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 2000, 64: 4205-4225. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00493-2
Vervoort J D, Patchett P J, Gehrels G E, et al. Constraints on early Earth differentiation from hafnium and neodymium isotopes[J]. Nature, 1996, 379: 624-627. doi: 10.1038/379624a0 Vervoort J D, Patchett P J, Gehrels G E, et al. Constraints on early Earth differentiation from hafnium and neodymium isotopes[J]. Nature, 1996, 379: 624-627. doi: 10.1038/379624a0




 下载:
下载: