Global IAB data excavation: The performance in basalt discrimination diagrams and preliminary interpretation
-
摘要:
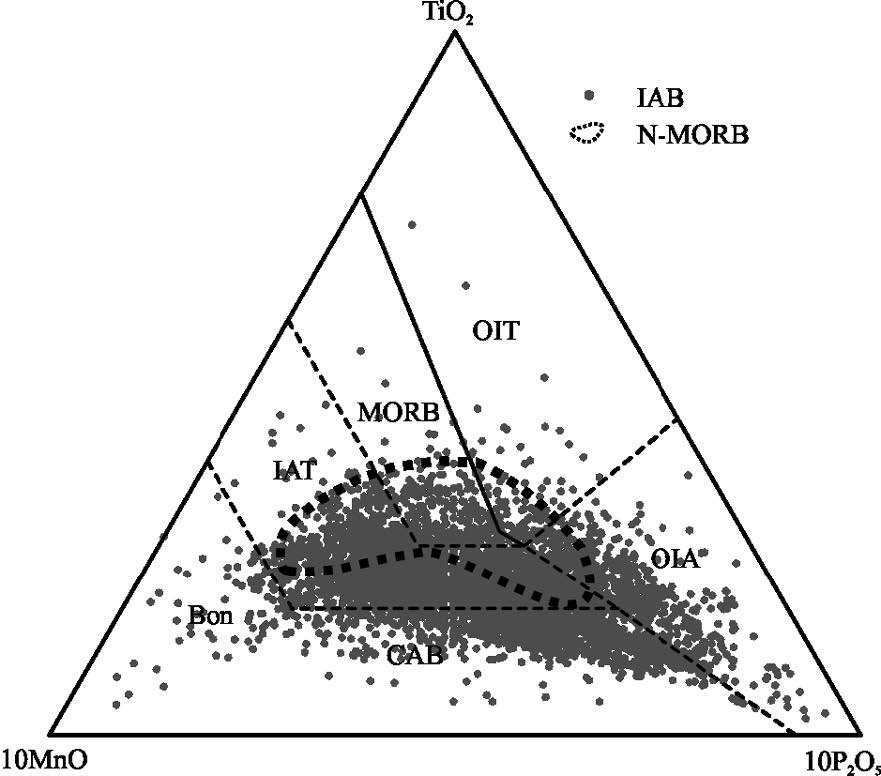
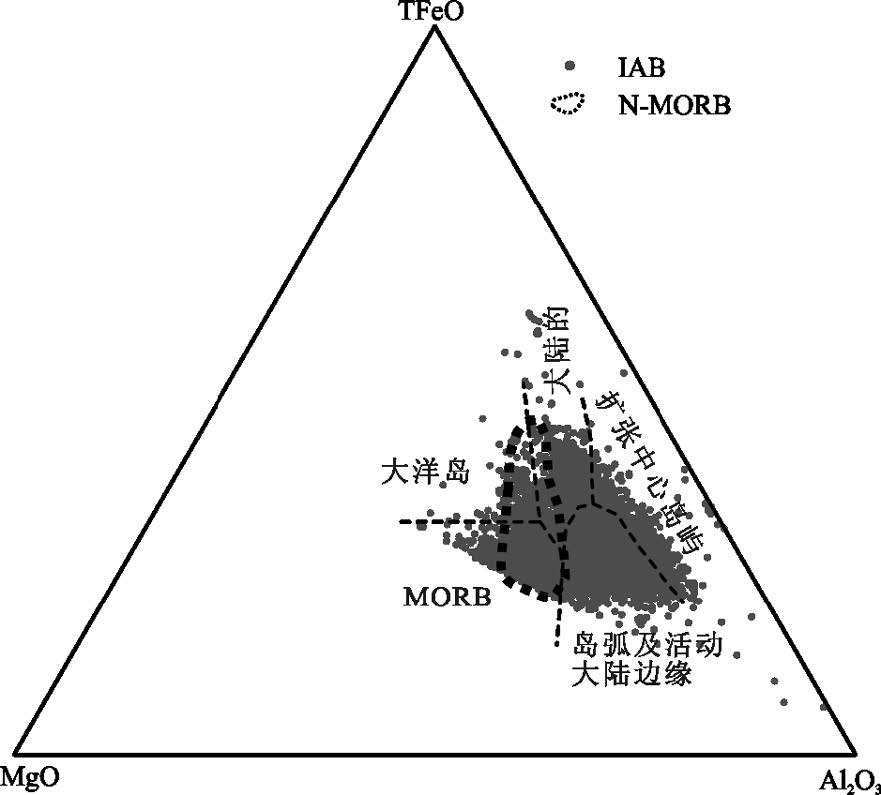
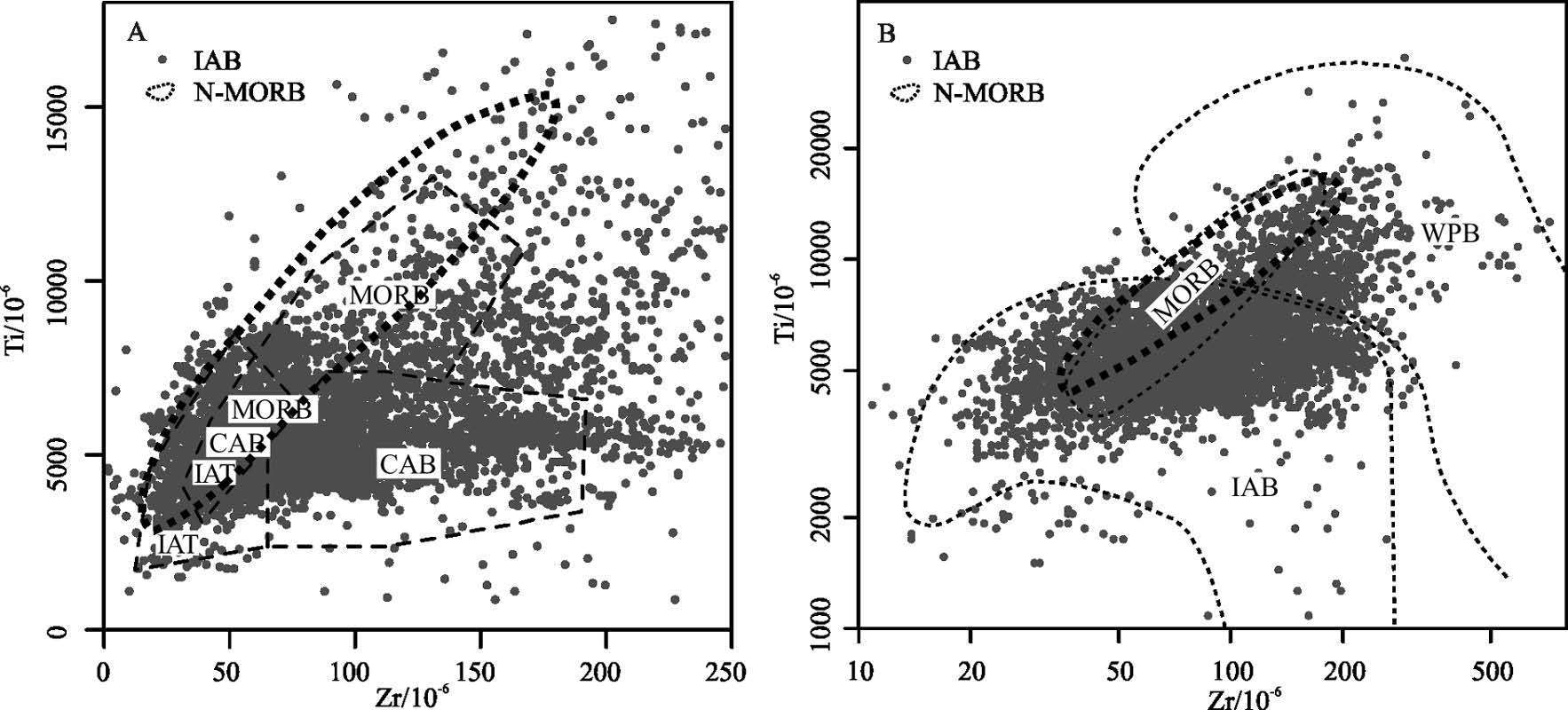
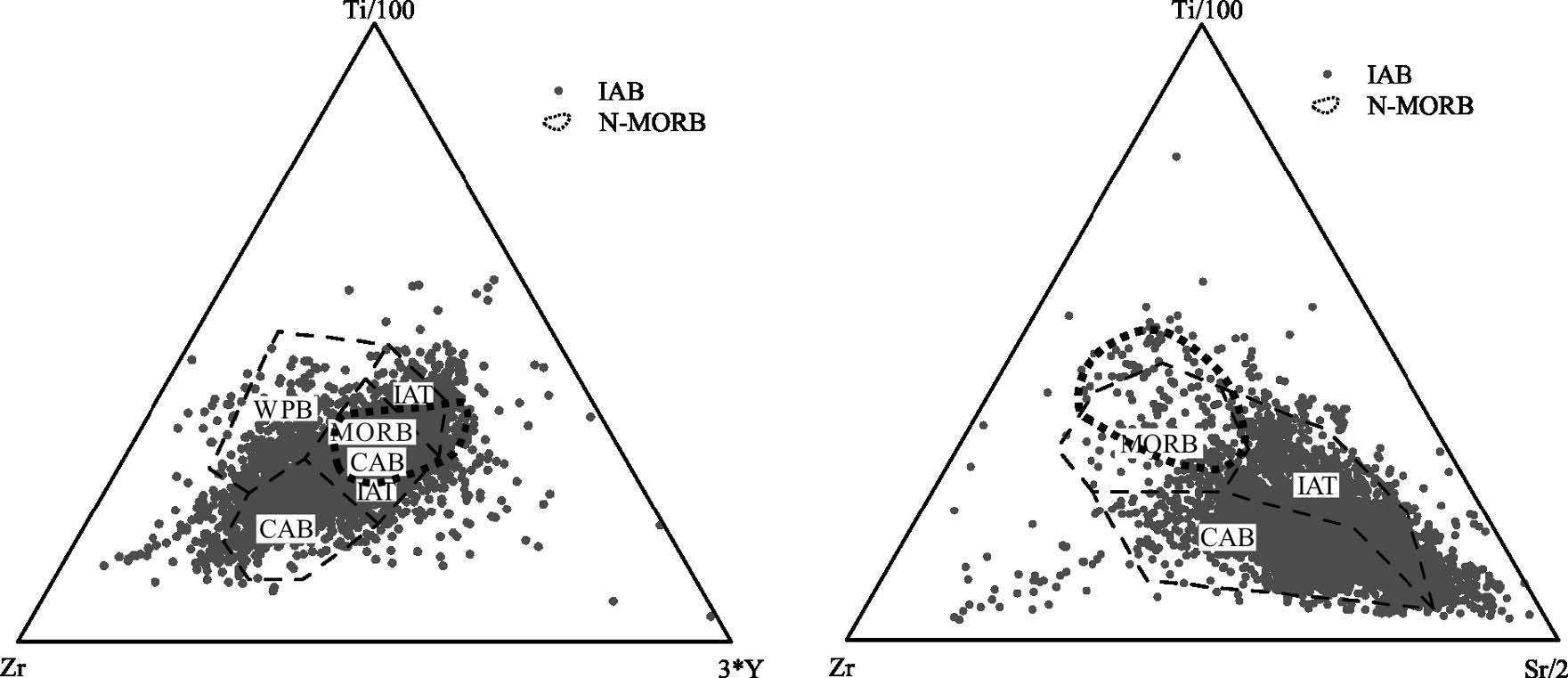
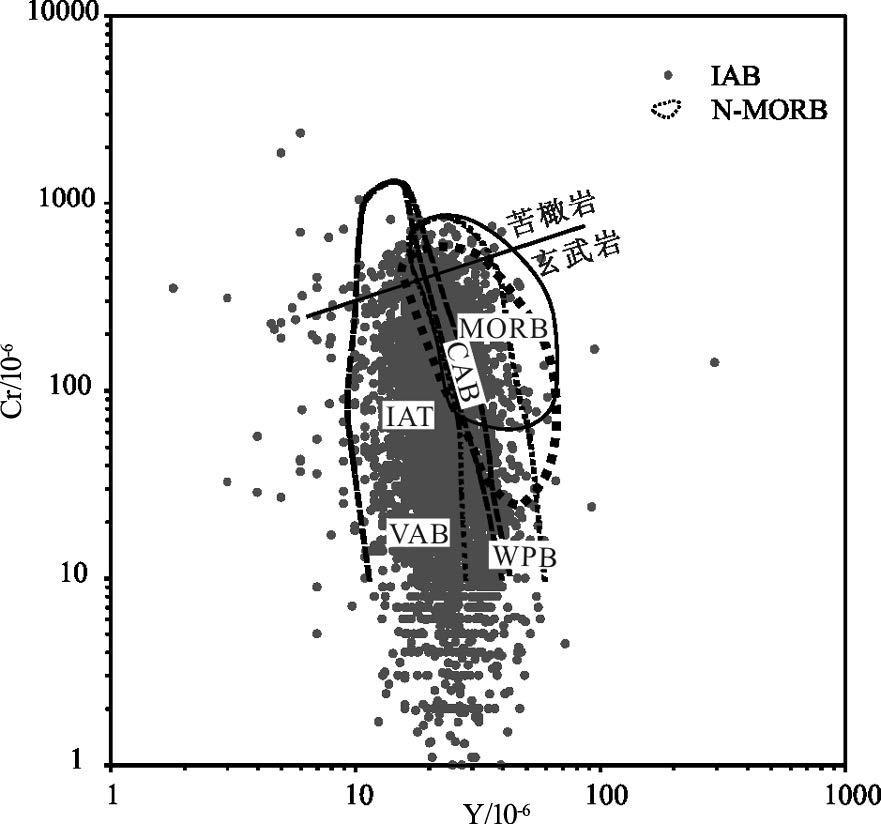
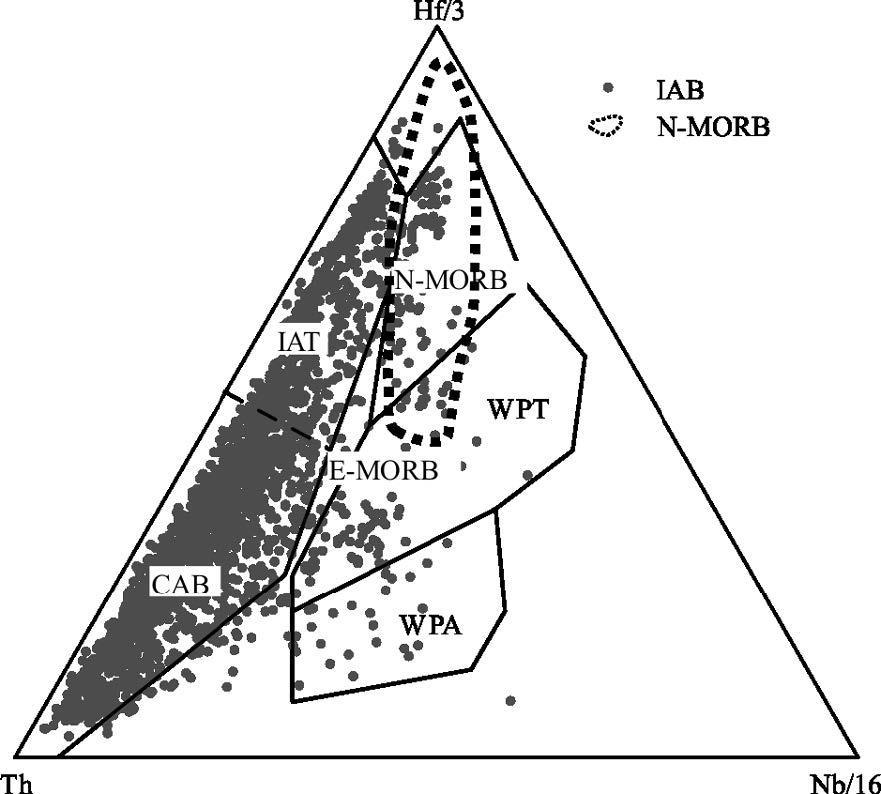
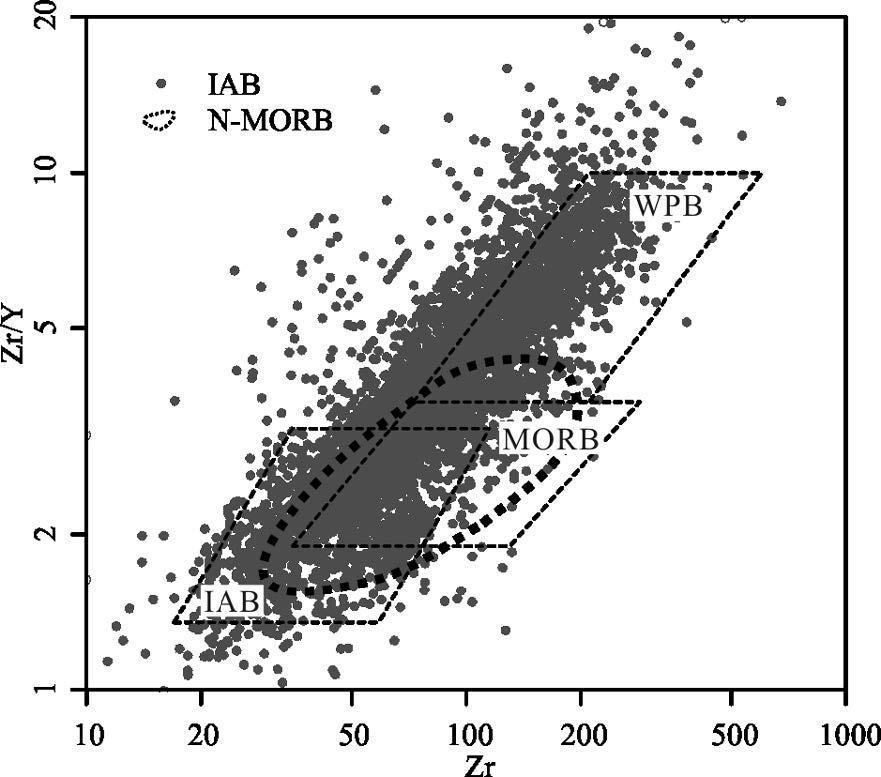
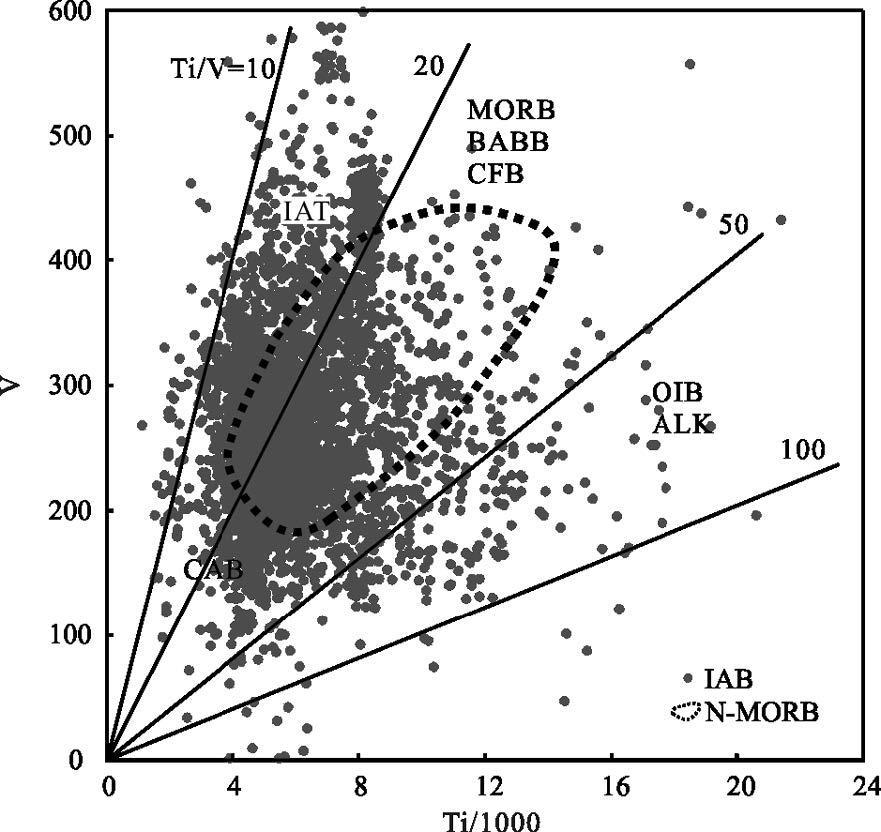
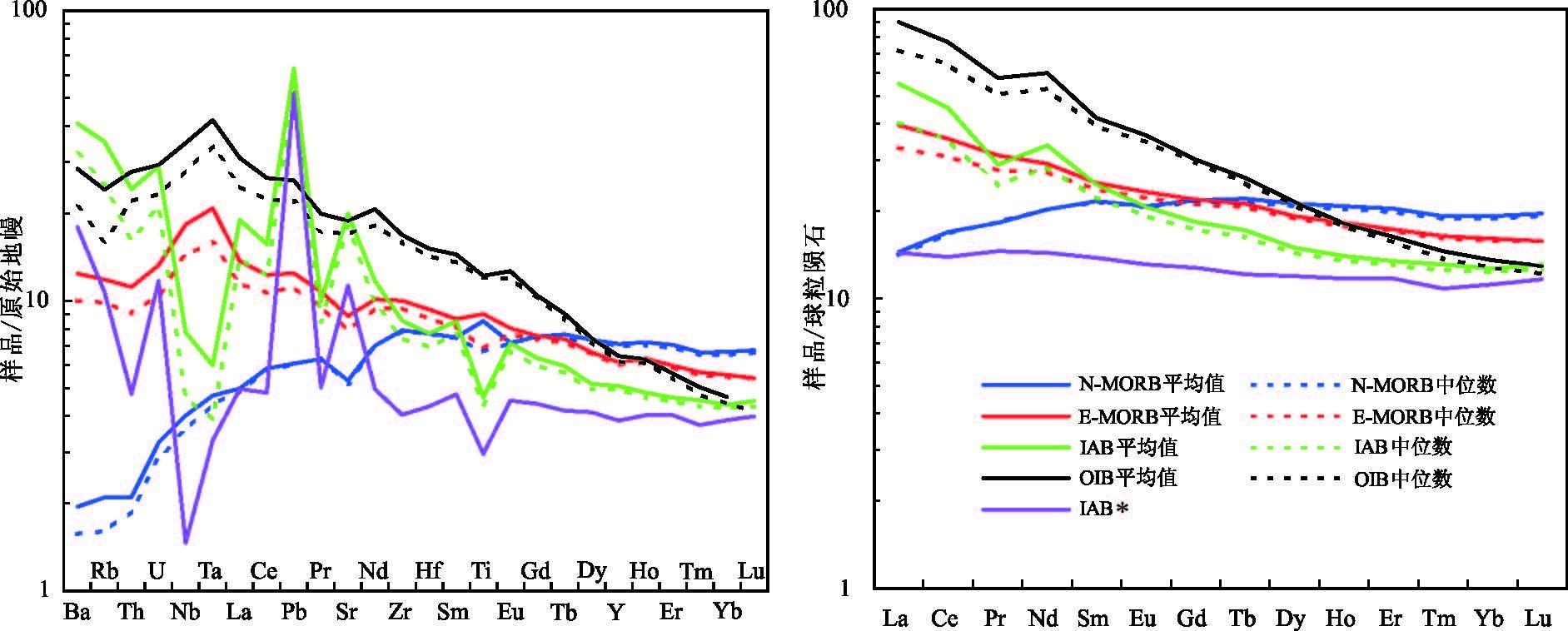
MORB(洋中脊玄武岩)、OIB(洋岛玄武岩)和IAB(岛弧玄武岩)是学术界最关心的3 种玄武岩类型,其中尤以与板块消减作用有关的岛弧岩浆活动备受关注。岛弧可分为洋内岛弧和大陆边缘岛弧(活动陆缘弧)2 类。对IAB 进行讨论,重点探讨IAB 的识别。IAT(岛弧拉斑玄武岩)和IAB 是前弧、岛弧和后弧岩浆作用的产物,其中,后弧组分更具多样性,它不同于弧后玄武岩,前者属于弧的范围,而后者形成的动力学过程与俯冲系统有关,但其是独立的构造单元,尽管其岩浆作用可能仍受到俯冲流体的影响。前人对IAB 进行了大量研究,提出了多种构造环境判别图解,并得到广泛应用。尝试应用全球玄武岩数据来验证上述判别图的可信度,研究发现,可信度高的判别图不多,且大多与Th、Ta(Nb)和Ti 元素有关的,如Hf-Th-Ta(Nb)、Ti-Zr-Sr 和Th/Yb-Ta/Yb 图,其余判别图的判别效果可信度低且具多解性,建议谨慎使用。IAB 与MORB 和OIB 的区别主要体现在Nb-Ta 亏损的特征上,是否受到俯冲流体的影响是区分IAB 与MORB 和OIB 最重要的标志。
Abstract:MORB, OIB and IAB (arc calc-alkaline basalt) have aroused much interest among geologists, with particular attention paid to igneous activities in island arcs related to plate subduction. Such island arcs can be divided into island arc and continental margin arc (active epicontinental arc). This paper discusses the IAB, mainly focusing on the identification of IAB. The IAT (island arc tholeiite) and the IAB are products of the fore-arc, the island arc and the rear-arc magmatism. Among them, the rear-arc is more diversified in composition and is different from back-arc (back arc):the former belongs to the scope of the arc, while the latter is related to the subduction system in the kinetics of formation; nevertheless, the back-arc is an independent tectonic unit, although its magmatism might still be affected by the subduction metasomatic fluids. Previous researchers made detailed studies of the IAB and put forward a variety of tectonic environment discrimination diagrams which have been widely used. In this paper, the authors tried to apply the global basalt data to verify the credibility of the discriminant figures. However, there only exist very few highly credible discrimination diagrams, and these figures are mostly related to Th, Ta (Nb), and Ti elements, such as the figures of Hf -Th-Ta (Nb), TiZr-Sr and Th/Yb-Ta/Yb, whereas the rest of the discriminant figures are of low credibility and characterized by multiple solutions, and hence should be used prudently. Researches show that the difference between the IAB and MORB, OIB mainly finds expression in the depletion of Nb-Ta, and this suggests that the most important criterion to distinguish the IAB from MORB and OIB is whether they are affected by subduction fluids or not.
-
Keywords:
- IAB /
- MORB /
- OIB /
- data excavation /
- discrimination diagram /
- island arc /
- rear arc
-
致谢: 研究中得到兰州大学研究生侯克选和马骊的帮助,特此致以衷心的感谢。
-
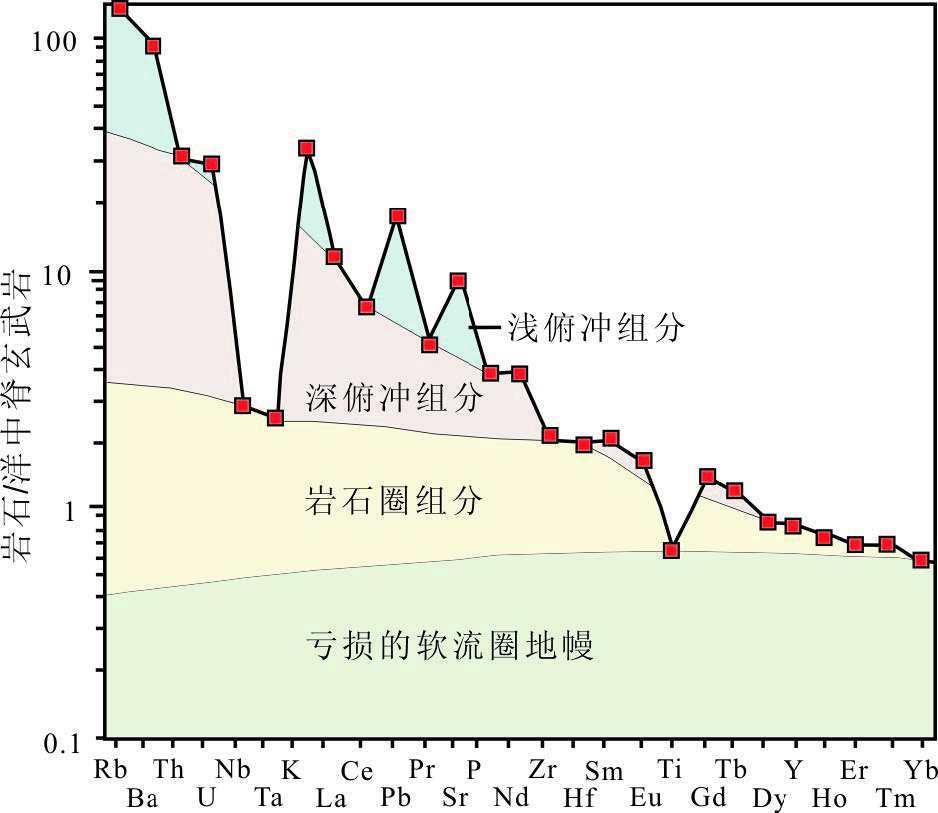
图 16 以马里亚纳弧盆系统为代表的IAB 四组分模式图[29]
Figure 16. Graphical evidence for the four-component model for the Mariana arc-basin system
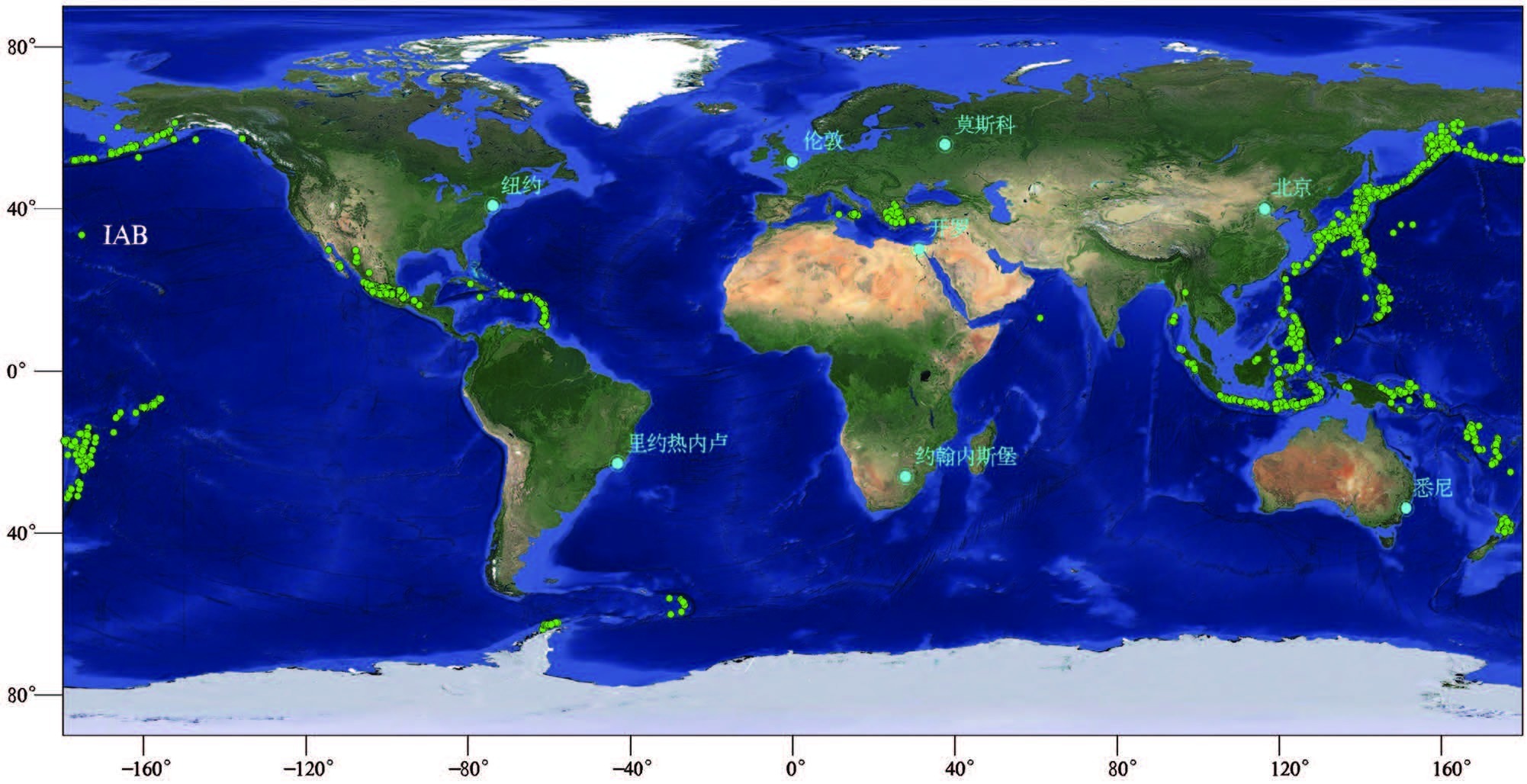
表 1 IAB 样品的数据来源与数据量
Table 1 Statistical chart of data sources and data volume of IAB samples
数据来源 所有文献/篇 共下载文献/篇 确定为IAB文献/篇 数据量/个 Aegean Arc 79 37 37 435 Aeolian Arc 122 80 80 1202 Aleutian Arc 149 91 77 475 Banda Arc 24 8 8 197 Bismarck Arc-New Britain Arc 99 55 40 210 Greater Antilles 35 18 13 226 Honshu Arc 649 347 264 1285 Izu-Bonin Arc 243 136 119 1670 Kamchatka Arc 114 77 72 575 Kermadec Arc 35 26 20 27 Kurile Arc 160 93 86 614 Lesser Antilles 134 83 72 625 Luzon Arc 77 34 29 246 Mariana Arc 130 60 40 220 Mexican Volcanic Belts 232 148 105 604 New Hebrides Arc 66 33 26 413 New Zealand 154 107 103 294 Ryukyu Arc 152 81 65 296 Scotia Arc 59 27 17 135 Solomon Island Arc 20 13 12 102 Sulawesi Arc 30 17 15 146 Sunda Arc 112 67 65 663 Tonga Arc 143 66 31 261 Yap Arc 13 5 4 9 共计 3031 1709 1400 10930 表 2 IAB、CAB 样品主量、微量和稀土元素含量
Table 2 Major,trace and rare earth element content of IAB and CAB
元素 IAB CAB 数据量 平均值 中位数 ∗ SiO2 7819 51.84 52.02 TiO2 7597 1.01 0.95 0.64 0.98 Al2O3 7526 17.03 17.17 FeOT 7575 9.21 8.94 MnO 7498 0.17 0.17 MgO 7661 5.39 5.16 CaO 7545 9.42 9.39 Na2O 7576 2.88 2.85 K2O 8013 0.97 0.81 0.94 P2O5 7280 0.22 0.19 0.19 TOTAL 98.15 97.65 Cs 2513 0.59 0.43 Rb 6345 22.46 16 6.8 23 Ba 5953 285.67 224 125.6 260 Th 4048 2.06 1.38 0.405 1.26 U 3203 0.61 0.44 0.245 Nb 4811 5.55 3.3 1.041 2.7 Ta 2522 0.25 0.16 0.135 1 La 4330 13.05 9.58 3.407 Ce 4279 27.84 21.67 8.546 29.3 Pb 3475 4.49 3.88 3.696 Pr 2541 2.75 2.33 1.384 Mo 329 0.97 0.95 237.3 428 Sr 6645 420.2 381 6.7 Nd 4023 15.81 13.29 2.112 3.78 Sm 3798 3.78 3.4 45.24 71 Zr 5846 95.61 83 1.333 2.23 Hf 3091 2.38 2.14 0.761 Eu 3558 1.2 1.12 3858 5880 Ti 7597 6044 5695 2.625 Gd 2851 3.77 3.55 0.452 Tb 3103 0.64 0.61 3.045 Dy 2851 3.8 3.65 Li 999 7.97 7.44 17.59 22 Y 5500 23.1 22.62 0.662 Ho 2547 0.79 0.76 1.938 Er 2805 2.23 2.16 0.276 Tm 2118 0.34 0.32 1.908 2.31 Yb 3579 2.16 2.1 0.295 Lu 3221 0.33 0.32 87Sr/86Sr 3077 0.704117 0.703901 143Nd/144Nd 2332 0.512897 0.512943 206Pb/204Pb 1615 18.64884 18.661 207Pb/204Pb 1617 15.57673 15.565 208Pb/204Pb 1617 38.44722 38.404 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量为10-6;IAB∗数据据参考文献[26-27],CAB 数据据参考文献[15] -
Capedri S, Venturelli G, Bocchi G, et al. The geochemistry and petrogenesis of an ophiolitic sequence from Pindos, Greece[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1980, 74(2): 189-200. doi: 10.1007/BF01132004 Capedri S, Venturelli G, Bocchi G, et al. The geochemistry and petrogenesis of an ophiolitic sequence from Pindos, Greece[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1980, 74(2): 189-200. doi: 10.1007/BF01132004
Galoyan G, Rolland Y, Sosson M, et al. Evidence for superposed MORB, oceanic plateau and volcanic arc series in the Lesser Caucasus (Stepanavan, Armenia)[J]. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 2007, 339(7): 482-492. doi: 10.1016/j.crte.2007.06.002 Galoyan G, Rolland Y, Sosson M, et al. Evidence for superposed MORB, oceanic plateau and volcanic arc series in the Lesser Caucasus (Stepanavan, Armenia)[J]. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 2007, 339(7): 482-492. doi: 10.1016/j.crte.2007.06.002
Glassley W. Geochemistry and tectonics of the Crescent volcanic rocks, Olympic Peninsula, Washington[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1974, 85(5): 785-794. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1974)85<785:GATOTC>2.0.CO;2 Glassley W. Geochemistry and tectonics of the Crescent volcanic rocks, Olympic Peninsula, Washington[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1974, 85(5): 785-794. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1974)85<785:GATOTC>2.0.CO;2
Harris N B W, Pearce J A, Tindle A G. Geochemical characteristics of collision-zone magmatism[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1986, 19(1): 67-81. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1986.019.01.04 Harris N B W, Pearce J A, Tindle A G. Geochemical characteristics of collision-zone magmatism[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1986, 19(1): 67-81. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1986.019.01.04
Meschede M. A method of discriminating between different types of mid-ocean ridge basalts and continental tholeiites with the Nb, Zr, Y diagram[J]. Chemical Geology, 1986, 56(3): 207-218. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222365828_A_method_of_discriminating_between_different_types_of_Mid-Ocean_Ridge_Basalts_and_continental_tholeiites_with_the_Nb-Zr-Y_diagram Meschede M. A method of discriminating between different types of mid-ocean ridge basalts and continental tholeiites with the Nb, Zr, Y diagram[J]. Chemical Geology, 1986, 56(3): 207-218. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222365828_A_method_of_discriminating_between_different_types_of_Mid-Ocean_Ridge_Basalts_and_continental_tholeiites_with_the_Nb-Zr-Y_diagram
Mullen E D. MnO-TiO2-P2O5: a minor element discriminant for basaltic rocks of oceanic environments and its implications for petrogenesis[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983, 62(1): 53-62. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(83)90070-5 Mullen E D. MnO-TiO2-P2O5: a minor element discriminant for basaltic rocks of oceanic environments and its implications for petrogenesis[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983, 62(1): 53-62. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(83)90070-5
Pearce J A, Cann J R. Tectonic setting of basic volcanic rocks determined using trace element analyses[J]. Earth and planetary science letters, 1973, 19(2): 290-300. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(73)90129-5 Pearce J A, Cann J R. Tectonic setting of basic volcanic rocks determined using trace element analyses[J]. Earth and planetary science letters, 1973, 19(2): 290-300. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(73)90129-5
Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Jour-nal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4): 956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956 Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Jour-nal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4): 956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
Pearce J A, Lippard S J, Roberts S. Characteristics and tectonic significance of supra-subduction zone ophiolites[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1984, 16(1): 77-94. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1984.016.01.06 Pearce J A, Lippard S J, Roberts S. Characteristics and tectonic significance of supra-subduction zone ophiolites[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1984, 16(1): 77-94. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1984.016.01.06
Pearce J A, Norry M J. Petrogenetic implications of Ti, Zr, Y, and Nb variations in volcanic rocks[J]. Contributions to mineralogy and petrology, 1979, 69(1): 33-47. doi: 10.1007/BF00375192 Pearce J A, Norry M J. Petrogenetic implications of Ti, Zr, Y, and Nb variations in volcanic rocks[J]. Contributions to mineralogy and petrology, 1979, 69(1): 33-47. doi: 10.1007/BF00375192
Pearce J A, Peate D W. Tectonic implications of the composition of volcanic arc magmas[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1995, 23: 251-286. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ea.23.050195.001343 Pearce J A, Peate D W. Tectonic implications of the composition of volcanic arc magmas[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1995, 23: 251-286. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ea.23.050195.001343
Pearce J A. Basalt geochemistry used to investigate past tectonic environments on Cyprus[J]. Tectonophysics, 1975, 25(1): 41-67. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1999194663&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Pearce J A. Basalt geochemistry used to investigate past tectonic environments on Cyprus[J]. Tectonophysics, 1975, 25(1): 41-67. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1999194663&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Pearce J A. Role of the sub-continental lithosphere in magma genesis at active continental margins[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1983, 147(6): 2162-2173. Pearce J A. Role of the sub-continental lithosphere in magma genesis at active continental margins[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1983, 147(6): 2162-2173.
Pearce J A. Statistical analysis of major element patterns in basalts[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1976, 17(1): 15-43. doi: 10.1093/petrology/17.1.15 Pearce J A. Statistical analysis of major element patterns in basalts[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1976, 17(1): 15-43. doi: 10.1093/petrology/17.1.15
Pearce J A. Supra-subduction zone ophiolites: the search for modern analogues[J]. Special Papers-Geological Society of America, 2003: 269-294. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1837708467&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Pearce J A. Supra-subduction zone ophiolites: the search for modern analogues[J]. Special Papers-Geological Society of America, 2003: 269-294. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1837708467&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Pearce J A. Trace element characteristics of lavas from destructive plate boundaries[J]. Andesites, 1982, 8: 525-548. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/304749002_Trace_Element_Characteristics_of_Lavas_from_Destructive_Plate_Boundaries Pearce J A. Trace element characteristics of lavas from destructive plate boundaries[J]. Andesites, 1982, 8: 525-548. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/304749002_Trace_Element_Characteristics_of_Lavas_from_Destructive_Plate_Boundaries
Pearce T H, Gorman B E, Birkett T C. The relationship between major element chemistry and tectonic environment of basic and intermediate volcanic rocks[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1977, 36(1): 121-132. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(77)90193-5 Pearce T H, Gorman B E, Birkett T C. The relationship between major element chemistry and tectonic environment of basic and intermediate volcanic rocks[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1977, 36(1): 121-132. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(77)90193-5
Shervais J W. Ti-V plots and the petrogenesis of modern and ophiolitic lavas[J]. Earth and planetary science letters, 1982, 59(1): 101-118. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(82)90120-0 Shervais J W. Ti-V plots and the petrogenesis of modern and ophiolitic lavas[J]. Earth and planetary science letters, 1982, 59(1): 101-118. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(82)90120-0
Wood D A, Joron J L, Treuil M. A re-appraisal of the use of trace elements to classify and discriminate between magma series erupted in different tectonic settings[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1979, 45(2): 326-336. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(79)90133-X Wood D A, Joron J L, Treuil M. A re-appraisal of the use of trace elements to classify and discriminate between magma series erupted in different tectonic settings[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1979, 45(2): 326-336. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(79)90133-X
Wood D A. The application of a Th Hf Ta diagram to problems of tectonomagmatic classification and to establishing the nature of crustal contamination of basaltic lavas of the British Tertiary Volca-nic Province[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1980, 50(1): 11-30. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(80)90116-8 Wood D A. The application of a Th Hf Ta diagram to problems of tectonomagmatic classification and to establishing the nature of crustal contamination of basaltic lavas of the British Tertiary Volca-nic Province[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1980, 50(1): 11-30. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(80)90116-8
Workman R K, Hart S R. Major and trace element composition of the depleted MORB mantle (DMM)[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 231(1): 53-72. http://www.doc88.com/p-1466074700260.html Workman R K, Hart S R. Major and trace element composition of the depleted MORB mantle (DMM)[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 231(1): 53-72. http://www.doc88.com/p-1466074700260.html
Allan J F, Carmichael I S E. Lamprophyric lavas in the Colima graben, SW Mexico[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1984, 88(3): 203-216. doi: 10.1007/BF00380166 Allan J F, Carmichael I S E. Lamprophyric lavas in the Colima graben, SW Mexico[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1984, 88(3): 203-216. doi: 10.1007/BF00380166
杨婧, 王金荣, 张旗, 等. 弧后盆地玄武岩(BABB)数据挖掘: 与MORB及IAB的对比[J]. 地球科学进展, 2016, 31(1): 66-77. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201601006.htm 王金荣, 潘振杰, 张旗, 等. 大陆板内玄武岩数据挖掘: 成分多样性及在判别图中的表现[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(7): 1919-1933. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201607001.htm Li C, Arndt N T, Tang Q, et al. Trace element indiscrimination diagrams[J]. Lithos, 2015, 232: 76-83. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.06.022 Li C, Arndt N T, Tang Q, et al. Trace element indiscrimination diagrams[J]. Lithos, 2015, 232: 76-83. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.06.022
Ewart A, Collerson K D, Regelous M, et al. Geochemical evolution within the Tonga-Kermadec-Lau arc-back-arc systems: the role of varying mantle wedge composition in space and time[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1998, 39(3): 331-368. doi: 10.1093/petroj/39.3.331 Ewart A, Collerson K D, Regelous M, et al. Geochemical evolution within the Tonga-Kermadec-Lau arc-back-arc systems: the role of varying mantle wedge composition in space and time[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1998, 39(3): 331-368. doi: 10.1093/petroj/39.3.331
Niu Y, O'Hara M J. Origin 捯潦洠灯潣獥楡瑮椠潩湳獬?普牤漠浢?关畡慬瑴敳爺渠慁爠祮?扷愠獰慥汲瑳楰捥?癴潩汶捥愠湦楲捯?爠潰捥歴獲?楬湯?湹漬爠瑧桥敯慣獨瑥敭物湳??慹瀬愠湡???浭灩汮楥捲慡瑬椠潰湨獹?晩潣牳?楣湯瑮敳物慤捥瑲楡潴湩?扮敳瑛睊敝攮渠?獯畵扲摮畡捬琠敯摦?潇捥敯慰湨楹捳?獣污慬戠?慥湳摥?浲慣湨琺氠敓?睬敩摤朠故孡?嵴???漲田爰渳愬氠?漰昸??攩漺瀠栲礸猳椭挲愹氹?刼敢獲放慛爲挸桝??卵潮氠楓搠??愠牍瑣桄????????ㄠう金???????ち?ㄠ??つ????扴牯?孩??嵳??獴桥業穡畴歩慣?夠??丠慯正慥条慮睩慣????偡敬瑴牳漺氠潩杭楰捬慩汣?整癩潯汮畳琠楦潯湲?潭晡?剴楬獥栠楣牯業?癯潳汩捴慩湯潮??湮潤爠瑰桲敯牣湥??潥歳歛慊楝搮漠???慬灯慧湩季?嵬???潣畩牥湴慹氬?潌景??楯湮攬爠慓汰潥杣祩?偬攠瑐牵潢汬潩杣祡????捳漬渠漱洹椸挹??攴漲氨漱朩示?″?????‵??????′代????????戠牊?孁??嵓??獲桮椠穒甠歊愬?奂??乯慭步慲朠慓眠慈???????爮?慇来敯獣?潥晭?摣慡捬椠瑭楡捰?汩慮癧愠?摦漠浴敨獥?潍晡?剩楡獮桡椠牡楲?瘭潢污捳慩湮漠??湳潴牥瑭栺攠牉湭??潩正歡慴楩摯潮?嬠?嵯???潨略爠湮慡汴?潲晥??楮湤攠牤慩汳潴杲祩?偵整瑩牯潮氠潯杦礠????捵潣湴潩浯楮挠??敭潰汯潮来祮?????????????????ひ?????ophysics, Geosystems, 2005, 6(7): 406-407. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/30051030_Origin_of_ocean_island_basalts_A_new_perspective_from_petrology_geochemistry_and_mineral_physics_considerations Niu Y, O'Hara M J. Origin of ocean island basalts: A new perspective from petrology, geochemistry, and mineral physics considerations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2003, 108(4): 283-299. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/30051030_Origin_of_ocean_island_basalts_A_new_perspective_from_petrology_geochemistry_and_mineral_physics_considerations
Zindler A, Hart S. Chemical geodynamics[J]. Annual review of earth and planetary sciences, 1986, 14: 493-571. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19 Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Rollinson H R. Using geochemical data: evaluation, presentation, interpretation[M]. Routledge, 2014. Pearce J A, Stern R J, Bloomer S H, et al. Geochemical mapping of the Mariana arc-basin system: Implications for the nature and distribution of subduction components[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2005, 6(7): 406-407.
Bloomer S H. Geochemical characteristics of boninite-and tholeiite-series volcanic rocks from the Mariana forearc and the role of an incompatible element-enriched fluid in arc petrogenesis[J]. Geological Society of America Special Papers, 1987, 215: 151-164. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ea.14.050186.002425 Zindler A, Hart S. Chemical geodynamics[J]. Annual review of earth and planetary sciences, 1986, 14: 493-571. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ea.14.050186.002425
Tatsumi Y, Maruyama S. Boninites and high-Mg andesites:tectonics and petrogenesis[C]//Crawford A J. Boninite and related rocks. Unwin Hyman, London, 1989: 50-71 Rollinson H R. Using geochemical data: evaluation, presentation, interpretation[M]. Routledge, 2014.
Kuritani T, Yokoyama T, Nakamura E. Generation of rear-arc magmas induced by influx of slab-derived supercritical liquids: implications from alkali basalt lavas from Rishiri volcano, Kurile arc[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2008, 49(7): 1319-1342. doi: 10.1130/SPE215 Bloomer S H. Geochemical characteristics of boninite-and tholeiite-series volcanic rocks from the Mariana forearc and the role of an incompatible element-enriched fluid in arc petrogenesis[J]. Geological Society of America Special Papers, 1987, 215: 151-164. doi: 10.1130/SPE215
Kuritani T, Kitagawa H, Nakamura E. Assimilation and fractional crystallization controlled by transport process of crustal melt: implications from an alkali basalt-dacite suite from Rishiri Volcano, Japan[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2005, 46(7): 1421-1442. Tatsumi Y, Maruyama S. Boninites and high-Mg andesites:tectonics and petrogenesis[C]//Crawford A J. Boninite and related rocks. Unwin Hyman, London, 1989: 50-71
Nakamura E, Campbell I H, Sun S S. The influence of subduction processes on the geochemistry of Japanese alkaline basalts[J]. Nature, 1985, 316(6023): 55-58. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egn027 Kuritani T, Yokoyama T, Nakamura E. Generation of rear-arc magmas induced by influx of slab-derived supercritical liquids: implications from alkali basalt lavas from Rishiri volcano, Kurile arc[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2008, 49(7): 1319-1342. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egn027
Shibata T, Nakamura E. Across-arc variations of isotope and trace element doi: 10.1093/petrology/egi021 Kuritani T, Kitagawa H, Nakamura E. Assimilation and fractional crystallization controlled by transport process of crustal melt: implications from an alkali basalt-dacite suite from Rishiri Volcano, Japan[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2005, 46(7): 1421-1442. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egi021
Nakamura E, Campbell I H, Sun S S. The influence of subduction processes on the geochemistry of Japanese alkaline basalts[J]. Nature, 1985, 316(6023): 55-58. doi: 10.1038/316055a0
Shibata T, Nakamura E. Across-arc variations of isotope and trace element compositions from Quaternary basaltic volcanic rocks in northeastern Japan: Implications for interaction between subducted oceanic slab and mantle wedge[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1997, 102(B4): 8051-8064. doi: 10.1029/96JB03661
Ishizuka Y, Nakagawa M. Petrological evolution of Rishiri volcano, northern Hokkaido, Japan[J]. Journal of Mineralogy Petrology & Economic Geology, 1999, 94(8): 279-294.
Ishizuka Y, Nakagawa M. K-Ar ages of dacitic lava domes of Rishiri volcano, northern Hokkaido.[J]. Journal of Mineralogy Petrology & Economic Geology, 1994, 89(9): 360-364.



 下载:
下载: