Reconstruction of the Holocene rela-tive sea level change for the south coast of Laizhou Bay
-
摘要:
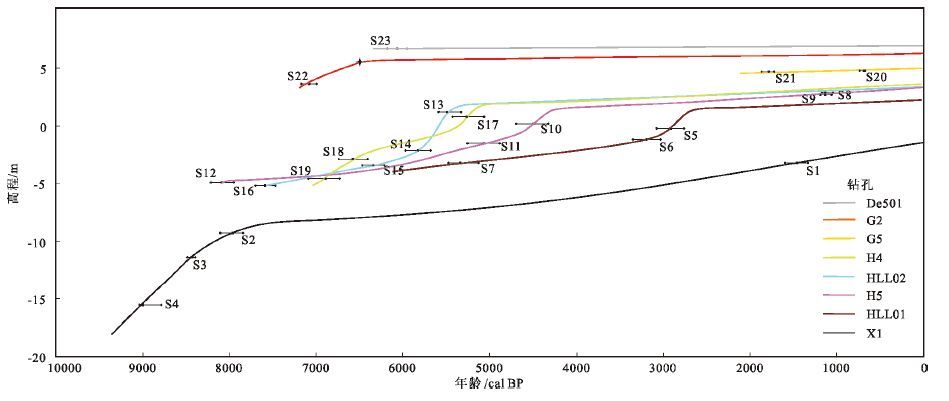
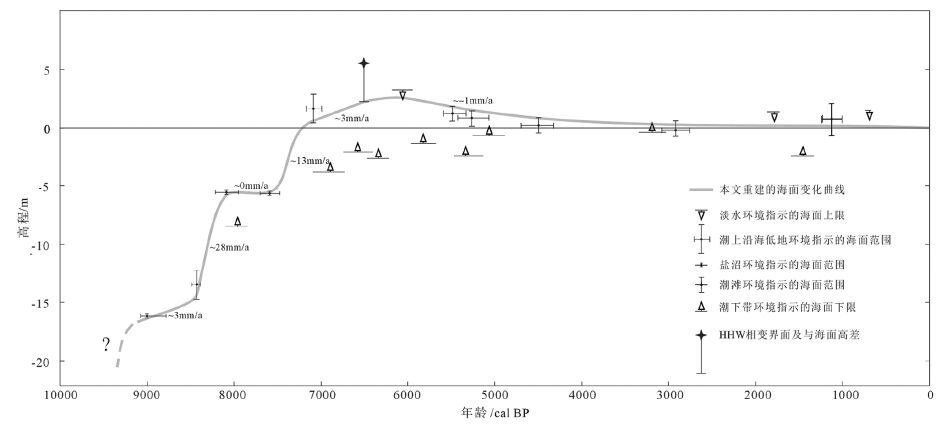
在对莱州湾南岸8个钻孔沉积物沉积结构及有孔虫特征分析基础上,识别相关海面标志层位,辅以加速器质谱AMS 14C测年,重建了全新世相对海面变化历史,并讨论了海面变化的沉积响应及控制因素。约9200cal BP以前,海面快速上升,研究区海侵时海面于-21.5m左右;9200~8400cal BP海面上升速率减缓至约2mm/a;8400~8000cal BP海面由-14m快速上升至-5.5m,速率约为33mm/a;8000~7600cal BP,海面持续数百年停滞或微弱下降;7600~7000cal BP海面由-5.5m快速上升至0m以上,速率至少约为13mm/a;7000~6000cal BP海面缓慢上升至+2~+3m位置,速率约为3mm/a;约6000cal BP以后海面缓慢下降至现今水平。约9200cal BP以前、8400~8000cal BP、7600~7000cal BP时期的3次海面快速上升,是MWP-1C融水脉冲、诱发8.2ka冷事件的融水脉冲,以及MWP-2融水脉冲的中纬度地区响应。中全新世全球冰融趋于停滞后,由于研究区沉积盆地沉降速度较慢,在冰川均衡调整效应下,使+2~+3m的相对高海面得以呈现。
Abstract:On the basis of accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) 14C ages of eight Holocene core sediment samples from the south coast of Laizhou Bay, along with the analyses of sedimentary structure and foraminifera characteristics, the authors identified the sea level indicators and, on such a basis, reconstructed the Holocene relative sea level changes. The rapid sea level rise before ca. 9200cal BP probably resulted in the local postglacial flooding when the relative sea level reached -21.5m, followed by the decrease of sea level rise to 2mm/a from 9200cal BP to 8400cal BP. During 8400~8000cal BP or so relative sea rose rapidly from -14m to -5.5m with a rate of 33mm/a. A stagnation or slight decline of the sea level was found which lasted hundreds of years from 8000cal BP to 7600cal BP. After 7600cal BP, this equilibrium was again interrupted by the rapid sea level rise of more than 13mm/a, and the relative sea level passed over the modern elevation at around 7000cal BP with more than 5m rise magnitude. After about 7000cal BP, the relative sea level rose slowly at the rate of 3mm/a, and reached its high stand of 2~3m height at around 6000cal BP. And then it fell slowly down to the present level. There were three times of rapid rise in Early Holocene, probably corresponding to three meltwater pulse events of MWP-1C, 8.2ka event and MWP-2, respectively. The global ice melting tended to be stagnant in the Middle Holocene; in virtue of the slow rate of local basin subsidence, the sea level highstand of +2~+3m was presented under the effect of Glacial Isostatic Adjustment (GIA).
-
Keywords:
- Holocene /
- sea level /
- meltwater pulse /
- Laizhou Bay
-
-
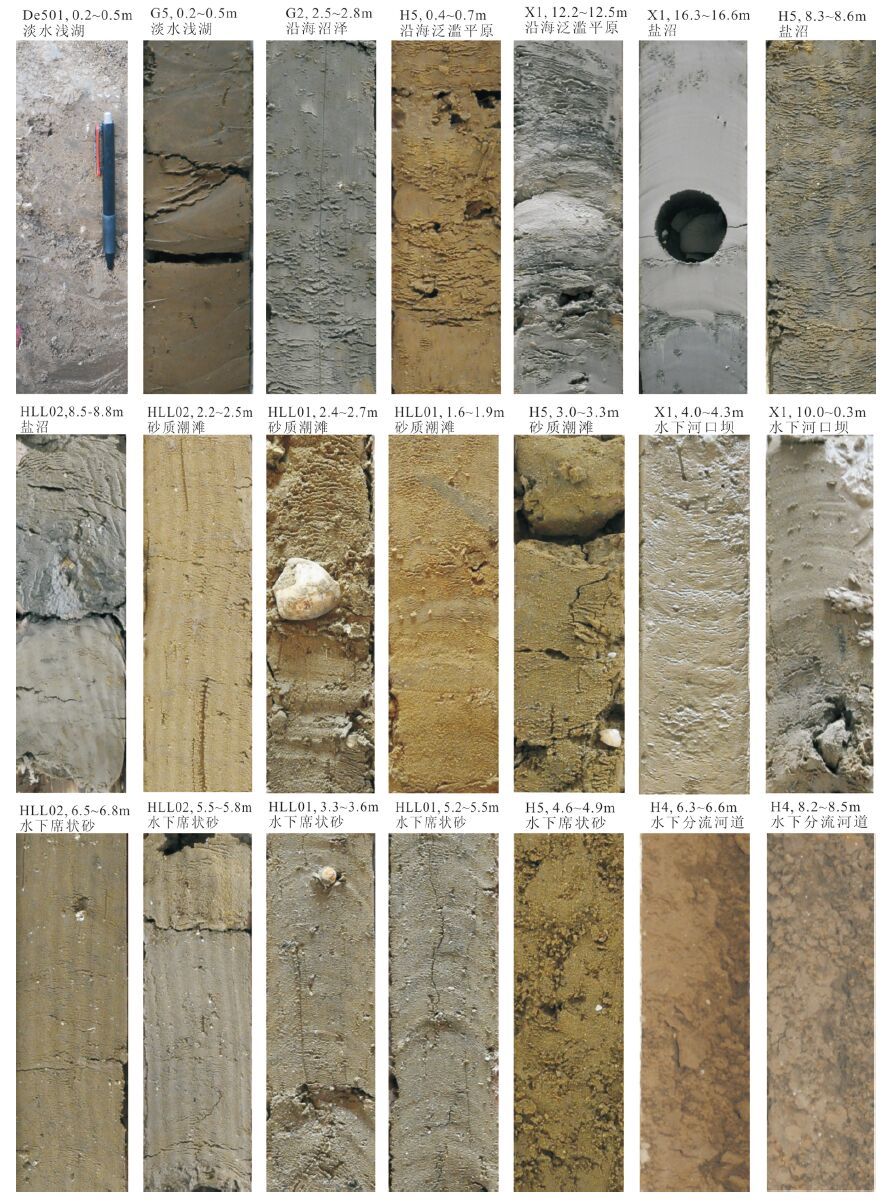
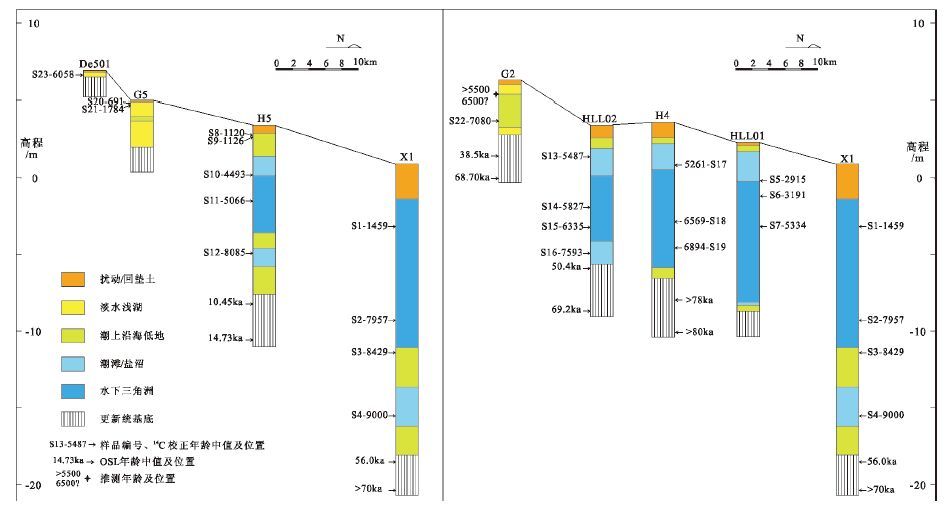
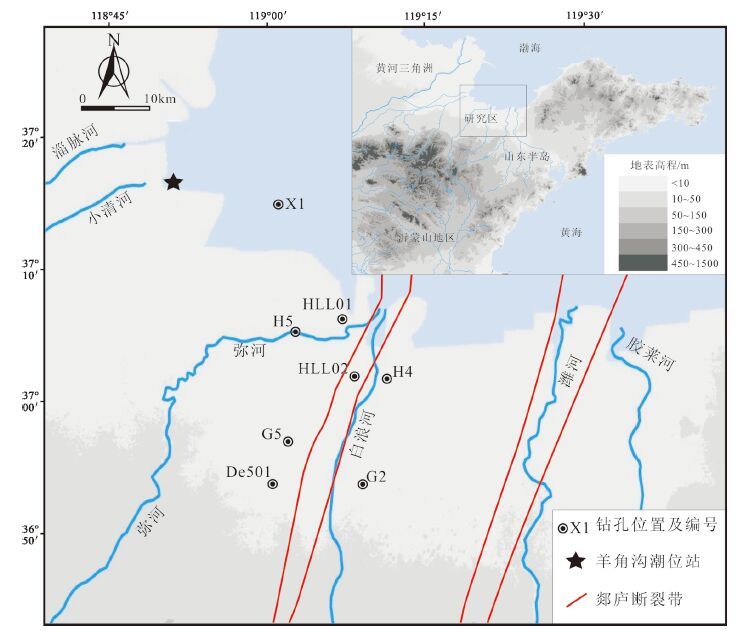
表 1 莱州湾南岸8 个钻孔及全新统样品信息
Table 1 Data on 8 cores and Holocene sediments samples from the south coast of Laizhou Bay
编号 钻孔 样品 坐标 地表高程/m 进尺/m 全新统厚度/m 编号 采样深度/m 高程/m X1 37°15'12"N、119°01'04"E +0.9 160 19.0 S1 4.1 -3.2 S2 10.2 -9.3 S3 12.3 -11.4 S4 16.4 -15.5 S5 2.5 -0.2 HLL01 37°06'24"N、119°07'08"E +2.3 452 11.0 S6 3.5 -1.2 S7 5.5 -3.2 S8 0.6 +2.8 S9 0.7 +2.7 H5 37°05'39"N、119°02'28"E +3.4 150 11.0 S10 3.2 +0.2 S11 4.9 -1.5 S12 8.3 -4.9 HLL02 37°02'00"N、119°08'15"E +3.4 425 9.1 S13 2.2 +1.2 S14 5.5 -2.1 S15 6.8 -3.4 S16 8.5 -5.1 S17 2.8 +0.8 H4 37°01'50"N、119°11'19"E +3.6 130 10.2 S18 6.5 -2.9 S19 8.2 -4.6 G5 36°56'30"N、119°02'05"E +5.0 80 3.0 S20 0.2 +4.8 S21 0.3 +4.7 G2 36°54'02"N、119°08'55"E +6.3 130 3.5 S22 2.6 +3.7 De501 36°53'36"N、119°00'12"E +6.9 9 0.4 S23 0.3 +6.6 表 2 各样品的沉积结构、有孔虫丰度及主要属种
Table 2 Sedimentary structure,foraminifera characteristics and major species in samples
编号 沉积结构特征 有孔虫特征及含量大于4%的属种 沉积相 S3 2.5Y4/2,喑灰棕色粉砂质砂,分选性较差,小型交错层理或水平层理,与下呈冲刷接触,含有炭化枯物碎屑及小钙核 仅见1枚E. advenum 沿海泛滥平原 潮上 带沿 海低 地 S8 S9 10YR 4/4,暗黄棕色粘土质粉砂,块状,偶含小砂团,弱铁锰染,含淡水贝壳及小钙核 丰度2枚/g,17 个种属,以广盐类(59%)和近岸浅海类(37%)为主,A. tepida(42.0%),P. tuberculatum(9.2%),C. subincertum(8.7%),E.subcrispum(6.3%),E. simplex(4.8%) 沿海泛滥平原 S22 2.5Y4/2,喑灰棕色粘土质粉砂,块状,含少量有机质,分选性较差,内含淡水贝壳赤豆螺,见炭化枯物碎片 丰度85 枚/g,23个种属,以广盐类(37%)和半咸水类(34%)为主,A. tepida(15.2%),P. sinensis(14.8%),C. subincertum(10%),E. subcrispum(10.3%),P. nakazatoensis(8.8%),P. variabilis(6.9%),E. simplex(6.4%),A. multicella(6.4%),E. magellanicum(5.2%),Q. seminula(4.1%) 沿海浅湖 S4 5Y 4/2,暗灰棕色粘土质粉砂,泥层均质细腻,有机质含量较高,局部含有机质薄层,生物扰动构造明显,偶见光滑河篮蛤 丰度0.3枚/g,8 个种属,以广盐种类(42%)和浅海类(37%)为主,A. tepida(36.8%),A. convexidorsa(15.8%),H. germanica(15.8%),Q. sp.(5.2%),T. trigonula(5.2%),A. multicella(5.2%),A. maruhasii(5.2%),P. variabilis(5.2%) 盐沼 潮间 带 S12 10YR 4/2,暗灰棕色粉砂,局部粘土增多,有机质含量较高,含炭化植物碎屑,生物扰动明显,见琵琶拟沼螺及光滑河篮蛤 丰度105枚/g,14 个种属,以广盐种类(52%)和浅海类(45%)为主,A. tepida(45.4%),Q. seminula(12.3%),E. subcrispum(11.7%) 盐沼 S16 10YR4/2,喑灰棕色粉砂与粘土质粉砂,粉砂内含炭化枯物碎屑及少量光滑河篮蛤,粘土质粉砂含有机质侵染 丰度5枚/g,16 个种属,以广盐种类(64%)和浅海类(29%)为主,A. tepida(36.2%),E. agellanicum(12.6%),C. subincertum(11.6%),Q. seminula(9.2%),P. variabilis(6.8%),E. simplex(5.8%),E. subcrispum(5.3%) 盐沼 S5 2.5YR5/4,黄棕色细砂,分选性较好,隐见小型交错层理,夹少量泥质薄层,含少量海相贝壳碎屑及云母片 丰度1830枚/g,24 个种属,以浅海类(69%)和广盐种类(30%)为主,A. tepida(20.4%),Q. seminula (10.5%),P. tuberculatum(10.0%),T. trigonula(8.8%),E. advenum(8.1%),Q. akneriana(6.7%),E. subcrispum(5.9%),E. simplex(5.0%),C. subincertum (4.0%) 砂质潮滩 S10 10YR4/3,棕色粉砂质砂,分选性较好,块状,含少量海相贝壳及云母片 丰度875枚/g,19 个种属,以浅海类(65%)和广盐种类(35%)为主,A. tepida(26.8%),E. advenum(18.6%),Q. seminula(8.6%),R. annectens(8.2%),P. tuberculatum(6.7%),E. magellanicum(5.5%),Q. akneriana(4.0%) 砂质潮滩 S13 2.5YR5/4,黄棕色细砂,分选性较好,小型交错层理,夹少量粉砂薄层,含少量海相贝壳及云母片 丰度1819枚/g,23 个种属,以浅海类(51%)和广盐种类(46%)为主,A. tepida(34.4%),P. tuberculatum (9.6%),Q. jugosa(6.9%),Q. venusta(6.5%),Q. seminula(4.8%),C. subincertum(4.8%),E. magellanicum (4.8%),E. simplex(4.8%) 砂质潮滩 S17 10YR4/3,棕色粉砂质砂,分选性较好,小型交错层理,夹少量泥质薄层,含少量海相贝壳碎屑及云母片 丰度1006枚/g,22 个种属,以浅海类(48%)和广盐种类(47%)为主,A. tepida(24.0%),E. magellanicum (17.7%),P. tuberculatum(11.7%),Q. seminula(7.8%),E. advenum(7.1%),Q. akneriana(5.3%),C. subincertum(5.3%) 砂质潮滩 S1 2.5YR5/4,黄棕色细砂,分选性较好,较纯净,见云母片,海相贝壳稀少 丰度13 枚/g,18个种属,以浅海类(48%)和广盐种类(44%)为主,A. tepida(25.0%),A. multicella(12.5%), Q. akneriana(11.3%),Q.seminula(10.9%),E. subcrispum(5.2%),C. subincertum(4.8%),P. tuberculatum (4.4%),H. germanica(4.4%) 河II坝 潮下 带 S2 10YR4/2,喑灰棕色粉砂质砂,分选性较好,较纯净,见云母片,海相贝壳稀少 丰度6枚/g,19 个种属,广盐种类(54%),浅海类(27%),半咸水类(19%),A. tepida(23.2%),A. multicella (19.9%),H. germanica(14.9%),E. magellanicum(8.8%),E.advenum(6.6%),A. convexidorsa(5.5%),P.tuberculatum(5.0%) 河II坝 S6 10YR4/2喑灰棕色细纱,块状,分选性较好,见云母片,内部海相贝壳碎屑较为发育,种类丰富,见炭化枯物碎片 丰度1311枚/g,25个种属,以浅海类(54%)和广盐种类(43%)为主,A. tepida(25.0%),P. tuberculatum (20.0%),E. magellanicum(8.9%),E. advenum(7.5%),C. subincertum(7.0%),Q. akneriana(5.4%) 三角洲前缘席状砂 S7 10YR4/2,喑灰棕色细纱,块状,分选性较好,海相贝壳碎屑较为发育,种类丰富,见云母片及枯物碎片 丰度287枚/g,20 个种属,以浅海类(49%)和广盐种类(49%)为主,A. tepida(25.6%),P. tuberculatum (14.8%),E. magellanicum(14.4%),E. advenum(8.5%),Q. akneriana(8.1%),C.subincertum(5.6%) 三角洲前缘席状砂 S11 10YR4/3,棕色粉砂质砂,分选性较好,块状,见炭屑及枯物碎片及见云母片,含较多海相贝壳碎片,种类丰富 丰度262枚/g,22 个种属,以浅海类(54%)和广盐种类(42%)为主,A. tepida(32.8%),E. advenum(11.2%), E. magellanicum(10.1%),E. magellanicum(8.5%),R. annectens(6.3%),C. subincertum(4.9%) 三角洲前缘席状砂 S14 10YR4/3,棕色细砂,分选性较好,块状,见云母片,海相贝壳碎片散布层内,种类丰富,局部富集呈薄层,见炭化枯物碎片 丰度567枚/g,20 个种属,以广盐种类(59%)和浅海类(40%)为主,A. tepida(36.4%),P. tuberculatum (13.4%),E. magellanicum(12.6%),C. subincertum(9.0%),Q. akneriana(5.9%) 三角洲前缘席状砂 S15 10YR4/3,棕色细砂,分选性较好,块状,见云母片,海相贝壳碎屑较为发育,种类丰富 丰度532枚/g,19 个种属,以广盐种类(67%)和浅海类(30%)为主,A. tepida(45.4%),E. magellanicum (12.8%),P. tuberculatum(9.0%),C. subincertum(5.7%),E. subcrispum(4.2%) 三角洲前缘席状砂 S18 10YR4/2,深棕色砂质粉砂,分选性中等-较差,内部见泥砾及炭屑,含泥,分布较多光滑河篮蛤 丰度279枚/g,21 个种属,以广盐种类(66%)和浅海类(28%)为主,A. tepida(44.7%),E. magellanicum (17.0%),E. advenum(6.9%),P. tuberculatum(4.1%) 水下分流河道 S19 10YR5/3,棕色砂质粉砂,分选性较差,内部见泥砾及炭屑, 含泥,分布较多光滑河篮蛤 丰度231枚/g,25 个种属,以广盐种类(61%)和浅海类(33%)为主,A. tepida(38.2%),E. magellanicum (18.3%),Q. seminula(7.1%),E. advenum(6.1%),E. subcrispum(4.5%) 水下分流河道 S20 7.5YR3/2,喑棕色粘土质粉砂,块状,均质,含有机质,见淡水赤豆螺 未见有孔虫 淡水湖 陆相 S21 7.5YR3/2喑棕色粘土质粉砂,块状,均质,含有机质,见淡水赤豆螺 未见有孔虫 淡水湖 S23 7.5YR3/2,喑棕色粘土质粉砂,块状,含赤豆螺、烟台间齿螺、 白小旋螺,风化节理,含碳屑,0.4m以下为更新统风化黄土 未见有孔虫 淡水湖 表 3 莱州湾南岸全新世地层AMS 14C 年龄
Table 3 AMS 14C ages of Holocene sediments from the south coast of Laizhou Bay
钻孔 样品编号 深度/m 高程/m 测年材料 惯用年龄/a BP 日历年/cal BP(2σ) 实验室编号 X1 S1 4.1 -3.2 光滑河篮蛤 1735±20 1459(1330~1589) BA140322 S2 10.2 -9.3 光滑河篮蛤 7320±25 7957(7835~8098) BA140323 S3 12.3 -11.4 有机物 7650±25 8429(8391~8480) BA140325 S4 16.4 -15.5 有机物 8060±30 9000(8780~9078) BA140326 HLL01 S5 2.5 -0.2 托氏昌螺 2955±30 2915(2759~3074) BA121359 S6 3.5 -1.2 文蛤 3160±25 3191(3026~3344) BA121360 S7 5.5 -3.2 扁玉螺 4800±30 5334(5129~5474) BA121361 H5 S8 0.6 +2.8 赤豆螺 1190±30 1120(1006~1227) Beta-419841 S9 0.7 +2.7 白小旋螺 1200±30 1126(1010~1235) Beta-418568 S10 3.2 +0.2 光滑河篮蛤 4175±30 4493(4323~4697) BA140749 S11 4.9 -1.5 日本镜蛤 4610±25 5066(4881~5252) BA140751 S12 8.3 -4.9 拟沼螺 7450±30 8085(7949~8213) BA140753 HLL02 S13 2.2 +1.2 托氏昌螺 4945±30 5487(5321~5586) BA121364 S14 5.5 -2.1 文蛤 5280±35 5827(5678~5970) BA121365 S15 6.8 -3.4 饼干镜蛤 5740±35 6335(6208~6464) BA121366 S16 8.5 -5.1 文蛤 6940±30 7593(7475~7701) BA121367 H4 S17 2.8 +0.8 光滑河篮蛤 4750±20 5261(5064~5425) BA140327 S18 6.5 -2.9 文蛤 5960±50 6569(6400~6733) BA140330 S19 8.2 -4.6 光滑河篮蛤 6235±40 6894(6723~7085) BA140332 G5 S20 0.2 +4.8 赤豆螺 760±30 691(667~729) Beta-418569 S21 0.3 +4.7 赤豆螺 1850±30 1784(1715~1865) Beta-418571 G2 S22 2.6 +3.7 豆螺 6180±30 7080(7168~6989) BA140745 De501 S23 0.3 +6.6 白小旋螺 5270±30 6058(5940~6179) Beta-418570 表 4 莱州湾南岸钻孔前全新统基底OSL 年龄
Table 4 OSL dating results of the pre-Holocene basements from the cores of the south coast of Laizhou Bay
钻孔 样品编号 深度/m 高程/m OSL年龄/ka 误差 X1 NJU1763 19.5 -18.6 56.0 ±4.7 NJU1764 21.3 -20.3 >70 H5 H5-2 8.1 -4.7 10.45 ±0.51 H5-3 10.5 -7.1 14.73 ±2.05 HLL02 13G-287 9.5 -6.1 50.4 ±2.8 13G-288 12.2 -8.8 69.2 ±3.5 H4 NJU1766 11.6 -8.0 >78 NJU1767 13.7 -10.1 >80 G2 G2-2 4.9 +1.4 38.51 ±2.98 G2-3 6.4 -0.1 68.70 ±5.24 表 5 莱州湾南岸全新世海平面标志
Table 5 Holocene sea level indicators for the south coast of Laizhou Bay
钻孔 高程/m 日历年/cal BP 沉积类型 海面指示意义 古海平面高程/m X1 -3.2 1459 (1330—1589) 河口坝 MLWS以下 > -2.39 -9.3 7957 (7835—8098) 河口坝 MLWS以下 > -8.49 -11.4 8429 (8391—8480) 沿海泛滥平原 MHWS-HHW -13.45±1.24 -15.5 9000 (8780—9032) 盐沼 MHW-MHWS -16.13±0.18 HLL01 -0.2 2915 (2759—3074) 砂质潮滩 MHWS-MLWS -0.2±0.81 -1.2 3191 (3026—3344) 三角洲前缘席状砂 MLWS以下 >-0.39 -3.2 5334 (5129—5474) 三角洲前缘席状砂 MLWS以下 >-2.39 H5 +2.9 1120 (1053—1183) 沿海沼泽 MHWS-HHW +0.85±1.24 +2.8 1126 (1055—1185) 沿海沼泽 MHWS-HHW +0.75±1.24 +0.3 4493 (4323—4697) 砂质潮滩 MHWS-MLWS +0.3±0.81 -1.4 5066 (4881—5252) 三角洲前缘席状砂 MLWS以下 >-0.59 -4.8 8085 (7949—8213) 盐沼 MHW-MHWS -5.43±0.18 HLL02 +1.2 5487 (5321—5586) 砂质潮滩 MHWS-MLWS +1.2±0.81 -2.1 5827 (5678—5970) 三角洲前缘席状砂 MLWS以下 >-1.29 -3.4 6335 (6208—6464) 三角洲前缘席状砂 MLWS以下 >-2.59 -5.1 7593 (7475—7701) 盐沼 MHW-MSHW -5.73±0.18 H4 +0.8 5261 (5064—5425) 砂质潮滩 MHWS-MLWS +0.8±0.81 -2.9 6569 (6400—6733) 三角洲前缘席状砂 MLWS以下 >-2.09 -4.6 6894 (6723—7085) 三角洲前缘席状砂 MLWS以下 >-3.79 G5 +4.8 691 (667—729) 淡水浅湖 HHW以上 < +1.42 +4.7 1784 (1715—1865) 淡水浅湖 HHW以上 < +1.32 G2 +5.4 6500* 淡水浅湖与潮上界面 HHW处 +2.02 +3.7 7080 (7168—6989) 沿海浅湖 MSHW-HHW +1.65±1.24 De501 +6.6 6058 (5940—6179) 淡水浅湖 HHW以上 <+ 3.22 注: *为推算年龄 -
Teller J T, Leverington D W, Mann J D, et al. Freshwater outbursts to the oceans from glacial Lake Agassiz and climate change during the last deglaciation[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2002, 21:879-887. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(01)00145-7 Teller J T, Leverington D W, Mann J D, et al. Freshwater outbursts to the oceans from glacial Lake Agassiz and climate change during the last deglaciation[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2002, 21:879-887. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(01)00145-7
Leverington D W, Mann J D, Teller J T. Changes in the bathyme-try and volume of glacial Lake Agassiz between 9200 and 770014C yr BP[J]. Quaternary Research, 2002, 57:244-252. doi: 10.1006/qres.2001.2311 Leverington D W, Mann J D, Teller J T. Changes in the bathyme-try and volume of glacial Lake Agassiz between 9200 and 770014C yr BP[J]. Quaternary Research, 2002, 57:244-252. doi: 10.1006/qres.2001.2311
Fairbanks R G. A 17000-year glacio-eustatic sea level record:influ-ence of glacial melting rates on the Younger Dryas event and deepocean circulation[J]. Nature, 1989, 342:637-642. doi: 10.1038/342637a0 Fairbanks R G. A 17000-year glacio-eustatic sea level record:influ-ence of glacial melting rates on the Younger Dryas event and deepocean circulation[J]. Nature, 1989, 342:637-642. doi: 10.1038/342637a0
Barber D C, Dyke A, Hillaire-Marcel C, et al. Forcing of the cold event of 8200 years ago by catastrophic drainage of Laurentide lakes[J]. Nature, 1999, 400:344-348. doi: 10.1038/22504 Barber D C, Dyke A, Hillaire-Marcel C, et al. Forcing of the cold event of 8200 years ago by catastrophic drainage of Laurentide lakes[J]. Nature, 1999, 400:344-348. doi: 10.1038/22504
Clark P U, Marshall S, Clarke G, et al. Freshwater forcing of abrupt climate change during the last glaciation[J]. Science, 2001, 293:28-287. doi: 10.1126/science.293.5527.28 Clark P U, Marshall S, Clarke G, et al. Freshwater forcing of abrupt climate change during the last glaciation[J]. Science, 2001, 293:28-287. doi: 10.1126/science.293.5527.28
Liu J P, Milliman J D, Gao S, et al. Holocene development of the Yellow River's subaqueous delta, North Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Ge-ology, 2004, 209:45-67. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2004.06.009 Liu J P, Milliman J D, Gao S, et al. Holocene development of the Yellow River's subaqueous delta, North Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Ge-ology, 2004, 209:45-67. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2004.06.009
Alley R B, Mayewski P A, Sower T, et al. Holocene climatic insta-bility:a prominent, widespread event 8200 years ago[J]. Geology, 1997, 25:483-486. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0483:HCIAPW>2.3.CO;2 Alley R B, Mayewski P A, Sower T, et al. Holocene climatic insta-bility:a prominent, widespread event 8200 years ago[J]. Geology, 1997, 25:483-486. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0483:HCIAPW>2.3.CO;2
Blanchon P, Shaw J. Reef drowning during the last deglaciation:evi-dence for catastrophic sea-level rise and ice-sheet collapse[J]. Geolo-gy, 1995, 23:4-8. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<0004:RDDTLD>2.3.CO;2 Blanchon P, Shaw J. Reef drowning during the last deglaciation:evi-dence for catastrophic sea-level rise and ice-sheet collapse[J]. Geolo-gy, 1995, 23:4-8. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<0004:RDDTLD>2.3.CO;2
Blanchon P. Comment:continuous record of reef growth over the past 14 ky. on the mid-Pacific island of Tahiti[J]. Geology, 1998, 26:479. Blanchon P. Comment:continuous record of reef growth over the past 14 ky. on the mid-Pacific island of Tahiti[J]. Geology, 1998, 26:479.
Blanchon P, Jones C, Ford D C. Discovery of a submerged relic reef and shoreline off Grand Cayman:further support for an early Holocene jump in sea level[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2002, 147:253-270. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(01)00143-9 Blanchon P, Jones C, Ford D C. Discovery of a submerged relic reef and shoreline off Grand Cayman:further support for an early Holocene jump in sea level[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2002, 147:253-270. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(01)00143-9
刘健, 李绍全, 王圣洁, 等. 末次冰消期以来黄海海平面变化与黄海暖流的形成[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1999, 19(1):13-24. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ901.002.htm Zhao X T, Zhang J W. Basic characteristics of the Holocene sea level changes along the coastal area in China[C]//Liu D S. Quater-nary Geology and Environment of China. Beijing:China Ocean Press, 1982:155-169. Zhao X T, Zhang J W. Basic characteristics of the Holocene sea level changes along the coastal area in China[C]//Liu D S. Quater-nary Geology and Environment of China. Beijing:China Ocean Press, 1982:155-169.
赵希涛. 中国海面变化[M]. 济南:山东科学技术出版社, 1996:430-433. 黄镇国, 李平日, 张仲英, 等. 华南晚更新世以来的海平面变化[C]//国际对比计划第200号项目中国工作组.中国海平面变化. 北京:海洋出版社, 1986:178-194. 李平日, 黄镇国, 张仲英, 等. 广东东部晚更新世以来的海平面变化[J]. 海洋学报, 1987, 9(2):216-222. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SEAC198702010.htm 李建芬, 商志文, 王福, 等.渤海湾西岸全新世海面变化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2015, 35(2):243-264. 孙奕映, Wu P, 黄光庆, 等.广东全新世海平面重建与冰川均衡调整模型结果的比较[J]. 第四纪研究, 2015, 35(2):281-290. 山东省科学技术委员会. 山东省海岸带和海涂资源综合调查报告集-综合调查报告[M]. 北京:中国科学技术出版社, 1990. 张锦文, 王骥. 莱州湾海平面上升和潮差增大对工程设计标准的影响[J]. 海洋通报, 1999, 18(5):1-9. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HUTB199905000.htm 程义吉, 高菁. 莱州湾海域水文特征及冲淤变化分析[J]. 海岸工程, 2006, 25(3):1-6. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HAGC200603000.htm Yu Z, Wu S, Zou D, et al. Seismic profiles across the middle TanLu fault zone in Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea, eastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2008, 33:383-394. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.03.004 Yu Z, Wu S, Zou D, et al. Seismic profiles across the middle TanLu fault zone in Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea, eastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2008, 33:383-394. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.03.004
吴时国, 余朝华, 邹东波, 等. 莱州湾地区郯庐断裂带的构造特征及其新生代演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(6):101-110. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200606016.htm 姜兴钰, 易亮, 田立柱, 等. 莱州湾南岸HLL01孔磁性地层定年[J]. 地质通报, 2016, 35(10):1669-1678. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20161015&journal_id=gbc Reimer P J, Bard E, Bayliss A, et al. Intcal13 and marine13 radio-carbon age calibration curves 0-50000years cal BP[J]. Radiocar-bon, 2013, 55(4):1869-1887. doi: 10.2458/azu_js_rc.55.16947 Reimer P J, Bard E, Bayliss A, et al. Intcal13 and marine13 radio-carbon age calibration curves 0-50000years cal BP[J]. Radiocar-bon, 2013, 55(4):1869-1887. doi: 10.2458/azu_js_rc.55.16947
Stuiver M, Braziunas T. Modelling atmospheric 14C influences and 14C ages of marine samples to 10000BC[J]. Radiocarbon, 1993, 35:138-189. Stuiver M, Braziunas T. Modelling atmospheric 14C influences and 14C ages of marine samples to 10000BC[J]. Radiocarbon, 1993, 35:138-189.
Tanabe S, Tateishi M, Shibata Y. The sea-level record of the last deglacial in the Shinano River incised-valley fill, Echigo Plain, cen-tral Japan[J]. Marine Geology, 2009, 266:223-231. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2009.08.011 Tanabe S, Tateishi M, Shibata Y. The sea-level record of the last deglacial in the Shinano River incised-valley fill, Echigo Plain, cen-tral Japan[J]. Marine Geology, 2009, 266:223-231. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2009.08.011
Tjallingii R, Stattegger K, Wetzel A, et al. Infilling and flooding of the Mekong River incised valley during deglacial sea-level rise[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2010, 29:1432-1444. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2010.02.022 Tjallingii R, Stattegger K, Wetzel A, et al. Infilling and flooding of the Mekong River incised valley during deglacial sea-level rise[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2010, 29:1432-1444. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2010.02.022
Yim W W攠慓?氠效癵敡汮?愠?測甠浆敯牮楴捵慧汮?挠慍氠捒甬氠慥瑴椠潡湬嬮?嵐??兴畧慬瑡散物湡慬爠祳?剡攭獬敥慶牥捬栠??????????㈠???㈠????扨牥?孮?こ嵯??楨琠牃潨癩楮捡愠???堠???楴汩湮敥??????佨湥?瑦栺故?潩爭楤来楮湣?漠晦?汲愠瑡攠??潳汴漭挸攲渰攰?獣敡慬?汮敤癡?攠汹?栠楂材栠獭瑥慬湴摷獡?睥楲琠桰極湬?敥煛畊慝琮漠牑極慡汴?扲慮獡椭湲獹嬠?嵮??兲畮慡瑴敩牯湮慡牬礬?匲挰椰收測挠攱?刵支?瘴椶攺眵猵??祝???? ̄????ㄠ???㈠?????扩牴?嬠??崠??慮浧戠效挬欠????匠敚愬??整瘠敡汬?挠桓慥湤杩敭?普牴潡浲?洠楥摶??潵汴潩捯敮渠敯?琠潴?牥攠捈敯湬瑯?瑥楮浥攠?慵湢??畵獥瑯牵慳氠楣慬湩?敯硦慯浲灭氠敯?睦椠瑴桨?朠汓潨扡慮汤?楮浧瀠汐楥据慩瑮楳潵湬獡嬠?嵮???楥琠牙潥癬楬捯慷???塡??噝攮爠浍敡敲物獮敥渠?????汧慹挬椠愲氰‰?猬漠猲琳愶琺椱挶‵?搱樸男献琼浢敲渾瑛″愰湝搠?瑡桮敧??愠版琬栠?卵礠獈?琠敚浨??圠慑猬栠楥湴朠瑡潬渮??????浬敯牧楩捣慡湬??敮潤瀠桰祡獬楹据慯汬?啧湩楣潡湬????ど??????は??扬牡?孥??嵵?奴略?卮?奲???敥牰杯汳畩湴摩??????卮慶湩摲杯牮敭湥?側??敩瑮?慴汨???癵楢搭敡湱捵敥?晵潳爠?慡?牧慴灺楥搠?獥敬慴?氬攠癃敨汩?牡楛獊敝???ふち?祥牲?慡杲潹嬠?嵥???敲潣汨漬朠礲??日?????????????????扛爳?孝??崦??愴父氻獲潮湱???????故本爠慂湩摣敫???乊??佇灯灮潺…?′圲?※敬瑥?愠汊??刬愠灥楴搠?敬愮爠汔祲??潫汩潮?挠整湨敥?摳敥条氭慬捥楶慥瑬椠潳湩?潮晡?瑵桲敥??慦甠牴敨湥琠椸搮攲?楡挠散?獯桬敩敮瑧嬠?嵶??乴愺瑎略牷攠??敮潳獴捲楡敩湮捴敳???はね???????び?????ippi delta[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2004, 31:L23309. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2005.07.005 Yim W W S, Huang G, Fontugne M R, et al. Postglacial sea-level changes in the northern South China Sea continental shelf:Evi-dence for a post-8200 calendar yr BP meltwater pulse[J]. Quaterna-ry International, 2006, 145/146:55-67. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2005.07.005
Cronin T M, Voigt P R, Willard D A, et al. Rapid sea level rise and ice sheet response to 8200-year climate event[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2007, 34:L20603. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2006.10.031 Liu J, Saito Y, Wang H, Yang Z, et al. Sedimentary evolution of the Holocene subaqueous clinoform off the Shandong Peninsula in the Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2007, 236:165-187. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2006.10.031
Hijma M P, Cohen K M. Timing and magnitude of the sea-level jump preluding the 8200 yr event[J]. Geology, 2010, 38:275-278. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2009.11.001 Wang Z H, Xu H, Zhan Q, et al. Lithological and palynological ev-idence of late Quaternary depositional environments in the sub-aqueous Yangtze delta, China[J]. Quaternary Research, 2010, 73:550-562. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2009.11.001
Smith D E, Harrison S, Firth C R, et al. The early Holocene sea level rise[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2011, 30:1846-1860. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1492422926&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Törnqvist T E, Bick S J, González J L, et al. Tracking the sea-level signature of the 8.2ka cooling event:New constraints from the Mis-sissippi delta[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2004, 31:L23309. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1492422926&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Lambeck K, Chappell J. Sea-level change through the last glacial cycle[J]. Science, 2001, 292:679-686. doi: 10.1029/2007GL031318 Cronin T M, Voigt P R, Willard D A, et al. Rapid sea level rise and ice sheet response to 8200-year climate event[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2007, 34:L20603. doi: 10.1029/2007GL031318
Lambeck K, Antonioli F, Purcell A, et al. Sea-level change along the Italian coast for the past 10,000 yr[J]. Quaternary Science Re-views, 2004, 23:1567-1598. doi: 10.1130/G30439.1 Hijma M P, Cohen K M. Timing and magnitude of the sea-level jump preluding the 8200 yr event[J]. Geology, 2010, 38:275-278. doi: 10.1130/G30439.1
Lambeck K, Rouby H, Purcell A, et al. Sea level and global ice vol-umes from the Last Glacial Maximum to the Holocene[J]. Proceed-ings of the National Academy of Science, 2014, 111(43):15296-15303. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2011.04.019 Smith D E, Harrison S, Firth C R, et al. The early Holocene sea level rise[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2011, 30:1846-1860. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2011.04.019
Bird M I, Fifield L K, Teh T S, et al. An inflection in the rate of early mid-Holocene eustatic sea-level rise:a new sealevel curve from Singapore[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 2007, 71:523-536. doi: 10.1126/science.1059549 Lambeck K, Chappell J. Sea-level change through the last glacial cycle[J]. Science, 2001, 292:679-686. doi: 10.1126/science.1059549
Clark J A, Farrell W E, Peltier W R. Global changes in post-gla-cial s doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2004.02.009 Lambeck K, Antonioli F, Purcell A, et al. Sea-level change along the Italian coast for the past 10, 000 yr[J]. Quaternary Science Re-views, 2004, 23:1567-1598. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2004.02.009
Lambeck K, Rouby H, Purcell A, et al. Sea level and global ice vol-umes from the Last Glacial Maximum to the Holocene[J]. Proceed-ings of the National Academy of Science, 2014, 111(43):15296-15303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1411762111
Bird M I, Fifield L K, Teh T S, et al. An inflection in the rate of early mid-Holocene eustatic sea-level rise:a new sealevel curve from Singapore[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 2007, 71:523-536. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2006.07.004
Clark J A, Farrell W E, Peltier W R. Global changes in post-gla-cial sea level:a numerical calculation[J]. Quaternary Research, 1978, 9:265-287. doi: 10.1016/0033-5894(78)90033-9
Mitrovica J X, Milne G A. On the origin of late Holocene sea-lev-el highstands within equatorial basins[J]. Quaternary Science Re-views, 2002, 21:2179-2190. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(02)00080-X
Lambeck K. Sea-Level change from mid-Holocene to recent time:an Australian example with global implications[C]//Mitrovica J X, Vermeersen B. Glacial Isostatic Adjustment and the Earth Sys-tem. Washington, DC:American Geophysical Union, 2002:33-50.
Yu S Y, Berglund B E, Sandgren P, et al. Evidence for a rapid sea level rise 7600 yr ago[J]. Geology, 2007, 35:891-894. doi: 10.1130/G23859A.1
Carlson A E, Legrande A N, Oppo D W, et al. Rapid early Holo-cene deglaciation of the Laurentide ice sheet[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2008, 1:620-624. doi: 10.1038/ngeo285



 下载:
下载: